Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machining cutting tools
In the fast-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality machining cutting tools is a paramount challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications ranging from milling and drilling to threading and turning, the choices available can be overwhelming. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of the machining cutting tools market, offering insights into various tool types, their applications, and best practices for supplier vetting.
Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil—will find actionable strategies to navigate the intricacies of procurement. We will explore critical factors influencing cost, performance, and durability, equipping you with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, this guide addresses the importance of aligning tool selection with specific machining operations, ensuring optimal efficiency and productivity in your manufacturing processes.
By providing a comprehensive overview of the machining cutting tools landscape, this resource empowers you to enhance your operational capabilities, streamline procurement processes, and ultimately achieve a competitive edge in your respective markets. Whether you’re a seasoned buyer or new to the industry, our insights will serve as a valuable tool in your sourcing arsenal.
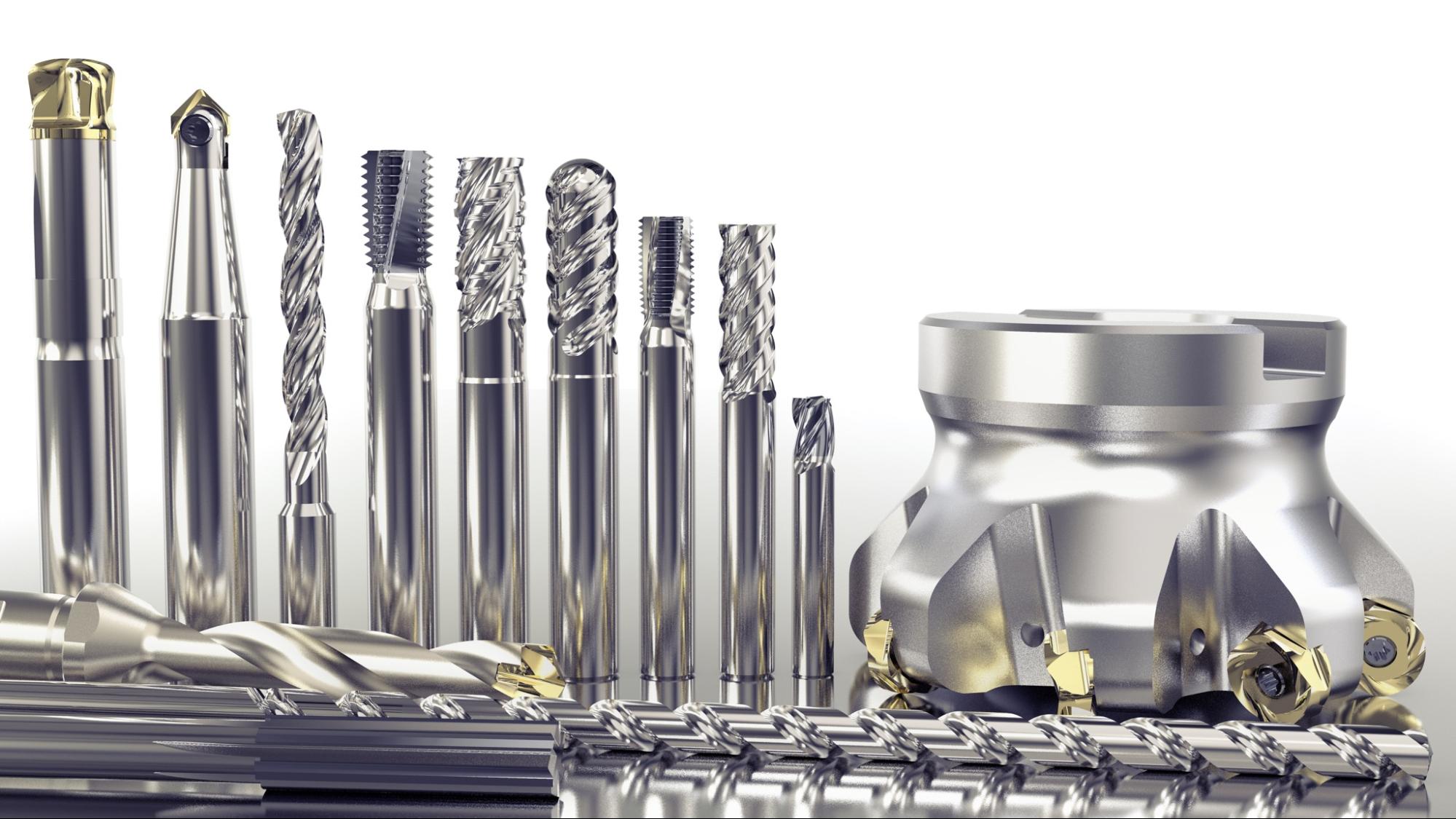
Understanding machining cutting tools Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| End Mills | Multi-flute design for efficient material removal | Machining complex shapes and profiles | Pros: Versatile, suitable for various materials; Cons: Can wear quickly with hard materials. |
| Indexable Inserts | Replaceable cutting edges for cost-effectiveness | Turning, milling, and drilling applications | Pros: Reduced downtime, customizable; Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| Drills | Pointed design for precise hole creation | General drilling in metal and plastic | Pros: Essential for various operations; Cons: Limited to hole-making applications. |
| Reamers | Designed for finishing and enlarging holes | Precision machining and fitting components | Pros: Achieves tight tolerances; Cons: Not suitable for initial hole making. |
| Taps | Used for creating internal threads | Threading applications in various materials | Pros: High accuracy for threaded holes; Cons: Can break easily if misused. |
What Are End Mills and Their Applications in B2B?
End mills are versatile cutting tools characterized by their multi-flute design, enabling efficient material removal. They are primarily used in milling operations to create complex shapes and profiles in a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. For B2B buyers, selecting the right end mill involves considering factors such as material compatibility, flute design, and coating options to enhance tool life. Proper application can lead to significant productivity gains, making them essential for manufacturers focused on precision and efficiency.
How Do Indexable Inserts Enhance Machining Efficiency?
Indexable inserts are a popular choice among B2B buyers due to their replaceable cutting edges, which provide a cost-effective solution for various machining operations. Commonly used in turning, milling, and drilling applications, these inserts allow for quick changes and adjustments, minimizing downtime. When purchasing indexable inserts, buyers should evaluate insert geometry, material grade, and coating to ensure optimal performance in their specific applications. This flexibility and efficiency can lead to reduced operational costs and improved machining accuracy.
What Makes Drills Essential for Machining Operations?
Drills are fundamental cutting tools with a pointed design that facilitates precise hole creation in a range of materials. They are widely utilized in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and general manufacturing. For B2B buyers, choosing the right drill involves considering factors such as diameter, length, and material type. While drills are indispensable for hole-making tasks, their limitations in other machining operations should be recognized. Investing in high-quality drills can enhance production efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
Why Are Reamers Important for Precision Machining?
Reamers are specialized cutting tools designed to finish and enlarge existing holes, achieving tight tolerances necessary for precise fitting of components. Commonly used in precision machining applications, reamers are ideal for ensuring high-quality finishes in industries such as aerospace and automotive. B2B buyers should consider reamer size, type (e.g., straight or spiral), and material when selecting the right tool for their needs. Though reamers are not suitable for initial hole creation, their role in enhancing accuracy makes them a valuable investment for manufacturers focused on quality.
How Do Taps Facilitate Threading in Manufacturing?
Taps are essential tools for creating internal threads in various materials, making them crucial for assembly and fastening applications. They are widely used across multiple industries, including construction and machinery manufacturing. For B2B buyers, selecting the right tap involves evaluating thread size, type, and material compatibility. While taps offer high accuracy for threaded holes, they can be prone to breakage if not used correctly. Understanding the specific threading requirements of a project can help buyers choose the most effective tap for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of machining cutting tools
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machining cutting tools | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision machining of aircraft components | Ensures high safety standards and regulatory compliance | Quality certifications, material compatibility, lead times |
| Automotive | Production of engine and transmission parts | Enhances efficiency and performance of vehicles | Tool durability, cost-effectiveness, and supplier reliability |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling and completion tools | Increases operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Resistance to extreme conditions, custom tooling options |
| Manufacturing | High-volume production of metal components | Reduces production costs and improves throughput | Scalability of tools, availability of replacement parts |
| Medical Devices | Machining of surgical instruments | Ensures precision and compliance with health regulations | Material certifications, precision tolerances, and delivery timelines |
How Are Machining Cutting Tools Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, machining cutting tools are essential for the precision manufacturing of components such as turbine blades and fuselage parts. These tools must meet stringent safety standards and regulatory requirements, necessitating high-quality materials and precise engineering. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and Europe, should prioritize suppliers with recognized quality certifications and proven track records in aerospace applications. This focus ensures compliance with global standards and minimizes the risk of operational failures.
What Role Do Machining Cutting Tools Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
The automotive industry relies heavily on machining cutting tools for the production of critical components such as engine blocks and transmission gears. These tools enhance the efficiency and performance of vehicles by enabling high-speed, high-precision machining processes. For B2B buyers in South America and the Middle East, sourcing durable and cost-effective tools is crucial. Suppliers should offer a comprehensive range of products that ensure compatibility with various materials and machining techniques to optimize production lines.
How Are Machining Cutting Tools Utilized in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, machining cutting tools are vital for drilling and completion operations, allowing for the efficient extraction of resources. These tools must withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures and corrosive environments. Buyers from international markets, especially in regions like Africa, should seek suppliers that provide custom tooling solutions designed for specific drilling applications. Additionally, the ability to source tools that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime is critical for maintaining competitive advantage in this sector.
Why Are Machining Cutting Tools Important for High-Volume Manufacturing?
Manufacturers utilize machining cutting tools to produce metal components at scale, significantly reducing production costs while improving throughput. These tools enable consistent quality and precision, which are essential for maintaining competitive pricing in global markets. For B2B buyers in regions like Brazil and Europe, sourcing scalable tools that come with reliable replacement parts is essential. This ensures uninterrupted production and the ability to meet fluctuating market demands efficiently.
How Do Machining Cutting Tools Contribute to Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device industry, precision machining cutting tools are used to manufacture surgical instruments and implants that meet strict health regulations. The need for high precision and compliance with material certifications makes sourcing from reputable suppliers a priority for international buyers. Additionally, understanding delivery timelines and precision tolerances is crucial to ensure that products meet both regulatory standards and market demands. By focusing on these factors, buyers can enhance their operational capabilities and maintain a competitive edge.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machining cutting tools’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulties in Selecting the Right Cutting Tool for Specific Materials
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate cutting tools for their specific machining applications, especially when dealing with a variety of materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or exotic alloys. The nuances in tool geometry, coating, and material properties can lead to confusion. Inadequate selection may result in poor machining performance, increased wear rates, and ultimately, higher operational costs. This challenge is particularly pronounced in regions with diverse manufacturing needs, where buyers may not have access to localized expertise or comprehensive product knowledge.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should engage in a thorough material analysis before making a purchase. Start by consulting with tool suppliers or manufacturers who offer detailed specifications and recommendations based on the materials being machined. Many suppliers provide guides or tools that help match cutting tools to materials. Furthermore, consider investing in cutting tool simulations or software that can predict tool performance based on specific machining parameters. This proactive approach not only ensures the selection of the right tool but also enhances productivity and reduces costs in the long run.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Tool Wear and Maintenance Challenges
The Problem: Tool wear is a significant pain point for B2B buyers, particularly in high-volume production environments. As cutting tools wear down, their efficiency decreases, leading to poor surface finishes and dimensional inaccuracies. This not only impacts product quality but also requires more frequent tool changes, resulting in increased downtime and labor costs. Companies operating in regions with limited access to replacement tools or maintenance services may find themselves at a further disadvantage.
The Solution: Implementing a robust tool monitoring and maintenance program can effectively mitigate wear issues. Buyers should consider investing in smart tooling solutions that feature embedded sensors to monitor tool condition in real-time. This technology allows for predictive maintenance, enabling companies to replace tools before they fail, thereby minimizing downtime. Additionally, establishing a regular maintenance schedule that includes tool sharpening and cleaning can significantly extend tool life. Training operators on proper tool handling and setup can also reduce premature wear, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions for Cutting Tool Procurement
The Problem: International B2B buyers frequently face supply chain disruptions that hinder timely access to essential machining cutting tools. Issues such as fluctuating demand, transportation delays, and geopolitical factors can lead to stock shortages, which subsequently slow down production processes. Buyers in emerging markets, particularly in Africa and South America, may experience these challenges more acutely due to limited local suppliers and reliance on imports.
The Solution: To address supply chain vulnerabilities, buyers should diversify their sourcing strategies. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions can create a buffer against localized disruptions. Additionally, consider engaging with suppliers who have robust inventory management systems and can provide insights into lead times and availability. Implementing just-in-time inventory practices can also help manage stock levels more effectively, ensuring that essential tools are on hand when needed without overcommitting resources. Finally, leveraging technology for supply chain visibility, such as tracking systems or procurement software, can enhance decision-making and responsiveness to changing market conditions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machining cutting tools
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Machining Cutting Tools?
When selecting materials for machining cutting tools, various factors such as performance, durability, and cost come into play. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of cutting tools: High-Speed Steel (HSS), Carbide, Ceramic, and Cobalt. Each material has distinct properties that influence its suitability for specific applications.
How Does High-Speed Steel (HSS) Perform in Cutting Tool Applications?
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is renowned for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures without losing its hardness. This material typically maintains its properties up to approximately 600°C. HSS is relatively easy to manufacture and can be sharpened multiple times, making it a cost-effective choice for various machining operations.
Pros: HSS tools are durable and versatile, suitable for a wide range of materials including steel and aluminum. They are also less expensive than carbide options.
Cons: Despite its advantages, HSS has a lower cutting speed compared to carbide tools, which may limit efficiency in high-volume production environments.
Impact on Application: HSS is ideal for applications requiring moderate cutting speeds and is often used in drilling, milling, and turning operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: HSS tools comply with various international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, making them accessible and reliable for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Advantages Does Carbide Offer for Machining Cutting Tools?
Carbide is a composite material made from tungsten carbide and cobalt, known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. It can withstand higher temperatures (up to 1000°C) and is suitable for high-speed cutting applications.
Pros: Carbide tools provide longer tool life and higher cutting speeds, which can significantly enhance productivity. They are particularly effective for machining hard materials.
Cons: The primary drawback of carbide tools is their cost; they are significantly more expensive than HSS. Additionally, they are more brittle and can break under excessive stress.
Impact on Application: Carbide is commonly used in high-precision machining tasks, including aerospace and automotive applications, where efficiency and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards like ISO and JIS, as well as consider local availability and supply chain logistics, especially in emerging markets.
How Do Ceramics Stand Out in Cutting Tool Manufacturing?
Ceramic cutting tools are made from advanced ceramic materials, offering high hardness and excellent wear resistance. They can perform well at elevated temperatures, often exceeding 1200°C.
Pros: The high hardness of ceramics allows for faster cutting speeds and longer tool life, making them suitable for high-volume production.
Cons: However, ceramics are brittle and can fracture under shock or impact, limiting their application in certain environments. They are also more challenging to manufacture and often require specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are best suited for machining hard materials, such as cast iron and hardened steel, where conventional tools may fail.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific machining conditions required for ceramics and ensure that their equipment can accommodate these tools.
What Role Does Cobalt Play in Cutting Tool Performance?
Cobalt is often used as an additive in tool steels and carbide to enhance hardness and wear resistance. It improves the toughness of cutting tools, making them less susceptible to chipping and cracking.
Pros: Cobalt-enhanced tools provide a good balance of hardness and toughness, making them versatile for various machining applications.
Cons: The addition of cobalt can increase the cost of the tool, and its performance is highly dependent on the manufacturing process.
Impact on Application: Cobalt tools are suitable for applications requiring high durability and performance, particularly in difficult-to-machine materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the sourcing of cobalt, as its availability can vary by region, impacting overall costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Machining Cutting Tools
| Material | Typical Use Case for machining cutting tools | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | General machining, drilling, milling | Versatile and cost-effective | Lower cutting speed than carbide | Low |
| Carbide | High-precision machining, aerospace | Longer tool life, higher cutting speeds | Brittle, higher cost | High |
| Ceramics | Machining hard materials, high-volume production | High hardness, excellent wear resistance | Brittle, requires specialized equipment | Med |
| Cobalt | Tough applications, difficult-to-machine materials | Good balance of hardness and toughness | Increased cost, dependent on manufacturing | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in machining cutting tools, enabling informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machining cutting tools
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Machining Cutting Tools?
The manufacturing of machining cutting tools involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary performance standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
This initial stage involves selecting the right materials, typically high-performance alloys or carbides, which provide the required hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. The chosen materials undergo processes such as heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties. For example, high-speed steel (HSS) and carbide are often used due to their superior characteristics in cutting applications.
Forming
In the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the desired tool geometry. Techniques such as forging, grinding, and machining are employed. Forging is common for producing tool blanks, while precision grinding ensures the cutting edges are sharp and accurately shaped. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining allows for intricate designs and tight tolerances, essential for modern cutting tools.
Assembly
For complex tools that require multiple components, the assembly stage involves combining various parts such as toolholders, inserts, and cutting edges. This process may also include the application of coatings, such as titanium nitride (TiN) or diamond-like carbon (DLC), which improve wear resistance and reduce friction during machining operations.
Finishing
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the surface quality and performance of the tools. Processes like polishing, coating application, and final inspections are conducted to ensure the tools meet stringent quality standards. This stage is crucial as it directly impacts the tool’s performance, longevity, and the quality of the machined parts.
How Does Quality Assurance Ensure High Standards for Machining Cutting Tools?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of machining cutting tools, ensuring that each tool meets international standards and customer expectations.
International Standards and Certifications
Adhering to recognized international standards, such as ISO 9001, is essential for manufacturers to demonstrate their commitment to quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE for European markets and API for oil and gas applications further reinforce quality assurance protocols. These certifications require regular audits and compliance checks, ensuring that manufacturers maintain high production and quality standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) measures are implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) checks raw materials upon receipt, ensuring they meet specified requirements. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) involves monitoring manufacturing processes, including tool geometry and dimensions during the forming stage. Finally, Final Quality Control (FQC) verifies that the finished products meet all design specifications and performance criteria before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance for Cutting Tools?
Quality assurance in machining cutting tools employs various testing methods to assess tool performance and durability. These methods include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Tools are measured for accuracy against specified tolerances using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or precision gauges.
- Hardness Testing: Techniques such as Rockwell or Vickers hardness tests determine the material’s hardness, which is critical for performance.
- Coating Thickness Measurement: For coated tools, the thickness of the coatings is measured to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- Performance Testing: Tools undergo operational tests to evaluate cutting efficiency, wear resistance, and overall performance under simulated working conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, need to ensure that their suppliers adhere to robust quality control practices. Here are several strategies for verification:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and overall compliance with international standards. This firsthand evaluation can reveal a supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC processes, including testing results and compliance with international standards. These reports should outline the QC checkpoints and any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance practices. These inspections can be particularly useful for buyers unfamiliar with local manufacturing standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances that can differ significantly by region. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective supplier management:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. For example, products sold in the European Union must comply with CE marking standards, while North American buyers may focus on ANSI or ASTM standards. Buyers should ensure suppliers are knowledgeable about and compliant with the relevant regulations for their target markets.
- Cultural Factors: Cultural attitudes towards quality and manufacturing processes can vary. Buyers should consider engaging in open dialogues with suppliers to understand their quality philosophies and practices.
- Logistical Challenges: Shipping and logistics can impact the quality of cutting tools, particularly in regions with less developed infrastructure. Buyers should discuss with suppliers how they manage these challenges to maintain product quality during transportation.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for machining cutting tools is vital for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. By focusing on key manufacturing stages, adhering to international standards, and implementing robust quality control measures, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality tools that enhance their operational efficiency. Establishing thorough verification processes will further support successful supplier relationships, fostering confidence in product quality across international markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machining cutting tools’
To effectively source machining cutting tools for your business, following a structured approach ensures you select the right products and suppliers. This checklist serves as a practical guide to streamline your procurement process, helping you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential for identifying the right cutting tools for your applications. Consider factors such as material type (steel, aluminum, plastics), machining processes (milling, turning, drilling), and desired tolerances. This clarity will guide your search and ensure that the tools you procure meet your production requirements.
Step 2: Research Available Tool Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of machining cutting tools available on the market. Key categories include indexable inserts, end mills, drills, reamers, and taps. Understanding the specific functions and applications of each tool type will help you make informed decisions based on your technical specifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before finalizing a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation to ensure they meet your quality and reliability standards. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies from similar industries to gauge their experience. Additionally, seek references from current clients to validate their reputation and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 or other quality management systems. Certifications indicate adherence to recognized quality standards and manufacturing practices. This step is crucial for mitigating risks associated with product quality and consistency.
Step 5: Assess Lead Times and Delivery Capabilities
Understanding lead times and delivery capabilities is vital for maintaining your production schedule. Discuss with suppliers their typical turnaround times and their ability to handle urgent orders. A reliable supplier should offer flexible shipping options to accommodate your business needs and minimize downtime.
Step 6: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a large purchase, request samples of the cutting tools you are considering. Testing these samples in your own production environment allows you to evaluate their performance, durability, and compatibility with your machines. This practical evaluation can save you time and money in the long run.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified suitable suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and bulk purchase discounts. Consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential tooling costs, rather than just the upfront price. Establishing favorable terms can enhance your long-term relationship with suppliers and improve your overall procurement efficiency.
By following this structured checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process for machining cutting tools, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business objectives and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machining cutting tools Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machining Cutting Tools?
When sourcing machining cutting tools, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and pricing negotiations. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. High-performance materials such as carbide or high-speed steel (HSS) usually command higher prices but offer better durability and longevity, ultimately reducing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the location of manufacturing. Countries with lower labor costs may provide more competitive pricing, but this can also affect quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, which is often passed on to buyers in the form of lower prices.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling can be substantial, particularly for custom tools. However, effective tooling design can lead to cost savings in production by enhancing efficiency and reducing waste.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that tools meet industry standards involves additional costs for quality inspections and certifications. Buyers should consider suppliers with robust QC processes to avoid costly rework and downtime.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international buyers. The choice of transportation method and the distance to the supplier can significantly affect overall costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins are influenced by market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the tools. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machining Cutting Tools?
Several factors can influence the pricing of machining cutting tools:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in larger volumes typically leads to price breaks. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom tools or those with specific specifications may incur additional costs. Standardized tools are generally more cost-effective, but it’s crucial to balance cost with performance needs.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material directly correlates with price. High-performance materials may have higher upfront costs but can lead to longer tool life and reduced replacement frequency.
-
Quality and Certifications: Tools that meet international quality standards (ISO, ANSI) may come at a premium. However, investing in certified tools can prevent costly failures and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers often offer better warranties and service levels, which can justify higher prices.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) involved in the transaction is crucial for cost management. They define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the final price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
Negotiating effectively is key to securing favorable pricing for machining cutting tools:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Highlight the long-term savings associated with higher-quality tools. Demonstrating how a higher upfront cost can lead to lower operational costs can strengthen your negotiation position.
-
Research and Compare: Gather pricing and specifications from multiple suppliers to create a competitive landscape. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Trust and loyalty often result in favorable treatment.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Pricing can vary significantly based on regional factors such as economic conditions and material availability. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider these factors when evaluating offers.
-
Be Open to Alternatives: If a supplier cannot meet your price, be willing to explore alternative materials or specifications that could lower costs without sacrificing performance.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for machining cutting tools can fluctuate based on market conditions, material costs, and supplier pricing strategies. Therefore, it is advisable to obtain quotes directly from suppliers to get the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machining cutting tools With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Machining Cutting Tools
When evaluating machining cutting tools, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to consider alternative solutions that may achieve similar outcomes. Each option presents unique advantages and drawbacks, influencing factors like operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and application suitability. This analysis aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between traditional machining cutting tools and two viable alternatives: additive manufacturing and laser cutting technology.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Machining Cutting Tools | Additive Manufacturing | Laser Cutting Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and durability for a wide range of materials. | Excellent for complex geometries but limited in material types. | High-speed cutting with precise edges, especially in thin materials. |
| Cost | Moderate upfront costs with variable long-term costs based on tool life. | Higher initial investment in equipment but can reduce waste and material costs. | Generally cost-effective for high-volume production but equipment can be expensive. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and setup time. | Requires specialized knowledge and training for operation. | Relatively easy to integrate into existing production lines with minimal training. |
| Maintenance | Regular tool replacement and maintenance needed. | Minimal maintenance; however, equipment can be complex. | Low maintenance, primarily focused on lens and optics care. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume production of standard parts. | Best suited for custom, low-volume production and prototyping. | Effective for cutting sheet materials and intricate designs in various industries. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, allows for the creation of parts layer by layer from digital models. This method excels in producing complex shapes that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional machining. However, the performance of additive manufacturing can be limited by the materials used, often restricting it to plastics and some metals. While the initial setup and equipment costs can be high, this process can significantly reduce material waste, making it a more sustainable choice for custom applications.
Laser Cutting Technology
Laser cutting technology utilizes focused laser beams to cut through materials with high precision. This method is particularly advantageous for cutting thin sheets of metal and intricate designs, making it popular in industries like automotive and aerospace. One of the primary benefits of laser cutting is its speed and accuracy, which can lead to increased productivity. However, it may not be suitable for thicker materials, and the initial investment in laser cutting equipment can be substantial. Additionally, operators must be knowledgeable to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the choice between machining cutting tools, additive manufacturing, and laser cutting technology should be guided by specific operational needs and constraints. Factors like production volume, material types, and the complexity of designs play a pivotal role in this decision. By thoroughly evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of each alternative, buyers can select the most effective solution that aligns with their business objectives and enhances their manufacturing capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machining cutting tools
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machining Cutting Tools?
Understanding the essential technical properties of machining cutting tools is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications that play a significant role in tool performance and longevity:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of cutting tools, often denoted by their composition (e.g., high-speed steel, carbide, or ceramic), affects their durability, wear resistance, and cutting efficiency. For instance, carbide tools typically offer higher hardness and wear resistance compared to high-speed steel, making them suitable for high-speed applications. Buyers must consider the material grade in relation to the materials being machined to ensure optimal performance. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. It is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assembly processes. In machining, tighter tolerances may be required for precision components. Understanding tolerance specifications can help buyers select the right tools that meet their project’s precision requirements, minimizing costly rework and ensuring product quality. -
Coating Type
Coatings such as titanium nitride (TiN) or diamond-like carbon (DLC) enhance the performance of cutting tools by reducing friction, increasing wear resistance, and improving surface hardness. The choice of coating can significantly influence tool life and performance in specific applications. Buyers should evaluate the coating type based on the machining conditions and the material of the workpiece. -
Cutting Edge Geometry
The geometry of the cutting edge, including its angle and shape, affects chip formation, cutting efficiency, and surface finish of the machined part. Different geometries are suited for various operations, such as roughing or finishing. B2B buyers must understand how these geometrical features can impact machining performance to select the most effective tools for their applications. -
Tool Life
Tool life is a measure of how long a cutting tool can perform its intended function before needing replacement. It is influenced by factors such as material, coating, and operating conditions. A longer tool life can lead to reduced downtime and lower operational costs, making it an essential consideration for buyers focused on optimizing their machining processes. -
Application Type
Different cutting tools are designed for specific applications, such as milling, drilling, or turning. Understanding the intended use of a tool helps buyers select the appropriate type for their machining needs, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in production processes.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Machining Cutting Tools?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several common trade terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers to understand, especially when negotiating bulk purchases or assessing whether a supplier can meet their volume needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other information for specific products or services. This is a key step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and select the best option based on price and specifications. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping, risk, and cost responsibilities, which can significantly impact the total landed cost of cutting tools. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times is crucial for buyers to plan their production schedules and inventory management effectively. -
TAP (Technical Assistance Program)
TAP refers to a program offered by manufacturers to provide technical support and training on product usage. Engaging with TAP can enhance a buyer’s understanding of cutting tools, leading to better usage and performance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes, ensuring they procure the most suitable cutting tools for their manufacturing needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machining cutting tools Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Machining Cutting Tools Sector?
The machining cutting tools sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving customer demands. A significant driver of market growth is the increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics. B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can offer high-quality tools that ensure efficiency and durability.
Emerging technologies such as CNC machining and automation are reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling manufacturers to optimize their production processes. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is fostering a shift towards smart manufacturing, where data analytics and IoT play crucial roles in enhancing operational efficiencies. Buyers should consider suppliers who integrate these technologies into their product offerings, as this can lead to significant cost savings and improved product quality.
Another critical trend is the growing emphasis on customization. As businesses strive to meet specific application requirements, suppliers are adapting by offering tailored solutions, including specialized tool geometries and materials. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who may require tools that can handle unique material properties or machining conditions prevalent in their regions. Understanding these market dynamics can empower B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions and stay ahead of the competition.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Machining Cutting Tools Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in the machining cutting tools sector, driven by increasing environmental regulations and a growing awareness of corporate social responsibility. B2B buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their environmental impact. This includes sourcing raw materials responsibly, minimizing waste during production, and ensuring energy efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Ethical supply chains are essential for fostering trust and transparency. Buyers should seek suppliers with certifications that verify sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or other green certifications. These certifications not only enhance a company’s brand image but also align with the values of environmentally-conscious consumers and businesses.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials is gaining traction. Tools made from recyclable or bio-based materials can significantly reduce environmental footprints. By prioritizing suppliers who utilize sustainable materials and practices, B2B buyers can contribute to a circular economy while also benefiting from the growing market demand for environmentally friendly products.
What Is the Historical Context of the Machining Cutting Tools Sector?
The machining cutting tools sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 19th century. Initially, cutting tools were crafted from basic materials like high-carbon steel, which limited their durability and performance. However, the industrial revolution brought about advancements in metallurgy, leading to the development of high-speed steel and carbide tools, which transformed machining processes by enabling faster cutting speeds and improved tool life.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of computer numerical control (CNC) technology revolutionized the sector, allowing for greater precision and automation in machining operations. This evolution has paved the way for modern innovations, such as coated tools that enhance wear resistance and performance. As the market continues to grow, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into current trends and future directions in the machining cutting tools sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machining cutting tools
-
How do I choose the right machining cutting tools for my application?
Selecting the appropriate machining cutting tools depends on several factors, including the material you are working with, the specific machining process (milling, drilling, turning), and the desired finish quality. Consider the tool geometry, coating, and material type (carbide, high-speed steel, etc.). Conducting a thorough analysis of your production requirements and consulting with suppliers can help identify the best tools that optimize performance and reduce costs. -
What is the best type of cutting tool for machining stainless steel?
For machining stainless steel, solid carbide end mills and high-speed steel tools with specific coatings, such as TiN (Titanium Nitride) or TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride), are recommended. These tools offer high wear resistance and thermal stability, which are crucial for handling the material’s toughness. Additionally, using tools designed for high feed rates can enhance productivity while maintaining the required surface finish. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for cutting tools?
When evaluating suppliers, consider their reputation, product quality, certifications (ISO, etc.), and customer service. Review their experience in the industry and their ability to provide customized solutions. Request samples or trial orders to assess product performance. Additionally, check for reviews or testimonials from other clients, especially those from your region, to gauge reliability and responsiveness. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machining cutting tools?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machining cutting tools can vary widely based on the supplier, the type of tool, and customization requirements. Generally, standard tools may have a lower MOQ (around 10-50 pieces), while specialized or custom tools could require higher quantities. Always discuss MOQs with potential suppliers to understand their policies and negotiate terms that align with your purchasing needs. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by cutting tool suppliers?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers, but common options include net 30, net 60, or payment in advance for first-time orders. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or bulk orders. It is advisable to establish clear payment terms before placing an order to avoid misunderstandings and to ensure that both parties are aligned on expectations. -
How can I ensure the quality of machining cutting tools I purchase?
To ensure quality, request certifications and quality assurance documentation from suppliers. Conduct thorough inspections upon receipt of goods, checking for defects or deviations from specifications. Many suppliers also provide performance guarantees or warranties. Establishing a relationship with reputable suppliers who adhere to stringent quality standards is essential for long-term success. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing cutting tools?
When importing cutting tools, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties specific to your country. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure compliance with local laws. It’s also beneficial to understand lead times and choose reliable logistics partners to minimize delays and ensure timely delivery. -
Can I customize machining cutting tools to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for machining cutting tools to meet specific application needs. This can include alterations in dimensions, coatings, or tool geometry. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers, and they can provide insights on feasibility and lead times for custom orders. Custom tools can enhance performance and efficiency in your machining processes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Machining Cutting Tools Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. MSC – Cutting Tools
Domain: mscdirect.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: MSC offers a complete line of cutting tools for indexables, holemaking, milling, threading, and turning applications. Key product categories include: Indexable Cutting Tools (Indexable Inserts, Indexable Milling, Indexable Holemaking, Indexable Threading, Indexable Turning & Boring), Replacement Parts & Accessories, Milling (End Mills, Milling Cutters, Milling Saws, Router Bits, Engraving Cutters)…
2. KBC Tools – Cutting Tools
Domain: kbctools.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: KBC Tools & Machinery specializes in cutting tools including bandsaw blades, boring bars, broaches, burrs, drills, end mills, counterbores, countersinks, hole cutters, milling cutters, reamers, saw blades, tapping heads, taps and dies, and tool bits. They offer KBC Brand cutting tools and products from world-class manufacturers such as Alvord-Polk Tool, Rock River Tool, Niagara Cutter, Starrett, D…
3. Ingersoll Cutting Tools – Metal Cutting Solutions
Domain: ingersoll-imc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Ingersoll Cutting Tools offers a wide range of metal cutting tools categorized into several product lines:
1. **Indexable Milling**: Includes Face Mills, End Mills, Modular Inserts, Plunge Mills, and Slotters.
2. **Solid Milling**: Features Solid Milling, Solid Modular, and Brazed PCD tools.
3. **Boring & Reaming**: Comprises Precision Boring and Reamers.
4. **Holemaking Tools**: Encompasses Cou…
4. MMS Online – Cutting Tools
Domain: mmsonline.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, MMS Online – Cutting Tools, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Harvey Tool – Variable Helix End Mills for High Temp Alloys
Domain: harveytool.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Harvey Tool offers a comprehensive selection of over 28,000 miniature and specialty cutting tools, including Variable Helix End Mills for High Temp Alloys with a variable helix design (approx. 34°) to reduce chatter and increase material removal rates. Key features include chipbreaker geometry, Ti Nano coating, and h6 shank tolerance. The product range includes Miniature End Mills (Square, Stub & …
6. Tormach – CNC Cutting Tools
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Tormach – CNC Cutting Tools, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Penn Tool Co – Metal and Steel Cutting Tools
Domain: penntoolco.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Metal and Steel Cutting Tools for Sale Online at Penn Tool Co. Types of cutting tools include: 1. Single Point Cutting Tools – e.g., bandsaws. 2. Multi-Point Cutting Tools – e.g., drill bits, reamers. 3. Abrasive Cutting Tools – e.g., bench grinders. Categories of hand-held metal cutting tools: – Counterbores and Countersinks – Cutters and Drills – Milling Cutters – Saws and Blades. Penn Tool Co. …
8. RedLine Tools – Cutting Tools
Domain: redlinetools.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Cutting Tools are critical components in manufacturing, made with quality materials and tight tolerances. RedLine Tools offers over 29,000 items including end mills, drills, taps, thread mills, reamers, carbide bars, and specialty tools like double angle cutters, chamfer and countersinks, key cutters, dovetail cutters, and engraving tools. All tools are made in the USA. Specific product categories…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machining cutting tools
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of machining cutting tools is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By investing in high-quality cutting tools—ranging from indexable inserts to specialized milling cutters—businesses can achieve superior performance and extended tool life. This not only minimizes downtime but also maximizes productivity across various machining applications.
The importance of aligning sourcing strategies with suppliers who understand regional market dynamics cannot be overstated. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer tailored solutions and robust support services. This approach ensures that businesses can adapt to evolving demands and technological advancements in the machining sector.
As we look to the future, the landscape of cutting tools will continue to evolve, driven by innovations in material science and machining technology. By embracing these changes and adopting a proactive sourcing strategy, companies can position themselves for sustained growth and competitiveness. Engage with trusted suppliers today to explore the latest advancements and unlock the full potential of your machining operations.