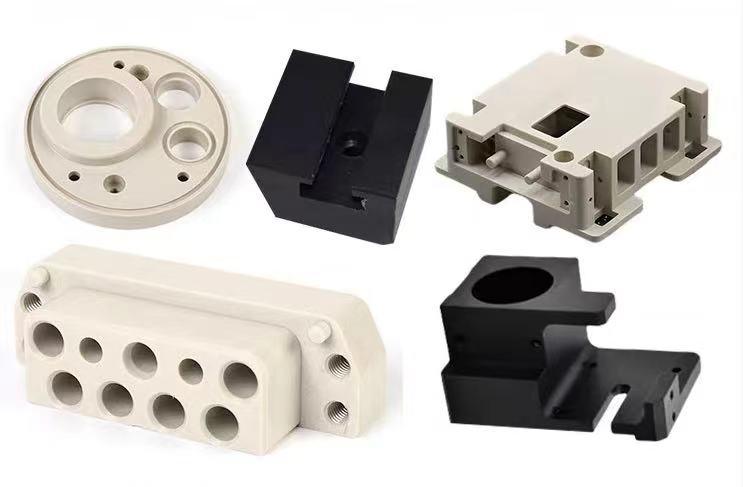
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machining peek
Navigating the intricate landscape of machining PEEK (polyether ether ketone) can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, especially those in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With its unique combination of lightweight strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, PEEK is increasingly sought after in industries ranging from aerospace to medical devices. However, understanding the nuances of sourcing and machining this high-performance thermoplastic is critical to ensuring quality and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide delves into various aspects of machining PEEK, including the different types of PEEK materials, their specific applications, and essential machining techniques. It also emphasizes the importance of supplier vetting to mitigate risks associated with material quality and machining precision. Furthermore, we explore cost considerations, allowing buyers to make informed financial decisions that align with their production goals.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this guide empowers you to navigate the global market for machining PEEK effectively. Whether you are looking to enhance your product offerings or streamline your manufacturing processes, understanding the intricacies of PEEK can lead to significant competitive advantages in your industry.
Understanding machining peek Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial-Grade PEEK | High impact strength, flame-retardant, abrasion resistant | Aerospace, automotive, electronics, chemical | Pros: Durable, versatile; Cons: Not biocompatible. |
| Medical-Grade PEEK | Biocompatible, sterilization compatible, radiolucent | Medical implants, surgical instruments | Pros: Safe for long-term contact with tissue; Cons: Higher cost. |
| Carbon-Fiber Reinforced PEEK | Enhanced stiffness, reduced weight | Aerospace components, high-performance parts | Pros: Superior mechanical properties; Cons: More complex machining requirements. |
| PEEK Optima | Specifically designed for medical use | Orthopedic devices, spinal implants | Pros: Excellent biocompatibility; Cons: Limited to medical applications. |
| PEEK Zeniva | High-performance for demanding applications | Custom medical devices, dental applications | Pros: Tailored for specialized applications; Cons: Cost can be prohibitive. |
What are the characteristics of Industrial-Grade PEEK and its suitability for B2B applications?
Industrial-grade PEEK is known for its exceptional mechanical properties, including high impact strength and resistance to extreme temperatures. This makes it suitable for demanding environments such as aerospace and automotive industries, where reliability is crucial. Buyers should consider its versatility across various applications but note that it is not biocompatible, limiting its use in medical contexts.
How does Medical-Grade PEEK differ from other types, and what should buyers consider?
Medical-grade PEEK is specifically engineered to meet biocompatibility standards, making it safe for use in implants and surgical instruments. Its sterilization compatibility and radiolucency are critical features for medical applications. While it offers significant advantages in terms of safety and functionality, buyers should be prepared for higher costs associated with this specialized material.
What advantages does Carbon-Fiber Reinforced PEEK provide for B2B applications?
Carbon-fiber reinforced PEEK offers enhanced stiffness and reduced weight, making it ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace and automotive sectors. This variation provides superior mechanical properties, allowing for more complex designs. However, the machining process can be more challenging, requiring specialized tools and techniques, which buyers must account for in their project planning.
What makes PEEK Optima a unique choice for medical applications?
PEEK Optima is tailored for medical use, providing excellent biocompatibility and mechanical properties. This type is particularly well-suited for orthopedic and spinal implants, where long-term contact with human tissue is necessary. Buyers should consider its regulatory compliance and the importance of sourcing from reputable suppliers to ensure quality and performance.
Why choose PEEK Zeniva for demanding applications, and what are the cost implications?
PEEK Zeniva is designed for high-performance applications, offering tailored properties for various specialized medical devices. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions while maintaining functionality makes it a preferred choice for dental applications and custom medical devices. However, the cost can be a barrier for some buyers, necessitating careful budget considerations when planning projects.
Key Industrial Applications of machining peek
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machining PEEK | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Lightweight components for aircraft structures | Reduces overall weight, improving fuel efficiency | Ensure compliance with aerospace standards and certifications. |
| Medical & Life Sciences | Custom implants and surgical instruments | High biocompatibility and durability | Verify medical-grade certification and sterilization compatibility. |
| Automotive | Engine components and fuel system parts | Enhanced performance and longevity under high stress | Assess thermal stability and chemical resistance properties. |
| Electronics | Insulators and housings for electronic devices | Improved electrical performance and reliability | Look for suppliers with expertise in precision machining. |
| Oil & Gas | Seals and gaskets for high-pressure applications | Reduced risk of failure in extreme conditions | Evaluate the supplier’s experience with high-performance polymers. |
How is Machining PEEK Used in Aerospace & Defense?
In the aerospace and defense industries, machining PEEK is critical for creating lightweight yet robust components, such as brackets and structural parts. These applications benefit from PEEK’s high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to extreme temperatures, which contribute to overall fuel efficiency. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing PEEK components requires ensuring compliance with stringent aerospace regulations and certifications, which can vary by country.
What Role Does Machining PEEK Play in Medical & Life Sciences?
Machining PEEK is integral in the production of custom medical implants and surgical instruments due to its exceptional biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Medical-grade PEEK can be used for long-term implants that mimic bone stiffness, making it ideal for orthopedic applications. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers who can provide validated medical-grade materials and ensure compliance with ISO standards for sterilization and biocompatibility.
How is PEEK Machined for Automotive Applications?
In the automotive sector, PEEK is machined into components like engine parts and fuel system components, where its high-temperature resistance and chemical stability are vital. These properties enhance performance and longevity, reducing the frequency of part replacements. B2B buyers in regions such as Brazil should consider sourcing from manufacturers with a proven track record in automotive applications to ensure that the materials meet industry-specific performance standards.
What are the Benefits of Machining PEEK in Electronics?
Machining PEEK for electronic applications involves creating insulators and housings that require excellent electrical performance and reliability. PEEK’s dielectric properties make it suitable for high-frequency applications, thus enhancing the functionality of electronic devices. International buyers, particularly from Europe and Asia, should focus on suppliers who can deliver precision-machined components that meet specific electrical and thermal requirements.
How is Machining PEEK Used in Oil & Gas Applications?
In the oil and gas industry, machining PEEK is essential for manufacturing seals and gaskets designed to withstand high-pressure environments. PEEK’s chemical resistance and low friction properties minimize the risk of failure, ensuring operational efficiency. Buyers in the Middle East should ensure that their suppliers have experience with high-performance polymers and can provide documentation on material properties to meet the demanding conditions of this sector.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machining peek’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Precision Tolerances in Aerospace Applications
The Problem: Aerospace components demand exceptionally tight tolerances, often within microns. When machining PEEK for aircraft parts, buyers face the challenge of maintaining these precision requirements while managing the thermal properties of PEEK, which can lead to warping or dimensional changes during machining. This is particularly concerning for parts that must endure extreme conditions, as even minor inaccuracies can compromise safety and performance.
The Solution: To achieve the required precision, buyers should implement a multi-stage annealing process before machining. This involves heating the PEEK material to relieve internal stresses, which reduces the risk of warping during cutting. Additionally, using CNC machines with advanced calibration settings tailored for PEEK can help ensure consistent precision. Employing high-quality, sharp tooling, such as polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools, will minimize tool wear and maintain cutting accuracy. Regular monitoring of the machining environment, including temperature and vibration, will also help maintain the integrity of the components throughout the process.
Scenario 2: Contamination Risks in Medical Device Manufacturing
The Problem: In the medical device industry, contamination is a critical concern, especially when machining medical-grade PEEK. Buyers often struggle with maintaining a clean environment that meets stringent regulatory standards, as even microscopic contaminants can jeopardize the biocompatibility of devices that will be implanted in the human body. This adds layers of complexity to the machining process, potentially leading to product recalls or regulatory fines.
The Solution: To mitigate contamination risks, buyers should establish a controlled machining environment equipped with HEPA filters and positive pressure systems to minimize airborne particles. It’s essential to utilize dry machining techniques when working with medical-grade PEEK to prevent coolant contamination, which can affect biocompatibility. If coolants are necessary due to the complexity of the components, air is the recommended option, as it poses the least risk. Additionally, regular cleaning and maintenance of machinery, along with thorough training for operators on contamination prevention, will ensure that the machining process remains compliant with medical standards.
Scenario 3: High Material Costs and Waste Management
The Problem: The high cost of PEEK material presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly when working with complex geometries that often lead to high waste rates. For instance, when fabricating intricate components, the scrappage of even a small percentage of expensive PEEK can result in substantial financial losses. This issue is further exacerbated when buyers are not fully aware of the specific machining parameters that optimize material utilization.
The Solution: To enhance material efficiency, buyers should invest in simulation software that allows for virtual machining trials before actual production. This enables them to identify the most efficient cutting paths and strategies, minimizing waste. Additionally, adopting advanced machining techniques such as adaptive machining can adjust cutting parameters in real-time, significantly reducing scrap rates. Buyers should also consider sourcing PEEK from suppliers who offer options for recycled or regrind material, which can lower costs without compromising quality. Finally, educating the machining team about optimal feeds, speeds, and tooling options tailored for PEEK can help maximize yield and reduce unnecessary waste.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machining peek
What Are the Key Materials for Machining PEEK?
When machining PEEK (polyether ether ketone), selecting the right materials for tools and components is crucial for achieving optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Below are some of the most common materials used in this process, along with their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Carbide Tools in PEEK Machining?
Carbide tools are widely used for machining PEEK due to their hardness and wear resistance. These tools can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for precision machining applications. Carbide tools also offer excellent edge retention, which is crucial for maintaining tight tolerances.
Pros: Carbide tools provide exceptional durability and can handle high-speed machining. They are suitable for both industrial-grade and medical-grade PEEK.
Cons: The initial cost of carbide tools can be high, and they may require specialized handling to prevent chipping.
Impact on Application: Carbide tools are compatible with various machining methods, including CNC milling and turning, making them versatile for different applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO for tool quality. Availability may vary by region, so consider local suppliers.
How Do High-Speed Steel (HSS) Tools Compare for Machining PEEK?
High-speed steel (HSS) tools are another option for machining PEEK. These tools are less expensive than carbide but may not offer the same level of performance.
Pros: HSS tools are cost-effective and easier to sharpen. They can be used for a variety of machining operations.
Cons: HSS tools wear out more quickly than carbide tools, especially when machining high-performance materials like PEEK.
Impact on Application: While HSS tools can be effective for lower-volume production runs, they may not provide the precision required for critical applications in aerospace or medical fields.
Considerations for International Buyers: HSS tools should meet local manufacturing standards, and buyers should consider the availability of replacement tools in their region.
What Role Do Diamond-Coated Tools Play in PEEK Machining?
Diamond-coated tools are specifically designed for machining PEEK and other high-performance thermoplastics. The diamond coating significantly enhances the tool’s hardness and wear resistance.
Pros: These tools offer superior performance, resulting in cleaner cuts and reduced machining time. They are particularly effective for machining reinforced PEEK.
Cons: The cost of diamond-coated tools is considerably higher than that of carbide or HSS tools, making them a significant investment.
Impact on Application: Diamond-coated tools are ideal for high-precision applications where surface finish and dimensional accuracy are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that diamond-coated tools meet the necessary certifications for their specific applications, especially in regulated industries.
How Do Coolants Impact the Machining of PEEK?
Coolants play a vital role in the machining process of PEEK, as they help dissipate heat and improve tool life. The choice of coolant can significantly affect the machining quality and biocompatibility of medical-grade PEEK.
Pros: Using the right coolant can enhance tool performance and reduce the risk of thermal deformation in PEEK components.
Cons: Some coolants can contaminate medical-grade PEEK, compromising its biocompatibility.
Impact on Application: For medical applications, air or biocompatible coolants are preferred to maintain the integrity of the material.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding coolant use is essential, particularly in the medical and food industries.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Machining PEEK
| Material | Typical Use Case for machining peek | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbide Tools | Precision machining of industrial-grade PEEK | Excellent durability and edge retention | Higher initial cost | High |
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | Lower-volume production runs of PEEK components | Cost-effective and easy to sharpen | Wears out quickly | Medium |
| Diamond-Coated Tools | High-precision machining of reinforced PEEK | Superior performance and clean cuts | Significant investment | High |
| Coolants | Cooling during machining processes | Enhances tool performance | Risk of contamination in medical-grade | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for machining PEEK, ensuring they can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machining peek
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Machining PEEK?
Machining PEEK (polyetheretherketone) involves a series of critical manufacturing processes that ensure the final product meets the stringent demands of industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive. The typical stages in the manufacturing process include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Machining PEEK?
The first step in the machining process is the preparation of the PEEK material. PEEK is often supplied in rods or sheets, with various dimensions based on the requirements of the final product. Before machining, it is essential to stress-relieve the material through an annealing process. This step reduces internal stresses and the likelihood of surface cracks during machining, while also enhancing the material’s crystallinity. Proper material preparation is crucial to achieving tight tolerances and maintaining dimensional stability throughout the machining process.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Machining PEEK?
Once the material is prepared, the forming stage begins. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is the primary technique used for shaping PEEK. This advanced technology allows for precise removal of material to create complex geometries. Key considerations during this stage include selecting appropriate cutting tools and determining optimal feed rates and cutting speeds. For instance, silicon carbide tools are recommended for natural PEEK, while diamond tools are preferred for PEEK reinforced with carbon fiber. The unique thermal properties of PEEK also necessitate careful management of heat generation, often requiring the use of coolants to prevent melting and degradation of the material.
How Is Assembly Handled in the Machining Process?
In many cases, machining PEEK components will require subsequent assembly with other parts. Proper alignment and fit are essential, particularly in applications where PEEK is used as a bearing or in load-bearing structures. Assembly techniques may involve adhesive bonding, mechanical fastening, or thermal bonding, depending on the application’s requirements. For medical applications, maintaining biocompatibility during assembly is crucial, which often involves using specific adhesives or avoiding contaminants during the process.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used for PEEK Products?
Finishing processes enhance the surface quality and overall performance of machined PEEK parts. Common techniques include polishing, sanding, or applying surface coatings. These finishing methods help to improve wear resistance and reduce friction, which is particularly important in applications such as bearings or seals. It is also vital to ensure that any finishing processes do not compromise the material’s integrity or biocompatibility, especially for medical-grade PEEK.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Machining PEEK?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the machining of PEEK to ensure that products meet both industry and regulatory standards. International standards, such as ISO 9001, provide a framework for quality management systems, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for medical devices and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications, ensure compliance with safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Machining?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential at various stages of the machining process to maintain product integrity. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw material quality upon receipt, ensuring it meets specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the machining process, including dimensional checks and visual inspections to identify any defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products, including functional tests and compliance checks against specifications.
These checkpoints help to identify and rectify issues before they impact the final product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is paramount. Buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain high standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits provides firsthand insight into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can help verify compliance with international standards and assess the effectiveness of their QA systems.
-
Requesting Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed reports on their quality control practices, including any certifications and results from internal audits. Buyers should review these documents carefully to ensure they align with their quality expectations.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality processes. This can be particularly useful for high-stakes applications, such as aerospace or medical devices, where compliance with strict regulations is essential.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification that may vary by region. For example, different countries may have unique regulatory requirements for medical-grade PEEK, necessitating additional certifications beyond ISO standards. Furthermore, language barriers and cultural differences can affect communication regarding quality expectations and certifications. Buyers are encouraged to build strong relationships with suppliers to facilitate clearer communication and ensure a mutual understanding of quality requirements.
In conclusion, the machining of PEEK involves a meticulous process that spans from material preparation to finishing, underpinned by robust quality assurance practices. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification methods, B2B buyers can ensure they receive high-quality, reliable components that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machining peek’
Introduction
This guide provides B2B buyers with a practical checklist for sourcing the machining of PEEK (polyetheretherketone) components. Given PEEK’s critical applications in industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive, understanding the nuances of sourcing and machining this high-performance thermoplastic is essential for ensuring product quality and operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before approaching suppliers, it’s vital to have a clear understanding of your technical requirements. This includes dimensions, tolerances, and specific performance characteristics needed for your application.
– Considerations: Identify whether you need industrial-grade or medical-grade PEEK, as each has unique properties and compliance standards.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with expertise in machining PEEK. Look for companies with a strong track record in your specific industry to ensure they understand your requirements.
– Key Actions: Review online resources, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of potential candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It’s crucial to verify that suppliers possess the necessary certifications, especially for medical-grade PEEK applications which require compliance with ISO standards.
– What to Check: Look for ISO 13485 certification for medical devices, as well as other relevant quality management systems that demonstrate commitment to maintaining high manufacturing standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you have narrowed down potential suppliers, request samples or prototypes of their PEEK machining capabilities. This step is vital for assessing their quality and precision.
– Why This Matters: Evaluating samples allows you to check for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and overall quality, which can save you from costly errors in full-scale production.
Step 5: Discuss Machining Processes and Tools
Engage with suppliers about their machining processes, including the tools and cooling methods they utilize. Understanding their approach can reveal their level of expertise and suitability for your needs.
– Important Factors: Inquire about the type of cutting tools used (e.g., diamond tools for carbon-fiber reinforced PEEK) and their strategies for managing heat during machining, as overheating can compromise the material’s integrity.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Production Capabilities
Consider the supplier’s lead times and their capacity to meet your production demands. This is especially important if you have tight project timelines or large batch requirements.
– What to Ask: Discuss their current workload, production capacity, and any potential bottlenecks that could affect delivery schedules.
Step 7: Verify Quality Control Measures
Inquire about the quality control processes that suppliers implement to ensure consistency and reliability in their machining operations.
– Key Elements: Look for suppliers who perform in-process inspections and have a robust final inspection protocol to catch any defects before shipment.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing PEEK machining services, ensuring they partner with capable suppliers who can meet their specific needs and maintain high standards of quality and performance.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machining peek Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Machining PEEK?
Machining PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) involves a multifaceted cost structure that includes several essential components. Materials account for a significant portion of the overall expense. PEEK is a high-performance thermoplastic, and its cost can range from $500 to $1,200 per kilogram, depending on the grade and specifications. Labor costs also play a vital role, particularly as skilled machinists are needed to handle the intricacies of PEEK machining. Specialized training may be required, further increasing labor costs.
Manufacturing overhead includes expenses associated with facility operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Given the precision required in machining PEEK, tooling costs are also substantial; high-quality cutting tools, such as polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools, are often necessary to achieve the desired finish and maintain efficiency. Additionally, quality control (QC) is critical, especially for industries like aerospace and medical, where compliance with certifications such as ISO 10993 is mandatory. This can add to the overall cost structure.
Finally, logistics must be factored in, especially for international buyers. The transportation of PEEK components, often requiring special handling, can add significant costs depending on the shipping distance and method. Finally, a reasonable margin must be included for suppliers to ensure sustainability.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machining PEEK Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of machined PEEK components. Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ) significantly impact costs; larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Specifications and customization also play a role; complex designs or stringent tolerances can drive up costs due to increased machining time and specialized equipment requirements.
The choice of materials can further influence pricing. For instance, medical-grade PEEK tends to be more expensive than industrial-grade due to its enhanced properties and the need for sterilization. Quality and certification requirements, particularly in regulated industries, can also affect pricing. Suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international standards may charge a premium for their services.
Additionally, supplier factors such as reputation, reliability, and geographical location can impact costs. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial, as they define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can add to the total cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs When Sourcing Machined PEEK?
Negotiation remains a powerful tool for buyers seeking to optimize costs. Engaging in discussions with suppliers about bulk discounts or long-term contracts can yield significant savings. Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is essential; while the upfront cost of PEEK may be high, its durability and performance can lead to lower long-term costs, particularly in demanding applications.
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of pricing nuances influenced by local market conditions and currency fluctuations. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can help mitigate shipping costs and lead times.
Lastly, always request detailed quotes that break down costs into individual components. This transparency allows for better comparison between suppliers and aids in identifying areas where cost savings can be achieved.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Please note that the prices mentioned are indicative and can vary based on several factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. It is advisable to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers for accurate pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machining peek With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Machining PEEK
When exploring alternatives to machining PEEK (polyetheretherketone), it is crucial to understand the various options available that can achieve similar goals in manufacturing and component production. The selection of an appropriate method can significantly impact performance, cost-efficiency, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we compare machining PEEK with two viable alternatives: machining metals and 3D printing with thermoplastics. This analysis will help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their unique operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Machining PEEK | Machining Metals | 3D Printing with Thermoplastics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High resistance to chemicals and heat; excellent fatigue resistance | Strong structural integrity; good thermal and electrical conductivity | Versatile designs; rapid prototyping capabilities |
| Cost | High material costs (approx. $500/sheet) | Moderate to high material and tooling costs | Lower material costs; initial setup can be high |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized tools and expertise | Widely understood processes; standard tools available | Requires advanced software and training |
| Maintenance | High due to tooling wear and contamination risks | Moderate; depends on the material used | Low; minimal maintenance but requires careful handling |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, medical devices, high-performance applications | Structural components, automotive parts | Prototyping, custom designs, low-volume production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Machining Metals
Machining metals remains a popular alternative to machining PEEK, particularly in applications where high strength and durability are paramount. Metals like aluminum and stainless steel are widely used due to their excellent mechanical properties. The primary advantages of machining metals include their structural integrity and ability to withstand extreme conditions. However, the cost of high-quality metal sheets can be significant, and the machining process often requires advanced tooling and skilled labor. Additionally, while metal machining is a well-established practice, it may not offer the same chemical resistance as PEEK, limiting its use in specific industries like pharmaceuticals or aerospace.
2. 3D Printing with Thermoplastics
3D printing has emerged as a compelling alternative, particularly for companies focused on rapid prototyping and custom designs. This method allows for the creation of complex geometries that may be difficult to achieve through traditional machining. The use of thermoplastics in 3D printing can significantly lower material costs and reduce waste, as components are built layer by layer. However, the initial investment in 3D printing technology and the need for specialized software can be barriers for some organizations. Additionally, while 3D-printed parts can be suitable for many applications, they may not meet the same performance benchmarks as machined PEEK in high-stress environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the best machining method or material for your specific application hinges on a careful assessment of your operational requirements, budget constraints, and desired performance outcomes. For high-performance applications in challenging environments, machining PEEK may be the optimal choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, for projects requiring rapid prototyping or where weight is less critical, machining metals or utilizing 3D printing with thermoplastics could provide more cost-effective and flexible solutions. By evaluating these alternatives against your specific needs, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machining peek
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machining PEEK?
1. Material Grades: Industrial vs. Medical
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is available in different grades, primarily industrial and medical. Industrial-grade PEEK is known for its high impact strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for aerospace, automotive, and chemical applications. Conversely, medical-grade PEEK complies with biocompatibility standards (ISO 10993) and is designed for use in implants and devices that require sterilization. Understanding the grade is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure the material meets specific application requirements and regulatory standards.
2. Tolerance Levels: Precision in Machining
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in manufactured parts. In machining PEEK, maintaining tight tolerances (often within ±0.005 inches) is essential for ensuring that components fit correctly in their applications. High precision is particularly critical in sectors like aerospace and medical, where even minor discrepancies can lead to failures or safety issues. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who can consistently deliver parts within specified tolerances.
3. Creep Resistance: Performance Under Load
Creep resistance is a material’s ability to resist deformation over time when subjected to a constant load. PEEK exhibits excellent creep resistance, allowing it to maintain structural integrity in demanding environments such as high-temperature applications. This property is vital for industries like aerospace, where components are subjected to prolonged stress. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to provide materials that meet creep resistance specifications.
4. Coefficient of Friction: Impact on Wear and Tear
The coefficient of friction is a measure of how much frictional force exists between two surfaces in contact. PEEK has a low coefficient of friction, which reduces wear and prolongs the lifespan of components in applications like bearings and seals. For B2B buyers, understanding this property can help in selecting materials that minimize maintenance costs and enhance the durability of products.
5. Annealing Process: Enhancing Material Stability
Annealing is a heat treatment process that relieves internal stresses in PEEK, enhancing its dimensional stability and reducing the likelihood of cracking during machining. This process is especially important for components that will undergo extensive machining or will be exposed to varying temperatures. Buyers should inquire about the annealing practices of potential suppliers to ensure they are capable of producing stable, high-quality parts.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Machining PEEK?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of machining PEEK, working with an OEM ensures that the components meet the specific design and quality standards required for integration into larger systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to produce for an order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers, as it impacts inventory management and cost-effectiveness. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to avoid excess inventory or supply shortages.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific materials or services. For machining PEEK, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing, lead times, and capabilities among different suppliers, ensuring they select the best option for their needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations when sourcing PEEK components globally. This knowledge is essential for effective negotiation and logistics planning.
5. Tolerance Specification
Tolerance specification outlines the acceptable limits of variation in a part’s dimensions. In machining PEEK, clearly defined tolerance specifications help ensure that components fit together correctly and function as intended, reducing the risk of costly errors during production.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in machining PEEK, enabling them to make informed decisions that align with their operational and financial goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machining peek Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Machining PEEK?
The global market for machining PEEK (polyetheretherketone) is experiencing significant growth, driven by its increasing adoption across high-performance sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. The lightweight and high-strength characteristics of PEEK make it an ideal material for applications that require durability and resistance to extreme conditions. International B2B buyers are particularly focused on sourcing high-quality PEEK materials, with demand surging from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where industries are evolving to adopt advanced materials for enhanced performance.
Emerging trends in the B2B landscape include the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies such as CNC machining and additive manufacturing. These innovations facilitate precision machining of PEEK, allowing for complex geometries and tighter tolerances that were previously unattainable. Moreover, the rise of digital supply chain solutions is enabling buyers to streamline procurement processes, improve inventory management, and enhance collaboration with suppliers.
A critical consideration for international buyers is the differentiation between industrial-grade and medical-grade PEEK. Medical-grade variants are gaining traction due to stringent regulations and the need for biocompatibility, making them essential for manufacturers in the healthcare sector. As industries increasingly prioritize performance and safety, the ability to source specialized grades of PEEK that meet these requirements is becoming a competitive advantage.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Machining PEEK Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the machining PEEK sector. As industries face pressure to reduce their environmental impact, the demand for eco-friendly materials and processes is on the rise. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as reducing waste, minimizing energy consumption, and utilizing renewable resources.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining prominence, with buyers seeking transparency in their supply chains. This includes ensuring that PEEK is sourced from manufacturers who adhere to responsible labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and the use of recycled materials are becoming key differentiators for suppliers looking to appeal to conscious buyers.
Furthermore, the development of ‘green’ PEEK alternatives, which incorporate bio-based feedstocks or exhibit lower carbon footprints during production, is an emerging trend. These innovations not only cater to the growing eco-conscious market but also provide a pathway for manufacturers to meet compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Growth of Machining PEEK?
PEEK was first developed in the 1980s, primarily for its exceptional mechanical and thermal properties. Initially used in aerospace applications, its versatility quickly attracted attention from various sectors, including medical and automotive. Over the years, advancements in machining technologies have enabled more efficient processing of PEEK, enhancing its accessibility for manufacturers.
As industries have evolved, so too have the applications for PEEK. Its use in medical implants and devices has particularly surged due to its biocompatibility and strength. The maturation of CNC machining techniques has further solidified PEEK’s position as a go-to material for high-performance applications, allowing manufacturers to produce intricate components that meet rigorous industry standards. This historical evolution underscores the material’s adaptability and the increasing importance of sophisticated machining capabilities in meeting diverse market needs.
In conclusion, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and the historical context of PEEK machining can empower international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machining peek
-
How do I solve machining challenges when working with PEEK?
Machining PEEK can present unique challenges due to its thermoplastic nature. To address issues such as melting or chip buildup, it’s crucial to use sharp tools and appropriate cutting speeds, typically between 250 to 2000 SFPM. Employing coolant, ideally air for medical-grade applications, can help manage heat without compromising biocompatibility. Regularly check for vibrations, as PEEK is stiff and can easily vibrate, impacting precision. Always monitor the machining process closely and adjust feeds and speeds to prevent overheating and ensure high-quality outputs. -
What is the best tooling for machining PEEK effectively?
When machining PEEK, the choice of tooling is critical. For virgin PEEK, polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools are recommended as they remain sharp and provide excellent precision. If you are working with reinforced PEEK, consider using silicon carbide or diamond tools for optimal results. Ensure that the tools are sharp to minimize melting and stringing instead of chip formation. This approach will enhance tool life and improve the overall machining efficiency. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing PEEK suppliers internationally?
When sourcing PEEK suppliers, especially internationally, it’s vital to evaluate their quality certifications, production capabilities, and experience in machining PEEK. Look for suppliers who have a proven track record in your industry, whether aerospace, medical, or automotive. Additionally, consider their ability to provide custom solutions that meet your specifications, including the grades of PEEK they offer. Request samples and references to gauge their reliability and product quality before committing to an order. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when purchasing PEEK?
MOQs for PEEK can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific grade of PEEK required. Typically, industrial-grade PEEK may have lower MOQs compared to specialized medical-grade PEEK due to the stringent manufacturing processes involved. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that suit your project requirements. Some suppliers may offer flexibility, especially for first-time orders or ongoing partnerships. -
What payment terms are common for international transactions involving PEEK?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers, but common practices include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms before finalizing any contracts to avoid misunderstandings. International buyers should also consider currency exchange rates and transaction fees, as these can impact the overall cost. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can facilitate smoother transactions and foster trust between you and your supplier. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my PEEK machining projects?
To ensure quality assurance in machining PEEK, establish a rigorous QA process that includes in-process inspections and final product evaluations. Collaborate with suppliers who can provide certifications and documentation of their machining processes. Implementing statistical process control (SPC) techniques can help monitor production quality in real-time. Additionally, consider third-party inspections or audits to further validate the supplier’s adherence to quality standards, particularly for critical applications in medical and aerospace industries. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing PEEK?
Logistics plays a crucial role in importing PEEK, particularly due to its specific handling and storage requirements. Ensure that the supplier adheres to proper packaging to prevent damage during transit. Also, consider customs regulations and tariffs that may apply to your importation process, as these can affect delivery timelines and costs. Working with a freight forwarder experienced in handling specialty materials can help navigate these complexities and ensure timely delivery. -
How can I customize PEEK components to meet specific project requirements?
Customizing PEEK components involves close collaboration with your supplier to define your exact specifications, such as dimensions, tolerances, and any specific mechanical properties required for your application. Many suppliers offer design support and prototyping services to help refine your ideas before full-scale production. Discussing your application’s performance requirements early in the process will enable the supplier to recommend the appropriate grade of PEEK and machining techniques, ensuring that the final product meets your needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Machining Peek Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AIP Precision – PEEK Thermoplastic Solutions
Domain: aipprecision.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: PEEK (polyetheretherketone) is a lightweight thermoplastic ideal for specialized applications in industries such as Aerospace & Defense and Medical & Life Sciences. It is a semi-crystalline, high-performance thermoplastic known for its strong mechanical properties, resistance to fatigue and stress-cracking, and suitability for bearing, wear, and structural applications. There are two grades of PEE…
2. PEEK – 12 x 12 Sheet, .500 Thick
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) plastic; sheet size: 12″ x 12″; thickness: .500″; cost: approximately $507.00; parts dimensions: .280″ thick x .500″ wide x 2.5″ long; machining tools: aluminum specific tooling recommended; feeds and speeds similar to steel; machining advice: use coolant, sharp tools, avoid melting, and manage chip removal.
3. Miller Plastics – PEEK Machining Solutions
Domain: millerplastics.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) is a high-performance thermoplastic material used for machining custom plastic parts. PEEK machining requires special expertise due to the material’s toughness and the need for annealing before fabrication. The annealing process involves heating the plastic to soften and stress-relieve it, ensuring better machinability and preventing surface cracks and imperfections. …
4. Reddit – PEEK Thermoplastic
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical properties and thermal stability. It machines well, often requiring flood cooling to manage chips effectively. Users have noted that it is easier to machine than other plastics and is suitable for use on manual mills and lathes. There are variations of PEEK, including glass-filled optio…
5. Ensinger – PEEK Machining Solutions
Domain: ensingerplastics.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: PEEK machining involves precision machined PEEK parts characterized by high dimensional stability and well-balanced mechanical properties. The material allows for high tool infeeds and feed rates, making PEEK CNC machining an efficient process for producing precision components. Ensinger offers a variety of PEEK semi-finished materials including: Unfilled PEEK, Reinforced grades, Heat resistant gr…
6. AT Machining – PEEK Thermoplastic Solutions
Domain: at-machining.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: PEEK is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent mechanical properties, high resistance to corrosive substances, and high melting point (melts at about 343°C, operates up to 250°C). It is available in various forms including granular, bar, and filaments. The major classifications of PEEK include:
1. PEEK 1000: 100% pure resin, suitable for tough applications, easy to sterilize, meets EU an…
7. PCBWay – PEEK Engineering Thermoplastic
Domain: pcbway.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: PEEK is a semicrystalline thermoplastic with excellent mechanical and chemical resistance properties that are retained to high temperatures. It is an engineering thermoplastic with high strength, heat resistance, weather resistance, and chemical resistance. PEEK can be used to replace metal parts. The CNC machining services offered include CNC Milling and CNC Turning.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machining peek
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of PEEK (polyetheretherketone) presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers across diverse sectors such as aerospace, medical, and automotive. Understanding the unique machining properties of PEEK is essential for achieving precision and performance in applications that demand high mechanical strength and thermal stability. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers who can ensure the quality and reliability of both industrial and medical-grade PEEK.
As the global demand for high-performance materials continues to rise, leveraging strategic sourcing practices can enhance supply chain efficiency and reduce costs. Engaging with suppliers who have a proven track record in machining PEEK will not only facilitate better outcomes in product development but also foster long-term partnerships that can adapt to evolving market needs.
Looking forward, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively explore collaborations with specialized machining firms. By doing so, they can harness the full potential of PEEK and stay ahead in competitive markets. Investing in high-quality materials and expert machining capabilities will pave the way for innovation and success in their respective industries.