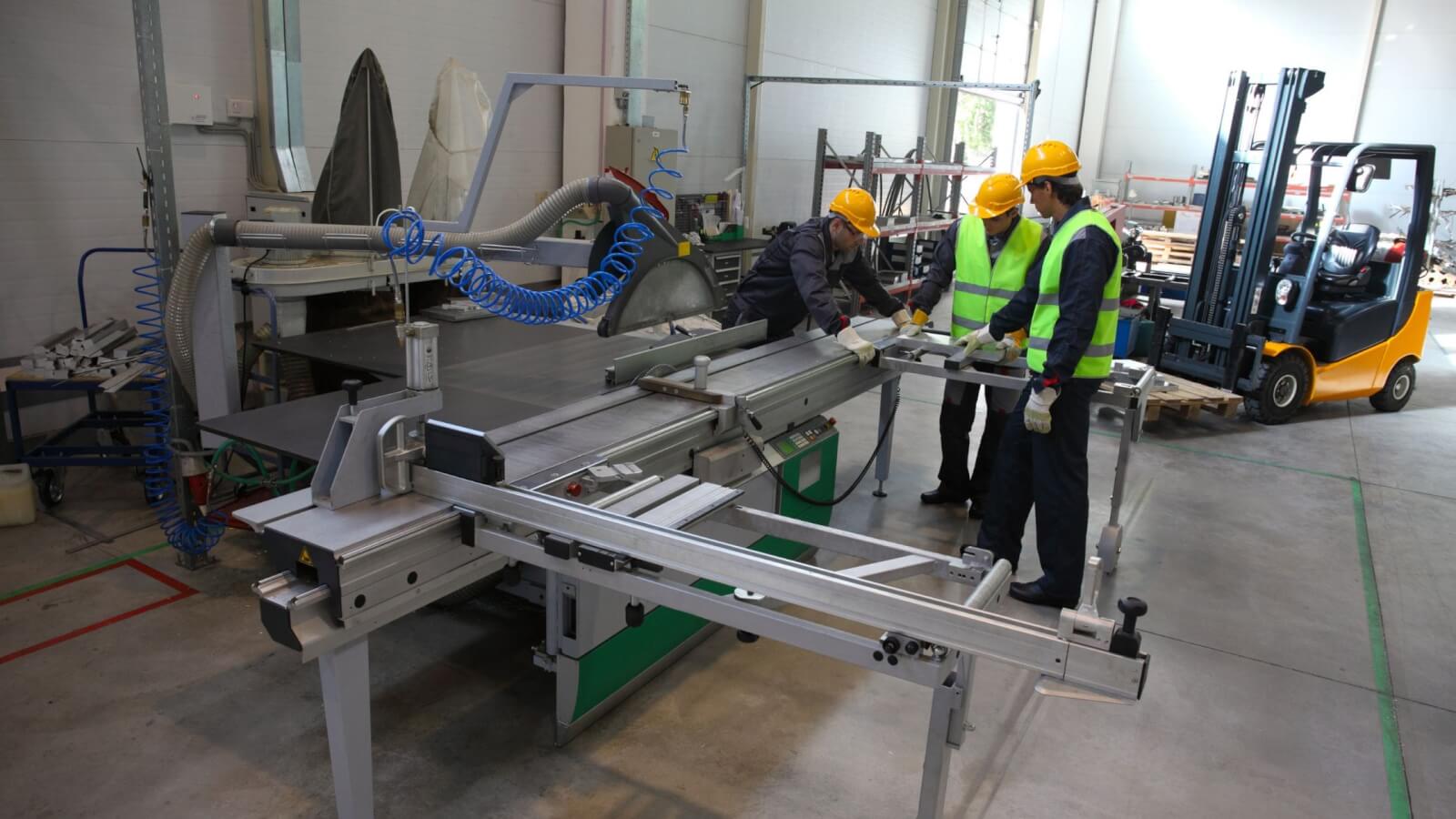
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machine shop machines
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing machine shop machines presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The complexity of selecting the right equipment—from lathes and milling machines to specialized CNC tools—demands a thorough understanding of various factors including application needs, supplier reliability, and cost implications. As businesses strive to enhance productivity and efficiency, the right machinery can be a game-changer in achieving operational excellence.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip B2B buyers with the insights necessary to navigate the global market for machine shop machines effectively. We delve into the different types of machines available, their applications across various industries, and the critical considerations for vetting suppliers. Additionally, we provide actionable tips on cost management, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals.
By offering a detailed exploration of the machine shop equipment landscape, this guide empowers decision-makers to identify the best tools for their specific operational needs. Whether you’re in Nigeria looking to optimize your manufacturing processes or in Germany seeking advanced machining solutions, the information contained herein will serve as a valuable resource in your procurement journey. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operations with confidence and clarity.
Understanding machine shop machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lathe Machine | Rotates workpieces for various machining operations. | Precision parts manufacturing, automotive | Pros: Versatile, high precision. Cons: Requires skilled operators. |
| Milling Machine | Uses rotary cutters to remove material, highly versatile. | Aerospace, automotive, and metalworking | Pros: Efficient for complex shapes. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Grinding Machine | Employs abrasive wheels for surface finishing and material removal. | Tool production, automotive parts finishing | Pros: Achieves fine tolerances. Cons: Slower than other machining methods. |
| Drilling Machine | Creates holes of various sizes, available in manual and CNC versions. | Construction, manufacturing of components | Pros: Essential for many applications. Cons: Limited to hole-making tasks. |
| CNC Machine | Computer-controlled for high precision and automation. | Mass production, intricate designs | Pros: High efficiency, repeatability. Cons: Higher maintenance costs. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Lathe Machines?
Lathe machines are essential tools in machine shops, characterized by their ability to rotate a workpiece against a cutting tool. This allows for various operations such as turning, drilling, and threading, making them versatile for different applications. Lathes are particularly suitable for industries requiring precision parts, such as automotive and aerospace. When purchasing, consider the machine’s size, power, and the skill level required for operation, as these factors can significantly impact productivity and efficiency.
How Do Milling Machines Stand Out in B2B Applications?
Milling machines are distinguished by their use of rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece, enabling the creation of complex shapes. They are widely used in sectors such as aerospace and automotive for producing intricate components. Their versatility allows for both horizontal and vertical milling operations. Buyers should evaluate factors like the machine’s capabilities, tooling options, and the availability of CNC features to ensure they select a model that meets their production needs.
Why are Grinding Machines Important for Precision Work?
Grinding machines utilize abrasive wheels to achieve high levels of surface finish and precision, making them indispensable in tool production and automotive parts finishing. They excel in producing fine tolerances and are often used for sharpening tools and finishing machined surfaces. B2B buyers should consider the type of grinding required, the machine’s speed, and its compatibility with various materials to make informed purchasing decisions.
What Role Do Drilling Machines Play in Manufacturing?
Drilling machines are vital for creating holes in various materials and are available in manual and CNC formats. They are commonly used in construction and manufacturing to produce components that require precise hole sizes. When choosing a drilling machine, consider the range of hole sizes, the machine’s power, and its ease of use, as these aspects will directly influence operational efficiency and output quality.
How Does CNC Technology Enhance Machine Shop Operations?
CNC machines are advanced tools that utilize computer numerical control for precision machining and automation. They are ideal for mass production and intricate designs, providing high efficiency and repeatability in operations. While they come with higher initial costs and maintenance requirements, the long-term benefits include reduced labor costs and increased production speed. B2B buyers should assess the software compatibility, training needs, and service support available when investing in CNC technology.
Key Industrial Applications of machine shop machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machine shop machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Precision machining of aircraft components | Enhances safety and performance through high precision | Certification of machinery, international standards |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of engine and transmission parts | Increases efficiency and reduces production costs | Supplier reliability, maintenance support, and service |
| Oil & Gas | Fabrication of drilling and pipeline equipment | Ensures durability and reliability in harsh environments | Material quality, compliance with industry regulations |
| Construction & Heavy Equipment | Custom parts for machinery and tools | Reduces downtime and improves operational efficiency | Local sourcing capabilities, lead times, and logistics |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing of surgical instruments | Enhances patient safety through precision and reliability | Quality assurance, certification, and traceability |
How are machine shop machines utilized in the aerospace and defense industries?
In the aerospace and defense sectors, machine shop machines are critical for the precision machining of components like turbine blades, landing gear, and structural parts. These components must meet stringent safety and performance standards, requiring advanced CNC machines and lathes capable of intricate designs. International B2B buyers must ensure that the machines sourced comply with ISO standards and possess necessary certifications to maintain quality and reliability in their production processes.
What role do machine shop machines play in automotive manufacturing?
Machine shop machines are indispensable in automotive manufacturing for producing engine blocks, transmission parts, and other critical components. Utilizing milling machines and grinders, manufacturers can achieve the high tolerances required for optimal vehicle performance. For buyers in regions like South America and Africa, it’s essential to consider the availability of spare parts and after-sales service to minimize downtime and ensure continuous production.
How are machine shop machines applied in the oil and gas industry?
In the oil and gas industry, machine shop machines are used to fabricate drilling equipment, valves, and pipeline components. These parts must withstand extreme conditions, making durability a priority. Sourcing considerations for international buyers include ensuring that materials meet industry specifications and that suppliers have a proven track record in producing equipment that complies with local and international safety regulations.
What is the significance of machine shop machines in construction and heavy equipment?
Machine shop machines are vital for producing custom parts for construction machinery and tools, such as excavators and cranes. By leveraging precision machining, businesses can reduce downtime due to equipment failure and enhance operational efficiency. Buyers should focus on sourcing from suppliers who offer rapid prototyping and short lead times, which are crucial in the fast-paced construction environment.
How do machine shop machines contribute to the medical device industry?
In the medical device industry, machine shop machines are employed to manufacture surgical instruments and implantable devices that require high precision and reliability. The quality of these devices directly impacts patient safety, making it essential for international buyers to ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality assurance processes and certifications. Traceability in the production process is also critical to meet regulatory requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machine shop machines’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Machine for Specific Tasks
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the appropriate machine for their specific manufacturing needs. With a vast array of options available—lathes, milling machines, grinders, and more—determining the right fit can be overwhelming. This decision is critical as it directly impacts production efficiency, quality of output, and overall operational costs. For instance, a company in Nigeria may require a lathe for precision parts but may struggle to understand the differences between manual and CNC models, leading to potential misinvestment.
The Solution:
To navigate this complexity, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their operational requirements. Start by defining the specific tasks the machine will perform, such as drilling, cutting, or shaping materials. Create a detailed list of necessary features, including size, power, and material compatibility. Leverage online resources, such as specifications from reputable suppliers, and consult with experienced technicians who can offer insights into the latest technologies and trends. Additionally, consider attending industry trade shows or webinars to see machines in action, which can significantly enhance understanding and confidence in the purchasing decision. Engaging with a supplier who offers comprehensive support, including training and after-sales service, can also ensure that the right machine is not only selected but utilized effectively.
Scenario 2: High Maintenance Costs and Downtime
The Problem:
Many businesses experience high maintenance costs and unexpected downtimes due to inadequate servicing of their machine shop equipment. For instance, a manufacturing plant in Germany may rely on multiple machines for production but finds that their equipment frequently breaks down, disrupting operations and increasing repair costs. This scenario is especially common when machines are not regularly maintained or when the wrong type of machine is used for a task, leading to premature wear and tear.
The Solution:
Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy is crucial for minimizing downtime and controlling costs. Establish a routine maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections, cleaning, and part replacements. Consider investing in a maintenance management system that can track machine usage and alert staff when servicing is due. Collaborate with suppliers who offer maintenance packages tailored to your specific equipment. These packages often include training for your staff on how to perform basic maintenance tasks, reducing reliance on external technicians and empowering your team. Moreover, incorporating predictive maintenance technologies can help identify potential issues before they lead to breakdowns, ensuring smoother operations and extending the lifespan of your machines.
Scenario 3: Navigating Import Regulations and Supply Chain Challenges
The Problem:
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, navigating import regulations and supply chain logistics can present significant obstacles. A machine shop in Nigeria might find it difficult to import specialized CNC machines due to complex tariffs and customs procedures, which can delay production and increase costs. This issue is compounded by supply chain disruptions that can affect the availability of spare parts and maintenance services.
The Solution:
To effectively manage these challenges, buyers should develop a clear understanding of their local regulations regarding machinery imports. Engage with a customs broker who specializes in industrial equipment to facilitate smoother transactions and ensure compliance with all legal requirements. Additionally, consider sourcing machines from local or regional suppliers who can provide timely support and maintenance services. This approach not only reduces lead times but also mitigates risks associated with international shipping and tariffs. Establishing a robust supply chain network that includes multiple suppliers for critical components can also provide flexibility and reduce dependency on single sources. Moreover, building strong relationships with local distributors can enhance access to technical support and spare parts, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machine shop machines
What Are the Key Materials Used in Machine Shop Machines?
In the realm of machine shop machinery, the selection of materials is critical to ensure optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four commonly used materials: steel, aluminum, cast iron, and composite materials. Each material has unique properties and implications for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Steel Perform in Machine Shop Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in machine shop machines due to its exceptional strength and versatility. Key properties include high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Steel’s durability makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications, such as lathes and milling machines.
Pros: Steel is highly durable and can be heat-treated to enhance its properties. It is readily available and can be manufactured into various shapes and sizes.
Cons: The main drawback is its susceptibility to corrosion unless properly treated. Additionally, steel can be heavier than other materials, which may impact machine mobility.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is essential. Buyers in regions like Nigeria may need to consider local availability and import regulations, while European buyers may prefer materials that meet EU standards for sustainability.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Machine Shop Machines?
Aluminum is another popular choice for machine shop machines, particularly for applications where weight is a concern. Key properties include lightweight, good corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability. Aluminum’s thermal and electrical conductivity also make it suitable for specific applications like heat exchangers.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier handling and reduces energy consumption in operations. Its resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of machines.
Cons: Aluminum is generally less strong than steel, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications. It can also be more expensive than steel, depending on the grade.
International buyers should consider standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In Europe, compliance with EN standards is crucial, while in South America, buyers should assess local suppliers for availability and pricing.
Why Is Cast Iron a Preferred Material for Certain Machines?
Cast iron is favored in the manufacturing of machine bases and frames due to its excellent vibration-damping properties and rigidity. Key properties include high compressive strength and good wear resistance, making it suitable for heavy machinery.
Pros: Cast iron is highly stable and can absorb vibrations, which enhances machining accuracy. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to other materials.
Cons: The main limitation of cast iron is its brittleness, which can lead to cracking under heavy impact. Additionally, it is heavier than both steel and aluminum, which may complicate transport and installation.
For international buyers, understanding compliance with ASTM A48 or DIN 1691 is important. Buyers in the Middle East may face challenges with sourcing high-quality cast iron, necessitating thorough supplier vetting.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Machine Shop Machinery?
Composite materials, such as reinforced plastics or carbon fiber, are increasingly used in machine shop applications due to their lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. Key properties include resistance to corrosion and fatigue, making them suitable for specialized applications.
Pros: Composites can be tailored for specific applications, offering design flexibility. They are also resistant to chemicals and environmental factors, enhancing durability.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly. Additionally, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
International buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM D3039 for composite materials. In Europe, compliance with EN ISO standards is essential, while buyers in Africa may need to consider local manufacturing capabilities.
Summary of Material Selection for Machine Shop Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for machine shop machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Lathes, milling machines | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machinery components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less strong than steel | High |
| Cast Iron | Machine bases and frames | Excellent vibration damping | Brittle and heavy | Low |
| Composite Materials | Specialized applications | Tailored properties and durability | Complex and costly manufacturing | Medium to High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for machine shop machines, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with relevant standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machine shop machines
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Machine Shop Machines?
The manufacturing process for machine shop machines is intricate and involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the quality and functionality of the final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, often metals like steel, aluminum, and various alloys. Suppliers typically perform rigorous inspections to verify material specifications, which may include chemical composition and mechanical properties. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting or water jet cutting are often employed to achieve precise dimensions before moving to the forming stage.
-
Forming: The forming stage is where the actual shaping of the materials occurs. Techniques such as machining, casting, and forging are prevalent. For instance, CNC machining is widely used for its precision and efficiency, allowing for complex geometries that are essential in machine tools. Other methods, like injection molding for plastic components or die casting for metal parts, may also be utilized, depending on the machine’s design requirements.
-
Assembly: After individual components are formed, they are brought together during the assembly stage. This process may involve manual labor or automated systems, depending on the complexity of the machine and production volume. It is critical that this stage adheres to specific alignment and torque specifications to ensure optimal performance.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes surface treatment processes such as grinding, polishing, and coating. These finishing touches not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also contribute to the machine’s durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. Techniques like anodizing, powder coating, or plating can provide additional protection, especially for machines intended for harsh environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated Into Machine Shop Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of machine shop machines to ensure that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Effective QA involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process.
-
International Standards: Compliance with recognized international standards such as ISO 9001 is crucial. This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), ensuring that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for European markets and API standards for oil and gas applications are vital for global competitiveness.
-
Quality Checkpoints: Various checkpoints are implemented to monitor quality throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of incoming materials to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC involves regular inspections and tests to monitor the ongoing production process, ensuring that any deviations are detected and corrected immediately.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, FQC is conducted to verify the machine’s performance against specifications, including functionality tests and safety checks. -
Testing Methods: Common testing methods include non-destructive testing (NDT), dimensional inspections using coordinate measuring machines (CMM), and performance testing under operational conditions. These methods help identify defects and ensure that machines operate as intended.
What Strategies Can B2B Buyers Use to Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential to mitigate risks associated with purchasing machine shop machines.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers allows buyers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality systems, and compliance with international standards. This firsthand evaluation can provide insights into the supplier’s operational capabilities and commitment to quality.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC documentation. These reports should outline the testing methods used, results achieved, and any corrective actions taken in response to defects. A well-documented quality assurance process is a strong indicator of a reliable supplier.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be particularly valuable in ensuring compliance with international standards and local regulations, especially when dealing with suppliers in different countries.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances that can impact their purchasing decisions.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the cultural and regulatory environment of the supplier’s country is essential. Different regions may have varying standards for quality assurance, which can affect product specifications and compliance. For example, the regulatory landscape in Europe is often more stringent than in other regions, requiring additional certifications for machinery.
-
Communication Barriers: Clear communication is vital to ensure that both parties understand quality expectations. Language differences and time zone challenges can complicate negotiations and quality discussions, making it crucial to establish a reliable communication channel early in the relationship.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: The logistics of transporting machine shop machines across international borders can introduce additional quality control challenges. Buyers should consider the potential for damage during shipping and ensure that suppliers use appropriate packaging and handling procedures to protect machinery.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing machine shop machines, ensuring they select suppliers that prioritize quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machine shop machines’
Introduction
Sourcing machine shop machines can be a complex process, especially for international B2B buyers. This checklist serves as a practical guide to help you navigate the procurement journey effectively, ensuring you acquire the right equipment that meets your operational needs while maximizing your investment.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical to ensure the machines you procure will meet your production requirements. Consider factors such as the types of materials you’ll be working with, the dimensions of the parts to be produced, and the desired precision levels. Documenting these specifications will provide a solid foundation for your search and help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their credentials and industry reputation. Look for certifications such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to quality management systems. Additionally, consider suppliers with experience in your industry to ensure they understand your specific needs and challenges.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Pay attention to their track record in delivering quality equipment and after-sales support, as these factors are essential for long-term success.
- Check Reviews and Testimonials: Look for feedback from existing customers to gauge satisfaction levels and reliability.
- Assess Communication and Support: A supplier’s responsiveness can indicate the quality of service you can expect post-purchase.
Step 4: Compare Equipment Options
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, compare the equipment options they offer based on your defined specifications. Look for machines that provide the best balance of performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Pay attention to technical features such as automation capabilities, energy efficiency, and ease of operation.
- Request Demonstrations: If possible, arrange for product demonstrations or visit the supplier’s facility to see the machines in action.
- Consider Upgrades and Accessories: Evaluate whether the machine can be upgraded or if there are essential accessories required for your operations.
Step 5: Assess Financing Options
Understanding the financing options available can significantly impact your purchasing decision. Explore different payment structures such as leasing or financing plans that fit your budget and cash flow needs. A well-structured payment plan can ease the financial burden while allowing you to acquire the necessary equipment.
- Inquire About Warranties: Ensure the machines come with warranties that cover repairs and replacements, protecting your investment.
- Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial purchase price, but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, parts, and energy consumption.
Step 6: Confirm Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the machines you plan to purchase comply with local regulations and safety standards in your region. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues, operational disruptions, and costly penalties.
- Request Documentation: Ask suppliers for compliance certifications and ensure they are up-to-date.
- Research Local Standards: Familiarize yourself with industry regulations specific to your country or region to avoid any oversight.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you’ve selected the right machine and supplier, carefully review the purchase agreement. Ensure all terms, including delivery schedules, installation support, and warranty conditions, are clearly defined. A comprehensive agreement protects both parties and lays the groundwork for a successful partnership.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing machine shop machines, ultimately leading to better procurement decisions and enhanced operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machine shop machines Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Machine Shop Machines?
When sourcing machine shop machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in manufacturing machines significantly influence pricing. High-grade metals and advanced composites often increase costs but result in better durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in both production and assembly. In regions with higher labor rates, such as Western Europe, these costs can be substantial. Conversely, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs may yield savings but could affect quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overheads.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the specialized tools required for production, which can vary depending on the machine’s complexity. Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment but is often necessary for achieving precision in manufacturing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that machines meet required specifications and standards. While this may add to initial costs, it reduces long-term risks associated with product failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are often underestimated. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can substantially impact total expenses, especially for international buyers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing structure. Understanding industry standards for margins can aid in negotiation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machine Shop Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the final price of machine shop machines:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounted pricing due to economies of scale. Conversely, low-volume orders may incur higher per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom machines tailored to specific needs typically command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines built with premium materials or those that meet international quality standards (like ISO certifications) generally cost more. However, they may offer enhanced performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record, while emerging suppliers might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery and responsibility for costs (like freight, insurance, and customs duties) is crucial for international purchases. These can significantly affect the total cost.
What Negotiation Strategies Can International B2B Buyers Employ?
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic negotiation is key to achieving favorable pricing:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs and secure better pricing.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Encourage suppliers to break down costs to identify areas where savings can be realized.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Machines that may appear cheaper upfront could incur higher TCO due to inefficiencies or frequent repairs.
-
Cultural Sensitivity in Negotiation: Understanding cultural differences in negotiation styles can aid in building rapport with suppliers, potentially leading to better deals.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets, several pricing nuances should be kept in mind:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate volatility can affect pricing. Consider locking in rates or negotiating contracts in stable currencies.
-
Tariffs and Import Duties: Be aware of any tariffs or duties that may apply to imported machines, as these can significantly increase overall costs.
-
Local Regulations: Compliance with local regulations may require additional investments in equipment or modifications, influencing total expenses.
Disclaimer
Prices for machine shop machines can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. Always seek detailed quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure that you are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machine shop machines With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Machine Shop Machines
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, machine shop machines are essential for precision machining and production. However, various alternative solutions exist that can achieve similar objectives, allowing businesses to optimize their operations based on specific needs. This analysis will compare traditional machine shop machines with two viable alternatives: 3D printing technology and CNC machining services.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Machine Shop Machines | 3D Printing Technology | CNC Machining Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and durability; suitable for mass production. | Versatile for complex designs but may have limitations in material strength. | Excellent precision and repeatability; ideal for custom parts. |
| Cost | High initial investment; long-term savings on bulk production. | Lower initial costs; material costs can vary significantly. | Moderate costs; pricing based on complexity and volume. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; setup can be time-consuming. | User-friendly; rapid prototyping capabilities. | Can be outsourced, reducing in-house expertise needs. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance; skilled technicians required. | Minimal maintenance; mostly software updates. | Maintenance dependent on service provider; often included in contracts. |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production with tight tolerances; metalworking. | Prototyping and small batch production; complex geometries. | Custom parts and low to medium volume runs; quick turnaround. |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
3D Printing Technology
3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing by allowing for rapid prototyping and the production of complex geometries that traditional machines might struggle to create. This technology enables manufacturers to quickly iterate designs and produce parts on demand, reducing lead times significantly. However, while 3D printing is cost-effective for small runs and prototypes, it may not provide the same material strength and durability as traditional machining methods. The choice of materials can also limit its application in high-stress environments.
CNC Machining Services
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining services offer precision and flexibility, making them a popular choice for custom parts production. With CNC machining, manufacturers can achieve high levels of accuracy and repeatability, which is critical for parts that require tight tolerances. Outsourcing CNC services can alleviate the burden of maintaining machinery and hiring specialized staff, allowing businesses to focus on their core competencies. However, costs can vary based on the complexity of the parts and the volume ordered, making it essential to evaluate the pricing structure beforehand.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between machine shop machines and alternative solutions like 3D printing or CNC machining services, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including their production volume, material requirements, and budget constraints. Machine shop machines are ideal for high-volume production where durability and precision are paramount. In contrast, 3D printing is better suited for rapid prototyping and designs that require flexibility. CNC machining strikes a balance, offering custom solutions with high precision and the ability to handle varying production volumes.
Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific operational needs and strategic goals of the business. By thoroughly assessing these alternatives, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their manufacturing capabilities and drive growth in competitive markets.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machine shop machines
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machine Shop Machines?
In the realm of machine shop operations, understanding the technical properties of machinery is crucial for effective procurement and use. Here are several essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality and type of material used in the construction of machine tools. Common materials include high-speed steel, carbide, and various alloys. Understanding material grade is important because it impacts the tool’s durability, wear resistance, and overall performance. Higher-grade materials often yield longer tool life and better machining accuracy, which can significantly affect production efficiency and costs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. It is critical in machining as it ensures that parts fit together correctly. In a B2B context, specifying tolerance levels can prevent costly errors and reworks. A tighter tolerance often means higher precision, which is essential in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where safety and performance are paramount.
3. Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), is a key performance indicator for machines like lathes and mills. It affects the material removal rate and the quality of the finished product. For B2B buyers, selecting machines with appropriate spindle speeds can enhance productivity and ensure compatibility with the materials being processed.
4. Power Rating
The power rating of a machine, usually expressed in horsepower or kilowatts, indicates its capacity to perform work. Machines with higher power ratings can handle more challenging materials and larger workloads. This specification is crucial for buyers who need machines that can operate efficiently under heavy demand, as it directly influences operational costs and output.
5. Weight and Size
The weight and size of a machine impact its stability and the space requirements in a workshop. Heavier machines tend to provide better stability during operations, while the size can affect the layout of the shop floor. B2B buyers must consider their facility’s capabilities and workflow when selecting equipment, as improper sizing can lead to inefficiencies and safety hazards.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Machine Shop Industry?
Familiarity with trade terminology can help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process more effectively. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality components compatible with their existing machinery, thereby enhancing reliability and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is vital for budgeting and inventory management. It can also influence negotiations; understanding MOQs can help businesses avoid overstocking or understocking critical components.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting price and delivery information for specific products or services. This process is essential for B2B buyers looking to compare offers and negotiate better terms. A well-structured RFQ can lead to significant cost savings and improved supplier relationships.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. They clarify issues such as shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer. For international B2B transactions, understanding Incoterms is crucial to avoid misunderstandings that can lead to costly delays or disputes.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automation of machine tools through computer programming. This technology allows for high precision and repeatability in machining operations. For B2B buyers, investing in CNC machines can lead to enhanced productivity and reduced labor costs, making it a key consideration in modern manufacturing environments.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their machine shop operations and contribute to their overall business success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machine shop machines Sector
What Are the Current Trends Driving the Machine Shop Machines Market?
The global machine shop machines market is being shaped by several key trends and dynamics that international B2B buyers must navigate. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for precision and automation in manufacturing processes. As industries evolve, there is a growing need for machine tools that can deliver higher accuracy and efficiency. This shift is particularly pronounced in sectors such as automotive and aerospace, where precision is critical.
Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is influencing sourcing trends, with manufacturers increasingly adopting smart technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) to enhance operational efficiency. These technologies facilitate predictive maintenance, which minimizes downtime and extends the life of machinery. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these technological advancements is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Moreover, the geographical diversification of supply chains is becoming a prominent trend. International buyers are increasingly looking beyond traditional markets to source machine shop machines from emerging economies that offer competitive pricing and innovative solutions. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in regions such as Nigeria and Germany, where local manufacturing capabilities are expanding.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing Decisions in the Machine Shop Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming non-negotiable aspects of the B2B procurement process for machine shop machines. Environmental concerns are prompting manufacturers to evaluate the lifecycle impact of their equipment, from production to disposal. As such, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now looking for suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and sustainable sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, are becoming vital in the decision-making process. Additionally, materials that are recyclable or made from sustainable sources are gaining traction in the market, aligning with the growing emphasis on green manufacturing.
For international buyers, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as Europe, sourcing machines that comply with these standards not only mitigates risk but can also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
How Have Machine Shop Machines Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of machine shop machines is a testament to the relentless pursuit of efficiency and precision in manufacturing. Historically, machine tools were primarily manual, requiring skilled operators to perform various machining tasks. However, the introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology revolutionized the sector by automating processes, reducing human error, and enabling complex designs that were previously unattainable.
Over the decades, advancements in materials science have also played a pivotal role, allowing for the creation of more durable and versatile machines. Today, machine shop machines are equipped with smart technology, enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics. This evolution not only enhances productivity but also aligns with the modern buyer’s demand for intelligent and adaptable solutions that can respond to changing market dynamics.
As international buyers navigate this ever-evolving landscape, understanding the historical context of machine shop machines can provide valuable insights into current capabilities and future trends, ultimately informing smarter purchasing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machine shop machines
-
How do I determine the right machine shop machines for my business needs?
To identify the best machine shop machines for your operations, start by assessing the specific tasks you need to accomplish. Consider the types of materials you will be working with, the precision required, and the volume of production. Engage with suppliers who can provide insights based on your industry and offer machines that cater to your specific applications, whether that’s lathes for turning, milling machines for shaping, or grinders for finishing. Additionally, request demonstrations or samples to evaluate the machines’ performance before making a purchase. -
What is the best milling machine for small-scale production?
For small-scale production, a CNC milling machine is often the best choice due to its versatility and precision. Look for models that offer a compact footprint without sacrificing functionality. Popular options include desktop CNC mills, which are ideal for prototyping and small parts manufacturing. Ensure the machine you choose has the capability to handle the materials you typically work with and offers features like variable speed controls for enhanced adaptability. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting machine shop suppliers?
When vetting suppliers for machine shop machines, evaluate their industry experience, customer reviews, and product range. Check if they provide after-sales support, including maintenance and training services. Assess their compliance with international quality standards and certifications, as this can impact the reliability of their machines. Additionally, consider their capacity for customization, as your business might require specific modifications to meet unique operational needs. -
What are typical payment terms for purchasing machine shop equipment internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary significantly based on the supplier and your negotiation. Common terms include upfront deposits (usually 30-50%), with the balance due upon delivery or after installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letter of credit arrangements, which can help mitigate risk. Always clarify payment terms in writing and ensure they are included in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for machine shop machines I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications for the machines you are considering. It’s advisable to conduct quality checks upon delivery, including performance testing and dimensional inspections to confirm adherence to agreed standards. Establishing a clear return and warranty policy with your supplier can also protect your investment. If possible, visit the manufacturer’s facility to observe their quality control processes firsthand. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machine shop machines?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machine shop machines typically depends on the supplier and the specific type of equipment. While some suppliers may have a low MOQ for standard machines, others might require bulk orders for specialized or customized equipment. It’s essential to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate the MOQ that aligns with your budget and operational requirements, especially if you’re a smaller business or a startup. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing machine shop machines?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with heavy machinery transport to ensure safe and timely delivery. Understand the customs clearance process in your country, including any documentation needed to facilitate importation. Additionally, factor in transportation costs from the port to your facility and consider insurance options to cover potential damages during transit. -
How do I handle installation and training for new machine shop equipment?
Installation and training are crucial for maximizing the efficiency of new machines. Most reputable suppliers will offer installation services and on-site training to ensure your team can operate the equipment safely and effectively. Prior to delivery, discuss the training options available, including hands-on sessions and manuals. Consider scheduling follow-up training sessions as needed to address any challenges your team might encounter as they become familiar with the new machines.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Machine Shop Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Penn Tool Co – Machine Tools
Domain: penntoolco.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Machine tools include a variety of products used to shape, cut, grind, shear, and form metal into desired parts by removing metal chips from the workpiece. They can be manually operated or powered electronically, pneumatically, or hydraulically. Popular examples include lathes, grinders, drill presses, and milling machines. Applications include drilling holes with precision, creating molds for cas…
2. Atlas Machine – Machining and Repair Equipment
Domain: atlasmachine.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Atlas Machine offers a comprehensive range of machining and repair equipment, including:
1. **Lathes**:
– 10 Engine Lathes (½” to 60″ Dia.) with various specifications.
– Manual and CNC Vertical Lathes (1 VTL Lathe: 42″ diameter x 35″ height; 1 CNC VTL Lathe: 96″ diameter x 59″ height).
– 11 CNC Lathes (½” to 78.74″ Dia.) with various specifications.
2. **Milling**:
– 4 CNC Vertical …
3. Machine Shop Equipment – Buy & Sell Community
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Machine Shop Equipment – Buy & Sell Community, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Norman Machine Tool – Metalworking Machinery
Domain: normanmachinetool.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Norman Machine Tool specializes in metalworking and fabricating machinery sales and service, offering both new and used machines. Their extensive inventory includes various categories such as: Lapping Machines, 3D Printers, Air Compressors, CNC Machines (including CNC Lathes, CNC Mills, CNC Press Brakes), Grinders (Belt Grinders, Surface Grinders), EDM Machines, Forklifts, Inspection Equipment, La…
5. Machinesused – Used CNC Machines
Domain: machinesused.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Machinesused.com is a used machinery dealer offering a variety of used CNC machines, machine tools, metalworking machinery, fabricating machinery, and tooling. Key products include: Haas CNC Machines, CNC Machining Centers, CNC Lathes, Mazak, Fadal, VMC, Grinders, Inspection Equipment, and Rotary Tables. The company provides services such as online auctions for selling machines, industrial apprais…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machine shop machines
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Machine Shop Machines?
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing of machine shop machines is pivotal for optimizing productivity and ensuring cost-effectiveness. By investing in high-quality tools like lathes, milling machines, and grinders, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and minimize downtime. The ability to select the right equipment tailored to specific needs not only fosters innovation but also strengthens market positioning.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing?
For international buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics and supplier capabilities is crucial. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, superior service, and access to advanced technology. Moreover, considering factors like maintenance support, financing options, and training for staff can significantly impact the long-term success of a machine shop.
How Can You Prepare for Future Trends in Machine Shops?
Looking ahead, the integration of smart technologies and automation will play a critical role in shaping the future of machine shops. Buyers should remain informed about advancements in CNC machinery and automated systems to stay competitive. Embracing these innovations not only streamlines operations but also prepares businesses for evolving market demands.
In conclusion, strategic sourcing is not merely a transactional process; it is a fundamental strategy for growth and sustainability. Engage with trusted suppliers today to ensure your machine shop is equipped for tomorrow’s challenges and opportunities.