Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Lost Wax Casting Materials
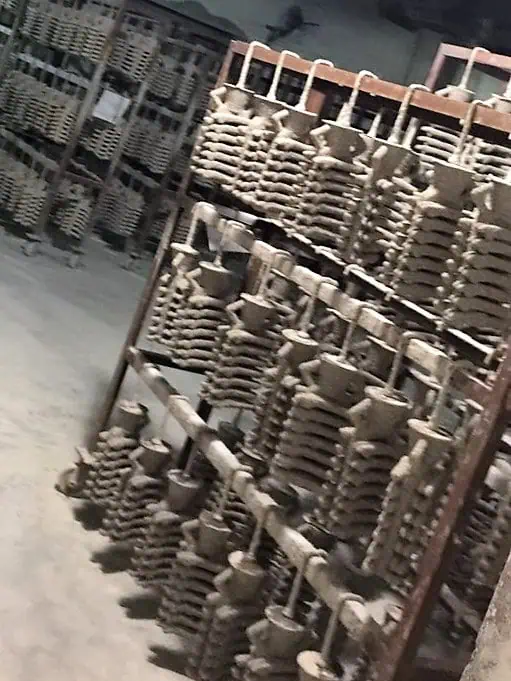

Precision Lost Wax Casting Materials Meet Advanced CNC Machining at Honyo Prototype
Lost wax casting remains a cornerstone process for producing complex, near-net-shape metal components, particularly with investment alloys like stainless steels, titanium, and nickel-based superalloys. However, achieving final dimensional accuracy and surface finish often requires secondary operations due to inherent limitations in as-cast material properties and mold fidelity. At Honyo Prototype, we address this critical gap by integrating our high-precision CNC machining capabilities directly into the casting workflow. This ensures your investment-cast parts meet stringent tolerance requirements—down to ±0.005 mm—without compromising design integrity or material performance.
Our end-to-end solution begins with optimizing the casting pattern and material selection, followed by in-house CNC milling, turning, and multi-axis machining to refine critical features, datum surfaces, and tight-tolerance geometries. This seamless transition from casting to machining eliminates supply chain delays, reduces scrap rates, and guarantees consistency for aerospace, medical, and industrial prototypes. By controlling both processes under one roof, Honyo delivers true turnkey manufacturing where material limitations no longer dictate final part quality.
Accelerate your development timeline with Honyo’s Online Instant Quote platform. Upload your CAD file, specify material and process requirements—including lost wax casting paired with CNC finishing—and receive a detailed, transparent cost and lead time estimate within hours. No manual submissions, no delays. Start optimizing your precision casting projects today.
Technical Capabilities
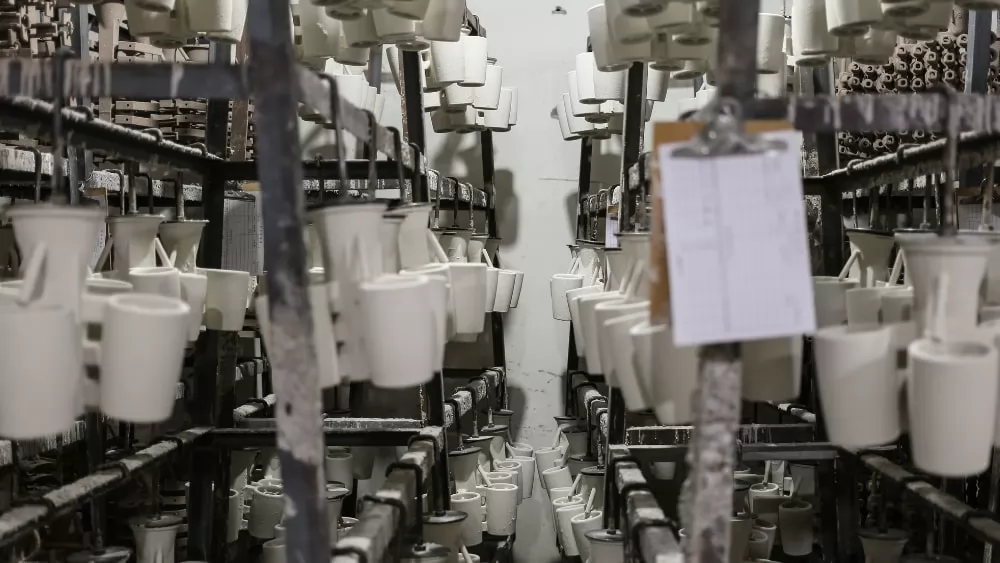

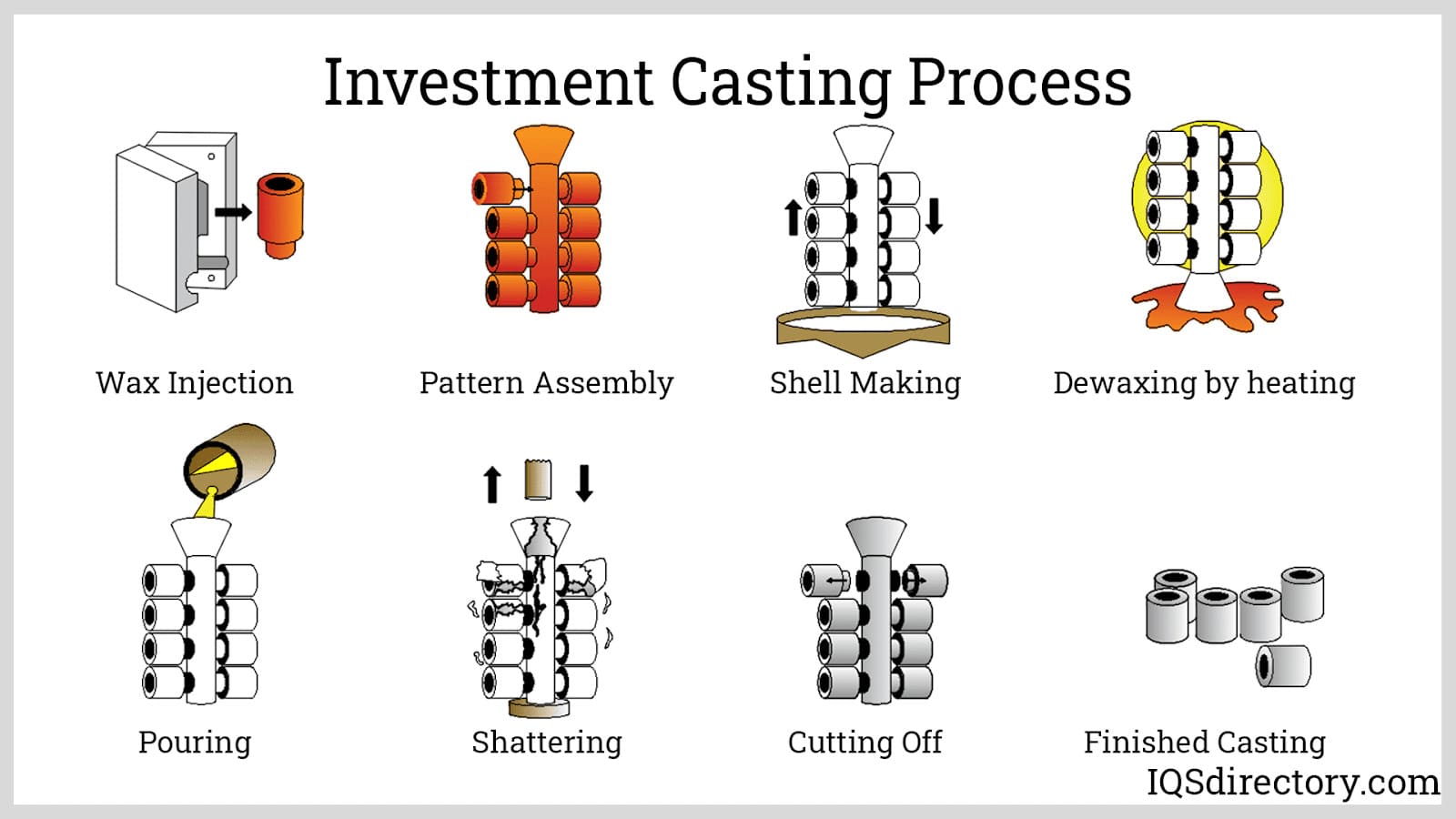
The term “lost wax casting materials” typically refers to the materials used in the investment casting process, where a wax pattern is created, coated in ceramic, and then melted out to form a mold for molten metal. However, in modern prototyping and manufacturing workflows—especially at Honyo Prototype—CNC machining is often used to produce high-precision wax or plastic patterns for lost wax casting. These patterns require tight tolerance control and are commonly machined using 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis milling and turning operations.
Below are technical specifications for common pattern and prototype materials used in the lost wax casting preparation process, particularly when CNC-machined for high accuracy. These materials include both traditional casting metals and engineering plastics used for prototyping or pattern creation.
| Material | Machinability (CNC) | Typical Tolerance (± mm) | Surface Finish (Ra, µm) | Max Complexity Support | Common Use in Lost Wax Casting | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (e.g., 6061-T6) | Excellent | 0.025 – 0.05 | 0.8 – 1.6 | High (5-axis) | Master patterns, bridge tooling | High thermal conductivity; lightweight; ideal for molds and fixtures |
| Steel (e.g., 4140, 17-4 PH) | Good to Moderate | 0.01 – 0.025 | 0.4 – 0.8 | High (5-axis) | Durable master patterns, injection molds | High wear resistance; used for long-life tooling; slower machining than Al |
| ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | Excellent | 0.05 – 0.1 | 1.6 – 3.2 | Medium to High (4/5-axis) | Wax alternative for patterns | Easily machined; good dimensional stability; burns out cleanly in shell |
| Nylon (PA6/PA66) | Moderate | 0.1 – 0.2 | 3.2 – 6.3 | Medium | Functional prototypes, test patterns | High toughness; hygroscopic—requires drying pre-machining; good burnout |
Key Process Notes:
CNC-machined patterns from ABS or Nylon are increasingly used as direct substitutes for wax in modern investment casting workflows. These plastics offer superior dimensional stability and strength, allowing for intricate geometries achievable through 5-axis milling. Aluminum and steel are not typically cast via lost wax but are used to fabricate master patterns or tooling for wax injection.
Tight tolerance requirements (down to ±0.01 mm) are achievable with steel and aluminum when using precision 5-axis milling centers with in-process probing and thermal compensation. For plastic materials like ABS and Nylon, environmental control (temperature, humidity) is critical during and after machining to maintain dimensional accuracy.
At Honyo Prototype, we leverage 5-axis CNC milling and turning centers with sub-micron repeatability to produce master patterns and prototypes that meet aerospace, medical, and high-performance industrial casting standards.
From CAD to Part: The Process
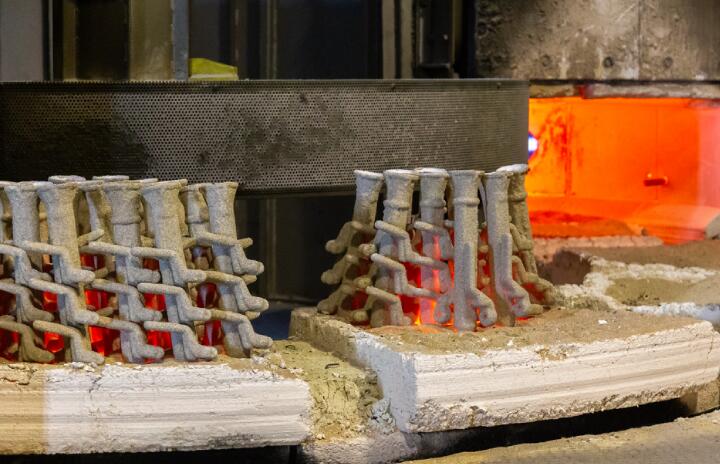

Honyo Prototype executes lost wax casting projects through a rigorously defined workflow designed for precision, efficiency, and manufacturability. This integrated process ensures client CAD data transitions seamlessly from digital concept to validated physical part while mitigating production risks. Key stages are detailed below with technical emphasis on material integration.
CAD Upload and Initial Processing
Clients initiate the process by uploading native or neutral-format CAD files (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) via our secure customer portal. Our system performs automated geometry validation to confirm watertightness, minimum feature resolution (≥0.5mm for investment casting), and orientation feasibility. Material specifications provided by the client—such as ASTM F75 cobalt-chrome for medical implants or AMS4928 Ti-6Al-4V for aerospace—are cross-referenced against our material database at this stage. Incomplete material data triggers an immediate client query to prevent downstream errors.
AI-Powered Quoting with Material Context
Honyo’s proprietary AI quoting engine analyzes the validated CAD geometry alongside client-specified material requirements. The AI factors in material-dependent variables: thermal expansion coefficients affecting shrinkage compensation, melting point constraints for shell firing cycles, and density impacts on gating system design. Crucially, this is not an automated price generator—the AI output provides preliminary cost drivers (material consumption, shell coats required, post-processing complexity) which our quoting engineers refine using real-time alloy market data and historical process yield metrics. Clients receive a formal quote within 4 business hours, including material certification options (e.g., MTRs to AMS, ASTM, or EN standards).
Engineering-Driven DFM Analysis
Upon quote acceptance, our manufacturing engineers conduct a comprehensive Design for Manufacturability review specific to investment casting physics. This phase is where material properties dictate critical adjustments:
Wall thickness optimization to prevent shrinkage porosity in high-solubility alloys like IN718
Draft angle recalibration for refractory shell release based on material surface tension
Gating system redesign to accommodate viscosity differences between superalloys (e.g., CMSX-4 vs. 316L stainless)
Shrinkage allowance application using material-specific coefficients (e.g., 1.8% for aluminum A356 vs. 2.2% for bronze)
DFM findings are presented via annotated CAD markups and simulation reports (ProCAST thermal analysis), requiring client sign-off before tooling. This stage typically reduces casting rework by 65% versus non-DFM workflows.
Precision Production Execution
Production commences only after DFM validation. For lost wax casting:
Pattern injection uses material-matched wax compounds (e.g., low-ash formulations for reactive titanium alloys). The ceramic shell system is tailored to the metal pour temperature—alumina-zirconia slurries for superalloys above 1400°C versus silica-based systems for aluminum. Vacuum induction melting ensures precise chemistry control, with in-process spectrographic analysis verifying material composition against client specifications. Post-casting, material-specific heat treatments (e.g., solution annealing for 17-4PH stainless) are applied before final CNC machining to net shape.
Quality-Controlled Delivery
All parts undergo material-verified inspection:
Dimensional validation via CMM against original CAD (AS9100 Rev D compliant)
Material certification matching MTRs to heat numbers
Microstructure analysis for critical alloys (e.g., beta grain size in titanium)
Non-destructive testing (X-ray, PT) per ASTM E505 or AMS 2644
Final packaging includes serialized traceability tags linking the part to its material lot, process parameters, and inspection records. Standard delivery is 15–20 business days from DFM approval, with expedited options available for medical and aerospace emergency orders.
This closed-loop process ensures material integrity from digital input to certified delivery, eliminating assumptions through physics-based engineering at every transition point. Honyo’s integration of AI with deep materials expertise in investment casting delivers first-time-right outcomes for mission-critical applications.
Start Your Project
For high-quality lost wax casting materials sourced directly from our manufacturing facility in Shenzhen, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. As a trusted partner in precision prototyping and production, Honyo Prototype delivers reliable materials and expert support tailored to your casting requirements. Reach out today to request samples, pricing, or technical specifications.
Contact Information
Name: Susan Leo
Email: [email protected]
Factory Location: Shenzhen, China
We respond to all inquiries within one business day.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.