Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for magnesium chips
In today’s dynamic global market, sourcing high-quality magnesium chips can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The demand for magnesium chips—essential for various applications including specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and alloy production—continues to rise. However, navigating the complexities of supplier selection, regulatory compliance, and pricing strategies can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of magnesium chips, covering critical aspects such as types, applications, and the importance of supplier vetting. It will delve into the nuances of sourcing ultra-high-purity magnesium chips, their role in Grignard reactions, and the emerging trends in magnesium recycling, which are vital for sustainable practices. Additionally, the guide will offer insights into cost considerations, helping buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
By addressing these key areas, this resource empowers international B2B buyers to confidently navigate the intricacies of the magnesium chips market. Whether you’re based in Saudi Arabia, Vietnam, or beyond, understanding these factors will enhance your procurement strategies and ensure you acquire the right products for your business needs. Embrace the opportunity to streamline your sourcing process and foster successful partnerships in the global magnesium supply chain.
Understanding magnesium chips Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Magnesium Chips | 99.98% purity, 6-35 mesh size, used as a reductant | Specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, agriculture | Pros: High purity ensures quality results. Cons: Higher cost compared to standard purity. |
| Standard-Purity Magnesium Chips | 99.8% purity, larger particle size options | General industrial applications, alloy production | Pros: Cost-effective for bulk use. Cons: Lower purity may affect chemical reactions. |
| Magnesium Alloy Chips | Contains aluminum and other metals, typically AM60 alloy | Fireworks, pyrotechnics, and aerial devices | Pros: Creates bright flashes; versatile. Cons: More flammable; requires careful handling. |
| Magnesium Turnings | Coarse, thin pieces; varied particle sizes | Metalworking, recycling, and alloying | Pros: Can be recycled; versatile applications. Cons: Handling precautions due to flammability. |
| Magnesium Fines | Smaller particles, highly reactive | Specialty chemical synthesis, recycling | Pros: High surface area for reactions. Cons: Increased handling risks due to reactivity. |
What are the Key Characteristics of High-Purity Magnesium Chips?
High-purity magnesium chips are characterized by their 99.98% purity and a particle size of 6-35 mesh. These chips are primarily utilized in specialty chemical applications, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural processes as a reductant in Grignard reactions. When purchasing, buyers should consider the high cost relative to standard purity options, but the superior quality often justifies the investment for critical applications.
How Do Standard-Purity Magnesium Chips Differ?
Standard-purity magnesium chips typically contain 99.8% magnesium and are available in larger particle sizes. They are commonly used in general industrial applications and alloy production. Buyers looking for cost-effective solutions for bulk orders may find these chips advantageous, but they should be aware that the lower purity could impact specific chemical reactions, making them less suitable for high-precision applications.
What Makes Magnesium Alloy Chips Unique?
Magnesium alloy chips, such as those made from the AM60 alloy, include a combination of magnesium and aluminum, enhancing their properties for specific uses. These chips are often employed in pyrotechnics and fireworks due to their ability to produce bright, white flashes when ignited. While their versatility is a significant advantage, buyers must take into account their high flammability and ensure proper handling protocols are in place.
Why Are Magnesium Turnings Valuable for Industry?
Magnesium turnings are coarse and thin pieces that can vary in size, making them suitable for diverse applications including metalworking and recycling. They are often used in alloying processes and can be recycled effectively. For buyers, the ability to repurpose turnings adds value, but the handling requirements due to their flammability should not be overlooked.
What Are the Considerations for Using Magnesium Fines?
Magnesium fines are characterized by their small particle size and high reactivity, making them particularly useful in specialty chemical synthesis and recycling processes. Their increased surface area allows for rapid reactions, which can be beneficial in certain applications. However, buyers must exercise caution due to the heightened risks associated with handling such reactive materials, ensuring compliance with safety protocols.
Key Industrial Applications of magnesium chips
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of magnesium chips | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Manufacturing | Used as a reductant in Grignard reactions | Enhances chemical synthesis efficiency and product quality | Ensure high purity (99.98%) and size specifications (6-35 mesh) |
| Aerospace and Automotive | Production of magnesium alloys for lightweight components | Reduces overall vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency | Source from reputable suppliers with certifications and quality control |
| Defense and Military | Utilization in flares and incendiary devices | Provides reliable ignition and bright visibility in low-light conditions | Compliance with safety regulations and proper handling instructions |
| Fireworks and Pyrotechnics | Employed in pyrotechnic compositions | Creates bright flashes and vibrant colors for visual effects | Consider particle size and purity to ensure safety and performance |
| Recycling and Waste Management | Recycling of magnesium chips from machining processes | Maximizes resource recovery and reduces waste management costs | Look for suppliers with advanced recycling technologies and processes |
How Are Magnesium Chips Used in Chemical Manufacturing?
In the chemical manufacturing sector, magnesium chips are commonly utilized as a reductant in Grignard reactions, which are essential for synthesizing complex organic compounds. This application allows for the efficient formation of carbon-carbon bonds, leading to high-quality chemical products. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-purity magnesium chips (99.98%) is crucial to ensure optimal reaction outcomes. Additionally, the specific mesh size of 6-35 is vital for achieving the desired reaction rate and consistency.
What Role Do Magnesium Chips Play in Aerospace and Automotive Industries?
Magnesium chips are integral in producing magnesium alloys, which are favored in the aerospace and automotive industries for their lightweight properties. These alloys contribute to significant weight reductions in vehicles and aircraft, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe must prioritize suppliers who adhere to stringent quality standards and offer certified alloys to meet industry requirements. Understanding the specific alloy compositions and the manufacturing process can also help in selecting the right material for applications.
Why Are Magnesium Chips Important for Defense and Military Applications?
In the defense sector, magnesium chips are essential for creating flares and incendiary devices, known for their bright ignition and visibility in dark environments. This application is critical for signaling and illumination during military operations. For B2B buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, compliance with safety regulations is paramount when sourcing magnesium chips. Proper handling and storage protocols must be established to mitigate the risks associated with their flammability.
How Are Magnesium Chips Used in Fireworks and Pyrotechnics?
Magnesium chips are a key ingredient in pyrotechnic compositions, providing the bright flashes and vibrant colors that are characteristic of fireworks displays. Their ability to burn brightly makes them an essential component for creating visually stunning effects. Buyers in the fireworks industry should consider the purity and particle size of magnesium chips to ensure safety and performance during manufacturing. Sourcing from suppliers with a solid reputation and experience in pyrotechnic materials is also advisable to maintain quality standards.
What Is the Role of Magnesium Chips in Recycling and Waste Management?
The recycling of magnesium chips from machining processes is becoming increasingly important in waste management. This practice allows for the recovery of valuable magnesium resources and minimizes waste. Advanced recycling technologies, such as solid-state recycling, can significantly enhance recovery rates compared to traditional methods. For international buyers, selecting suppliers that specialize in these advanced recycling processes can lead to cost savings and sustainable practices. It’s crucial to understand the supplier’s capabilities and certifications to ensure effective recycling solutions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘magnesium chips’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance for Magnesium Chips
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when it comes to ensuring the quality and purity of magnesium chips. With stringent regulations in industries such as pharmaceuticals and aerospace, any impurities or deviations from specifications can lead to costly production delays or even product failures. Buyers from diverse regions, including Africa and South America, may struggle to find reliable suppliers who can consistently deliver high-purity magnesium chips (99.98% or higher). This inconsistency not only affects their production timelines but can also harm their reputations in the marketplace.
The Solution: To overcome quality assurance issues, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who provide comprehensive documentation, including Certificates of Analysis (COA) for each batch. Buyers should also consider suppliers that specialize in ultra-high-purity magnesium and have established quality control processes. It’s advisable to conduct regular audits or assessments of the suppliers’ production facilities to ensure compliance with international standards. Additionally, establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can lead to improved consistency and reliability in product quality. Leveraging technology, such as blockchain for supply chain transparency, can further enhance traceability and accountability in sourcing magnesium chips.
Scenario 2: Addressing Handling and Safety Concerns
The Problem: Magnesium chips are highly flammable and pose significant safety risks during handling and storage. For companies operating in regions with varying safety regulations, ensuring compliance while maintaining operational efficiency can be daunting. B2B buyers may find themselves at a crossroads, trying to balance the need for effective storage solutions with the imperative of meeting safety standards, particularly in industries like defense and chemical manufacturing.
The Solution: To mitigate safety risks, companies should invest in specialized storage solutions that comply with relevant safety regulations. This includes using fire-resistant containers and ensuring that storage areas are well-ventilated and equipped with appropriate fire suppression systems. Implementing comprehensive training programs for employees on the safe handling of magnesium chips is also critical. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to understand the best practices for storage and handling, including temperature control measures and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Additionally, creating a culture of safety within the organization will empower employees to prioritize safety and adhere to established protocols.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Global supply chain disruptions can severely impact the availability of magnesium chips, particularly for B2B buyers reliant on just-in-time manufacturing practices. Buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe may encounter delays due to geopolitical factors, transportation issues, or supplier insolvencies. These disruptions can lead to production halts, increased costs, and strained customer relationships.
The Solution: To combat supply chain vulnerabilities, B2B buyers should diversify their supplier base, seeking multiple sources for magnesium chips. This strategy reduces dependence on a single supplier and can provide alternative options during disruptions. Establishing partnerships with local suppliers can also mitigate transportation risks and reduce lead times. Additionally, implementing robust inventory management systems that incorporate demand forecasting can help companies maintain sufficient stock levels to withstand short-term disruptions. Buyers should also consider creating strategic agreements or contracts with suppliers that include clauses for supply continuity, ensuring a reliable flow of materials even in challenging circumstances.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for magnesium chips
What Are the Key Properties of Different Magnesium Chip Materials?
When selecting magnesium chips for various applications, it is essential to consider the specific material properties that can affect performance. Common materials include high-purity magnesium, magnesium alloys, and recycled magnesium. Each material presents unique characteristics that can influence their suitability for specific applications.
High-Purity Magnesium Chips
High-purity magnesium chips, typically with a purity of 99.98%, are known for their excellent reactivity and low impurity levels. They are often used in chemical reactions, such as Grignard reactions, due to their high reactivity with organic compounds. The temperature and pressure ratings are generally favorable, with a melting point of 648 °C and a boiling point of 1090 °C, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros: High-purity magnesium chips provide consistent performance and are ideal for specialized chemical applications. Their low impurity content enhances the quality of the end products.
Cons: They are more expensive than lower-purity alternatives and may require careful handling due to their flammability.
Impact on Application: Their high reactivity makes them suitable for applications in pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals, where purity is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and EN is crucial. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide certificates of analysis to verify purity levels.
Magnesium Alloy Chips
Magnesium alloy chips, such as AM60 (93% magnesium, 6% aluminum), are commonly used in applications where strength and lightweight properties are essential. These alloys exhibit improved mechanical properties, including enhanced corrosion resistance compared to pure magnesium.
Pros: Magnesium alloys offer a favorable balance between weight and strength, making them suitable for automotive and aerospace applications.
Cons: The presence of aluminum and other elements can reduce the reactivity of these alloys, which may limit their use in specific chemical processes.
Impact on Application: Their enhanced durability makes them ideal for structural applications, but their lower reactivity may restrict their use in chemical synthesis.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with stringent regulations on materials should verify alloy compositions to ensure compliance with local standards.
Recycled Magnesium Chips
Recycled magnesium chips provide an environmentally friendly option while maintaining reasonable performance characteristics. The recycling process often results in materials that retain much of the original magnesium’s properties, although the purity may vary.
Pros: Using recycled magnesium chips can significantly reduce costs and environmental impact, making them an attractive option for sustainability-focused companies.
Cons: Variability in purity and composition can affect performance, making quality assurance critical.
Impact on Application: Suitable for applications where cost is a significant factor, but buyers must ensure the recycled materials meet their specific performance requirements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should inquire about the recycling processes used and any certifications that validate the quality of recycled materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Magnesium Chips
| Material | Typical Use Case for magnesium chips | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Magnesium | Chemical synthesis | High reactivity and purity | Higher cost and flammability | High |
| Magnesium Alloy | Automotive and aerospace components | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Reduced reactivity compared to pure magnesium | Medium |
| Recycled Magnesium | Cost-sensitive applications | Environmentally friendly and cost-effective | Variability in purity and performance | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for magnesium chips, offering valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for magnesium chips
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Magnesium Chips?
The manufacturing of magnesium chips involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the production of high-purity material suitable for various applications, such as chemical synthesis and alloy production. The key stages typically include:
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with sourcing ultra-high-purity magnesium ingots, typically with a purity level of 99.98% or higher. These ingots undergo rigorous inspections to ensure they meet the necessary chemical composition and purity standards.
-
Forming Techniques: The prepared ingots are then subjected to mechanical processing techniques, which can include cutting, milling, or grinding. This step is crucial as it determines the size and surface characteristics of the magnesium chips. The standard particle size ranges from 6 to 35 mesh, which is essential for applications that require specific surface area and reactivity levels.
-
Assembly and Processing: Depending on the end-use, additional processing techniques may be employed. For instance, magnesium chips can be alloyed with other metals to enhance their properties, such as strength and corrosion resistance. This may involve controlled melting and mixing processes.
-
Finishing Treatments: The final stage involves finishing treatments that may include surface cleaning or coating to enhance performance and stability during storage and transportation. This is especially important for magnesium, which is highly reactive, particularly in the presence of moisture.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Magnesium Chip Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of magnesium chip production, ensuring that the final product meets international and industry-specific standards. Here’s how QA is typically structured:
-
International Standards Compliance: Manufacturing facilities often adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which emphasize quality management systems that enhance customer satisfaction through effective process control. Additionally, specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be relevant depending on the application of the magnesium chips.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, multiple quality control (QC) checkpoints are established:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt, ensuring they meet specified criteria before processing.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing allows for the identification of deviations from quality standards in real-time.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Upon completion of production, the finished magnesium chips undergo comprehensive testing to validate their purity, size, and overall quality. -
Common Testing Methods for Magnesium Chips: Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of magnesium chips, including:
– Spectroscopy: Used to analyze the chemical composition and purity.
– Particle Size Analysis: Ensures that the chips fall within the specified mesh size.
– Flammability Tests: Given magnesium’s reactive nature, assessing its flammability under controlled conditions is critical.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure reliability and safety. Here are several strategies:
-
Conducting Supplier Audits: Regular audits can provide firsthand insight into a supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. These audits should be thorough, covering all aspects from material sourcing to final product testing.
-
Requesting Quality Reports and Certifications: Buyers should ask for documented evidence of compliance with international standards, including ISO certifications and any relevant industry-specific certifications. Suppliers should also provide detailed quality reports that outline testing results and any corrective actions taken.
-
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services: Engaging independent third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s production processes and product quality. These agencies can conduct random sampling and testing to confirm that the products meet specified standards.
-
Understanding Quality Control Nuances for International Transactions: B2B buyers must be aware of the specific regulatory and quality control requirements in their own regions. For instance, some regions may have stricter import regulations or additional certifications needed for hazardous materials like magnesium.
What Are the Challenges and Considerations in Quality Assurance for Magnesium Chips?
Quality assurance in the production of magnesium chips is not without its challenges. Here are some considerations for B2B buyers:
-
Handling and Storage: Given magnesium’s highly flammable nature, stringent handling and storage protocols must be in place. Suppliers should demonstrate compliance with safety regulations to mitigate risks during transportation and storage.
-
Variability in Supplier Standards: Not all suppliers may adhere to the same quality standards, which can lead to discrepancies in product quality. Buyers should establish clear expectations and continuously monitor supplier performance to ensure consistency.
-
Market-Specific Regulations: Different markets may have varying requirements for magnesium products. Buyers must stay informed about local regulations regarding chemical imports and ensure that suppliers are compliant.
-
Technological Advancements: As manufacturing technologies evolve, suppliers may adopt new methods that enhance product quality. Buyers should remain engaged with suppliers to understand any changes in production processes that could affect product specifications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for magnesium chips are critical to ensuring the delivery of high-quality products that meet industry standards. By understanding the manufacturing stages, QA practices, and methods for verifying supplier reliability, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. As the demand for high-purity magnesium chips continues to grow globally, maintaining rigorous quality standards will be essential for suppliers aiming to serve international markets effectively.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘magnesium chips’
Introduction
This guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing magnesium chips, a critical material used in various applications including chemical synthesis and alloy production. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can ensure that you select the right supplier and product specifications to meet your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is essential for sourcing magnesium chips. Consider factors such as purity levels (e.g., 99.8% vs. 99.98%), particle size (e.g., 6-35 mesh), and specific applications (e.g., Grignard reactions). This clarity will facilitate better communication with suppliers and ensure you receive products that meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers in the magnesium market. Look for companies with a proven track record in producing high-purity magnesium chips. Check for online reviews, industry certifications, and their history of compliance with international safety standards, which is particularly important given the flammability of magnesium.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a decision, verify that your potential suppliers hold relevant certifications. This might include ISO certifications or compliance with local and international safety regulations. Certifications not only demonstrate a supplier’s commitment to quality but also assure you that the products meet industry standards.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Don’t hesitate to ask suppliers for product samples. Testing samples allows you to assess the quality and performance of the magnesium chips in your specific applications. Ensure that the samples reflect the specifications you require, and conduct your own quality checks to confirm their suitability.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a shortlist of suppliers, compare pricing structures and payment terms. Be wary of prices that seem too good to be true, as they may reflect lower quality. Additionally, consider factors such as minimum order quantities and shipping costs, which can significantly impact your overall budget.
Step 6: Discuss Customization Options
If your application requires specific characteristics or formulations, inquire about customization capabilities. Some suppliers offer tailored solutions, such as custom alloy development, which can enhance the performance of your end products. Understanding these options can give you a competitive advantage in your market.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Channel
Finally, set up a reliable communication channel with your chosen supplier. Open lines of communication are vital for addressing any issues that may arise during the ordering process. Regular updates on production schedules, shipping, and potential delays can help you manage your supply chain effectively.
By following this practical sourcing guide, you can navigate the complexities of procuring magnesium chips with confidence, ensuring that your business operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for magnesium chips Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Magnesium Chips?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing magnesium chips, several critical components must be considered. These include raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the magnesium itself, which can vary in price based on purity levels (standard vs. ultra-high purity) and market demand. Prices can range from $7.79 per pound for lower purity alloys to higher rates for high-purity magnesium chips, which may exceed $20 per pound depending on specifications.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to workers involved in the manufacturing process. This can include machine operators, quality inspectors, and maintenance staff. Labor costs may vary by region, affecting total costs for international buyers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and other indirect costs necessary for production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help lower these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Specific equipment and tooling may be required to produce magnesium chips to desired specifications. This investment can be substantial but is necessary for ensuring quality and consistency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that magnesium chips meet industry standards and customer specifications requires rigorous QC processes, which add to the overall cost structure. Certifications such as ISO can also impact pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can significantly affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on supplier reputation, demand, and market conditions.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect the Cost of Magnesium Chips?
Several factors influence the pricing of magnesium chips, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders may qualify for volume discounts, reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to optimize costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications or unique sizes can lead to higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs upfront to avoid unexpected pricing.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: Higher purity materials and additional certifications can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the added expense aligns with their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their quality assurance and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for buyers. These terms dictate shipping responsibilities and costs, impacting the total landed cost of the goods.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Magnesium Chips?
To achieve cost efficiency when sourcing magnesium chips, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better negotiation outcomes. Buyers should leverage their purchasing power and market knowledge during negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should evaluate the TCO, which includes not only the purchase price but also costs related to logistics, storage, and quality assurance. A lower upfront cost may not always translate to savings in the long run.
-
Monitor Market Trends: Keeping an eye on market trends, supply chain disruptions, and raw material prices can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions. Timing purchases strategically can lead to cost savings.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, enhancing overall efficiency.
-
Stay Informed on Regulatory Requirements: Understanding the regulatory landscape in different regions can prevent unexpected costs related to compliance and customs.
Conclusion
The sourcing of magnesium chips involves various cost components and pricing influencers that international B2B buyers must navigate. By understanding these elements and employing strategic sourcing practices, buyers can optimize their procurement processes and achieve better cost efficiencies. Always remember that prices may fluctuate based on market conditions, and it is prudent to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing magnesium chips With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Magnesium Chips: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the realm of industrial applications, magnesium chips serve as a vital resource, particularly in chemical synthesis and alloy production. However, buyers should consider alternative solutions that may better suit their specific needs, based on factors like performance, cost, and ease of implementation. This analysis presents a comparative overview of magnesium chips against two viable alternatives: aluminum powder and calcium metal.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Magnesium Chips | Aluminum Powder | Calcium Metal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High purity, effective as a reductant in chemical reactions | Good for lightweight applications, oxidizes easily | Excellent reducing agent, reacts vigorously with water |
| Cost | Moderate (~$7.79/lb) | Generally lower (~$5.50/lb) | Higher (~$10.00/lb) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires handling precautions; flammable | Easy to handle; non-flammable | Requires specific handling due to reactivity |
| Maintenance | Minimal; requires safe storage | Low; stable under standard conditions | Moderate; needs careful storage away from moisture |
| Best Use Case | Chemical synthesis, alloy production | Aerospace, automotive components | Chemical reactions, metallurgy |
Analyzing Alternatives: Pros and Cons
Aluminum Powder
Aluminum powder is a lightweight material commonly used in various industries, including aerospace and automotive. It is less reactive than magnesium, making it easier to handle and store. The cost-effectiveness of aluminum powder makes it attractive for large-scale applications. However, its performance as a reductant is inferior to that of magnesium chips, particularly in Grignard reactions. Additionally, aluminum can oxidize quickly when exposed to moisture, which may limit its shelf life and usability in certain applications.
Calcium Metal
Calcium metal is known for its vigorous reactivity, particularly with water, producing hydrogen gas. It serves as a powerful reducing agent and is useful in metallurgical processes. While calcium can be effective in specific chemical reactions, its cost is generally higher than both magnesium and aluminum. Furthermore, it requires careful handling and storage due to its reactivity, making it less user-friendly than magnesium chips. Its specialized applications may limit its appeal for buyers looking for versatile solutions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between magnesium chips and alternative solutions such as aluminum powder or calcium metal, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements. Magnesium chips excel in chemical synthesis and alloy production due to their high purity and effectiveness as a reductant. However, if cost and ease of handling are primary concerns, aluminum powder may be the more suitable option. On the other hand, calcium metal is ideal for specialized chemical applications where its unique properties can be fully leveraged, albeit at a higher cost and with more handling precautions. By evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for magnesium chips
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Magnesium Chips in B2B Transactions?
Magnesium chips, an essential material in various industries, possess specific technical properties that significantly impact their application and suitability for different processes. Understanding these properties is vital for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Grade
The purity of magnesium chips is often classified into standard and ultra-high purity grades, typically 99.8% and 99.98% respectively. This specification is critical, especially in applications requiring high reactivity, such as Grignard reactions in pharmaceuticals. Buyers must ensure they source the appropriate grade to meet their specific application needs, as impurities can affect performance and yield.
2. Particle Size
Magnesium chips are usually available in various mesh sizes, commonly ranging from 6 to 35 mesh. The particle size affects the surface area and reactivity of the chips. Smaller particles have higher reactivity, making them suitable for rapid chemical reactions, while larger chips may be preferred in applications requiring slower reactions. Buyers should consider their processing methods to select the appropriate size.
3. Autoignition Temperature
The autoignition temperature of magnesium chips is approximately 950 °F (510 °C). This property is crucial for safety considerations during storage and handling. Buyers must implement proper safety protocols to mitigate the risk of spontaneous combustion, particularly in high-temperature environments.
4. Density
With a density of about 1.74 g/mL at 25 °C, the density of magnesium chips affects their transport and storage requirements. A higher density implies a more compact form of material, which can influence shipping costs and storage space. Buyers should factor in density when calculating logistics and storage solutions.
5. Reactivity
Magnesium chips are classified as reactive materials, particularly when exposed to moisture or air. Understanding their reactivity is essential for applications in chemical synthesis, where controlled environments are necessary to prevent unwanted reactions. Buyers must ensure that appropriate handling and storage conditions are maintained to preserve the integrity of the chips.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing Magnesium Chips?
Navigating the procurement of magnesium chips involves familiarizing oneself with industry-specific terminology that can influence purchasing decisions.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of magnesium chips, OEM refers to companies that manufacture products using magnesium as a raw material. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to source magnesium chips that meet specific application requirements and quality standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should be aware of MOQs when negotiating contracts to ensure they align with their production schedules and budget constraints.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request from buyers to suppliers for pricing and terms on specific quantities of magnesium chips. This process is crucial for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding the terms of sale. It allows buyers to compare offers from different suppliers effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) specify who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for buyers to negotiate favorable shipping terms and understand their liabilities.
5. Technical Data Sheet (TDS)
A TDS provides essential information about the properties, specifications, and safe handling practices of magnesium chips. Buyers should always request a TDS to ensure they are aware of the product characteristics and compliance with safety regulations.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing magnesium chips, ensuring they meet their operational needs effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the magnesium chips Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Magnesium Chips Market for B2B Buyers?
The magnesium chips market is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing demand across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and pharmaceuticals. One of the primary global drivers is the push for lightweight materials that enhance fuel efficiency and reduce carbon emissions. As manufacturers seek to develop high-performance magnesium alloys, the need for high-purity magnesium chips has surged. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where industries are rapidly evolving to adopt advanced materials.
Emerging technologies in the sourcing of magnesium chips are also reshaping the market landscape. Digital platforms for procurement are gaining traction, allowing buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and compare product specifications and prices effortlessly. Additionally, innovations in recycling processes for magnesium chips are becoming a focal point, as companies aim to reduce waste and promote circular economy practices. Suppliers that offer comprehensive recycling solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
B2B buyers should also be aware of geopolitical factors impacting supply chains. Trade policies, tariffs, and local regulations can significantly affect the availability and pricing of magnesium chips. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers who understand these dynamics will be crucial for navigating market fluctuations.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Magnesium Chips Procurement Strategy?
Sustainability has become a central theme in the procurement of magnesium chips. The environmental impact of mining and processing magnesium is substantial, necessitating a shift towards ethical sourcing practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient production methods. This not only mitigates environmental harm but also enhances brand reputation and compliance with international standards.
Certifications for ‘green’ materials are gaining importance in the magnesium chips sector. Buyers should look for suppliers with certifications that validate their commitment to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or certifications that demonstrate adherence to responsible sourcing practices. These certifications provide assurance that the materials sourced are produced with minimal environmental impact, further supporting corporate sustainability goals.
Moreover, sustainable sourcing can lead to cost savings in the long run. Companies that invest in recycling processes for magnesium chips can reduce waste disposal costs and create new revenue streams from reclaimed materials. As the demand for sustainable products continues to grow, B2B buyers must align their procurement strategies with sustainability principles to remain competitive.
What Is the Historical Context of Magnesium Chips in B2B Applications?
The use of magnesium chips dates back to the early 19th century when magnesium was first isolated. Initially, magnesium was utilized in pyrotechnics due to its bright flame and lightweight properties. Over the decades, the applications of magnesium expanded significantly, particularly in the aerospace and automotive industries, where its strength-to-weight ratio made it an attractive material for components.
By the late 20th century, advancements in metallurgy led to the development of high-purity magnesium alloys, enhancing the performance characteristics of magnesium chips. Today, these chips are critical in various applications, including as reductants in chemical reactions and as key components in the production of high-performance alloys. Understanding this evolution helps B2B buyers appreciate the material’s value and its growing role in modern industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of magnesium chips
-
How do I ensure the quality of magnesium chips before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of magnesium chips, request a Certificate of Analysis (COA) from your supplier, which verifies the purity and composition of the material. Look for suppliers who adhere to international standards, such as ASTM or ISO certifications. Additionally, consider third-party testing for an unbiased assessment. Engaging in samples prior to bulk orders can also help you evaluate the product’s performance in your specific applications. Establishing a quality assurance process with your supplier will further mitigate risks. -
What is the best type of magnesium chips for Grignard reactions?
For Grignard reactions, ultra-high-purity magnesium chips (99.98% purity) are recommended due to their superior reactivity and minimal contamination. They are specifically designed for specialty chemical, pharmaceutical, and agricultural applications, providing consistent results. Ensure the chips are within the appropriate mesh size (typically 6-35 mesh) to optimize surface area and reaction efficiency. Discuss your specific needs with your supplier to confirm that their product aligns with your application requirements. -
How can I find reliable suppliers for magnesium chips in international markets?
To find reliable suppliers, start by researching industry-specific trade directories and platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or ThomasNet. Attend trade shows and exhibitions focused on chemicals and materials, which provide networking opportunities. Verify suppliers by checking their certifications, customer reviews, and references. Engaging in a dialogue with potential suppliers can also help assess their responsiveness and willingness to meet your needs. Finally, consider local regulations and trade agreements that may affect sourcing from certain regions. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for magnesium chips?
Minimum order quantities for magnesium chips can vary significantly among suppliers. Generally, MOQs range from 50 kg to several tons, depending on the supplier’s production capacity and the specific product type. When negotiating, consider your own usage rates and storage capabilities to avoid overcommitting. Some suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time buyers or trial orders, so it’s worth discussing your requirements directly with them. -
What payment terms should I expect when ordering magnesium chips internationally?
Payment terms for international orders of magnesium chips can vary widely but typically include options like wire transfers, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for larger orders. It’s important to clarify the terms before committing to an order, including any potential fees for currency conversion or international transactions. Ensure that both parties agree on the payment schedule to avoid misunderstandings. -
How should I handle the logistics of shipping magnesium chips?
Shipping magnesium chips requires careful consideration due to their flammability. Ensure that your supplier complies with international shipping regulations and provides proper packaging to mitigate risks during transport. Work with logistics providers experienced in handling hazardous materials to ensure compliance with local and international laws. Additionally, consider lead times for customs clearance, especially when shipping between continents, to avoid delays in your supply chain. -
Can magnesium chips be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for magnesium chips, including variations in purity, size, and shape to meet specific application needs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options. Custom alloy development may also be possible, particularly for specialized applications in industries such as aerospace or automotive. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and potentially engage in a trial phase to validate the product’s performance in your application. -
What are the safety considerations when handling magnesium chips?
Handling magnesium chips requires strict safety protocols due to their flammable nature. Ensure that all personnel involved in handling the material are equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection. Store magnesium chips in a cool, dry place away from sources of ignition. Additionally, familiarize yourself with emergency procedures in case of fire or chemical exposure. Training employees on safe handling practices is essential to mitigate risks effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Magnesium Chips Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sigma-Aldrich – Magnesium Chips
Domain: sigmaaldrich.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Magnesium chips”,”Mesh Size”: “6-35 mesh”,”Purity”: “99.98% trace metals basis”,”CAS Number”: “7439-95-4″,”Molecular Weight”: “24.31”,”Beilstein/REAXYS Number”: “4948473”,”EC Number”: “231-104-6″,”MDL Number”: “MFCD00085308″,”UNSPSC Code”: “12141502”,”PubChem Substance ID”: “24855356”,”NACRES”: “NA.23″,”Vapor Pressure”: “1 mmHg (621 °C)”,”Autoignition Temperature”: “950 °F”,”Resi…
2. Skylighter – Magnesium Turnings and Chips
Domain: skylighter.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
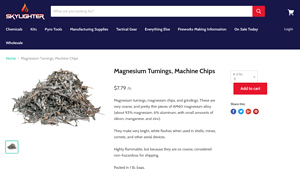
Introduction: {“name”: “Magnesium Turnings and Chips”,”mesh_size”: “+1-80 Mesh”,”price”: “$7.79 / lb”,”composition”: “AM60 magnesium alloy (about 93% magnesium, 6% aluminum, with small amounts of silicon, manganese, and zinc)”,”features”: [“Very coarse and thin pieces”,”Produces bright, white flashes when used in shells, mines, comets, and other aerial devices”,”Highly flammable but considered non-hazardous for…
3. Luxfer – Magnesium Chips & Granules
Domain: luxfermagtech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Magnesium Chips & Granules
Description: Magnesium chips (also known as magnesium turnings) and granules are produced by mechanically processing standard-purity (99.8% Mg) or ultra-high-purity (99.98% Mg) magnesium ingots. They are commonly used in Grignard reactions for specialty chemical, pharmaceutical, and agricultural applications.
Purity Specifications:
– Standard Purity Magnesi…
4. Alpha Chemicals – Magnesium Chips
Domain: alphachemicals.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Magnesium Chips – Small
Chip Size: 10-40 Mesh
Quality: High quality magnesium chips
Uses: Suitable for Grignard reagent preparation
Safety: Emits bright white light when burned; eye protection required
Packaging: Minimum of 50 grams or 250 grams packed in a resealable plastic bag depending on size ordered
Shipping: Shipped via USPS ORM-D or UPS ORM-D
MSDS and Spec Sheets: Available
H…
5. MagReTech – Magnesium Recycling Services
Domain: magretech.us
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: MagReTech offers various magnesium recycling services including tolling conversion programs for different alloy types, specifically tailored to customer needs. They recycle magnesium turnings and chips from machining die castings, utilizing a process that involves aqueous washing and centrifugal force to remove lubricants and oils. The clean material is then either pressed into briquettes or extru…
6. Magnesium Chips – Key Product
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Key Product Details:
– Product Type: Magnesium Chips/Shavings
– Purity: 99.9% or 99% Purity
– Common Uses: Emergency Fire Starter, Camping, Hiking, Bushcraft, Survival Kits
– Packaging: Available in various weights (e.g., 1 lb bag, 8 oz bag, 200g)
– Features: Lightweight, Waterproof, Works When Wet, Nontoxic, Odorless
– Condition: New or Used
– Price Range: Typically under $25.00 to over $45.00
– …
7. Reddit – Magnesium Chips
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for magnesium chips
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Magnesium Chips?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of magnesium chips is paramount for B2B buyers in diverse sectors such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and aerospace. The high purity levels (99.98% and above) and versatile applications of magnesium chips make them indispensable for innovative chemical processes, including Grignard reactions and alloy production. By engaging with reliable suppliers, businesses can ensure consistent quality, mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions, and capitalize on cost efficiencies.
What Should International Buyers Consider in Sourcing Magnesium Chips?
Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers who not only meet stringent quality standards but also offer flexibility in product specifications. The growing trend of magnesium recycling and sustainable sourcing practices can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce environmental impact, making it a critical consideration for modern businesses.
How Can You Prepare for the Future of Magnesium Chips?
As the demand for lightweight, durable materials continues to rise, the outlook for magnesium chips remains robust. International buyers are encouraged to stay informed about advancements in magnesium alloy technologies and to explore partnerships with innovative suppliers. By doing so, they can position themselves strategically to leverage emerging opportunities in this dynamic market. Embrace the potential of magnesium chips today to drive your business forward into a sustainable and efficient future.