Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machined acrylic
In today’s dynamic global market, sourcing high-quality machined acrylic components can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses increasingly seek alternatives to glass for applications ranging from medical devices to decorative products, understanding the nuances of acrylic’s properties and machining processes becomes essential. This comprehensive guide aims to address the key challenges faced by international buyers by exploring various types of acrylic, their applications, and best practices for supplier vetting.
With its exceptional optical clarity, durability, and versatility, machined acrylic has emerged as a preferred material in numerous industries. This guide will delve into the intricacies of sourcing machined acrylic, providing insights into the different machining techniques, cost considerations, and quality assurance practices. By equipping buyers with actionable knowledge, this resource empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers that align with their operational needs.
Whether you are navigating the complexities of CNC machining or evaluating potential suppliers, this guide serves as a valuable tool for enhancing your procurement strategy. In a market where precision and quality are paramount, understanding the landscape of machined acrylic is crucial for achieving competitive advantage.
Understanding machined acrylic Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Acrylic | Made by pouring liquid acrylic into molds; excellent clarity | Signage, displays, protective barriers | Pros: High optical clarity, easy to fabricate. Cons: More prone to scratches than other types. |
| Extruded Acrylic | Produced by forcing acrylic through a die; uniform thickness | Windows, light fixtures, automotive parts | Pros: Cost-effective, consistent thickness. Cons: Less impact-resistant than cast acrylic. |
| Impact-Resistant Acrylic | Enhanced with additives for superior durability | Safety glasses, protective shields | Pros: High impact resistance, lightweight. Cons: Can be more expensive than standard acrylic. |
| Cell Cast Acrylic | Similar to cast acrylic but with a more controlled process | Optical lenses, medical devices | Pros: Superior optical properties, less internal stress. Cons: Higher production costs. |
| UV-Resistant Acrylic | Specially formulated to withstand UV exposure | Outdoor signage, greenhouse panels | Pros: Maintains clarity and color over time. Cons: May have limitations in high-temperature applications. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Cast Acrylic?
Cast acrylic is produced by pouring liquid acrylic into molds, resulting in a material with excellent optical clarity and surface finish. This type is particularly suitable for applications where aesthetics are crucial, such as signage and display cases. When purchasing cast acrylic, B2B buyers should consider its susceptibility to scratching and the need for protective coatings to maintain its appearance over time.
How Does Extruded Acrylic Differ from Other Types?
Extruded acrylic is manufactured by forcing acrylic through a die, creating sheets with uniform thickness. This type is often more cost-effective and is widely used in applications such as windows and light fixtures. Buyers should note that while extruded acrylic is economical, it may not offer the same impact resistance as cast acrylic, making it less suitable for high-stress environments.
Why Choose Impact-Resistant Acrylic for Safety Applications?
Impact-resistant acrylic is enhanced with additives that improve its durability, making it ideal for safety applications like protective shields and safety glasses. This type provides a lightweight alternative to glass while ensuring high impact resistance. Buyers should evaluate their specific safety requirements, as the cost may be higher compared to standard acrylic options.
What Are the Advantages of Cell Cast Acrylic?
Cell cast acrylic is created through a more controlled casting process, resulting in superior optical properties and reduced internal stress. This makes it an excellent choice for precision applications such as optical lenses and medical devices. B2B buyers should consider the higher production costs associated with cell cast acrylic, balanced against its performance benefits.
How Does UV-Resistant Acrylic Enhance Outdoor Applications?
UV-resistant acrylic is specially formulated to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without degrading. This makes it an ideal choice for outdoor signage and greenhouse panels, where maintaining clarity and color is essential. Buyers should assess the specific environmental conditions their products will face, as UV-resistant acrylic may not perform well in extreme temperatures.
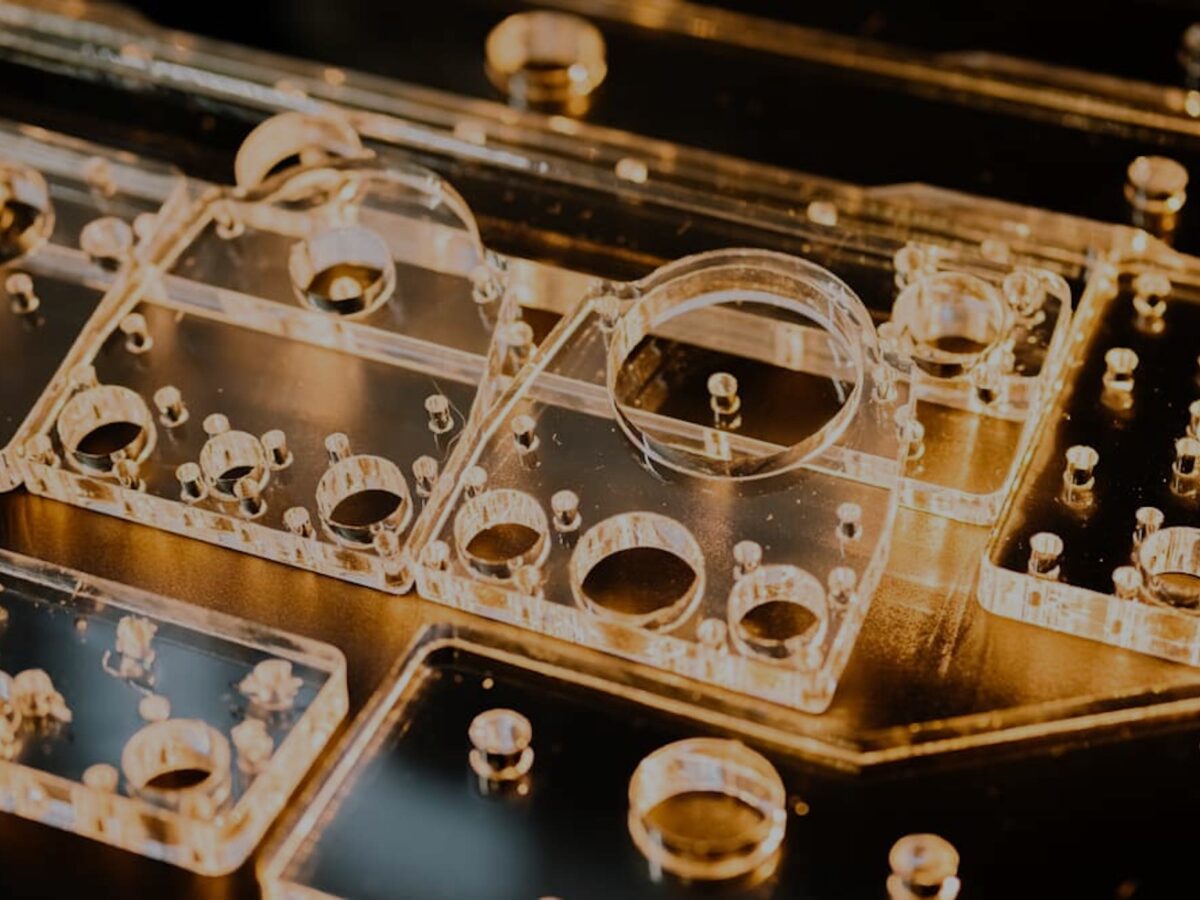
Key Industrial Applications of machined acrylic
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machined acrylic | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Surgical trays and fluid management systems | Enhanced durability and biocompatibility | Ensure compliance with medical standards and biocompatibility certifications. |
| Automotive | Dashboard components and trim | Lightweight materials improve fuel efficiency | Consider UV resistance and aesthetic finish for consumer appeal. |
| Signage and Display | Retail signage and promotional displays | High visibility and optical clarity | Require precise machining for intricate designs and durability against weather elements. |
| Optical Products | Lenses and optical components | Excellent light transmission and clarity | Focus on precision machining to meet optical specifications and tolerances. |
| Consumer Electronics | Light diffusers and electronic housings | Improved aesthetics and functionality | Assess thermal stability and electrical insulation properties for safety. |
How is Machined Acrylic Used in Medical Devices?
In the medical sector, machined acrylic is crucial for manufacturing surgical trays and fluid management systems. Its biocompatibility and resistance to environmental wear make it ideal for components that require frequent sterilization. For international buyers, particularly from Africa and the Middle East, understanding local regulatory requirements for medical devices is essential. Buyers should also focus on sourcing acrylic materials that meet international medical standards to ensure patient safety and product reliability.
What are the Applications of Machined Acrylic in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, machined acrylic is utilized for producing lightweight dashboard components and trim pieces. The use of acrylic helps improve fuel efficiency while offering a durable alternative to traditional materials. Buyers in Europe and South America should consider the material’s UV resistance and aesthetic qualities, as these factors significantly impact consumer satisfaction. It is vital to source acrylic that complies with automotive industry standards for safety and performance.
How is Machined Acrylic Beneficial for Signage and Display?
Machined acrylic plays a pivotal role in signage and display applications, especially in retail environments. Its high visibility and optical clarity make it an excellent choice for promotional displays. International buyers should prioritize sourcing suppliers that can provide precise machining to create intricate designs while ensuring the finished product can withstand various weather conditions. Additionally, understanding local market preferences for color and design can enhance the effectiveness of signage.
What Role Does Machined Acrylic Play in Optical Products?
In the realm of optical products, machined acrylic is widely used for lenses and other optical components due to its excellent light transmission and clarity. The material’s properties allow for the creation of high-quality optical devices that meet stringent performance standards. Buyers, particularly from Europe and Asia, need to focus on precision machining capabilities to achieve the necessary tolerances required in optical applications. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers with a proven track record in optical product production is essential for ensuring quality.
How is Machined Acrylic Used in Consumer Electronics?
Machined acrylic is increasingly being utilized in consumer electronics, particularly for light diffusers and electronic housings. Its lightweight nature and aesthetic appeal enhance product design while providing functional benefits such as thermal stability. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should evaluate the sourcing of acrylic based on electrical insulation properties to ensure safety in electronic applications. Collaborating with manufacturers who understand the specific requirements for electronics can lead to better product outcomes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machined acrylic’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Fragile Components Leading to High Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the issue of ordering machined acrylic components that are too fragile for their applications. Fragility can lead to increased breakage during shipping or installation, resulting in wasted materials and significant costs due to reorders and delays. For industries such as automotive or medical, where precision and durability are critical, receiving components that cannot withstand operational stresses can halt production lines and impact overall business efficiency.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of receiving fragile machined acrylic parts, buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers with proven expertise in CNC machining acrylic. Request detailed information about their machining processes, including the type of equipment used and the qualifications of their technicians. Furthermore, specify the intended application of the acrylic parts clearly. For instance, if the components will be subjected to high impact or stress, consider opting for a thicker material or one that has been treated for enhanced durability. Additionally, suppliers should provide insights into the appropriate acrylic grades, such as impact-modified PMMA, which offers greater resistance to breakage. Establishing a collaborative relationship with your supplier can lead to better material recommendations and design adjustments that enhance the performance and longevity of the components.
Scenario 2: Difficulty Achieving Desired Aesthetic Finishes
The Problem: Buyers often encounter challenges in achieving the desired aesthetic finish for machined acrylic products, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction and potential loss of business. Acrylic’s optical clarity and smooth surface are critical for applications such as signage, displays, and lighting fixtures. However, if the machining process is not performed correctly, buyers may receive parts with unsightly scratches, uneven edges, or dull surfaces that detract from their visual appeal.
The Solution: To ensure a high-quality aesthetic finish, it is essential to communicate specific finishing requirements to your supplier. Before placing an order, discuss the desired surface finish, whether it be polished, frosted, or tinted. Suppliers should be equipped to offer various post-processing options, such as flame polishing or chemical smoothing, which can enhance the visual qualities of acrylic. Additionally, buyers should consider conducting a small batch test run with their supplier to evaluate the aesthetic results before committing to larger orders. This approach allows for adjustments in the machining parameters or finishing techniques, ensuring that the final product meets the expected standards and contributes positively to brand perception.
Scenario 3: Complications with Precision and Tolerances
The Problem: In industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace or medical manufacturing, B2B buyers often face challenges with achieving the necessary tolerances in machined acrylic parts. Inaccurate dimensions can lead to improper fit in assemblies, affecting functionality and potentially leading to safety issues. This problem can be exacerbated when working with international suppliers, where communication barriers and varying machining standards may contribute to discrepancies in part specifications.
The Solution: To address precision issues, buyers should engage in thorough planning and clear communication with their suppliers from the outset. Start by providing detailed CAD drawings that specify tolerances, dimensions, and any critical design features. It’s beneficial to work with suppliers who have advanced CNC machining capabilities and are familiar with the intricacies of acrylic machining. They should be able to utilize precise cutting tools and adjust machine settings to accommodate the specific requirements of the part. Furthermore, requesting a first-article inspection or a prototype can help verify that the dimensions and tolerances meet expectations before large-scale production begins. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of errors, ensures compliance with industry standards, and helps maintain the quality and integrity of the final product.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machined acrylic
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Machined Acrylic?
When selecting materials for machined acrylic applications, several options stand out due to their unique properties and performance characteristics. Below, we analyze four common materials: standard acrylic (PMMA), polycarbonate, PETG, and acrylic with UV resistance.
Standard Acrylic (PMMA)
Key Properties: PMMA is known for its excellent optical clarity and light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility. It has a tensile strength of approximately 8,038 psi and is resistant to UV light and environmental wear.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PMMA is its lightweight nature and durability, which makes it a popular choice for signage, displays, and optical devices. However, it is prone to stress cracking and crazing if not handled correctly during machining, which can lead to increased manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: PMMA is compatible with various media, including water and air, making it suitable for applications like aquariums and lighting fixtures. However, its brittleness can limit its use in high-impact environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile strength. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, awareness of local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact is crucial.
Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a robust thermoplastic with a high impact resistance, rated at around 9,500 psi tensile strength. It can withstand higher temperatures than PMMA, with a heat deflection temperature of about 130°C.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of polycarbonate is its exceptional toughness, making it suitable for high-impact applications like safety glasses and protective shields. However, it is more expensive than acrylic and can be more challenging to machine due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is ideal for applications requiring high durability, such as automotive parts and security equipment. Its compatibility with various chemicals makes it versatile, but it can yellow over time when exposed to UV light unless treated.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with stringent safety regulations, such as Germany, should consider polycarbonate for applications requiring high impact resistance. Compliance with DIN standards is essential for market acceptance.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified)
Key Properties: PETG combines the clarity of acrylic with the toughness of polycarbonate, featuring a tensile strength of about 7,000 psi. It is also resistant to impact and has good chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of PETG is its ease of machining and thermoforming, making it a cost-effective alternative for various applications. However, it is less rigid than PMMA and polycarbonate, which may limit its use in structural applications.
Impact on Application: PETG is commonly used in packaging, medical devices, and displays due to its clarity and toughness. Its chemical resistance allows it to be used in environments with exposure to various substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with JIS standards in Japan and similar regulations in other regions. PETG’s suitability for food contact applications can be a significant advantage in markets focused on safety and hygiene.
Acrylic with UV Resistance
Key Properties: UV-resistant acrylic is specially formulated to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without yellowing or degrading. It retains the standard acrylic’s properties while enhancing its longevity in outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is its durability in outdoor settings, making it ideal for signage and architectural applications. However, it tends to be more expensive than standard acrylic, which may deter cost-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly beneficial for applications exposed to harsh weather conditions, ensuring longevity and maintaining aesthetics. Its compatibility with various outdoor media enhances its usability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with local UV resistance standards, as different regions may have varying requirements. Understanding the environmental conditions in target markets is essential for selecting the right material.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for machined acrylic | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Acrylic (PMMA) | Signage, displays, optical devices | Excellent optical clarity | Prone to stress cracking | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Safety glasses, protective shields | High impact resistance | More expensive and harder to machine | High |
| PETG | Packaging, medical devices, displays | Easy to machine and thermoform | Less rigidity than PMMA | Medium |
| Acrylic with UV Resistance | Outdoor signage, architectural elements | Durable in outdoor settings | Higher cost than standard acrylic | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for machined acrylic, tailored to meet the needs of international B2B buyers across diverse regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machined acrylic
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Machined Acrylic?
The manufacturing process for machined acrylic involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is critical to ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing acrylic components is selecting the appropriate acrylic material, typically polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). Suppliers should provide information regarding the material’s properties, including its transparency, rigidity, and UV resistance. The acrylic sheets or blocks are then cut to size, ensuring they are free from defects such as bubbles or scratches that could compromise the final product. Before machining, the material undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets the specified tolerances and quality standards.
Forming Techniques
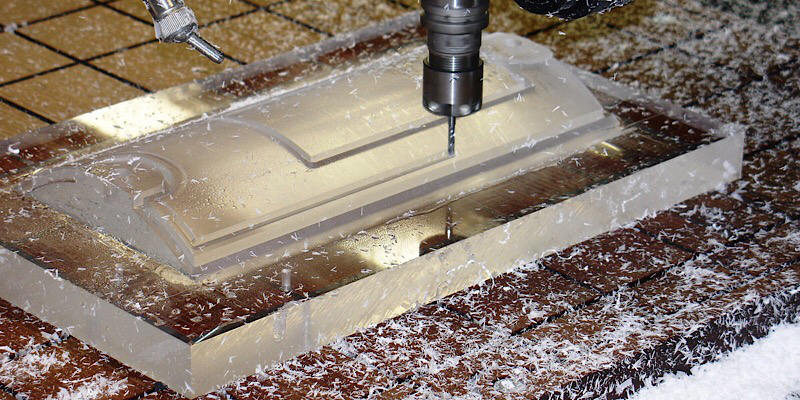
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is the predominant method used for forming acrylic parts. This technique allows for high precision and the ability to create complex shapes. CNC mills and lathes are commonly employed; the choice depends on the geometry of the component. For intricate designs, CNC milling is preferred due to its multi-axis capabilities, which allow for greater flexibility in cutting angles. Additionally, waterjet cutting may be used for 2D shapes, providing clean edges without thermal distortion.
Assembly
In cases where acrylic components require assembly, techniques such as solvent bonding, mechanical fastening, or adhesive applications are employed. It is essential to select the right adhesive that is compatible with acrylic to maintain transparency and structural integrity. During the assembly phase, meticulous attention must be paid to avoid introducing stress points that could lead to cracking or failure during use.
Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic qualities and functional performance of the acrylic parts. Common finishing techniques include edge polishing, surface coating, and UV treatment to improve durability against environmental factors. Polishing not only improves appearance but also reduces the risk of stress cracking. Buyers should specify their finishing requirements upfront to ensure that the final product meets their expectations.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Machined Acrylic Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of machined acrylic, ensuring that each part meets stringent industry standards and customer specifications. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QA processes.
International Standards and Certifications
Many suppliers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the supplier has established processes for consistent quality and continuous improvement. Other relevant certifications may include CE marking for products sold within Europe, ensuring compliance with safety and environmental regulations. For industries like medical or automotive, adherence to specific standards such as API (American Petroleum Institute) can be critical.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Initial inspection of raw materials upon receipt to verify they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the machining process to identify any deviations from the desired specifications. This may include real-time assessments of dimensions, surface finish, and machining accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished products to ensure they meet all quality and performance criteria before shipping. This can involve testing for structural integrity, optical clarity, and surface finish.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Machined Acrylic?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality and performance of machined acrylic parts. Some of the most common include:
-
Visual Inspection: A straightforward method that involves checking for surface defects, clarity, and overall appearance.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing calipers and gauges to ensure that parts meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
-
Mechanical Testing: This may include tensile strength tests to evaluate the material’s ability to withstand stress without breaking. Specific tests, such as ASTM D638, are used to determine tensile properties.
-
Impact Resistance Testing: Given acrylic’s susceptibility to cracking, conducting drop tests or impact tests can help verify the material’s durability under various conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are several strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Buyers can request audits of the supplier’s facilities to assess their adherence to quality standards and processes. This can include reviewing quality management systems and compliance with relevant certifications.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports that outline inspection results, testing methods used, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of product quality. This is particularly important for buyers from regions with stringent import regulations.
-
Check References and Reviews: Buyers should seek references from other clients and review feedback on the supplier’s performance regarding quality and delivery.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the cultural context and regulatory environment of the supplier’s country can help buyers better navigate quality expectations and compliance requirements.
-
Shipping and Handling Considerations: Quality assurance does not end at manufacturing. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping practices to protect parts from damage during transit.
-
Language Barriers: Clear communication is crucial. Buyers should ensure that specifications, standards, and quality expectations are well documented and communicated in a language that both parties understand.
By taking these factors into account, B2B buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers who adhere to stringent quality control measures, ultimately leading to successful procurement of machined acrylic components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machined acrylic’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for international B2B buyers seeking to procure machined acrylic. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions while sourcing high-quality acrylic components that meet their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the specific requirements for your machined acrylic parts. Consider factors such as dimensions, tolerances, surface finishes, and intended applications. Clearly defined specifications help ensure that suppliers understand your needs, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving the quality of the final product.
- Key Considerations:
- Specify the type of acrylic (e.g., transparent, colored, UV-resistant) based on the application.
- Include details about any complex shapes or designs that may require advanced machining techniques.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in machined acrylic. Look for companies with a strong track record in CNC machining and relevant industry experience. A well-established supplier is more likely to deliver quality parts on time.
- Where to Look:
- Online directories and industry forums.
- Trade shows and exhibitions related to plastics and machining.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing, assess the manufacturing capabilities of each supplier. Ensure they have the necessary equipment and technology, such as CNC mills and lathes, to handle your specifications accurately. Additionally, inquire about their production capacity to meet your order volume and timeline.
- Questions to Ask:
- What types of CNC machines do you use for acrylic machining?
- Can you provide examples of similar projects you’ve completed?
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Ask potential suppliers to provide samples or prototypes of machined acrylic parts. This allows you to evaluate the quality of their work firsthand. Check for precision, surface finish, and any defects that could impact performance.
- What to Look For:
- Consistency in dimensions and tolerances.
- Clarity and smoothness of the acrylic surface.
Step 5: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers adhere to industry standards and possess relevant certifications. Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 can indicate a commitment to quality management systems. This step is critical for ensuring that the products meet safety and regulatory requirements.
- Certifications to Check:
- ISO certifications relevant to manufacturing and quality assurance.
- Any industry-specific certifications based on your application.
Step 6: Discuss Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions regarding pricing, lead times, minimum order quantities, and payment terms. Transparency in these areas is essential to establish a solid working relationship. Ensure that the terms are clear and mutually beneficial to avoid misunderstandings later on.
- Important Considerations:
- Ask about bulk order discounts and shipping options.
- Review the return policy for defective parts.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Set up clear communication channels with your chosen supplier. Regular updates on production status, potential delays, and quality checks are crucial for maintaining a smooth workflow. Effective communication can significantly enhance collaboration and project outcomes.
- Recommended Practices:
- Schedule regular check-ins via email or video calls.
- Use project management tools for real-time updates and feedback.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for machined acrylic, ensuring they select the right suppliers who can meet their specific requirements effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machined acrylic Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machined Acrylic Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of machined acrylic is essential for B2B buyers aiming for effective sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of acrylic type significantly impacts pricing. Standard PMMA is generally more affordable, while specialty grades with enhanced properties (e.g., UV resistance or enhanced clarity) may command higher prices. Bulk purchasing can lead to cost savings.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for CNC machining processes, especially when precise cuts and finishes are required. Labor costs can vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the machining tasks. In regions with a skilled workforce, such as Europe or parts of the Middle East, expect higher labor costs compared to emerging markets.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to machine maintenance, facility costs, and utilities. Efficient operations can help reduce overhead, which in turn can lower the overall cost of machined acrylic parts.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs include the price of custom molds or cutters specifically designed for acrylic machining. While these costs can be significant, they can be amortized over large production runs, making it essential to evaluate the volume of required parts.
-
Quality Control (QC): QC processes are crucial for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of machined acrylic components. Investing in robust QC can prevent costly reworks or returns, particularly for high-stakes applications like medical devices or automotive parts.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling fees can vary widely based on the origin and destination of the acrylic parts. International buyers must consider import duties and taxes, which can impact total landed costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a markup on the base costs to cover their operational risks and ensure profitability. Understanding a supplier’s pricing strategy can aid in negotiations.
How Do Volume and Specifications Influence Pricing in Machined Acrylic Sourcing?
Price influencers in machined acrylic sourcing primarily revolve around order volume and product specifications:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing models that significantly reduce costs for bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or complex geometries often require additional setup time and specialized tooling, increasing costs. Buyers should consider standard designs whenever possible to maintain cost-efficiency.
-
Material Choices: The specific type of acrylic selected can affect pricing. For example, while standard acrylic is less expensive, specialized materials that provide greater durability or optical clarity can drive costs up.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts that require specific quality standards or certifications (such as ISO or FDA compliance) may incur additional costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications based on the application.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and geographic location can all influence pricing. Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge a premium but often provide superior quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen shipping terms (Incoterms) can significantly affect pricing. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can shift responsibility for costs and risks, impacting overall expenditure.
What Strategies Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices for Machined Acrylic?
B2B buyers can implement various strategies to achieve cost savings and optimize their sourcing processes:
-
Effective Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Building a strong relationship can lead to better terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and performance of machined acrylic parts. Choosing higher-quality materials may result in lower TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa or South America should be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and logistics challenges that may affect pricing. Thorough research can mitigate risks.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize online platforms and CAD software to streamline the design process, potentially reducing costs associated with revisions and miscommunications.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Comparing quotes from various suppliers can provide insight into market rates and help identify the most competitive pricing.
By understanding the intricate cost structures and price influencers associated with machined acrylic sourcing, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember that indicative prices may vary based on market conditions and specific project requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machined acrylic With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Machined Acrylic for B2B Buyers
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing materials, machined acrylic stands out due to its unique properties, including lightweight durability and UV resistance. However, businesses often face the dilemma of selecting the most suitable material for their specific applications. This section explores viable alternatives to machined acrylic, comparing their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Machined Acrylic | Polycarbonate | Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High optical clarity, UV stable, impact-resistant | Superior impact resistance, less scratch-resistant | Excellent optical clarity, heavy, breakable |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally higher cost | Variable, often lower for bulk |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise machining techniques | Easier to mold, less machining required | Heavier, requires special handling |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Low maintenance, prone to scratching | Requires careful cleaning to avoid scratches |
| Best Use Case | Signage, display products, lenses | Safety glasses, automotive components | Windows, architectural features |
Analyzing Polycarbonate as an Alternative to Machined Acrylic
Polycarbonate is a robust thermoplastic known for its exceptional impact resistance, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring high durability. Unlike acrylic, polycarbonate is less prone to shattering, which is a significant advantage in safety-critical environments, such as automotive or protective eyewear manufacturing. However, it is generally more expensive than acrylic and can be more challenging to achieve the same level of optical clarity. Additionally, polycarbonate tends to scratch more easily, requiring protective coatings for extended use.
Exploring Glass as a Viable Alternative
Glass remains a traditional material widely used in various applications due to its excellent optical clarity and aesthetic appeal. It is ideal for architectural features and offers a premium feel that acrylic and polycarbonate cannot replicate. However, glass is heavier and more fragile, making it less suitable for applications where weight and impact resistance are critical. Additionally, the installation and handling of glass products require special considerations to avoid breakage during transport and installation, which can increase overall project costs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right material for your project, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your application. Machined acrylic offers a balanced mix of performance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for a wide range of uses, from signage to medical devices. On the other hand, polycarbonate may be preferable for applications demanding higher impact resistance, while glass can be the choice for aesthetic and architectural projects. By assessing factors such as performance characteristics, cost, and application needs, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machined acrylic
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machined Acrylic?
When evaluating machined acrylic (PMMA), understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
Acrylic comes in different grades, such as cast and extruded. Cast acrylic is typically more durable and offers superior optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring high visual quality, such as signage and displays. Extruded acrylic, while less expensive, may be less resistant to scratching and UV light. Selecting the right grade can affect both the performance and cost of the final product. -
Tensile Strength
The tensile strength of machined acrylic generally ranges around 8,000 psi. This property defines the material’s ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking. For B2B applications, high tensile strength is essential in ensuring the durability and reliability of components used in demanding environments, such as automotive or industrial settings. -
Dimensional Tolerances
Dimensional tolerances specify the allowable variation in a part’s dimensions. For machined acrylic parts, tolerances can be as tight as ±0.005 inches. This precision is vital for applications that require exact fitting, such as in medical devices or optical equipment, where even minor deviations can affect functionality. -
UV Resistance
One of the notable properties of acrylic is its inherent UV resistance, which helps prevent yellowing and degradation over time. This is particularly important for outdoor applications or products exposed to sunlight, such as signage and lighting fixtures. Choosing UV-resistant acrylic enhances the longevity of products, thereby reducing replacement costs. -
Impact Resistance
Acrylic exhibits excellent impact resistance, making it a safer alternative to glass. It is approximately 10-20 times more impact-resistant than glass, which is crucial for applications in environments where breakage could pose safety risks. This property is especially important in sectors like construction and automotive.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Machined Acrylic?
Understanding industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication with suppliers. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of machined acrylic, an OEM might source acrylic components for incorporation into larger products, such as appliances or automotive parts. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to understand, as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should assess their needs against the MOQ to avoid overstocking or incurring higher costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For machined acrylic, submitting an RFQ can provide insights into competitive pricing and lead times, allowing buyers to make informed procurement decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms can help B2B buyers navigate shipping logistics, costs, and risks associated with importing machined acrylic from different regions. -
CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining refers to automated processes used to cut and shape materials, including acrylic. Familiarity with CNC machining can help buyers understand production capabilities, lead times, and design options, ensuring they select suppliers that meet their specific requirements.
In summary, a clear understanding of the technical properties and trade terminology associated with machined acrylic can significantly enhance decision-making for B2B buyers. By considering material specifications and familiarizing themselves with industry jargon, businesses can optimize their purchasing strategies and build successful supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machined acrylic Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Global Machined Acrylic Market?
The machined acrylic sector is witnessing significant growth driven by a variety of global trends. One of the primary factors is the increasing demand for lightweight yet durable materials across diverse industries, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods. Acrylic’s resistance to UV light and environmental wear makes it a preferred choice in applications such as signage, displays, and optical devices. Furthermore, the rise of automation and advanced CNC machining technologies is enhancing precision and efficiency in production, enabling manufacturers to meet stringent quality requirements.
Emerging sourcing trends include a shift towards local suppliers to reduce lead times and transportation costs, especially relevant for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America. The integration of digital platforms for sourcing and procurement is also gaining traction, allowing buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and compare quotes easily. Additionally, there is a growing trend toward customization in acrylic products, as businesses seek tailored solutions to meet specific market needs.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Machined Acrylic Sector?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly vital in the machined acrylic industry. Environmental concerns surrounding plastic production and waste management are prompting businesses to seek eco-friendly alternatives and processes. The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated; buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate transparency and responsibility in their sourcing practices. This includes the use of recycled acrylic materials and adherence to environmental regulations.
To support these initiatives, many suppliers are obtaining ‘green’ certifications, which signify compliance with environmental standards and practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of low-impact manufacturing processes are becoming essential for businesses aiming to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles. For international buyers, especially in the Middle East and Europe, partnering with suppliers that prioritize sustainability can not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance brand reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
How Has the Machined Acrylic Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the machined acrylic sector can be traced back to the mid-20th century when acrylic, or PMMA, began to gain popularity as a lightweight and shatter-resistant alternative to glass. Initially used primarily in signage and displays, advancements in CNC machining technology have expanded its applications significantly. Today, acrylic is widely utilized in medical devices, automotive components, and consumer electronics, thanks to its superior optical clarity and versatility.
As the industry continues to innovate, the focus has shifted toward enhancing the properties of acrylic, such as improving its thermal stability and impact resistance. This evolution underscores the importance of staying informed about material advancements and machining techniques for B2B buyers looking to leverage the full potential of machined acrylic in their product offerings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machined acrylic
-
How do I ensure high-quality machined acrylic parts?
To ensure high-quality machined acrylic parts, start by selecting a reputable supplier with a proven track record in CNC machining acrylic. Verify their quality assurance processes, including material certifications and machining standards. Request samples or prototypes to assess their craftsmanship. Additionally, inquire about their post-processing capabilities, such as polishing and finishing, to ensure the final product meets your specifications. Establish clear communication regarding your design requirements and tolerances to facilitate accurate production. -
What is the best type of acrylic for CNC machining applications?
The best type of acrylic for CNC machining largely depends on your application. For high optical clarity and durability, opt for cast acrylic, which offers superior surface finish and is less prone to stress cracking than extruded acrylic. If impact resistance is a priority, consider using impact-modified acrylic. For applications requiring specific colors or translucency, colored acrylic sheets can be tailored to your needs. Consult with your supplier to determine the most suitable acrylic type based on your project requirements. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for machined acrylic parts?
Minimum order quantities for machined acrylic parts vary by supplier and project complexity. Some manufacturers may accommodate low-volume orders, while others may have higher MOQs to justify production costs. Generally, you can expect MOQs to range from 50 to several hundred pieces, depending on the part size and intricacy. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to determine if they can meet your order volume and explore options for smaller runs if needed. -
How can I vet suppliers for machined acrylic products?
When vetting suppliers for machined acrylic products, consider their industry experience, client testimonials, and certifications such as ISO. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality of service. Evaluate their production capabilities, including machinery and technology used, to ensure they meet your specific machining requirements. Conduct site visits if possible or request virtual tours to inspect their facilities. Establishing clear communication about expectations and timelines is also crucial in the vetting process. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing machined acrylic internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of machined acrylic typically vary based on the supplier and the relationship established. Common terms include advance payment, net 30, or letters of credit. It’s essential to clarify these terms upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow management. Some suppliers may offer discounts for upfront payments or larger orders. Discuss payment options and any potential for financing or escrow services to mitigate risk, especially for high-value orders. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing machined acrylic?
When importing machined acrylic, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling fragile materials to minimize the risk of damage during transport. Understand the lead times involved in production and shipping, as delays can impact your project timelines. Additionally, ensure all documentation, such as invoices and certificates of origin, is in order to facilitate smooth customs clearance. -
What types of finishes can I request for machined acrylic parts?
Machined acrylic parts can be finished in various ways to enhance aesthetics and functionality. Common finishing options include polishing for a “glass smooth” appearance, flame polishing for clarity, and matte finishes to reduce glare. You can also request edge treatments such as chamfering or rounding to improve safety and aesthetics. Discuss your desired finish with your supplier to ensure they can accommodate your specifications and provide recommendations based on your application. -
How can I address stress cracking in machined acrylic components?
To address stress cracking in machined acrylic components, focus on proper machining techniques and post-processing care. Use sharp cutting tools and appropriate feed rates to minimize heat buildup during machining, which can cause stress. Avoid sharp internal corners in your designs, as these can be stress concentration points. After machining, consider annealing the acrylic to relieve internal stresses. Communicate with your supplier about your concerns and request guidance on best practices for handling and processing acrylic to prevent cracking.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Machined Acrylic Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. eMachineShop – Custom Acrylic Parts
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom Acrylic Parts from eMachineShop, molded and machined for over 15 years. Design and order using free CAD software or upload CAD files for fast quotes. Features include: FREE Shipping in the USA, No Minimum Order Quantity, 100% Quality Guaranteed. Acrylic is a thermoplastic available in opaque and transparent forms, used as an alternative to glass. It is electrically insulative, resistant to …
2. Sybridge – Acrylic Solutions
Domain: sybridge.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Acrylic, also known as Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), is a clear, colorless polymer that is lightweight, durable, and resistant to shattering, scratching, weathering, UV light, and environmental wear-and-tear. It is biocompatible and widely used in manufacturing optical devices, window panes, greenhouse panels, light fixtures, and electronic screens. In the medical industry, acrylic is used for c…
3. Protolabs – Acrylic CNC Machining Service
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Acrylic (PMMA) CNC Machining Service offers cost-efficient machined parts in any quantity. Key benefits include being lightweight, durable, and highly machinable. Common applications for acrylic CNC parts include light pipes, lenses, light shades, optical fibers, and signs. Material properties include tensile strength of 8,038 psi, elongation at break of 2.7%, tensile modulus of 350,000 – 500,000 …
4. Practical Machinist – Translucent Red Acrylic
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Translucent red acrylic, preferably cast acrylic for better machining results. Recommended machining tools include hand sharpened HSS tools with a sharp cutting edge and zero top rake. Suggested machining parameters: moderate depth of cut (0.05″), feed rate (0.005″ or less), and use of soapy water as coolant/lubricant. Techniques for finishing include using progressively finer grades of wet/dry sa…
5. PCBWay – PMMA (Acrylic) Solutions
Domain: pcbway.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: PMMA (Acrylic) is an economical alternative to polycarbonate (PC) when tensile strength, flexural strength, transparency, polishability, and UV tolerance are more important than impact strength, chemical resistance, and heat resistance. PMMA is also known as Polymethyl methacrylate, Acrylic, or Plexiglass. It has high transparency, low price, and is easy to machine. CNC machining services offered …
6. Tap Plastics – Acrylic Sheets
Domain: tapplastics.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Acrylic Sheets Cast Clear, available in various sizes, ideal for a range of applications including displays, signage, and protective barriers. Offers high clarity and excellent weather resistance. Lightweight and shatter-resistant, making it a safer alternative to glass.
7. Controlled Fluidics – Acrylic CNC Machined Parts
Domain: controlledfluidics.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Acrylic (polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA) is a popular, versatile, and cost-efficient plastic for CNC machined parts, especially in medical and diagnostic applications. Key features include:
– Transparent and clear
– Lightweight
– Shatter resistant
– Excellent impact resistance compared to glass
– Weather and UV resistant
– Recyclable (depending on local guidelines)
Acrylic is available in cast or …
8. Makerverse – CNC Machined Acrylic Solutions
Domain: makerverse.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Acrylic, also known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is a popular choice for CNC machining due to its optical clarity, durability, weather resistance, and ease of machining. Common applications include retail displays, automotive components, and medical devices. Key benefits of CNC machined acrylic parts include high transparency, lightweight nature, shatter resistance, and the ability to produc…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machined acrylic
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Machined Acrylic?
In the competitive landscape of machined acrylic, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring quality, cost-effectiveness, and reliability. By partnering with experienced manufacturers who understand the complexities of CNC machining, businesses can leverage advanced technologies to produce high-quality acrylic components with precise tolerances. This not only enhances product performance but also minimizes waste and operational costs, creating significant competitive advantages.
What Are the Key Benefits for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the versatility of acrylic makes it an ideal choice across various industries—from medical applications to automotive components. The lightweight and durable nature of acrylic, coupled with its UV stability and machinability, allows for innovative designs and applications. By focusing on robust supplier relationships, buyers can access tailored solutions that meet specific regional needs and compliance standards.
How Can You Position Your Business for Future Success?
As the demand for machined acrylic continues to grow, especially in emerging markets, businesses must remain proactive. Embrace the opportunities presented by advancements in CNC technology and materials science. Now is the time to engage with trusted suppliers, explore new applications, and invest in sustainable practices that align with global trends. By doing so, your business will not only thrive in the present but also be well-positioned for future growth in the dynamic landscape of machined acrylic.