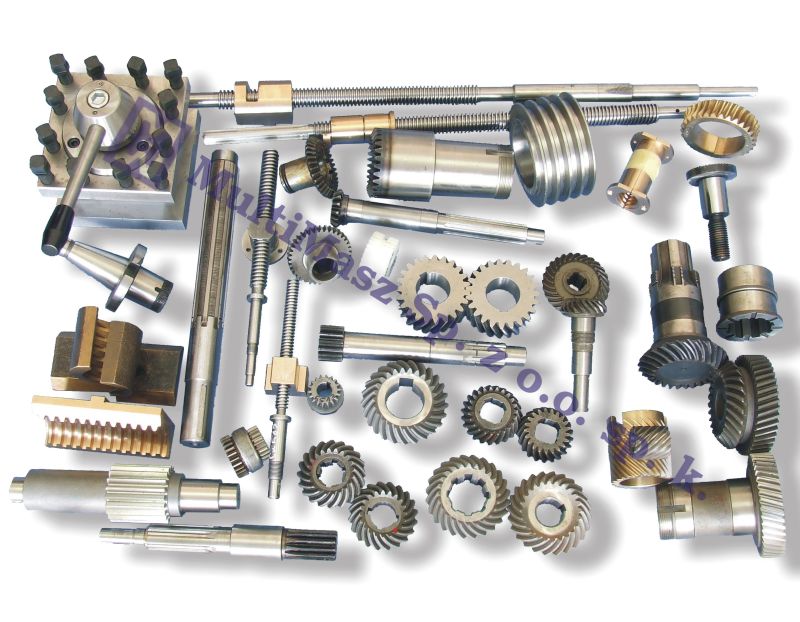
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machine tool parts
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality machine tool parts presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With varying standards, availability issues, and fluctuating costs, navigating this complex market can often feel overwhelming. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process, offering invaluable insights into the types of machine tool parts available, their specific applications, and effective strategies for supplier vetting.
We delve into critical considerations such as cost analysis, quality assurance, and logistical factors that impact procurement decisions. By providing a clear framework for evaluating suppliers and understanding market dynamics, this guide empowers B2B buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Brazil and Saudi Arabia)—to make informed purchasing decisions.
With actionable strategies and expert advice, you will be equipped to enhance operational efficiency and ensure the longevity of your manufacturing equipment. Whether you are seeking replacement parts for a specific machine or looking to establish long-term supplier relationships, this guide is your essential resource for navigating the global market for machine tool parts.
Understanding machine tool parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Tools | Various shapes (e.g., end mills, drills) for shaping materials | Metalworking, woodworking, manufacturing | Pros: Versatile, high precision. Cons: Requires regular replacement; can be costly. |
| Replacement Parts | Components designed to replace original parts in machines | Equipment maintenance, repair services | Pros: Extends machinery life, readily available. Cons: Quality may vary; compatibility issues. |
| Tool Holders | Devices that secure cutting tools in place | CNC machining, manual lathes | Pros: Enhances tool stability, easy to change tools. Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| Machine Accessories | Additional components that enhance machine functionality | Production efficiency, setup customization | Pros: Improves productivity, tailored solutions. Cons: May require extensive training; compatibility checks needed. |
| Power Feeds | Mechanisms that automate the movement of the workpiece | CNC machining, milling operations | Pros: Increases efficiency, reduces operator fatigue. Cons: Higher upfront costs; potential for mechanical failure. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Cutting Tools?
Cutting tools are essential in shaping materials across various industries. They come in numerous forms, including end mills, drills, and reamers, each designed for specific cutting actions. Buyers should consider the material of the tool (e.g., high-speed steel, carbide) as this influences durability and performance. The versatility of cutting tools makes them suitable for both metalworking and woodworking applications, but they require regular replacements, which can impact long-term costs.
How Do Replacement Parts Impact Machinery Performance?
Replacement parts are critical for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of machine tools. These components are specifically designed to replace worn or damaged parts, ensuring that machinery operates at optimal levels. When purchasing replacement parts, it’s vital for buyers to verify compatibility with existing equipment. While they can significantly extend the life of machinery, buyers should be cautious of varying quality and the potential for compatibility issues that may arise.
What Are the Advantages of Tool Holders in Machining?
Tool holders are integral in securing cutting tools, providing stability and precision during machining processes. These devices come in various designs, including collet chucks and tool posts, which allow for easy tool changes. In B2B settings, tool holders can enhance production efficiency and reduce setup times. However, the initial investment can be substantial, and buyers should ensure that the holders are compatible with their existing machines to avoid operational disruptions.
How Do Machine Accessories Enhance Production Efficiency?
Machine accessories play a significant role in optimizing the performance of machine tools. These can include items like vises, coolant systems, and digital readouts, which enhance functionality and improve production accuracy. When considering machine accessories, buyers should assess their specific production needs and the potential for increased efficiency. While these accessories can lead to significant productivity gains, they may also necessitate additional training for operators to maximize their benefits.
Why Are Power Feeds Essential for Modern Machining?
Power feeds automate the movement of workpieces during machining, significantly improving operational efficiency and reducing operator fatigue. They are particularly beneficial in CNC machining and milling operations, where precision and speed are paramount. Buyers should evaluate the upfront costs against the long-term efficiency gains when considering power feeds. While they offer substantial benefits, potential mechanical failures can pose risks, making it essential to choose reliable brands and models.
Key Industrial Applications of machine tool parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machine tool parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision machining of components | High-quality parts ensure safety and reliability | Compliance with aerospace standards; material quality |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission parts production | Enhanced performance and durability of vehicles | OEM specifications; rapid delivery for just-in-time production |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling equipment maintenance | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs | Availability of specialized parts; robust supply chain |
| Construction Machinery | Fabrication of heavy machinery | Increased productivity and reduced wear and tear | Customization options; compatibility with existing equipment |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Production of circuit boards | Precision and reliability in electronic components | Supplier certifications; lead times for parts availability |
How Are Machine Tool Parts Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, machine tool parts are crucial for the precision machining of components such as turbine blades and structural frames. These parts must meet stringent safety and reliability standards due to the critical nature of aerospace applications. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and the Middle East, must ensure that suppliers can provide parts that comply with industry regulations and are manufactured from high-quality materials to withstand extreme conditions.
What Role Do Machine Tool Parts Play in Automotive Production?
Machine tool parts are integral to the production of engine and transmission components in the automotive sector. These parts enhance vehicle performance and longevity by ensuring precise tolerances in manufacturing processes. For buyers in South America and Africa, sourcing from manufacturers who adhere to original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications is vital. Rapid delivery options are also essential to support just-in-time production methodologies, minimizing inventory costs while ensuring timely assembly.
Why Are Machine Tool Parts Important for Oil & Gas Maintenance?
In the oil and gas industry, machine tool parts are used extensively in the maintenance of drilling equipment. The reliability of these parts directly impacts operational efficiency and safety. Buyers must consider sourcing from suppliers with a robust supply chain to ensure the availability of specialized components. Additionally, the ability to provide parts that minimize downtime during maintenance is crucial for maintaining production levels and controlling costs.
How Do Machine Tool Parts Enhance Construction Machinery?
Machine tool parts are essential for fabricating heavy machinery used in construction, such as excavators and bulldozers. These components help increase productivity and reduce wear and tear during operation. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets, it’s important to seek suppliers who can offer customization options to meet specific machinery requirements. Compatibility with existing equipment is also a key consideration, as it ensures seamless integration and optimal performance.
What Is the Importance of Machine Tool Parts in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, machine tool parts are vital for producing circuit boards and other electronic components. The precision of these parts ensures the reliability and performance of electronic devices. Buyers must prioritize suppliers with the necessary certifications and quality assurance processes in place. Additionally, lead times for parts availability are critical, as delays can significantly affect production schedules and market competitiveness.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machine tool parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Challenge of Downtime Due to Unavailable Parts
The Problem: For many manufacturers, unplanned downtime caused by machine breakdowns is a significant pain point. When a critical machine tool part fails, the inability to quickly access replacement parts can lead to extended production delays, increased operational costs, and missed deadlines. This is particularly challenging for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where logistics and supply chain issues can exacerbate delays. The frustration mounts when parts are out of stock, leading to a cascade of operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To mitigate downtime, B2B buyers should establish a proactive parts management strategy. This includes maintaining an inventory of critical spare parts that are prone to wear and tear. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to identify which parts are essential for their operations and ensure they have a reliable source for these components. Partnering with suppliers that offer quick-ship options can significantly reduce lead times. Additionally, consider implementing a vendor-managed inventory (VMI) system, where the supplier monitors stock levels and automatically replenishes inventory. This ensures that essential parts are always on hand, reducing the risk of unexpected downtime.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Identifying the Right Parts for Older Machinery
The Problem: Many manufacturers operate older machine tools that may not have readily available documentation or support for replacement parts. B2B buyers often struggle to identify the correct components needed for repairs, especially if the machinery is obsolete or lacks clear labeling. This confusion can lead to incorrect orders, additional costs, and delays in getting production back on track.
The Solution: B2B buyers should prioritize developing a comprehensive parts catalog that includes all machinery, regardless of age. This catalog should detail specifications, part numbers, and compatibility information. When sourcing parts, buyers can consult with experienced suppliers who specialize in legacy equipment. Engaging with these suppliers often provides access to hard-to-find parts and expert advice on compatibility. Additionally, maintaining a relationship with a knowledgeable technician can help identify parts during breakdowns. They can assist in interpreting serial numbers and machine specifications, ensuring accurate orders and reducing the risk of mistakes.
Scenario 3: Quality Assurance Concerns with Replacement Parts
The Problem: The manufacturing industry frequently faces challenges concerning the quality of replacement parts. For B2B buyers, sourcing lower-quality components can lead to inconsistent product quality, increased waste, and ultimately, damage to the brand’s reputation. This is particularly concerning in competitive markets where precision and reliability are paramount.
The Solution: To ensure quality, B2B buyers should establish strict criteria for evaluating suppliers. This includes researching their reputation, quality control processes, and certifications. Buyers should request samples of replacement parts to assess their performance before making bulk orders. Additionally, leveraging third-party quality assurance services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the parts’ quality. Implementing a rigorous inspection process upon receiving parts will also help catch potential issues early. Regularly collaborating with suppliers to provide feedback on parts performance can foster a relationship that encourages continuous improvement and innovation, ultimately leading to higher-quality outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machine tool parts
When selecting materials for machine tool parts, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring compatibility with specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of machine tool parts, with a focus on their implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of High-Speed Steel (HSS) for Machine Tool Parts?
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is widely recognized for its excellent hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for cutting tools. It can withstand high temperatures without losing its temper, which is essential for maintaining performance during intense machining processes. HSS typically offers good toughness and is less brittle than carbide, allowing for better performance in shock-loading applications.
Pros and Cons of High-Speed Steel
The primary advantage of HSS is its cost-effectiveness compared to carbide. It is easier to manufacture and grind, which can lower production costs. However, HSS has a lower wear resistance than carbide, leading to shorter tool life in high-volume applications. Additionally, it may not be suitable for high-speed machining due to its thermal limitations.
Impact on Application
HSS is particularly effective for machining softer materials and is often used in drills, end mills, and taps. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, but its limitations in high-speed applications can restrict its use in advanced machining environments.
Considerations for International Buyers
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and compliance with international standards such as ASTM A681. Understanding the specific machining conditions in their operations can help determine if HSS is the right choice.
How Does Carbide Compare as a Material for Machine Tool Parts?
Carbide, particularly tungsten carbide, is favored for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools that require high durability. Carbide tools can operate at higher speeds and temperatures than HSS, significantly enhancing productivity.
Pros and Cons of Carbide
The key advantage of carbide is its longevity, which reduces the frequency of tool changes and downtime. However, carbide is more expensive than HSS and can be more challenging to manufacture and sharpen. Its brittleness can also lead to chipping or breaking under shock loads.
Impact on Application
Carbide is well-suited for machining hard materials and is commonly used in applications involving high-speed cutting. Its ability to maintain sharp edges for extended periods makes it a preferred choice in demanding environments.
Considerations for International Buyers
International buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, should be aware of the varying standards for carbide tools, including DIN and ISO specifications. Ensuring compliance with these standards can help in sourcing high-quality materials.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Machine Tool Parts?
Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it a popular choice for parts exposed to harsh environments. Its ability to withstand oxidation and rust makes it suitable for applications where moisture is a concern.
Pros and Cons of Stainless Steel
The main advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, which extends the lifespan of machine parts. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to machine due to its toughness. This can lead to increased manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application
Stainless steel is often used in parts that require both strength and corrosion resistance, such as fixtures and components in food processing or chemical industries. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, but its machining characteristics may require specialized tools.
Considerations for International Buyers
Buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia should consider the specific grades of stainless steel that meet local regulations and industry standards, such as ASTM A276. Understanding the environmental conditions where the parts will be used can also guide material selection.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Machine Tool Parts?
Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, making it an attractive option for machine tool parts that require reduced weight without sacrificing performance. Its good machinability and thermal conductivity are additional benefits.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low density, which can lead to reduced energy costs during transportation and operation. However, it is less durable than steel and may not be suitable for high-stress applications. Its susceptibility to corrosion can also be a concern unless properly treated.
Impact on Application
Aluminum is frequently used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace and automotive components. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, but considerations regarding strength and durability must be addressed.
Considerations for International Buyers
International buyers should be aware of the specific aluminum alloys that comply with local standards, such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe. Understanding the intended application and environmental conditions is essential for selecting the appropriate aluminum grade.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for machine tool parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel | Drills, end mills, taps | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Lower wear resistance than carbide | Low |
| Carbide | High-speed cutting tools | Exceptional hardness and durability | More expensive and brittle | High |
| Stainless Steel | Fixtures, components in harsh environments | Corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and machining complexity | Med |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive components | Lightweight and good machinability | Less durable and corrosion-prone | Med |
This guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions about material selection for machine tool parts based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machine tool parts
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Machine Tool Parts?
The manufacturing process for machine tool parts involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers ensure that their suppliers adhere to high standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Machine Tool Parts?
Material preparation is the foundational stage of manufacturing. It typically begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials such as high-speed steel, carbide, or cobalt, depending on the application requirements. The selected materials undergo processes like cutting, shearing, and machining to achieve the desired dimensions and specifications.
Furthermore, effective material preparation includes heat treatment processes, such as annealing or quenching, which enhance the mechanical properties of the material. This step is crucial for ensuring durability and resistance to wear, which are vital for machine tool parts that experience high stress during operation.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Machine Tool Parts Manufacturing?
Once materials are prepared, forming techniques come into play. Common methods include:
- CNC Machining: This technique utilizes computer numerical control to produce precise components. It allows for complex geometries and high repeatability, making it ideal for producing intricate parts like end mills and drill bits.
- Casting: In instances where shapes are complex, casting can be used. This involves pouring molten metal into a mold and allowing it to solidify, creating the required part shape.
- Forging: This process involves shaping the material under high pressure, which improves its structural integrity. Forged parts typically exhibit superior strength and are often used in critical applications.
Each technique has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the required tolerances, material characteristics, and production volume.
What Is Involved in the Assembly of Machine Tool Parts?
The assembly stage is where individual components are brought together to create the final product. This may involve:
- Joining Techniques: Techniques such as welding, riveting, or using adhesives are employed to connect various parts securely.
- Integration of Systems: For complex machinery, integrating electronic systems or hydraulic components may be necessary. This requires precise alignment and calibration to ensure optimal performance.
Proper assembly is critical, as any misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies or failures in the field.
How Are Machine Tool Parts Finished?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of machine tool parts. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing, plating, or coating protect parts from corrosion and wear, extending their lifespan.
- Grinding and Polishing: These techniques are employed to achieve fine tolerances and a smooth surface finish, which is crucial for components that require high precision.
The finishing stage not only improves the appearance of the parts but also enhances their performance characteristics.
What Quality Assurance Processes Are Relevant for Machine Tool Parts?
Quality assurance is vital in ensuring that machine tool parts meet international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with the following aspects of quality control.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Several international standards govern quality assurance in the manufacturing of machine tool parts. Among them, ISO 9001 is the most recognized, focusing on quality management systems. Compliance with this standard signifies that a manufacturer has established processes for consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, specific industries may require adherence to standards such as:
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold within the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for parts used in the oil and gas sector, ensuring that components meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
B2B buyers should verify their suppliers’ certifications to ensure compliance with these standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are critical in monitoring the manufacturing process and ensuring product quality. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing help identify any deviations from the required specifications, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all design specifications and quality standards.
By implementing these checkpoints, manufacturers can minimize defects and ensure reliability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality of machine tool parts, including:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers to verify that parts conform to specified dimensions.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle inspection detect internal flaws without damaging the parts.
- Functional Testing: This ensures that the parts perform as intended under operational conditions, often simulating real-world usage scenarios.
These testing methods help ensure that only high-quality components reach the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to mitigate risks associated with product quality. Here are several approaches:
What Role Do Audits Play in Supplier Quality Verification?
Conducting audits of suppliers is a proactive approach to assessing their quality control measures. Buyers can:
- Perform On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe processes firsthand and evaluate compliance with quality standards.
- Request Audit Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of previous audits conducted by third-party organizations, which can offer insights into their quality management practices.
Regular audits help build a trustworthy relationship and ensure ongoing compliance with quality standards.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services provides an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These services can:
- Conduct Random Inspections: Third-party inspectors can perform unannounced checks during various production stages, ensuring adherence to quality standards.
- Validate Testing Procedures: They can review and validate the testing methods employed by suppliers, ensuring that they align with industry best practices.
This additional layer of scrutiny helps buyers ensure that they are receiving quality products.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate specific quality control nuances:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations can help buyers tailor their quality assurance efforts effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should be aware of the regulatory landscape in their target markets, ensuring that suppliers comply with local laws and standards.
- Logistical Challenges: Coordinating inspections and audits across borders can present logistical challenges. Buyers should establish clear communication channels with suppliers to facilitate this process.
By addressing these nuances, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure that they receive high-quality machine tool parts.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machine tool parts’
To successfully procure machine tool parts, a structured approach is essential for ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers, helping you navigate the complexities of sourcing machine tool parts from international suppliers, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the precise technical specifications of the machine tool parts you need. This includes dimensions, materials, tolerances, and any specific performance requirements. Clear specifications help in communicating your needs to suppliers and ensure that the parts meet your operational standards.
- Consider compatibility with your existing machinery to avoid costly modifications later.
- Document your specifications in a detailed format to facilitate accurate quotations and comparisons from different suppliers.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Thorough market research is vital in identifying potential suppliers and understanding market trends. Look for suppliers with a solid reputation in the industry, especially those who specialize in machine tool parts.
- Review online platforms and industry forums to gather insights on suppliers’ performance and customer satisfaction.
- Attend trade shows or industry events where you can meet suppliers in person and evaluate their offerings.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
- Check for certifications such as ISO or industry-specific standards that demonstrate a commitment to quality.
- Inquire about their supply chain practices to ensure they can deliver on time and handle potential disruptions.
Step 4: Request Samples or Prototypes
Obtaining samples or prototypes allows you to assess the quality of the parts before making a bulk purchase. This step is especially important for critical components that impact your production processes.
- Evaluate the samples against your specifications for fit and function.
- Test for durability and performance under your operational conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate terms that protect your interests. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty provisions.
- Ensure clarity on lead times to avoid production delays.
- Discuss after-sales support and the process for handling defective parts or returns.
Step 6: Verify Logistics and Shipping Options
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of machine tool parts. Confirm the supplier’s shipping capabilities and ensure they can handle international logistics if sourcing from overseas.
- Understand the incoterms (International Commercial Terms) that will apply to your order.
- Evaluate shipping times and costs to ensure they align with your project timelines and budgets.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful supplier relationship. Establish a plan for regular updates on order status, potential issues, and feedback on received parts.
- Designate a contact person on both sides to streamline communication.
- Set up periodic reviews to discuss performance and any adjustments needed in future orders.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy for machine tool parts, ensuring they procure high-quality components that support their production needs while maintaining cost efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machine tool parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machine Tool Parts Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of machine tool parts is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. Common materials include high-speed steel, carbide, and cobalt, each varying in price based on quality and availability. Premium materials often lead to longer tool life and better performance, justifying higher upfront costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in manufacturing and assembly. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to consider the potential impact on quality and service.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead, thus lowering prices.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs relate to the equipment and molds needed to manufacture parts. High-quality tooling can reduce defects and enhance production efficiency, which may lead to cost savings in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that parts meet required specifications, which can prevent costly rework and delays. The investment in QC is often reflected in higher prices but can save buyers from future complications.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary significantly based on geographical location, shipping methods, and the volume of the order. Understanding Incoterms is vital to determining who bears these costs and responsibilities.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on market competition and the supplier’s positioning.
What Influences Pricing in Machine Tool Parts?
Several factors can influence pricing for machine tool parts, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts tailored to specific requirements may incur higher costs due to the additional labor and materials involved. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. High-performance materials may have higher costs but can provide better durability and efficiency.
-
Quality Certifications: Parts that meet international quality standards may come at a premium. Certification can assure buyers of the product’s reliability, particularly in critical applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service level can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while emerging suppliers may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of various Incoterms can help buyers manage costs effectively. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who is responsible for shipping costs and risks.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Prices and Ensuring Cost Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are several actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms, especially if you’re placing large orders. Discuss bulk pricing, payment terms, and potential discounts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational efficiency, and the lifespan of parts. A slightly higher initial cost may lead to lower TCO if it results in fewer replacements or repairs.
-
Research Market Prices: Understanding the market landscape can provide leverage in negotiations. Compare prices across multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
-
Clarify Quality Expectations: Clearly communicate quality expectations upfront to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to disputes or additional costs later.
-
Stay Informed About International Pricing Nuances: Be aware of tariffs, taxes, and currency fluctuations that can affect costs. Local regulations in your region may also impact pricing structures.
Conclusion
The landscape of machine tool parts sourcing is complex, with various cost components and pricing influencers. By understanding these elements and employing effective negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machine tool parts With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Machine Tool Parts
In the realm of manufacturing, machine tool parts are essential for maintaining precision and efficiency. However, alternative solutions can sometimes offer similar benefits, depending on the specific requirements of a business. This section will compare machine tool parts with two viable alternatives: 3D printing of components and CNC machining services. Understanding these alternatives will help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Machine Tool Parts | 3D Printing Components | CNC Machining Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and durability | Variable; dependent on printer quality | High precision and consistent results |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Lower initial cost, but may vary with volume | Generally higher due to setup and labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires knowledge of parts and sourcing | Relatively easy; designs can be uploaded directly | More complex; requires design specifications and setup time |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to ensure performance | Minimal maintenance once printed | Regular maintenance required; can be costly |
| Best Use Case | Replacement or enhancement of existing machines | Prototyping and low-volume production | High-volume production with complex designs |
What Are the Pros and Cons of 3D Printing Components?
3D printing technology has gained traction for its ability to produce complex geometries with relative ease. One of its significant advantages is the lower initial cost, especially for low-volume production runs. Additionally, the rapid prototyping capabilities allow manufacturers to iterate designs quickly. However, the performance can be inconsistent based on the printer’s quality and the materials used. For instance, while some 3D printed components may suffice for prototyping, they may not offer the durability required for heavy-duty applications.
How Do CNC Machining Services Compare?
CNC machining services provide an alternative that excels in precision and repeatability. This method involves using computer-controlled tools to create parts from various materials, ensuring high-quality outcomes. CNC machining is particularly beneficial for high-volume production runs where consistency is critical. However, it generally comes with a higher cost due to setup and labor. Moreover, the implementation process can be more complex, requiring detailed design specifications and technical knowledge. Regular maintenance is also necessary, which can add to operational costs over time.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When choosing between machine tool parts and alternative solutions like 3D printing or CNC machining, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and production volume. If precision and durability are paramount, machine tool parts remain a robust choice. However, for businesses focused on rapid prototyping or with lower production needs, 3D printing may be more suitable. Conversely, CNC machining services could be ideal for those requiring high-volume production with complex designs. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the unique requirements of the business and its long-term goals in the manufacturing landscape.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machine tool parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machine Tool Parts?
When evaluating machine tool parts, understanding their technical specifications is critical for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type and quality of material used in the manufacturing of machine tool parts. Common materials include High-Speed Steel (HSS), Carbide, and Cobalt. The choice of material affects the durability, cutting efficiency, and cost of the tool. For instance, carbide tools are more expensive but offer superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-performance applications. B2B buyers must assess the material grade based on the intended application to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. It is crucial for ensuring that machine parts fit together correctly and function as intended. Tight tolerances are essential in precision machining, where even minor deviations can lead to significant operational issues. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers select parts that meet their specific manufacturing requirements, ultimately impacting the quality of the final product.
3. Hardness
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation, typically assessed using scales such as Rockwell or Brinell. In the context of machine tools, hardness is vital for determining the tool’s ability to maintain sharpness and withstand wear over time. Tools with higher hardness ratings can perform better in demanding applications, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime. B2B buyers should consider hardness ratings when evaluating tools for specific machining tasks.
4. Coating Type
Coating types, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN), enhance the performance of cutting tools by reducing friction and improving wear resistance. Coatings can also increase the tool’s thermal stability, making it suitable for high-speed machining operations. For B2B buyers, selecting the right coating can significantly impact tool life and overall machining efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Machine Tool Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the machine tool industry, purchasing OEM parts ensures compatibility and reliability, as these parts are designed to meet the original specifications of the machinery. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts to avoid issues related to quality and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Buyers must balance their needs with the supplier’s requirements to optimize their purchasing strategy.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. This document outlines the buyer’s requirements, allowing suppliers to provide accurate and competitive quotes. Utilizing RFQs helps buyers compare options and negotiate better deals.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the delivery of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, especially in international trade, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks at various stages of the shipping process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers to plan production schedules effectively. Longer lead times can impact project timelines and inventory levels, making it essential to consider this factor when selecting suppliers.
Conclusion
Understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology associated with machine tool parts empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality. By focusing on material grades, tolerances, hardness, coating types, and familiarizing themselves with industry-specific terms, buyers can optimize their procurement strategies and foster successful supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machine tool parts Sector
What Are the Key Trends Affecting the Machine Tool Parts Market Globally?
The machine tool parts sector is experiencing transformative changes driven by several global dynamics. The ongoing digital revolution is reshaping sourcing trends, with an increasing emphasis on automation and Industry 4.0 technologies. This shift is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where demand for advanced manufacturing capabilities is rising. Countries such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in modernizing their manufacturing sectors, which necessitates a reliable supply of high-quality machine tool parts.
Moreover, the trend towards just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing is compelling buyers to seek suppliers who can provide rapid delivery and flexible inventory solutions. Buyers are also leveraging data analytics and supply chain management software to optimize their procurement processes, ensuring they can respond swiftly to market fluctuations. The integration of e-commerce platforms is enabling smoother transactions, making it easier for buyers to access a diverse range of products and suppliers globally.
In addition, sustainability is emerging as a pivotal consideration, with more companies prioritizing eco-friendly practices in their sourcing strategies. This shift is not only a response to consumer demand but also a regulatory necessity in many regions. As international buyers navigate these market dynamics, they must remain agile and informed, aligning their sourcing strategies with the latest technological advancements and sustainability standards.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing B2B Decisions in Machine Tool Parts?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming integral to the procurement strategies of B2B buyers in the machine tool parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek parts that are produced with minimal ecological footprints. This includes the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient production methods, and waste-reduction initiatives. Buyers are increasingly demanding transparency in the supply chain to ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical practices.
The importance of certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for sustainable building practices, is also on the rise. These certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also align with consumer expectations for corporate responsibility. Additionally, many manufacturers are exploring partnerships with suppliers who can provide green materials and sustainable components, which can lead to competitive advantages in the marketplace.
For B2B buyers, embracing sustainability not only meets regulatory requirements but also caters to an evolving consumer base that prioritizes responsible sourcing. As a result, companies that proactively adopt ethical sourcing practices can differentiate themselves, build customer loyalty, and position themselves as leaders in a rapidly changing industry.
What Is the Historical Context of the Machine Tool Parts Industry?
The machine tool parts industry has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from manual craftsmanship to highly automated production processes. The early 20th century marked the rise of mass production techniques, which allowed manufacturers to produce machine tools at scale, leading to a surge in demand for high-quality replacement parts. Post-World War II, advancements in materials science and precision engineering further transformed the sector, enabling the production of more durable and efficient machine components.
The advent of computer numerical control (CNC) technology in the late 20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for unprecedented levels of accuracy and customization. This evolution has paved the way for today’s sophisticated manufacturing ecosystems, where digital technologies and data analytics play crucial roles. As the industry continues to adapt to the demands of a globalized economy, the focus on innovation, quality, and sustainability remains paramount, shaping the future landscape for international B2B buyers in the machine tool parts sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machine tool parts
-
How do I solve supply chain disruptions when sourcing machine tool parts?
Supply chain disruptions can be mitigated by diversifying your supplier base and establishing relationships with multiple vendors across different regions. Implementing a robust inventory management system allows you to forecast demand accurately and maintain stock levels. Additionally, consider engaging suppliers who offer quick-ship options and have local warehouses to ensure timely delivery. Regular communication with your suppliers about potential delays and changes in lead times is essential for proactive problem-solving. -
What is the best type of machine tool part for precision machining?
For precision machining, high-speed steel (HSS) and carbide cutting tools are often recommended. HSS is versatile and cost-effective for a range of materials, while carbide tools provide superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-volume production. Depending on the specific application, you may also want to consider specialized tools such as coated inserts for enhanced performance. Always consult with your supplier to match the tool type with your machining requirements. -
How can I ensure quality when purchasing machine tool parts internationally?
To ensure quality, start by vetting suppliers through their certifications (like ISO 9001) and customer reviews. Request samples before placing bulk orders to evaluate the quality of materials and workmanship. Establish clear quality assurance standards and communicate them with your supplier. Additionally, consider using third-party inspection services to verify compliance with your quality requirements before shipment. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for machine tool parts?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, production capacity, and quality control processes. Investigate their financial stability and reputation in the market by checking references and reviews. It’s also crucial to assess their ability to meet your specific customization needs and delivery timelines. Engaging in direct communication can reveal their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate, which are important for long-term partnerships. -
What are typical payment terms for international purchases of machine tool parts?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common options include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Depending on your relationship with the supplier, you may negotiate terms that suit both parties. Ensure that payment methods are secure and protect against fraud, especially for international transactions. Always clarify the currency of payment and any additional fees associated with currency conversion. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machine tool parts?
The MOQ for machine tool parts often depends on the supplier and the type of parts being ordered. Some suppliers may have a low MOQ for standard items, while custom parts may require larger orders to justify production costs. Discussing your specific needs with the supplier can lead to more flexible arrangements. It’s advisable to consolidate orders to meet MOQ requirements, especially if you are working with multiple suppliers. -
How can I manage logistics effectively for international shipments of machine tool parts?
Effective logistics management involves selecting reliable freight forwarders who understand international shipping regulations and customs procedures. Utilize tracking systems to monitor shipments in real-time and establish clear communication with your suppliers regarding shipping schedules. Consider using incoterms to clarify responsibilities for shipping costs and risks. Proper documentation is crucial; ensure all customs paperwork is accurate to avoid delays. -
What should I do if I encounter issues with machine tool parts after delivery?
If issues arise post-delivery, promptly contact your supplier to report the problem and request support. Document the issue with photos and detailed descriptions to assist in troubleshooting. Most reputable suppliers will have customer service teams to handle complaints and may offer solutions such as replacements or refunds. Familiarize yourself with the warranty policies of your supplier to understand your rights and responsibilities in these situations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Machine Tool Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Machine Tool Products – Essential Machinery Solutions
Domain: machinetoolproducts.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: All Machine Parts Products include: 1. Additive Machinery: Industrial 3D Printers, Print Accessories. 2. CNC Retrofit Kits: Milling Machine CNC Retrofit Kits, Lathe CNC Retrofit Kits, Turnkey CNC Retrofit Solutions. 3. Collaborative Robots: Automation Solutions, Cobot Arms, Cobot End-of-Arm Tools. 4. Digital Readouts: DRO Displays, DRO Kits, DRO Scales, Digital Readout Parts & Accessories. 5. Powe…
2. Little Machine Shop – Tooling & Accessories
Domain: littlemachineshop.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Little Machine Shop – Tooling & Accessories, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Summit Machine Tool – Metal Lathes & CNC Machines
Domain: summitmt.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Summit Machine Tool offers a wide range of machine tools including: 14″ to 100″ Metal Lathes, CNC Lathes, Vertical Knee Mills, Horizontal Milling Machines, Vertical Bed Mills, Horizontal Boring Mills, and Radial Drills. They provide a dedicated parts team with a million dollar inventory of machine tool supplies, lathe parts, and accessories for quick shipping. Services include machine tool install…
4. Methods Machine – CNC Tool Parts and Accessories
Domain: methodsmachine.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: CNC Machine Tool Parts and Accessories: Order best-in-class machine parts and accessories that maintain and enhance CNC machining equipment for improved accuracy, productivity, and ROI. Quality components designed to maximize productivity, profitability, and lifespan. Tooling solutions include: workholding (power chucks, collet chucks, jaws, adapter plates, tombstones, vises), driven and static to…
5. H&W Machine Repair – Bridgeport Parts
Domain: machinerypartsdepot.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: H&W Machine Repair & Rebuilding offers a wide range of machine replacement parts and services, specializing in Bridgeport machines. Key product categories include:
– Machine Parts: Bridgeport Parts (Series I & II), Sharp Parts, Import 3VK/3VS Parts.
– Accessories: Milling Machine Accessories, Power Drawbar Systems, Digital Readout Systems (ACU-Rite, Mitutoyo, Newall, Fagor).
– Rebuild Kits: Milli…
6. Productivity Inc. – CNC Machine Tools & Equipment
Domain: productivity.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: Productivity Inc. is a supplier of metalworking CNC machine tools and equipment, offering a range of products and services since 1968. Key offerings include: CNC Machine Tools (new and used), Fabrication Equipment, Machine Parts, Tooling & Industrial Supplies, Automation & Robotics (including RoboFlex™ systems and FANUC robots), and various services such as machine service and repair, preventive m…
7. Best Pack – PLATE, SBLT REAR MOUNT (R)
Domain: machinepartstoolbox.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Best Pack – PLATE, SBLT REAR MOUNT (R) – D2124001, Price: $119.49; Dekka – Plastic Cap, Tape Mandrel Assembly – # 29-333, Original Price: $9.25, Special Price: $8.79; X-Rite – Seal Pad 42″, 706, 710 070055 – # 710-104, Original Price: $12.00, Special Price: $11.40; X-Rite – Seal Wire 706, 710 – 710-173, Original Price: $17.00, Special Price: $16.15; X-Rite – Seal Wire Spring – # 76-50, Original Pr…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machine tool parts
In the ever-evolving landscape of machine tool parts, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging a comprehensive sourcing strategy, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of their machinery. The emphasis on high-quality components, such as cutting tools and replacement parts, is essential for maintaining competitive advantage in a global market.
Investing in reliable suppliers with robust inventories ensures quick access to essential parts, safeguarding production levels and minimizing disruptions. Moreover, developing partnerships with manufacturers that offer technical support and service capabilities can further enhance your sourcing strategy, providing invaluable assistance in troubleshooting and maintenance.
Looking forward, the demand for precision and efficiency in machining processes is set to grow. As an international buyer, now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and explore innovative solutions that align with your business goals. Take proactive steps to engage with trusted suppliers and optimize your procurement processes, ensuring that your operations remain agile and resilient in the face of future challenges.