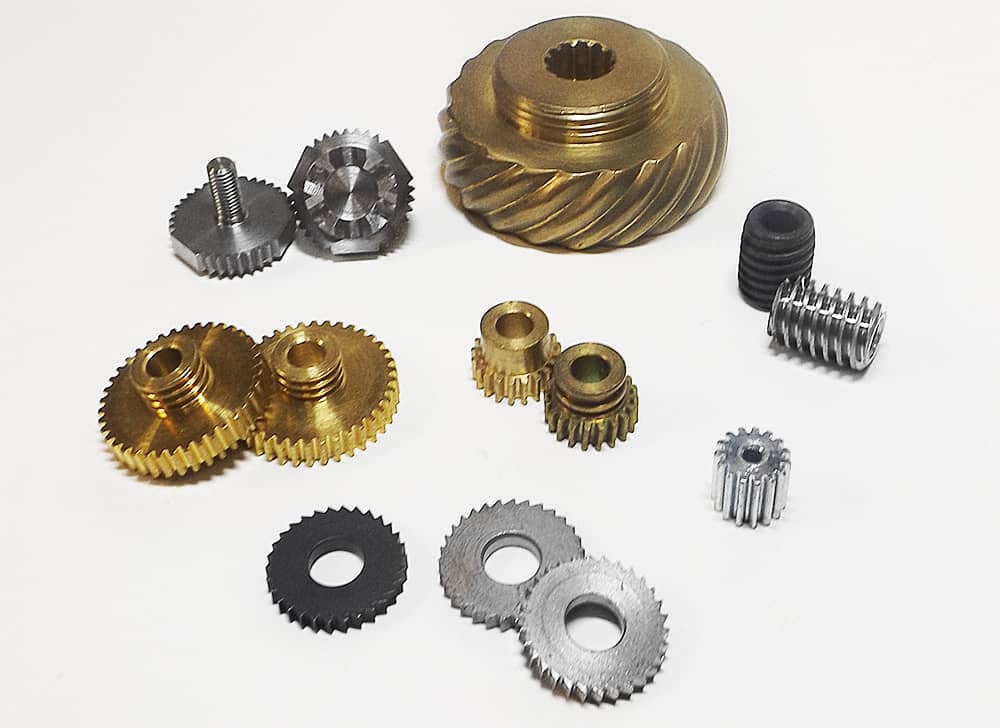
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machine products
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality machine products poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those in dynamic markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the intricacies of various products—from CNC machinery and robotics to fabrication tools—requires a comprehensive approach. This guide serves as an essential resource, providing insights into the diverse types of machine products available, their numerous applications, and the best practices for supplier vetting.
Buyers will find in-depth information on cost factors, payment options, and the latest industry trends that can impact their purchasing decisions. By empowering stakeholders with knowledge about product specifications, supplier reliability, and market conditions, this guide aims to streamline the sourcing process and mitigate risks associated with procurement.
Moreover, we highlight tailored strategies for navigating regulatory environments and logistical challenges unique to different regions. Whether you’re a manufacturer in Brazil seeking automation solutions or a distributor in Vietnam looking for reliable partners, this guide equips you with the actionable insights necessary for making informed and strategic decisions in the global machine products market. With an authoritative focus, we aim to enhance your competitive edge as you navigate the complexities of international trade.
Understanding machine products Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machines | Computer-controlled, high precision, automated tools | Aerospace, automotive, electronics manufacturing | Pros: High accuracy, repeatability. Cons: High initial cost. |
| Robotics | Automated machines with programmed movements | Assembly lines, packaging, warehousing | Pros: Labor-saving, enhanced efficiency. Cons: Integration complexity. |
| Fabrication Equipment | Manual or automated tools for cutting and shaping metal | Metalworking, construction | Pros: Versatility, diverse applications. Cons: Requires skilled operators. |
| Tooling and tooling accessories | Devices used for holding and shaping tools | Manufacturing, maintenance workshops | Pros: Improves production speed. Cons: Initial setup can be time-consuming. |
| Edge Banding Machines | Machines that apply edge banding to panels | Cabinet making, furniture production | Pros: Enhanced product aesthetics. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
What Are CNC Machines and Their B2B Applications?
CNC machines, or Computer Numerical Control machines, are sophisticated tools programmed to execute precise machining tasks with minimal human intervention. They are popular in high-stakes industries like aerospace and automotive where precision is non-negotiable. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment against the long-term savings gained through improved accuracy and reduced waste. It’s essential to evaluate the machine’s specifications based on production needs and maintenance costs.
How Do Robotics Impact B2B Manufacturing Efficiencies?
Robotics in manufacturing refers to the use of automated machines programmed to carry out specific repetitive tasks. Ideal for assembly lines and warehousing, they significantly reduce the need for manual labor and improve operational efficiency. B2B companies must assess the complexity of integration and the potential return on investment, taking into account the cost of programming and ongoing maintenance.
What Versatile Applications Does Fabrication Equipment Offer?
Fabrication equipment encompasses a variety of machines used for cutting, shaping, and assembling raw materials, primarily metals. Its versatility caters to both automated production lines and manual workshops, making it a staple in industries such as construction and metal fabrication. Buyers should weigh the benefits of increased productivity against the requirement for skilled labor, as effective operation often requires specialized knowledge.
Why Are Tooling and Tooling Accessories Vital for Manufacturers?
Tooling and tooling accessories are essential devices that facilitate the manufacturing process by holding and shaping materials. Commonly utilized across various sectors, including manufacturing and maintenance workshops, these tools can dramatically enhance production speed and product quality. However, buyers need to consider the time investment for setup and the possibility of trial and error to find the optimal tooling solutions for their specific production needs.
How Do Edge Banding Machines Enhance Product Aesthetics?
Edge banding machines play a crucial role in cabinetry and furniture production by applying protective and aesthetic edging to panels. This not only enhances the visual appeal of the finished product but also increases its durability against wear and tear. B2B buyers should evaluate how these machines integrate into existing lines and the long-term benefits versus the product’s niche application limits.
Key Industrial Applications of machine products
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machine products | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | CNC Machining for Precision Parts | Increased efficiency and reduced production costs | Quality certifications, machine compatibility, pricing |
| Aerospace | Automated Assembly Systems | Enhanced quality control and lowered labor costs | Reliability of suppliers, compliance with industry standards |
| Automotive | Robotics for Component Assembly | Boosted production output and improved safety | Technical support availability, integration capabilities |
| Energy | Machine Tools for Renewable Energy Equipment | Sustainable production and cost-effectiveness | Material specifications, supplier reputation, lead time |
| Construction | Heavy-Duty Machinery for Industrial Projects | Increased project efficiency and reduced downtime | Equipment durability, maintenance support, warranty terms |
How is CNC Machining Applied in the Manufacturing Sector?
CNC machining is a cornerstone of the manufacturing industry, providing the precision needed for high-quality parts. Manufacturers utilize CNC machines to create components that meet stringent specifications and tolerances. The value lies in enhanced productivity and cost reduction via automated processes, crucial for businesses operating internationally, especially in regions like Africa and South America. When sourcing CNC machines, buyers must consider certifications, after-sales support, and the right fit for their production needs, ensuring they can maintain efficiency and competitiveness.
What Role do Automated Assembly Systems Play in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, automated assembly systems are critical in ensuring that components are assembled with precision and consistency. These systems significantly reduce the manual effort involved, leading to improved accuracy and quality control. Businesses benefit from reduced labor costs and minimized error rates. For international buyers, especially in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing such systems requires attention to compliance with aerospace standards and reliability of the supplier, affecting overall operational efficiency and safety.
How are Robotics Transforming Automotive Component Assembly?
Robotic technology in automotive component assembly has revolutionized the production line, leading to higher output and enhanced safety. Robots can perform repetitive tasks without fatigue, improving both speed and accuracy in manufacturing processes. For automotive companies, particularly those targeting fast-growing markets in South America, sourcing robotics should include evaluating the provider’s technical support capabilities and compatibility with existing systems, which can be crucial for seamless integration into their production workflows.
What is the Application of Machine Tools in the Energy Sector?
Machine tools in the energy sector, particularly renewable energy, play a vital role in fabricating components for solar panels, wind turbines, and other equipment. This application allows companies to adopt sustainable practices while also benefiting from cost efficiencies in production. International buyers from regions focused on energy innovation must assess material specifications and supplier reliability, while also ensuring that partners are committed to sustainability practices and technology advancements.
What Role Does Heavy-Duty Machinery Play in Construction Projects?
Heavy-duty machinery is essential in the construction sector, facilitating projects that require robust performance and reliability. These machines enhance project efficiency by enabling rapid completion and reducing the likelihood of downtime. For businesses involved in construction across different continents, key factors when sourcing include the machinery’s durability, after-sales service, and warranty terms—which are vital for maintaining operational strength over the life of extensive construction projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machine products’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Complex Configuration Needs
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers encounter challenges when sourcing machine products that require extensive customization to fit specific operational needs. For instance, a manufacturing firm in Brazil may require CNC machines that integrate seamlessly with existing technology while adhering to local regulations. These customizations can lead to miscommunications with suppliers, delays, and potentially increased costs if the necessary specifications are not conveyed clearly from the beginning.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should develop comprehensive specifications documents that detail every requirement, including preferred dimensions, materials, capacities, and regulatory standards. Engaging with suppliers early in the procurement process can also facilitate discussions about customization capabilities. Additionally, forming a collaborative relationship with the supplier allows for ongoing adjustments and feedback, ensuring the final product meets the unique operational demands of the business. Leveraging CAD software for digital prototyping can also help visualize modifications before production, thereby reducing errors and costs associated with revisions.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Technical Support and Training
The Problem: A common issue among B2B buyers is the lack of adequate support and training once machine products have been purchased. For instance, a company in South Africa might invest in advanced robotic automation systems, only to find that their team lacks the skills needed to implement and maintain these systems effectively. This gap in knowledge can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased downtime, and an inability to realize the full potential of the investment.
The Solution: It is crucial for buyers to prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive training and support as part of their service package. Before finalizing any purchase agreements, buyers should inquire about the level of training available and whether ongoing support is provided. Setting up initial training sessions with the vendor’s experts can greatly enhance the efficiency of the workforce. Furthermore, creating a dedicated internal team focused on continuous learning and development in machine operation and maintenance can help adapt to technological advancements. Establishing regular check-ins with the supplier or technical support can also ensure recurring issues are identified and addressed proactively.
Scenario 3: Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Disruptions in the supply chain can severely impact a B2B buyer’s ability to maintain production schedules, especially for those procuring machine products from overseas suppliers in Europe or Asia. For instance, a manufacturer in the Middle East may face delayed shipments due to customs issues or freight disruptions, causing significant operational slowdowns.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, buyers should diversify their supplier base by establishing relationships with multiple vendors across different regions. This strategy can provide alternatives in times of disruption. Additionally, implementing demand forecasting tools can help predict future needs, allowing for bulk purchasing or preemptive orders on critical components. Buyers might also consider working with local suppliers who can provide faster delivery times for consumables or maintenance parts. Collaborating closely with logistics partners can enhance visibility and transparency in the supply chain, allowing for quicker responses to any potential issues that arise. Regularly reviewing inventory levels and adjusting safety stock measures can also help buffer against unexpected supply chain shocks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machine products
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Machine Products?
When selecting materials for machine products, several core properties influence performance and application suitability. The three most common materials utilized in machine product manufacturing are steel, aluminum, and plastics, each serving distinct needs and industries.
How Does Steel Perform in Machine Products?
Steel is renowned for its strength and durability, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring high tensile strength and impact resistance. Key properties of steel include excellent fatigue resistance, withstanding high temperatures (up to approximately 600°C) and significant pressure, making it suitable for heavy-duty machinery.
Pros & Cons: While steel’s robustness is an advantage, it also tends to be heavier and may require complex manufacturing processes that can increase costs. Corrosion resistance can be an issue unless special coatings or stainless alternatives are deployed.
Impact on Applications: In industries such as construction and automotive, steel parts are indispensable due to their ability to support substantial loads. However, international buyers need to consider standards like ASTM A36 for structural steel to ensure compliance with local and international regulations.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Bring to Machine Products?
Aluminum has become increasingly popular in machine product manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. This metal performs well up to about 200°C and is often used in applications where weight savings are crucial, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, making it suited for mobile applications. However, aluminum generally has a lower tensile strength compared to steel and can be more expensive, particularly when considering alloyed varieties.
Impact on Applications: With its corrosion resistance, aluminum is ideal for products exposed to harsh environments. Buyers from regions prone to humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, can benefit greatly from using aluminum in their products, aligning with standards such as ASTM B209.
What Role Do Plastics Play in Machine Products?
Plastics offer a vast array of applications in machine product manufacturing, owing to their versatility, chemical resistance, and ease of fabrication. Common types include polycarbonate, nylon, and PVC, which can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C, depending on the type.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are lightweight and usually have lower manufacturing costs compared to metals, significantly reducing production expenses. However, they may not possess the same durability as metals and can deform under extreme pressures or temperatures.
Impact on Applications: Plastics can be used in various applications where weight, wear resistance, and corrosion protection are vital, such as in electronics or household appliances. B2B buyers must evaluate relevant safety and material standards, such as JIS K 6734 for various plastic materials, to ensure compliance.
Overview of Material Considerations for International Buyers
International buyers should factor in material compliance with regional standards like DIN in Europe and ASTM in the U.S. Special attention must be paid to the material sourcing and potential trade regulations, particularly for machine products that involve cross-border transactions. Additionally, understanding the preferences within specific regions—such as durability in harsh climates in Africa or lighter materials for transport in Brazil—can greatly influence product performance and market acceptance.
Summary of Material Selection for Machine Products
| Material | Typical Use Case for machine products | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components in heavy machinery | High tensile strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive parts | Lightweight with excellent corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength compared to steel | High |
| Plastics | Encasing electronics and lightweight consumer products | Versatility and lower manufacturing costs | May deform and less durable | Low |
By understanding these materials’ properties, advantages, and disadvantages, B2B buyers can effectively strategize their procurement processes for machine products that meet their specific operational requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machine products
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Machine Products?
The manufacturing of machine products typically involves several distinct stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is vital to ensuring the end product meets required specifications and standards.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting the right materials based on the product’s application. Materials can range from metals like aluminum and steel to plastics and composites. Proper material handling, including storage and climate control, is crucial to avoid contamination or degradation. Material testing for quality—checking for impurities or structural integrity—often occurs during this phase.
-
Forming: During the forming stage, raw materials undergo processes such as machining, casting, forging, or laser cutting. Advanced techniques like CNC machining offer precision and repeatability, crucial for high-quality machine products. Manufacturers may rely on large-scale automated systems to optimize this process, which also reduces labor costs and minimizes waste.
-
Assembly: Once components are formed, they are assembled to create the final product. This can involve manual labor or automated systems, such as robotics. Effective assembly processes often require cross-functional teams to ensure all parts fit correctly and function together. Quality assurance begins here, with preliminary checks to prevent defects from moving further along the production line.
-
Finishing: The finishing stage enhances the product’s performance and appearance. Techniques include surface treatment such as anodizing, painting, and coating. Inspection follows to ensure that the finished product complies with specifications. This is often where aesthetic aspects and functionality undergo final scrutiny.
How Is Quality Assurance Ensured Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of machine products is critical, particularly for international B2B transactions. It ensures compliance with customer expectations and regulatory standards, such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications like CE or API.
-
International Standards: The ISO 9001 standard serves as a benchmark for quality management systems worldwide. Adhering to this standard can facilitate international trade by demonstrating a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, specific industries may require compliance with standards like the International Organization for Standardization API, particularly in the oil and gas sector.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, several checkpoints should be established:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials to ensure they meet specified quality standards before they enter the production process.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): At this stage, constant monitoring occurs during production to detect any deviation from quality standards early. Techniques may include real-time measurement and testing.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Upon completion of the product, FQC ensures it meets all requirements and specifications through thorough inspections and testing. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods can determine whether a machine product meets quality standards. These include destructive testing (e.g., tensile strength tests), non-destructive testing (e.g., ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing), and performance testing in simulated operating conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers seeking to ensure quality in their supply chain have several avenues to verify the quality control processes of their manufacturers.
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits is one effective way to assess a supplier’s manufacturing and quality systems. An audit can reveal the actual operational procedures and whether they align with the stated quality assurance practices. Buyers should prepare a checklist to evaluate both processes and finished products.
-
Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide comprehensive quality reports that detail their QA methodologies, test results, and compliance with international standards. Buyers should seek reports that include KPIs such as product rejection rates, claim resolution times, and overall product performance metrics.
-
Third-Party Inspection: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality processes and product compliance. These services often follow standardized methodologies to inspect materials, processes, and end products, offering added assurance to buyers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating quality control in international trade can be challenging. B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, need to be aware of some key nuances.
-
Cultural Considerations: Differences in business practices and cultural expectations can affect quality outcomes. Understanding the local manufacturing environment, workforce capabilities, and common practices is crucial. Establishing clear communication channels helps bridge cultural differences, ensuring that expectations regarding quality standards are universally understood.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with both local and international regulations varies significantly. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with the necessary certifications and product compliance laws of their home jurisdictions and those of the suppliers. This will help avoid pitfalls related to non-compliance and related penalties.
-
Trade Policies: Tariffs, duties, and import regulations may impact the final cost and quality of machine products. Buyers should consider these factors when selecting suppliers, as they may affect the overall production process and adherence to quality standards.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for machine products are integral to ensuring high-quality outcomes. B2B buyers must be proactive in understanding these processes, verifying suppliers through audits and reports, and navigating the nuances of international trade. By doing so, they can mitigate risks and build robust manufacturing partnerships that deliver superior products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machine products’
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right machine products requires careful consideration and a strategic approach. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procurement, ensuring they make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining the technical specifications required for your project. This includes dimensions, weight capacities, and performance criteria specific to the machine products you need. By having precise specifications, you can set clearer expectations, avoid miscommunication with suppliers, and streamline the evaluation process.
- Consider industry standards that your products must adhere to for safety and efficiency.
- Identify compatibility requirements with existing machinery or processes within your operations.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Research the current market for machine products to gain insights into the available options and suppliers. This step is crucial for understanding pricing, identifying trends, and evaluating the competitive landscape. Utilize online resources, such as industry reports, trade shows, and expert reviews.
- Leverage platforms that are well-regarded in the machinery sector to gather information on potential suppliers.
- Network within industry associations to gain insights and referrals from fellow professionals.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before finalizing a supplier, it’s imperative to conduct thorough due diligence. Review company profiles, seek case studies specific to your industry, and request references from previous clients. This evaluation helps ensure the supplier’s capabilities align with your production needs.
- Look for suppliers with extensive experience in your sector, particularly those with a track record of high-quality delivery.
- Request visits to their facilities or virtual tours to assess production capabilities and quality management systems.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers hold the relevant certifications and comply with regulatory standards in your industry. Valid certifications can include ISO 9001 for quality management or specific industry-related safety standards. Compliance demonstrates a commitment to quality and consistent operational excellence.
- Request documented proof of certifications and audit results to verify compliance.
- Check for any recent audits or reviews that highlight the supplier’s performance in quality controls.
Step 5: Assess Payment Terms and Warranty Policies
Understanding payment terms and warranty policies is crucial for managing your financial exposure. Assess the flexibility of payment schedules and the implications of different terms on your cash flow. Additionally, a robust warranty policy can safeguard against potential defects or performance issues.
- Negotiate terms that align with your financial practices while protecting your interests.
- Evaluate warranty offerings to ensure adequate coverage for repairs, servicing, and product returns.
Step 6: Request Samples or Prototypes
If possible, request samples or prototypes before making a bulk purchase. This allows you to directly assess the quality and functionality of the machine products against your specifications. Prototypes can also reveal potential issues that may not be evident from product datasheets alone.
- Use this opportunity to test performance in real-world applications relevant to your operation.
- Provide feedback to the supplier to clarify any modifications needed before full-scale production.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Once you select a supplier, establish effective communication protocols. Clear channels help facilitate timely updates on production and delivery schedules and allow for quick responses to any issues that arise.
- Use project management tools to track communications and deadlines effectively.
- Regularly schedule updates to maintain transparency and reinforce strong supplier relationships.
By following this sourcing checklist, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement process for machine products, enabling them to make confident, strategic purchasing decisions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machine products Sourcing
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis for machine products sourcing is vital for international B2B buyers. This analysis involves several cost components and pricing influencers that can significantly affect the total expenditure associated with acquiring machine products.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machine Products Sourcing?
1. Material Costs
The cost of raw materials is the most significant expenditure in the machine products sector. The prices of steel, aluminum, plastics, and specialized alloys fluctuate due to market demand, geopolitical situations, and availability. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who can provide transparency around these costs and any potential price escalations.
2. Labor Costs
Labor costs include both direct and indirect expenses associated with producing machine products. Skilled labor is essential for the precise manufacturing processes that CNC machining and robotic assembly require. Variations in the cost of labor across different regions can influence the overall pricing structure, making it essential for buyers to evaluate the labor market conditions of the supplier’s location.
3. Manufacturing Overhead
Overhead encompasses costs related to utilities, operation of machinery, and maintenance. Buyers should inquire about how suppliers allocate overhead costs to their pricing to ensure clarity on what influences the final cost.
4. Tooling and Equipment Costs
Tooling represents a substantial investment in the machine production process. Custom tooling may be necessary for specialized products, and this cost can vary widely based on the complexity of the manufacturing process. Ensure that the pricing reflects both the initial and any ongoing costs related to tooling.
5. Quality Control (QC) Expenses
Investments in QC processes are critical for ensuring that machine products meet industry standards. Buyers should examine the supplier’s quality assurance protocols, certifications, and frequency of audits, as these factors can contribute to variances in cost.
6. Logistics and Distribution Costs
Logistics costs involve everything from freight charges to customs duties, which can vary widely based on product size and shipment method. Understanding the logistics process, including Incoterms agreed upon—such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight)—is crucial for predicting the final price.
7. Supplier Margin
The profit margins that suppliers incorporate into their pricing should be evaluated. Margins typically depend on the supplier’s positioning in the market, competition, and brand reputation. A higher margin might reflect greater service levels or specialized offerings, but it’s essential to balance quality and price.
How Are Prices Influenced for Different Machine Products?
What is the Impact of Volume and MOQ on Pricing?
Buyers often benefit from tiered pricing based on volume. Higher order quantities can lead to significant cost savings; however, suppliers may impose minimum order quantities (MOQ) which can limit smaller buyers. Establishing the right volume commitments can create an opportunity for price negotiation.
How Do Specifications and Customizations Affect Costs?
Customization often leads to increased pricing due to additional labor and tooling requirements. Buyers should clearly outline their specifications to evaluate if the resultant costs align with their budget. Simple, standardized products typically have lower costs compared to bespoke solutions.
What Role Do Materials and Quality Certifications Play?
The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. High-quality materials that meet specific certifications (ISO, ASTM, etc.) often come at a premium. Buyers should verify the certificates to avoid subsequent costs stemming from low-quality parts.
Which Supplier Factors Should Be Considered for Better Pricing?
A reliable supplier not only ensures quality but also offers competitive pricing. Factors such as the supplier’s history, reviews from previous clients, and their responsiveness contribute to long-term cost savings. A strategic partnership can lead to favorable pricing structures over time.
What Are the Best Tips for B2B Buyers in Machine Products Sourcing?
How to Negotiate Effectively for Better Pricing?
Engaging in open dialogue with suppliers about their cost structures and exploring potential discounts based on loyalty or future projects can lead to better pricing arrangements. Being informed about market trends will enhance negotiation strength.
Why Is Total Cost of Ownership Important?
Buyers should focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just initial purchase costs but also maintenance, operation, and disposal costs. This holistic approach can reveal long-term savings opportunities.
What Are the Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the local market dynamics in regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East is crucial for international pricing strategies. Specific regional challenges—like risks of currency fluctuations and customs changes—should be factored into the budgeting to prevent unexpected expenses.
Conclusion
A thorough understanding of the cost components and pricing dynamics in machine product sourcing can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By focusing on these critical elements, buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies while ensuring alignment with their operational goals.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machine products With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Machine Products: A Comparative Analysis
B2B buyers often face a pivotal choice when seeking solutions for manufacturing and production needs. Machine products—ranging from CNC machines to robotic automation systems—offer unique benefits. However, alternative technologies can similarly address industrial challenges, enabling informed decisions. This section explores the alternatives to machine products, focusing on their comparative advantages and limitations.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Machine Products | 3D Printing Technology | Traditional Hand Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in mass production, excellent repeatability | Suitable for rapid prototyping and complex geometries | Variable precision; reliant on user skill |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment; long-term cost savings through efficiency | Lower initial costs for low volume; materials can be expensive | Initial low cost; maintenance and replacements add up over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training and setup; may need supporting infrastructure | Easier to implement for small-scale users; often plug and play | Minimal setup, but skill-intensive |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required, parts can be costly | Minimal maintenance for machines; material sourcing can be challenging | Low-maintenance, but replacement is time-consuming |
| Best Use Case | Mass production runs, precision manufacturing | Prototyping, low-volume production, custom parts | Simple tasks, one-off projects |
Exploring 3D Printing Technology as an Alternative
3D printing has become a key player in modern manufacturing, particularly for companies seeking flexibility and rapid turnaround times. This technology thrives in creating prototypes and complex geometries that traditional manufacturing might struggle with. The initial costs are lower for small production runs, making it an appealing option for startups or R&D departments. However, the cost of materials can become a concern in larger projects. Additionally, while the technology requires less initial setup than conventional machines, a lack of operational knowledge can hinder its effective use.
Considering Traditional Hand Tools
Traditional hand tools continue to hold their ground, especially in scenarios demanding craftsmanship or quick, low-budget solutions. They have minimal initial costs and require little to no complex infrastructure to operate, making them accessible to a broad swath of industries. The downside lies in their reliance on the operator’s skill, which can lead to inconsistencies in output quality. Furthermore, although maintenance is minimal, ongoing usage can lead to significant wear and necessitate frequent replacements, which can accumulate costs over time.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution
Selecting the right manufacturing solution for your needs goes beyond mere cost comparisons. It’s essential to align the capabilities of machine products with your production requirements, workforce expertise, and financial constraints. For businesses involved in high-volume or precise manufacturing, investing in machine products might yield the best long-term return. Conversely, 3D printing could be ideal for organizations focused on innovation and flexibility, while traditional hand tools may suffice for simpler applications. Assessing the specific context of your operations will empower you to make choices that enhance productivity and competitive advantage in a global marketplace.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machine products
What are the Essential Technical Properties for Machine Products?
The technical specifications of machine products are crucial for international B2B buyers looking for reliable equipment that meets their operational needs. Understanding these specifications will enable decision-makers to make informed choices.
-
Material Grade
Material grade indicates the quality and mechanical properties of the metal or composite used in a machine product. Common grades, such as stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316), aluminum (e.g., 6061, 7075), or carbon steel, significantly impact product durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For B2B operations, selecting the appropriate material grade not only affects the longevity of the machinery but also minimizes maintenance and replacement costs. -
Tolerance
Tolerance measures how much deviation is acceptable in the dimensions of a component. Tight tolerances (e.g., +/- 0.001 inches) are crucial in precision machining and applications where parts must fit together accurately, such as in CNC machining or assembly processes. In B2B terms, understanding tolerance levels can help buyers assess the overall quality and suitability of machine parts for their specific applications and can directly influence product performance and compatibility. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of the machined component’s exterior. Common finish types include polished, anodized, and coated surfaces. This property is essential for reducing friction, enhancing aesthetic appeal, and improving component durability. For B2B buyers, selecting the proper surface finish can lead to better functionality, especially in industries like aerospace, automotive, or manufacturing, where thermal and chemical resistance are critical. -
Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum weight a machine product can handle during operations. It is especially relevant for products such as machinery lifts, conveyors, or loading equipment. For international buyers, understanding load capacity ensures their equipment can meet operational demands without performance issues or safety hazards. -
Power Consumption
Power consumption metrics indicate how much energy machinery uses during operation. Lower energy consumption often translates to decreased operational costs over time, making it a key consideration when evaluating the total cost of ownership. For B2B buyers in regions with varying energy costs, power efficiency can significantly impact profitability.
What are Common Trade Terminology Terms in the Machine Products Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation among B2B buyers and suppliers.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products or components that are purchased by another company and sold under that company’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers ensure they are sourcing from reputable manufacturers, which can be critical for quality assurance and after-sales support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for buyers as it affects inventory management and pricing strategies. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses gauge their procurement capacity and budget accordingly. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This formal request allows businesses to compare offers, ensuring they select the best value. Mastering the RFQ process can expedite procurement and improve supplier relations. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions regarding shipping, insurance, and costs. Understanding Incoterms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), can help businesses mitigate risks and clarify expectations during the procurement process. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Knowing the lead times is essential for B2B buyers to effectively plan their production schedules and maintain operational efficiency.
Mastering these essential technical properties and trade terminologies equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary for making informed purchasing decisions in the competitive machine products market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machine products Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Influencing the Machine Products Sector?
The machine products sector is experiencing dynamic shifts influenced by a variety of global drivers, including technological advancements, geopolitical impacts, and sustainability concerns. Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are paramount, as manufacturers increasingly integrate smart technologies to enhance operational efficiency and reduce production costs. Moreover, the rise of Industry 4.0—characterized by connected factories and the Internet of Things (IoT)—empowers international B2B buyers by providing real-time data and analytics that improve decision-making.
Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe present unique opportunities as the demand for sophisticated machinery, including CNC machines and robotics, rises due to burgeoning manufacturing sectors. Countries like Vietnam and Brazil are becoming manufacturing hubs, attracting international investments that foster competition and innovation. Additionally, as global supply chains become more interconnected, buyers face challenges such as fluctuating tariffs, supply shortages, and logistics complications that require closer monitoring and responsiveness.
Sourcing decisions are increasingly influenced by the need for agility, with companies favoring suppliers that offer flexible solutions, short lead times, and the capability for customization. The trend toward Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing is becoming prevalent, pushing suppliers to offer integrated solutions that reduce waste and enhance production efficiency.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Machine Products Buying Landscape?
Sustainability has become a critical focus for companies aiming to fulfill corporate social responsibility (CSR) obligations while also addressing rising consumer expectations. The environmental impact of machine production, particularly regarding waste and energy consumption, is now under scrutiny, driving buyers to consider the full lifecycle of the products they procure.
Ethical sourcing is no longer optional; B2B buyers must vet suppliers thoroughly, ensuring compliance with environmental standards and human rights practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and adherence to the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) frameworks are becoming standard requirements for suppliers in machine products.
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ materials is escalating as businesses seek to incorporate recyclable or biodegradable components into their manufacturing processes. By prioritizing sustainable practices, companies not only mitigate their environmental footprint but also discover new market opportunities, engage a socially conscious demographic, and enhance their brand reputation.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Modern Machine Product Development?
The development of machine products has evolved from primitive hand tools to advanced automated systems. The Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal turning point, introducing mechanization that significantly transformed production methods and scaled up output. This era laid the foundation for today’s complex machinery and precision manufacturing techniques.
As technology progressed, the introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining revolutionized how products are designed and manufactured, enabling high precision and repeatability. In recent decades, the emergence of digital technologies has further catalyzed this evolution, shifting the landscape toward smart manufacturing. Today, B2B buyers are encouraged to consider not only the technological capabilities of machine products but also their origins, production methods, and the broader implications for sustainability and ethical practices in the supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machine products
-
How do I select the right machine products for my manufacturing needs?
Choosing the right machine products requires a thorough understanding of your specific manufacturing requirements. Start by clearly defining your project specifications, including material types, production volumes, and desired outcomes. Review different machine options, focusing on features such as precision capability, speed, and adaptability to various tasks. Moreover, engage with manufacturers or distributors who can offer insights and recommendations tailored to your industry. Evaluate customer reviews and case studies to ensure the equipment has proven performance in conditions similar to yours. -
What are the common materials used in machine products, and how do they impact performance?
Machine products are typically made from materials like steel, aluminum, plastic, and composites. The choice of material affects durability, weight, and machining complexity. For instance, steel offers high strength but may be heavier and more challenging to machine compared to aluminum, which is lightweight and easier to manipulate. Understanding the properties of each material and their suitability for your application is crucial. Consult with suppliers to find machine products that align with your desired performance characteristics and project goals. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for machine products?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with a proven track record of quality and reliability. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 that demonstrate adherence to industry standards. Request references from past clients and evaluate their experiences. Additionally, investigate the supplier’s financial stability and capacity to meet your order demands. Pay attention to their communication responsiveness and willingness to provide technical support. Finally, ensure that they are capable of meeting international trade regulations and logistics standards pertinent to your region. -
How can I negotiate favorable payment terms when sourcing machine products internationally?
Negotiating payment terms involves clear communication and understanding both parties’ needs. Start by researching standard payment practices within the industry and region. Propose options like net 30 or net 60 terms to allow for financial flexibility. It may be beneficial to suggest a partial upfront payment, followed by the balance upon delivery or performance verification. Establish a mutual agreement documented in a purchase contract, detailing all terms including currency, payment methods, and deadlines to ensure transparency and accountability. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for machine products?
The MOQ for machine products can vary greatly depending on the supplier, product type, and manufacturing process. Larger suppliers may set higher MOQs due to fixed costs associated with production, whereas smaller manufacturers might offer lower MOQs to attract clients. Always inquire about the MOQ before initiating a purchase to avoid unexpected costs or unsatisfactory supply levels. If your needs are low, consider seeking suppliers who specialize in custom orders or smaller production runs to ensure flexibility. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing machine products?
Quality assurance starts with selecting reputable suppliers who implement robust QC processes. Request documentation of their quality management systems, including ISO certifications. During your sourcing process, utilize tools like inspection reports, material certifications, and performance testing data. Establish clear quality criteria in your agreements and consider audits or third-party quality checks pre- and post-delivery. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers about any quality concerns fosters a strong partnership commitment to meeting your standards. -
What logistics considerations should I take into account when importing machine products?
Logistics is a critical factor in importing machine products. First, understand the shipping methods, costs, and timelines associated with air versus sea freight. Factor in customs duties, taxes, and potential delays that could arise during the transport process. Select a freight forwarder experienced in international trade to navigate these complexities. Finally, ensure proper documentation, including bills of lading and import permits, to facilitate a smooth customs clearance process and minimize the risk of unexpected penalties. -
Can machine products be customized to fit specific operational requirements?
Yes, many machine products can be customized based on operational needs. Organizations often collaborate with manufacturers to modify existing designs or create entirely new solutions tailored to their workflows. Discuss your requirements early in the purchasing process to evaluate options for customization. This may include adjustments in size, specifications, or any unique features that could enhance efficiency. Be explicit about your goals and budget constraints to ensure the customization is feasible without inflating costs unduly.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Machine Products Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bambu Lab – X1E
Domain: machinetoolproducts.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Bambu Lab X1E”,”price”:”$3,299.00″},{“name”:”Productive Robotics – Deburring Package, No-Code Programming, Includes OB7 7-Axis Cobot”,”price”:”N/A”},{“name”:”beROBOX – All-in-One Palletizing Work Cell, 20kg – PALTZ.17c, 2 Pallet Zones w/Conveyor, 65′ Stack Height, Includes Doosan H2017″,”price”:”$125,000.00″},{“name”:”WEBB CHAMP 4-EVS-XL-HC CNC Knee Mill with 3-Axis Siemens 8…
2. MPC Dayton – Motor Manufacturing Equipment
Domain: mpcdayton.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Machine Products Corporation Motor Manufacturing Equipment, Visual Flow Indicator, over 66 years in business.
3. Little Machine Shop – CNC Machines
Domain: littlemachineshop.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Little Machine Shop – CNC Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. MMPCO – Precision Machining Solutions
Domain: precinmac.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: MMPCO – Maine Machine Products Company, located in South Paris, Maine, is one of the largest CNC facilities in the Northeastern United States, featuring a 65,000 square foot state-of-the-art facility with 60+ CNC and multi-axis machines. Key capabilities include precision machining for semiconductor, defense, aerospace, oil & gas, and commercial customers, with a significant focus on quality assur…
5. National Machine Products – Heavy Duty Industrial Vacuums
Domain: nationalmachineproducts.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: {“CNC Machine Tool Accessories”: {“Environmental Solutions”: {“Heavy Duty Industrial Vacuums”: “Industrial vacuums designed to capture everything from metal shavings to large debris.”, “Metal Chip Processing & Recycling”: “Maximize scrap value and reuse coolant with our efficient chip processing solutions.”, “Velum Protective Filters”: “These filters shield CNC machines and air compressors from co…
6. General Machine Products – Aerial Cable Construction Equipment
Domain: gmesupply.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, General Machine Products – Aerial Cable Construction Equipment, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Quality Machine Products – Precision CNC Services
Domain: qualitymachineproducts.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {“company_name”: “Quality Machine Products”, “services”: [“CNC Milling”, “CNC Turning”, “Mechanical Assembly Services”], “production_run_capacity”: “over 10,000 parts”, “quality_control”: {“initial_inspection”: “100% inspection on the First Article”, “ongoing_inspection”: “sample testing during production run and final inspection”}, “equipment_list”: [“CNC Milling”, “CNC Turning”, “Conventional Ma…
8. Penn Tool Co – Machine Tools
Domain: penntoolco.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Machine tools include products used to shape, cut, grind, shear, and form metal into parts by removing metal chips. Types of machine tools offered include lathes, grinders, drill presses, milling machines, abrasive cut-off saws, bandsaws, belt grinders, and more. These tools can be manually operated or powered electronically, pneumatically, or hydraulically. They are essential for various applicat…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machine products
How Can International B2B Buyers Optimize Their Strategic Sourcing?
In the competitive landscape of machine products, strategic sourcing has become an essential practice for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Key takeaways from this guide include the importance of understanding regional market trends, leveraging technological advances in manufacturing, and fostering reliable supplier relationships. These elements collectively sustain a robust sourcing strategy, helping buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
The future of strategic sourcing in the machine products sector looks promising, with innovations in automation and supply chain technologies set to transform how companies interact with vendors. By embracing these advancements, buyers not only optimize procurement processes but also secure a competitive edge in their respective markets.
As you navigate your sourcing journey, consider the unique opportunities presented in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Collaborating with established suppliers, adapting to regional specifics, and investing in advanced manufacturing solutions can pave the way for sustainable success. Act now to capitalize on these trends, ensuring your business not only meets current demands but is also poised for future growth.