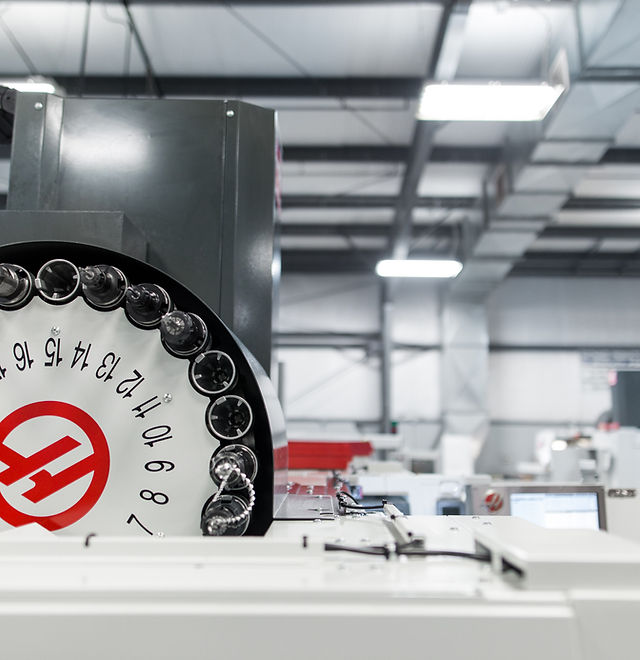
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machined products co
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing precision machined products can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the growing demand for high-quality components across industries such as automotive, energy, and medical, understanding the complexities of the global supply chain is essential. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the machined products sector, addressing key elements such as types of products, applications, and effective supplier vetting strategies.
As you navigate through this guide, you will gain insights into the intricacies of contract manufacturing, including the significance of ISO certifications and the importance of value engineering in achieving cost-effective solutions. We will also explore the latest advancements in automated manufacturing processes, which can enhance productivity and reliability, ultimately leading to cost savings.
By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business goals. Whether you are a seasoned buyer or new to the industry, this guide serves as a vital resource to help you identify reputable suppliers, understand pricing structures, and leverage the best practices in sourcing machined products. Your journey toward securing high-quality components starts here, paving the way for successful partnerships and sustained growth in your respective markets.
Understanding machined products co Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machined Parts | High precision, automated machining, and complex geometries | Aerospace, Automotive, Medical | Pros: High accuracy, repeatability. Cons: Higher initial setup costs. |
| Custom Fabricated Components | Tailored designs, specific material requirements, and secondary operations | Industrial Equipment, Construction | Pros: Tailored solutions, flexibility in design. Cons: Longer lead times. |
| High-Volume Production Parts | Mass production capabilities, cost-effective unit pricing | Consumer Electronics, Appliances | Pros: Economies of scale, lower per-unit costs. Cons: Less customization. |
| Precision Tooling | Specialized tools, rigorous quality control, and material selection | Manufacturing, Assembly Lines | Pros: Enhanced efficiency, improved product quality. Cons: Higher upfront investment. |
| Rapid Prototyping | Quick turnaround, iterative design processes, and 3D modeling | Product Development, Testing | Pros: Fast feedback, reduced time to market. Cons: May not reflect final production quality. |
What are the characteristics of CNC Machined Parts?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machined parts are known for their exceptional precision and ability to produce complex geometries. These parts are typically manufactured using automated machines that execute programmed commands, ensuring high levels of accuracy and repeatability. Industries such as aerospace and automotive heavily rely on CNC machining due to the critical tolerances required for safety and performance. When considering CNC machined parts, buyers should evaluate the initial setup costs against the long-term benefits of consistent quality and reduced labor costs.
How do Custom Fabricated Components differ from standard products?
Custom fabricated components are designed to meet specific requirements, allowing for tailored solutions that fit unique applications. These components often undergo secondary operations such as welding or assembly, which adds to their versatility. Industries like industrial equipment and construction frequently utilize custom fabrication to achieve desired specifications. Buyers should consider the trade-off between the flexibility of custom designs and the potential for longer lead times, which can impact project schedules.
What benefits do High-Volume Production Parts offer to businesses?
High-volume production parts are designed for mass manufacturing, enabling companies to benefit from economies of scale. This type of machining is ideal for industries such as consumer electronics and appliances, where cost-effective unit pricing is essential. The primary advantage is the significant reduction in per-unit costs, making it attractive for large orders. However, buyers should be aware that this approach may limit customization options, which could be a critical factor for specific applications.
Why is Precision Tooling important in manufacturing?
Precision tooling involves the creation of specialized tools that enhance manufacturing efficiency and product quality. This type of machining is characterized by rigorous quality control and careful material selection, making it vital for industries like manufacturing and assembly lines. The key benefits include improved operational efficiency and reduced waste, leading to better profitability. Buyers should weigh the higher upfront investment against the long-term gains in productivity and quality.
How does Rapid Prototyping support product development?
Rapid prototyping is a process that allows for quick iterations of design concepts, utilizing 3D modeling and advanced manufacturing techniques. This approach is particularly beneficial for product development and testing, as it enables companies to receive fast feedback and make necessary adjustments before full-scale production. While rapid prototyping can significantly reduce time to market, buyers should consider that prototypes may not always reflect the quality of final production parts, which could impact decision-making for subsequent phases.
Key Industrial Applications of machined products co
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machined products co | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision components for engine assembly | Enhanced reliability and performance of vehicles | Compliance with international automotive standards |
| Medical | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency | ISO certifications and biocompatibility of materials |
| Energy | Machined parts for renewable energy systems | Increased efficiency and reduced operational costs | Robustness against environmental conditions |
| Aerospace | High-performance components for aircraft systems | Safety and compliance with strict aerospace regulations | Precision engineering and weight optimization |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Custom fittings and connectors for machinery | Streamlined construction processes and reduced downtime | Material durability and compatibility with existing systems |
How Does Machined Products Co Serve the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, machined products co provides precision components critical for engine assembly. These parts, such as valve bodies and connecting rods, are designed to enhance the reliability and performance of vehicles. For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, it is crucial to ensure compliance with international automotive standards. This guarantees that the components can withstand rigorous testing and meet the expectations of end-users.
What Role Does Machined Products Co Play in the Medical Field?
In the medical industry, machined products co specializes in producing custom surgical instruments and implants. The precision of these machined products is vital for improving patient outcomes and ensuring operational efficiency in healthcare settings. Buyers, especially from the Middle East and Europe, must consider ISO certifications and the biocompatibility of materials used in these products. This ensures that the instruments meet stringent health regulations and are safe for patient use.
How Are Machined Products Co Solutions Beneficial to the Energy Sector?
Machined products co supplies vital machined parts for renewable energy systems, including wind turbines and solar panels. These components help increase efficiency and reduce operational costs, which is essential for companies looking to optimize their energy production. For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing durable and robust parts that can withstand various environmental conditions is a key consideration, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
What Advantages Does Machined Products Co Offer to the Aerospace Industry?
In aerospace applications, machined products co delivers high-performance components that are essential for aircraft systems. These components must comply with strict aerospace regulations to ensure safety and reliability during flight. Buyers from Europe and other regions should prioritize precision engineering and weight optimization in their sourcing decisions. This not only enhances aircraft performance but also contributes to fuel efficiency.
How Does Machined Products Co Support Construction and Infrastructure Projects?
For the construction and infrastructure sector, machined products co manufactures custom fittings and connectors for various machinery. These machined components streamline construction processes and reduce downtime, which is critical for project timelines. Buyers, particularly in developing regions, should focus on the material durability and compatibility of these products with existing systems to ensure seamless integration and long-term functionality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machined products co’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance in Machined Products
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the automotive industry is sourcing machined components for a new vehicle model. They are concerned about the quality and reliability of the parts, especially given the stringent safety standards required in the industry. The buyer has experienced issues in the past with parts that did not meet specifications, leading to production delays and costly recalls. The challenge lies in ensuring that the selected supplier adheres to rigorous quality assurance processes and can provide proof of compliance with international standards.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize suppliers with established quality management systems, such as ISO 9001:2015 certification. When engaging with Machined Products Co, for instance, buyers should request detailed documentation of their quality assurance protocols, including inspection reports, compliance certifications, and any relevant testing results. Additionally, establishing a clear communication channel with the supplier’s quality assurance team can help address concerns proactively. Implementing regular quality audits and performance reviews can also provide ongoing assurance that the supplier maintains high standards throughout the production process.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Long Lead Times for Custom Orders
The Problem: A buyer in the medical device sector requires a series of custom machined components for a new product launch. However, they face the challenge of lengthy lead times that could jeopardize their project timeline. With strict deadlines for regulatory approvals and market entry, the buyer cannot afford delays caused by inefficient manufacturing processes or supply chain issues.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should engage in early and detailed discussions with suppliers about lead times and production capabilities. When working with Machined Products Co, buyers can leverage their in-house engineering and rapid prototyping services to accelerate the development process. Providing comprehensive specifications and drawings upfront can streamline the quoting and production phases. Furthermore, considering the use of automated manufacturing solutions, such as robotic machining, can significantly reduce lead times while maintaining quality. Establishing a flexible contract that allows for adjustments based on demand can also help manage timelines effectively.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost Efficiency in Production Runs
The Problem: A buyer from the aerospace industry is looking to produce a high volume of precision machined parts but is concerned about the escalating costs associated with production. The buyer has encountered fluctuating prices due to material costs and inefficient manufacturing processes, impacting their budget and profitability.
The Solution: To address cost concerns, buyers should focus on value engineering and collaboration with their suppliers. Machined Products Co offers value engineering services that can help identify cost-saving opportunities without compromising on quality. Buyers should work closely with the engineering team to explore alternative materials or manufacturing methods that could reduce costs. Additionally, negotiating long-term contracts or bulk order agreements can provide price stability and predictability. Implementing lean manufacturing principles can also enhance efficiency and reduce waste, ultimately leading to significant cost savings over time. Regularly reviewing production processes with the supplier can help identify areas for improvement and further optimize expenses.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machined products co
When selecting materials for machined products, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for international B2B buyers. This guide analyzes four common materials used in precision machining, focusing on their performance, application suitability, and considerations for global markets.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum Alloys in Machined Products?
Aluminum alloys are lightweight materials known for their excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. They typically have a temperature rating up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressures, making them suitable for various applications. The most common alloys used include 6061 and 7075, which provide good strength-to-weight ratios.
Pros: Aluminum alloys are easy to machine, reducing manufacturing complexity and costs. They are also highly recyclable, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
Cons: While durable, aluminum alloys can be less suitable for high-temperature applications compared to steel or titanium. They may also be more expensive than some alternatives, which can impact overall project budgets.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. However, it may not be compatible with highly corrosive environments without proper coatings.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as EN 573 and ASTM B221, which govern aluminum alloy specifications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Machined Products?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and high strength, making it a popular choice in industries like medical and food processing. Common grades include 304 and 316, with temperature ratings exceeding 800°C and excellent pressure ratings.
Pros: Stainless steel offers durability and longevity, making it suitable for critical applications. Its resistance to oxidation and corrosion ensures reliability in harsh environments.
Cons: The machining process for stainless steel can be complex and costly, often requiring specialized tools and techniques. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where minimizing mass is essential.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including acids and chlorides, making it ideal for chemical processing applications.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 and DIN 17440 is essential for buyers in Africa and South America, ensuring the material meets required specifications.
What Are the Advantages of Using Titanium in Machined Products?
Titanium is a high-performance material known for its strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in extreme environments. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and is often used in aerospace and medical applications.
Pros: Titanium’s lightweight nature combined with high strength makes it ideal for applications where performance is critical. Its biocompatibility also makes it a preferred choice for medical implants.
Cons: The cost of titanium is significantly higher than other materials, which can be a barrier for some projects. Additionally, machining titanium requires specialized equipment and expertise, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly suited for applications in the aerospace and medical sectors, where performance and reliability are paramount.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM F136 for medical applications and AMS 4911 for aerospace, which are critical for ensuring quality and safety.
How Does Carbon Steel Compare in Machined Products?
Carbon steel is widely used due to its strength and affordability. It can handle high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for structural applications. Common grades include A36 and 1018, with temperature ratings up to 400°C.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively low-cost and easy to machine, making it a popular choice for various applications. Its strength makes it suitable for heavy-duty components.
Cons: Carbon steel is prone to corrosion, which can limit its use in certain environments unless properly treated. Its weight can also be a disadvantage in applications where weight savings are essential.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is commonly used in construction and manufacturing applications where strength is prioritized over corrosion resistance.
International Considerations: Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 and DIN 17100, which govern the quality and specifications of carbon steel.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Machined Products
| Material | Typical Use Case for machined products co | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Aerospace, Automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less suitable for high-temperature use | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Medical, Food Processing | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Complex machining process | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace, Medical Implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex machining | High |
| Carbon Steel | Construction, Heavy Machinery | Cost-effective and strong | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for machined products, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, application suitability, and compliance with relevant standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machined products co
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Machined Products?
The manufacturing process for machined products typically involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is essential for ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Machined Products?
Material preparation is the initial step in the manufacturing process. This stage involves selecting the appropriate materials, which may include metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium, depending on the product requirements. The selected material undergoes inspection to verify its quality and properties, ensuring it meets the necessary standards for strength and durability.
Once the material is approved, it is cut to size using techniques such as shearing or sawing. This is followed by machining operations like turning, milling, or drilling, where the material is shaped into the desired form. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are commonly used in this process, allowing for high precision and repeatability.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming and Assembly?
Forming involves shaping the machined parts into their final configurations. Techniques such as forging, stamping, and casting may be employed, depending on the complexity of the part and the material used. For example, forging is often used for high-strength components, while casting is suitable for intricate shapes.
The assembly stage involves putting together various machined components to create the final product. This may include fastening parts with screws, welding, or using adhesives, depending on the design requirements. Automated assembly systems are frequently utilized to enhance efficiency and reduce the potential for human error.
How Is Finishing Achieved in Machined Products?
Finishing is the final stage in the manufacturing process, aimed at enhancing the surface quality and functionality of the product. Techniques such as polishing, anodizing, plating, and painting can be applied to improve appearance, corrosion resistance, and wear properties. Rigorous quality checks are conducted during this phase to ensure that the finished product meets all specifications.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Machined Products?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing machined products, ensuring that the final products meet or exceed customer expectations. Adhering to internationally recognized standards such as ISO 9001:2015 is fundamental in establishing a robust QA framework.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001:2015 certification indicates that a manufacturer has implemented a quality management system focused on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. In addition, industry-specific standards like CE marking for compliance with European safety regulations, and API specifications for oil and gas applications, may also be relevant depending on the industry.
B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers maintain the necessary certifications, as these standards not only ensure product quality but also reflect the manufacturer’s commitment to best practices.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure consistent quality. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, periodic checks are performed to monitor key parameters and ensure that the production is on track and compliant with specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After the manufacturing process, finished products undergo comprehensive testing and inspection to verify that they meet all specifications and quality standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods include dimensional inspections using calibrated gauges, mechanical testing (such as tensile and hardness tests), and non-destructive testing techniques like ultrasonic and radiographic inspections. These methods help to identify any defects or inconsistencies before products are shipped to customers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. This can be achieved through:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess the quality control measures in place. Buyers can evaluate equipment, processes, and employee practices firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC performance over time, including metrics on defect rates and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality, adding an additional layer of assurance.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of various nuances in quality control and certification.
Understanding local regulations, industry standards, and cultural practices can significantly affect the procurement process. For instance, certain markets may have specific certification requirements that differ from international standards. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international standards to mitigate risks associated with quality discrepancies.
Additionally, language barriers and differences in documentation practices may pose challenges. It is advisable to establish clear communication channels and request documentation in a language that is mutually understood to facilitate smooth transactions.
Conclusion
An in-depth understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for B2B buyers when selecting suppliers for machined products. By familiarizing themselves with the stages of manufacturing, relevant quality standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their quality expectations and business objectives. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize quality assurance will ultimately lead to enhanced product performance and reliability, fostering long-term partnerships in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machined products co’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring precision machined products. It outlines essential steps to ensure that your sourcing process is efficient and effective, ultimately leading to successful procurement and strong supplier relationships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for successful sourcing. This includes detailed drawings, material requirements, tolerances, and finish specifications. By defining these parameters upfront, you will ensure that potential suppliers understand your needs and can provide accurate quotes.
- Considerations:
- What materials will be used?
- Are there specific industry standards (e.g., ISO, ANSI) that must be met?
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in the types of machined products you need. Look for companies with a strong reputation, extensive experience, and a proven track record in your industry.
- Key Resources:
- Online directories (like MFG.com)
- Industry associations and trade shows for networking
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify the certifications of potential suppliers, such as ISO 9001:2015. These certifications indicate adherence to quality management systems and processes, which are crucial for ensuring product consistency and reliability.
- What to Check:
- Does the supplier have a history of passing audits?
- Are there any customer reviews or testimonials regarding their compliance?
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline pricing, lead times, and payment terms. A well-structured quote should include all costs associated with the production, including tooling and shipping.
- Important Aspects:
- Ensure that quotes are based on your defined specifications.
- Compare quotes not just on price, but also on service and delivery timelines.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Inspections
If feasible, conduct site visits or arrange for virtual inspections of the supplier’s facilities. This allows you to assess their manufacturing capabilities, equipment, and quality control processes firsthand.
- What to Look For:
- Are the facilities well-maintained?
- How is quality assurance implemented in their operations?
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is essential for a successful supplier relationship. Establish clear points of contact and ensure that both parties understand the communication process for updates, issues, and feedback.
- Best Practices:
- Set regular check-in meetings during the production phase.
- Use collaborative tools for sharing updates and documents.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Before finalizing the contract, negotiate terms and conditions that protect your interests. This includes delivery schedules, penalties for late deliveries, and warranty terms for the products supplied.
- Key Considerations:
- What are the consequences for non-compliance?
- How will disputes be resolved?
By following this practical checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for machined products, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers capable of meeting their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machined products co Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machined Products Sourcing?
When engaging in the sourcing of machined products, understanding the intricate cost structure is essential for making informed decisions. The primary components that contribute to the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts pricing. High-performance materials such as stainless steel or specialized alloys may incur higher costs but can offer greater durability and functionality.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the machining processes involved. Skilled labor may command a premium, particularly in regions with a high demand for precision machining.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient overhead management can lead to competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs include the initial investment in machinery and tools required for production. Custom tooling can increase upfront costs but may result in lower per-unit costs over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Stringent QC measures ensure that products meet specified standards. The costs associated with testing and validation processes must be factored into the overall pricing strategy.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, mode of transport, and trade regulations. Incoterms play a crucial role in determining who bears these costs and risks.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. Understanding a supplier’s margin expectations can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machined Products Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the machined products market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can impact pricing. Higher volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly specialized or customized components usually cost more due to the additional engineering and manufacturing complexities involved.
-
Material Choices: The type and quality of materials selected will directly affect the cost. For instance, using premium materials will increase the base price.
-
Quality Certifications: Products that meet specific industry standards or certifications (such as ISO) may carry a premium price due to the additional compliance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect total costs, as they dictate the division of responsibilities and costs between buyers and suppliers during shipping and delivery.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Always inquire about pricing structures based on order volume. Committing to larger quantities can yield significant savings.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with a product, including maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime. A lower upfront price may not always equate to overall savings.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Understand the local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade tariffs that may affect pricing in your region.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ask suppliers for itemized quotes that break down costs. This transparency will enable you to identify areas for potential negotiation.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time, as trust and reliability are built.
In conclusion, understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing machined products. Always remember that indicative prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so staying updated on industry trends is crucial.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machined products co With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Machined Products
In the realm of precision manufacturing, businesses often seek solutions that not only meet their specifications but also align with their operational goals. As international B2B buyers evaluate their options, it is essential to compare various solutions available in the market. This analysis focuses on Machined Products Co. and examines viable alternatives such as additive manufacturing and traditional metal fabrication. Each method has unique attributes that can significantly impact project outcomes, costs, and implementation.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Machined Products Co | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Traditional Metal Fabrication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and consistency; suited for complex geometries | Offers flexibility in design; lower precision than CNC machining | High strength and durability; suitable for large parts |
| Cost | Competitive for medium to large volumes; setup costs can be high | Generally lower for low-volume production; material costs can vary | Lower initial costs but higher for small batches due to setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires detailed planning and engineering; established processes | Quick setup; design changes can be made rapidly | Requires skilled labor and specific machinery; longer lead times |
| Maintenance | High standards with rigorous quality control; ongoing maintenance needed | Minimal maintenance; equipment requires occasional calibration | Requires regular maintenance of machinery and tools |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume production across various industries | Best for prototyping and low-volume production | Suitable for large-scale production with high structural integrity |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing represents a transformative approach to production, allowing for the creation of complex geometries that are often impossible with traditional methods. One of the primary advantages is its flexibility; designs can be modified quickly without significant retooling costs. This method is particularly beneficial for prototyping and producing low-volume components. However, the precision may not match that of Machined Products Co., which can be a drawback for applications requiring stringent tolerances. Additionally, material costs can fluctuate widely, impacting overall project budgets.
Traditional Metal Fabrication
Traditional metal fabrication encompasses a range of processes including welding, cutting, and machining. This method excels in producing robust components that require high structural integrity, making it ideal for industries such as construction and heavy machinery. The initial setup costs can be lower compared to Machined Products Co., but the expenses can escalate for small batch productions due to the need for specific tooling and longer lead times. Additionally, the reliance on skilled labor can present challenges, particularly in regions where such expertise is scarce.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right manufacturing solution requires a careful assessment of specific project requirements, including volume, complexity, and budget. Buyers should consider the operational capabilities of Machined Products Co. in delivering high-quality, precision machined parts, especially for medium to large volumes. In contrast, for projects focused on rapid prototyping or low-volume runs, additive manufacturing may offer a more agile and cost-effective solution. Meanwhile, traditional metal fabrication remains a strong contender for projects demanding high durability and structural integrity. By weighing these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machined products co
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Machined Products?
In the manufacturing of precision machined products, several critical specifications play a vital role in ensuring quality and functionality. Understanding these properties is essential for B2B buyers when sourcing machined components.
Material Grade: Why Is It Crucial for Performance?
Material grade refers to the specific type of material used in manufacturing, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or titanium. Each material has distinct mechanical properties, including strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. Selecting the appropriate material grade is essential for ensuring the product meets application requirements, such as in automotive or aerospace sectors, where durability and safety are paramount.
Tolerance: What Does This Mean for Precision?
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a machined part. It is expressed as a range (e.g., ±0.005 inches). High precision tolerances are critical in applications requiring exact fits, such as in medical devices or machinery. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to product failure, increased costs, and potential safety hazards, making it vital for B2B buyers to communicate these specifications clearly.
Surface Finish: How Does It Affect Functionality?
Surface finish describes the texture and smoothness of a part’s surface, often specified in microinches or Ra (Roughness Average). A proper surface finish can enhance performance by reducing friction, improving wear resistance, and facilitating better adhesion of coatings. In industries like automotive or aerospace, where aerodynamics and performance are crucial, understanding the surface finish requirements is vital for ensuring optimal product functionality.
Hardness: Why Is It Important?
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation or scratching, typically assessed using scales like Rockwell or Brinell. This property is particularly relevant in applications where parts are subjected to wear and tear, such as gears or bearings. B2B buyers should consider hardness specifications to ensure that the machined parts can withstand operational stresses over time.
Heat Treatment: What Role Does It Play?
Heat treatment is a controlled process used to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material. This process can enhance hardness, strength, and ductility, making it essential for parts used in demanding environments. Understanding heat treatment specifications is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that the machined components can endure specific operational conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Machined Products?
Navigating the jargon of the machined products industry can be challenging for B2B buyers. Familiarity with key terms can facilitate better communication and decision-making.
What Is an OEM?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. It refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for quality assurance and compatibility with existing systems.
What Does MOQ Stand For?
MOQ, or Minimum Order Quantity, specifies the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for B2B buyers to understand, as it can affect inventory management and overall costs. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their purchases effectively.
How Is an RFQ Used?
RFQ stands for Request for Quotation. It is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. An RFQ is a critical tool for B2B buyers to gather competitive offers and assess supplier capabilities.
What Are Incoterms?
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are a set of predefined rules published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping responsibilities, risk, and costs associated with their orders.
What Does Lead Time Mean in Manufacturing?
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to effectively plan their supply chains and ensure timely product availability.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, enhance procurement strategies, and foster stronger relationships with suppliers in the machined products industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machined products co Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Machined Products Sector?
The machined products sector is currently experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. Increased demand for precision components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and energy is a primary driver. Emerging markets in Africa and South America, particularly Brazil, are seeing a rise in infrastructure and manufacturing investments, creating opportunities for international B2B buyers. Additionally, the Middle East, with its focus on diversifying economies, is investing heavily in technology and manufacturing capabilities, further driving demand for high-quality machined products.
Technology is revolutionizing the sourcing landscape in this sector. The adoption of Industry 4.0, including advanced manufacturing technologies like CNC machining, additive manufacturing, and robotic automation, allows suppliers to produce complex parts with greater efficiency and accuracy. This trend is particularly relevant for B2B buyers seeking reliable partners that can handle both prototyping and large-scale production runs. Furthermore, digital platforms for sourcing and procurement are streamlining the purchasing process, enabling buyers to compare suppliers globally, thereby enhancing competitive pricing and reducing lead times.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting B2B Buying Decisions in the Machined Products Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in B2B procurement strategies, especially as companies face increasing pressure to minimize their environmental impact. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as reducing waste, optimizing energy use, and implementing recycling programs. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent regarding environmental compliance.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers seeking to ensure that their supply chains are free from unethical practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to ethical labor standards are becoming essential criteria for supplier selection. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials—such as recycled metals or bio-based composites—is gaining traction. By partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, international buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Context of Machined Products Companies That Influences Today’s Market?
The machined products sector has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from traditional machining methods to advanced technologies that dominate today’s landscape. Companies like Machined Products Co., which has been operational for over 75 years, exemplify this evolution. Initially focused on simple machining tasks, these firms have integrated sophisticated manufacturing techniques, such as CNC machining and automated systems, into their operations.
This historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it reflects the depth of experience and adaptability that established firms bring to the table. As these companies continue to innovate and refine their processes, they are better equipped to meet the diverse and complex needs of modern industries. Understanding this legacy can inform buyers’ decisions, guiding them toward suppliers with a proven track record of quality and reliability in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machined products co
-
How do I ensure quality when sourcing machined products internationally?
To guarantee quality in international sourcing, prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications like ISO 9001:2015. Request detailed quality assurance procedures and documentation, including test reports and inspection records. Establish clear communication channels to discuss specifications and expectations. Conduct a factory audit if feasible, or consider third-party inspection services to assess manufacturing processes and quality controls. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also enhance transparency and trust, ensuring that your quality standards are consistently met. -
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a machined products supplier?
When choosing a supplier for machined products, evaluate their experience in your specific industry and their technical capabilities. Review their manufacturing processes, equipment, and certifications to ensure they meet your quality standards. Assess their capacity to handle your order volume and timelines, as well as their flexibility for customization. Additionally, consider their financial stability and reputation by checking references and reviews from other clients. A supplier’s commitment to customer service and support is also crucial for a successful partnership. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machined products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as the complexity of the part, manufacturing processes, and material costs. Generally, MOQs for precision machined components can range from a few dozen to several hundred units. It’s important to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for initial orders or prototype runs, allowing you to test the product before committing to larger quantities. -
How can I customize machined products to meet my specifications?
Customizing machined products typically involves collaborating closely with your supplier’s engineering team. Begin by providing detailed drawings, specifications, and any specific requirements you have. Discuss design changes that can enhance performance or reduce costs, as suppliers often have valuable insights from their manufacturing experience. Utilizing rapid prototyping services can help you visualize and test your designs before full-scale production. Ensure that the supplier has the necessary capabilities to execute your customization requests effectively. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing machined products?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include upfront deposits, net 30, or net 60 days after delivery. Some suppliers may offer payment milestones based on project progress, especially for large orders. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using secure payment methods and contracts to protect your interests. Building a trustworthy relationship with your supplier can also lead to more favorable payment terms over time. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international orders of machined products?
Logistics for international orders involve several steps, including choosing a reliable shipping method, calculating shipping costs, and understanding customs regulations. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, as they may have established relationships with freight forwarders that can streamline the process. Ensure that you are aware of any import duties or taxes that may apply in your country. Tracking shipments and maintaining open communication with your supplier during transit can help mitigate potential delays. -
What should I know about the return policy for machined products?
Before placing an order, inquire about the supplier’s return and warranty policies. A reputable supplier should have a clear and fair return policy that outlines conditions for returns, such as defects or non-conformance to specifications. Understand the process for returning products and any associated costs. In case of disputes, having documented communication regarding specifications and quality expectations can aid in resolving issues effectively. It’s beneficial to establish a good rapport with your supplier to facilitate smooth resolutions. -
What industries typically require machined products and what applications do they serve?
Machined products are essential across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, energy, and military sectors. In automotive, they are used for precision components like engine parts and transmission systems. Aerospace applications include critical components for aircraft and satellites. In the medical field, machined products are vital for surgical instruments and implants. Understanding the specific applications within your industry can help you communicate your needs more effectively to suppliers and ensure you receive suitable products for your requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Machined Products Co Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Machined Products – High-Volume Production Machining
Domain: machinedproducts.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Machined Products – High-Volume Production Machining, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Machined Products Co. – Contract Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Machined Products Co. – Contract Manufacturing Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Maine Machine Products Company – Key Product
Domain: precinmac.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: MMPCO (Maine Machine Products Company) is located in South Paris, Maine, and is one of the largest CNC facilities in the Northeastern United States. Key product details include:
– Facility Size: 65,000 square feet
– Equipment: Over 60 CNC machines, multi-axis machines, precision inspection equipment
– Cleanroom: Class 1,000 hard wall cleanroom
– Certifications: ISO 9001:2015 and AS 9100D
– Ca…
4. Machined Products Company – Machinery and Equipment Solutions
Domain: bloomberg.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: Machined Products Company manufactures machinery and equipment, providing aluminum extrusions, iron castings, steel forgings, machining operations, and swaging bending services. Machined Products serves customers in the United States.
5. Meaden Precision Machined Products – High Quality Components
Domain: theorg.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Meaden Precision Machined Products Co. manufactures high quality precision machined metal and plastic components. They produce both simple and complex components for various industries including Agriculture, Medical, Gas, Hydraulic, Food Processing, Beverage, Firearm, Automotive, Packaging, and Plumbing.
6. GMP Tools – Continuous Duct Rodders
Domain: gmptools.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: GMP Tools offers a range of products including: 1. Continuous Duct Rodders: Available in 1/4, 3/8, and 1/2 inch sizes, featuring length markings every 2 feet and large airless tires for stability. Options include standard core or detectable copper core. 2. eRodder Electric Duct Rod Pusher: Powered by DEWALT FLEXVOLT® battery technology, it provides 180 lbs of force at 125 feet per minute, with var…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machined products co
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain for Machined Products?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing plays a critical role in optimizing the supply chain for machined products. By partnering with experienced manufacturers like Machined Products Co, buyers can leverage over 75 years of industry expertise and rigorous quality standards, such as ISO 9001:2015 certification. This not only ensures high-quality outputs but also fosters long-term relationships that can lead to cost savings and improved efficiency.
International B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should focus on the value of collaboration with reliable suppliers. The ability to access advanced manufacturing technologies, such as robotic automation and rapid prototyping, allows for tailored solutions that meet specific project needs while maintaining competitive lead times.
As the global market continues to evolve, now is the time to act. By embracing strategic sourcing with trusted partners, businesses can position themselves for success and innovation. Explore the opportunities available with Machined Products Co and secure a competitive edge in your industry today. Reach out for a quote and begin your journey towards enhanced operational excellence.