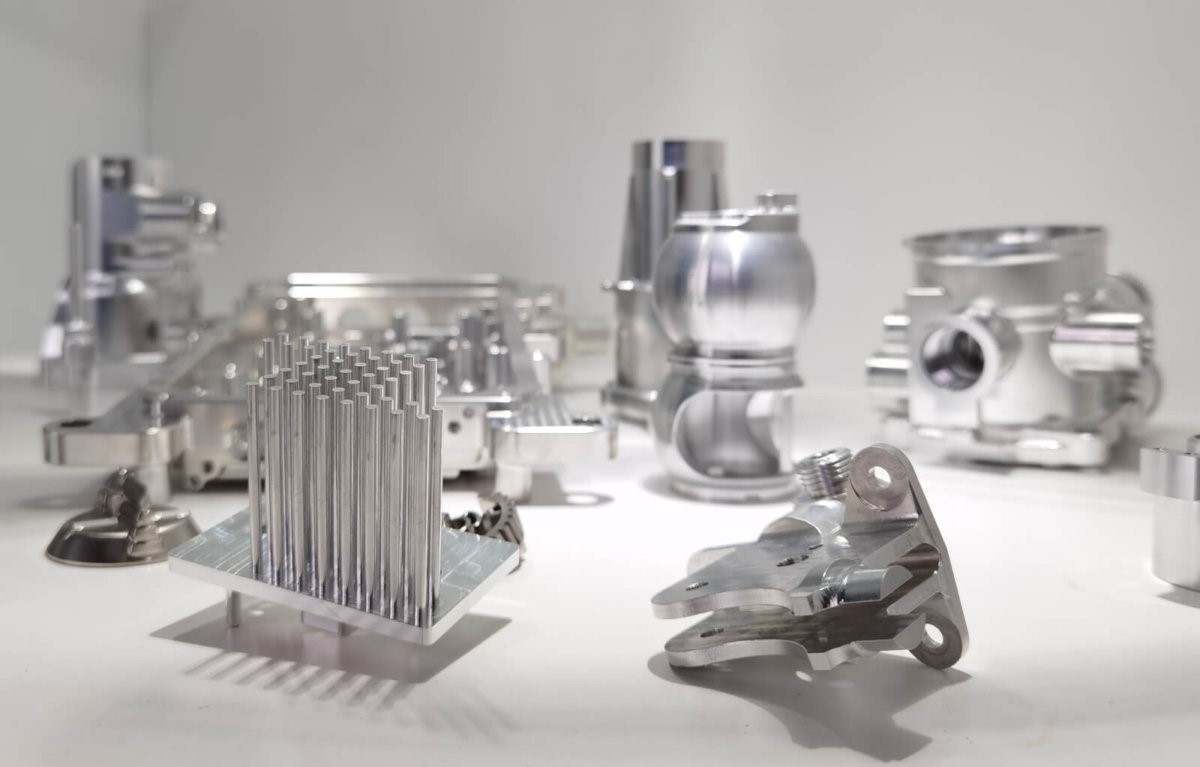
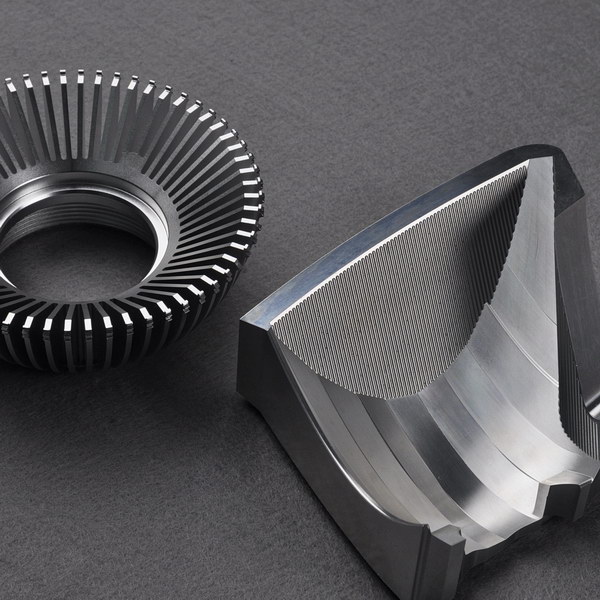
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machined aluminium
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing quality machined aluminium presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The diverse range of aluminium alloys—each with unique properties and applications—can complicate procurement decisions, especially for companies in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide aims to equip you with the essential knowledge you need to navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminium, covering various factors from alloy selection and machining processes to supplier vetting and cost considerations.
As we delve into the myriad applications of machined aluminium—from automotive components to high-tech electronics—this guide will also highlight how to assess and engage with suppliers effectively. You will learn about the critical importance of material characteristics such as machinability, strength-to-weight ratio, and corrosion resistance. Furthermore, insights into the latest advancements in anodizing and finishing techniques will help you enhance the performance and aesthetics of your machined parts.
By consolidating this information, we empower you to make informed purchasing decisions and optimize your supply chain. This guide serves as a strategic resource to help you leverage the advantages of machined aluminium, ensuring that you remain competitive in a global market driven by innovation and demand for efficiency.
Understanding machined aluminium Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6061 | Good corrosion resistance, average strength | Automotive, aerospace, industrial equipment | Pros: Excellent finish, versatile; Cons: Less strength than 7075 |
| Aluminum 7075 | High strength, low weight, often heat-treated | Aerospace, military, structural applications | Pros: Superior strength; Cons: More expensive, less corrosion resistance |
| Aluminum 2024 | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistant | Aerospace, automotive parts needing weight efficiency | Pros: Great for high-stress applications; Cons: Requires anodizing for better corrosion resistance |
| Aluminum 5083 | Excellent corrosion resistance, weldable | Marine, cryogenic equipment, pressure vessels | Pros: High strength, superior in marine environments; Cons: Limited use at high temperatures |
| Aluminum 2011 | Excellent machinability, good surface finish | Precision machining, fasteners, fittings | Pros: Ideal for intricate designs, easy to machine; Cons: Less strength compared to other alloys |
What Are the Characteristics and Benefits of Aluminum 6061?
Aluminum 6061 is renowned for its good corrosion resistance and ease of machineability, making it a frequently used choice in many industries. This alloy is ideal for applications requiring excellent finish quality and moderate strength, such as in automotive and aerospace components. Buyers should note that while it provides a versatile option, its strength is lower than that of Aluminum 7075, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
How Does Aluminum 7075 Compare for Strength and Application?
Aluminum 7075 is among the strongest aluminum alloys, often selected for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios. This alloy is commonly used in aerospace and military applications where structural integrity is crucial. However, the higher cost and susceptibility to corrosion suggest that buyers ought to assess protective treatments such as anodizing before finalizing their selections.
Why is Aluminum 2024 Preferred for Aerospace Applications?
Known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, Aluminum 2024 is predominantly utilized in aerospace and automotive sectors where lightweight components are essential. It is highly corrosion-resistant, particularly when anodized, enhancing its durability in demanding environments. Buyers should keep in mind the need for additional protective measures when considering this alloy for long-term applications.
What Makes Aluminum 5083 Suitable for Marine Environments?
Aluminum 5083 boasts exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments, making it a favored choice for ships and offshore structures. This alloy maintains its strength even after welding, which is invaluable when constructing pressure vessels. However, buyers should be aware that while it excels in low-temperature conditions, its utility in high-temperature settings is limited.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum 2011 in Precision Machining?
Aluminum 2011 is highly regarded for its machinability and ability to yield superior surface finishes, ideal for precision parts and intricate designs. Common applications include fasteners and fittings where accuracy is paramount. While its excellent ease of machining is advantageous, it’s important for buyers to consider that its strength may not match other alloys, limiting its use in heavy-load scenarios.
Key Industrial Applications of machined aluminium
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machined aluminium | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Airframe and structural components | Lightweight design improving fuel efficiency | Compliance with aviation standards, supplier certifications. |
| Automotive | Engine parts, body panels, and chassis components | Enhanced strength-to-weight ratio for fuel economy | Material specifications, precision machining tolerances. |
| Industrial Equipment | Machinery frames and operational parts | Increased durability leading to lower maintenance costs | Customization options, part longevity, and machining precision. |
| Electronics | Enclosures and heat sinks for electronic devices | Improved thermal management and product aesthetics | Anodizing options, EMI shielding capabilities, dimensional accuracy. |
| Marine | Hull fittings and components for boats and ships | Resistance to corrosion and harsh marine environments | Weight considerations, compliance with maritime regulations. |
How is Machined Aluminium Utilized in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, machined aluminium is primarily used for airframe and structural components where lightweight materials are crucial. Aluminium alloys offer high strength with significantly lowered weight, directly impacting fuel efficiency and performance. For B2B buyers in this sector, understanding regulatory requirements is essential, as compliance with aviation safety standards significantly influences sourcing decisions. Additionally, suppliers must be certified to provide materials that meet rigorous quality and performance specifications mandated by aerospace authorities.
What Role Does Machined Aluminium Play in the Automotive Sector?
Machined aluminium is extensively found in the automotive industry, where it is transformed into engine parts, body panels, and chassis components. The lightweight nature of aluminium contributes to a higher strength-to-weight ratio, which improves vehicle fuel efficiency and performance. For international B2B buyers, factors such as material certifications and machining precision are critical to ensure compliance with automotive industry standards and achieve a competitive edge in manufacturing.
Why is Machined Aluminium Important for Industrial Equipment?
In the industrial equipment sector, machined aluminium is utilized for constructing machinery frames and operational parts that require high durability and performance. The strength and lightweight characteristics of aluminium alloys help mitigate wear and tear, leading to lower maintenance costs. For buyers across Africa, South America, and Europe, it is vital to consider customization capabilities and precise machining specifications when sourcing parts to meet specific operational demands.
How Does Machined Aluminium Benefit the Electronics Sector?
Machined aluminium finds a significant application in the electronics industry, where it is used for enclosures and heat sinks. The material’s excellent thermal conductivity enhances cooling efficiency, imperative for electronic devices. Buyers in this sector must focus on finishing options, such as anodizing and coatings that can provide both aesthetics and functional benefits, like electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Precision in machining ensures that enclosures fit specific device dimensions seamlessly.
In What Ways is Machined Aluminium Utilized in the Marine Industry?
In the marine sector, machined aluminium components are vital for hull fittings and other parts exposed to harsh aquatic environments. Aluminium’s inherent corrosion resistance makes it an ideal choice for marine applications, significantly prolonging the lifespan of equipment. When sourcing these materials, international buyers must consider weight specifications and compliance with maritime safety standards, ensuring that components can endure both structural loads and environmental challenges.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machined aluminium’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality in Machined Aluminium Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter issues with the inconsistent quality of machined aluminium parts from different suppliers. Variability in hardness, corrosion resistance, and finish can lead to performance issues in final products, resulting in costly recalls or project delays. When suppliers do not maintain stringent quality control measures, manufacturers face challenges meeting specifications, which can jeopardize contracts and strain client relationships.
The Solution: To mitigate quality discrepancies, B2B buyers should implement rigorous supplier evaluation criteria before committing to a manufacturing partner. This includes assessing the supplier’s quality management certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality assurance processes. Buyers should request batch certifications for material properties, machining tolerances, and finish specifications for each order. Establishing a clear communication protocol about expectations and conducting regular audits or reviews of the supplier’s operations can ensure ongoing compliance with quality standards. Additionally, integrating a robust feedback loop post-delivery allows for timely adjustments and enhances long-term collaboration with suppliers.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Aluminium Alloy
The Problem: Choosing the right aluminium alloy can be daunting for B2B buyers, especially when numerous options with varying mechanical properties, machinability, and corrosion resistance are available. Misidentifying the appropriate alloy can lead to inadequate performance in the intended application, affecting overall product longevity and reliability.
The Solution: To alleviate this pain point, buyers should start with a comprehensive understanding of their product requirements, including mechanical stresses, environmental conditions, and application specifics. Consult technical datasheets for different aluminium alloys to compare their properties—such as tensile strength, elongation, and thermal conductivity. Creating a matrix that lists the strengths and weaknesses of commonly used alloys (such as 6061, 7075, and 2024) can facilitate easier decision-making. Additionally, buyers can engage in discussions with knowledgeable suppliers or technical consultants who can provide insights tailored to their specific needs. Leveraging prototyping services that allow for testing various alloys before committing to large-scale production can also reduce the risks associated with alloy selection.
Scenario 3: Rapid Design Changes Leading to Production Delays
The Problem: The fast-paced nature of many industries often results in design modifications, which can be particularly challenging when working with machined aluminium parts. Such changes can lead to production delays, increased costs, and a continuous back-and-forth between buyers and manufacturers, ultimately threatening project timelines.
The Solution: To promote agility in handling design changes, B2B buyers should establish a collaborative relationship with their machining supplier. Encouraging open communication about design parameters and anticipated changes early in the process allows manufacturers to incorporate flexibility into production schedules. Additionally, integrating advanced technologies like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) can streamline communication. By requesting initial rapid prototypes from manufacturers, buyers can assess designs before committing to full production. It is also advantageous to negotiate contract terms that allow for some level of adaptability without incurring significant penalties for changes within defined parameters, thereby fostering a proactive rather than reactive approach to design evolution.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machined aluminium
What Are the Key Properties of Common Aluminium Alloys for Machining?
Aluminium is a versatile metal favored for numerous applications due to its excellent properties. Different alloys offer unique characteristics, making them suitable for various machining needs. Here we analyze four commonly used aluminium materials: 6061, 7075, 2024, and 5083 alloys.
How Does Aluminium 6061 Perform in Machined Parts?
Aluminium 6061 is well-known for its outstanding corrosion resistance and machinability, making it a go-to choice among manufacturers. This alloy has a good tensile strength, rated at approximately 45 ksi, and maintains its performance in multiple environments, including industrial and marine settings. The elevated corrosion resistance, especially post-anodization, allows it to meet stringent industry standards.
Pros: Excellent machinability, good corrosion resistance, and a relatively low cost make this alloy highly attractive for mass production.
Cons: While it is stronger than many other alloys, it does not reach the strength levels of options like 7075. This can be a limitation in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Practically, 6061 is ideal for structural components in construction, automotive parts, and cookware.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should check compliance with local standards (e.g., EN AW-6061) and consider the alloy’s anodizing before delivery.
Why Choose Aluminium 7075 for High-Strength Applications?
Aluminium 7075 is particularly popular in the aerospace and military industries due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Its ultimate tensile strength can reach up to 78 ksi, making it one of the strongest aluminium alloys available. It is also heat-treatable, which enhances its performance under load.
Pros: Offers high strength, low weight, and strong corrosion resistance, making it ideal for athletic equipment and aircraft construction.
Cons: It is more expensive than many other alloys and less corrosion-resistant in its untreated state, which can necessitate additional surface treatments.
Impact on Application: This alloy is suited for high-stress components, such as aircraft wings and gears.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the additional costs associated with surface treatments and ensure material quality complies with ASTM or other relevant international standards.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminium 2024 in Machined Parts?
Aluminium 2024 is known for its high strength and is mainly used in aerospace applications. It has a tensile strength rating of 68 ksi and demonstrates superior fatigue resistance, making it ideal for structural applications.
Pros: Exceptional strength and resilience, good hardening properties, and suitability for high-stress applications.
Cons: It has lower corrosion resistance than other alloys, requiring protective treatments such as anodizing to meet durability expectations.
Impact on Application: Primarily used in airframe components and military vehicles, its performance under tension must be a determining factor.
Considerations for Buyers: Ensure compliance with aerospace and military standards and take into account potential increased manufacturing complexity due to corrosion treatments.
Why Is Aluminium 5083 Favored for Marine Applications?
Aluminium 5083 is distinguished by its excellent resistance to corrosion in saltwater environments, making it a popular choice for marine applications. It has good weldability and retains strength even after welding, which is crucial for assembling marine vessels and structures.
Pros: High resistance to corrosion, strength, and versatility in harsh environments.
Cons: While it is robust, it lacks the high strength provided by other alloys such as 7075 and may be more costly.
Impact on Application: Commonly found in shipbuilding, pressure vessels, and marine architecture, 5083 excels where prolonged exposure to seawater is expected.
Considerations for Buyers: Ensure compliance with marine standards and consider additional protective coatings for marine applications.
Summary Table of Machined Aluminium Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for machined aluminium | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium 6061 | Structural components, automotive parts, cookware | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to 7075 | Low |
| Aluminium 7075 | Aircraft parts, high-stress components | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive; lower corrosion resistance | High |
| Aluminium 2024 | Aerospace airframe components, military vehicles | Exceptional strength | Lower corrosion resistance | Med |
| Aluminium 5083 | Marine applications, pressure vessels | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lacks ultra-high strength | Med |
This guide helps B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding aluminium alloy selection based on requirements and environmental considerations while ensuring compliance with relevant international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machined aluminium
When it comes to machined aluminum, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is crucial for B2B buyers looking for reliability and performance in their products. This section will break down the typical stages involved in the manufacturing of machined aluminum components, key techniques employed, and the international standards and quality control measures that should be prioritized.
What Are the Main Stages in the Machined Aluminum Manufacturing Process?
Material Preparation: Why Choosing the Right Aluminum Alloy Matters
The manufacturing journey begins with material selection, where specific aluminum alloys are chosen based on their properties and the requirements of the final product. Common alloys include 6061-T651, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and finish, and 7075-T651, celebrated for its superior strength. Once selected, the aluminum undergoes cutting or preparation processes to create manageable block sizes suitable for machining.
Forming Techniques: How Are Aluminum Parts Created?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is the predominant technique used to form aluminum parts. In this process, a computer-controlled milling machine removes material from the aluminum block to achieve the desired shape and dimensions. Key operations in CNC machining include turning, drilling, and milling.
- Turning involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material, producing cylindrical shapes.
- Milling allows for more complex components, where the machine moves the tool and workpiece on multiple axes simultaneously.
- Drilling creates holes in aluminum for fastening or assembly purposes.
These methods are favored for their precision and ability to maintain tight tolerances.
Assembly: What Role Does Assembly Play in Manufacturing?
In many cases, aluminum parts are not standalone products but components of larger assemblies. During this stage, parts are carefully assembled using various techniques, including welding, riveting, or adhesive bonding. The choice of assembly method depends on the specific applications and mechanical requirements of the final product.
What Finishing Processes Are Used on Machined Aluminum Parts?
Anodizing is one of the most common surface treatments for machined aluminum. This electrochemical process enhances corrosion resistance while offering aesthetic customization through coloration. Different types of anodizing exist, such as Type II and Type III, each providing varying degrees of hardness and durability suitable for specific applications, like aerospace and military components.
Other finishing processes may include:
- Powder Coating for superior durability and color.
- Polishing to provide a reflective and aesthetically pleasing surface.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Machined Aluminum Manufacturing?
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Machining?
Quality control in the machining of aluminum must align with international and industry-specific standards. ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard that lays the foundation for quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in product delivery. Industries may also require compliance with specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold within the EU or API certifications for materials used in the oil and gas sector.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints (IQC, IPQC, FQC)?
Quality control is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process, which can be categorized into:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials, including aluminum alloys, are inspected for compliance with specified standards and standards before proceeding to production. Ensuring the right quality at the start can prevent issues later in the process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This involves monitoring machinery, techniques, and dimensions during production. Regular inspections and measurements are conducted to confirm that the fabrication processes meet specified tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After machining and assembly, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify adherence to design specifications and quality standards. Common tests include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and performance evaluations, depending on the intended application.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance in Machined Aluminum?
B2B buyers should be familiar with various testing methods to ensure their suppliers are meeting quality expectations. These testing methods may include:
- Tensile Testing: To measure the material’s strength and ductility.
- Hardness Testing: To ensure the aluminum meets hardness specifications, often conducted using Rockwell or Brinell scales.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Assessing how materials will hold up in various environments, particularly important for industries such as marine or chemical processing.
Performing these tests provides insights into the material’s reliability and usability in specific applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence when selecting suppliers for machined aluminum. Key steps include:
-
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation that outlines their quality control processes, standards compliance (like ISO 9001), and testing results.
-
Conducting Supplier Audits: Regular audits allow buyers to assess the machinery, processes, and overall quality culture within the manufacturing facility. This can also include interviews with quality assurance personnel to understand practices and challenges.
-
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party organizations for inspections provides an unbiased evaluation of the suppliers’ quality control measures and product specifications.
What Are the Nuances of QC/Certifications for International Buyers?
International buyers need to be particularly cautious regarding certifications and standards that vary globally. Buyers from regions like Africa or South America may not have as stringent regulations as those in Europe or the Middle East. Understanding these nuances can bridge potential gaps in expectations and help establish clear standards for quality, delivery, and compliance.
By ensuring suppliers adhere to robust manufacturing processes and quality control systems, B2B buyers can mitigate risks, enhance product reliability, and sustain successful international business operations in the vibrant market of machined aluminum products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machined aluminium’
When sourcing machined aluminium parts, it is essential to follow a systematic approach to ensure that you select the right supplier and materials for your needs. This guide outlines key actions to take, providing a practical checklist for B2B buyers entering the machined aluminium market.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline the technical specifications for your machined aluminium parts. This includes dimensions, tolerances, surface finish, and specific alloy grades suitable for your application. This step ensures you communicate your needs effectively, allowing suppliers to offer tailored solutions that meet your requirements.
Step 2: Choose the Right Aluminum Alloy
Understanding the properties and applications of various aluminium alloys is critical. Commonly used alloys like 6061, 7075, and 2024 each offer unique benefits such as corrosion resistance and strength. Select an alloy that fits the specific demands of your project, whether it’s for lightweight construction in the aerospace sector or high strength for automotive applications.
Step 3: Research and Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reliable suppliers. Evaluate their expertise, experience, and capabilities in manufacturing machined aluminium parts. Seek out case studies and references from similar industries to gauge their performance and reliability. A well-established supplier can often provide added value through engineering support and quality assurance processes.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
It’s crucial to confirm that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 or AS9100, depending on your industry. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to international quality management standards, which is vital for maintaining product consistency and compliance with regulatory requirements. Don’t hesitate to request documentation to validate their claims.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a bulk order, ask for samples or prototypes of the machined aluminium parts. Evaluating physical samples allows you to assess craftsmanship, material quality, and adherence to your specifications. This step can help avoid costly mistakes in large orders and offers a tangible demonstration of the supplier’s capabilities.
Step 6: Discuss Capacity and Lead Times
Communicate with suppliers about their production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your project timelines. Reliability in delivery is critical, especially in sectors where time-to-market is crucial. Ensure the supplier can scale production if your demand increases or adjust timelines to fit your project schedule.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Obtain Quotes
Once you’ve narrowed down your supplier options, negotiate terms of service, pricing, and payment conditions. Be sure to obtain detailed quotes that outline costs, including shipping and additional services such as finishing options like anodizing. A comprehensive quote will help you compare options and make an informed decision based on total cost of ownership rather than just initial pricing.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for machined aluminium parts, ensuring they find quality suppliers and meet their operational needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machined aluminium Sourcing
When analyzing the cost structure and pricing for machined aluminum, it is essential to consider several crucial components that contribute to the overall expenditure. The cost of machined aluminum typically encompasses materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margins.
What are the primary cost components for sourcing machined aluminum?
-
Materials: Aluminum alloys like 6061, 7075, and 2024 are widely used in CNC machining due to their favorable properties. The choice of alloy significantly influences material costs, with specific alloys commanding higher prices due to their superior strength or special characteristics such as corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: This includes the costs associated with skilled personnel required for machining processes. Labor costs can vary by region; countries with higher wages will naturally lead to increased pricing. In contrast, regions with a high availability of skilled labor at lower wages can provide cost benefits.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient operations can help mitigate these overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer better pricing.
-
Tooling: Specific machining processes often require specialized tools, which can be a considerable upfront investment. These costs can be amortized over larger production runs, thereby reducing per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in stringent QC processes ensures the production of high-quality parts, which is critical for maintaining client satisfaction. However, additional QC measures will increase overall costs but are necessary to prevent costly rework or returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the distance from the supplier to the end-user and the weight of the products. Incorrect assumptions about logistics can lead to unexpected expenses, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up product prices to ensure profitability. Understanding the market pricing benchmarks helps both parties engage in fair negotiations.
How do pricing influencers impact sourcing decisions for machined aluminum?
Several factors influence the pricing of machined aluminum, which are essential for buyers to understand:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) can yield better pricing but requires a careful assessment of inventory holding and cash flow.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique specifications may necessitate additional machining time or special tools, which can escalate costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of custom features against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Premium materials that adhere to stricter industry standards might be more expensive but ensure higher performance and longevity. Certifications may also add a layer of trust and credibility.
-
Supplier Factors and Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, preferences for allocation during peak demand, or more favorable payment terms.
-
Incoterms: The conditions defined by Incoterms affect shipping responsibilities and costs. Buyers should clarify these terms to avoid unexpected expenditures that could arise during shipping and delivery.
What are some buyer tips for achieving cost-efficiency in machined aluminum sourcing?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing machined aluminum, buyers should consider the following:
-
Negotiation: Always seek opportunities for negotiation. Suppliers may have some flexibility in pricing, especially for larger orders or repeat business.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not only the purchase price but also factors such as maintenance, lifecycle performance, and disposal when assessing the cost of aluminum parts.
-
Strategic Sourcing Decision: Understand the benefits of regional suppliers versus international ones. Local suppliers may have faster delivery times, but international suppliers may offer lower base costs due to lower labor or materials costs.
In conclusion, while pricing for machined aluminum can heavily vary, informed decision-making based on cost components and pricing influencers can lead to substantial savings. Buyers should always prioritize the total cost of ownership and leverage negotiations to achieve the best deal. Be mindful that indicative prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, exchange rates, and supply chain disruptions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machined aluminium With Other Solutions
When evaluating materials for manufacturing, especially in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and equipment, it is crucial to consider alternatives to machined aluminium. Each alternative offers distinct properties and benefits depending on the intended application. This analysis presents viable options to help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance needs, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Machined Aluminium | Carbon Steel | Titanium Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, good machinability | Strong but heavy; lower corrosion resistance | Excellent strength and corrosion resistance; lightweight |
| Cost | Generally low, with wide availability | Moderately priced but varies by grade | High initial cost; more expensive than aluminium and steel |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally easy to machine; readily available alloys | Requires more power and tooling | Specialized machining required; less common availability |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance with anodizing options | Moderate maintenance; prone to oxide formation | Low maintenance but requires specialized care |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace components, automotive parts, electronics | Structural applications, heavy machinery | Aerospace, medical implants, and high-end components |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Carbon Steel Compared to Machined Aluminium?
Carbon steel is a robust alternative to machined aluminium, known for its strength and hardness. It is ideal for structural applications requiring significant load-bearing capacity. However, one significant drawback is its weight and susceptibility to corrosion, which necessitates protective coatings that can add to overall costs and maintenance efforts. While carbon steel is readily available and usually less expensive than aluminium for high-volume manufacturing, its heavier nature makes it less suitable for applications where weight is a consideration.
Why Would You Consider Titanium Alloys Over Machined Aluminium?
Titanium alloys represent a premium alternative characterized by exceptional strength, low density, and impressive corrosion resistance. These properties make them invaluable for applications in aerospace and medical fields where failure is not an option, and performance is critical. However, the high cost of titanium alloys and the complex machining processes required make them less accessible for many manufacturers. While they excel in demanding environments, the cost and specialized tooling required to machine titanium can be a barrier for businesses focused on budget and efficiency.
How Can B2B Buyers Determine the Right Material for Their Projects?
Choosing the right material depends on the specific requirements of the project. B2B buyers should consider factors such as weight limitations, environmental conditions, mechanical properties, and budget constraints. For industries prioritizing performance and lightweight solutions, machined aluminium often stands out due to its combination of advantages. However, in scenarios where strength is paramount, or where weight is less of a concern, carbon steel may suffice. For high-stakes applications requiring the best in terms of performance and reliability, titanium alloys could prove worth the investment. Ultimately, understanding the trade-offs will empower buyers to select the most suitable solution for their unique manufacturing challenges.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machined aluminium
When it comes to sourcing machined aluminum parts for various applications, understanding the critical technical properties and industry terminology is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. This section provides insights into key specifications and jargon that will aid B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of aluminum machining.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machined Aluminum?
-
Material Grade
Aluminum is available in numerous alloys, each with distinct mechanical properties. Common grades like 6061, 7075, and 2024 offer varying strengths, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Selection of the appropriate grade is crucial, as it directly affects part performance in end-user applications, such as automotive or aerospace manufacturing. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a part’s dimensions. In the context of machined aluminum, tighter tolerances yield parts that fit precisely in complex assemblies, reducing the risk of failure in critical applications. Specifying the correct tolerance ensures that the final product meets performance expectations and reduces costs related to rework and waste. -
Machinability
Machinability is the ease with which aluminum can be machined into the desired shape. Superior machinability leads to efficient production, reduced cycle times, and lower tool wear. This property is especially important for B2B buyers aiming to minimize production costs while maximizing output quality. -
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
One of aluminum’s standout features is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, which outperforms many metals, including steel. This property is particularly beneficial in industries that require lightweight components without compromising structural integrity, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. Making the right decision concerning alloy selection can enhance performance in critical applications. -
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminums ability to resist corrosion, especially when treated through anodizing, is a significant consideration for parts used in harsh environments. Understanding how corrosion resistance varies among grades ensures that buyers select materials suited for their specific applications—be it marine, chemical, or general outdoor use. -
Electrical Conductivity
Aluminum is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a suitable choice for electrical components. However, conductivity can vary with different alloys; thus, it’s essential for buyers to clearly define electrical requirements when sourcing components.
What Are Common Terminologies Used in the Machined Aluminum Industry?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM manufactures products or components that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding the nuances of OEM relationships can better inform buyers about the specifications and performance expectations required for machined aluminum parts. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest order quantity that suppliers are willing to process. For B2B buyers, being aware of MOQs helps in budgeting and planning inventory levels, ensuring that projects have the necessary materials without incurring excess costs from over-ordering. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a critical document issued by buyers seeking pricing information from suppliers. It outlines material specifications, quantities, and any other relevant details. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ fosters competitive pricing and better alignment with supplier capabilities. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, detailing the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is essential for international buyers to avoid unexpected costs and logistical issues. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving the finished product. Understanding lead times is crucial for project management, ensuring that components arrive when needed to maintain production schedules and avoid delays. -
CNC Machining (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC machining is a manufacturing process governed by pre-programmed computer software that dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. This technology is central to machining aluminum, providing precision and repeatability in producing complex geometries.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terminologies, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement of machined aluminum parts, aligning specifications with project needs and optimizing supply chain efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machined aluminium Sector
What Are the Current Dynamics in the Machined Aluminium Market?
The machined aluminium market is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials. Key trends include the shift towards automation and digital sourcing platforms, enabling seamless communication and transaction processes. The adoption of advanced CNC machining technologies is streamlining production, enhancing precision, and reducing lead times.
Sourcing trends are also evolving, with a greater emphasis on local partnerships to mitigate geopolitical risks and supply chain disruptions. For international B2B buyers, understanding the properties of different aluminium alloys—such as the high strength-to-weight ratio of 7075-T651 and excellent corrosion resistance of 6061-T651—is crucial. The focus on speed and efficiency is further amplified by just-in-time inventory strategies, which are being adopted to lower holding costs while ensuring availability. Additionally, growing environmental regulations compel buyers to consider sustainable sourcing options.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Aluminium Sourcing Decisions?
Sustainability is becoming a key factor in aluminium sourcing, as environmental concerns and regulatory pressures influence production practices. The significant environmental impact of conventional aluminium production—characterized by high energy consumption and emissions—makes recycling and green certifications more appealing. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, such as using low-emission production methods and sourcing recycled aluminium.
In the machined aluminium sector, certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) certification are becoming popular indicators of ethical sourcing. Such certifications assure B2B buyers of responsible supply chain management, including reduced carbon footprint and adherence to environmental standards. In many regions, particularly in Europe, sustainable sourcing is not just a preference but has become a prerequisite for entering procurement processes.
Moreover, the importance of recycled materials, which require less energy to produce compared to primary aluminium, is gaining attention. Suppliers using recycled aluminium not only contribute to environmental conservation but also provide added value through cost savings in production.
What Is the Historical Context of Machined Aluminium’s Rise?
The use of aluminium in machining can be traced back over a century, characterized by its growing utilization in various industrial applications. Initially, its adoption was slow due to the abundance of more traditional materials, like steel. However, the introduction of aluminium alloys in the 1950s, notably the 6061 and 7075 series, marked a turning point. These alloys presented better strength, weight, and machinability, facilitating increased use in sectors such as aviation and automotive.
Post the 1980s, as manufacturing methods improved, aluminium’s dominance in machined parts surged remarkably. The material gained a reputation for its versatility across a variety of applications, leading to innovations that optimized its use in critical sectors. As global trade expanded, the machined aluminium market began flourishing, particularly in regions with robust demands for lightweight yet strong materials. Today, the blend of its mechanical properties with growing sustainability trends is not only reinforcing aluminium’s role in the manufacturing landscape but also shaping the future directions towards greener technologies and practices.
In conclusion, understanding market dynamics, embracing sustainability, and recognizing historical evolution will empower B2B buyers to navigate the machined aluminium sector with greater confidence and strategic foresight.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machined aluminium
-
How do I select the right aluminum alloy for my CNC machined parts?
Choosing the appropriate aluminum alloy for CNC machining depends on your project’s specific requirements. Key factors include strength, corrosion resistance, weight, and manufacturing costs. Commonly used alloys like 6061 and 7075 offer a blend of strength and machinability, while 2024 is excellent for high-stress applications. Consider the final application’s environment, such as exposing parts to marine conditions, which may necessitate alloys with higher corrosion resistance like 5083. Customization options and specific industry norms can also guide your choice. -
What finishing options are available for machined aluminum parts?
Machined aluminum parts can be enhanced through various finishing options, including anodizing, which protects against corrosion and improves aesthetics. Different anodizing types exist: Type I (Chromic Acid) for a thin protective layer, Type II (Sulfuric Acid) for durability, and Type III (Hard Anodize) for heavy-duty applications. Other finishing options include powder coating for color and texture, and machining to specific tolerances and surface finishes. Collaborate with your manufacturer to determine the most suitable finishing process for your part’s function and aesthetic needs. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering machined aluminum parts?
Lead times for machined aluminum parts can vary significantly based on factors such as complexity, order size, and production capacity of the supplier. Typically, you can expect lead times between 2 to 4 weeks for standard projects, but expedited options may be available. When placing orders, ensure to communicate your timeline clearly and inquire about potential delays due to material sourcing or manufacturing schedules. Building a reliable relationship with your supplier can improve lead time predictability for future orders. -
How can I ensure the quality of my machined aluminum parts?
To guarantee quality, it’s vital to engage in thorough supplier vetting. Look for manufacturers with certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request samples or prototypes to evaluate craftsmanship before placing a larger order. Establish clear quality assurance protocols, including dimensions, tolerances, and performance metrics. Continuous communication and updates throughout the manufacturing process will also help ensure your parts meet specifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for machined aluminum parts?
Minimum order quantities for machined aluminum can vary widely based on the manufacturer’s capacities and your project’s specifics. Some suppliers may accept small orders for prototypes or custom projects, while others may set higher MOQs to optimize production efficiency. It’s important to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to find one who can accommodate your order size. Keep in mind that larger orders often result in lower unit costs, making bulk purchasing an appealing option for significant projects. -
What payment terms are typically offered for sourcing machined aluminum?
Payment terms for machined aluminum parts often depend on the supplier’s policies and the size of the order. Common practices include a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon completion or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer credit terms based on established relationships. Ensure you clarify payment methods, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, and review any potential discounts for early payment or bulk orders. Being transparent about your budget and financial constraints can lead to mutually beneficial arrangements. -
How can I navigate international shipping logistics for my aluminum orders?
International shipping for machined aluminum requires careful planning, including customs regulations, shipping methods, and potential tariffs. It’s advisable to partner with suppliers who have experience in international logistics and can assist with documentation. Determine whether you’ll handle shipping or if the supplier will manage it, as that can impact overall costs. Research the best shipping methods for your destination, keeping in mind factors like delivery speed and potential customs fees. -
What should I consider regarding supplier reliability when sourcing machined aluminum?
Assessing supplier reliability involves reviewing their track record, customer feedback, and ability to meet delivery timelines. Look for collaboration opportunities and whether they maintain clear communication regarding production updates or concerns. Establish whether they possess necessary certifications (ISO, CE, etc.) and have successful relationships in your industry. A reliable supplier should also demonstrate flexibility to adapt to your changing needs while ensuring consistent quality. Regular audits and ongoing communication can further enhance supplier reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Machined Aluminium Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Protolabs – Key Product Details for Aluminum CNC Machining
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Key Product Details for Aluminum CNC Machining Service: 1. **Materials**: Aluminum alloys (6061-T651, 7075-T651, 2024-T351) known for excellent machinability, strength, durability, low weight, and corrosion resistance. 2. **Benefits**: Exceptional machinability, high strength and hardness, heat tolerance, corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. 3. **Appl…
2. eMachineShop – Custom CNC Aluminum Parts
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom CNC Aluminum Parts Machining Service from eMachineShop. Key features include: 15+ years of experience in machining aluminum parts, use of free CAD software for design and ordering, option to upload existing CAD files for quick quotes, free shipping in the USA, no minimum order quantity, and 100% quality guarantee. Aluminum characteristics: lightweight, non-magnetic, corrosion resistant, hig…
3. Howard Precision – Aluminum Alloys Overview
Domain: howardprecision.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The text provides an overview of various aluminum alloys suitable for machining, classified into several series based on their mechanical and chemical properties. Key details include:
– **Series 1xxx**: 99% pure aluminum, highly ductile, excellent corrosion resistance, mainly used in electrical and chemical industries (e.g., aluminum bus bars, heat sinks).
– **Series 2xxx**: Primarily contains co…
4. Xometry – Aluminium CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: xometry.pro
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Aluminium CNC machining processes are second only to steel, indicating their popularity due to excellent machinability. Benefits of aluminium for CNC machined parts include:
– Machinability: Soft, ductile, easy to cut, less expensive and requires less power than steel, leading to high accuracy and tighter tolerances.
– Strength-to-weight Ratio: Approximately one-third the density of steel, strong…
5. At-Machining – Precision Machined Aluminum
Domain: at-machining.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Machined Aluminum: 1. Suitable for precision applications requiring tight tolerances and intricate parts. 2. Common alloys include: – Aluminum 6061: Strong mechanical abilities, high weldability, withstands severe conditions. – Aluminum 7075: High fatigue and wear resistance, higher cost, unsuitable for welding. – Aluminum 2024: Good mechanical properties, high tensile strength, low weldability, n…
6. Makerverse – CNC Machined Aluminum Parts Guide
Domain: makerverse.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: The guide explains the benefits of CNC machined aluminum parts, highlighting their lightweight, strength-to-weight ratio, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, ease of machining, and cost-effectiveness. It details popular aluminum alloys for CNC machining: Aluminum 6061 (strength, weldability, corrosion resistance), Aluminum 6060 (formability, weldability), Aluminum …
7. Moseys – Premium Aluminum Alloys for Machining
Domain: moseys.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The best aluminum for machining is versatile, lightweight, and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. Common aluminum alloys used in machining include:
– 2XXX Group: Used in automotive and aerospace industries; strong but corrosion-susceptible, e.g., aluminum 2024.
– 3003: Nearly pure aluminum with manganese; non-heat treatable, ideal for kitchen equipment.
– 5052: Strong, corrosion-resistant; used…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machined aluminium
Aluminum remains a critical material choice across multiple industries due to its unmatched blend of strength, lightweight characteristics, and corrosion resistance. Strategic sourcing of machined aluminum allows B2B buyers to capitalize on these advantages through high-quality, customized solutions tailored to their operational needs. By focusing on reliable suppliers of optimal aluminum grades, including alloys like 6061 and 7075, companies can ensure the precision, durability, and performance of their components.
The ability to leverage advanced finishing techniques, such as anodizing, enhances the aesthetic and functional properties of aluminum products, making them suitable for diverse applications in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and beyond. Sourcing strategically from multiple international suppliers can not only mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also grant access to competitive pricing, thus maximizing budget efficiencies.
As B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe explore new avenues for procurement, it’s crucial to stay informed about market trends and innovative sourcing strategies. Prioritizing relationships with trustworthy partners will be key to navigating future challenges. Embrace the potential of machined aluminum to elevate your business performance and position your company at the forefront of your industry.