Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machining aluminum wheels
The global market for machining aluminum wheels presents both opportunities and challenges for international B2B buyers. A persistent issue faced by many in this sector is the difficulty in achieving a flawless finish on alloy wheels due to variations in aluminum casting quality. This guide aims to address this key challenge by offering insights into the complexities of sourcing high-quality aluminum wheels and the intricacies involved in machining processes.
Within this comprehensive resource, buyers will explore various types of aluminum wheels, their applications across different industries, and essential factors to consider when vetting suppliers. Additionally, the guide delves into cost structures, enabling informed budget planning. By equipping B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Vietnam and established players like Saudi Arabia—with actionable knowledge, this guide empowers them to make strategic purchasing decisions.
Understanding the nuances of machining aluminum wheels is crucial not only for ensuring product quality but also for maintaining competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving marketplace. Whether you’re looking to refine your existing supply chain or seeking new partnerships, this guide will serve as a valuable asset in navigating the complexities of the global aluminum wheel machining landscape.
Understanding machining aluminum wheels Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | High precision, automated processes, versatile tooling options | Automotive, aerospace, custom wheel design | Pros: High accuracy, scalability. Cons: Initial cost can be high. |
| Forged Aluminum Wheels | Made from solid aluminum, lightweight, high strength | High-performance vehicles, racing | Pros: Superior strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: Higher manufacturing costs. |
| Cast Aluminum Wheels | Produced via casting methods, often more decorative | Standard vehicles, aftermarket products | Pros: Cost-effective, diverse designs. Cons: Heavier, less durable than forged. |
| Rim Refinishing | Specialized processes to restore used rims, focuses on aesthetics | Automotive repair shops, wheel refurbishers | Pros: Cost-saving for customers. Cons: May not restore original strength. |
| Multi-Axis Machining | Advanced machining with multiple tool paths for complex shapes | Custom wheel manufacturers, aerospace | Pros: Complex geometries achievable. Cons: Requires skilled operators and higher investment. |
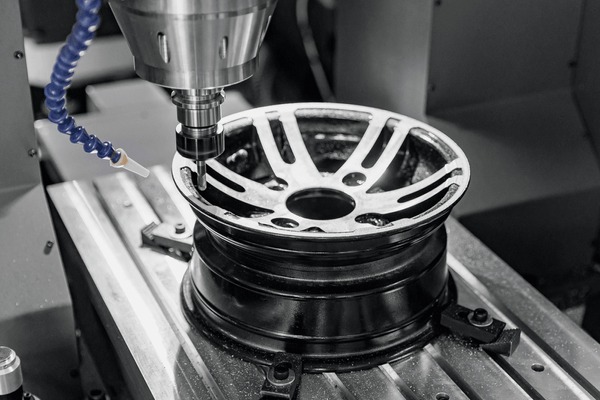
CNC Machining is a cornerstone of aluminum wheel production, utilizing computer-controlled machinery for high precision and repeatability. This method is particularly suitable for manufacturers looking to scale production while maintaining tight tolerances. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs, but the ability to produce complex designs efficiently makes it a favored choice in automotive and aerospace applications.
Forged Aluminum Wheels are crafted from solid aluminum billets, resulting in a lightweight and robust product. These wheels are ideal for high-performance vehicles and racing applications where strength and weight are critical. While they offer superior performance, B2B buyers should be prepared for higher manufacturing costs compared to cast options, making them a premium choice.
Cast Aluminum Wheels are produced using various casting methods, allowing for intricate designs and cost-effective manufacturing. These wheels are commonly used in standard vehicles and aftermarket applications, appealing to a broad market. Buyers should note that while cast wheels are generally less expensive, they may not offer the same durability or weight savings as forged wheels.
Rim Refinishing is a specialized service that restores used aluminum wheels to their former glory, focusing on aesthetic improvements. This service is valuable for automotive repair shops and refurbishers looking to provide cost-saving solutions to customers. However, buyers should be cautious, as refinishing may not restore the original structural integrity of the wheels.
Multi-Axis Machining offers advanced capabilities for creating complex wheel shapes through multiple tool paths. This method is particularly beneficial for custom wheel manufacturers and aerospace applications where design intricacy is paramount. While it allows for innovative designs, B2B buyers should consider the need for skilled operators and the associated higher investment costs.
Key Industrial Applications of machining aluminum wheels
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machining aluminum wheels | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of lightweight alloy wheels | Enhances vehicle performance through weight reduction | Quality of aluminum alloy, precision machining tools |
| Aerospace | Machining components for aircraft wheels | Ensures safety and durability in high-stress environments | Compliance with aviation standards, material certifications |
| Heavy Equipment | Fabrication of wheels for construction machinery | Increases operational efficiency and load capacity | Strength of materials, resistance to wear and tear |
| Motorsport | Custom wheel designs for racing vehicles | Improves speed and handling through optimized weight | Specialized machining capabilities, rapid prototyping |
| Aftermarket Wheel Refinishing | Refurbishing used wheels | Cost-effective solution for extending wheel lifespan | Surface finishing techniques, quality control measures |
How is machining aluminum wheels utilized in the automotive manufacturing sector?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, machining aluminum wheels is pivotal for producing lightweight wheels that enhance vehicle performance. This process reduces the overall weight of vehicles, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and handling. Buyers in this sector must consider the quality of aluminum alloys, as well as the precision of machining tools, to ensure that the wheels meet the stringent safety and performance standards required in the industry.
What role does machining aluminum wheels play in the aerospace industry?
In aerospace, machining aluminum wheels is essential for creating components that must withstand extreme conditions while maintaining high safety standards. These wheels are often used in landing gear and other critical applications. International buyers must prioritize compliance with aviation regulations and seek suppliers who can provide material certifications to guarantee the integrity and performance of the machined components.
How does machining aluminum wheels benefit the heavy equipment sector?
The heavy equipment industry relies on the machining of aluminum wheels for construction machinery to enhance operational efficiency and load capacity. These wheels are designed to endure harsh working environments and heavy loads. For businesses in this sector, sourcing considerations include the strength of materials used and the wear resistance of the machined wheels, ensuring longevity and reduced downtime.
Why is machining aluminum wheels crucial in motorsport?
In the motorsport sector, custom wheel designs are machined to optimize performance in racing vehicles. The focus is on reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity, which is critical for speed and handling. Buyers in this industry should look for suppliers with specialized machining capabilities and rapid prototyping services to meet the fast-paced demands of racing.
How does aftermarket wheel refinishing leverage machining aluminum wheels?
Aftermarket wheel refinishing utilizes machining aluminum wheels to refurbish used wheels, providing a cost-effective solution that extends their lifespan. This process not only improves aesthetics but also restores functionality. Buyers in this sector should consider the quality of surface finishing techniques and implement stringent quality control measures to ensure that the refurbished wheels meet industry standards for safety and performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machining aluminum wheels’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Achieving Consistent Surface Quality in Machined Aluminum Wheels
The Problem: One common challenge faced by manufacturers machining aluminum wheels is achieving a uniform surface finish. Many buyers report issues such as mottling or white spots on the wheel surfaces, which can arise from the silicon content in the aluminum alloy used by different manufacturers. This inconsistency not only affects the aesthetic appeal of the wheels but also their marketability and customer satisfaction. For businesses focused on high-quality finishes, these defects can lead to increased production costs and waste, as extra time and resources are spent on reworking or polishing the affected parts.
The Solution: To address this issue, it is essential to establish a robust quality control process when sourcing aluminum wheels. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure they provide high-quality alloys with consistent chemical compositions. Implementing a pre-machining inspection process can help identify potential defects early on. Additionally, investing in advanced machining tools designed for aluminum, such as those with specialized coatings and geometries, can significantly enhance the surface finish. Utilizing high-speed machining techniques and optimizing cutting parameters—such as feed rates and spindle speeds—can also help achieve a superior finish while reducing the risk of defects.
Scenario 2: Managing Tool Wear and Longevity During Aluminum Wheel Machining
The Problem: Tool wear is a significant pain point for companies machining aluminum wheels. High cutting speeds and the abrasive nature of aluminum alloys can lead to rapid deterioration of cutting tools, impacting production efficiency and increasing costs. B2B buyers often struggle to find a balance between maintaining high productivity rates and ensuring that their tooling lasts long enough to justify the investment. Frequent tool replacements not only drive up costs but also result in downtime, which can severely affect delivery schedules.
The Solution: To mitigate tool wear, buyers should focus on selecting high-quality cutting tools specifically designed for aluminum machining. Opting for tools made from advanced materials, such as polycrystalline diamond (PCD) inserts, can provide superior wear resistance. Additionally, buyers should establish a comprehensive tool management program that includes regular monitoring of tool conditions and performance metrics. Implementing predictive maintenance practices will allow companies to anticipate tool failures and schedule replacements during planned downtimes. Furthermore, optimizing machining parameters—like reducing cutting speeds and adjusting the coolant application—can extend tool life and maintain overall productivity.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Meeting International Standards and Regulations
The Problem: As international trade in automotive components continues to grow, B2B buyers face the challenge of ensuring that their machined aluminum wheels comply with various regional standards and regulations. Different markets, such as those in Europe and the Middle East, have specific quality and safety standards that must be met. Navigating these regulatory environments can be complex and time-consuming, particularly for companies looking to expand their market reach.
The Solution: To effectively manage compliance with international standards, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their engineering and production teams on the relevant regulations for each target market. Collaborating with local regulatory bodies or industry associations can provide valuable insights into compliance requirements. Buyers should also implement quality assurance processes that align with international standards, such as ISO 9001, to ensure their manufacturing processes meet required specifications. Additionally, establishing strong relationships with certified suppliers can help streamline compliance efforts, as these partners will likely be familiar with the necessary regulations and can assist in documentation and certification processes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machining aluminum wheels
What Are the Common Materials Used for Machining Aluminum Wheels?
When selecting materials for machining aluminum wheels, it’s crucial to consider the specific properties and performance requirements that will impact the final product. Here, we analyze four common materials used in this industry, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum Alloy (e.g., 6061, 7075)
Key Properties:
Aluminum alloys like 6061 and 7075 are known for their excellent strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and good machinability. They can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for various applications in automotive and aerospace industries.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum alloys is their lightweight nature, which contributes to fuel efficiency in vehicles. However, they can be more expensive than other metals, and their manufacturing complexity may increase due to the need for specialized machining tools and techniques.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum alloys are compatible with various media, including water and oil, which are often used in machining processes. Their corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and ISO, which govern material quality and performance. The availability of specific alloys can vary by region, impacting sourcing strategies.
2. Cast Aluminum
Key Properties:
Cast aluminum is characterized by its excellent fluidity and ability to form complex shapes. It typically has good corrosion resistance and can handle moderate thermal and mechanical stresses.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of cast aluminum is its cost-effectiveness for producing intricate designs. However, it may not have the same strength as wrought aluminum alloys, which can limit its application in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application:
Cast aluminum is suitable for applications where weight savings are essential, but it may not perform well under extreme conditions. Its compatibility with various machining processes makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of regional manufacturing capabilities and standards. Compliance with local regulations regarding casting processes and material properties is essential, especially in markets with stringent quality controls.
3. Magnesium Alloy
Key Properties:
Magnesium alloys are known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and good machinability. They exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, particularly when treated with protective coatings.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of magnesium alloys is their lightweight nature, which can significantly enhance vehicle performance. However, they can be more challenging to machine compared to aluminum, leading to higher manufacturing costs and complexity.
Impact on Application:
Magnesium alloys are often used in high-performance applications where weight reduction is critical. They are compatible with various machining fluids, but care must be taken to prevent corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should consider the availability of magnesium alloys in their region and ensure compliance with relevant standards. Additionally, understanding the local market’s acceptance of magnesium in wheel applications is vital.
4. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP)
Key Properties:
CFRP is a composite material known for its high strength and stiffness while being significantly lighter than metals. It offers excellent fatigue resistance and thermal stability.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of CFRP is its lightweight properties, making it ideal for high-performance applications. However, it is generally more expensive and requires specialized machining techniques, which can complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application:
CFRP is suitable for applications where weight reduction and performance are critical. Its compatibility with various environmental conditions makes it versatile, but its machining requires careful handling to avoid damage.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific machining capabilities required for CFRP and ensure compliance with international standards. The cost and availability of CFRP may vary significantly by region, impacting procurement strategies.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for machining aluminum wheels | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloy (6061, 7075) | Automotive and aerospace wheels | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Cast Aluminum | Complex-shaped wheels | Cost-effective for intricate designs | Lower strength compared to alloys | Medium |
| Magnesium Alloy | High-performance automotive wheels | Exceptional lightweight properties | More challenging to machine | High |
| Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer | High-performance racing wheels | High strength and stiffness | Expensive and requires specialized machining | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material options for machining aluminum wheels, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machining aluminum wheels
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Aluminum Wheels?
The manufacturing process for aluminum wheels involves several critical stages that ensure both quality and performance. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques and technologies designed to optimize efficiency and product quality.
How Is Material Prepared for Aluminum Wheel Machining?
The process begins with the selection of high-quality aluminum alloys, which are crucial for producing lightweight yet durable wheels. The materials are typically sourced from certified suppliers to meet international quality standards. Once the aluminum is received, it undergoes rigorous inspection (Incoming Quality Control or IQC) to verify its composition and structural integrity.
After inspection, the aluminum is cut into pre-defined shapes using techniques such as sawing or shearing. The cut pieces are then subjected to processes like heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties. This preparation ensures that the raw material will perform well during machining.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Aluminum Wheel Manufacturing?
Forming is a pivotal stage in the manufacturing of aluminum wheels. Techniques such as forging, casting, and extrusion are commonly utilized.
-
Forging: This involves shaping the aluminum under high pressure to create a dense and strong structure. Forged wheels are known for their superior strength and are often preferred for high-performance vehicles.
-
Casting: This method involves pouring molten aluminum into molds. While casting can produce complex shapes, it often results in wheels that are slightly heavier and less strong than forged options.
-
Extrusion: This technique is used to create specific profiles and is often followed by machining to refine dimensions. Extruded wheels can have unique designs while maintaining strength.
Regardless of the forming technique, the formed wheels must be cooled and treated to relieve any internal stresses before proceeding to the assembly stage.
How Are Aluminum Wheels Assembled?
Once the wheels are formed, they are assembled. This involves the integration of various components such as valve holes and screw holes, which are critical for tire mounting and inflation. Techniques like drilling and CNC machining ensure that these components are accurately placed and sized.
Quality checks are conducted at this stage (In-Process Quality Control or IPQC) to ensure that all components fit correctly and meet design specifications. This minimizes the risk of defects in the final product.
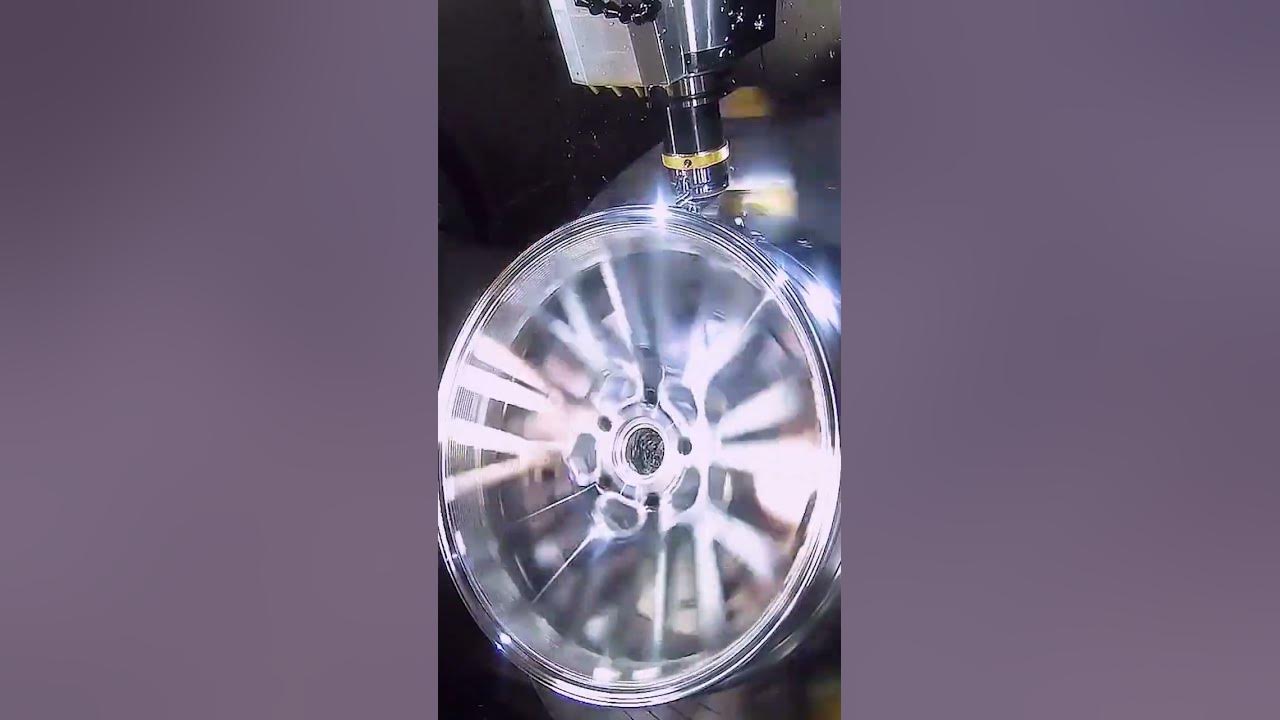
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed for Aluminum Wheels?
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process and is essential for aesthetic appeal and surface protection. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Machining: CNC machines are used to achieve precise dimensions and smooth surface finishes. This stage is critical to avoid issues such as mottling, which can arise from improper machining techniques or tool wear.
-
Polishing and Coating: After machining, wheels may be polished to enhance their appearance. Protective coatings are often applied to prevent corrosion and wear, ensuring longevity.
-
Anodizing: This electrochemical process enhances corrosion resistance and can also add color to the wheels. Anodized surfaces are more durable and less prone to scratches.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Aluminum Wheel Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to ensuring that aluminum wheels meet the high standards expected in the automotive industry. Various international and industry-specific standards guide QA practices.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems. It ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes, which is critical for B2B buyers. Additionally, certifications like CE mark and API standards are important for specific markets, ensuring compliance with safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Checks performed on raw materials before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to ensure that machinery and processes are functioning correctly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive examination of the finished product to verify compliance with specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to robust quality control practices. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with quality standards. Buyers should request access to audit reports and corrective action plans.
-
Request Certification Documentation: Ensure suppliers provide copies of relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, and any industry-specific certifications.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and product quality.
-
Assess Quality Metrics: Buyers should ask suppliers for key quality metrics, such as defect rates and customer satisfaction scores, to gauge their performance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is critical. Different regions may have varying standards and expectations, which can impact product performance and compliance.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Being aware of cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and enhance supplier relationships.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Each region may have specific regulatory requirements that need to be met, so it’s crucial for buyers to familiarize themselves with local regulations.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: The global supply chain can introduce risks, so buyers should evaluate their suppliers’ logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery of quality products.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in aluminum wheel production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who deliver high-quality products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machining aluminum wheels’
To successfully procure machining aluminum wheels, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers to ensure they make informed and strategic purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical for aligning your needs with supplier capabilities. Consider factors such as wheel size, material composition, and desired finish quality. Be specific about tolerances and any special features, such as lightweight designs or unique aesthetics.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Standards
Understanding current trends in aluminum wheel machining will enable you to stay competitive. Investigate innovations in materials and machining technologies, as well as industry standards that might affect your sourcing decision. This knowledge will help you identify suppliers that can meet or exceed these benchmarks.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in aluminum wheel machining, particularly those familiar with specific regional requirements.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards.
Step 4: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
Inspect the manufacturing capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers. Inquire about their machinery, technology, and production capacity. Pay attention to their ability to handle high-speed machining and the use of advanced cutting tools, which are crucial for achieving the desired quality in aluminum wheels.
Step 5: Understand Material Sourcing and Quality Control
Verify how suppliers source their aluminum and the quality control measures they have in place. High-quality aluminum is essential for preventing issues like mottling or white spots during machining. Ask about their testing processes and how they ensure consistent material quality from different manufacturers.
- Inquire About Material Certifications: Request documentation that verifies the aluminum meets industry standards and specifications.
Step 6: Request Sample Products
Before finalizing a supplier, request sample products to evaluate the machining quality firsthand. Analyze the finish, dimensions, and overall craftsmanship of the wheels. This step is vital for assessing whether the supplier can meet your expectations and specific requirements.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Review Contracts
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate terms that protect your interests. Review contracts carefully, focusing on delivery timelines, payment terms, and quality guarantees. Ensure that the agreement includes provisions for handling defects or issues that may arise post-delivery.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminum wheels effectively, ensuring they partner with suppliers who can deliver quality products that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machining aluminum wheels Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Machining Aluminum Wheels?
When sourcing aluminum wheels, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of aluminum alloys varies based on quality and sourcing. High-silicon content in alloys can lead to machining challenges, impacting overall costs if additional processing is required to achieve desired finishes.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the machining process. Labor costs will fluctuate based on the region, with higher costs in developed markets like Europe compared to emerging markets in Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses facility costs, utilities, maintenance, and depreciation of machinery. Efficient operations can mitigate overhead costs, but manufacturers may pass on higher costs if they invest in advanced technologies or high-quality machinery.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling, such as high-speed cutting inserts and modular tool systems, can significantly impact costs. Investing in quality tooling can enhance efficiency and reduce the frequency of tool replacement, balancing initial costs with long-term savings.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet stringent quality standards is critical. The cost of QC processes can vary based on the complexity of inspections and certifications required, especially for international buyers needing compliance with specific regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. For international buyers, understanding these costs upfront can prevent budget overruns.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin in their pricing to cover risks and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s position in the supply chain.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Costs for Aluminum Wheels?
Several factors influence pricing when sourcing aluminum wheels, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific tolerances can drive up costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-grade materials and recognized quality certifications can add to costs but are often necessary for compliance and performance requirements in specific markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and production capabilities of suppliers can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but provide better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers calculate total costs more accurately.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Aluminum Wheel Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms and prices. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially when offered larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the overall cost of ownership, including maintenance, potential downtime, and quality issues that could arise from lower-quality materials.
-
Research Market Trends: Understanding regional market dynamics can provide leverage in negotiations. For instance, knowing peak seasons for aluminum demand can help buyers time their orders for better pricing.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into market trends and upcoming changes that may affect costs.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should stay informed about tariffs, duties, and exchange rates that can impact final costs. Consulting with local experts or logistics companies can provide valuable insights.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for machining aluminum wheels can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including market conditions, geographic location, and supplier capabilities. Buyers are encouraged to obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers and consider all cost components before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machining aluminum wheels With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Machining Aluminum Wheels
When considering the production and refinement of aluminum wheels, various methods can achieve similar results. While machining is a prevalent technique, alternatives such as casting, forging, and 3D printing offer distinct advantages and challenges. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to select the most suitable solution for their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and quality expectations.
Comparison Table of Machining Aluminum Wheels and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Machining Aluminum Wheels | Casting | Forging | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, smooth finish | Good for mass production but less precision | Strong structural integrity, less intricate detail | Custom designs, variable strength |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing tooling costs | Lower cost per unit in large volumes | High initial setup cost; lower per unit cost | Higher material and machine costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and specialized machinery | Relatively straightforward for high-volume production | Requires specialized tools and skilled labor | Requires advanced technology and expertise |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of CNC machines | Low maintenance once molds are set | Moderate; requires tool upkeep | High due to technology and material sensitivity |
| Best Use Case | Custom, high-quality wheels | High-volume, low-cost production | Heavy-duty applications requiring strength | Prototyping and complex geometries |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Casting
Casting involves pouring molten aluminum into a mold to create the wheel shape. This method is particularly advantageous for producing large quantities of wheels at a lower cost. However, while casting can achieve good surface finishes, it may lack the precision and detail offered by machining. Additionally, the risk of defects such as porosity or inclusions can compromise the strength and appearance of the wheels, making it less suitable for high-performance applications.
Forging
Forging aluminum wheels involves shaping the metal through compressive forces, resulting in a strong and durable product. This method is ideal for applications requiring high structural integrity, such as in automotive racing or heavy-duty vehicles. While forging can produce excellent mechanical properties, it typically involves a higher initial investment in tooling and equipment. Furthermore, the complexity of designs is limited compared to machining or 3D printing, making it less versatile for custom designs.
3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, allows for the creation of complex and customized wheel designs layer by layer. This technology is particularly useful for prototyping and low-volume production runs where design flexibility is critical. However, the costs associated with high-quality materials and advanced printers can be significant. Additionally, the mechanical properties of 3D printed wheels may not match those produced by traditional methods, limiting their application in high-stress environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the most appropriate solution for aluminum wheel production hinges on your specific requirements, including volume, design complexity, and budget. Machining offers precision and customization, making it ideal for bespoke projects, while casting and forging cater to high-volume production needs with varying strengths and weaknesses. Meanwhile, 3D printing excels in flexibility but may not be suitable for all applications. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machining aluminum wheels
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for Machining Aluminum Wheels?
When machining aluminum wheels, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring quality, performance, and efficiency. Here are some key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Aluminum wheels are typically made from various grades of aluminum alloys, such as 6061 or 7075. The choice of material grade impacts the wheel’s strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is vital to balance performance requirements with cost-effectiveness, especially in high-stress applications like automotive and aviation. -
Tolerances
Tolerances refer to the allowable variation in dimensions during the machining process. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 mm) are often required for critical components like bolt holes and mounting surfaces. Understanding tolerances is essential for buyers to ensure that the wheels fit correctly, minimizing the risk of failure and ensuring safety. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of aluminum wheels can significantly affect aesthetics and performance. Common finishes include anodized, polished, or painted. A higher surface finish quality can improve corrosion resistance and visual appeal. B2B buyers must consider how the desired surface finish aligns with branding and customer expectations. -
Cutting Speeds and Feed Rates
These parameters are crucial for optimizing machining operations. High cutting speeds enhance productivity but can lead to tool wear and surface defects if not managed correctly. Feed rates influence the amount of material removed per pass. Buyers should understand these terms to evaluate machining efficiency and cost implications. -
Weight
The weight of aluminum wheels is a critical factor in automotive applications, impacting fuel efficiency and performance. Lightweight alloys can improve vehicle performance while maintaining strength. B2B buyers should assess the weight specifications to align with industry standards and customer preferences.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Machining of Aluminum Wheels?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and decision-making in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture products that are then marketed by another company. In the context of aluminum wheels, OEMs often dictate specifications that suppliers must meet. Understanding OEM requirements helps buyers ensure compliance with industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and cash flow. A high MOQ may necessitate larger upfront investments, which could be a barrier for smaller businesses. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to potential suppliers to obtain price quotes for specific quantities of goods or services. It is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs and negotiate terms effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to clarify shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities, ensuring smoother transactions across borders. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to automated machining processes controlled by computer systems. This technology enhances precision and efficiency in manufacturing aluminum wheels. Buyers should be aware of CNC capabilities when selecting machining partners to ensure they meet production needs. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to manage production schedules and inventory levels effectively. Longer lead times may affect project timelines, making it critical to establish clear expectations with suppliers.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of machining aluminum wheels more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machining aluminum wheels Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Machining Aluminum Wheels Sector?
The machining aluminum wheels sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by several global factors. The rising demand for lightweight vehicles, particularly in the automotive industry, is a key driver, as manufacturers seek to enhance fuel efficiency and performance. Additionally, advancements in machining technology, including CNC machining and automated processes, are enabling manufacturers to achieve higher precision and better surface finishes, catering to the increasing expectations of consumers and regulatory standards.
Emerging B2B technology trends are reshaping sourcing strategies in this sector. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and data analytics, allows for real-time monitoring of machining processes, leading to improved efficiency and reduced waste. Moreover, artificial intelligence is being utilized to predict maintenance needs and optimize production schedules, minimizing downtime and costs. For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these technological advancements present opportunities for sourcing high-quality machining services and products that meet stringent performance criteria.
Market dynamics also reflect a shift towards collaborative partnerships between suppliers and manufacturers. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that can provide not only high-quality products but also value-added services, such as technical support and training. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia, where local capabilities are evolving rapidly, and businesses are looking to enhance their competitive edge in global markets.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Machining Aluminum Wheels Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the machining aluminum wheels sector. The environmental impact of aluminum extraction and processing is significant, prompting stakeholders to prioritize sustainable practices. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting energy-efficient technologies and recycling initiatives to minimize their carbon footprints. This shift not only meets regulatory requirements but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and socially responsible. This encompasses the procurement of raw materials from suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract international buyers. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can enhance their reputations and foster long-term partnerships with conscientious buyers.
Furthermore, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recycled aluminum, is gaining traction. Recycled aluminum requires significantly less energy to process compared to virgin aluminum, which helps reduce overall environmental impact. As the demand for sustainable practices continues to rise, international buyers must consider suppliers that offer certified green materials and demonstrate a commitment to sustainable operations.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of the Machining Aluminum Wheels Sector?
The machining aluminum wheels sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, aluminum wheels were primarily used in high-performance vehicles due to their lightweight and aesthetic appeal. However, as manufacturing techniques advanced, aluminum wheels became more accessible and widely adopted across various vehicle segments, including economy cars and commercial vehicles.
The introduction of CNC machining in the late 20th century revolutionized the production of aluminum wheels, allowing for greater precision and consistency in machining processes. This technology enabled manufacturers to produce complex designs and finishes that were previously unattainable. Today, the sector continues to innovate, with a strong focus on improving machining efficiency, surface quality, and sustainability practices. As the industry moves forward, the integration of advanced technologies and a commitment to ethical sourcing will shape its future landscape, ensuring that it meets the demands of a global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machining aluminum wheels
-
How do I solve the issue of mottling on machined aluminum wheels?
To address mottling or white spots on machined aluminum wheels, begin by assessing the quality of the raw materials used. Variability in silicon content from different manufacturers can lead to inconsistent finishes. Experiment with different cutting speeds, feed rates, and insert types, including high-shear inserts that minimize friction. Additionally, consider using specialized lubricants or coolants to reduce heat and improve surface finish. If issues persist, consult with experienced machinists or tool suppliers who can provide tailored solutions based on your equipment and materials. -
What is the best cutting tool for machining aluminum wheels?
The ideal cutting tool for machining aluminum wheels is one that offers high cutting speeds and durability. Tools made from polycrystalline diamond (PCD) or high-speed steel (HSS) are highly recommended for their ability to withstand the centrifugal forces experienced during the machining process. Additionally, modular tool systems, such as OvalFlex or HubStar, can enhance stability and efficiency while providing excellent surface quality. Selecting the right tool will depend on your specific machining requirements, including wheel size and desired finish. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for aluminum wheel machining services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for aluminum wheel machining services can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the machining process. Typically, MOQs may range from 50 to 500 units. It’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and flexibility regarding order sizes. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for customized orders, especially if they are looking to build long-term relationships with buyers. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing aluminum wheels?
Payment terms for sourcing aluminum wheels often depend on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s relationship with them. Common terms include a 30% deposit upfront with the balance due upon delivery or net 30-60 days after receipt of goods. International buyers should also be aware of currency fluctuations and potential additional fees related to wire transfers or letters of credit. It is advisable to negotiate payment terms upfront to ensure clarity and avoid potential disputes. -
How do I vet suppliers for machining aluminum wheels?
Vetting suppliers for machining aluminum wheels involves assessing their certifications, production capabilities, and quality control processes. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications and a proven track record in the industry. Request samples of their work to evaluate finish quality and consistency. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities or conducting virtual audits to understand their operations better. Engaging with existing clients for references can also provide insights into their reliability and service levels. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for aluminum wheel machining?
Quality assurance measures in aluminum wheel machining should include regular inspections of raw materials, in-process quality checks, and final product assessments. Implementing statistical process control (SPC) can help monitor production consistency. Suppliers should provide documentation of quality checks, including surface finish measurements and dimensional tolerances. Additionally, consider certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management practices. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing aluminum wheels internationally?
When sourcing aluminum wheels internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to navigate tariffs and ensure compliance with import/export regulations. It’s also vital to choose reliable freight forwarders who can provide tracking and timely delivery. Lastly, factor in potential delays due to customs processing, especially in regions with stringent import controls. -
Can I customize aluminum wheels for my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for aluminum wheels, including variations in size, design, and finish. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and any design files you may have. Be clear about your performance requirements, such as weight, strength, and aesthetic considerations. Customization may involve higher costs and longer lead times, so it’s essential to communicate your needs early in the sourcing process to align with the supplier’s capabilities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Machining Aluminum Wheels Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Practical Machinist – Automotive Wheel Machining Solutions
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Machining automotive wheels from aluminum, specifically focusing on the joining of the finished ‘face’ to the rim section. Discussion includes one-piece machined billet wheels, OEM automotive wheels made from shell cast aluminum, and high-performance two or three-piece wheels. Mention of PCD (poly-crystalline diamond) insert tools for machining, cutting speeds over 1000 sfm, and various types of w…
2. Runsom – CNC Machining for Aluminum Wheels
Domain: runsom.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining for Aluminum Wheel Machining and Repair:
– Aluminum is the predominant material for crafting wheel rims in the automotive sector, with aluminum alloy wheels increasingly replacing steel wheels.
– Benefits of aluminum alloy wheels include:
– Lighter weight (approximately two-thirds lighter than steel wheels), improving fuel efficiency by 6% to 8%.
– High thermal conductivity, …
3. Swihart Industries – GA1R Lightweight Forged Aluminum Wheel
Domain: swihartindustries.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {“Project Description”:”Lightweight forged aluminum GA1R Wheel”,”CNC Machining Capabilities Applied/Processes”:{“Primary”:”Material Procurement, CNC Machining – Milling and Turning”,”Secondary”:”Deburring”},”Tightest Tolerances”:”± .001\””,”Material Used”:”Forged 6061-T6 Aluminum”,”Material Finish”:”63 RA”,”In Process Testing/Inspection Performed”:”Dimensional Inspection, Visual Inspection”,”Indus…
4. Real Wheels – 8×16 Aluminum Wheels
Domain: jalopyjournal.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Aluminum wheels, specifically Real Wheels, 8×16 size, with a hub thickness of 1 inch. The user is considering machining off a quarter inch from the back to gain fender clearance, leaving a hub thickness of 3/4 inch. The wheels have a neutral offset and solid shank (shouldered) lug holes. They are rear wheels designed for vehicles without high power outputs.
5. OpenBuilds – Robust Milling Machine for Aluminium Wheels
Domain: builds.openbuilds.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Robust milling machine for aluminium wheels; Work area: 600x600x350mm; Suitable for milling car wheel centers (3-piece design); Suggested machine types: 5-axis mill for complex shapes, 3- or 4-axis for 2.5D designs; Recommended components: aluminum frame, linear rails, ballscrews, NEMA 34 or hybrid stepper motors, DC servos; Material for wheels: 6062 T6 aluminum; Considerations for construction: s…
6. PowerHouse Wheels – Custom Wheel Machining
Domain: powerhousewheels.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Wheel Drilling / Machining
Suggested Price: $1.00
Brand: PowerHouse Wheels
Services Offered: Custom wheel machining and drilling services, including precision machining and drilling techniques to modify bolt patterns, offsets, and hub bores.
Key Features:
– Customization to fit specific vehicle requirements.
– CNC machining technology for precision.
– Ability to modify wheels withou…
7. Custom Alloy Wheel – CNC Machined Aluminum Wheels
Domain: customalloywheel.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining for aluminum wheels with precise dimensions and smooth edges. Equipped with 46 CNC machining tools achieving accuracy up to 0.02mm. Capable of producing various styles of wheels. Annual production capacity of 1,500,000 cast aluminum alloy wheels. Established in 1993, specializing in design and manufacturing of aluminum alloy wheels. Offers competitive pricing and fast delivery. Proce…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machining aluminum wheels
In conclusion, strategic sourcing for machining aluminum wheels is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance product quality and operational efficiency. Understanding the complexities of aluminum alloys and the challenges faced during machining—such as the “mottling” effect—allows businesses to make informed decisions. Collaborating with reliable suppliers who offer advanced cutting tools and technologies can significantly mitigate production issues, ensuring superior finishes and reducing waste.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality aluminum wheels will rise. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that leverage state-of-the-art machinery and tooling solutions, which can handle the specific requirements of aluminum wheel machining. Investing in these strategic alliances not only fosters innovation but also enhances competitive advantage in a global marketplace.
Looking ahead, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay abreast of industry trends and technological advancements. By doing so, they can ensure that their sourcing strategies align with future demands, ultimately driving growth and success in their operations. Now is the time to evaluate your current sourcing practices and explore new partnerships that can elevate your machining capabilities.