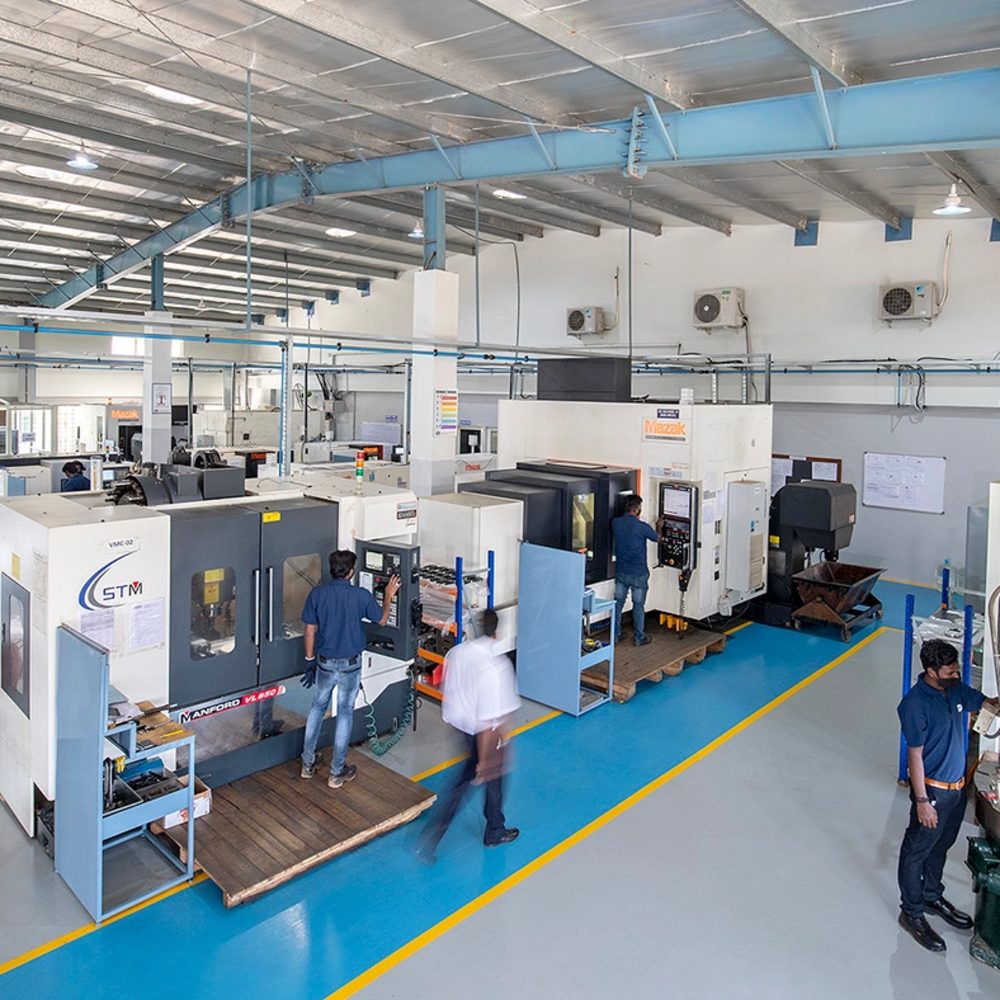
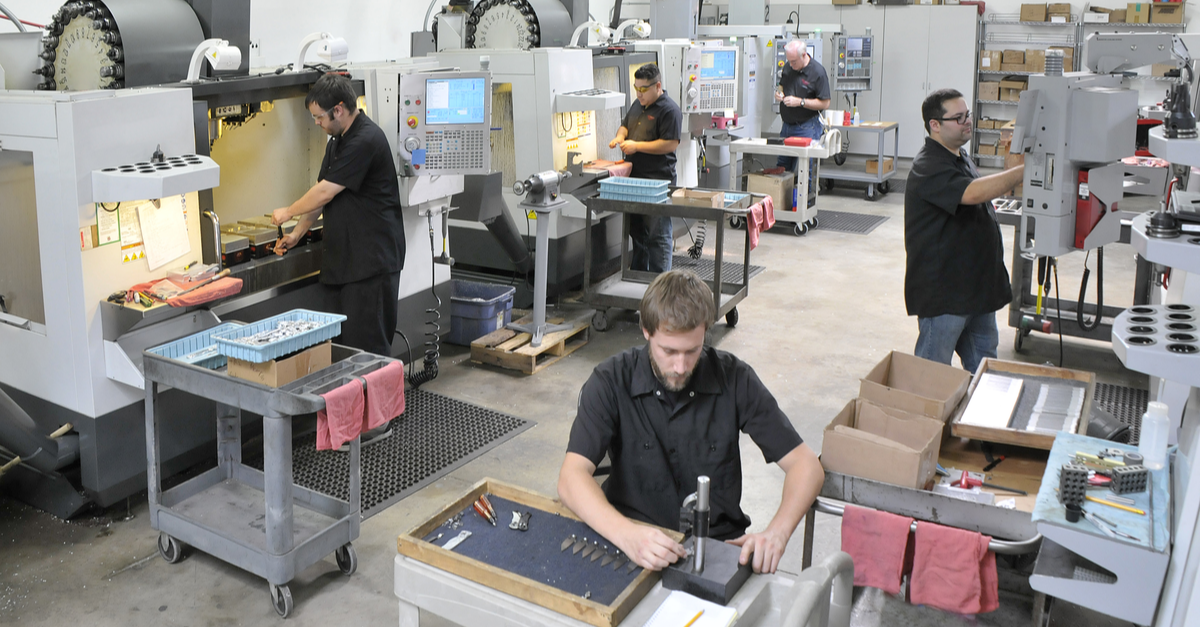
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for local cnc machine shops
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing reliable local CNC machine shops can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re in Nigeria seeking precision components for electronics or in Saudi Arabia looking to procure specialized parts for aerospace applications, understanding the landscape of CNC machining is crucial. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing various types of CNC machining services, their applications across diverse industries, and the essential criteria for vetting suppliers.
Buyers will gain insights into cost structures, quality assurance processes, and the importance of logistical considerations when partnering with local machine shops. By providing a thorough understanding of the capabilities available in different regions—including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions.
Furthermore, it addresses the nuances of working with machine shops that may differ significantly from your local options, ensuring that you can navigate the global market with confidence. Equipped with this knowledge, B2B buyers can enhance their supply chain reliability and secure the precision parts they need to thrive in competitive markets.
Understanding local cnc machine shops Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| General CNC Machine Shops | Versatile machining capabilities across various materials | Automotive, Aerospace, General Manufacturing | Pros: Wide range of services; Cons: May lack specialization for niche applications. |
| High-Volume CNC Machining | Focus on efficiency and scalability for mass production | Consumer Goods, Electronics, Medical Devices | Pros: Cost-effective for large orders; Cons: Less flexibility for custom orders. |
| Prototype CNC Machining | Emphasis on rapid prototyping and design iteration | Product Development, Research & Development | Pros: Quick turnaround; Cons: Higher cost per unit for small runs. |
| Specialty CNC Machine Shops | Expertise in niche materials and complex geometries | Aerospace, Defense, Medical Equipment | Pros: High precision and quality; Cons: Limited capacity for volume production. |
| Contract Manufacturing Shops | Comprehensive services including machining, assembly, and logistics | Industrial Equipment, Custom Projects | Pros: Streamlined supply chain; Cons: Potentially higher costs due to added services. |
What are the characteristics of General CNC Machine Shops?
General CNC machine shops offer a broad range of machining services, including milling, turning, and grinding. They are equipped to handle various materials, making them suitable for diverse industries such as automotive and aerospace. Buyers should consider their specific needs when selecting a shop, as these facilities may not have the specialized skills required for highly technical projects. The flexibility of general CNC shops allows them to cater to both small and large orders, but their lack of specialization can be a drawback for complex tasks.
How do High-Volume CNC Machining services operate?
High-volume CNC machining shops focus on producing large quantities of parts efficiently. These facilities often utilize advanced automation and multi-axis machines to maximize output while maintaining quality. They are ideal for industries such as consumer goods and electronics, where consistent quality at scale is crucial. Buyers should weigh the cost benefits of bulk production against the potential limitations in customization. These shops typically operate on tighter schedules, making them a reliable partner for ongoing projects.
What benefits do Prototype CNC Machining services provide?
Prototype CNC machining is designed for rapid development and testing of new products. This type of shop emphasizes speed and flexibility, enabling businesses to iterate designs quickly. Ideal for research and development sectors, prototype machining allows for adjustments based on real-world testing. However, the costs per unit can be higher than in mass production scenarios. Buyers looking for innovation should prioritize shops with strong prototyping capabilities, as they can provide valuable insights during the design phase.
What makes Specialty CNC Machine Shops unique?
Specialty CNC machine shops focus on machining difficult materials or complex geometries, often required in high-stakes industries like aerospace and medical equipment. These shops are equipped with advanced technology and skilled personnel capable of producing high-precision parts. While they excel in quality and precision, buyers should consider their volume capabilities, as specialty shops may not handle large orders efficiently. Selecting a specialty shop is ideal for projects requiring exceptional detail and quality assurance.
How do Contract Manufacturing Shops streamline processes?
Contract manufacturing shops provide a comprehensive suite of services, including CNC machining, assembly, and logistics. This integrated approach simplifies the supply chain for businesses, making it easier to manage multiple aspects of production. They are particularly beneficial for custom projects that require tailored solutions. While the convenience of a one-stop shop is appealing, buyers should be aware of the potential for increased costs due to the breadth of services offered. It’s crucial to evaluate whether the added value aligns with project requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of local cnc machine shops
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of local cnc machine shops | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components for aircraft systems | Enhanced safety and performance through high-quality parts | Certifications (e.g., AS9100), material traceability |
| Medical Devices | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Improved patient outcomes with reliable, precise devices | Regulatory compliance (FDA, ISO), biocompatibility |
| Automotive | Engine components and assembly fixtures | Increased efficiency in production and reduced downtime | Just-in-time delivery capabilities, scalability |
| Electronics | Enclosures and circuit board mounts | High durability and functionality in electronic devices | Material options (plastics, metals), prototyping services |
| Energy | Components for renewable energy systems | Support for sustainable practices and reduced operational costs | Experience with exotic materials, long lead times |
How Are Local CNC Machine Shops Leveraged in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, local CNC machine shops produce precision components critical for aircraft systems, such as brackets, housings, and engine parts. The stringent requirements for safety and performance necessitate high-quality machining capabilities. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize sourcing from shops with certifications such as AS9100 to ensure compliance with industry standards. Additionally, buyers must consider the shop’s ability to provide material traceability, which is essential for maintaining safety and reliability in aerospace applications.
What Role Do CNC Machine Shops Play in Medical Device Manufacturing?
CNC machine shops are instrumental in the production of custom surgical instruments and implants in the medical device industry. These shops utilize advanced machining techniques to create precise and complex parts that enhance patient outcomes. For international B2B buyers in South America and Europe, regulatory compliance is critical; thus, sourcing from shops that adhere to FDA and ISO standards is essential. Furthermore, the biocompatibility of materials used in medical devices is a significant consideration, emphasizing the need for shops experienced in working with medical-grade materials.
How Do CNC Machine Shops Improve Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, local CNC machine shops manufacture engine components and assembly fixtures that streamline production processes. The ability to produce high-quality parts quickly contributes to increased efficiency and reduced downtime for automotive manufacturers. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should evaluate the shop’s just-in-time delivery capabilities, as timely production is vital for maintaining supply chain efficiency. Additionally, scalability in production volume can be a key factor for businesses looking to expand their operations.
What Are the Applications of CNC Machining in Electronics?
Local CNC machine shops are essential for producing enclosures and mounts for electronic devices, ensuring durability and functionality. Precision machining allows for the creation of intricate designs that meet the specific needs of electronics manufacturers. International buyers must consider the availability of various material options, including plastics and metals, to suit their product requirements. Prototyping services offered by these shops can also facilitate the rapid development of new electronic components, allowing businesses to innovate faster.
How Can Energy Sector Companies Benefit from Local CNC Machining?
In the energy sector, particularly for renewable energy systems, local CNC machine shops fabricate components such as turbine parts and supports. These components are crucial for the efficiency and sustainability of energy systems. For international B2B buyers, it is important to source from shops experienced with exotic materials that can withstand harsh operational conditions. Additionally, understanding the lead times associated with production can help businesses plan their projects more effectively, ensuring timely implementation of energy solutions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘local cnc machine shops’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality and Delivery Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the frustration of inconsistent quality and missed deadlines when partnering with local CNC machine shops. This can lead to production delays, increased costs, and ultimately damage to their reputation. For example, a manufacturer in the aerospace industry might experience quality variations in machined components, causing them to fail inspection and requiring costly rework. This not only strains the supplier relationship but can also jeopardize project timelines and financial forecasts.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize machine shops with a proven track record of quality assurance and timely deliveries. Start by researching potential partners through industry reviews and certifications, such as ISO 9001. Request detailed documentation of their quality control processes, including metrics on defect rates and on-time delivery percentages. Additionally, establish clear communication channels and set expectations upfront regarding quality standards and timelines. Implementing a Just In Time (JIT) inventory strategy can also help manage supply chain disruptions, ensuring that parts arrive only as they are needed, minimizing excess inventory and associated costs.
Scenario 2: Limited Machining Capabilities
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the limited machining capabilities of local CNC shops. For instance, a company might need complex parts made from exotic materials like Inconel or PEEK, but the local shop may not have the necessary equipment or expertise to handle such requests. This can lead to delays in project timelines or force the buyer to seek multiple suppliers, complicating logistics and increasing costs.
The Solution: To address this challenge, B2B buyers should conduct thorough assessments of a machine shop’s capabilities before initiating a partnership. This includes inquiring about their equipment, such as the type of CNC machines they utilize (e.g., 5-axis vs. 3-axis), as well as their experience with specific materials. Engaging in initial discussions about project requirements can also help gauge the shop’s versatility. For more complex projects, consider leveraging shops that offer prototyping services, as they are often better equipped to handle diverse and challenging machining tasks. Additionally, establishing a long-term relationship with a capable shop may yield better pricing and priority service for future projects.
Scenario 3: Communication Breakdowns
The Problem: Communication breakdowns are a frequent challenge faced by B2B buyers when working with local CNC machine shops. Misunderstandings about project specifications, timelines, and changes can lead to mistakes and rework. For example, a buyer might specify a certain tolerance for a part, but if the shop misunderstands or lacks clarity, the delivered product may not meet requirements, resulting in costly delays and frustration.
The Solution: To enhance communication, buyers should adopt a collaborative approach from the outset. Utilize detailed specifications and drawings, accompanied by 3D models if possible, to minimize ambiguity. Implement regular check-ins throughout the production process to discuss progress and address any potential issues proactively. Establishing a single point of contact on both sides can streamline communication and ensure that everyone is aligned. Furthermore, consider employing project management tools that allow for real-time updates and feedback, making it easier to track changes and maintain transparency. By fostering a culture of open dialogue, both parties can work together more effectively, reducing the likelihood of errors and enhancing the overall partnership.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for local cnc machine shops
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in CNC Machining?
When selecting materials for CNC machining, understanding their properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Here are four common materials that local CNC machine shops frequently work with, along with their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and high tensile strength. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,600°F (870°C) and is often used in environments that require hygiene and durability, such as food processing and medical applications.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and staining, making it ideal for long-lasting applications. However, it is more expensive than other metals and can be challenging to machine due to its toughness, which may increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including water, steam, and various chemicals, making it suitable for diverse industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades. Understanding local preferences for specific grades, such as 304 or 316, is also essential for meeting project requirements.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has a good strength-to-weight ratio, and is highly resistant to corrosion. It can be easily machined and formed, making it a popular choice for various applications, particularly in aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low cost and ease of machining, allowing for faster production times. However, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications, as it has a lower melting point compared to steel or titanium.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with many environmental conditions but may not perform well in highly corrosive environments unless anodized or treated.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the relevant standards, such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Understanding local market preferences for specific aluminum alloys can also help in selecting the right material for their needs.
3. Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It can withstand extreme temperatures and is biocompatible, making it ideal for medical implants and aerospace components.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of titanium is its ability to perform in harsh environments and its lightweight nature. However, it is significantly more expensive than other materials and requires specialized machining techniques, which can complicate the manufacturing process.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is suitable for applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, such as in marine and aerospace industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards like ASTM F136 for medical-grade titanium is crucial for buyers in the medical field. Additionally, understanding the local supply chain for titanium can help mitigate costs and ensure timely delivery.
4. Plastics (e.g., PEEK, Nylon)
Key Properties:
Plastics like PEEK and Nylon offer excellent chemical resistance, low friction, and good thermal stability. They are lightweight and can be machined to precise tolerances.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of plastics is their versatility and lower cost compared to metals. However, they may not be suitable for high-load applications and can be less durable than metals.
Impact on Application:
Plastics are ideal for applications in the electronics and medical industries, where lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials are required.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific grades and compliance standards, such as ASTM D638 for plastics. Understanding local preferences for specific plastic materials can also influence procurement decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machining
| Material | Typical Use Case for local cnc machine shops | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower temperature resistance | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and requires specialized machining | High |
| Plastics (PEEK, Nylon) | Electrical housings, medical devices | Versatile and cost-effective | Less durable under high loads | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for CNC machining, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for local cnc machine shops
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes in Local CNC Machine Shops?
Local CNC machine shops follow a systematic approach to manufacturing that ensures precision and efficiency. The primary stages of the manufacturing process include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages incorporates specific techniques and technologies tailored to meet the demands of various industries.
How Is Material Prepared for CNC Machining?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting the right type of material based on the specifications of the project. Common materials machined in local shops include metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and various plastics.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes several preparatory steps, including cutting the raw stock to manageable sizes and ensuring that it meets the dimensional requirements set by the engineering team. This may involve the use of saws, shears, or laser cutting machines. Proper material preparation is crucial as it directly affects the quality and precision of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Parts?
The forming stage is where the actual machining takes place. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are programmed to execute precise movements to create parts according to the design specifications. Techniques employed in this stage include:
-
CNC Milling: This involves removing material from a workpiece using rotating tools. It is ideal for creating complex shapes and is commonly used for both prototype and production runs.
-
CNC Turning: In this process, the workpiece is rotated against a cutting tool. It is particularly effective for producing cylindrical components.
-
Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): This technique is used for cutting intricate shapes in hard materials, making it suitable for precision applications.
By utilizing multi-axis machining capabilities, local CNC shops can produce complex geometries and ensure tight tolerances, which are essential for industries such as aerospace and medical devices.
How Is Assembly Conducted in CNC Machining?
After the individual parts are formed, assembly may be required. While many local CNC shops focus primarily on machining, some offer assembly services as well. This involves fitting together various components to create a finished product.
Assembly can require additional techniques, such as welding, fastening, or adhesive bonding, depending on the materials and design specifications. Effective assembly processes are critical for ensuring that the final product meets the intended functionality and performance criteria.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process and plays a significant role in enhancing the appearance and performance of the machined parts. Techniques may include:
-
Surface Treatment: This can involve processes like anodizing, plating, or painting to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
-
Grinding and Polishing: These processes help achieve a smooth surface finish and precise dimensions.
-
Parts Inspection and Quality Control: Before shipping, finished parts are often subjected to rigorous inspection processes to verify that they meet the specified tolerances and quality standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in Local CNC Machine Shops?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process in CNC machine shops. It involves systematic monitoring and evaluation of various aspects of production to ensure that the final products meet industry standards and customer requirements.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
Local CNC machine shops often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for effective quality management systems. This certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement, which is particularly important for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may also be relevant. For instance, companies in the medical device sector may require compliance with ISO 13485, while those in the aerospace industry may need to meet AS9100 standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to ensuring that products meet the required specifications throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify their quality and compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, parts are monitored at various stages to identify any deviations from the expected quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, finished products undergo thorough inspections and tests to confirm they meet all necessary standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Employed?
Local CNC machine shops utilize various testing methods to ensure product quality. Common techniques include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) to check the dimensions of machined parts.
-
Functional Testing: Verifying that the parts perform as intended in their application.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection may be employed to detect internal defects without damaging the parts.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of local CNC machine shops is essential to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and subpar products.
What Steps Can Buyers Take for Quality Verification?
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess the quality management systems and manufacturing capabilities of potential suppliers.
-
Request Documentation: Buyers should ask for quality certificates, inspection reports, and compliance documentation to understand a supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide unbiased verification of the supplier’s quality processes and product integrity.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certifications. For example, certain regions may have unique regulatory requirements or standards that must be met.
In regions such as Africa and South America, where local infrastructure may vary, buyers should inquire about a supplier’s ability to meet international standards. Similarly, in the Middle East and Europe, understanding regional certifications and compliance can help buyers make informed decisions.
In conclusion, local CNC machine shops employ a comprehensive manufacturing process coupled with rigorous quality assurance protocols to deliver precision-engineered components. For international B2B buyers, understanding these processes and actively engaging in quality verification can lead to successful partnerships and reliable supply chains.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘local cnc machine shops’
Introduction
Navigating the world of CNC machining can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers seeking reliable local suppliers. This practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to ensure you select a CNC machine shop that meets your specific requirements. By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process and establish a partnership with a trustworthy machining provider.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your project, including dimensions, tolerances, materials, and quantities. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for your sourcing process. Be specific about the types of machining services you need, such as CNC milling, turning, or advanced capabilities like 5-axis machining.
- Material Requirements: Specify the materials you require, such as stainless steel, titanium, or plastics.
- Complexity and Volume: Indicate whether you need low, medium, or high-volume production to find a shop equipped for your needs.
Step 2: Research Local CNC Machine Shops
Conduct thorough research to identify potential CNC machine shops within your target regions. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and recommendations from peers to compile a list of candidates. This step is vital to ensure you have a variety of options to choose from.
- Online Reviews: Check customer testimonials and ratings to gauge the reliability and quality of services.
- Industry Experience: Look for shops that have experience in your specific industry, such as medical, aerospace, or automotive.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to vet each supplier thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients in similar industries. This diligence helps you assess their capabilities and past performance.
- Visit Facilities: If possible, arrange site visits to inspect their equipment and processes.
- Quality Certifications: Verify that they hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) that demonstrate their commitment to quality.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Reach out to your shortlisted suppliers for detailed quotes based on your specifications. Comparing quotes not only helps you understand the market rates but also reveals the value each supplier offers.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure that the quotes include a detailed breakdown of costs, such as material, labor, and additional services.
- Lead Times: Pay attention to delivery times, as this can impact your production schedule.
Step 5: Assess Communication and Support
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Evaluate how responsive and helpful each supplier is during your initial interactions. This step is important as it reflects their customer service culture and how they handle inquiries.
- Technical Support: Inquire about their capabilities in providing design assistance or prototyping services.
- After-Sales Support: Understand their policies on revisions, repairs, or replacements in case of issues with the final products.
Step 6: Verify Shipping and Logistics Capabilities
For international buyers, understanding the shipping and logistics arrangements is essential. Confirm that the machine shop can efficiently handle shipping and delivery to your location.
- Freight Options: Inquire about their partnerships with freight carriers and the estimated shipping times.
- Customs Handling: Ensure they can assist with any necessary customs documentation to prevent delays.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize the contracts with clear terms regarding pricing, delivery schedules, quality standards, and payment terms. This step is crucial to protect both parties and ensure mutual understanding.
- Terms and Conditions: Ensure all expectations are documented to avoid misunderstandings.
- Review Clauses: Pay special attention to clauses related to quality assurance and liability.
By following this checklist, you can confidently select a local CNC machine shop that aligns with your project requirements and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for local cnc machine shops Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing from Local CNC Machine Shops?
When sourcing from local CNC machine shops, understanding the cost structure is critical for international B2B buyers. Key cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly influences pricing. Common materials like aluminum and stainless steel are generally more affordable than exotic alloys such as titanium or Inconel. Additionally, fluctuations in raw material prices due to market demand can affect overall costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for precision machining. Labor costs vary by region, influenced by local wage rates and the expertise of the machinists. Higher complexity projects requiring specialized skills will incur higher labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with running a machine shop, such as utilities, rent, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient machine shops often have lower overheads due to optimized processes, which can translate to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, particularly for custom projects. Tooling costs are often amortized over the production run, so larger orders can benefit from lower per-unit tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the precision and quality of machined parts involves rigorous inspection and testing processes. Shops with advanced QC systems may charge more but often deliver higher-quality results.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the destination and the shipping method chosen. International buyers should consider Incoterms, which determine who bears the risk and cost during shipping.
-
Margin: Each machine shop will factor in a profit margin, which can vary based on competition, reputation, and service quality. Buyers should assess the value offered relative to the margin included in the pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Machining Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of CNC machining services:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) and the volume of parts ordered significantly impact pricing. Higher volumes usually lead to lower unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique designs or tolerances, can increase costs. Standard parts are typically cheaper, while complex designs often require additional programming and setup.
-
Materials: As mentioned earlier, the choice of materials affects pricing. Some materials require specialized machining processes, which can also elevate costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts that require specific quality certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100) may incur additional costs. Suppliers who provide these certifications often charge a premium for their assurance of quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and capabilities of the supplier can influence pricing. Established shops may charge more for their expertise and reliability.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Navigate CNC Machining Costs Effectively?
-
Negotiate Pricing: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial price but the total cost of ownership, including shipping, potential rework, and downtime. A lower upfront cost might lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of potential tariffs, import duties, and currency fluctuations that can affect the final cost. Understanding local market conditions is essential for accurate budgeting.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: When seeking quotes, ask for itemized pricing to understand how costs break down. This transparency can help in comparing suppliers effectively.
-
Evaluate Supplier Capabilities: Assess whether the supplier can meet your specific needs regarding volume, lead times, and quality. A supplier that can adapt quickly to changes may save you costs in the long run.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing in CNC machining can vary widely based on numerous factors. The costs presented in this analysis are indicative and should be verified through direct engagement with suppliers to ensure accurate and up-to-date pricing tailored to your specific project requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing local cnc machine shops With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Local CNC Machine Shops
In the realm of precision manufacturing, buyers often seek alternatives to local CNC machine shops due to factors such as cost, performance, and specialized needs. Understanding the available options can help international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions. This analysis compares local CNC machine shops with two viable alternatives: 3D printing and overseas machining services.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Local CNC Machine Shops | 3D Printing | Overseas Machining Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and quality; limited by material types | Good for complex geometries; material limitations exist | Comparable to local shops; quality varies by provider |
| Cost | Moderate to high; setup costs can be significant | Lower for low-volume runs; material costs can add up | Often lower due to cheaper labor; shipping costs can offset savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward; requires specifications and lead time | Fast prototyping; design flexibility, but requires CAD skills | May involve longer lead times and communication challenges |
| Maintenance | Regular equipment upkeep; skilled labor required | Minimal; mostly software updates and maintenance of printers | Varies by provider; may lack local support |
| Best Use Case | High-volume, precision parts; prototyping | Rapid prototyping; custom parts in low volumes | Cost-sensitive projects; large batch production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing offers significant advantages, particularly in rapid prototyping and the ability to create intricate designs that may be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional machining methods. The flexibility in design allows for quick adjustments and iterations, making it ideal for startups and innovative projects. However, its limitations include material constraints and generally lower mechanical properties compared to machined parts. Additionally, for large production runs, the cost of materials can accumulate, making it less economical than traditional machining methods.
How Do Overseas Machining Services Compare?
Overseas machining services are often attractive due to lower labor costs, which can significantly reduce the price of large-volume orders. Companies in regions such as Asia or Eastern Europe may offer competitive pricing and a wide range of capabilities. However, challenges may arise in terms of communication, time zone differences, and potential quality variability. Furthermore, shipping costs and longer lead times can negate some of the anticipated savings, making careful consideration essential for B2B buyers.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right solution depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your project, budget constraints, and desired turnaround time. Local CNC machine shops excel in delivering high-quality, precise components but may come with a higher price tag. In contrast, 3D printing serves well for rapid prototyping and customization, while overseas machining services can offer cost benefits for high-volume production. It is crucial for B2B buyers to assess their project needs thoroughly, weigh the pros and cons of each option, and consider long-term implications such as quality assurance and supply chain reliability before making a decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for local cnc machine shops
What Are the Key Technical Properties Relevant to Local CNC Machine Shops?
Understanding the technical specifications of CNC machining is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing components for complex projects. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
Material grade indicates the specific type of material used in manufacturing parts, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or exotic alloys like Inconel. Each material has unique properties affecting strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring that the final product meets the required performance criteria and complies with industry standards. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In CNC machining, tolerances can be extremely tight, often within +/- 0.0001 inches. Understanding tolerance requirements is essential for ensuring that parts fit and function correctly in their intended applications, particularly in industries like aerospace and medical devices where precision is paramount. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of a machined part affects both aesthetics and functionality. It is usually classified in terms of roughness (Ra values) and can influence wear resistance, adhesion properties, and corrosion resistance. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure that parts not only meet visual standards but also perform effectively in their applications. -
Machining Process
Different machining processes (e.g., CNC milling, turning, EDM) are suited to different applications and materials. Understanding the capabilities of each process allows buyers to choose the most efficient and cost-effective method for their needs. For instance, 5-axis milling can create complex geometries that 2-axis turning cannot. -
Volume Production Capability
This indicates the machine shop’s ability to produce parts in low, medium, or high volumes. Understanding volume capabilities helps in planning production schedules and managing supply chain logistics. High-volume capabilities can lead to cost savings through economies of scale, while low-volume runs may be more suited for prototyping or custom orders. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from order placement to delivery. It is a critical factor in supply chain management and can significantly impact project timelines. Knowing the lead time helps buyers align their production schedules and avoid costly delays.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Machining?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication between buyers and machine shops. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Buyers often work with OEMs to ensure compatibility and quality standards for their products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for managing inventory levels and ensuring that production requirements are met without incurring excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and details for specific products or services. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, helping buyers compare costs and capabilities across multiple suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liability, helping prevent misunderstandings. -
Just-In-Time (JIT) Delivery
JIT is a supply chain strategy that aims to reduce inventory costs by receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process. Understanding JIT is important for companies seeking to optimize their inventory management and minimize waste. -
Secondary Operations
These are additional processes applied to machined parts after the primary machining has been completed. Examples include surface treatments, heat treating, or assembly. Knowing about secondary operations can help buyers plan for the entire production lifecycle of a component.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right local CNC machine shop to meet their specific project needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the local cnc machine shops Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Local CNC Machine Shops Sector?
The CNC machining sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by globalization, technological advancement, and evolving buyer expectations. For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these dynamics present both opportunities and challenges. The demand for precision machining services is surging due to the rise of advanced manufacturing sectors, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. These industries require high-quality, customized components, which local CNC machine shops are well-positioned to deliver.
Emerging technologies, such as automation, IoT, and AI, are reshaping production methodologies. Machine shops are increasingly adopting smart manufacturing techniques to enhance efficiency and reduce lead times. For buyers, this means access to real-time data on production status and quality control, which aids in making informed decisions. Additionally, a trend towards low-volume, high-mix production is emerging, allowing manufacturers to cater to niche markets and specific client requirements without sacrificing quality.
Sourcing trends are also evolving. International buyers are seeking partnerships with local CNC shops that can offer not only competitive pricing but also reliability and rapid turnaround. The focus on just-in-time (JIT) production and Kanban systems ensures that buyers can manage inventory more effectively, minimizing costs associated with holding stock.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing Decisions of B2B Buyers in CNC Machining?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming pivotal considerations for B2B buyers in the CNC machining sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting machine shops to adopt greener practices. This includes the use of sustainable materials, waste reduction techniques, and energy-efficient machinery. Buyers from regions such as Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory frameworks for environmental protection are stringent, particularly prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to green manufacturing standards are increasingly influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are keen on collaborating with local CNC machine shops that can provide transparent supply chains and sustainable practices. This not only helps in mitigating environmental risks but also enhances brand reputation.
Moreover, the demand for eco-friendly materials is on the rise. Local CNC shops that offer recyclable or biodegradable materials can position themselves favorably in the market. As buyers become more environmentally conscious, they are likely to favor suppliers who can align their offerings with sustainability goals, thus creating a competitive advantage in sourcing decisions.
What Is the Historical Context of Local CNC Machine Shops and Their Evolution?
The evolution of local CNC machine shops can be traced back to the industrial revolution, where the introduction of automated machinery marked a significant turning point in manufacturing. Initially, machining was a labor-intensive process, but with the advent of computer numerical control (CNC) technology in the late 20th century, the industry underwent a radical transformation. CNC machining allowed for greater precision and efficiency, enabling shops to produce complex parts with minimal human intervention.
Over the years, the industry has continuously adapted to technological advancements and changing market demands. The rise of globalization has further influenced local shops to enhance their capabilities, diversify their service offerings, and improve customer engagement. Today, local CNC machine shops are not just service providers; they are strategic partners for international buyers, offering tailored solutions that cater to specific industry needs while maintaining high standards of quality and service. This historical context underscores the importance of innovation and adaptability in sustaining competitiveness in the local CNC machining sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of local cnc machine shops
-
1. How do I evaluate the quality of a CNC machine shop?
To evaluate the quality of a CNC machine shop, consider their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Review their machinery capabilities and maintenance practices to ensure they have modern, well-maintained equipment. Request samples of previous work and check references from other clients in similar industries. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including inspection methods and materials used, to ensure they can meet your specific requirements. -
2. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a CNC machine shop for international sourcing?
When sourcing a CNC machine shop internationally, consider factors such as their experience in your industry, production capacity, and lead times. Evaluate their communication capabilities, including language proficiency and responsiveness. Research their shipping and logistics practices to ensure timely delivery and compliance with international trade regulations. Lastly, assess the shop’s reputation through reviews and testimonials from previous clients, particularly those located in your region. -
3. What customization options should I expect from a CNC machine shop?
Most CNC machine shops offer a range of customization options, including variations in materials, sizes, and tolerances. Inquire about their capabilities for producing complex geometries or machining exotic materials, as these factors may impact your project’s feasibility. Additionally, discuss design assistance, prototyping services, and any post-machining processes like finishing or assembly. A capable shop should be able to provide tailored solutions that align with your specific project requirements. -
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machining services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) vary significantly among CNC machine shops and depend on factors such as the complexity of the part, material, and production methods. Some shops may accept low-volume orders, while others focus on high-volume production runs. When sourcing, communicate your needs clearly and ask about their flexibility with MOQs. Understanding their capacity for both small and large orders can help you make informed decisions based on your project timeline and budget. -
5. What payment terms can I expect when dealing with CNC machine shops?
Payment terms for CNC machining services can vary widely based on the shop’s policies and your relationship with them. Many shops may require a deposit upfront, especially for larger orders, while others might offer net 30 or 60 days upon delivery. Always clarify payment expectations during negotiations and ensure they align with your financial processes. Additionally, consider discussing payment methods, such as wire transfers or credit terms, to facilitate smoother transactions. -
6. How does quality assurance work in CNC machining?
Quality assurance (QA) in CNC machining involves a series of processes designed to ensure that parts meet specified tolerances and quality standards. Shops typically implement in-process inspections using various measurement tools, including CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines) and gauges. They may also conduct final inspections before shipping. Inquire about their QA procedures and certifications to gauge their commitment to delivering high-quality components consistently. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing from a CNC machine shop?
Logistics play a crucial role in sourcing from CNC machine shops, especially internationally. Consider shipping methods, delivery times, and the shop’s experience with customs regulations in your region. Discuss packaging methods to ensure parts arrive undamaged and inquire about tracking options for shipments. Additionally, evaluate their ability to handle any potential delays and their policies regarding returns or rework if the parts do not meet specifications. -
8. How do I establish a long-term partnership with a CNC machine shop?
To establish a long-term partnership with a CNC machine shop, focus on clear and open communication from the outset. Share your business goals, expectations, and specific project requirements to build trust. Regularly engage with them for updates on projects and seek feedback on your needs. Consider involving them early in the design process to leverage their expertise. A collaborative approach fosters a mutually beneficial relationship that can enhance efficiency and innovation over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Local Cnc Machine Shops Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Yelp – Best CNC Machine Shops in Brooklyn
Domain: yelp.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: This company, Yelp – Best CNC Machine Shops in Brooklyn, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Owens Industries – Precision CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: owensind.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Precision CNC Machine Shop Services for New York, including:
– CNC Machining Solutions with high-complexity manufacturing and customized parts production.
– Established in 1944, known for ultra-precision machining solutions.
– Capabilities include:
– Simultaneous 5-axis machining
– CNC milling and turning
– Wire EDM services
– CNC lathe turning
– Precision deburring
– Accuracy within ±0….
3. CNC Machining Services – Small Quantity Prototypes
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC machining services for small quantities (less than 5 units) in materials like aluminium and brass. Recommendations include looking for local small job shops, independent machinists, or trade schools that may offer affordable prototype-level manufacturing. Mention of contacting manufacturers through platforms like Alibaba for quotes.
4. Hubs – CNC Machining Services
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: CNC machining service in New York offering high-quality, competitively priced custom prototypes and production parts. Instant quotes available by uploading CAD files. Services include CNC milling (3-, 4-, & 5-axis), CNC turning, and various surface finishes. Materials include a wide range of metals (aluminum, brass, copper, steel, titanium) and plastics (ABS, Nylon, PEEK, Polycarbonate). Lead time…
5. Lot 19 – Precision Design & Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: machineshopnyc.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Lot 19 is a precision design, engineering, consulting, and manufacturing firm based in New York City. They offer custom parts manufacturing, short run production, design manufacturability consultation, and design-to-delivery product development. Their capabilities include:
Design:
– Computer Aided Design (CAD) and Manufacturing (CAM)
– Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
– Design for Manufacturing (DFM…
6. Zala Machine – CNC Machining Services
Domain: zalamachine.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Zala Machine offers a variety of CNC machining services including CNC Turning, CNC Milling, 5 Axis Milling, Honing, Large Machining, Shaft Machining, Large Vertical Turning, Gundrilling, Large Fabrication, and Gear Box Repair. The company specializes in high-precision machining with a focus on complex parts requiring high tolerance. They utilize advanced technology, including the Mori Seiki NTX200…
7. Distinctive Manufacturing – Precision CNC Machining Services
Domain: distinctivemfg.co
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Syracuse CNC Machine Shop offers precision CNC machining and metal fabrication services. Key services include: 1. CNC Milling Services – Utilizing state-of-the-art CNC milling machines for intricate, close-tolerance parts. 2. CNC Turning Services – Expert machinists perform turning, facing, grooving, parting, threading, drilling, boring, reaming, and tapping on various materials. 3. 5-Axis CNC Mac…
8. WasteGas – CNC Machining Services
Domain: wastegas.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Services, CNC Milling Service, Custom CNC machining, ISO 9001:2015 certified, CNC milling of aluminum, steel alloys, stainless steel, large parts, vertical machining centers, 20 x 40 Bridge Mill, High Torque Mazak machining centers, multi-axis turning center with Big Bore spindle, production speeds over 10,000 rpm, 100% Employee Owned, over 110 employees, diverse equipment including …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for local cnc machine shops
In summary, the strategic sourcing of local CNC machine shops presents significant advantages for international B2B buyers. By leveraging the diverse capabilities and technological advancements of these shops, companies can access high-quality machining services that cater to a wide range of industries, including aerospace, medical, and automotive. The emphasis on precision, reliability, and timely delivery further enhances the value proposition, allowing businesses to streamline their supply chains and minimize operational disruptions.
As you consider your sourcing options, remember that partnering with established local machine shops can lead to improved product quality and reduced lead times. Building relationships with these suppliers not only fosters innovation but also ensures that your specific needs are met with expertise and attention to detail.
Looking ahead, the global demand for precision machining is set to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increasing customization requirements. Now is the time for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to explore the potential of local CNC machine shops. Engage with these providers to unlock new opportunities for collaboration, efficiency, and competitive advantage in your supply chain.