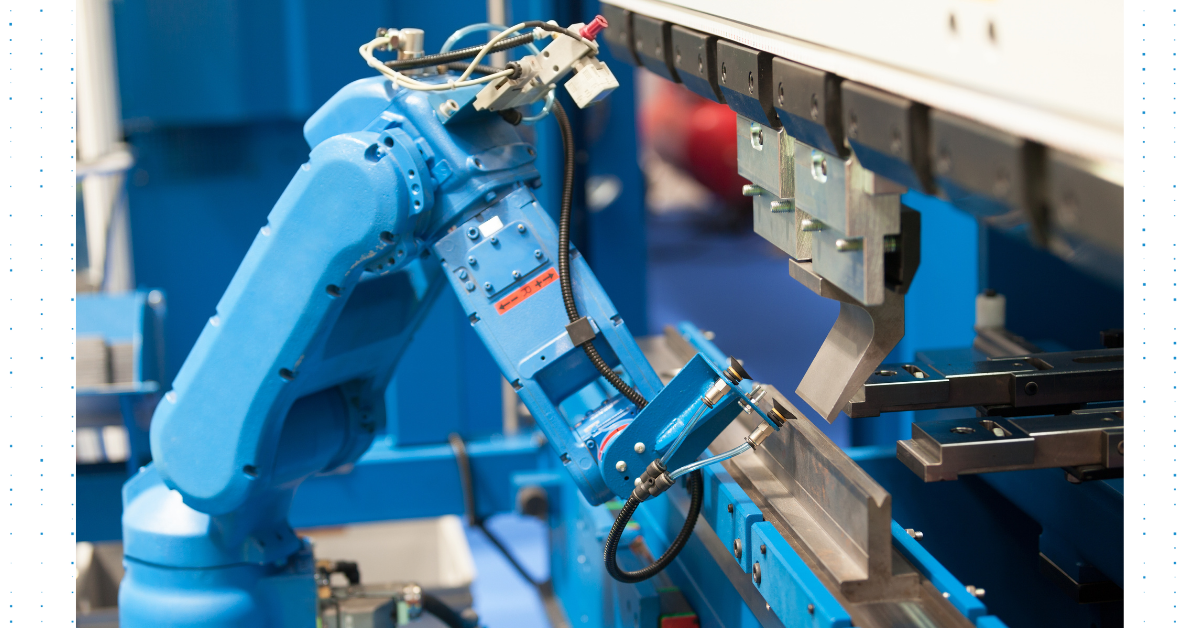
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machine tending
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, businesses face the critical challenge of optimizing their production processes while navigating a global market that demands efficiency and adaptability. Machine tending, a crucial aspect of automation, can significantly enhance operational performance by streamlining the loading and unloading of materials in CNC and injection molding systems. However, many international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, struggle with the complexities of sourcing the right solutions to meet their unique needs.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower decision-makers by providing in-depth insights into various types of machine tending solutions, their applications across industries, and essential criteria for supplier vetting. Additionally, we will explore cost considerations and return on investment (ROI) scenarios, helping businesses make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the landscape of automated machine tending, buyers can enhance productivity, mitigate labor shortages, and elevate product quality while reducing operational risks.
Whether you are a manufacturer in Nigeria looking to modernize your processes or a European firm aiming to expand your automation capabilities, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the global market effectively. With actionable insights and expert recommendations, you will be well-prepared to leverage machine tending solutions that align with your strategic goals.
Understanding machine tending Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collaborative Robots (Cobots) | Designed to work alongside human operators; easy to program and integrate | CNC machining, injection molding | Pros: Flexible, safe, high ROI; Cons: Initial setup and training required. |
| Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Mobile robots that transport materials autonomously within facilities | Warehousing, assembly lines | Pros: Reduces labor costs, enhances efficiency; Cons: Limited to transport tasks. |
| Traditional Industrial Robots | High-speed, high-capacity machines for repetitive tasks; often require extensive programming | Heavy manufacturing, automotive assembly | Pros: High throughput, robust performance; Cons: High initial investment, limited flexibility. |
| Robotic Arm Systems | Versatile systems with interchangeable end-effectors for various tasks | Pick-and-place operations, quality control | Pros: Highly customizable, suitable for diverse applications; Cons: Complexity in programming. |
| Vision-Guided Robots | Equipped with cameras and sensors for precise handling and inspection | Quality assurance, assembly verification | Pros: Enhances accuracy and reduces errors; Cons: Higher cost due to advanced technology. |
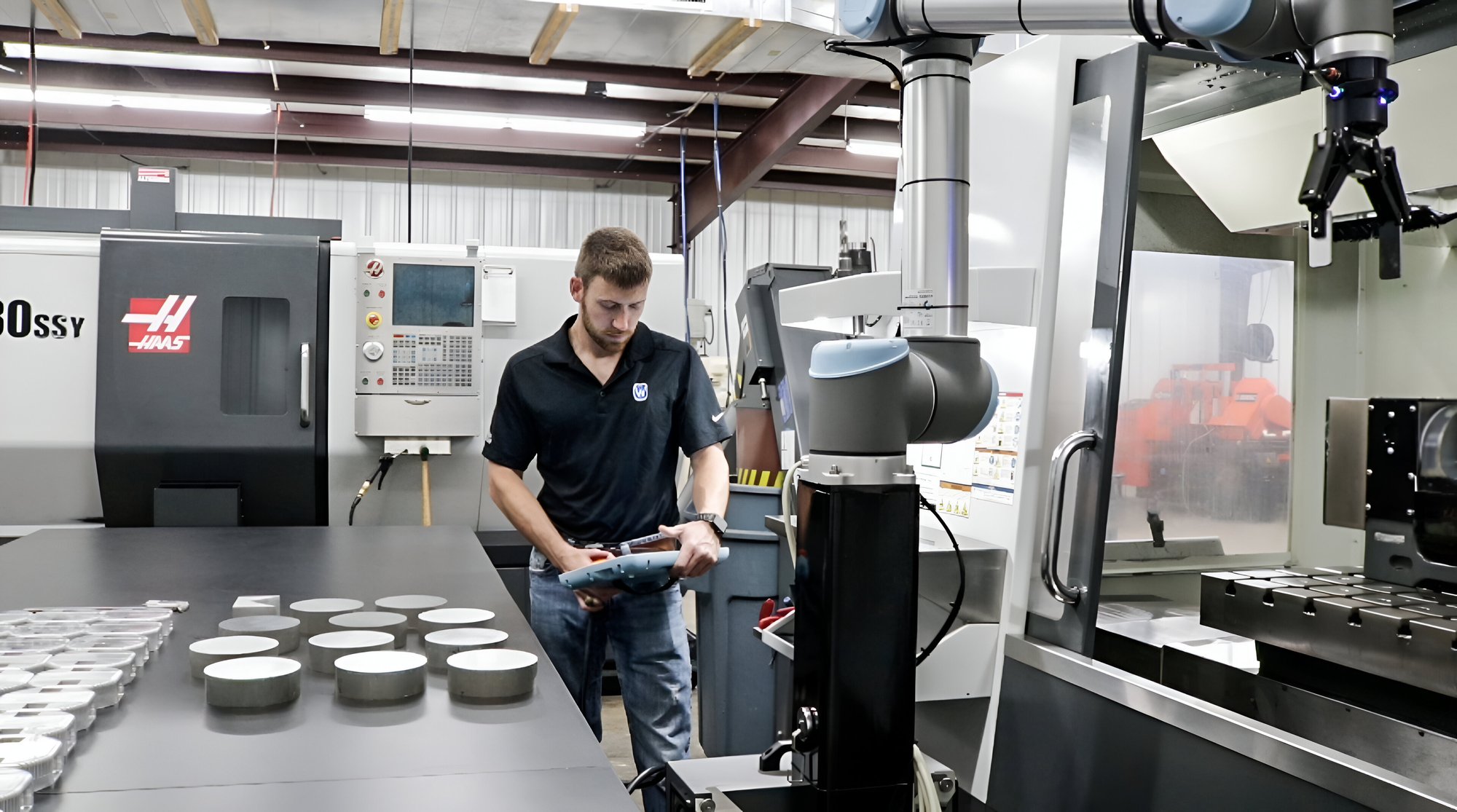
What Are Collaborative Robots (Cobots) and How Can They Benefit My Business?
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work safely alongside human operators. Their ease of programming and integration into existing workflows makes them ideal for various applications, particularly in CNC machining and injection molding. Businesses looking to enhance productivity without sacrificing safety will find cobots beneficial. However, initial setup and training may be necessary to maximize their potential, which could be a consideration for companies with limited resources.
How Do Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) Enhance Material Handling Efficiency?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are mobile robots that autonomously transport materials within facilities, significantly streamlining logistics processes. They are particularly effective in warehousing and assembly lines, where they can move components between stations without human intervention. While AGVs reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency, their functionality is limited to transport tasks, necessitating other solutions for machine tending.
What Are the Advantages of Traditional Industrial Robots?
Traditional industrial robots are known for their high-speed and high-capacity performance, making them suitable for repetitive tasks in heavy manufacturing and automotive assembly. Their robust capabilities can lead to high throughput and efficiency. However, the initial investment can be substantial, and their limited flexibility may restrict their use in dynamic environments where tasks frequently change.
Why Consider Robotic Arm Systems for Diverse Applications?
Robotic arm systems offer versatility through interchangeable end-effectors, allowing them to perform a range of tasks from pick-and-place operations to quality control. Their customization capabilities make them suitable for various industries. However, programming complexity can be a challenge, requiring skilled personnel to manage the systems effectively. Businesses must weigh the benefits of customization against the potential need for specialized training.
How Do Vision-Guided Robots Improve Quality Assurance?
Vision-guided robots utilize cameras and sensors for precise handling and inspection, making them invaluable for quality assurance and assembly verification. Their ability to enhance accuracy and reduce errors can significantly improve product quality. However, the advanced technology required for these systems can lead to higher costs, which may be a barrier for smaller businesses. Investing in vision-guided robots can yield long-term benefits through improved quality and reduced waste.
Key Industrial Applications of machine tending
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Machine Tending | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | CNC machining for engine components | Increased production efficiency and reduced labor costs | Compatibility with existing CNC machines and ease of integration |
| Aerospace | Precision part handling for assembly lines | Enhanced quality control and minimized human error | Need for high precision and compliance with safety standards |
| Metal Fabrication | Loading and unloading of metal stamping machines | Maximized uptime and reduced operational costs | Robustness of the robotic system and adaptability to various tasks |
| Electronics Assembly | Automated handling of circuit boards | Improved assembly speed and reduced defect rates | Flexibility in programming for different product types |
| Food & Beverage | Handling packaging lines and bottling machines | Increased throughput and consistency in product quality | Hygiene standards and ease of cleaning for food-safe operations |
How is Machine Tending Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, machine tending is essential for CNC machining of engine components. The integration of collaborative robots (cobots) allows for seamless material loading and unloading, significantly increasing production efficiency. This automation addresses the challenges of skilled labor shortages and repetitive tasks, enabling human workers to focus on higher-value activities. Buyers in this sector should prioritize solutions that are compatible with existing CNC machines and offer easy integration to maximize return on investment.
What Role Does Machine Tending Play in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, machine tending is vital for handling precision parts during assembly. Automated systems can manage the loading and unloading of complex components, ensuring high-quality control while minimizing the risk of human error. This is particularly important given the stringent safety regulations governing aerospace manufacturing. Buyers must consider the need for high precision in their automation solutions, as well as compliance with industry-specific safety standards, to ensure reliability and performance.
How is Machine Tending Applied in Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication facilities leverage machine tending to optimize the loading and unloading processes of metal stamping machines. This automation enhances uptime by allowing machines to operate continuously without manual intervention, leading to reduced operational costs. For international buyers, sourcing robust and adaptable robotic systems is crucial, as these machines must handle various tasks and withstand the demanding environments typical of metal fabrication operations.
What Benefits Does Machine Tending Offer in Electronics Assembly?
In electronics assembly, machine tending automates the handling of circuit boards, significantly improving assembly speed and reducing defect rates. By integrating cobots into the production line, manufacturers can ensure consistent quality while alleviating the burden of repetitive tasks on human workers. Buyers should seek flexible programming capabilities to accommodate different product types and variations, which is essential in the fast-paced electronics market.
How Does Machine Tending Enhance Food & Beverage Operations?
Machine tending is increasingly utilized in food and beverage operations for handling packaging lines and bottling machines. Automated solutions can increase throughput while maintaining consistency in product quality, addressing the industry’s need for efficiency. When sourcing these systems, businesses must prioritize hygiene standards and the ease of cleaning, ensuring that automation solutions comply with food safety regulations and can be maintained effectively in a production environment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machine tending’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Skilled Labor Shortages in Manufacturing
The Problem: Many manufacturing companies, especially in regions like Africa and South America, are grappling with a significant shortage of skilled labor. This challenge is exacerbated by a general disinterest in repetitive, low-skilled jobs, leading to underutilization of CNC machines that operate at only 60-70% capacity. Consequently, businesses face revenue losses due to inefficient operations and an inability to meet production demands. This issue not only affects output but also places added pressure on existing staff, leading to burnout and increased turnover rates.
The Solution: Implementing a collaborative robot (cobot) for machine tending can effectively bridge the skills gap. These robots are designed to work alongside human operators, taking over repetitive tasks such as loading and unloading CNC machines. Companies should look for solutions that require minimal reprogramming and can integrate seamlessly with existing machinery. For instance, a standardized machine tending solution like Robotiq’s can be set up without the need for custom modifications, allowing for rapid deployment. By automating routine tasks, skilled workers can be redirected to higher-value activities, thereby enhancing overall productivity and job satisfaction.
Scenario 2: High Rates of Machine Downtime Due to Inefficient Operations
The Problem: Frequent machine downtimes caused by improper loading or unloading of materials can lead to costly production halts. This is particularly problematic for manufacturers in the Middle East and Europe, where maintaining operational efficiency is critical to compete in a global market. Downtime not only results in lost revenue but can also damage the reputation of a business that fails to deliver on time. Additionally, the fear of safety hazards associated with manual handling can deter companies from maximizing their machine capabilities.
The Solution: Adopting automated machine tending solutions can significantly reduce downtime and improve operational efficiency. Businesses should consider investing in cobots equipped with advanced gripping technologies and safety features that allow them to operate safely alongside human workers. For example, Universal Robots’ cobots come with built-in safety protocols that can be customized to fit the unique needs of any manufacturing environment. This approach ensures that machines are loaded and unloaded consistently and accurately, minimizing the risk of jams and misalignments. Furthermore, integrating monitoring software can help businesses track machine performance in real-time, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing unexpected downtimes.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Quality and Production Outputs
The Problem: Maintaining consistent product quality can be a daunting task for manufacturers, particularly when relying on human labor for repetitive machine tending operations. Variability in human performance often leads to defects, increased scrap rates, and ultimately, customer dissatisfaction. This issue is prevalent across various industries in diverse markets, including those in Nigeria and Vietnam, where quality assurance is paramount for building trust and retaining customers.
The Solution: To combat quality inconsistencies, businesses should leverage robotic automation for machine tending tasks. Cobots offer precision and repeatability that human operators may struggle to achieve over extended periods. By utilizing a machine tending solution that includes tailored end-of-arm tooling, manufacturers can ensure that components are handled correctly, reducing the likelihood of defects. For instance, solutions that come pre-assembled with user-friendly programming interfaces can help companies rapidly adapt to production changes without sacrificing quality. Investing in training for employees on how to work alongside these robots will further enhance product quality, as staff can focus on monitoring and quality control rather than the tedious tasks of loading and unloading materials. By streamlining operations in this way, manufacturers can achieve higher output rates while maintaining rigorous quality standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machine tending
What are the Key Materials Used in Machine Tending Applications?
In the realm of machine tending, the selection of materials is critical for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in machine tending applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various machine tending applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which facilitates easier handling and installation. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to other metals. However, aluminum is less durable than steel and can deform under high stress, limiting its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s lightweight nature allows for faster robotic movements, improving efficiency in machine tending tasks. However, it may not be suitable for environments with high temperatures or where heavy loads are involved.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local sourcing to reduce costs and ensure compliance with regional standards such as ASTM. Additionally, understanding the local market’s preferences for aluminum alloys can guide material selection.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers high corrosion resistance, strength, and durability, withstanding harsh environments and high temperatures. It is available in various grades, each with specific properties.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and ability to maintain structural integrity in demanding applications. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and may require specialized machining processes, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for machine tending applications involving corrosive materials or environments, ensuring the longevity of equipment. Its strength allows for the handling of heavier components without deformation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as DIN and JIS is crucial for stainless steel applications. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific grades in their region to avoid delays in procurement.
3. Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic known for its impact resistance and transparency. It can withstand a range of temperatures, making it suitable for various applications in machine tending.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its lightweight and high impact resistance, which can reduce the overall weight of robotic systems. However, it has lower heat resistance compared to metals and may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is often used for protective covers or components in machine tending systems, enhancing safety while maintaining visibility. Its flexibility allows for innovative designs but may limit its use in high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that polycarbonate materials meet local safety and compliance standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulations. Understanding the specific grades available in local markets can also influence material choice.
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composites, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. They can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements, including temperature and pressure ratings.
Pros & Cons: Composites offer significant advantages in terms of weight reduction and customization for specific applications. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly useful in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in robotic arms or end-effectors. Their durability ensures long-lasting performance in various environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the availability of composite materials in their regions and any potential import regulations. Additionally, understanding local industry standards for composites can help ensure compliance and performance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for machine tending | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight robotic arms and fixtures | Low weight and corrosion resistance | Less durable under high stress | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Heavy-duty machine components | High strength and longevity | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Polycarbonate | Protective covers and lightweight parts | Impact resistance and visibility | Lower heat resistance | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Custom robotic components and fixtures | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and specialized manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with insights into the properties and implications of various materials used in machine tending. Understanding these factors will empower businesses to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machine tending
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Machine Tending?
The manufacturing process for machine tending can be broken down into several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chain and production efficiency.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Readied for Machine Tending?
Material preparation involves selecting and preparing raw materials for processing. This stage is critical as it directly impacts the quality of the final product. For machine tending applications, materials must be inspected for defects, cleaned, and often cut to size. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting or CNC machining are commonly employed to ensure precision.
In the context of machine tending, it’s vital to assess the compatibility of materials with the machinery involved. For instance, metals, plastics, and composites each require specific handling and processing methods. Buyers should ensure their suppliers have robust material preparation protocols that align with international standards.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Materials?
The forming stage encompasses the techniques used to shape materials into desired components. This can involve processes such as injection molding, CNC machining, or 3D printing. Machine tending robots, particularly collaborative robots (cobots), are increasingly utilized during this stage to handle the loading and unloading of parts, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing human error.
Employing automated machine tending systems can significantly improve cycle times and maintain consistent quality. Buyers should inquire about the forming techniques used by suppliers and whether they integrate automation in their processes, which can lead to increased throughput and reduced scrap rates.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated into Final Products?
The assembly phase involves the integration of various components into a finished product. This stage may include tasks such as fastening, welding, or adhesive bonding. Automated machine tending solutions can streamline assembly processes, allowing for the rapid and accurate placement of components.
For B2B buyers, understanding the assembly methods employed by suppliers is crucial. Automation can help reduce labor costs and improve product quality. Buyers should evaluate whether suppliers use standardized processes that adhere to international quality standards, ensuring consistency across batches.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure High-Quality Final Products?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of a product. Techniques such as painting, coating, or polishing are commonly used. Quality assurance during the finishing stage is vital to meet customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Buyers should seek suppliers that implement rigorous quality control measures during the finishing stage. This may include surface inspections, adhesion tests, and dimensional checks to ensure that products meet specified standards.
What Quality Control Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality control (QC) is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet specific requirements and standards. For international B2B buyers, understanding applicable standards and QC practices is essential.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Machine Tending?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems. It provides a framework for consistent product quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement. Suppliers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality, making them more reliable partners for B2B buyers.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area or API standards for the oil and gas sector may be relevant. Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold the necessary certifications to ensure compliance with local regulations and market requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
- IQC involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process, ensuring they meet predefined specifications.
- IPQC focuses on monitoring the manufacturing process itself, which may include regular inspections and testing of components as they are produced.
- FQC is the final step, verifying that finished products meet quality standards before they are shipped to customers.
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers have robust QC processes in place at each of these checkpoints to minimize defects and ensure high-quality outputs.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for mitigating risks in the supply chain. Buyers can take several steps to ensure their suppliers adhere to stringent QC measures.
What Methods Can Be Used for Supplier Audits and Inspections?
Conducting supplier audits is a proactive way to assess quality control practices. Buyers should evaluate the supplier’s quality management system, including documentation, processes, and employee training. On-site inspections can provide further insights into the supplier’s operations and their adherence to quality standards.
Additionally, buyers can request QC reports that detail inspection results and corrective actions taken. This transparency can help build trust and ensure that the supplier is committed to maintaining high quality.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections in Quality Assurance?
Third-party inspections can add an additional layer of confidence for B2B buyers. Engaging an independent inspection agency to assess product quality can validate the supplier’s claims and ensure compliance with international standards. This is particularly important for buyers in regions where local quality assurance practices may vary.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, navigating the nuances of quality control and certification can be complex. It is essential to understand the specific quality requirements of the target market, as these can vary significantly between regions.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, different regulatory bodies may impose varying quality standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these standards to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties. For example, products exported to the European Union must meet CE marking requirements, while products sold in the Middle East may need to comply with Gulf Standards Organization (GSO) regulations.
What Should Buyers Know About Language and Cultural Barriers?
Language and cultural differences can also impact the quality assurance process. Buyers should consider engaging local representatives or consultants familiar with the region’s standards and practices to facilitate communication with suppliers. This can help ensure that quality expectations are clearly understood and met.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with machine tending, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality. Emphasizing robust QC practices and compliance with international standards can ultimately lead to stronger partnerships and successful outcomes in global markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machine tending’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure machine tending solutions. By following these steps, you can ensure a well-informed purchase decision that aligns with your operational needs, maximizes productivity, and minimizes risks.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical specifications required for your machine tending application. Consider factors such as payload capacity, compatibility with existing machinery, and the types of materials being handled.
– Key Considerations:
– Determine the weight and dimensions of parts to be manipulated.
– Assess the types of machines (e.g., CNC, injection molding) that the machine tending system will serve.
Step 2: Assess Your Automation Needs
Evaluate the specific automation requirements of your operations. Identify whether you need a solution for simple tasks like loading and unloading or more complex operations such as quality inspection and process monitoring.
– Key Points:
– Consider the volume of production and the desired level of automation.
– Determine if a collaborative robot (cobot) is necessary for tasks requiring human interaction.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and customer references relevant to your industry.
– Important Actions:
– Look for suppliers with a proven track record in machine tending automation.
– Verify their ability to provide ongoing support and maintenance services.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Safety Standards
Ensure that the machine tending solutions comply with international safety standards. This is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment and preventing accidents.
– Key Standards:
– Check for certifications like ISO 10218 for industrial robots and ISO/TS 15066 for collaborative robots.
– Inquire about safety features such as emergency stop buttons and collision detection systems.
Step 5: Consider Integration Capabilities
Investigate how easily the machine tending solution can be integrated into your current operations. Compatibility with existing machinery and software is critical to avoid costly modifications.
– Integration Tips:
– Ensure the system can connect seamlessly with your CNC or other machines without extensive reprogramming.
– Look for solutions that allow for easy scalability as your production needs grow.
Step 6: Request a Demonstration
Before finalizing your purchase, request a demonstration of the proposed solution. This will provide insights into the system’s functionality and ease of use.
– Demonstration Insights:
– Assess the user interface and programming simplicity.
– Evaluate the performance of the machine tending system in real-time scenarios.
Step 7: Review Cost and ROI Potential
Finally, analyze the total cost of ownership and the expected return on investment (ROI) from the machine tending solution. This involves considering initial costs, maintenance, and potential productivity gains.
– Financial Considerations:
– Calculate the expected savings from reduced labor costs and increased output.
– Investigate financing options or payment plans that suppliers may offer to ease the initial financial burden.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing machine tending solutions, ensuring they choose a system that enhances operational efficiency and supports business growth.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machine tending Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Machine Tending Solutions?
When sourcing machine tending solutions, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the cost of the robotic systems, including collaborative robots (cobots), end-of-arm tooling, and any additional accessories required for operation. The choice of materials—ranging from standard to high-grade components—can significantly influence pricing.
-
Labor: While automation reduces the need for skilled operators, initial setup and programming require skilled labor. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting may necessitate technician involvement. Factoring these labor costs is crucial for a comprehensive analysis.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses associated with producing machine tending solutions. A higher overhead can lead to increased prices for the end buyer.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling designed for specific applications can add to the overall cost. Buyers should assess whether standard tools meet their needs or if investment in specialized tooling is justified.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that machine tending solutions meet quality standards incurs costs related to inspections, testing, and certifications. Suppliers that offer robust QC processes may charge higher prices but can provide assurance of reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping, customs duties, and transportation costs are significant, especially for international buyers. Understanding the logistics involved in sourcing machine tending solutions can help in anticipating additional expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a profit margin based on their operational costs and market demand. This margin can vary significantly across regions and industries, affecting the final pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machine Tending Costs?
Several factors can influence the price of machine tending solutions, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate volume discounts, especially when sourcing large quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific operational needs generally come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) typically result in higher prices. Buyers should assess the necessity of these features based on their operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and geographic location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer additional support and warranty services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in international transactions is critical. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and customs clearance, impacting the overall cost structure.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Machine Tending?
To maximize value when sourcing machine tending solutions, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing flexibility. Leverage volume purchases and long-term contracts to secure better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with machine tending solutions, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may not translate to overall savings if long-term expenses are high.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and local market dynamics that can affect pricing. Conduct thorough research to identify competitive suppliers and understand regional pricing trends.
-
Focus on Value Addition: Rather than solely considering price, evaluate the value added by suppliers, such as training, support, and the potential for increased productivity through automation.
-
Request for Quotes (RFQs): Utilize RFQs to compare prices from multiple suppliers. This approach can help identify the most competitive pricing and uncover hidden costs that may not be immediately apparent.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for machine tending solutions can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machine tending With Other Solutions
Introduction: Why Consider Alternatives to Machine Tending?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, organizations are increasingly seeking solutions that maximize efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance flexibility. While machine tending, particularly through the use of collaborative robots (cobots), has gained traction, it’s essential for B2B buyers to explore viable alternatives that may also meet their operational needs. This section evaluates machine tending against other solutions, providing insights that can help businesses make informed decisions.
Comparison Table: Evaluating Machine Tending Against Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Machine Tending | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput; reduces downtime | High efficiency in data-driven tasks; limited in physical tasks | Continuous material transport; limited by navigation and load capacity |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; rapid ROI | Lower initial cost; may require ongoing software licensing | High initial investment; longer ROI due to infrastructure needs |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly with quick setup; compatible with existing machinery | Requires specialized software knowledge; integration can be complex | Requires significant planning and infrastructure; may disrupt existing processes |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance with cobots; regular checks necessary | Minimal maintenance post-setup; software updates required | Regular maintenance for vehicles and navigation systems |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for repetitive loading/unloading tasks in CNC operations | Best for automating business processes, data entry, and analysis | Suitable for warehouses and large facilities needing material handling |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is a technology that automates repetitive tasks typically performed by humans, particularly in data management and business processes. Its primary advantage lies in its ability to enhance efficiency and reduce human error in administrative tasks. However, RPA is not suitable for physical operations such as machine tending or material handling. Its implementation can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge to integrate with existing systems, which may deter smaller businesses.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs are mobile robots that transport materials around a manufacturing or warehouse facility. They excel in environments where continuous movement of goods is necessary, providing a streamlined solution for logistics. However, their implementation often requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure, such as designated pathways and charging stations. AGVs can also be limited in load capacity and navigation flexibility, making them less versatile compared to machine tending solutions that can operate alongside human workers.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When deciding between machine tending and its alternatives, businesses should consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Machine tending is particularly advantageous for companies focused on enhancing production efficiency in environments with repetitive tasks, while RPA suits those looking to automate administrative processes. AGVs are ideal for large-scale logistics needs but may not be practical for all settings. By carefully evaluating these factors, B2B buyers can select the solution that best aligns with their operational objectives and workforce capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machine tending
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machine Tending Solutions?
Understanding the essential technical properties of machine tending solutions is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to enhance productivity and efficiency in their operations. Here are some critical specifications that can influence purchasing decisions:
-
Payload Capacity
This refers to the maximum weight a robotic arm or cobot can handle. It is vital for determining whether the machine can accommodate the parts being processed. A higher payload capacity allows for greater flexibility in the types of tasks the machine can perform, enabling buyers to automate a wider range of operations and reduce the need for multiple machines. -
Precision and Tolerance Levels
Precision defines how accurately the machine can perform tasks, while tolerance indicates the acceptable deviation from a specified measurement. High precision and tight tolerance levels are essential for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where even minor discrepancies can lead to significant safety issues and increased costs. Understanding these metrics helps buyers select machines that meet their quality requirements. -
Cycle Time
This is the total time taken to complete one cycle of operation, including loading, processing, and unloading. Shorter cycle times directly correlate with increased productivity and reduced operational costs. Buyers should evaluate cycle times to ensure that the machinery can keep up with production demands, especially in high-volume environments. -
Integration Compatibility
This refers to how easily a machine can be integrated into existing systems and workflows. Compatibility with various CNC machines, control systems, and software is crucial for minimizing installation time and costs. Buyers benefit from understanding the integration capabilities to ensure seamless operation and maximize return on investment. -
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in any manufacturing environment. Features such as emergency stop buttons, safety sensors, and collaborative operation modes (where robots work alongside human operators) are essential for minimizing workplace accidents. Buyers should prioritize machines that meet industry safety standards to protect their workforce and comply with regulations.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Machine Tending?
Familiarizing yourself with industry-specific jargon can significantly enhance communication and decision-making. Here are some common terms relevant to machine tending:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is crucial for buyers when sourcing components for machine tending solutions, as it impacts quality assurance and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for smaller operations looking to automate without overcommitting financially. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, submitting RFQs can help in comparing costs and understanding market rates, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of predefined international sales terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing shipping, risk, and costs effectively, particularly for international transactions in regions like Africa and South America. -
ROI (Return on Investment)
ROI measures the gain or loss generated relative to the investment cost. This metric is crucial for evaluating the financial viability of implementing machine tending solutions, as it helps buyers project the benefits over time and justify expenditures.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting machine tending solutions, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machine tending Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends in the Global Machine Tending Market?
The machine tending sector is experiencing transformative growth driven by several global factors. Automation has become a cornerstone for manufacturers aiming to enhance efficiency and productivity, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Collaborative robots (cobots) are at the forefront of this evolution, offering flexibility and ease of integration into existing workflows. For international B2B buyers, the ability to adapt to diverse production requirements without extensive reprogramming is particularly appealing.
Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also shaping market dynamics. These technologies facilitate real-time data collection and analysis, leading to smarter decision-making and predictive maintenance capabilities. As a result, companies can optimize machine uptime and reduce operational costs significantly. Furthermore, the increasing emphasis on just-in-time manufacturing models is pushing businesses to seek solutions that minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
In terms of sourcing trends, buyers are increasingly favoring modular and scalable solutions that allow for quick deployment and adaptability. This trend is particularly relevant for regions experiencing rapid industrialization, where businesses must respond swiftly to changing market demands. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is enabling easier access to diverse machine tending solutions, empowering international buyers to explore a wider range of options.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Machine Tending in B2B?
Sustainability is becoming an essential consideration for B2B buyers in the machine tending sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing practices is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener technologies and processes. For instance, the use of energy-efficient cobots not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with global sustainability goals. These robots can operate continuously, leading to higher output with lower energy consumption.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical, as businesses face pressure to ensure their supply chains are free from exploitation and environmentally harmful practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainability.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ materials in machine tending solutions is rising. Suppliers who can provide eco-friendly components, such as recyclable end-of-arm tooling or biodegradable packaging, will likely attract conscientious buyers. Adopting these practices not only fosters a positive brand image but also can lead to long-term cost savings and compliance with increasingly stringent regulations.
How Has Machine Tending Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of machine tending can be traced back to the early days of industrial automation, where rigid robots performed repetitive tasks with limited flexibility. As manufacturing processes advanced, the need for more adaptable solutions became evident, leading to the development of collaborative robots. These modern machines are designed to work alongside human operators, addressing the challenges of skilled labor shortages and increasing production efficiency.
In recent years, the integration of smart technologies has further enhanced the capabilities of machine tending solutions. The ability to program cobots rapidly and adapt them for various tasks has revolutionized the sector, allowing for more agile manufacturing environments. This evolution not only improves productivity but also enhances job satisfaction, as human operators can focus on more complex, value-added tasks rather than monotonous loading and unloading duties.
Today, the machine tending market is characterized by its emphasis on flexibility, sustainability, and technological integration, making it a vital component of modern manufacturing strategies. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machine tending
-
How do I solve the issue of underutilization in my CNC machines?
Underutilization of CNC machines is often due to labor shortages and inefficient manual processes. Implementing an automated machine tending solution can significantly enhance productivity. Collaborative robots (cobots) are designed to work alongside human operators, providing seamless loading and unloading of materials while maintaining consistent quality. By automating these repetitive tasks, you can maximize machine uptime and productivity, potentially increasing operational efficiency to 95% or more. Additionally, this allows your skilled workforce to focus on higher-value tasks, further driving productivity improvements. -
What is the best automation solution for machine tending in my industry?
The best automation solution for machine tending largely depends on your specific industry needs and machine types. Collaborative robots (cobots) are highly recommended due to their versatility and ease of integration. They can be adapted to various applications, including CNC milling and injection molding, without the need for extensive modifications. Solutions like those from Universal Robots and Robotiq offer user-friendly interfaces and quick programming, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes. Assess your production requirements, machine specifications, and workforce capabilities to identify the most effective solution. -
How can I ensure the safety of my workers when implementing machine tending automation?
Safety is paramount when integrating machine tending automation. Cobots come equipped with advanced safety features, such as force-limiting technology and integrated sensors, which allow them to operate alongside human workers without posing risks. It’s crucial to conduct a thorough risk assessment of your facility and implement safety protocols tailored to your specific operations. Regular training for employees on safe interaction with automated systems is also essential to maintain a safe working environment while enhancing productivity. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for machine tending solutions?
When vetting suppliers for machine tending solutions, consider their industry experience, reputation, and the versatility of their products. Look for suppliers who offer robust customer support and training resources, as this is vital for successful implementation. Additionally, evaluate their compliance with international safety standards and certifications. Request case studies or references from existing clients to gauge the effectiveness of their solutions. Finally, assess their ability to provide customization options that meet your unique operational needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for machine tending equipment?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for machine tending equipment can vary widely among suppliers and depend on the type of equipment. Some suppliers may offer flexible options for smaller businesses, while others may have higher MOQs for specialized or customized solutions. It is essential to communicate your specific needs with potential suppliers and inquire about their MOQ policies. Exploring options for pilot projects or leasing arrangements can also help mitigate risks associated with high initial investments. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing machine tending solutions?
Payment terms for machine tending solutions can differ depending on the supplier and the scale of your order. Common terms include upfront deposits (typically 20-50%), with the remainder due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans, particularly for larger projects. It is advisable to clarify payment structures, including any potential additional costs for shipping, installation, or training, to ensure transparency and avoid unexpected expenses. -
How do I assess the quality assurance (QA) processes of machine tending suppliers?
To assess the quality assurance (QA) processes of machine tending suppliers, request information about their quality control standards and certifications. Reputable suppliers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which ensures consistent quality across their products. Inquire about their testing procedures, warranty policies, and after-sales support. Additionally, seeking customer feedback and reviews can provide insights into the reliability and performance of their solutions in real-world applications. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing machine tending solutions internationally?
When sourcing machine tending solutions internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and duties that may apply to your order. It’s essential to work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide clear timelines for delivery. Ensure you understand the total landed cost, including transportation, insurance, and any potential tariffs. Collaborating with a freight forwarder can help streamline the shipping process and ensure compliance with local regulations, minimizing delays and additional costs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Machine Tending Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Universal Robots – Collaborative Robots for Machine Tending
Domain: universal-robots.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Universal Robots offers collaborative robots (cobots) designed for machine tending applications, enhancing efficiency, speed, and precision in manufacturing processes. Key features include:
– Seamless integration with existing setups and collaboration with human operators.
– Versatile and easily reprogrammable for various tasks, reducing downtime and increasing production output.
– Specific end-of…
2. Robotiq – Machine Tending Solution
Domain: robotiq.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Robotiq Machine Tending Solution is designed to maximize CNC machine productivity through simplified robotic automation. Key features include:
– Increases productivity rates by automating loading and unloading of CNC milling and lathe machines.
– Offers a one-year ROI, helping recover lost CNC runtime.
– Eliminates the need for custom programming or permanent modifications to CNC machine control p…
3. FANUC America – Machine Tending Robots
Domain: fanucamerica.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Machine Tending Robots from FANUC America offer extreme flexibility, speed, and reliability for maximizing productivity in the machining industry. They are designed for loading and unloading CNC machines, including lathes, mills, machining centers, forges, presses, and injection molding machines. Key applications include assembly, CNC milling, CNC motion control, CNC turning, complex machining, di…
4. Automation Within Reach – Automated Machine Tending Solutions
Domain: automationwithinreach.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Automated machine tending involves the use of advanced robotics to load raw materials into CNC machines and unload finished parts, enhancing efficiency, precision, and safety in manufacturing. Key benefits include continuous operation without fatigue, enhanced precision with high accuracy, improved safety by reducing worker exposure to hazardous conditions, increased profitability through minimize…
5. Photoneo – MotionCam-3D & PhoXi 3D Scanner
Domain: photoneo.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: MotionCam-3D: The highest accuracy and highest resolution 3D camera in the world, capable of scanning in motion at speeds of up to 40 m/s. PhoXi 3D Scanner: A line of best-in-class industrial grade scanners that meet the needs of every industry, available in sizes XS, S, M, L, XL. Alpha 3D Scanner: A structured light 3D vision scanner designed to upgrade from outdated technology, available in size…
6. Kawasaki – Machine Tending Robots
Domain: kawasakirobotics.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Kawasaki machine tending robots are designed to automate tasks such as part loading, unloading, transferring finished parts, and material handling. They enhance productivity, reliability, and worker safety while reducing idle time. The robots range from lightweight collaborative models to strong industrial robots, suitable for various machinery including CNC machines, injection molding machines, a…
7. OnRobot – Machine Tending Solutions
Domain: onrobot.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Machine tending solutions from OnRobot automate dull and dangerous jobs, increasing safety and productivity. Key features include:
– Dual gripper solution for handling 2 objects simultaneously, reducing cycle times.
– D:PLOY solutions for quick setup and adaptation of applications such as CNC Machine Tending, Packaging, and Transferring.
– Recommended products include:
– 2FG7: Parallel gripper f…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machine tending
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Machine Tending Operations?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing has emerged as a critical factor for optimizing machine tending processes. By investing in collaborative robots (cobots), businesses can significantly enhance operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve product quality. These automated solutions not only mitigate the risks associated with human error but also enable your workforce to focus on higher-value tasks, ultimately driving innovation and productivity.
Moreover, the adaptability of modern machine tending solutions allows companies to seamlessly integrate advanced automation into their existing setups, regardless of machinery age or type. This flexibility is crucial for international buyers looking to capitalize on the growing demand for efficient manufacturing processes, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As you evaluate your sourcing strategies, consider the long-term benefits of investing in cutting-edge machine tending technologies. By doing so, you position your organization to thrive in a competitive marketplace, ensuring you meet the challenges of tomorrow with agility and confidence. Embrace the future of manufacturing—explore the potential of automated solutions today to secure a prosperous tomorrow.