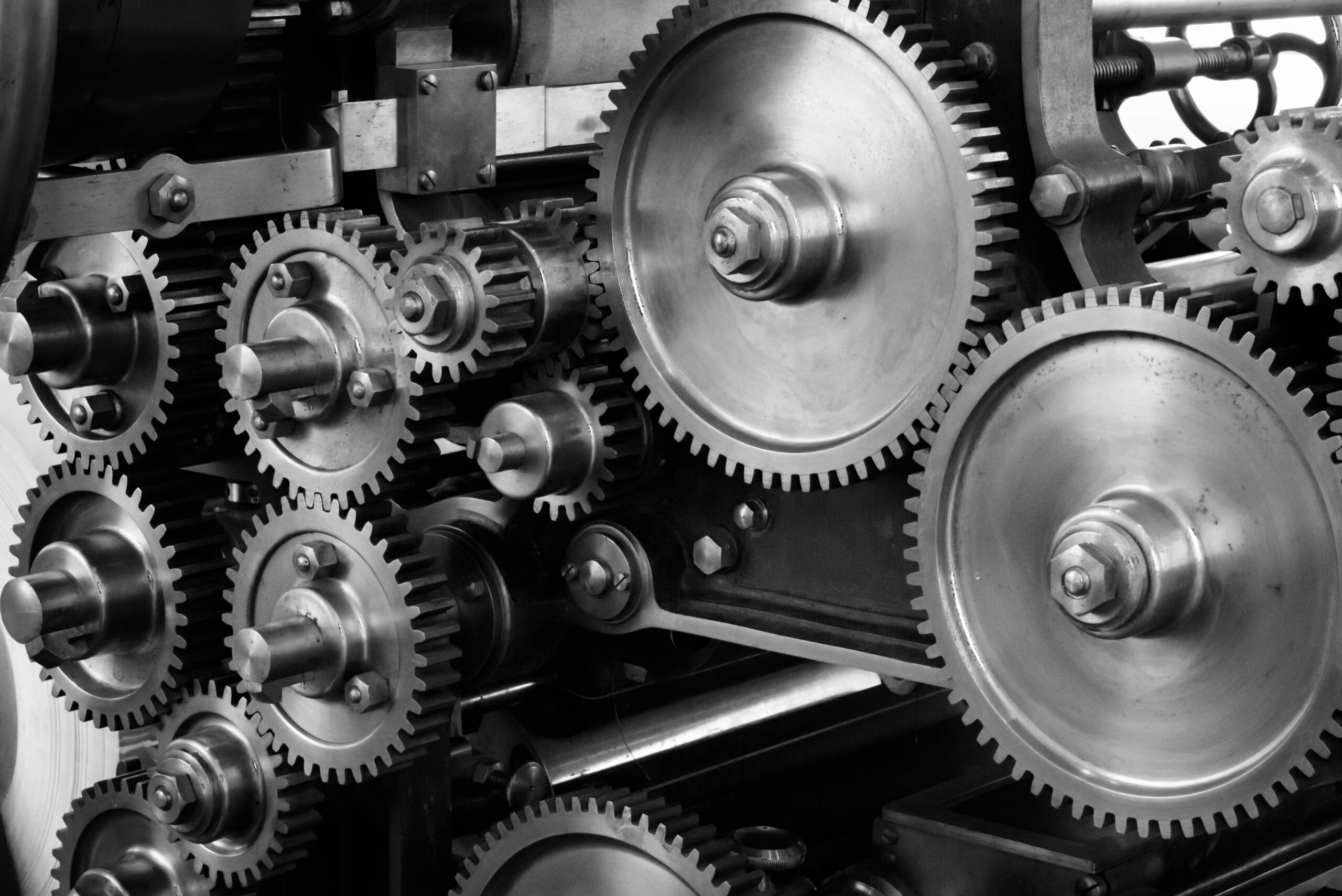
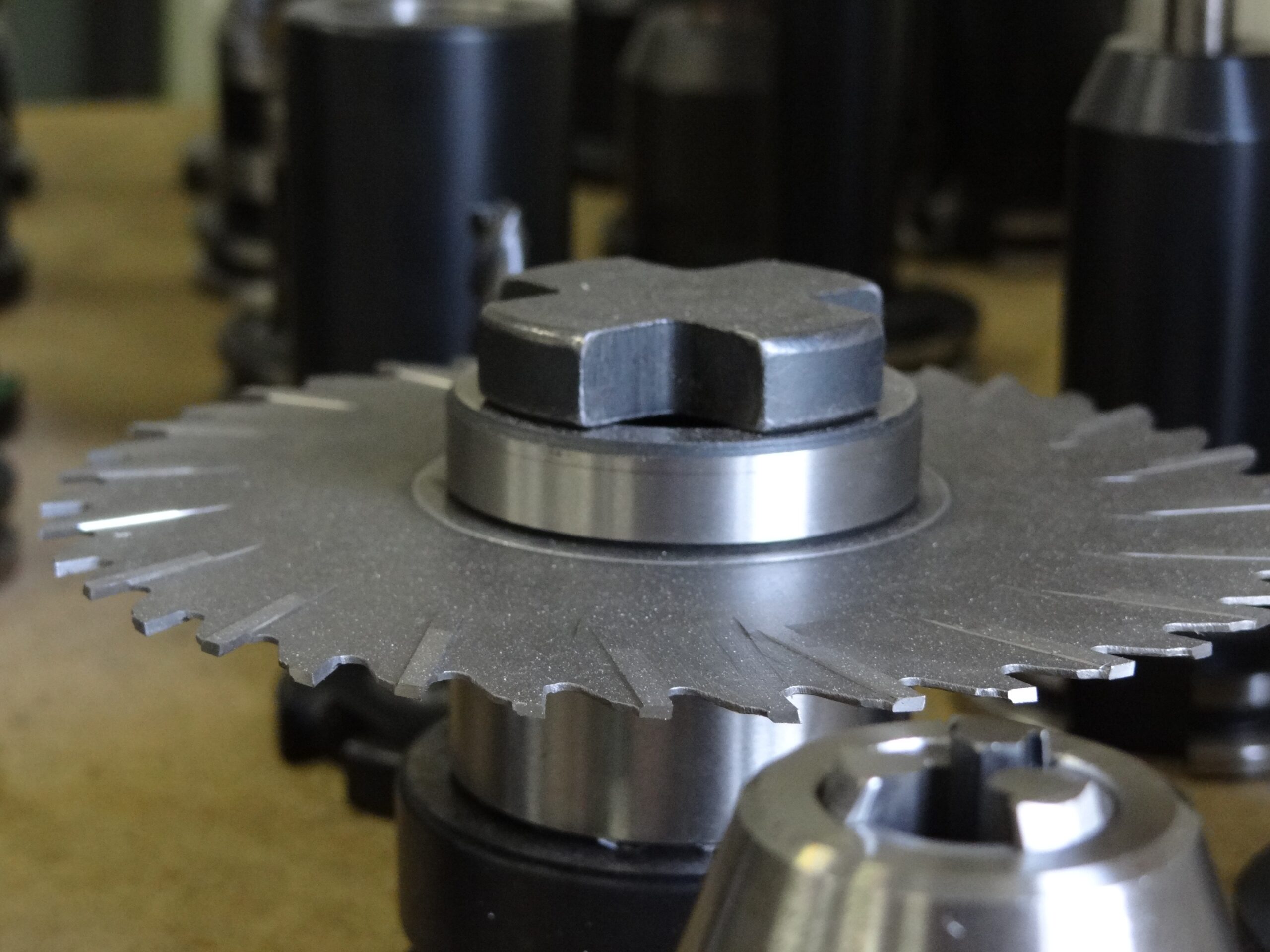
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machine tool gear
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality machine tool gear can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating across diverse international markets. The intricacies involved in selecting the right gears—considering factors such as precision, durability, and compatibility with existing machinery—can significantly impact operational efficiency and product quality. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the global market for machine tool gear by exploring various types, applications, and key considerations for effective sourcing.
Throughout this guide, readers will gain insights into the different gear types, including spur, helical, and bevel gears, alongside their specific applications in industries ranging from manufacturing to aerospace. We will delve into critical aspects of supplier vetting, highlighting the importance of assessing quality certifications, technological capabilities, and service offerings. Additionally, the guide will provide an overview of cost considerations, enabling informed financial planning.
By equipping international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Vietnam and established economies like Saudi Arabia—with actionable knowledge, this guide empowers them to make strategic purchasing decisions. Understanding the nuances of machine tool gear procurement not only enhances operational performance but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers, ensuring sustained growth in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Understanding machine tool gear Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spur Gears | Straight teeth, parallel to the axis of rotation. | General machinery, conveyors, and pumps. | Pros: Simple design, easy to manufacture. Cons: Noisy at high speeds, limited load capacity. |
| Helical Gears | Teeth cut at an angle, allowing for smoother operation. | Automotive, industrial gearboxes, and milling machines. | Pros: Quieter operation, higher load capacity. Cons: More complex design, requires precise alignment. |
| Bevel Gears | Cone-shaped gears that transmit power between shafts at an angle. | Gearboxes, differential systems, and machine tools. | Pros: Effective for changing shaft direction. Cons: Complex manufacturing process, requires precise installation. |
| Worm Gears | Gear with a screw-like thread that meshes with a worm wheel. | Lifts, conveyor systems, and tuning instruments. | Pros: High torque output, compact design. Cons: Lower efficiency, can generate heat at high speeds. |
| Rack and Pinion | Converts rotational motion into linear motion using a gear (pinion) and a linear bar (rack). | Steering systems, CNC machines, and automation equipment. | Pros: Simple design, allows for precise linear movement. Cons: Limited to specific applications, wear can occur over time. |
What Are Spur Gears and Their B2B Applications?
Spur gears are characterized by their straight teeth, which run parallel to the axis of rotation. They are widely used in various industrial applications, including conveyors, pumps, and general machinery. Their straightforward design makes them easy to manufacture, making them a cost-effective choice for many businesses. However, they can be noisy at high speeds and have a limited load capacity, which may be a consideration for buyers looking for high-performance applications.
How Do Helical Gears Enhance Machinery Performance?
Helical gears feature teeth that are cut at an angle, allowing for smoother engagement and operation compared to spur gears. This design is particularly beneficial in automotive applications, industrial gearboxes, and milling machines, where reduced noise and increased load capacity are essential. While they provide significant advantages in performance, their more complex design necessitates precise alignment, which can increase installation costs for buyers.
What Makes Bevel Gears Ideal for Direction Changes?
Bevel gears are conical in shape and are designed to transmit power between shafts that are typically at right angles to each other. They are commonly used in gearboxes, differential systems, and machine tools. The primary advantage of bevel gears is their effectiveness in changing the direction of power transmission. However, they can be more complex to manufacture and require precise installation, which may affect procurement decisions for businesses focused on reliability.
Why Choose Worm Gears for High Torque Applications?
Worm gears consist of a screw-like thread that meshes with a worm wheel, providing high torque output in a compact design. They are often used in lifts, conveyor systems, and tuning instruments, where space constraints and torque requirements are critical. While worm gears offer significant advantages in terms of torque, they tend to have lower efficiency and can generate heat at higher speeds, which buyers should consider when evaluating their options.
How Do Rack and Pinion Gears Facilitate Linear Motion?
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion through the interaction of a circular gear (pinion) and a linear bar (rack). This mechanism is widely utilized in steering systems, CNC machines, and automation equipment. Their simplicity and effectiveness in providing precise linear movement make them an attractive option for many applications. However, their usage is somewhat limited to specific applications, and wear over time can lead to performance issues, which buyers must take into account.
Key Industrial Applications of machine tool gear
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machine tool gear | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Gear hobbing for transmission systems | Enhanced precision in gear shaping, leading to improved vehicle performance and reliability | Quality certifications, precision tolerances, and lead times |
| Aerospace | Custom gear fabrication for aircraft systems | High-strength, lightweight gears that meet stringent safety standards | Compliance with aerospace regulations, material specifications, and testing protocols |
| Industrial Machinery | Gear grinding for heavy machinery | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime due to high-quality gear performance | Availability of aftermarket support, customization options, and maintenance services |
| Renewable Energy | Gears for wind turbine applications | Improved energy efficiency and durability under harsh conditions | Supplier reliability, material durability, and performance history |
| Oil & Gas | Gearboxes for drilling equipment | Enhanced reliability and performance in extreme environments | Certifications for hazardous environments, lead times, and custom engineering capabilities |
How is Machine Tool Gear Utilized in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, machine tool gears are critical for the precise manufacturing of transmission systems. Gear hobbing processes allow manufacturers to produce gears that are essential for vehicle performance and durability. The precision of these gears directly impacts fuel efficiency and overall vehicle reliability. International buyers from regions like Africa and South America should prioritize suppliers that offer quality certifications and can meet specific tolerances to ensure optimal performance.
What Role Does Machine Tool Gear Play in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace manufacturing, custom gears are fabricated to meet the strict safety and performance standards required for aircraft systems. The use of lightweight yet high-strength gears is essential in reducing overall aircraft weight while maintaining structural integrity. Suppliers must comply with aerospace regulations and provide detailed material specifications and testing protocols to ensure safety and reliability in flight operations, which is crucial for buyers in the Middle East and Europe.
How Does Machine Tool Gear Improve Industrial Machinery Efficiency?
Machine tool gears are pivotal in the grinding processes for heavy industrial machinery. By ensuring high-quality gear performance, manufacturers can achieve significant operational efficiency and reduce downtime. For buyers in various regions, it is essential to consider the availability of aftermarket support and customization options, as these factors can greatly influence the longevity and reliability of the machinery.
Why Are Gears Important in Renewable Energy Applications?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly wind energy, machine tool gears are utilized in turbine applications to enhance energy efficiency and durability. These gears must withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining performance. When sourcing, international buyers should focus on the supplier’s reliability and the durability of materials used, as these aspects are vital for long-term operational success.
What Are the Sourcing Considerations for Gears in Oil & Gas Industries?
In the oil and gas industry, machine tool gears are integral to the functionality of drilling equipment. High-performance gearboxes ensure reliability in extreme conditions, which is critical for operational success. Buyers must consider suppliers that have certifications for hazardous environments, as well as those that can provide custom engineering capabilities to meet specific project requirements and timelines.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machine tool gear’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing Gear Precision and Tolerances in Production
The Problem:
In industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing, B2B buyers often encounter challenges with maintaining the required tolerances in machine tool gears. Inaccurate gears can lead to inefficient operations, increased wear on machinery, and ultimately, costly production delays. Buyers may struggle with sourcing gears that not only meet the specified tolerances but also maintain performance under varying operational conditions. This is especially critical in regions with diverse manufacturing capabilities, where the availability of high-precision components can be inconsistent.
The Solution:
To address these precision issues, buyers should prioritize working with manufacturers who specialize in high-quality custom gears. It is essential to conduct a thorough assessment of potential suppliers by reviewing their quality control processes, certifications, and previous client testimonials. When specifying gears, buyers should provide detailed information regarding the operational environment and the specific tolerances required. Engaging in a dialogue with suppliers about the expected load conditions and any potential environmental factors (like temperature fluctuations or humidity) can lead to tailored solutions that enhance gear performance. Additionally, considering manufacturers that offer gear audits and failure analysis can provide insights into improving existing setups, ensuring that new gears are not only precise but also reliable under real-world conditions.
Scenario 2: Reducing Downtime Due to Gear Failures
The Problem:
Unexpected gear failures can lead to significant downtime in production lines, causing financial strain and disrupting supply chains. B2B buyers may face challenges in identifying the root causes of these failures, which could stem from inadequate maintenance, poor-quality materials, or misalignment during installation. This scenario is particularly prevalent in sectors where machinery operates continuously, and the cost of halted operations can be devastating.
The Solution:
Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy can greatly reduce the likelihood of unexpected gear failures. Buyers should invest in comprehensive training programs for their maintenance teams, focusing on proper installation techniques, routine inspections, and preventive maintenance schedules. Partnering with suppliers that offer technical support, including installation guidance and alignment services, can also be beneficial. Additionally, utilizing condition monitoring technologies, such as vibration analysis or thermal imaging, can provide real-time insights into the health of gear systems. By adopting a holistic approach to maintenance, buyers can enhance the longevity of their machine tool gears and minimize costly downtime.
Scenario 3: Navigating Supply Chain Challenges for Gear Components
The Problem:
B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa and South America, often face supply chain disruptions that affect their ability to source machine tool gears. Issues such as fluctuating prices, inconsistent lead times, and geopolitical factors can complicate procurement processes. Buyers may find it difficult to maintain a steady supply of high-quality gears, which can impact production schedules and overall operational efficiency.
The Solution:
To mitigate supply chain challenges, buyers should consider diversifying their supplier base to include both local and international manufacturers. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can help create a buffer against disruptions. Buyers should also engage in strategic planning by forecasting demand and placing orders well in advance, allowing for any potential delays in shipping or production. Additionally, implementing a just-in-time inventory system can optimize stock levels and reduce holding costs. Collaborating with suppliers who have robust logistics capabilities and a proven track record in international shipping can further enhance reliability. By taking these proactive steps, buyers can navigate supply chain complexities more effectively and ensure a consistent flow of necessary components.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machine tool gear
What Are the Key Materials Used in Machine Tool Gears?
When selecting materials for machine tool gears, several factors come into play, including performance characteristics, cost, and manufacturing complexity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the production of machine tool gears: steel, aluminum, brass, and plastic composites. Each material has distinct advantages and limitations that can impact the overall performance of the gear systems.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Machine Tool Gears?
Steel is the most widely used material for machine tool gears due to its excellent strength and durability. Key properties of steel include high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is often used in heavy-duty applications where high load-bearing capacity is essential.
Pros: Steel gears exhibit exceptional durability and can handle high torque loads. They also have good machinability, allowing for complex gear shapes and designs.
Cons: The primary drawbacks of steel are its weight and susceptibility to corrosion, which can be mitigated through surface treatments. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, particularly for high-precision applications.
Impact on Application: Steel gears are compatible with a wide range of media and are suitable for high-performance applications in various industries, including automotive and aerospace.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing steel that meets these standards may require careful supplier evaluation.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Machine Tool Gear Production?
Aluminum is increasingly being used for machine tool gears due to its lightweight properties and good corrosion resistance. It is particularly advantageous in applications where weight reduction is critical.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum gears is their lightweight nature, which can lead to reduced energy consumption and improved efficiency in machines. They also resist corrosion, making them suitable for humid or chemically aggressive environments.
Cons: However, aluminum gears typically have lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit their use in high-load applications. They can also be more expensive to manufacture due to the need for specialized machining techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum gears are ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in aerospace and portable machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum gears comply with relevant standards such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe. Additionally, understanding the local supply chain for aluminum can be crucial in regions like the Middle East.
How Does Brass Compare as a Material for Machine Tool Gears?
Brass is known for its excellent machinability and good corrosion resistance, making it a suitable choice for specific gear applications, particularly in low-load environments.
Pros: Brass gears are easy to machine and can be produced with high precision. They also exhibit good wear resistance and are less prone to galling, making them suitable for applications with frequent movement.
Cons: The limitations of brass include lower strength compared to steel and aluminum, which restricts its use in high-torque applications. Additionally, brass can be more expensive than steel, affecting cost-effectiveness.
Impact on Application: Brass gears are often used in applications like small machinery, where precision and corrosion resistance are more critical than high load-bearing capacity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the alloy composition of brass to ensure compliance with local regulations. In Europe, for example, certain brass alloys may be restricted due to environmental regulations.
What Are the Advantages of Plastic Composites in Machine Tool Gears?
Plastic composites are becoming increasingly popular in machine tool gear applications due to their lightweight and versatile properties. These materials can be engineered to meet specific performance needs.
Pros: Plastic composite gears are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can operate quietly, reducing noise levels in machinery. They can also be manufactured in complex shapes with relative ease.
Cons: However, plastic composites generally have lower strength and wear resistance compared to metals, which may limit their use in high-load or high-temperature applications. They can also be sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
Impact on Application: These gears are suitable for applications where noise reduction and weight savings are essential, such as in consumer electronics and small machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic composites meet relevant international standards and are suitable for the specific environmental conditions of their region.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Machine Tool Gears
| Material | Typical Use Case for machine tool gear | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Exceptional strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and portable machinery | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength than steel | Medium |
| Brass | Small machinery and precision gears | Excellent machinability and wear resistance | Lower strength than steel and aluminum | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Consumer electronics and small machinery | Lightweight and quiet operation | Lower strength and wear resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide aims to empower international B2B buyers with actionable insights into the materials best suited for their machine tool gear applications, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machine tool gear
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Machine Tool Gears?
Manufacturing machine tool gears involves a series of critical stages that ensure precision and performance. The typical process can be broken down into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting the right materials, which can include various grades of steel, aluminum, or specialized alloys. These materials are then cut to size, often using advanced laser cutting or water jet cutting technologies to ensure accuracy. Material properties such as hardness and tensile strength are crucial, as they directly affect the gear’s performance and durability.
Forming Techniques
Forming is where the raw material begins to take shape. Techniques such as forging, casting, or machining are employed depending on the required specifications. For high-precision gears, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is commonly used, allowing for intricate designs and tight tolerances. Gear hobbing and shaping are also prevalent methods, particularly for producing complex tooth profiles.
Assembly Process
Once the components are formed, they undergo an assembly process, which may involve fitting together multiple gear parts. This stage is critical, as any misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies. Advanced technologies like robotic assembly can enhance precision and speed, particularly in high-volume production settings.
Finishing Techniques
The final stage involves various finishing processes that enhance the gears’ surface quality and performance characteristics. Techniques such as grinding, honing, and surface hardening are often used to achieve the desired finish. The choice of finishing technique can significantly affect the gear’s wear resistance, noise levels, and overall lifespan.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Machine Tool Gear Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that machine tool gears meet international standards and customer expectations. A robust QA system encompasses various international standards, industry-specific certifications, and multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas sectors ensure compliance with stringent safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection verifies that raw materials meet predefined specifications before production begins. Materials that do not meet the criteria are rejected or sent back to suppliers.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to ensure that components are being produced to the correct specifications. This can include dimensional checks and functional tests at various stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs before the gears are shipped to customers. This step often includes comprehensive testing, such as load testing, noise testing, and dimensional checks, to ensure all components meet quality standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Machine Tool Gears?
Several testing methods are utilized to verify the quality and performance of machine tool gears. These methods can include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing precision measuring tools to ensure that gears meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
-
Material Testing: Techniques like hardness testing, tensile testing, and metallographic examination ensure that the materials used are suitable for their intended application.
-
Functional Testing: This involves running gears under load to evaluate performance characteristics such as noise, vibration, and thermal behavior.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods like ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection are employed to detect internal flaws without damaging the gear.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
What Are the Best Practices for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers should look for:
-
Documentation of Quality Control Processes: Suppliers should provide clear documentation of their QA processes, including ISO certifications and test results.
-
Site Visits: If feasible, visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe the QA practices firsthand and engage directly with the production team.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Enlisting independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and adherence to quality standards.
How Do Quality Reports Play a Role?
Requesting regular quality reports can help buyers stay informed about any issues or trends in production quality. These reports should detail inspection results, non-conformities, and corrective actions taken, providing insight into the supplier’s commitment to maintaining high standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges regarding quality control and certification due to varying standards across different regions. Understanding these nuances is critical for successful procurement.
Navigating Regional Standards
Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific standards and certifications required in their target markets. For example, CE marking is essential for products sold within the European Union, while other regions may prioritize different certifications.
Cultural Considerations
Cultural differences may also impact communication and expectations regarding quality. Establishing clear lines of communication and setting mutual expectations can mitigate misunderstandings and ensure smoother transactions.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for machine tool gears is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the stages of manufacturing, implementing rigorous quality control measures, utilizing various testing methods, and verifying supplier capabilities, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality components that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machine tool gear’
When sourcing machine tool gears, it’s essential to follow a structured approach to ensure that you select the best products for your operational needs. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist that will help international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procurement, from defining requirements to evaluating potential suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of successful gear procurement. This includes understanding the type of gear (e.g., spur, helical, bevel), size, material, and load capacity required for your machines. Precise specifications will help you communicate your needs effectively and avoid costly mistakes later in the process.
- Identify performance requirements: Consider factors such as speed, torque, and durability.
- Assess compatibility: Ensure the gears will fit and function correctly with your existing machinery.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in machine tool gears. Look for companies with a proven track record, quality certifications, and extensive product offerings that match your specifications. Supplier reputation can greatly impact your production efficiency.
- Utilize online resources: Explore supplier websites, industry forums, and trade publications.
- Seek recommendations: Consult industry peers and trade associations for reliable supplier referrals.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before making a commitment, it’s vital to assess the capabilities of potential suppliers. This includes their manufacturing processes, technology, and quality control measures. A capable supplier will not only meet your requirements but also provide ongoing support.
- Inquire about machinery: Ensure they have advanced gear cutting and inspection machines to maintain high precision.
- Request case studies: Ask for examples of similar projects they have completed successfully.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Standards
Ensuring that suppliers meet industry standards and hold relevant certifications is crucial for quality assurance. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems.
- Check compliance: Ensure the gears meet any specific industry standards relevant to your application.
- Ask for documentation: Request copies of certifications and quality assurance processes.
Step 5: Request Samples and Quotes
Once you have narrowed down your suppliers, request samples of the gears to evaluate their quality and compatibility with your machinery. Additionally, obtain detailed quotes to understand pricing structures and terms of service.
- Evaluate quality: Testing samples can reveal important information about performance and durability.
- Compare quotes: Look beyond price to consider factors such as lead time, shipping costs, and warranty terms.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
After-sales support can significantly impact your operational efficiency. Assess the level of technical assistance, warranty provisions, and availability of spare parts that suppliers offer. Reliable support can minimize downtime and enhance productivity.
- Inquire about training: Check if suppliers provide training for your staff on installation and maintenance.
- Evaluate service responsiveness: Test their customer service by reaching out with questions or concerns.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in a contract. This should include pricing, delivery schedules, warranty conditions, and service agreements. A well-defined contract protects both parties and sets clear expectations.
- Review all clauses: Ensure that all terms are fair and reasonable.
- Seek legal advice if needed: Consider consulting with a legal expert to review contracts before signing.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for machine tool gears, ensuring they make informed decisions that support their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machine tool gear Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machine Tool Gear Sourcing?
When sourcing machine tool gears, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. High-strength alloys and specialized composites may incur higher prices but offer better durability and performance.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the precision machining and assembly of gears. Labor costs can vary widely based on the region and the complexity of the gear manufacturing process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, equipment maintenance, and depreciation. Effective management of overhead can lead to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling is another critical component. Custom tooling for specialized gear profiles increases initial costs but can enhance production efficiency and quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are necessary to ensure that gears meet industry standards and specifications. Investing in quality assurance can prevent costly defects and enhance product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, particularly for international transactions, can add significantly to the total cost. This includes freight, customs duties, and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on market conditions, supplier reputation, and the complexity of the gear.
What Influences Pricing for Machine Tool Gears?
Several factors influence the pricing of machine tool gears, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers often have MOQs that can affect pricing flexibility.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom gear specifications can result in higher costs due to the need for specialized manufacturing processes. Standardized gears are usually more cost-effective.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials impacts both cost and performance. Advanced materials may come at a premium but can provide enhanced longevity and efficiency.
-
Quality and Certifications: Gears that meet international standards and possess relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, AGMA) may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and financial stability of a supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more, but they often provide better service and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms of shipment can affect costs significantly. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers anticipate potential extra charges related to shipping and insurance.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs When Sourcing Machine Tool Gears?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in gear sourcing:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume purchasing to negotiate better prices. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to favorable terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, downtime, and replacement of gears. Investing in higher-quality gears may reduce TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local market conditions that can impact pricing. Engaging with local suppliers can sometimes yield better deals due to reduced logistics costs.
-
Quality Over Price: Prioritize suppliers who offer a balance of quality and cost. Choosing cheaper options can lead to higher long-term costs due to failures and replacements.
-
Utilize Technology: Implement technology for better inventory management and supplier communication to streamline procurement processes and reduce costs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of cost components and pricing influencers, it is important to note that actual prices can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always seek quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machine tool gear With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Machine Tool Gear
In the competitive landscape of industrial machinery, B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the most effective solution for their operational needs. While machine tool gears are pivotal for numerous applications, several alternative technologies can also achieve similar objectives. Understanding these alternatives helps buyers make informed decisions that align with their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Machine Tool Gear | Alternative 1: Direct Drive Systems | Alternative 2: Belt Drive Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and durability | Excellent torque and speed control | Moderate performance, dependent on belt quality |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Potentially lower long-term costs | Generally lower initial costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled installation | Simpler installation process | Easy to implement, but maintenance required |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Low maintenance requirements | Requires periodic replacement of belts |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty machinery | Applications needing high efficiency | General-purpose applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Direct Drive Systems?
Direct drive systems eliminate the need for gears, relying instead on motors directly connected to the load. This method offers excellent torque and speed control, making it ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and precision. However, the initial investment can be significant, and the technology is often more complex to install. While maintenance is minimal, should a failure occur, the repair process can be more intricate and costly due to the specialized components involved.
How Do Belt Drive Systems Compare in Performance and Cost?
Belt drive systems are a common alternative, particularly in applications where cost is a primary concern. They are generally easier to implement and maintain, making them suitable for smaller operations or less demanding tasks. However, their performance can be variable, heavily influenced by the quality of the belts used. They may not provide the same level of precision and durability as machine tool gears, especially in heavy-duty applications. While the initial costs are lower, the need for periodic belt replacements can add to long-term operational expenses.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Selecting the right solution for your machinery requirements is critical for operational efficiency and cost management. While machine tool gears provide unmatched precision and durability for heavy-duty applications, alternatives like direct drive and belt drive systems offer varying benefits depending on the specific use case. Buyers should evaluate their operational demands, budget constraints, and the importance of maintenance when deciding. By aligning the technology with their unique requirements, B2B buyers can enhance productivity and achieve better returns on their investments.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machine tool gear
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machine Tool Gears?
When selecting machine tool gears, understanding critical specifications is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some of the most important technical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a gear significantly affects its strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Common materials used for machine tool gears include steel, cast iron, and various alloys. High-carbon steel, for instance, is favored for its toughness and ability to maintain its shape under high stress. Selecting the appropriate material grade can lead to improved performance and a reduction in downtime due to maintenance or failures.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. In gear manufacturing, tighter tolerances usually result in better fit and function, which is crucial for high-speed applications. For instance, gears with AGMA (American Gear Manufacturers Association) standards are often required in precision applications to ensure compatibility and performance. Understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers assess the expected performance and reliability of the gears.
3. Gear Ratio
The gear ratio is the ratio of the number of teeth on two meshing gears. It determines the mechanical advantage and speed of the output shaft. A higher gear ratio can provide more torque but less speed, while a lower gear ratio results in higher speed but less torque. For B2B buyers, understanding gear ratios is essential to ensure that the machinery operates at the desired efficiency and power levels.
4. Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture of the gear’s surface, which can impact its performance, noise levels, and wear resistance. Gears may undergo processes such as grinding or polishing to achieve specific surface finishes. A smoother surface reduces friction and wear, leading to longer service life and lower maintenance costs. Buyers must consider surface finish requirements based on their operational environment.
5. Load Capacity
The load capacity of a gear indicates the maximum load it can handle without failure. This property is influenced by the gear’s material, design, and size. Understanding load capacity is vital for B2B buyers to match gears with the intended application, ensuring that the machinery can withstand operational demands without incurring damage.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Machine Tool Gear Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and clearer communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of machine tool gears, an OEM might provide specific gear designs tailored to particular machinery. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for ensuring compatibility and quality in gear procurement.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For machine tool gears, MOQs can vary widely based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the gear. Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory levels and cost-effectiveness in procurement.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for machine tool gears can provide a clear understanding of costs and lead times, facilitating better budget planning and supplier comparison.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect the overall cost of acquiring machine tool gears. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international buyers to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. In the machine tool gear industry, lead times can be influenced by factors such as manufacturing processes and shipping logistics. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their operations and avoid production delays.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and minimize risks associated with machine tool gears.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machine tool gear Sector
What Are the Current Trends Shaping the Machine Tool Gear Market?
The machine tool gear sector is witnessing significant transformations driven by globalization, technological advancements, and changing consumer demands. The increasing need for precision manufacturing and automation across industries is propelling the demand for high-quality gears. Key trends include the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, which enhance operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these technologies represent an opportunity to streamline production processes and reduce downtime.
Emerging sourcing trends highlight a shift towards digital platforms that facilitate direct connections between manufacturers and buyers. E-commerce in the industrial sector is expanding, enabling buyers to access a wider range of machine tool gear products and services. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on local sourcing to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions, particularly in light of recent geopolitical tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate agility in their operations and the ability to deliver customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Machine Tool Gear Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming integral to the machine tool gear sector as environmental concerns and regulatory pressures mount. The production of gears often involves materials and processes that can have substantial environmental impacts, including energy consumption and waste generation. As such, buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize sustainability in their manufacturing processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies that adhere to sustainable practices are not only minimizing their environmental footprint but also enhancing their brand reputation and customer loyalty. In this context, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to responsible sourcing standards are critical. Buyers should look for suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials and have transparent sourcing practices, ensuring that their gear products contribute positively to both business and environmental goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Machine Tool Gear Development?
The evolution of machine tool gears can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, where the demand for efficient power transmission systems began to rise. Early gears were crafted from wood and later transitioned to metals, significantly enhancing their durability and performance. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and machining technologies have led to the production of high-precision gears that meet the rigorous standards of modern manufacturing.
As industries evolved, so did the complexity and capabilities of machine tool gears. The introduction of computer numerical control (CNC) technology in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for unprecedented precision and automation in gear manufacturing. Today, the sector continues to innovate, integrating advanced materials and smart technologies to meet the evolving demands of global industries. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers to understand the reliability and technological advancements that underpin modern machine tool gear solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machine tool gear
1. How do I choose the right gear for my machine tools?
Selecting the right gear involves understanding your machine’s specifications, including load capacity, speed, and application requirements. Assess the gear type (spur, helical, bevel, etc.) based on how it transmits power and motion. It’s also crucial to consider material durability and manufacturing tolerances. Collaborating with suppliers who offer customization can ensure that the gears meet specific operational demands, enhancing performance and longevity.
2. What is the best gear type for high-speed applications?
For high-speed applications, helical gears are often the best choice due to their smoother operation and higher load capacity compared to spur gears. They reduce noise and vibration, allowing for efficient power transmission. Additionally, consider gear materials and heat treatment processes that can withstand high speeds, such as carbon steel or alloy steel, which can also enhance durability and performance.
3. What are common quality assurance practices for machine tool gears?
Quality assurance for machine tool gears typically includes rigorous inspection processes such as dimensional checks, hardness testing, and performance evaluations. Suppliers often use advanced technologies like CNC machines for precise manufacturing and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) for dimensional accuracy. Ensure that your suppliers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, to guarantee consistent product quality and reliability.
4. How do I vet suppliers for machine tool gears?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, production capabilities, and reputation. Request references from previous clients and review case studies to gauge their expertise. Additionally, assess their certifications and quality control measures. Conduct site visits if possible, and ensure they can meet your specific needs, including customization options and compliance with international standards.
5. What are typical payment terms for international gear suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits (20-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment upon completion of specific milestones. It’s essential to clarify these terms during negotiations to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions.
6. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machine tool gears?
The MOQ for machine tool gears can vary based on the supplier and the complexity of the gear. Typically, suppliers may require a MOQ ranging from 10 to 100 units for standard products. For custom gears, the MOQ may be higher due to setup costs. Always discuss your specific needs with suppliers to find a mutually agreeable MOQ that aligns with your production requirements.
7. How does logistics affect the sourcing of machine tool gears?
Logistics plays a critical role in sourcing machine tool gears, impacting lead times, shipping costs, and delivery reliability. Consider factors such as the supplier’s location, shipping methods, and customs regulations in your country. Partnering with suppliers who have efficient logistics networks can help minimize delays and ensure timely delivery, which is essential for maintaining production schedules.
8. What customization options are available for machine tool gears?
Customization options for machine tool gears often include variations in size, material, tooth design, and gear ratios. Suppliers may offer tailored solutions to meet specific operational requirements or environmental conditions. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the sourcing process to explore available options, ensuring the final product aligns with your performance expectations and application demands.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Machine Tool Gear Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Machine Tool Builders – Gear Machine Rebuilding Services
Domain: machinetoolbuilders.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Machine Tool Builders, Inc. specializes in machine rebuilding, recontrols, and service for the gear industry. Key offerings include:
– Rebuilding services for various machines including Pfauter P400G Form Grinding Machine, Pfauter P4000H Gear Hobbing Machine, and Lorenz LS-180 Gear Shaper.
– CNC conversion services.
– New equipment from brands such as HAMAI, SMG, BURRI, DONNER + PFISTER, TFG, SEN…
2. HMC Gears – Custom Gear Solutions
Domain: hmcgears.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: HMC Gears specializes in high-quality custom gears and offers a range of products including: Custom Gears, Double Helical Gears, Close-Gap Double Helical Gears, Helical Gears, Spur Gears, Internal Gears, Pinions, CNC Machining, Gearboxes, Repair & Rebuild services, Field Service, and Welding. The company is known for its advanced gear cutting and inspection machines, allowing for precision custom …
3. Bourn & Koch – Remanufactured Gear Shapers
Domain: bourn-koch.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Fellows Gear Shapers by Bourn & Koch are remanufactured gear shaping machines located in Rockford, Illinois. They can shape gears to AGMA class 10 without grinding. The machines are rebuilt with precise remanufacturing and reassembly, utilizing in-house machining capabilities and precision assemblers. Available in mechanical or Hydrostroke™ vertical stroking configurations, they include classic mo…
4. Nidec – Machine Tools and CNC Solutions
Domain: nidec.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Nidec Corporation offers a diverse lineup of machine tools designed to meet various machining needs, including lathes, machining centers, multitasking machines, and gear cutting machines. The product categories include:
– Lathe (CNC Lathe, Large CNC Lathe, Parallel Twin-Spindle CNC Lathe, Vertical CNC Lathe, Combined Machining CNC Lathe, CNC/Manual Lathe, Manual Lathe)
– Multi-Tasking Machine (in…
5. Minchen Gear – Precision Machine Tool Gears
Domain: minchen-tw.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Minchen Gear offers a wide array of gear types for machine tools, including spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, worm gears, and rack and pinion gears. These gears are available in various sizes, configurations, and materials, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of the machine tools industry. Key features include exceptional precision, durability, and resistance to wear and tear, designed to o…
6. Liebherr – Gear Cutting Tools
Domain: liebherr.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Liebherr offers a comprehensive range of gear cutting tools, including skiving tools, shaper cutters, wafer cutters, solid wafer cutters, rolling racks, master gears, and CBN grinding tools. Key features include:
1. **Skiving Tools**: Available in PM-HSS and carbide, designed for high production numbers. Offers conical and cylindrical options with optimized cutting angles.
2. **Shaper Cutters**: …
7. Machine Tool & Gear – Machining Services
Domain: bloomberg.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: Machine Tool & Gear, Inc. provides machining, heat treating, grinding, and finishing services. The Company offers products such as axles, differentials, pinion and transmission shafts, gears, and engine bracket systems. Machine Tool & Gear serves customers in the transportation industries worldwide.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machine tool gear
In the evolving landscape of machine tool gear, strategic sourcing stands as a pivotal factor for success in manufacturing across diverse international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing quality and precision in gear procurement, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, minimize downtime, and ultimately improve product quality. Suppliers offering a range of capabilities, from custom gear manufacturing to advanced machine rebuilding services, are essential partners in achieving these goals.
Investing in high-quality gear solutions not only supports smooth power transmission but also contributes to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Companies should leverage partnerships with reputable manufacturers who demonstrate expertise in gear technology and provide comprehensive support, including troubleshooting and alignment services.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative and reliable machine tool gears will continue to rise as industries embrace automation and precision engineering. International buyers are encouraged to explore diverse sourcing options, ensuring they align with suppliers that can meet their specific operational needs. By taking proactive steps in strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market.