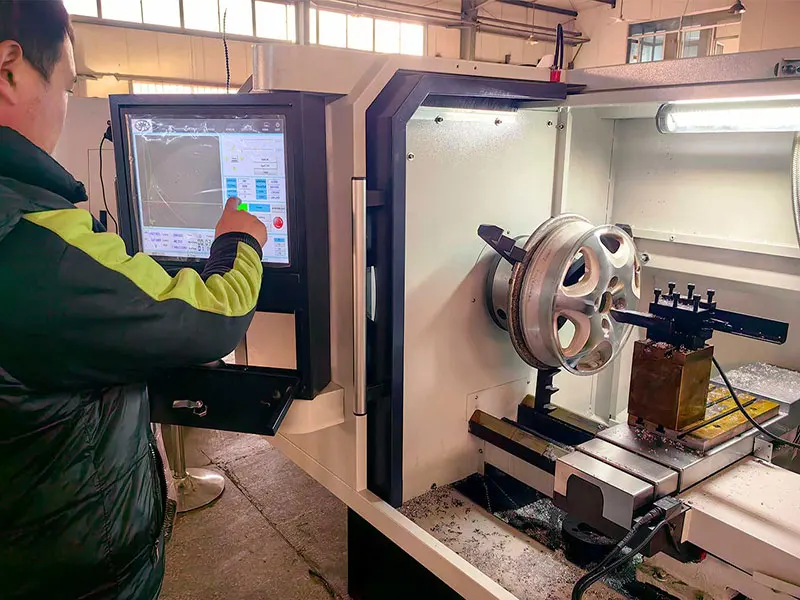
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lathe repair
Navigating the complexities of lathe repair can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a myriad of options available, sourcing reliable lathe repair services that ensure precision and efficiency is crucial to maintaining productivity. This guide aims to demystify the lathe repair landscape by providing insights into various types of repairs, applications across industries, and essential considerations when vetting suppliers.
We delve into the critical aspects of the lathe repair process, including the evaluation of machine conditions, sourcing quality replacement parts, and understanding cost implications. Our comprehensive analysis not only highlights the technical nuances of lathe repair but also empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions by offering practical strategies for navigating supplier relationships.
By focusing on the specific needs and challenges faced by businesses in diverse markets, this guide ensures that you can confidently approach the lathe repair process. Whether you are operating in Vietnam, Saudi Arabia, or elsewhere, you will find valuable information tailored to your unique context, enabling you to optimize your machinery investments and enhance operational efficiency.
Understanding lathe repair Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lathe Bed Grinding | Involves grinding the lathe bed to restore alignment and flatness | Precision machining, tool room operations | Pros: Restores accuracy; suitable for heavy use. Cons: Time-consuming; potential for high costs. |
| Way Scraping | Manual scraping of ways to improve contact surfaces and precision | Custom machining, high-tolerance work | Pros: Customized fit; enhances performance. Cons: Labor-intensive; requires skilled technicians. |
| Component Replacement | Replacing worn-out parts such as spindles, gears, or bearings | General manufacturing, maintenance services | Pros: Quick solution; often cost-effective. Cons: May not address underlying issues; limited longevity. |
| Alignment and Calibration | Ensuring all components are properly aligned for optimal function | Production lines, assembly operations | Pros: Improves overall performance; reduces wear. Cons: Requires regular maintenance; potential disruption during service. |
| Complete Rebuild | Comprehensive disassembly, inspection, and reassembly of the lathe | Heavy-duty machining, high-volume production | Pros: Restores to like-new condition; long-term reliability. Cons: High initial investment; lengthy downtime. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Lathe Bed Grinding?
Lathe bed grinding is a repair technique focusing on restoring the flatness and alignment of the lathe’s bed. This process is essential for maintaining precision in machining operations, especially in industries that require high tolerances. Buyers should consider the extent of wear on their equipment, as this method is particularly suitable for lathes that have seen significant use. While effective, it can be time-consuming and may involve substantial costs.
How Does Way Scraping Improve Lathe Performance?
Way scraping is a manual method used to enhance the contact surfaces of the lathe’s ways. This technique allows for a customized fit, improving the precision and smoothness of the lathe’s movement. It is particularly beneficial for custom machining tasks or projects requiring tight tolerances. Buyers should factor in the availability of skilled technicians, as this process is labor-intensive and requires expertise.
When Should You Consider Component Replacement?
Component replacement involves swapping out worn parts, such as spindles or bearings, to restore the lathe’s functionality. This approach is often quicker and more cost-effective than extensive repairs. It is suitable for general manufacturing environments where downtime needs to be minimized. However, buyers should be cautious, as this method may not resolve underlying issues that could affect the lathe’s long-term performance.
What Is the Importance of Alignment and Calibration?
Alignment and calibration are crucial for ensuring that all components of the lathe work harmoniously. This process can significantly enhance the machine’s overall performance and reduce wear on parts. Regular alignment checks are vital for production lines and assembly operations where precision is paramount. Buyers should be prepared for potential disruptions during service but can expect improved efficiency post-calibration.
Why Opt for a Complete Rebuild of Your Lathe?
A complete rebuild involves disassembling, inspecting, and reassembling the lathe to restore it to like-new condition. This comprehensive approach is ideal for heavy-duty machining applications or high-volume production environments. While the initial investment may be high and involve lengthy downtime, the long-term reliability and performance gains make it a worthwhile consideration for businesses looking to maximize their equipment’s lifespan.
Key Industrial Applications of lathe repair
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lathe repair | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision component fabrication | Enhanced accuracy and reduced scrap rates | Quality of repair services, turnaround time, and cost |
| Aerospace | Repair of specialized aerospace lathes | Improved safety and compliance with stringent regulations | Certification of repair technicians and parts used |
| Automotive | Restoration of lathes used in engine component production | Longer equipment lifespan and reduced downtime | Experience with specific lathe models and OEM standards |
| Oil and Gas | Overhauling lathes used for drilling equipment | Increased operational efficiency and reliability | Knowledge of industry-specific requirements and materials |
| Metalworking Services | General lathe maintenance and repair | Cost-effective maintenance solutions and improved performance | Availability of spare parts and technical expertise |
How is Lathe Repair Used in the Manufacturing Sector?
In the manufacturing industry, lathe repair is crucial for precision component fabrication. Lathes are often subjected to heavy use, leading to wear and tear that can affect accuracy. Repairing lathe ways and aligning components can enhance the precision of machined parts, resulting in reduced scrap rates and improved product quality. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer comprehensive assessments and quick turnaround times to minimize production delays.
What Role Does Lathe Repair Play in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, lathe repair is vital for maintaining specialized equipment used in the production of aircraft components. Given the stringent safety regulations, repairing lathes to restore their precision is essential for compliance and safety assurance. Buyers in this sector must ensure that repair technicians are certified and experienced with aerospace-grade materials and processes, as any failure can have catastrophic consequences.
How is Lathe Repair Important for the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry relies heavily on lathes for manufacturing engine components and other precision parts. Regular lathe repair ensures that these machines remain operational and efficient, thereby extending their lifespan and reducing downtime. International buyers should look for service providers with experience in repairing specific models and adherence to OEM standards, as this can significantly impact production reliability.
Why is Lathe Repair Critical for Oil and Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas sector, lathes are often used for drilling equipment, where precision is critical. Overhauling these lathes can lead to increased operational efficiency and reliability, which are essential in high-stakes environments. Companies should consider suppliers who understand the unique demands of the oil and gas industry, including the use of specialized materials and adherence to safety standards.
How Does Lathe Repair Benefit Metalworking Services?
Metalworking services frequently utilize lathes for various applications, making regular maintenance and repair essential for optimal performance. Lathe repair can provide cost-effective solutions that improve machine performance and reduce the frequency of breakdowns. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide a reliable inventory of spare parts and possess the technical expertise to handle diverse lathe models efficiently.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘lathe repair’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Aligning for Precision – Headstock Misalignment
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers, especially in machining facilities, is headstock misalignment in lathes. This issue often manifests as inconsistent cuts or tapering in finished parts, leading to significant operational inefficiencies. When precision is paramount, misalignment can result in costly rework, scrapped materials, and extended downtime. It can be particularly frustrating when operators are unaware of the root cause, leading to a cycle of trial and error with no clear solution.
The Solution: To effectively address headstock misalignment, B2B buyers should implement a systematic approach. Start by ensuring that the lathe is level and properly supported. Utilize precision leveling tools, such as a machinist’s level, to check the alignment of the bed. If misalignment is detected, adjust the headstock using the alignment pin, if available. It may also be beneficial to consult the machine’s maintenance manual for specific alignment procedures. For long-term accuracy, consider establishing a regular maintenance schedule, including alignment checks at least once a year, to prevent reoccurrence and ensure the longevity of the lathe’s performance.
Scenario 2: Battling Wear and Tear – Deteriorating Lathe Ways
The Problem: Over time, lathe ways can experience significant wear due to constant friction and load during machining operations. This deterioration can lead to poor surface finishes, inaccuracies in part dimensions, and increased tool wear. For international buyers operating in demanding environments, such as those in Africa or South America, the challenge is even more pronounced, as sourcing high-quality parts and repair services can be difficult.
The Solution: To combat wear on lathe ways, proactive maintenance is key. Regularly inspect the ways for signs of wear, such as scoring or uneven surfaces. If wear is detected, consider a two-pronged approach: first, use scraping techniques to restore flatness and improve the mating surfaces of the saddle and bed. Second, explore the application of high-performance materials, such as Turcite or similar polymer-based materials, which can be applied under the saddle to reduce friction and restore lost height. For a more comprehensive solution, partner with specialized lathe repair services that can offer expert evaluations, precision grinding, and tailored rebuilding plans to revitalize worn components.
Scenario 3: Managing Downtime – The Cost of Lathe Repairs
The Problem: Downtime can be one of the most significant pain points for B2B buyers when dealing with lathe repairs. Unexpected failures can disrupt production schedules and lead to financial losses, particularly for manufacturers operating on tight deadlines. The challenge intensifies when buyers struggle to find reliable service providers or face delays in sourcing necessary parts, further extending the downtime.
The Solution: To mitigate the impact of downtime, B2B buyers should take a proactive stance towards maintenance and repair planning. Establish a relationship with a reputable lathe repair service that offers comprehensive assessments and quick turnaround times. Look for providers that can manage both on-site repairs and off-site rebuilding, ensuring that you have options depending on the severity of the issue. Additionally, maintaining an inventory of critical spare parts can significantly reduce downtime. Regularly scheduled preventive maintenance, including inspections and minor repairs, can also help identify potential issues before they lead to major failures, keeping production on track and minimizing costly interruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lathe repair
What Are the Key Materials Used in Lathe Repair?
When it comes to lathe repair, the selection of materials is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of the machinery. Various materials offer distinct properties that can significantly impact the repair process and the functionality of the lathe post-repair. Below, we analyze four common materials used in lathe repair, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Which Metals Are Commonly Used in Lathe Repair?
1. Cast Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and vibration-damping capabilities. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of cast iron is a significant advantage, as it can last for many years without significant degradation. However, it is relatively heavy, which can complicate transport and installation. Additionally, cast iron can be more expensive compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is particularly effective in applications where stability and precision are paramount. Its compatibility with various media, including oils and lubricants, makes it a preferred choice for lathe components like beds and bases.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards for cast iron, such as ASTM A48 or equivalent. The availability of cast iron can vary, so sourcing from reputable suppliers is crucial.
2. Steel Alloys
Key Properties: Steel alloys, particularly those with high carbon content, offer excellent tensile strength and toughness. They can withstand significant stress and are often treated to enhance corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of steel alloys is their versatility and strength, which make them suitable for various lathe components, including spindles and gears. However, they can be more costly and may require specialized machining processes.
Impact on Application: Steel alloys are compatible with a wide range of operating conditions, including high-speed machining. Their ability to resist wear and tear makes them ideal for components subject to frequent use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as JIS G4051 or DIN 17200 is essential. Buyers should also consider the local availability of specific steel grades to avoid delays in repair projects.
3. Turcite
Key Properties: Turcite is a thermoplastic material known for its low friction and excellent wear resistance. It operates effectively in a wide temperature range and is resistant to many chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of Turcite is its ability to reduce friction between moving parts, which enhances the overall efficiency of the lathe. However, it may not be as durable as metals and can be more expensive than traditional lubricants.
Impact on Application: Turcite is particularly effective in applications requiring smooth movement, such as sliding surfaces in lathes. Its compatibility with various lubricants makes it a valuable addition to lathe repairs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that Turcite meets local compliance standards, as variations in formulation can exist. Additionally, understanding the local market for thermoplastics is important for sourcing.
4. Bronze
Key Properties: Bronze is a metal alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good wear properties. It can operate effectively under high loads and has good thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of bronze is its resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for components exposed to moisture and chemicals. However, it is generally more expensive than other materials and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Bronze is often used for bearings and bushings in lathes, where its low friction properties can significantly enhance performance. Its compatibility with various lubricants further extends its application.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B505 is crucial for bronze components. Buyers should also consider the availability of bronze in their region, as it may not be as readily available as other materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Lathe Repair
| Material | Typical Use Case for lathe repair | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Lathe beds and bases | Excellent wear resistance | Heavy and more expensive | High |
| Steel Alloys | Spindles and gears | Versatile and strong | Higher cost and specialized machining | Medium |
| Turcite | Sliding surfaces | Low friction and wear resistance | Less durable and potentially costly | Medium |
| Bronze | Bearings and bushings | Corrosion resistance and low friction | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This guide provides insights into the strategic selection of materials for lathe repair, catering to the needs of international B2B buyers across diverse regions. Understanding these materials will help in making informed decisions that ensure optimal performance and longevity of lathe machinery.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lathe repair
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Lathe Repair?
Repairing lathes involves a structured manufacturing process that ensures precision and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How Is It Done?
The first step in the repair process is material preparation, which involves sourcing high-quality replacement parts. Suppliers must ensure that all materials meet the necessary specifications for durability and performance. This may include sourcing steel alloys for structural components or specialized materials for wear resistance. Proper documentation and traceability of materials are crucial, especially for international buyers who need to confirm compliance with local standards.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used?
Forming processes in lathe repair often involve machining, grinding, and scraping. Machining is used to achieve precise dimensions on components like spindles and gears. Grinding is critical for restoring the flatness and alignment of bedways and saddles, which are essential for the lathe’s performance. Hand-scraping is a traditional technique that ensures tight tolerances and perfect fit between moving parts, which is particularly important for high-precision applications.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated?
During assembly, each component is meticulously integrated, ensuring that all parts function harmoniously. This stage often involves alignment checks to guarantee that the headstock, tailstock, and other critical components are positioned correctly. Technicians may use dial indicators and other measuring tools to verify alignment and precision, ensuring that the lathe will perform accurately once reassembled.
Finishing: What Quality Measures Are Implemented?
Finishing processes include cleaning, lubrication system flushing, and final adjustments. This stage ensures that all surfaces are free from contaminants and that lubrication systems are functional. The final inspection is critical, as it verifies that the lathe meets all operational specifications before it is returned to the customer.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Standard in Lathe Repair?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the lathe repair process, ensuring that every repaired machine meets international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should look for compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, which emphasizes a process-based approach to quality management. This certification indicates that the supplier has implemented a quality management system that consistently provides products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, other certifications, such as CE marking for European compliance and API standards for the oil and gas industry, may be relevant depending on the application of the lathe.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the lathe repair process. Commonly implemented checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials and components upon receipt. It ensures that all materials meet specified criteria before they enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During various stages of the manufacturing process, technicians perform checks to ensure that components are being machined and assembled correctly. This may involve measuring tolerances and alignment at critical stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the lathe is returned to the customer, a comprehensive final inspection is conducted. This includes testing the machine’s operational performance to ensure it meets the required specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, verifying the quality control measures of potential suppliers is paramount. Here are several strategies to ensure that suppliers meet high-quality standards:
What Role Do Audits Play?
Conducting audits of suppliers is an effective way to assess their quality control processes. Buyers should consider scheduling regular audits, either internally or via third-party services, to verify that suppliers adhere to their claimed quality management systems and standards. This can include checking documentation, processes, and even the manufacturing environment.
What Are the Benefits of Requesting Quality Reports?
Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their QC processes and performance metrics. These reports can include data on defect rates, inspection results, and compliance with international standards. Consistent reporting can help buyers gauge a supplier’s reliability and commitment to quality.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services adds an additional layer of verification. These independent organizations can perform inspections during and after the repair process, ensuring that the lathe meets all specified requirements. This is particularly important for buyers from regions where local standards may differ from international expectations.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International Buyers?
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances in quality control should be considered:
How Do Cultural and Regulatory Differences Affect QC?
Cultural differences can impact how quality is perceived and enforced. Buyers should ensure that they understand the local practices and regulatory requirements of the supplier’s country. This may include specific documentation needs or compliance with local safety standards.
What Should Buyers Know About Logistics and Transportation Risks?
Logistics also plays a role in quality assurance. International shipping can expose equipment to risks such as damage or corrosion. Buyers should work with suppliers who have robust packaging and handling protocols to minimize these risks during transit.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in lathe repair are critical for ensuring that equipment meets performance expectations. By understanding these processes and engaging in thorough supplier evaluations, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘lathe repair’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure lathe repair services. Whether you operate in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, ensuring that your lathe machinery is in optimal condition is crucial for maintaining productivity and quality in your operations. Follow these steps to effectively source reliable lathe repair services.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific needs of your lathe repair. Consider factors such as the model of your lathe, the nature of the repairs required (e.g., scraping, grinding, or component replacement), and any particular performance standards you expect post-repair. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with potential service providers and ensure they understand your requirements.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in lathe repair. Look for companies with a proven track record and positive customer reviews. Key aspects to evaluate include:
– Experience: Suppliers should have extensive experience with your specific lathe model.
– Certifications: Verify that they hold relevant industry certifications, ensuring adherence to quality standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing, it’s crucial to assess the capabilities of each supplier. Request detailed information about their repair processes and technology used. Look for suppliers who can:
– Disassemble and inspect: They should provide a comprehensive assessment before starting repairs.
– Source high-quality parts: Ensure they use OEM or equivalent parts to maintain the integrity of your lathe.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Ask potential suppliers to submit detailed proposals that outline the scope of work, timelines, and costs involved. A well-structured proposal should include:
– Breakdown of services: Understand what is included in the repair, such as cleaning, grinding, and calibration.
– Estimated turnaround time: Knowing how long repairs will take helps manage your operational planning.
Step 5: Check References and Past Work
Request references from previous clients to gain insights into the supplier’s reliability and service quality. Inquire about:
– Project outcomes: Did the repairs meet expectations for performance and durability?
– Client support: How responsive was the supplier during and after the repair process?
Step 6: Assess Warranty and After-Service Support
Inquire about warranty terms for the repair work. A reputable supplier should offer a warranty that covers both parts and labor. Additionally, evaluate their after-service support, including:
– Maintenance options: Do they provide ongoing maintenance plans to ensure long-term performance?
– Training: Can they offer training for your staff on the proper operation of the repaired lathe?
Step 7: Finalize the Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, review the contract thoroughly. Ensure it includes all agreed-upon terms, including costs, timelines, and warranties. Clear communication at this stage helps prevent misunderstandings and sets the foundation for a successful partnership.
By following this checklist, you can confidently source lathe repair services that meet your operational needs and maintain the efficiency of your manufacturing processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lathe repair Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Lathe Repair?
When considering lathe repair, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the cost of replacement parts such as bearings, screws, and other critical components. Quality of materials directly influences the longevity and performance of the repaired lathe.
-
Labor: Skilled technicians are required to perform repairs, which can significantly impact labor costs. Depending on the complexity of the repair, labor rates can vary widely by region and technician expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the operational costs of the repair facility, such as utilities, rent, and administrative salaries. Overhead can be a hidden cost that affects the final price.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment may be necessary for certain repairs, adding to the overall cost. This is particularly relevant for complex repairs that require precise machining or alignment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that repairs meet industry standards may involve rigorous QC processes, which can add to labor and material costs. Certifications and quality assurance can enhance the perceived value of the service.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for shipping the lathe to and from the repair facility are crucial, especially for international buyers. Incoterms will dictate who bears these costs and should be considered in the total pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding average margins in your region can help you evaluate the competitiveness of the quotes you receive.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Lathe Repair Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of lathe repair services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk repair orders often lead to discounts. Establishing a relationship with a repair provider can lead to better pricing for regular maintenance or multiple machines.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized repairs or parts can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality materials or certified parts often come at a premium. However, investing in quality can lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over time.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and service history.
-
Incoterms: Understand the shipping terms outlined in your contracts. Different Incoterms can significantly affect the final cost of repair due to shipping responsibilities.
What Are the Best Tips for Buyers When Negotiating Lathe Repair Prices?
B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to optimize costs when sourcing lathe repair services:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate the price and terms upfront. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts, especially if you are bringing multiple units for repair.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the immediate costs but the long-term savings associated with higher-quality repairs. A lower initial price may lead to higher maintenance costs down the line.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: When dealing with suppliers from different regions (e.g., Africa, South America, the Middle East, Europe), be aware of currency fluctuations, import taxes, and additional fees that may arise.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ask for itemized quotes that break down labor, materials, and other costs. This transparency can help you identify areas for negotiation and ensure you are not overpaying.
-
Evaluate Supplier Reliability: Research the supplier’s track record, including reviews and testimonials. Reliable suppliers may charge more, but the assurance of quality can justify the expense.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the cost and pricing landscape for lathe repair requires a comprehensive understanding of various components and influencing factors. By employing strategic negotiation tactics and considering the long-term implications of repair choices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that maximize value and minimize costs. Always remember that indicative prices can vary widely based on specific circumstances, so thorough research and communication with suppliers are crucial.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing lathe repair With Other Solutions
Introduction to Lathe Repair Alternatives
In the realm of machining, lathe repair is a crucial service that ensures precision and longevity of equipment. However, businesses may seek alternatives to traditional lathe repair to address their operational needs more effectively. This section examines several viable alternatives to lathe repair, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Lathe Repair | CNC Machine Replacement | Tooling Upgrades |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Restores precision and functionality | Offers enhanced precision and automation | Improves cutting efficiency and precision |
| Cost | Moderate; typically $9,900 – $10,400 | High initial investment | Variable; often lower than repairs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled technicians and downtime | Extensive training needed; longer setup | Quick installation with minimal downtime |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed post-repair | Requires regular software updates and maintenance | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for older machinery needing refurbishment | Best for operations requiring high volume and precision | Suitable for businesses looking to enhance existing setups |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Machine Replacement
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines represent a leap forward in machining technology, offering automation and enhanced precision. The primary advantage of CNC machines is their ability to produce complex parts with minimal human intervention, leading to higher productivity. However, the initial cost of purchasing a CNC machine can be significant, which may not be feasible for all businesses. Additionally, transitioning to CNC requires comprehensive training for operators, which can result in extended downtime during the changeover period.
Tooling Upgrades
Investing in tooling upgrades can be a cost-effective alternative to lathe repair, particularly for businesses that already own operational lathes. By upgrading tools such as cutting inserts, tool holders, or even software that optimizes machining processes, companies can significantly enhance performance without the need for extensive repairs. This approach typically incurs lower costs and requires less downtime compared to lathe repairs. However, it may not address underlying mechanical issues, and the effectiveness of tooling upgrades is often limited by the existing machinery’s condition.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When considering the right solution for lathe repair, B2B buyers must assess their operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Lathe repair is ideal for companies looking to extend the life of existing machinery while maintaining precision. In contrast, CNC machine replacement is suited for those needing automation and high-volume production capabilities, albeit at a higher cost. Tooling upgrades provide a flexible, lower-cost option to enhance existing setups but may not resolve deeper mechanical issues. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, businesses can make strategic decisions that align with their operational objectives and financial considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lathe repair
What Are the Key Technical Properties Critical for Lathe Repair?
When considering lathe repair, understanding the essential technical properties is vital for ensuring machine performance and longevity. Here are the critical specifications that B2B buyers should focus on:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in lathe construction significantly affect durability and performance. Common materials include cast iron for the bed due to its rigidity and vibration-damping properties, and hardened steel for components like the spindle. Selecting the right material grade ensures that the lathe can withstand operational stresses and maintain precision over time. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension. In lathe repair, maintaining tight tolerances (often within ±0.001 inches) is essential for producing accurate parts. Tighter tolerances lead to better quality in finished products, making it crucial for manufacturers in competitive markets to invest in repairs that uphold these standards. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of lathe components impacts their performance and wear resistance. A smoother finish reduces friction, which is critical in high-speed operations. Specifications for surface finish are often defined in microinches (μin) or Ra values, and achieving the required finish can significantly enhance the longevity of repaired parts. -
Alignment Specifications
Proper alignment of the headstock, tailstock, and ways is crucial for achieving accurate machining. Misalignment can lead to tapering, which affects part quality. Regular checks and adjustments according to manufacturer specifications can prevent issues and ensure that the lathe operates within acceptable parameters. -
Load Capacity
Each lathe has a specified load capacity that indicates the maximum weight it can handle while maintaining performance. Understanding this property helps businesses select the right lathe for their specific applications and prevents overloading, which can lead to premature wear or failure. -
Lubrication System Efficiency
A well-maintained lubrication system is vital for reducing wear and preventing overheating. Regular inspections and maintenance of lubrication lines, oil meters, and reservoirs ensure that all moving parts are adequately lubricated, enhancing the lathe’s operational efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Lathe Repair?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication in lathe repair. Here are some key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the assembly of machinery. In lathe repair, sourcing OEM parts ensures that replacements meet the original specifications for quality and fit, which is critical for maintaining machine integrity. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to avoid excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. When initiating lathe repairs, sending an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive quotes, facilitating informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses understand shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs associated with lathe parts procurement. -
Turnkey Solutions
This term refers to a comprehensive service that delivers a complete solution, including repair, installation, and training. For companies looking to overhaul their lathe operations, turnkey solutions can simplify the process and ensure that all aspects of the project are managed efficiently. -
Downtime
Downtime refers to periods when equipment is not operational, which can lead to lost productivity and revenue. Minimizing downtime during lathe repairs is a priority for businesses, as efficient repair processes directly impact the bottom line.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding lathe repair, ensuring they select the right services and parts to enhance their operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the lathe repair Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Lathe Repair?
The lathe repair sector is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. The resurgence of manufacturing, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, is stimulating demand for efficient and reliable machinery. The need for precision tools in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing is also increasing. As international B2B buyers seek to optimize production capabilities, lathe repair services are becoming crucial to maintaining machine longevity and performance.
Emerging trends in B2B technology are reshaping the lathe repair landscape. The adoption of predictive maintenance software, powered by IoT and AI, allows businesses to monitor equipment health proactively. This technology can identify wear and tear before it leads to significant breakdowns, thus minimizing downtime and repair costs. Moreover, sourcing trends indicate a shift towards local suppliers who can offer quicker turnaround times and personalized service. This is particularly relevant for international buyers who require reliable partners capable of understanding local market dynamics and regulations.
Another critical trend is the increasing focus on comprehensive service packages. Many repair firms are expanding their offerings to include maintenance plans, operator training, and parts sourcing, which not only enhance customer satisfaction but also ensure smoother operations. As competition intensifies, repair service providers are differentiating themselves through value-added services, emphasizing quality and reliability.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Lathe Repair Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the lathe repair sector, reflecting a broader global trend towards environmental responsibility. The manufacturing process and lifecycle of machinery can have significant environmental impacts, from resource consumption to waste generation. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing emissions, recycling materials, and minimizing waste.
Ethical sourcing is another essential aspect of sustainability. Buyers are now more conscious of the origins of replacement parts and the ethical standards upheld by suppliers. This shift is prompting repair firms to seek certifications that demonstrate compliance with environmental and social governance (ESG) criteria. Green certifications, like ISO 14001, signal that a company is committed to sustainable practices, making them more appealing to international buyers who prioritize corporate responsibility.
Furthermore, the use of eco-friendly materials in lathe repair, such as biodegradable lubricants and recycled components, is gaining traction. These choices not only mitigate environmental impact but also enhance the reputation of companies that commit to sustainability. As such, B2B buyers should assess potential partners based on their sustainability credentials and ethical practices, ensuring alignment with their corporate values and compliance with global standards.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Lathe Repair in a B2B Context?
The lathe repair sector has evolved significantly over the decades, reflecting advancements in technology and changes in manufacturing practices. Historically, lathe repair was primarily a manual process, relying heavily on skilled technicians to assess and restore machines. As industries grew and the demand for precision increased, the need for specialized repair services became evident.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of computerized numerical control (CNC) lathes revolutionized the industry, necessitating a new approach to repair and maintenance. The complexity of these machines required technicians to possess advanced skills and knowledge, leading to the emergence of specialized training programs and certifications.
Today, the integration of digital technologies has transformed lathe repair into a more proactive and data-driven process. Predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring are now standard practices, enabling businesses to extend the life of their equipment while reducing costs. This evolution highlights the importance of ongoing training and adaptation in the lathe repair sector, ensuring that service providers can meet the evolving needs of international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lathe repair
-
How do I solve taper issues in my lathe?
To address taper issues in your lathe, start by checking the alignment and leveling of the machine. Misalignment can often cause tapering in the workpiece. Use a dial indicator to measure the taper accurately, and inspect the lathe ways for wear. If wear is evident, you may need to consider scraping the ways or having them ground. Additionally, ensure that the tailstock is aligned correctly, as it can contribute to taper if offset. Regular maintenance checks can also help prevent these issues from occurring. -
What is the best method for lathe ways repair?
The best method for lathe ways repair typically involves a two-step process: grinding and scraping. Grinding is used to restore the flatness and alignment of the ways, while scraping ensures that the saddle fits properly against the ways. Depending on the extent of wear, you may also need to apply a material like turcite to restore height under the saddle. Always consult with experienced technicians who can assess your specific lathe model and condition to determine the most effective repair strategy. -
What factors should I consider when choosing a lathe repair service?
When selecting a lathe repair service, consider their experience and expertise with your specific lathe model. Look for a provider that offers comprehensive assessments and tailored repair plans. It’s crucial to check reviews and references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality of work. Additionally, inquire about their turnaround times, warranty on repairs, and whether they provide maintenance plans to help prolong the life of your machine after repairs. -
How can I ensure the quality of lathe repair parts?
To ensure the quality of lathe repair parts, source them from reputable suppliers who specialize in machinery components. Verify that the parts meet OEM specifications and inquire about the materials used in their manufacturing. Request certifications or quality assurance documentation when possible. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer a warranty on their parts, as this can indicate confidence in their quality and performance. -
What are the typical payment terms for lathe repair services?
Payment terms for lathe repair services can vary widely based on the service provider and the scope of work involved. Many companies may require a deposit upfront, followed by the balance upon completion of the repair. Others may offer flexible payment options, including installment plans. It’s important to discuss and agree on payment terms before commencing work to avoid any misunderstandings later. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for lathe repair services?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for lathe repair services can differ depending on the service provider and the specific repairs needed. Some companies may not have an MOQ for one-off repairs, while others might set a minimum for bulk services or parts. When engaging with service providers, clearly communicate your needs and ask about their policies regarding MOQs to ensure they align with your project requirements. -
How can I vet potential lathe repair suppliers?
To vet potential lathe repair suppliers, start by researching their reputation within the industry. Look for customer reviews and testimonials on independent platforms. Check if they have relevant certifications or affiliations with professional organizations. Additionally, request case studies or references from previous clients, particularly those with similar lathe models. Engaging in direct communication can also help assess their responsiveness and willingness to address your specific needs. -
What logistics should I consider when shipping my lathe for repair?
When shipping your lathe for repair, consider the logistics of packaging and transporting the machine safely. Ensure that the lathe is disassembled and securely packed to prevent damage during transit. Research shipping options that provide tracking and insurance coverage. Additionally, factor in customs regulations and potential import duties if shipping internationally. Collaborate with your repair service provider to understand their preferred shipping methods and any specific requirements they may have.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Lathe Repair Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Practical Machinist – Lathe Ways Repair
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Lathe ways repair involves checking for wear, leveling the lathe, and potentially scraping or grinding the ways. Common issues include taper over distance, misalignment of the headstock, and tailstock offset. Maintenance practices such as annual leveling checks and proper chuck mounting are crucial for optimal performance. The discussion highlights the importance of ensuring the lathe is true and …
2. H&W Machine Repair – Expert Milling & Lathe Services
Domain: machinerypartsdepot.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: H&W Machine Repair & Rebuilding specializes in the expert repair and rebuilding of manual milling machines, lathes, and grinders. Services include disassembly, cleaning, inspection, repair or replacement of major components (spindle, motor, gearbox, bearings), refurbishing or fabricating parts, reassembly, alignment, and calibration. They service brands such as Bridgeport, Sharp, Alliant, Lagun, C…
3. Machine Techs – Lathe & Mill Repair Services
Domain: machinetechs.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Conventional Lathe + Mill Repair services offered by Machine Techs include: full-time maintenance, general field services and repair, laser calibration and alignment, and preventive maintenance. They specialize in on-site heavy mechanical repairs for various machine tools including machining centers, grinders, vertical and horizontal lathes, boring mills, gantries, and bridge-style mills. The comp…
4. Vico Vital – Vintage Lathe Issues
Domain: hobby-machinist.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Vintage Vico Vital Corporation lathe; Taiwanese origin; issues with cross slide slop; adjustments made to gib; cross slide leadscrew wear suspected; used for artistic projects; user experience with ROMI 13-5 lathe; potential need for repair or replacement; advice sought from community members.
5. Delta – Gap Bed Lathe Model 46-541 to 544
Domain: finewoodworking.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Delta Gap bed lathe, variable speed model, 12″, made in the 90’s, model number 46-541 to 544. Requires two belts, length unspecified. Tailstock slipping issue, potential solutions include tightening nuts on the locking mechanism or replacing the cam activated by a lever.
6. Lathe Repair – Discussion Forum
Domain: dentallabnetwork.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Lathe repair services are discussed in the forum, with recommendations to send lathes back to manufacturers like Red Wing or Wells for repairs. Users mention issues such as stalling when starting and unusual sounds, suggesting potential problems with internal components like the armature, switch, or carbon brushes. Local motor shops are also suggested as repair options. Users emphasize the importa…
7. Model Engineer – Mini-Lathe Solutions
Domain: model-engineer.co.uk
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Mini-lathe, plastic (nylon) gears, low speed range issue, lubrication concerns, potential gear replacement with metal gears, design flaws in gear construction, recommendations for lubrication access, and bearing upgrades.
8. Delta – 46-460 Lathe
Domain: lumberjocks.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Delta 46-460 lathe, purchased used, originally sold for about $700 in 2017, has a 5-year warranty, experienced electrical failure in the electrical box, motor is fine, replacement electrical box or speed controller costs approximately $300, parts are difficult to find as they are discontinued.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lathe repair
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing for lathe repair is not merely a necessity but a strategic advantage for international B2B buyers. By understanding the critical factors such as machine wear, alignment issues, and the importance of routine maintenance, companies can significantly enhance their operational efficiency. Prioritizing quality repairs and sourcing expertise ensures that machinery remains reliable and productive, ultimately reducing downtime and associated costs.
Investing in expert repair services, whether through local providers or global partnerships, can lead to significant improvements in precision and longevity of lathes. This approach not only fosters better relationships with suppliers but also positions businesses to respond agilely to market demands, particularly in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As the industry moves forward, the call to action is clear: prioritize strategic sourcing in lathe repair to safeguard your competitive edge. By leveraging the insights and practices discussed, organizations can ensure their machinery operates at peak performance, thus driving innovation and growth in their respective markets. Engage with trusted repair specialists today to explore tailored solutions that align with your operational goals.