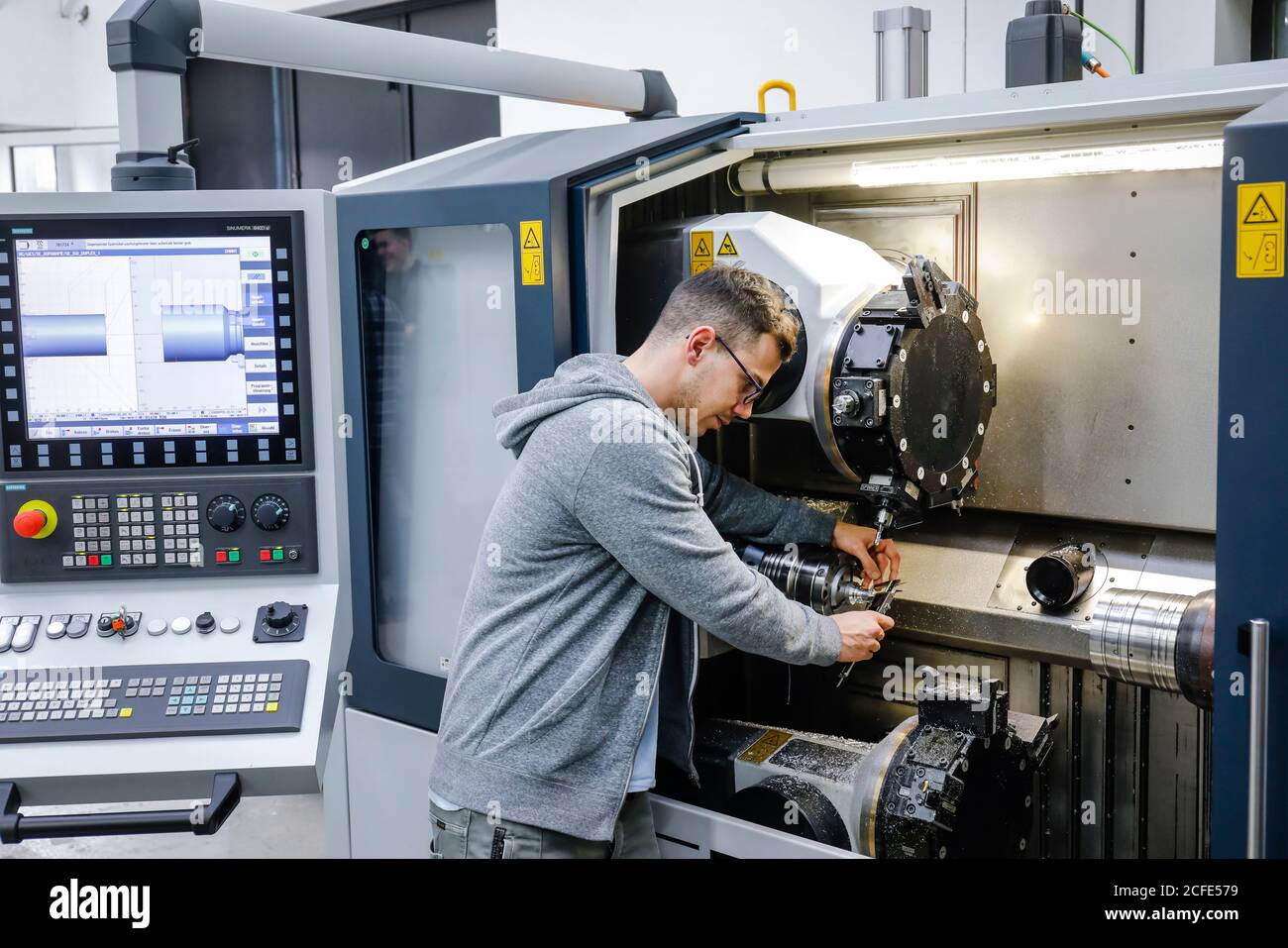
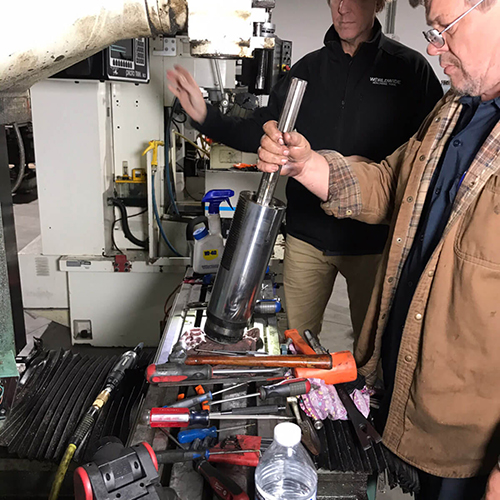
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machine tool repair
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, the urgent need for reliable machine tool repair services cannot be overstated. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including rapidly growing markets such as Vietnam and Brazil—navigating this complex terrain is fraught with challenges. Sourcing effective machine tool repair solutions involves understanding not only the various services available, such as preventive maintenance, emergency repairs, and equipment alignment but also the importance of selecting the right supplier who can deliver quality consistently and efficiently.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of the machine tool repair market, outlining essential factors like service types, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations. It addresses the common pain points associated with machine breakdowns and the critical role timely repairs play in avoiding costly downtimes. To empower B2B buyers, the guide offers actionable insights to help you make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational needs.
By identifying leading service providers and discussing industry standards, this resource equips buyers with the knowledge necessary to enhance their manufacturing efficiency, ensuring that your machines are running at optimal capacity. Whether you’re looking for immediate solutions or developing a long-term maintenance strategy, leveraging the insights within this guide will allow you to successfully navigate the global market for machine tool repair.
Understanding machine tool repair Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive Maintenance | Focuses on regular inspection and part replacement | Production environments aiming to minimize unplanned downtime | Pros: Reduces long-term costs; increases equipment lifespan. Cons: Requires upfront investment and scheduling. |
| Emergency Repairs | Quick response to unexpected equipment failures | Manufacturing settings where uptime is critical | Pros: Rapid restoration of machine functionality. Cons: Can be more costly than planned maintenance. |
| On-site Machine Repair | Repairs conducted at the customer’s facility | Factories with ample machines needing localized service | Pros: Reduced transport costs; minimizes downtime. Cons: May require more logistics coordination depending on location. |
| Installation and Relocation | Setup or movement of machinery to new locations | Shops expanding or reconfiguring layouts | Pros: Professional setup; minimizes risk of damage during relocation. Cons: Requires careful planning and timing. |
| Laser Calibration & Alignment | Ensures precision in machine setups through laser technology | High-precision industries such as aerospace or automotive | Pros: Meets certification standards; improves quality control. Cons: Initial cost for calibration tools and service. |
What are the Characteristics of Preventive Maintenance in Machine Tool Repair?
Preventive maintenance involves scheduled inspections and replacements designed to preemptively address wear and tear before equipment failure occurs. This proactive approach ensures that machines in manufacturing environments operate at peak performance, reducing the likelihood of unplanned downtime. Companies should evaluate their production schedules to implement a suitable preventive plan, weighing the upfront costs against the potential savings from avoided interruptions. This service is ideal for B2B buyers looking to enhance the lifespan of their machines while maintaining optimal operational efficiency.
How Do Emergency Repairs Differ from Other Repair Types?
Emergency repairs are characterized by their ability to respond swiftly to machine breakdowns, prioritizing rapid restoration of service. This service is often essential in environments where every minute of downtime translates to significant revenue loss. B2B buyers should consider having an emergency response plan in place, partnered with reliable service providers who can ensure their machines are back online quickly. However, they should also keep in mind that reliance on emergency repairs can lead to higher costs over time compared to preventive strategies.
What is Involved in On-site Machine Repairs?
On-site machine repairs allow technicians to carry out diagnostics and fix issues directly at the customer’s location. This service minimizes logistics costs and downtime associated with transporting heavy machinery to a repair facility. B2B buyers benefit from quicker response times and less risk of additional damage during transport. It’s crucial for businesses, especially those with multiple machines, to establish relationships with skilled technicians for efficient on-site service.
What Are the Key Aspects of Installation and Relocation Services?
Installation and relocation services are pivotal when businesses expand or reorganize their manufacturing setups. Skilled personnel ensure machinery is set up correctly according to manufacturer specifications or relocated safely with minimal disruption to operations. For B2B buyers, the value lies in reducing the risk of operational delays and potential damage during machine transit. Careful planning and coordination are vital to ensure successful relocations.
Why is Laser Calibration and Alignment Important for Machine Tool Precision?
Laser calibration and alignment utilize advanced technology to ensure machinery operates with the utmost precision. This service is particularly valuable to sectors requiring strict adherence to quality standards, such as aerospace and automotive. Buyers should evaluate the impact of precise calibration on their overall product quality and compliance with industry standards. While the initial investment can be significant, the long-term benefits in quality control often justify the cost.
Key Industrial Applications of machine tool repair
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machine tool repair | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | CNC machine calibration and alignment | Enhances precision, ensuring safety and compliance with stringent regulations | Ability to perform ISO/AS9100 certification; experience with advanced CNC control systems |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Preventive maintenance of assembly line tools | Reduces downtime, boosting overall operational efficiency and productivity | Reliability in emergency repair response and availability of spare parts |
| Construction Equipment | Hydraulic systems repair | Increases equipment longevity and minimizes operational disruptions | Expertise in various equipment brands and adherence to safety standards |
| Metalworking | Repair and refurbishment of lathes & mills | Maximizes machine lifecycle and improves overall machining accuracy | Access to skilled technicians familiar with older and contemporary models |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Diagnostics and repair of pick-and-place machines | Ensures consistent production quality and minimizes cycle time | Prompt service availability and knowledge of automated equipment |
In the Aerospace sector, machine tool repair focuses heavily on CNC machine calibration and alignment. Accurate calibration is essential for maintaining safety and compliance with industry regulations such as ISO and AS9100. For international B2B buyers, sourcing a repair provider with experience in advanced CNC control systems is critical, ensuring that machine performance meets both production and regulatory standards.
For Automotive Manufacturing, regular preventive maintenance is vital for assembly line tools. By proactively scheduling maintenance, companies can significantly reduce unplanned downtime, which can lead to costly production delays. Buyers should seek repair providers who can offer reliable emergency repair services and maintain an adequate supply of essential spare parts.
In the Construction Equipment industry, repair services for hydraulic systems are crucial to ensure machinery remains operable and efficient. A well-maintained hydraulic system increases equipment longevity and minimizes the risk of operational failures, which can halt projects altogether. For buyers, it is important to work with providers who have a broad understanding of various equipment brands and can meet safety standards.
Metalworking companies benefit greatly from the repair and refurbishment of lathes and mills, which are integral to production processes. Proper maintenance can maximize machine lifecycles and enhance machining accuracy, leading to higher quality outputs. Sourcing technicians with both historical and contemporary knowledge of machine models can provide assurance of effective repairs.
Finally, in Electronics Manufacturing, diagnostics and repair of pick-and-place machines are fundamental to maintaining consistent production quality. Quick turnaround on repairs decreases cycle times, which is critical in this fast-paced industry. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from providers that offer prompt service and have a solid understanding of automated equipment maintenance. This ensures minimal disruption to production activities and continuous operational flow.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machine tool repair’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unexpected Machine Downtime Disrupts Production
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers face the frustrating reality of unexpected machine downtime, which can halt production lines and lead to significant revenue losses. Such disruptions not only affect immediate operational efficiency but can also tarnish customer trust when delays occur in fulfilling orders. Buyers may struggle with identifying the root cause of machine failures, especially when faced with limited in-house expertise to handle complex repairs or diagnostics.
The Solution:
To mitigate unexpected downtimes, companies should establish a proactive preventive maintenance program tailored to their specific production needs. Working with a reliable machine tool repair service, buyers can schedule regular inspections focusing on potential failure points. It’s essential to document and analyze machine performance data regularly, identifying trends that may indicate wear and tear before a complete breakdown occurs. Additionally, creating a close partnership with dedicated technicians allows for quicker responses when problems arise. This approach ensures greater machine availability and efficiency while maintaining production schedules.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Finding Skilled Repair Technicians
The Problem:
In regions such as Africa or South America, sourcing skilled technicians for machine tool repairs can be a significant hurdle. Given the complex and diverse nature of machine tools, from CNC lathes to grinding machines, finding versatile technicians who can adapt to various models and brands can often feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. This difficulty can exacerbate downtime and lead to extended repairs if the right expertise is not readily available.
The Solution:
Investing in a machine tool repair service with a global reach and diverse technician team can alleviate this pain point effectively. B2B buyers should prioritize service providers that offer extensive training and certification for their technicians, ensuring they are well-versed in a broad array of machine tool brands. For specific locations, establishing long-term maintenance contracts can also ensure that skilled technicians are available on call. This eliminates the need for lengthy searches during emergencies and fosters ongoing relationships that help build tailored support for your equipment.
Scenario 3: Managing Consistent Maintenance Across Multiple Machines
The Problem:
For manufacturers with multiple machines and complex processes, managing consistent maintenance can pose a daunting challenge. Overseeing a broad spectrum of machine tools—from older models to the latest technologies—can cause maintenance processes to become inconsistent, leading to problems like misalignment, ineffective performance, or increased wear. Managing schedules and ensuring high-quality maintenance can stretch in-house teams too thin, resulting in neglected machines.
The Solution:
Adopting a centralized maintenance management system (CMMS) can tremendously streamline the maintenance process across all machines. This technology allows B2B buyers to consolidate maintenance records, schedules, and inspections in one user-friendly platform. By using this system, companies can set and automate reminders for routine maintenance, track service history for each machine, and prioritize repairs based on urgency and production needs. Furthermore, partnering with a service provider who can offer insights and recommendations based on CMMS data can enhance machine operation reliability, leading to better production outcomes and minimized downtime.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machine tool repair
When repairing machine tools, selecting the right materials is crucial to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Below, we analyze several common materials used in machine tool repair, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and the specific considerations relevant to international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Machine Tool Repair?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in machine tool repair due to its versatility and strength. Key properties include a high tensile strength rating, excellent impact resistance, and good thermal conductivity. Steel can handle high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various repair tasks.
Pros: Steel is robust and enduring, which makes it ideal for parts that require high durability, such as gears and shafts. The widespread availability of various steel grades allows for flexibility in performance requirements.
Cons: On the downside, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly protected or coated, which can lead to degradation over time. Additionally, the complexity of manufacturing processes may increase costs, especially for precision components.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM or DIN standards for steel grades. Countries in the Middle East and Africa may have specific regulations regarding materials and quality that need to be observed.
What Benefits Do Brass Components Offer in Machine Tool Repair?
Brass is another common material used in machine tool parts due to its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It is well-suited for components that experience wear and friction, such as fittings and bushings.
Pros: Brass has a lower friction coefficient compared to steel, leading to extended component life with reduced maintenance. Its resistance to corrosion makes it particularly advantageous for environments where moisture is prevalent.
Cons: However, brass is generally softer than steel, meaning it may not withstand high loads as effectively. This limitation can affect its suitability in high-pressure applications.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Europe and South America must ensure that brass components comply with local chemical composition standards (e.g., JIS standards), particularly regarding lead content, which is strictly regulated.
How Do Polymeric Materials Enhance Machine Tool Repair?
Polymeric materials, primarily used for seals, gaskets, and insulators, offer properties such as flexibility, chemical resistance, and lightweight characteristics. Materials like polyurethane and PTFE are commonly utilized, providing excellent compatibility with various media.
Pros: One significant advantage of polymers is their resistance to chemical attack from various fluids, which extends the service life of seals under adverse conditions. Additionally, they can significantly reduce noise and vibration in machine operations.
Cons: Yet, polymers can exhibit lower thermal and mechanical strength compared to metals, limiting their application in high-temperature or load-bearing scenarios.
International Considerations: B2B buyers in diverse markets must pay attention to compliance with global standards for polymeric materials, such as ASTM D2000, to ensure consistent quality and reliability.
Why is Stainless Steel Often the Material of Choice in Machine Tool Repair?
Stainless Steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength, making it an ideal choice for critical machine tool components exposed to harsh conditions.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its exceptional durability in corrosive environments. This property makes it a preferred option for machine tools operating in moist or chemically reactive environments.
Cons: The higher cost of stainless steel compared to carbon steels can be a major drawback, especially for cost-sensitive projects. Additionally, machining stainless steel can require specialized tools, increasing manufacturing complexity.
International Considerations: Particularly for buyers from Africa and South America, understanding the international standards (like ASTM 240) for stainless steel grades is essential for ensuring material compliance across regions.
Summary Markdown Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for machine tool repair | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Gears, shafts | High durability | Prone to corrosion; complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Brass | Fittings, bushings | Excellent machinability | Softer than steel; limited load capacity | Medium |
| Polymeric | Seals, gaskets | Chemical resistance | Lower thermal strength; not suitable for high loads | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Critical components in harsh environments | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost; specialized machining required | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machine tool repair
The intricacies of machine tool repair encompass a broad range of manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures that are critical for maintaining equipment efficiency. By exploring the typical stages in the manufacturing and repair of machine tools—along with industry-standard quality checks—international B2B buyers can ensure they partner with reliable equipment service providers.
What are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Machine Tool Repair?
Understanding the manufacturing process of machine tool repair is crucial for buyers interested in enhancing their operational efficiency. The typical processes involved include:
Material Preparation
Material prep is the foundational stage where technicians assess the condition of machine tools. Components such as spindles, motors, and gearboxes are disassembled, with parts carefully inspected for wear or damage. This often involves ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection to detect hidden flaws. Use of original or certified aftermarket replacement parts is prioritized to ensure compatibility and reliability.
Forming: Machining and Repair Techniques
In the forming stage, skilled technicians employ various machining techniques to restore or modify the components. Common methods include:
- CNC Machining: High precision is achieved through Computer Numerical Control (CNC) operations, which can restore dimensions and tolerances to factory specifications.
- Grinding and Abrasive Techniques: This is used for surface finishing and precision alignment, ensuring that repaired components fit together seamlessly.
- Welding and Fabrication: For damaged parts, welding techniques including MIG and TIG welding are utilized, particularly for metal repairs where strength and durability are paramount.
Assembly
Following repairs, the assembly stage involves reassembling machine components with meticulous attention to detail. Proper alignment and calibration are essential to avoid issues during operation. Field service engineers often utilize laser calibration tools during this phase to ensure that machines meet precise specifications, which is essential for maintaining ISO and other certifications.
Finishing: Quality Checks
The finishing stage includes a series of tests to guarantee the reliability and performance of repaired machine tools. This can involve final machining operations and surface treatment processes to enhance wear resistance. It is also during this phase that detailed documentation of work done, including measurements and recalibrations, is compiled for client records.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Machine Tool Repair Services?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of machine tool repair, ensuring that all services meet international and industry-specific standards.
What Are the Relevant International Quality Standards for Machine Tool Repair?
International standards such as ISO 9001 set the benchmark for quality management systems across various industries, including machine tool repair. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a company’s ability to continually provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
Additionally, sector-specific standards such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications signify adherence to rigorous quality and safety protocols, particularly relevant for buyers operating in industries such as aerospace and oil and gas.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Essential in Machine Tool Repair?
To maintain high quality, machine tool repair services implement several quality control checkpoints, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Initial inspection of parts and materials received to ensure they meet specifications before being incorporated into repair processes.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the repair process help identify issues in real-time, allowing for immediate corrections, thereby preventing further complications and potential failures.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive audit conducted after repairs are completed guarantees that the machine tool operates as intended. This stage often requires detailed testing, verification of dimensions, and functionality assessments.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Machine Tool Repair?
Various testing methods can be employed to verify the quality of repaired tools, including:
- Functional Testing: Assessing the machine’s operations under expected workload conditions to determine its reliability and performance.
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers, micrometers, or coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure that all parts conform to predefined tolerances.
- Load Testing: Simulating operational stresses to evaluate the integrity and durability of the machine after repair.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, ensuring that a supplier adheres to high-quality standards can significantly mitigate risks associated with machine tool repairs. Here are actionable strategies:
Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits can reveal a supplier’s commitment to quality. Buyers should investigate whether potential suppliers maintain comprehensive quality management certifications and assess their QA processes in real-time. A well-documented audit trail that includes records of repairs, inspections, and test results can provide insight into operational reliability.
Review Quality Reports
Requesting detailed quality reports from your machine tool repair provider can enhance transparency. These documents should outline testing procedures, compliance with international standards, and the results of any inspections conducted. This transparency builds trust and ensures that you are making informed decisions regarding your machinery.
Engage Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspectors can validate a supplier’s claims concerning their quality control processes. Independent verification of compliance, especially for international transactions, can reduce the risk of discrepancies and ensure that maintenance meets the expected standards.
What Unique Considerations Exist for B2B Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
International B2B buyers, especially from developing regions, should consider regional industry regulations and standards as they pertain to machine tool calibration and maintenance. It’s also critical to ascertain logistics capabilities—understanding the supply chain’s ability to provide timely parts and services can significantly influence efficiency and downtime recovery.
Additionally, cultural factors affecting service communication and maintenance expectations underscore the need for buyers to establish clear contracts that outline quality expectations, service levels, and accountability measures. Investing time in building trusted relationships with local suppliers can also yield long-term benefits, as they can better navigate specific market dynamics and regulatory frameworks.
By being informed about these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their operational productivity and equipment longevity in the machine tool domain. This attention to detail ensures a return to optimal machine performance while minimizing costly downtimes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machine tool repair’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring machine tool repair services, this practical checklist outlines critical steps in the sourcing process. Adhering to these steps will ensure that you select the right partner, reduce downtime, and enhance the operational efficiency of your machinery.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for your machine tools and the required repair services. This includes identifying the type of machines (e.g., CNC, manual, or fabrication equipment) and the nature of repairs (emergency, planned maintenance, or calibrations). Defining these specifications ensures that potential suppliers can meet your specific service needs.
Step 2: Assess Provider Experience and Expertise
Evaluate the experience level of potential service providers in machine tool repair. Look for firms that have handled repairs on similar types of machines or industries. An experienced provider will likely have better problem-solving abilities, especially for complex repairs.
- Key Considerations:
- Years in business and types of machines serviced.
- Industry-specific certifications or qualifications.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
It’s crucial to confirm that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications to provide machine tool repair services. Certification can indicate compliance with industry standards, which is especially pertinent for quality assurance.
- Examples of Certifications to Look For:
- ISO Certification
- Manufacturer-specific authorizations (e.g., Heidenhain, Fagor)
Step 4: Request and Review Case Studies or References
Gather case studies or references from previous clients, ideally from your industry or region. Understanding how the service provider has successfully resolved similar challenges in the past will give you confidence in their capabilities and approach.
- Questions to Ask References:
- How timely and effective was the repair service?
- Were there any challenges faced during the project and how were they handled?
Step 5: Inquire about Preventive Maintenance Programs
Evaluate whether the service provider offers preventive maintenance contracts, as these can significantly reduce the likelihood of unexpected downtimes. A tailored preventive maintenance plan extends the life of your machinery and enhances production efficiency.
- Benefits of Preventive Maintenance:
- Detailed maintenance history tracking
- Reduced emergency repairs and associated costs
Step 6: Compare Pricing Models and Contracts
Different suppliers may offer various pricing structures—such as hourly rates or fixed contracts for ongoing support. Compare these models carefully to ensure alignment with your budget while considering the potential costs of machine downtime.
- Comparison Metrics:
- Overall costs versus expected service quality
- Included services in maintenance contracts versus a la carte offerings
Step 7: Evaluate Customer Service and Response Time
Finally, assess the supplier’s customer service and support response times. Quick and effective communication can be crucial during emergencies when downtime directly impacts productivity and profitability.
- Factors to Consider:
- Availability of support (e.g., 24/7 services)
- Responsiveness to inquiries and the promptness of repairs
By following this step-by-step checklist, you’ll position your organization to make informed decisions when sourcing machine tool repair services. A thorough procurement process minimizes risks and enhances the overall performance of your machinery.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machine tool repair Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machine Tool Repair?
When analyzing the costs associated with machine tool repair, it’s essential to break down the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. Key components include:
- Materials: This includes replacement parts such as gears, motors, and bearings, among others. The cost here can vary widely depending on the brand, availability, and whether the parts are OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or aftermarket.
- Labor: Skilled labor is often one of the largest cost drivers. The complexity of the repair, technician expertise, and geographical location can significantly influence labor costs.
- Manufacturing Overhead: Costs such as equipment rental, utilities, and facility maintenance that are indirectly associated with the repair services fall into this category.
- Tooling: Specialized tools may be required for precise repairs and calibrations. The investment in such tools is often amortized over multiple repairs.
- Quality Control (QC): QA processes ensure that repairs meet industry standards. This can include testing and certifying the machine post-repair to ensure operational safety and efficiency.
- Logistics: The transportation of parts and machinery, both to and from the repair facility, can add additional costs, particularly for international shipping.
- Margin: Service providers typically include a profit margin in their pricing to ensure sustainability and growth.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machine Tool Repair Costs?
Multiple factors can influence the pricing of machine tool repair services, making it vital for buyers to understand these nuances:
- Volume (MOQ): Orders placed in larger quantities can often secure discounts. Buyers should consider consolidating repair needs across multiple tools to negotiate lower rates.
- Specifications and Customization: Custom repairs or specialized modifications can increase costs. Being clear about your requirements can help in receiving accurate quotes.
- Material Choices: The type of materials selected for repairs can significantly impact pricing. Higher-quality materials may have an upfront cost, but can lead to longer-lasting repairs and lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
- Quality and Certifications: Repair services that include ISO or other certifications often justify higher prices due to an extra layer of assurance regarding the repair quality.
- Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect prices. More established suppliers may charge premium rates for their recognized expertise.
- Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping can influence overall costs. Those who are adept at negotiating Incoterms (such as FOB or CIF) can reduce logistics costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Machine Tool Repair Costs?
For international B2B buyers—particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—navigating the complexities of pricing in machine tool repair can be challenging. Here are actionable tips to enhance cost efficiency:
- Negotiate Effectively: Always seek quotes from multiple suppliers and leverage these competitive prices in negotiations. Don’t hesitate to ask about discounts for repeat business or referrals.
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Consider the long-term implications of repair costs. Cheaper services might result in more frequent repairs, increasing TCO. It’s crucial to balance initial repair costs with expected durability and performance.
- Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of local economic factors, currency fluctuations, and shipping costs when working with international suppliers. For example, securing a service provider that can offer localized support may reduce both logistical and communication barriers.
- Clarify Terms Upfront: Ensure clarity on warranties, service agreements, and liability issues in the contract phase, which can protect against unexpected costs later down the line.
Conclusion: Why is It Important to Have a Comprehensive Understanding of Machine Tool Repair Costs?
Ultimately, understanding the detailed cost structure and pricing influencers in machine tool repair services empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By focusing on negotiation strategies and seeking opportunities to optimize costs, businesses can not only enhance their operational efficiency but also secure a reliable supply chain in the competitive landscape of machine tooling services. As always, prospective buyers should be aware that the prices discussed should be regarded as indicative and will vary based on specific circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machine tool repair With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Machine Tool Repair
In an increasingly competitive global market, B2B buyers must weigh their options when facing machine tool issues. While traditional machine tool repair services offer direct solutions, alternative methods can prove advantageous, depending on specific operational needs and budget constraints. Below, we explore how machine tool repair compares to two viable alternatives: equipment replacement and the adoption of predictive maintenance technologies.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Machine Tool Repair | Equipment Replacement | Predictive Maintenance Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Restores equipment functionality; may depend on technician skill. | New equipment typically has superior performance and efficiency. | Optimizes machine uptime through data analysis and early fault detection. |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront costs but can accumulate over time. | High initial investment; potential long-term savings due to energy efficiency and lesser downtime. | Moderate investment in technology but cost-effective by minimizing unexpected breakdowns. |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick to mobilize, especially with local technicians. | Longer lead times for procurement, installation, and training. | Requires initial setup time, but once established, it runs almost autonomously. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance is required to prolong lifespan. | Minimal as new machinery often comes with warranties and requires less immediate care. | Ongoing costs associated with software updates, but less frequent physical downtime. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for existing machines with historical value or specific configurations. | Best for outdated equipment or when operational demands increase significantly. | Most suitable for high-utilization environments seeking to maximize productivity and reduce unplanned downtime. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Equipment Replacement
Replacing old machines with new models presents an attractive alternative for companies dealing with persistent repair issues. New equipment often includes advanced technologies that improve efficiency and offer better performance, potentially leading to energy savings and reduced operational costs. However, the upfront costs can be significant, and organizations must prepare for a learning curve regarding the use of new systems. While replacement can seem daunting due to the investment required, it can ultimately pay off with lower maintenance needs and improved output capabilities.
Predictive Maintenance Technologies
Harnessing advancements in IoT (Internet of Things) and analytics, predictive maintenance tools monitor machine performance in real time to predict failures before they occur. This approach can significantly reduce unplanned downtime, allowing companies to optimize production schedules more effectively. The investment in such technologies can be moderate, but the ROI can be impressive as businesses experience fewer disruptions. However, organizations may face challenges during the initial setup and integration into their existing systems, alongside ongoing costs for software and technology upgrades.
Conclusion
Choosing the right solution—whether it be machine tool repair, equipment replacement, or predictive maintenance—depends on various factors unique to each business. Companies need to consider their operational priorities, budget constraints, and the long-term strategy for their manufacturing processes. By evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their productivity goals and financial outlook. Balancing immediate needs with future planning is crucial in ensuring machine performance and operational efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machine tool repair
Understanding the critical technical properties and terminology in machine tool repair is essential for buyers seeking effective solutions. Here’s a rundown of the key specifications and trade terms that every decision-maker should be familiar with.
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Machine Tool Repair?
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of materials used in machine tools based on their mechanical and physical properties. This includes steel grades for structural parts or specialty alloys for components that endure high wear. Understanding the correct material grade is vital; it affects durability, performance, and overall lifecycle costs. Using inappropriate materials can lead to increased downtime and maintenance costs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in dimensions for manufactured components. In machine tool repair, this is crucial, as precise tolerances ensure that parts fit correctly and operate efficiently. Poor tolerance can lead to misalignments, reducing machine accuracy and productivity. Buyers should emphasize suppliers’ capabilities in delivering tight tolerances to ensure high-quality outputs.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish defines the texture of a surface after machining. In the context of machine tools, a smoother surface finish can reduce friction, enhance part life, and improve the aesthetic appeal of components. Buyers should discuss surface finishing requirements with service providers, as the chosen finish can significantly impact machine performance, especially in high-precision applications.
4. Alignment and Calibration
Proper alignment is critical for the optimal functioning of machine tools. This refers to the positioning of components and ensuring they are level and aligned according to factory specifications. Calibration involves adjusting machines to ensure accurate performance. For organizations, this affects productivity and can prevent costly errors. It’s recommended to partner with service providers that offer on-site laser calibration for accuracy.
5. Load Capacity
Load capacity denotes the maximum weight or stress a machine can handle during operation. This specification is essential for buyers to ensure that their tools can manage the demands of their production processes. Inadequate load capacity can lead to premature machine failure, impacting production schedules and financial performance.
6. Power Consumption
Power consumption indicates the electrical energy required for the operation of a machine tool. Understanding this property is essential for operational cost calculations. Buyers should consider energy-efficient machine tools to reduce long-term operating expenses and improve environmental sustainability.
Which Trade Terms Are Essential in the Machine Tool Repair Industry?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products or components that are used in another company’s end product. In machine tool repair, partnering with OEMs guarantees that parts used in repairs meet the original design specifications, ensuring reliability and quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan their procurement strategies effectively, ensuring they have enough components on hand to avoid production delays.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers inviting them to bid on providing specific products or services. This term is crucial for procurement, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms effectively, ensuring they select the best value for their machine tool repair needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in export and import agreements. Understanding these terms helps in clarifying shipping responsibilities and costs, thereby reducing the risk of disputes over delivery conditions.
5. Preventive Maintenance
This term describes the regular and systematic inspection and maintenance of equipment to prevent breakdowns. Effective preventive maintenance plans enhance machine longevity and reduce unanticipated shutdowns, leading to cost savings.
6. Calibration Certificate
A calibration certificate is a document that confirms a machine’s accuracy following a calibration process. It is often essential for ISO compliance and can be a deciding factor for buyers when selecting repair service providers, who must demonstrate their machines meet industry standards.
Understanding these technical properties and terms is crucial for effective decision-making in machine tool repair, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machine tool repair Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Machine Tool Repair Sector?
The machine tool repair sector is evolving rapidly due to several global drivers that B2B buyers need to consider. Increased demand for precision manufacturing and automation is pushing companies to maintain higher operational standards. Consequently, machine tool reliability and efficiency have become paramount, leading to an uptick in the demand for comprehensive repair and maintenance solutions. Internationally, markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in services that extend beyond mere repairs to include predictive and preventative maintenance strategies. These trends are influenced by technological advancements, including IoT-enabled machines providing real-time diagnostic data, facilitating timely repairs and maintenance.
Emerging B2B technologies such as cloud-based asset management systems and predictive analytics are reshaping sourcing strategies in the sector. Buyers are increasingly interested in integrated solutions that link repair services with spare part suppliers and maintenance contracts. This shift not only streamlines operations but also enhances the overall lifecycle management of machine tools. The market dynamics are further propelled by a growing preference for local suppliers, particularly in regions like Vietnam and Brazil, enabling responsiveness and quicker turnaround times.
Given these trends, B2B buyers must prioritize partnerships with service providers who can offer a wide range of capabilities, including installation, and proactive maintenance solutions. In addition, engaging with companies that demonstrate a strong understanding of local conditions and equipment needs can enhance operational efficiency and minimize costly downtimes.
How is Sustainability Reflecting in the Machine Tool Repair Industry?
Sustainability is an increasingly vital component of B2B sourcing strategies in the machine tool repair sector. Environmental awareness is prompting buyers to seek out repair services that minimize waste and foster a circular economy approach. This encompasses not just the sustainable disposal of defective machinery but also a proactive stance on extending the lifecycle of existing equipment through timely maintenance.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as organizations strive to create value while adhering to socially responsible practices. B2B buyers are leaning toward suppliers that engage in ethical labor practices, transparent supply chains, and local sourcing of materials. Accreditation and certifications, such as ISO for environmental management, are becoming essential criteria for evaluating potential partners in the machine tool repair industry.
Moreover, demand for “green” repair solutions—a process that emphasizes recycling and using eco-friendly materials—is on the rise. This trend is largely driven by regulatory pressures and the desire to achieve corporate environmental goals. Suppliers demonstrating tangible commitments to sustainability—by using energy-efficient tools and implementing waste-reduction programs—are better positioned to attract discerning purchasers.
What is the Historical Context of the Machine Tool Repair Market?
The history of the machine tool repair sector traces back to the early days of industrialization. Initially focused on basic maintenance, the industry has gradually evolved into a complex web of specialized services catering to an increasingly sophisticated array of machine tools. With the advent of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology in the late 20th century, repair services had to adapt rapidly to accommodate the new operational dynamics and complexities of digital equipment.
In recent decades, as globalization reshaped manufacturing landscapes, machine tool repair has transitioned towards offering more comprehensive service packages, including preventative maintenance and emergency repair services. Today, B2B players face a highly competitive environment where rapid technological advancements and customer expectations around service efficiency continue to redefine service propositions. Understanding this evolution is critical for any B2B buyer looking to navigate the current market landscape effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machine tool repair
-
How do I choose the right machine tool repair service for my facility?
Selecting a machine tool repair service requires a thorough evaluation of each provider’s expertise, experience, and range of services offered. Confirm that the technicians are knowledgeable about your specific machine types and brands, as expertise complements quick and effective repairs. Additionally, check for certifications and customer testimonials to gauge reliability. Consider providers who offer tailored preventive maintenance contracts, as they can help minimize future downtime and expedite troubleshooting. -
What type of maintenance plan is best for my machine tools?
The ideal maintenance plan depends on your operational needs and machine usage. A custom preventive maintenance program is often the best choice, allowing for regular inspections and servicing tailored to your equipment’s specific demands. Ensure the plan includes scheduling for daily, weekly, and annual checks, and that it addresses both routine and emergency repair needs. It is also valuable to partner with a provider who can adjust the plan as your production requirements evolve. -
How can I minimize downtime during machine repairs?
To minimize downtime, establish a clear communication channel with your machine repair provider. Implement a structured preventive maintenance program to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. During emergencies, prioritize repairs by having a dedicated response team that is familiar with your equipment. Additionally, ensure that critical spare parts are readily available to facilitate quicker repairs, which will enhance your operational efficiency. -
What payment terms should I expect when contracting machine tool repair services?
Payment terms vary among service providers and are often influenced by the scope of work. Many companies offer flexible options such as upfront payment, payment on account, or installment plans for large projects. It’s essential to clarify these terms during negotiations and ensure that they align with your financial protocols. Additionally, inquire about any warranties or guarantees that may be tied to payment conditions as they can safeguard your investment. -
What logistics should I consider when sourcing machine tool repair internationally?
When sourcing international machine tool repair services, it’s important to consider shipping logistics, potential customs duties, and the timelines for parts and service. Establish a reliable supply chain, ensuring that both communication and documentation are clear across borders to avoid delays. Partner with providers experienced in international operations, as they will likely have a better understanding of logistical challenges and can help streamline the process. -
How do I vet potential machine tool repair suppliers?
Vetting suppliers involves assessing several factors, including their experience, certifications, and customer references. Ask to see case studies or testimonials from businesses similar to yours to validate their expertise. Additionally, consider their communication responsiveness, as quick and reliable communication can be vital during emergencies. It’s also prudent to request service agreements outlining terms for parts and repair warranties, ensuring alignment with your service expectations. -
Can machine tool repair services be customized to meet specific business needs?
Yes, many machine tool repair services offer customization to fit specific operational requirements. This can include tailored maintenance schedules, specialized training for in-house staff, and specific focus on certain types of machinery or brands. Engaging with potential repair providers about your unique production needs and challenges early on will help them design a service package that aligns seamlessly with your operations. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in machine tool repair services?
Quality assurance in machine tool repair can include adherence to industry standards and certifications (such as ISO), comprehensive documentation of repairs and maintenance, and the use of OEM parts where necessary. Inquire about the repair provider’s protocols for testing and calibrating machines post-repair. Additionally, it is beneficial to understand their claims process for any warranties or service guarantees which can offer added peace of mind regarding the quality of work performed.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Machine Tool Repair Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Machinery Selection – CNC Machinery Repair and Sales
Domain: machineryselection.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Machine Tool Repair and Sales, Inc. specializes in CNC Machinery Repair and Sales, established in 1986. The company occupies a 6400 square foot showroom in New York, featuring both new and used CNC equipment. They offer services related to Fanuc parts and controls, including support for types 3, 5, 6, 10, 11, 15, 16, 0, 18, 21, as well as Vickers PC Based, Fidia, Mitsubishi, and Heidenhain control…
2. Yelp – Power Tool Repair Services
Domain: yelp.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Power Tool Repair services in New York, NY include appliance repair, lawn mower repair, outdoor power equipment services, and various types of installations and repairs for appliances such as washing machines, dishwashers, dryers, and more. Notable businesses in the area provide a range of services including same-day repair, transparent pricing, and specialized repairs for brands like Bosch, Kenmo…
3. MTS – Machine Tool Services
Domain: machinetoolpros.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Key services offered by MTS Machine Tool Service include Preventive Maintenance, On-site Machine Tool Repair (emergency repairs, troubleshooting, scheduled repairs), Precision Leveling & Alignment, and Machine Installation & Relocation. Established in 1994, MTS is a family and partially veteran-owned business dedicated to enhancing operational productivity. They offer tailored maintenance packages…
4. KRC Machine Tool Solutions – CNC Products & Custom Machines
Domain: krcmachinetoolsolutions.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Machine Tool Service – Machine Tool Repair Services | KRC Machine Tool Solutions offers a wide range of products including CNC products, multi-axis machines such as Fusion VI Series, HELIX HMC Series, and Velocity VTC. Products also include custom machines like Gel Injection Machine, ECDM, Fan Case Grinder, and Fan Case Mill. KRC Stock Machines include models like KRC HBM-160T, Giddings and Lewis …
5. Prime Field Service – Machine Tool Repair & Calibration
Domain: primefieldservice.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Machine Tool Repair and Calibration services by Prime Field Service include skilled millwrights specialized in repair, maintenance, and calibration of machine tools essential for manufacturing. Key services involve diagnosing machine issues such as wear and tear, alignment problems, electrical issues, coolant system failures, and software glitches. The repair process includes diagnosis, quotation,…
6. Peiffer Machine Services – Machine Tool Repair and Retrofit
Domain: peiffer-machine.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Peiffer Machine Services offers machine tool repair, rebuild, and retrofit services. Key capabilities include: Machine Tool Repairs, Rebuilds, Field Service, Preventive Maintenance, Machine Way Repair, Laser Alignment Services, Custom Machine Builds, and Machine Tool Moving and Installation. The company is based in Pennsylvania and has been operating for over 65 years, providing nationwide service…
7. Productivity Inc. – CNC Machine Tool Repair
Domain: productivity.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: Productivity Inc. is a CNC machine tool repair provider serving manufacturing facilities and machine shops in the Upper Midwest and Rocky Mountain regions. They provide services for various types of CNC machinery, including milling machines, lathes, machining centers, fabrication equipment, micro-milling machines, lasers, grinding machines, and more. The service goal is to maximize uptime with fas…
8. Practical Machinist – Machine Repair Services
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Practical Machinist – Machine Repair Services, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machine tool repair
In today’s competitive landscape, adopting a strategic approach to sourcing machine tool repair services is more critical than ever for businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of preventive maintenance, comprehensive service contracts, and the value of partnerships with experienced providers. By implementing tailored maintenance programs, companies can minimize downtime, enhance productivity, and prolong the lifespan of essential machinery.
Engaging with reliable machine tool repair experts ensures that your equipment receives timely and skilled attention, which directly contributes to operational efficiency. As the manufacturing sector evolves, leveraging innovative diagnostic and calibration technologies will be vital to meeting international standards and competing effectively in global markets.
Looking ahead, businesses must prioritize ongoing collaborations with machine tool service providers that demonstrate a commitment to quality and responsiveness. By doing so, international buyers can secure a robust foundation for their operations. Don’t wait for breakdowns to occur; invest in preventive options and maintenance contracts today to safeguard your production capabilities. As the industry progresses, those who adapt and plan strategically will thrive. Reach out to industry leaders now to explore customized solutions tailored to your specific needs.