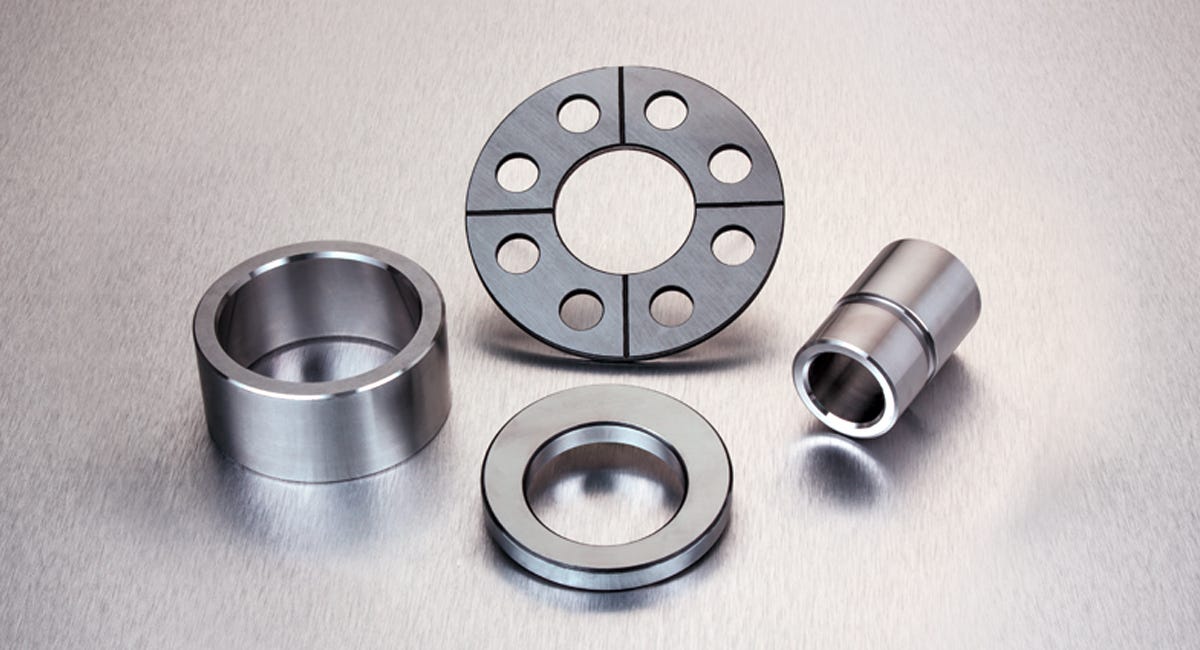
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machined metal parts
In today’s fast-paced global economy, sourcing high-quality machined metal parts can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The need for precision, reliability, and cost-effectiveness has never been greater, as companies strive to meet the demands of their industries while maintaining competitive advantages. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the various types of machined metal parts, their applications across different sectors, and essential strategies for supplier vetting.
From automotive components to aerospace fittings, understanding the nuances of the machined parts market is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. We delve into the complexities of materials, manufacturing processes, and the latest technological advancements in CNC machining. Additionally, we provide insights into cost factors, helping buyers assess pricing structures and negotiate effectively.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers you to navigate the global market for machined metal parts with confidence. Whether you are in Brazil, Nigeria, or any other region, you will be better positioned to identify reliable suppliers and make strategic investments that enhance your operational efficiency and product quality.
Understanding machined metal parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machined Parts | High precision, automated production using CNC technology | Aerospace, automotive, electronics | Pros: High accuracy, repeatability; Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
| Swiss-style Machined Parts | Capable of machining small, complex components with tight tolerances | Medical devices, electronics | Pros: Excellent for intricate designs; Cons: Limited to smaller parts. |
| Refractory Metal Parts | Made from metals resistant to high temperatures and corrosion | Aerospace, high-performance applications | Pros: Durable under extreme conditions; Cons: Higher material costs. |
| Hydraulic & Pneumatic Parts | Designed for fluid power systems, often requiring precise dimensions | Industrial machinery, automotive | Pros: Essential for system functionality; Cons: May require custom designs. |
| Custom Machined Components | Tailored designs to meet specific client requirements | Various industries, including manufacturing | Pros: Fully customizable; Cons: Longer lead times for production. |
What are CNC Machined Parts and Their Key Characteristics?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machined parts are produced through automated processes that ensure high precision and repeatability. These parts are widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where exact specifications are critical. Buyers should consider the initial setup costs and the complexity of the part design, as these factors can influence overall production costs. The ability to produce large volumes without sacrificing quality makes CNC machining a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
How Do Swiss-style Machined Parts Stand Out?
Swiss-style machined parts are characterized by their ability to produce small, complex components with tight tolerances, often using a sliding headstock to enhance precision. Commonly found in the medical device and electronics sectors, these parts are ideal for intricate designs that require meticulous attention to detail. Buyers should weigh the benefits of high precision against the limitations in size, as this method is typically suited for smaller components.
What Are Refractory Metal Parts and Their Applications?
Refractory metal parts are crafted from materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. These components are essential in aerospace and high-performance applications, where durability and reliability are paramount. While they offer significant advantages in terms of longevity, buyers must be prepared for higher material costs, which can impact project budgets.
What Are Hydraulic and Pneumatic Parts Used For?
Hydraulic and pneumatic machined parts are specifically designed for fluid power systems, requiring precise dimensions to ensure optimal performance. These components find applications in industrial machinery and automotive systems. Buyers should consider the necessity of custom designs to meet specific system requirements, which can add complexity to the purchasing process.
Why Choose Custom Machined Components?
Custom machined components are tailored to meet unique client specifications, allowing for flexibility across various industries, including manufacturing. While they offer the advantage of being specifically designed for particular applications, buyers should be aware of potential longer lead times associated with the production of customized parts. This trade-off can be worthwhile for projects that require specialized solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of machined metal parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machined metal parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components for aircraft engines | Enhanced performance and safety in flight operations | Certification standards (e.g., AS9100), material traceability, and lead times. |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission components | Improved efficiency and durability of vehicles | Compliance with automotive standards (e.g., IATF 16949), cost-effectiveness, and scalability. |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implantable devices | Critical for patient safety and operational reliability | Regulatory compliance (e.g., ISO 13485), biocompatibility, and precision tolerances. |
| Oil & Gas | Valve and pump components for extraction processes | Increased reliability in harsh environments | Material selection for corrosion resistance, durability, and supply chain logistics. |
| Electronics | Custom connectors and housing for electronic devices | Optimized performance and compact designs | Rapid prototyping capabilities, precision machining, and international shipping considerations. |
How Are Machined Metal Parts Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, machined metal parts are critical for manufacturing precision components such as turbine blades, fuel systems, and landing gear assemblies. These parts must meet stringent safety and performance standards to ensure the aircraft’s reliability and efficiency. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with aerospace certifications like AS9100, ensuring high-quality materials and processes. Additionally, they should consider lead times and the ability to provide detailed material traceability.
What Role Do Machined Parts Play in the Automotive Sector?
The automotive sector relies heavily on machined metal parts for components such as engine blocks, transmission gears, and suspension systems. These parts enhance vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing from manufacturers that adhere to IATF 16949 standards is essential. This ensures that the components not only meet quality requirements but also align with industry practices for cost-effectiveness and scalability, crucial for both OEMs and aftermarket suppliers.
Why Are Machined Metal Parts Essential for Medical Devices?
In the medical device industry, machined metal parts are utilized for creating surgical instruments, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment. The precision and quality of these components are vital for ensuring patient safety and the functionality of medical devices. Buyers, especially from Africa and South America, must focus on suppliers who comply with ISO 13485 regulations and can guarantee biocompatibility and tight tolerances. This ensures that the products meet both regulatory requirements and the high standards demanded by healthcare professionals.
How Do Machined Metal Parts Benefit the Oil & Gas Industry?
Machined metal parts are integral to the oil and gas industry, particularly in the production of valves, pumps, and drilling equipment. These components must withstand extreme conditions and corrosive environments, making material selection crucial. Buyers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil should seek suppliers that can provide materials specifically designed for durability and corrosion resistance. Additionally, understanding supply chain logistics is important to ensure timely delivery, especially in remote locations where operations are often based.
What Applications Exist for Machined Parts in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, machined metal parts are used to create custom connectors, housings, and heat sinks for various devices. These components are essential for optimizing performance and ensuring compact designs in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and industrial applications. International buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer rapid prototyping services, as this can significantly reduce time-to-market. Additionally, precision machining capabilities and considerations for international shipping logistics are critical to ensure that components meet design specifications and are delivered on schedule.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machined metal parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance Challenges in Machined Metal Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties in ensuring that the machined metal parts they source meet stringent quality standards. This challenge is amplified when dealing with international suppliers, where differences in manufacturing processes and quality control protocols can lead to inconsistencies. Buyers may receive parts that do not meet their specifications, resulting in costly delays, rework, and potential damage to their reputation. This scenario is particularly pressing for industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is critical.
The Solution: To mitigate quality assurance challenges, buyers should establish clear specifications and quality requirements upfront. This includes detailed drawings, tolerance levels, and material certifications. It’s essential to engage with suppliers who are certified to international standards such as ISO 9001 or AS9100. Implementing a robust supplier evaluation process can also help—consider conducting audits or requesting samples before placing large orders. Additionally, buyers can utilize online platforms that connect them with a network of vetted suppliers, allowing for quick comparisons of capabilities and quality assurances. Regular communication and feedback loops with the supplier can further enhance quality control, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Lead Time Issues for Urgent Projects
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter lead time challenges when sourcing machined metal parts, especially for urgent projects. Lengthy production times can hinder project timelines, leading to missed deadlines and lost business opportunities. This is particularly problematic for sectors that require rapid prototyping or quick-turn production runs, such as medical devices and consumer electronics, where market demands can shift rapidly.
The Solution: To tackle lead time issues, buyers should adopt a proactive approach to sourcing. Start by identifying suppliers who specialize in rapid prototyping and quick-turn production. These suppliers often have the infrastructure and capabilities to expedite orders. Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory strategy can also be beneficial; this approach allows for smaller, more frequent orders that align with production schedules, reducing the need for large stockpiles of inventory. Additionally, leveraging custom online CNC machining services can provide instant quotes and faster turnaround times. Buyers should communicate their timelines clearly and explore options for premium shipping or expedited manufacturing processes to ensure timely delivery of parts.
Scenario 3: Managing Material Selection and Compatibility Issues
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of selecting the right materials for machined metal parts. With various options available, including stainless steel, titanium, and brass, it can be overwhelming to choose the appropriate material that balances strength, weight, and cost. This decision is critical, as using the wrong material can lead to component failure, increased costs, and performance issues, especially in demanding applications like aerospace and defense.
The Solution: To effectively manage material selection, buyers should conduct thorough research on the properties of different metals and how they relate to their specific application requirements. Engaging with knowledgeable suppliers who can provide insights into material performance, machining capabilities, and cost implications is crucial. Utilizing material selection guides and tools can also streamline the process. Additionally, considering prototyping with alternative materials can help assess performance without committing to large orders. Collaboration with engineers or materials scientists during the selection process can provide an added layer of expertise, ensuring that the chosen materials meet both functional and regulatory requirements. Regularly reviewing and updating material specifications based on industry advancements can also keep buyers ahead in their sourcing strategies.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machined metal parts
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Machined Metal Parts?
When selecting materials for machined metal parts, it’s essential to consider their properties and how they align with the intended application. Below, we analyze four commonly used materials: Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Brass, and Titanium.
Stainless Steel: A Versatile Choice for High-Performance Applications
Stainless steel is favored for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications, including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. The most common grades include 304 and 316, with 316 offering superior resistance to saltwater and chemicals.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable, resistant to rust and staining, and can be easily machined. Its strength-to-weight ratio is favorable, and it is widely available, which aids in cost-effectiveness.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to other metals, and it can be challenging to machine due to its toughness, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for components exposed to harsh environments, such as valves and fittings in chemical processing. Its compatibility with various media, including water and oils, enhances its applicability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A240 or DIN 1.4401 is crucial. Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers can meet local regulations regarding corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Aluminum is known for its lightweight and excellent machinability. It is often used in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where weight reduction is critical. Aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, are commonly machined for their mechanical properties.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive, easy to machine, and offers good corrosion resistance. It is also lightweight, which is advantageous for applications requiring reduced weight.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is not as durable as stainless steel or titanium. It can also be prone to deformation under high stress or temperature conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum parts are suitable for applications where weight savings are essential, such as in aircraft components or automotive frames. Its compatibility with various coatings can enhance its performance in specific environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B221 or EN AW-6060. Buyers should also consider the availability of aluminum alloys in their region, as some may be more readily accessible than others.
Brass: The Choice for Electrical and Plumbing Applications
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is known for its excellent machinability and electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in plumbing fittings, electrical connectors, and decorative applications.
Pros: Brass is easy to machine and offers good corrosion resistance, particularly in water applications. Its aesthetic appeal makes it suitable for decorative components.
Cons: Brass is less durable than stainless steel and can be more expensive than aluminum. It is also susceptible to dezincification in certain environments, which can compromise its integrity.
Impact on Application: Brass is ideal for applications involving electrical components due to its conductivity. It is also used in plumbing where corrosion resistance is necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B36 or EN 12164 is important. Buyers should also be aware of local preferences for brass alloys, as some regions may have specific requirements.
Titanium: High Strength for Specialized Applications
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-performance applications in aerospace and medical industries.
Pros: Titanium is incredibly strong and lightweight, with excellent resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. It is biocompatible, making it ideal for medical implants.
Cons: The primary drawback of titanium is its high cost and complexity in machining. Specialized tools and techniques are often required, which can increase production times.
Impact on Application: Titanium is ideal for components that must withstand extreme conditions, such as aircraft parts and surgical instruments. Its compatibility with various media, including seawater, enhances its applicability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM F136 or ISO 5832-2 is essential. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide the necessary certifications for aerospace or medical applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Machined Metal Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for machined metal parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Automotive, Aerospace, Medical Devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive frames, Aircraft components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under stress | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings, Electrical connectors | Good machinability and corrosion resistance | Susceptible to dezincification | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace parts, Medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex machining | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machined metal parts
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Machined Metal Parts?
The manufacturing of machined metal parts involves several critical stages that ensure precision, quality, and efficiency. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Machining?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of raw materials. Typically, metals such as steel, stainless steel, brass, and titanium are selected based on the specific requirements of the part being produced. This stage involves cutting the raw material into manageable sizes, ensuring that it meets the required specifications. The choice of material directly impacts the strength, durability, and machinability of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Machined Metal Parts?
Once the material is prepared, the forming process begins. The most common techniques used in this stage include:
-
CNC Turning: This process involves rotating the material against a cutting tool to create cylindrical shapes. It is particularly effective for producing parts with symmetry and precise dimensions.
-
CNC Milling: Utilizing a rotating cutting tool, CNC milling machines remove material from the workpiece to create complex shapes and features. It allows for high precision and versatility in design.
-
Drilling and Threading: These techniques are essential for creating holes and internal threads, which are critical for assembly and functionality.
The use of advanced CNC machines ensures that these processes are executed with high accuracy, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Machined Metal Parts?
Finishing is a crucial step that enhances the aesthetic and functional properties of machined parts. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Grinding: This process smooths the surface of the part, reducing roughness and improving tolerance levels.
-
Polishing: Often used for aesthetic purposes, polishing enhances the visual appeal of the metal surface and provides corrosion resistance.
-
Coating: Various coatings can be applied to protect against wear, corrosion, and other environmental factors.
These finishing techniques not only improve the appearance of the parts but also extend their lifespan and functionality.
How Is Quality Assurance Maintained Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of machined metal parts. It involves several international and industry-specific standards that help ensure the reliability and safety of the components produced.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant quality standards is essential. Key certifications include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across industries. It ensures that the manufacturing processes meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently.
-
ISO 13485: Specifically for medical devices, this standard ensures that manufacturers meet stringent quality requirements.
-
API (American Petroleum Institute) Standards: These are crucial for components used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring safety and reliability.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established to monitor and verify the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the work being produced. This includes dimensional checks and visual inspections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the parts are completed, they undergo a final inspection to verify that they meet all specifications and standards before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Machined Metal Parts?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality and performance of machined parts. Common testing methods include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: This checks whether the finished part meets specified dimensions and tolerances using tools such as calipers and coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection are used to detect internal defects without damaging the part.
-
Material Testing: Hardness tests and tensile tests assess the mechanical properties of the metal to ensure it meets the required specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality assurance practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are some strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their quality control processes and adherence to standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from inspections and tests performed.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
What Are the Quality Assurance Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality assurance:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with local regulations and international standards.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the business culture and practices in different regions can impact communication and the execution of quality assurance processes.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who offer transparency in their supply chain processes, allowing for better tracking of materials and quality assurance measures.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing machined metal parts, ensuring they meet their specific requirements for quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machined metal parts’
To assist international B2B buyers in procuring machined metal parts effectively, this checklist provides a structured approach to ensure quality, reliability, and efficiency in the sourcing process. The steps outlined below will guide you through critical considerations, helping you make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications is vital for ensuring the machined parts meet your operational needs. Detail dimensions, tolerances, material types, and surface finishes required for your project. Clear specifications minimize the risk of errors and miscommunication with suppliers.
- Considerations:
- Tolerances: Ensure they align with your application requirements.
- Material Selection: Choose materials that offer the necessary strength and durability for your use case.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a solid reputation in the industry. Look for manufacturers that specialize in the specific types of machined parts you need. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather information.
- Key Aspects to Investigate:
- Supplier History: Experience in producing similar parts.
- Industry Certifications: ISO, AS9100, or other relevant standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before finalizing a supplier, assess their machining capabilities to ensure they can meet your specifications. Inquire about their equipment, technology (such as CNC machines), and the range of materials they can work with.
- What to Look For:
- Technology: Advanced capabilities like 4-axis CNC or EDM.
- Production Capacity: Ability to handle both small batches and large-scale orders.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Prices
Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures and terms. A detailed quote should outline costs, lead times, and any additional fees, such as shipping or tooling charges.
- Comparison Criteria:
- Total Cost: Analyze the complete pricing model, not just the unit cost.
- Value-added Services: Look for services like prototyping or design assistance.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your selected suppliers possess the necessary certifications and adhere to quality management standards. This step is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring product quality.
- Important Certifications:
- ISO 9001: Ensures quality management processes.
- Industry-specific certifications: For sectors like aerospace or medical devices.
Step 6: Conduct Quality Assurance Checks
Implement quality assurance measures by requesting samples or prototypes before committing to large orders. Testing samples helps verify that the parts meet your specifications and quality standards.
- Testing Considerations:
- Tolerance Checks: Ensure parts meet specified tolerances.
- Material Testing: Validate the integrity and performance of materials used.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Maintain open lines of communication with your supplier throughout the production process. Regular updates on production status, potential delays, and changes in specifications can help mitigate risks.
- Best Practices:
- Schedule regular check-ins.
- Use project management tools for real-time updates and documentation.
Following this checklist will empower you to make informed decisions when sourcing machined metal parts, ensuring that you select a reliable partner who can meet your business needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machined metal parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machined Metal Parts Sourcing?
In sourcing machined metal parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials like steel, stainless steel, brass, and titanium have varying costs based on market availability, quality, and specific material properties. For instance, titanium parts tend to be more expensive due to their strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the machining process. Labor costs can vary based on geographic location, skill level, and the complexity of the parts being manufactured. Countries with higher labor costs may affect the overall pricing structure, making it essential for buyers to consider sourcing from regions with competitive labor markets.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Modern CNC machines can have high initial investments, but they typically offer efficiency and precision that justify the overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are incurred for the creation of custom tools and fixtures necessary for specific machining operations. These costs can be amortized over larger production runs, making them less impactful per unit in high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that machined parts meet specified tolerances and quality standards requires investment in QC processes. This may involve inspection equipment, testing procedures, and certifications, all of which contribute to the final price.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, customs duties, and handling fees must be factored into the overall pricing, especially for international transactions. Effective logistics management can reduce costs and improve delivery times.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that reflects their operational costs, market conditions, and the value they provide. Understanding this margin can help buyers gauge the competitiveness of supplier pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machined Metal Parts Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of machined metal parts:
-
Volume/MOQ: Manufacturers often provide better pricing for larger orders due to economies of scale. Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can also dictate pricing; negotiating lower MOQs can be beneficial for smaller buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts with specific tolerances or complex geometries usually command higher prices. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material not only affects the base cost but also influences machining time and complexity, thereby impacting labor and tooling costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts requiring specific certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100) may incur additional costs due to the stringent QC processes involved. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications based on end-use applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with advanced technology may offer higher quality but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly affect the final cost. Buyers should be clear on responsibilities regarding shipping costs, insurance, and duties.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
Buyers looking to optimize their sourcing costs should consider the following strategies:
-
Engage in Volume Negotiations: If feasible, consolidating orders or collaborating with other buyers can help achieve better pricing through increased volume.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider long-term costs associated with maintenance, quality, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial price might be justified by lower long-term operational costs.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ask suppliers for itemized quotes that break down costs. This transparency can help identify areas for negotiation or cost savings.
-
Leverage International Pricing Nuances: When sourcing from different regions, be aware of local pricing trends and currency fluctuations. Understanding regional market dynamics can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms over time. Trust and reliability can often result in suppliers being more flexible with pricing.
Conclusion: Navigating Pricing Complexity in International B2B Sourcing
Sourcing machined metal parts involves navigating a complex landscape of costs and pricing influencers. By understanding the key components, leveraging negotiation strategies, and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can make informed decisions that enhance their sourcing efficiency and effectiveness. Always remember that pricing can vary significantly based on market conditions and supplier capabilities, so staying informed is essential for successful procurement.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machined metal parts With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Machined Metal Parts for B2B Buyers
In the manufacturing landscape, selecting the appropriate components for production is critical for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. While machined metal parts offer a high degree of precision and reliability, various alternative solutions may suit specific project requirements. This analysis compares machined metal parts against additive manufacturing (3D printing) and stamped metal parts, providing insights into their respective advantages and limitations.
| Comparison Aspect | Machined Metal Parts | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Stamped Metal Parts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, excellent mechanical properties | Varies; suitable for complex designs | High volume production, consistent quality |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; cost-effective for low volumes | Lower upfront costs; variable for large runs | Economical for high volume, less so for low |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and specialized equipment | User-friendly for design iterations | Requires tooling and setup, less flexible |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable parts | Minimal maintenance on 3D printers | Tooling maintenance can be high |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, and medical devices | Prototyping, custom components | Mass production of simple shapes |
Analyzing Additive Manufacturing as an Alternative
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has gained traction in various industries due to its ability to produce complex geometries and reduce material waste. One significant advantage is its flexibility in design; components can be modified quickly, facilitating rapid prototyping. However, while 3D printing offers lower initial costs for small batches, it may fall short in terms of material strength and finish quality compared to machined parts. This makes it less suitable for high-stress applications, particularly in sectors like aerospace and medical, where reliability is paramount.
Evaluating Stamped Metal Parts for High-Volume Production
Stamped metal parts are created by pressing metal sheets into specific shapes using dies. This method is highly efficient for mass production, as it allows for quick and consistent output at a lower cost per unit compared to machining. Stamping is ideal for high-volume runs of simpler shapes, such as brackets or housings. However, the need for custom tooling can lead to significant upfront costs and longer lead times, making it less advantageous for lower production volumes or highly complex designs that require the precision offered by machining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When evaluating which solution to adopt, B2B buyers should consider their specific project requirements, including production volume, complexity, and material properties. Machined metal parts excel in precision and durability, making them suitable for critical applications. In contrast, if flexibility and speed in prototyping are vital, additive manufacturing may be the way to go. For projects focused on cost-effectiveness and volume, stamped metal parts could offer a practical solution. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational goals and budget constraints of the business, ensuring that the chosen method effectively meets production needs while maintaining quality standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machined metal parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machined Metal Parts?
Understanding the technical properties of machined metal parts is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right components for their applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of the metal used in the part’s production. Common grades include stainless steel (like 316L), brass, aluminum, and titanium. Each material has unique properties such as corrosion resistance, strength, and machinability. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring the part meets performance requirements and can withstand environmental factors in its intended application.
Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from a specified dimension of a machined part. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.0005 inches signifies that the actual measurement can vary by that amount from the intended size. Tight tolerances are essential in industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where precision is critical. Understanding tolerances helps buyers ensure that parts will fit and function as intended in their assemblies.
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a part’s surface after machining. Common finishes include polished, anodized, and sandblasted. The surface finish can impact the part’s performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal. For example, a smoother finish may be required for parts that interact with other components to reduce friction. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to avoid operational issues.
Hardness
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation or scratching. It is typically evaluated using scales such as Rockwell or Brinell. Different applications require varying hardness levels; for example, components in high-wear environments may need materials with higher hardness. Understanding hardness helps buyers select parts that will endure specific operational stresses without failure.
Machining Process
The machining process defines how material is removed to create the final part. Common processes include CNC turning, milling, and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining). Each method has advantages depending on the part’s design and material. For instance, CNC milling is suitable for complex shapes, while turning is ideal for cylindrical parts. Buyers should be familiar with these processes to ensure the chosen method aligns with their production needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Machined Metal Parts Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms used in the machined metal parts sector:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers as it often indicates the quality and reliability of the parts they procure. Buyers should consider sourcing from reputable OEMs to ensure they receive high-quality components.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers, especially when budgeting for production. Buyers should assess their needs against the MOQ to avoid excess inventory or supply shortages.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used by buyers to solicit pricing and terms from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. Providing a detailed RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes and better negotiations, helping buyers secure favorable terms.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, risk, and costs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in international transactions, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from the placement of an order to its delivery. Understanding lead times is crucial for production planning and inventory management. Buyers should communicate their timelines clearly to ensure suppliers can meet their delivery expectations.
Conclusion
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring machined metal parts. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right components but also fosters effective communication with suppliers, ultimately leading to successful procurement strategies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machined metal parts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Machined Metal Parts?
The machined metal parts sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand across various industries, and the globalization of supply chains. Key trends include the rise of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, which offers enhanced precision and efficiency, allowing manufacturers to meet stringent quality standards. The proliferation of automation and robotics in machining processes is also noteworthy, as these technologies reduce labor costs and improve production speed, making them attractive to international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Emerging B2B tech trends are reshaping sourcing strategies. For instance, online platforms that connect buyers with a network of vetted suppliers enable quick and efficient sourcing of custom machined parts. This digital transformation facilitates rapid prototyping and shortens lead times, providing businesses with the agility needed to respond to market demands. Furthermore, the increasing importance of data analytics allows manufacturers to optimize production processes and predict trends, which is crucial for buyers looking to maintain a competitive edge.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and trade policies, which can affect sourcing and supply chain logistics. B2B buyers must navigate these complexities while considering local market conditions and regulations. The ability to source locally while ensuring quality and cost-effectiveness will be paramount as international buyers seek reliable partnerships.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Machined Metal Parts Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of machined metal parts. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, has led to a demand for ‘green’ practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that implement sustainable production methods and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies face pressure to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitative labor practices and environmentally harmful materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade standards are gaining traction. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also ensure compliance with international regulations, making them essential for B2B buyers in regions like Europe, where sustainability standards are stringent.
Moreover, the use of recycled materials in the production of machined metal parts is on the rise, aligning with the global push towards circular economy principles. By sourcing from suppliers that utilize recycled metals, buyers can contribute to resource conservation while potentially reducing costs. This growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing is reshaping supplier selection criteria for international buyers, influencing their purchasing decisions significantly.
How Has the Machined Metal Parts Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the machined metal parts sector can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution when manual machining techniques were the norm. The introduction of machine tools dramatically improved precision and efficiency, paving the way for mass production. The advent of CNC technology in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, enabling manufacturers to produce complex components with high accuracy and repeatability.
Today, the sector is characterized by a blend of traditional machining techniques and advanced technologies, such as additive manufacturing and automation. This evolution has not only increased production capabilities but has also expanded the applications of machined metal parts across various industries, from aerospace to automotive. As the sector continues to innovate, B2B buyers must stay informed about these developments to leverage opportunities for cost savings and efficiency improvements in their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machined metal parts
-
How do I ensure the quality of machined metal parts from suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by requesting certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Ask for samples to evaluate craftsmanship and tolerances. Establish clear specifications and tolerances in your order, and consider conducting factory audits if feasible. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including inspections and testing methods, to gain confidence in their ability to meet your standards. -
What factors should I consider when choosing a supplier for machined metal parts?
Consider the supplier’s experience and specialization in your required parts. Review their production capabilities, technology (such as CNC machines), and certifications. Geographic location can affect lead times and shipping costs, so evaluate proximity to your operations. Finally, assess their customer service, responsiveness, and ability to provide references from other clients to ensure a reliable partnership. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machined metal parts?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the parts. Typically, for custom machined parts, MOQs may range from a few dozen to several hundred units. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness in production. Always clarify MOQs upfront and explore whether they can accommodate smaller orders, especially for prototypes or initial runs. -
What are the payment terms I should expect when sourcing from international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include upfront deposits (usually 30-50%), with the balance due upon completion or prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment through escrow services for added security. Ensure you understand the terms and any potential currency exchange implications, especially when dealing with international transactions. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping for my orders of machined metal parts?
Effective logistics management starts with discussing shipping options with your supplier. Explore whether they handle shipping or if you need to arrange it. Consider the shipping method (air vs. sea), which impacts cost and delivery time. Understand customs regulations and duties in your country to avoid delays. Collaborate with a freight forwarder experienced in international trade to streamline the process. -
What customization options are available for machined metal parts?
Customization options typically include material selection, dimensions, tolerances, surface finishes, and specific design features. Many suppliers can work with you to create prototypes before full production. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly and provide detailed CAD drawings or specifications to ensure the final product meets your expectations. -
What industries commonly use machined metal parts, and how can I find suppliers specializing in my industry?
Machined metal parts are utilized across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. To find specialized suppliers, consider industry trade shows, online directories, and professional networks. Engage with industry associations, as they often provide resources and recommendations. Look for suppliers with experience in your specific application for better alignment with your needs. -
How do international trade regulations affect sourcing machined metal parts?
International trade regulations can significantly impact sourcing, including tariffs, import/export restrictions, and compliance with local standards. Ensure you understand the regulations in both your country and the supplier’s country. It’s advisable to work with legal or trade experts to navigate these complexities. Staying informed about trade agreements can also help in reducing costs and ensuring smoother transactions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Machined Metal Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sabner – High-Quality Machined Parts
Domain: sabner.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Machined Parts – Highest Quality, 5 Times Faster Machining. Serial production of small machined parts for demanding customers. Machined metal parts produced by removing material from a full block using CNC machining (turning, milling, drilling, threading). Applications in various industries: Pneumatic parts, Hydraulic parts, Automotive parts, Aerospace parts. Materials: Steel, Stainless steel, Bra…
2. Hubs – CNC Metal Machining Services
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: CNC metal machining services for custom metal parts. Ideal for prototypes and end-use custom parts. Materials include Aluminum, Stainless steel, Mild steel, Brass, Copper, Alloy steel, Tool steel, Titanium, Inconel, and Invar 36. Features high machinability, tensile strength, corrosion resistance, low friction, excellent conductivity, and more. Services include CNC milling and CNC turning with fas…
3. eMachineShop – Custom Steel Parts Fabrication
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom steel parts fabrication with over 15 years of experience. Design and order parts using free CAD software or upload your own CAD file. Features include: FREE Shipping in the USA, No Minimum Order Quantity, 100% Quality Guaranteed. Steel is a popular alloy primarily made of iron and carbon, known for its thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, ductility, and malleability. Machining option…
4. Modern Group – CNC Machining Materials
Domain: moderngroupusa.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: At Modern Group, we work with a wide variety of raw CNC machining materials to suit all your machining needs. Our experience includes machining a wide range of materials from basic carbon steels to superalloys. These materials come in different forms, ranging from bar stock to complex investment castings. Key materials include:
– Aluminum (6000 Series, 7000 Series, etc.)
– Carbon Steels (1020, 1…
5. Forster Tool – Custom CNC Machined Steel Parts
Domain: forstertool.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Forster Tool specializes in custom machined CNC steel parts with over 60 years of machining experience. They offer a variety of steel components including screws, shafts, brackets, and mounts. The company is ISO 9001/2015 and AS9100D certified, and ITAR registered, ensuring high-quality manufacturing and data protection. They utilize advanced machining methods and equipment, including Keyence and …
6. SendCutSend – Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: SendCutSend offers custom sheet metal fabrication services including laser cutting, CNC routing, waterjet cutting, anodizing, bending & forming, countersinking, dimple forming, hardware insertion, plating, powder coating, tapping, tumbling, and deburring. They provide instant pricing for custom parts uploaded in STEP, DXF, or EPS formats, with no minimum quantities and free US shipping on orders o…
7. Zetwerk – Machined Parts
Domain: zetwerk.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Machined parts are vital components in the manufacturing industry, essential across various sectors such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare. They are produced through machining, a subtractive manufacturing method that ensures high precision and accuracy. Key benefits of machined parts include exceptional precision and accuracy, reliability and consistency, enhanced functionality…
8. HLC – Distraction Pin
Domain: hlc-metalparts.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: {“Item Name”:”Distraction Pin”,”Material”:”SUS630 Stainless Steel”,”Surface Treatment”:”Heat treatment”,”Tolerance”:”0.001mm”,”Application”:”For medical & healthcare products”,”Purchasers”:”USA”,”Dimensions”:”Length 12mm/14mm/16mm”,”Craftsmanship”:”CNC Turning & CNC Milling”,”Price”:”2.33USD/PCS”,”Packing”:”PE Bag”,”Services”:”OEM & ODM available.”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machined metal parts
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of machined metal parts is essential for companies aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. By leveraging advanced CNC machining capabilities, businesses can achieve superior precision, rapid turnaround times, and the ability to scale production to meet fluctuating demands. Understanding the diverse applications of machined parts—from automotive to aerospace—empowers international buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific industry needs.
Investing in reliable suppliers who prioritize quality and customer service is crucial. As highlighted, the availability of materials like stainless steel and titanium, coupled with innovative machining techniques, enables suppliers to deliver high-performance components that meet rigorous standards. For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, fostering partnerships with established manufacturers can significantly streamline operations and bolster supply chain resilience.
Looking ahead, the global market for machined metal parts will continue to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for precision components. We encourage international buyers to actively explore opportunities for collaboration and innovation within this dynamic sector. Your next step could redefine your manufacturing capabilities—engage with trusted suppliers today to secure a competitive edge.