Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Magnetic Stainless Steel Grades Chart
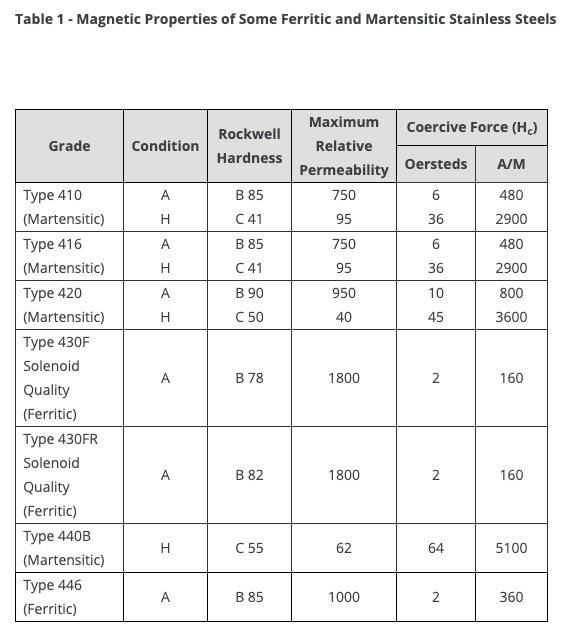
Magnetic Stainless Steel Grades Chart Introduction
Understanding the magnetic properties of stainless steel is critical for precision engineering applications where material behavior impacts performance, assembly, and compatibility. While austenitic grades like 304 and 316 are generally non-magnetic in annealed conditions, ferritic and martensitic variants such as 430 and 410 exhibit ferromagnetism due to their crystal structure—a distinction that directly influences CNC machining parameters, tooling selection, and final part functionality. Misinterpreting these properties can lead to costly design revisions or field failures, particularly in industries like medical, aerospace, and electronics where magnetic interference must be controlled.
Honyo Prototype provides this comprehensive Magnetic Stainless Steel Grades Chart to clarify material characteristics and support informed decision-making during the design phase. Our CNC machining services leverage deep material-specific expertise to optimize processes for both magnetic and non-magnetic stainless alloys, ensuring dimensional accuracy, surface integrity, and adherence to stringent industry standards. From prototyping to low-volume production, we mitigate risks associated with material variability through advanced toolpath strategies and in-process quality validation.
Access this resource to streamline your material selection, then accelerate your project timeline using Honyo Prototype’s Online Instant Quote platform. Submit your CAD file for a precise, real-time cost and lead time estimate—engineered for efficiency from inquiry to delivery.
Technical Capabilities
The term “magnetic stainless steel grades chart” refers to a reference guide that classifies stainless steel alloys based on their magnetic properties, which are directly influenced by their microstructure (austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, or duplex). However, the machining performance—especially in high-precision 3/4/5-axis milling and turning operations requiring tight tolerances (±0.0005″ or tighter)—depends on multiple factors including hardness, thermal conductivity, work hardening rate, and chip formation behavior.
Below is a technical comparison of common materials used in precision CNC machining, including magnetic stainless steel grades, non-magnetic stainless steels, aluminum, carbon steel, ABS, and nylon. This table highlights key properties relevant to multi-axis CNC machining and tight tolerance production.
| Material Type | Common Grades | Magnetic? | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HB) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Machinability Rating | Work Hardening Tendency | Notes for 3/4/5-Axis Milling & Turning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | 303, 304, 316 | No (typically) | 500–700 | 150–200 | 15–20 | Fair to Poor | High | High work hardening; requires sharp tools, high rigidity, low vibration setups; not ideal for deep cavities in 5-axis without proper strategy |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | 430, 409 | Yes | 450–550 | 180–220 | 25–30 | Moderate | Low | Better thermal conductivity than austenitic; stable for tight tolerance turning; minimal distortion |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | 410, 420, 440C | Yes | 600–1900 | 200–700 | 25–30 | Moderate to Good | Low | Can be heat treated; 440C is abrasive—use coated carbide; suitable for high-precision shafts and molds |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | 2205, 2507 | Yes (partial) | 650–900 | 280–320 | 15–20 | Poor | Moderate | High strength and corrosion resistance; requires high spindle power and rigid toolpaths; not ideal for fine 5-axis features without adaptive clearing |
| Carbon Steel | 1018, 1045, 4140 | Yes | 400–1000 | 120–300 | 40–50 | Good to Excellent | Low | Excellent for tight tolerance turning and milling; predictable tool life; minimal thermal drift |
| Aluminum Alloys | 6061, 7075, 2024 | No | 300–570 | 95–150 | 150–180 | Excellent | Very Low | High thermal conductivity; allows high feed rates; ideal for complex 5-axis aerospace parts; prone to built-up edge—use sharp, polished tools |
| Engineering Plastics | ABS, Nylon (PA6, PA66) | No | 40–80 (ABS), 70–90 (Nylon) | 80–100 (Rockwell M) | 0.1–0.3 | Excellent | None | Low cutting forces; minimal tool wear; requires low RPM and high feed to avoid melting; ideal for rapid iteration and jigs; non-magnetic and corrosion-resistant |
Key Considerations for Tight Tolerance 3/4/5-Axis Machining:
Precision multi-axis CNC operations demand dimensional stability, minimal thermal expansion, and consistent material response. Magnetic stainless steels (ferritic and martensitic) are often preferred over austenitic grades in high-precision environments due to lower work hardening and better dimensional predictability.
Aluminum remains the top choice for complex 5-axis geometries where tight tolerances and light weight are critical, such as in aerospace and medical devices. Plastics like ABS and nylon are frequently machined for prototypes, fixtures, and non-conductive components, offering fast cycle times and excellent surface finishes.
When selecting a material, consider:
Use 410 or 440C stainless for magnetic, wear-resistant components requiring ±0.001″ tolerances.
Opt for 6061 or 7075 aluminum when non-magnetic, high-strength, and complex 5-axis features are needed.
Avoid 304/316 for high-speed, tight-tolerance milling unless corrosion resistance is paramount—use 303 for better machinability.
For non-structural, high-speed prototypes, ABS and nylon offer cost-effective, low-risk options with excellent dimensional control under stable shop conditions.
From CAD to Part: The Process
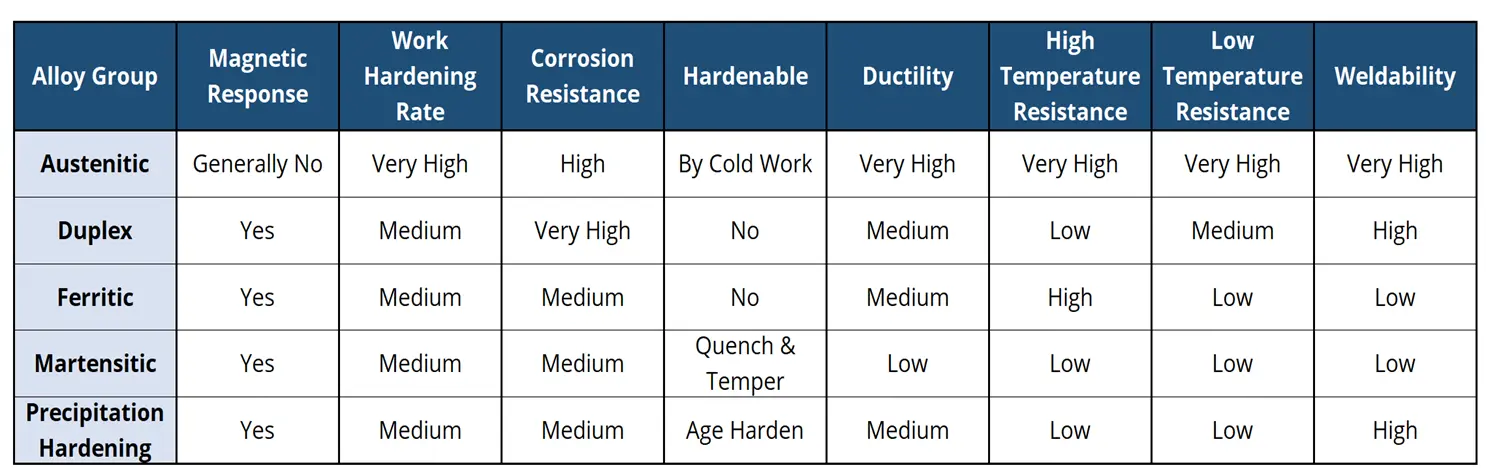
Honyo Prototype delivers precision rapid prototyping services with specialized expertise in magnetic stainless steel grades. Our streamlined workflow ensures technical accuracy and manufacturability for materials like 430, 410, 17-4PH, and other ferromagnetic alloys. Below is the precise sequence for processing magnetic stainless steel components:
CAD Upload and Material Specification
Clients initiate the process by uploading detailed CAD files through our secure portal. Crucially, the material requirement must be explicitly specified within the CAD metadata or accompanying documentation as a magnetic stainless steel grade (e.g., AISI 430, 17-4PH H1150). Our system validates material nomenclature against ASTM/AMS standards to prevent ambiguity. Generic terms like “magnetic stainless” trigger an automated clarification request, as magnetic properties vary significantly across grades due to ferritic/austenitic/martensitic microstructures.
AI-Powered Quoting with Material Intelligence
Our proprietary AI engine analyzes the CAD geometry alongside the declared magnetic stainless grade. The system cross-references real-time material cost databases, supplier availability, and grade-specific processing constraints. For instance, 430’s susceptibility to weld decay or 17-4PH’s precipitation hardening requirements automatically adjust machining parameters and cost factors in the quote. The AI flags non-standard grades requiring special sourcing and provides lead time estimates based on current mill inventory. Clients receive a transparent quote within 2 hours, including material certification costs.
DFM Analysis Focused on Magnetic Alloy Challenges
During Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review, our engineers conduct grade-specific assessments:
Work Hardening Evaluation: For 410/430 grades, we verify minimum bend radii to prevent cracking.
Thermal Management: 17-4PH components undergo HAZ (Heat-Affected Zone) simulation for welding/joining operations.
Magnetism Validation: Critical for sensor applications, we confirm expected permeability ranges based on grade and heat treatment.
Surface Integrity: Electropolishing requirements for corrosion resistance in ferritic grades are prescribed.
The DFM report details actionable recommendations, such as avoiding tight tolerances in annealed 430 due to magnetic anisotropy effects.
Precision Production with Certified Materials
All magnetic stainless steel stock originates from mills with full EN 10204 3.1 certification. Machining employs grade-optimized parameters:
Low-speed cutting for 430 to minimize work hardening
Cryogenic cooling during 17-4PH milling to maintain dimensional stability
Non-magnetic tooling to prevent contamination in critical applications
In-process material verification includes PMI (Positive Material Identification) testing and magnetic permeability checks per ASTM A342. Heat treatment cycles strictly follow AMS 5604 (for 17-4PH) or equivalent standards.
Delivery with Comprehensive Documentation
Shipments include:
Material test reports (MTRs) with actual magnetic properties (e.g., relative permeability at 200 Oe)
Dimensional inspection reports using CMM data
Process validation records for critical features
Traceability documentation linking each part to certified heat numbers
Material-Specific Production Parameters
| Grade | Key Challenge | Honyo Mitigation Strategy | Typical Lead Time |
|————|————————|—————————————–|——————-|
| AISI 430 | Weld decay sensitivity | Laser welding with <0.5mm penetration | 7-10 business days|
| 17-4PH H1150| Distortion in aging | Pre-aging stress relief + fixturing | 12-15 business days|
| AISI 410 | Low ductility | Annealed stock + progressive forming | 8-11 business days|
This integrated process ensures magnetic stainless steel prototypes meet functional requirements while eliminating material-related delays. We do not provide generic “magnetic stainless steel charts” as material behavior is application-dependent; instead, we deliver grade-specific engineering validation through each phase of production. Clients receive actionable data for their specific use case, not theoretical reference tables.
Start Your Project

Explore our comprehensive magnetic stainless steel grades chart to identify the right material for your precision manufacturing projects. Understanding magnetic properties is critical for applications in demanding environments, and our guide helps you select the optimal grade with confidence.
For technical support or custom prototyping solutions using magnetic stainless steel, contact Susan Leo directly at [email protected]. As a trusted manufacturing partner with an advanced facility in Shenzhen, Honyo Prototype delivers high-accuracy components with fast turnaround, backed by rigorous material verification and quality control.
Let us help you engineer better prototypes—reach out today to discuss your project requirements.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.