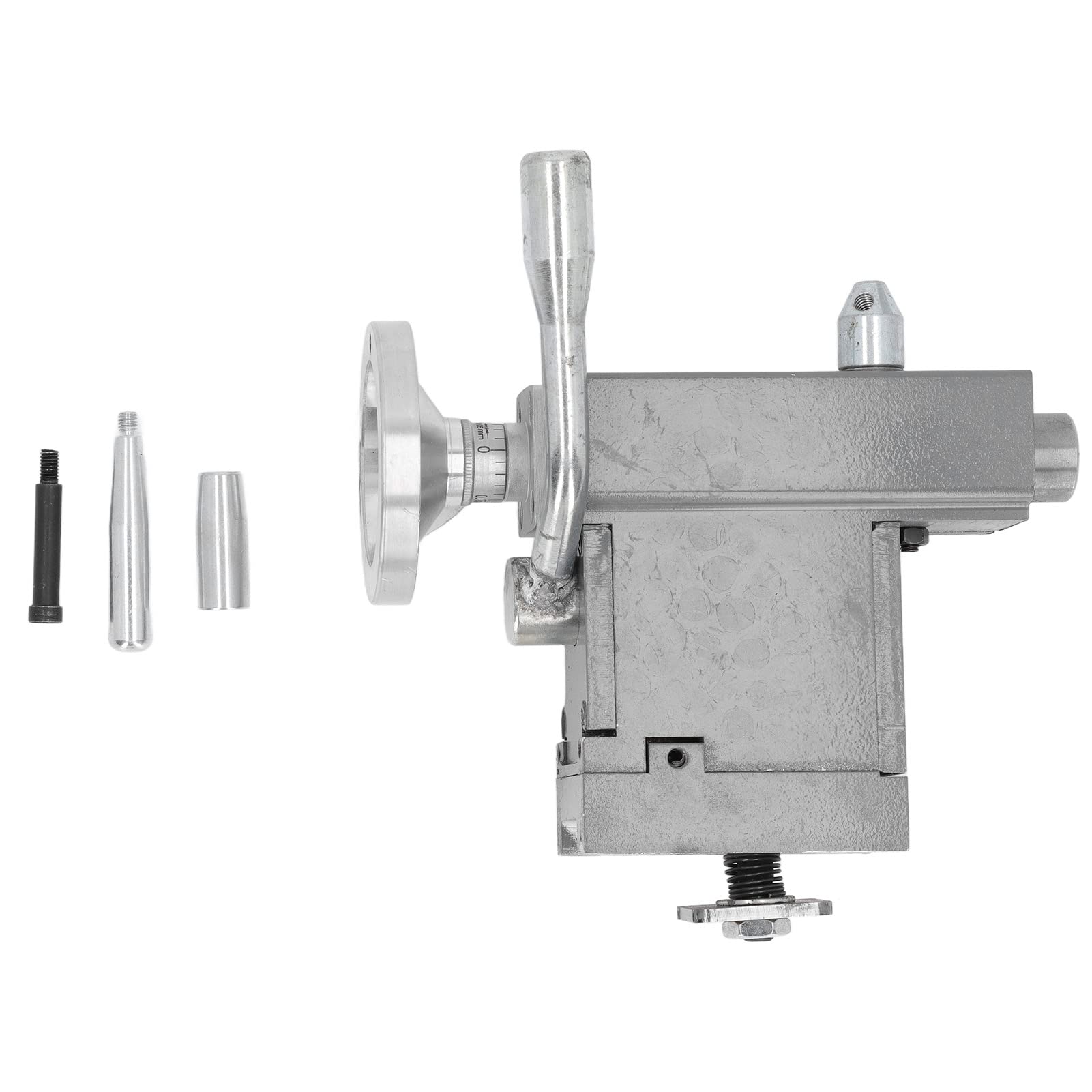
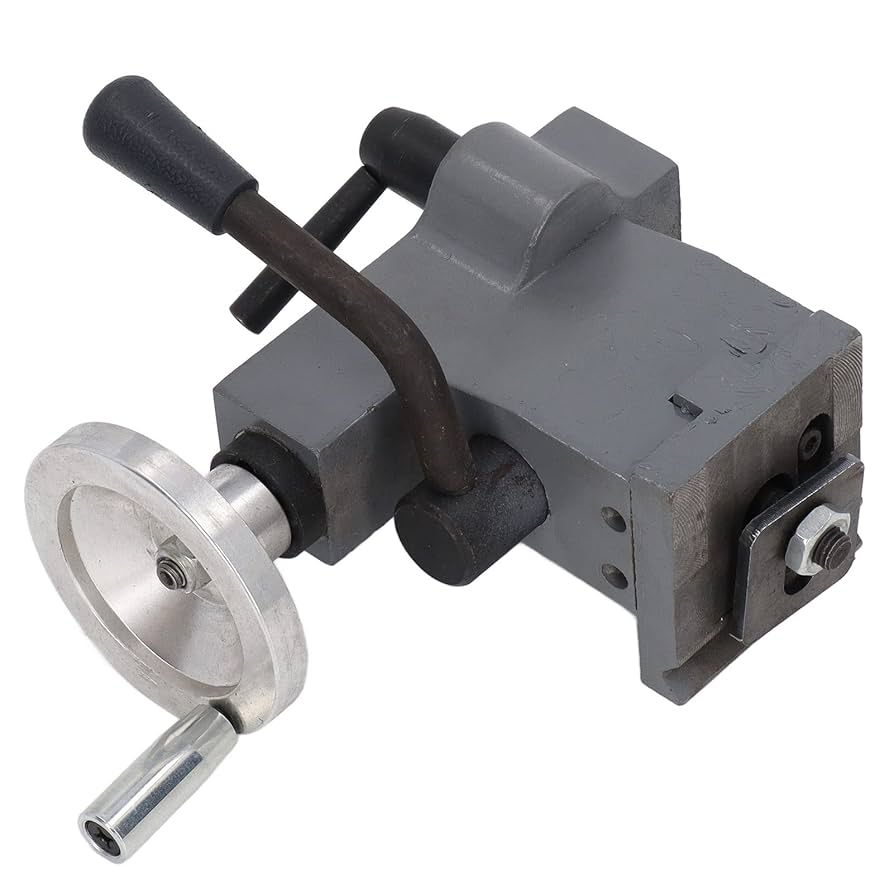
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lathe parts tailstock
In the complex landscape of manufacturing, sourcing high-quality lathe parts tailstock can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Tailstocks are critical components that support workpieces and facilitate various machining operations, making their reliability essential for maintaining productivity and precision. However, navigating the vast array of suppliers, evaluating product specifications, and understanding the associated costs can be daunting, especially for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower B2B purchasers by providing essential insights into the diverse types of lathe parts tailstock available in the global market. We will delve into the various applications of tailstocks, from drilling to workpiece support, and discuss the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers, such as quality standards, delivery timelines, and after-sales support. Additionally, we will explore pricing strategies and cost considerations, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
By equipping international buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing lathe parts tailstock, this guide not only facilitates smarter purchasing decisions but also fosters long-term partnerships that can enhance operational efficiency and drive growth.
Understanding lathe parts tailstock Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Tailstock | Non-rotating spindle, handwheel for adjustment | General machining, turning operations | Pros: Versatile, widely available; Cons: May lack advanced features for specialized tasks. |
| Drilling Tailstock | Lever-operated, often includes a dead center | Drilling operations, precision hole-making | Pros: Efficient for drilling; Cons: Limited to drilling applications. |
| Tapered Tailstock | Tapered spindle for secure tool holding | Woodworking, metalworking | Pros: Secure tool fit; Cons: Tooling may be limited to specific taper sizes. |
| Adjustable Tailstock | Features adjustable height and locking mechanisms | Custom applications requiring variable support | Pros: Customizable for various workpieces; Cons: Complexity may increase maintenance needs. |
| Live Center Tailstock | Equipped with a rotating center for dynamic workpieces | High-speed machining, precision turning | Pros: Reduces friction, increases accuracy; Cons: Higher cost and may require more maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics and Applications of Standard Tailstocks?
Standard tailstocks are the most commonly used type in lathe operations. They feature a non-rotating spindle that can be adjusted using a handwheel, allowing for precise positioning of workpieces. This type is highly versatile and is suitable for a wide range of machining applications, from basic turning to more complex operations. When considering a standard tailstock, buyers should evaluate the availability of replacement parts and compatibility with existing lathe setups.
How Do Drilling Tailstocks Enhance Precision in Machining?
Drilling tailstocks are specifically designed for drilling operations and often come with a dead center. They are lever-operated, making them easy to adjust and use during the machining process. These tailstocks are ideal for businesses focused on precision hole-making, such as in the manufacturing of components that require accurate dimensions. Buyers should assess the tailstock’s compatibility with various drill chucks and the ease of integration into their current systems.
What Advantages Do Tapered Tailstocks Offer in Tooling?
Tapered tailstocks feature a tapered spindle that provides a secure fit for tooling such as live or dead centers. This design is particularly beneficial in woodworking and metalworking applications where tool stability is crucial. Buyers should consider the specific taper size required for their tooling and the availability of compatible accessories to ensure optimal performance.
Why Choose an Adjustable Tailstock for Custom Applications?
Adjustable tailstocks are designed to accommodate various workpiece sizes by allowing height adjustments and incorporating locking mechanisms. This flexibility makes them ideal for businesses that handle a diverse range of machining tasks. However, buyers should be aware that the added complexity may lead to increased maintenance requirements, and they should evaluate the ease of adjustment and locking reliability.
What Are the Key Benefits of Live Center Tailstocks for High-Speed Machining?
Live center tailstocks incorporate a rotating center that minimizes friction, making them suitable for high-speed machining and precision turning tasks. They enhance the accuracy of machining operations, which is crucial for industries that demand tight tolerances. Buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced friction and increased accuracy against the higher costs and potential maintenance needs associated with these specialized tailstocks.
Key Industrial Applications of lathe parts tailstock
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lathe parts tailstock | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision machining of components | Enhances accuracy and productivity in production | Quality of materials, compatibility with existing lathes, lead times |
| Aerospace | Support for long, slender aerospace components | Improves safety and precision in critical applications | Certification of parts, adherence to industry standards, traceability |
| Automotive | Machining of engine components and shafts | Reduces production time and increases operational efficiency | Robustness of parts, availability of replacements, supplier reliability |
| Construction | Fabrication of heavy machinery parts | Ensures durability and performance in demanding environments | Customization options, weight limits, delivery logistics |
| Woodworking | Drilling and shaping of wood materials | Increases versatility and precision in woodworking tasks | Range of attachments, ease of use, maintenance support |
How is the lathe tailstock utilized in manufacturing processes?
In the manufacturing sector, lathe tailstocks are crucial for precision machining. They support long workpieces during turning operations, ensuring stability and accuracy. This is particularly important when producing components with tight tolerances. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, need to consider the compatibility of tailstock parts with their existing machinery to avoid costly downtimes.
What role does the tailstock play in the aerospace industry?
In aerospace applications, lathe tailstocks are employed to support and machine long, slender components such as shafts and landing gear parts. The precision offered by a well-functioning tailstock enhances safety and performance, which is vital in this highly regulated industry. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe must prioritize sourcing certified parts that adhere to stringent aerospace standards to ensure compliance and reliability.
How does the automotive industry benefit from lathe tailstocks?
The automotive industry leverages lathe tailstocks for the machining of critical engine components and shafts. By providing stability during machining, these tailstocks help reduce production time and enhance operational efficiency. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on the robustness and reliability of the tailstock parts, as well as the availability of replacements to minimize production disruptions.
Why are tailstocks important in construction machinery fabrication?
In the construction industry, lathe tailstocks are essential for fabricating heavy machinery parts, ensuring that components can withstand demanding environments. Their ability to support large workpieces contributes to durability and performance. Buyers must consider customization options to meet specific machinery requirements and the logistics of sourcing heavy parts, particularly in remote areas.
How does woodworking benefit from the use of lathe tailstocks?
Woodworking applications utilize lathe tailstocks for drilling and shaping wood materials, allowing artisans to achieve higher precision in their projects. The versatility of tailstock attachments enhances the range of woodworking tasks that can be performed. Buyers should evaluate the ease of use and maintenance support offered by suppliers to ensure smooth operations in their workshops.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘lathe parts tailstock’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Replacement Parts for Lathe Tailstock
The Problem:
For many B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions such as Africa or South America, sourcing replacement parts for lathe tailstocks can be a daunting challenge. This often stems from limited local suppliers, high shipping costs, and long lead times. Buyers may find themselves facing downtime as they wait for critical components like tailstock spindles or handwheels, directly impacting their production schedules and profitability. The lack of reliable suppliers can lead to uncertainty about part compatibility and quality, further complicating the purchasing process.
The Solution:
To mitigate these issues, B2B buyers should develop relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions, ensuring a diversified supply chain. Utilizing online platforms that specialize in industrial components can provide access to a broader range of tailstock parts. When sourcing, buyers should verify the compatibility of parts with their specific lathe model, often indicated in the product specifications. Investing in local distributors who stock common parts can also reduce lead times and shipping costs. Additionally, establishing a regular inventory of critical components can prevent unexpected downtime, allowing for smoother operations.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Performance of Tailstock Components
The Problem:
Another common pain point is the inconsistent performance of tailstock components, such as the tailstock spindle or locking mechanisms. Buyers often report issues with parts that do not fit properly, leading to misalignment during machining processes. This can result in poor product quality, increased waste, and a damaged reputation in the market. In regions where precision engineering is paramount, such inconsistencies can have severe consequences for businesses.
The Solution:
To address these performance issues, buyers should prioritize the procurement of high-quality, precision-engineered components from reputable manufacturers. Conducting thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record of quality can significantly enhance performance. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in maintenance training for their staff to ensure that tailstock components are properly installed and calibrated. Regular maintenance checks can also help identify wear and tear before they lead to significant performance issues, thereby extending the lifespan of the components.
Scenario 3: Lack of Technical Knowledge for Effective Tailstock Usage
The Problem:
Many buyers encounter difficulties due to a lack of technical knowledge regarding the proper use and adjustments of lathe tailstocks. This is especially true for companies that may not have dedicated engineering staff or training programs in place. Misuse can lead to inefficient machining processes, reduced accuracy, and even damage to the lathe itself. For businesses in competitive markets, this can hinder their ability to deliver high-quality products on time.
The Solution:
Investing in training and resources is essential for overcoming this knowledge gap. B2B buyers should seek out manufacturers that provide comprehensive manuals and technical support for their tailstock products. Participating in workshops or online courses focused on lathe operation and maintenance can also empower employees with the necessary skills to use tailstocks effectively. Creating a knowledge-sharing culture within the organization, where experienced operators mentor newer staff, can further enhance competency and ensure optimal use of lathe components. Additionally, leveraging online forums and communities can provide valuable insights and troubleshooting tips from other industry professionals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lathe parts tailstock
What Are the Key Materials Used in Lathe Parts Tailstock?
When selecting materials for lathe parts tailstock, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly influence the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the tailstock. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of lathe tailstocks.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Lathe Tailstock?
Steel, particularly alloy steel, is widely used for lathe tailstock components due to its excellent strength and durability. It typically offers high tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is essential for maintaining precision during machining operations.
Pros: Steel is highly durable and can be heat-treated to enhance its mechanical properties. It is relatively easy to machine, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
Cons: The main drawback is its susceptibility to corrosion, which can be mitigated with coatings but may increase costs. Additionally, the weight of steel can be a disadvantage in applications requiring lighter components.
Application Impact: Steel tailstocks are ideal for heavy machining tasks but may require regular maintenance to prevent rust, especially in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or JIS. The availability of quality steel can vary, impacting lead times and costs.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in Lathe Tailstocks?
Aluminum is another material option, particularly for smaller or lightweight lathes. It is known for its low density and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications where weight is a concern.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, which can enhance the maneuverability of the lathe. It is also resistant to corrosion, reducing the need for protective coatings.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is not as durable as steel and can deform under high stress. Its machining can be more complex and may require specialized tools.
Application Impact: Aluminum tailstocks are suitable for lighter machining tasks and are often used in portable or hobbyist lathes. However, they may not be appropriate for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum alloys that meet specific strength requirements. Compliance with local standards is also essential to ensure product reliability.
Why Is Cast Iron a Popular Choice for Lathe Tailstocks?
Cast iron is traditionally used in lathe tailstocks due to its excellent vibration-damping properties and inherent stability. This material is particularly effective in reducing chatter during machining, leading to improved surface finishes.
Pros: Cast iron is highly stable and can absorb vibrations, which enhances machining precision. It also has good wear resistance and can withstand high temperatures.
Cons: The brittleness of cast iron can be a significant drawback, as it may crack under heavy impact. Additionally, it is heavier than steel and aluminum, which can be a disadvantage in certain applications.
Application Impact: Cast iron tailstocks are ideal for precision machining tasks where stability is critical. However, they may not be suitable for environments where impact resistance is necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that cast iron components meet relevant international standards. The availability of high-quality cast iron can vary by region, impacting procurement strategies.
How Does Composite Material Fit into Tailstock Manufacturing?
Composite materials, such as reinforced plastics or carbon fiber, are emerging as alternatives for specific lathe tailstock applications. These materials offer unique properties, including low weight and high resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Composites can be engineered for specific applications, providing tailored mechanical properties. They are lightweight and resistant to many chemicals, making them suitable for diverse environments.
Cons: The primary limitation of composites is their cost and the complexity of manufacturing processes. They may not provide the same level of strength as metals in heavy-duty applications.
Application Impact: Composite tailstocks can be advantageous in specialized applications where weight and corrosion resistance are priorities, such as in aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of composite materials and ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material properties.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Lathe Parts Tailstock
| Material | Typical Use Case for lathe parts tailstock | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty machining | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight or portable lathes | Low weight and corrosion resistance | Less durable under high stress | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Precision machining | Excellent vibration damping | Brittle and heavy | Medium |
| Composite | Specialized applications | Tailored properties and lightweight | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for lathe parts tailstock, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lathe parts tailstock
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Lathe Parts Tailstock?
The manufacturing of lathe parts tailstock involves several critical stages that ensure high precision and functionality. Each stage plays a vital role in transforming raw materials into finished products ready for assembly and use.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Selected and Processed?
The first step in manufacturing lathe tailstocks is the careful selection of raw materials, typically high-grade steel or aluminum alloys. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Once selected, the raw materials undergo a series of processes, including cutting and machining, to create the initial shapes required for the tailstock components. This stage may involve techniques such as:
- CNC Machining: Automated machines cut the material to exact specifications, ensuring high precision.
- Casting: For more complex shapes, casting techniques may be employed, where molten metal is poured into molds to form components like the tailstock body.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Tailstock Manufacturing?
After material preparation, the forming stage shapes the components into their final forms. This stage is crucial for achieving the desired dimensions and tolerances.
- Turning: A lathe is used to rotate the workpiece against cutting tools, forming cylindrical shapes, such as the tailstock spindle.
- Milling: Flat surfaces and intricate features are created using milling machines, which remove material in a controlled manner.
- Drilling: Holes for fasteners and tool attachments are precisely drilled to facilitate assembly and operation.
How Are Tailstock Components Assembled for Optimal Functionality?
Once individual components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage involves fitting together various parts, including the tailstock spindle, handwheel, and locking mechanisms. Key techniques during assembly include:
- Fitting and Alignment: Ensuring components fit together with minimal play is critical for operational accuracy. Alignment tools and fixtures may be used to achieve this.
- Fastening: Components are secured using screws, bolts, or pins, depending on the design specifications.
- Calibration: Adjustments are made to ensure that the tailstock operates smoothly, particularly the spindle’s extension and retraction mechanisms.
What Finishing Processes Enhance the Quality of Tailstock Parts?
The finishing stage improves both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the tailstock components. It involves several techniques aimed at enhancing durability and performance.
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing, painting, or powder coating are applied to protect against corrosion and wear.
- Grinding: Precision grinding is often employed to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy, particularly for mating surfaces.
- Inspection: Final inspection ensures that all dimensions meet specified tolerances and that the surface finish is up to standard.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Tailstock Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of lathe tailstocks. It ensures that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers typically adhere to various international quality standards to ensure product reliability. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard specifies requirements for a quality management system, emphasizing consistent quality and continual improvement.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking demonstrates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for manufacturers catering to the oil and gas industry, these standards ensure that products meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Common in Tailstock Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early on. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks during manufacturing help catch deviations from specifications early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes a thorough inspection and testing process to verify its functionality and compliance with standards.
What Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Tailstock Quality?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of lathe tailstocks, including:
- Dimensional Inspection: Calipers, micrometers, and gauges are used to verify that components meet specified dimensions.
- Functional Testing: Tailstocks are tested for operational efficiency, ensuring smooth spindle movement and secure locking mechanisms.
- Material Testing: Techniques like hardness testing and tensile strength testing ensure that materials meet performance requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and QC measures in place.
- Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of quality control processes and test results can help assess a supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate product quality before shipment can further safeguard against defects.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Understanding these can help avoid compliance issues.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Recognizing cultural differences in business practices can facilitate better communication and negotiation with suppliers.
- Logistics Considerations: Ensure that the QC measures account for the complexities of international shipping, including handling and transport conditions that could affect product quality.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing lathe parts tailstock, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘lathe parts tailstock’
Introduction
This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure lathe parts tailstock. The tailstock is a critical component in lathe operations, ensuring precision and stability while machining. Following this checklist will help streamline the sourcing process and ensure you make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is crucial before engaging with suppliers. Consider factors such as the type of lathe you operate, the size of the tailstock, and the materials needed for durability. Clear specifications will help suppliers provide accurate quotes and relevant options tailored to your needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in lathe parts tailstock. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, especially those with experience in your region. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and trade shows to gather a list of potential candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications and quality assurance processes in place. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate adherence to international quality standards, which is critical for ensuring the reliability of the tailstock components you purchase. Don’t hesitate to ask for documentation that proves their compliance.
Step 4: Request Product Samples or Specifications
To assess the quality of the products, request samples or detailed specifications from shortlisted suppliers. Examine materials, finishes, and any additional features that may affect performance. This step is essential to ensure that the tailstock parts will meet your operational requirements and quality expectations.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and analyze the pricing structures. Look beyond the initial costs to understand the total cost of ownership, including shipping, duties, and any potential import taxes. Additionally, review payment terms, including deposits, payment schedules, and available discounts for bulk purchases.
Step 6: Check References and Reviews
Request references from previous clients and read reviews to gauge the reliability and service quality of potential suppliers. Engaging with other businesses in your industry can provide insights into their experiences, helping you to make an informed decision. Pay attention to feedback regarding delivery times, customer service, and product performance.
Step 7: Finalize the Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize the agreement with clear terms regarding delivery timelines, warranties, and after-sales support. Ensure that all specifications and conditions discussed are documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. This step is vital for securing a smooth procurement process and ensuring accountability from the supplier.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement of lathe parts tailstock, ensuring quality products and reliable supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lathe parts tailstock Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Lathe Parts Tailstock Sourcing?
When analyzing the cost structure for lathe parts tailstock sourcing, several components contribute to the overall pricing. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Common materials for tailstock components include steel and aluminum, with higher-grade alloys or specialized coatings incurring additional expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for precision machining, which may lead to higher costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Overhead can vary widely depending on the efficiency of the manufacturing facility and its location.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, particularly for specialized parts. However, these costs can be amortized over larger production runs, reducing per-unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that parts meet specific standards, which can add to costs but ultimately enhances reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the destination and method of transport. International shipping often involves customs fees and insurance, which must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their costs and profit. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand and competitive pressures.
What Factors Influence Prices for Lathe Parts Tailstock?
Several influencers affect pricing beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to lower prices per unit. Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can also dictate pricing structures; suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications or modifications to standard components can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials: Higher-quality materials or specialized finishes will increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the benefits of premium materials justify the added expense.
-
Quality/Certifications: Parts that meet international quality standards or have specific certifications (e.g., ISO) may command higher prices. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms can prevent unexpected expenses and delays.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant savings:
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing flexibility. Long-term partnerships often yield better deals.
-
Leverage Volume: If possible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs, which can reduce per-unit costs. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate on larger orders.
-
Discuss Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Emphasize the importance of TCO over initial pricing. Highlighting factors such as durability and maintenance costs can justify a higher upfront price if the long-term savings are clear.
-
Research Market Rates: Understanding the market can provide leverage in negotiations. Being informed about competitor pricing and industry standards helps in advocating for fair pricing.
-
Be Cautious with Price Sensitivity: Recognize that suppliers may have limited flexibility based on their cost structures. Pushing too hard may risk the relationship or lead to subpar quality.
Conclusion: Understanding Pricing Nuances in Tailstock Sourcing
When sourcing lathe parts tailstocks, it’s crucial to consider all cost components and price influencers. International buyers should approach negotiations with a comprehensive understanding of their needs and the market landscape. By leveraging these insights, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to cost-effective sourcing while ensuring high-quality parts that meet their operational requirements.
Disclaimer: The prices mentioned in various sources can vary based on multiple factors, including supplier location, order size, and market conditions. Always conduct due diligence and request quotes for precise pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing lathe parts tailstock With Other Solutions
When considering solutions for workpiece support and drilling operations in lathe applications, it’s essential to evaluate the available options beyond traditional lathe parts tailstocks. Alternatives may offer different benefits depending on the specific requirements of your operations, such as precision, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. This analysis compares the lathe parts tailstock with two viable alternatives: the live center and the drilling tailstock.
| Comparison Aspect | Lathe Parts Tailstock | Live Center | Drilling Tailstock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for support | Excellent for rotating workpieces | Good for drilling applications |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower | Low to moderate |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and adjustment | Simple installation | Easy to attach and use |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed | Minimal maintenance | Low maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Long workpieces, general use | Turning operations | Drilling and offset drilling |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Live Center Instead of a Tailstock?
The live center is a popular alternative that excels in supporting rotating workpieces during turning operations. It offers high precision and minimizes friction, resulting in smoother operations and better surface finishes. The installation process is straightforward, allowing quick integration into existing setups. However, live centers are typically less versatile compared to tailstocks, as they cannot provide the same level of support for non-rotating tasks or heavy workpieces. Additionally, they may not be the best choice for operations requiring extensive drilling capabilities.
How Does a Drilling Tailstock Compare to a Traditional Lathe Parts Tailstock?
The drilling tailstock provides a specialized solution for drilling operations. It often comes with a built-in drill chuck and is designed for easy setup and operation. This makes it an excellent option for users focused primarily on drilling. The cost is usually lower than traditional tailstocks, making it an attractive choice for budget-conscious buyers. However, it lacks the versatility of a standard tailstock, which can accommodate various tooling options and support diverse machining tasks. Its performance is limited to drilling applications, which may not suit all machining needs.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between lathe parts tailstock, live centers, and drilling tailstocks, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their operations. Factors such as the type of workpieces, the primary machining tasks, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities are crucial in the decision-making process. For businesses that frequently handle long or heavy workpieces, a traditional tailstock may provide the necessary support. Conversely, those primarily focused on drilling might find the drilling tailstock or live center more advantageous. Ultimately, understanding the unique demands of your operations will guide you toward the most suitable solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lathe parts tailstock
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Lathe Parts Tailstock?
When sourcing lathe tailstock components, understanding the critical specifications is essential for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility with existing machinery. Here are several key properties to consider:
-
Material Grade: The materials used in tailstock construction typically include cast iron, aluminum, or high-grade steel. Cast iron is favored for its vibration-damping qualities, while aluminum offers lightweight benefits. Selecting the appropriate material is crucial as it affects durability, weight, and the ability to withstand machining stresses.
-
Tolerance Levels: Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For tailstock parts, tighter tolerances (usually in the range of ±0.001 inches) are critical for precision machining applications. Proper tolerance ensures that the tailstock aligns perfectly with the lathe’s spindle, reducing the risk of inaccuracies during operation.
-
Spindle Diameter and Taper: The spindle diameter and taper are vital for compatibility with tooling accessories such as live centers or drill chucks. Common tapers include Morse Taper #1, #2, and #3. Understanding these specifications helps ensure that the tailstock can accommodate the required tools, facilitating diverse machining tasks.
-
Load Capacity: The load capacity indicates the maximum weight the tailstock can support. This is particularly important when working with long or heavy workpieces. A tailstock that can handle higher loads will enhance productivity and reduce the risk of mechanical failure.
-
Locking Mechanism: Tailstocks often include locking mechanisms to secure the spindle in place during operation. Understanding the type of locking mechanism (e.g., lever or screw lock) is essential for ensuring ease of use and stability during machining.
-
Graduation Scale: Many tailstocks feature a graduated scale for quick adjustments. This scale allows operators to make rapid positional changes, which is essential in high-production environments. A clearly marked scale improves efficiency and accuracy in setup.
What Are the Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Used in Lathe Parts Tailstock Procurement?
In the realm of B2B transactions for lathe parts, familiarity with industry terminology is crucial. Here are some commonly used terms that buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When sourcing tailstock components, verifying if a supplier is an OEM can ensure you receive high-quality, compatible parts.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ refers to the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is vital for budget management, especially for international buyers looking to optimize their inventory without incurring excessive costs.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. When looking for lathe tailstock components, sending out RFQs can help buyers compare prices and terms, leading to better purchasing decisions.
-
Incoterms: International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps mitigate risks related to shipping, insurance, and delivery, ensuring clarity on who bears costs and risks at different points in the transaction.
-
Lead Time: This term indicates the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and inventory management, particularly in industries with tight deadlines.
-
Aftermarket Parts: These are components made by companies other than the OEM. While often more affordable, it’s important to assess the quality and compatibility of aftermarket tailstock parts to avoid potential operational issues.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their machining operations and ensure the longevity of their equipment.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the lathe parts tailstock Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Lathe Parts Tailstock Sector?
The global lathe parts tailstock market is experiencing a transformative phase driven by technological advancements and evolving manufacturing practices. Key drivers include the increasing demand for precision machining and the growing adoption of automation in manufacturing processes. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for efficiency and quality, there is a notable shift towards sourcing high-quality lathe tailstock components that enhance productivity and reduce downtime.
Emerging B2B tech trends such as Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) are reshaping sourcing strategies. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating smart technologies into their operations, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of lathe machines, including tailstock assemblies. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains and ensure seamless operations.
Furthermore, with the rise of e-commerce platforms, B2B buyers are gaining access to a broader range of suppliers and products. This digital transformation allows for better price comparison, quality assessment, and supply chain transparency. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are particularly benefiting from these developments, as they can now engage with manufacturers globally and access specialized tailstock components tailored to their specific needs.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing B2B in the Lathe Parts Tailstock Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly critical in the lathe parts tailstock sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. For B2B buyers, this means sourcing from suppliers that prioritize sustainable materials and processes.
The use of recycled materials and environmentally friendly manufacturing techniques can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with lathe tailstock production. Additionally, suppliers offering certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or using materials that meet green standards provide buyers with assurance of their commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are gaining importance as buyers seek to ensure that their sourcing practices align with corporate social responsibility goals. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are becoming stricter regarding sustainable practices. By choosing suppliers who emphasize ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship, businesses can enhance their brand reputation while contributing positively to the global supply chain.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Lathe Parts Tailstock?
The lathe tailstock has evolved significantly since the advent of machining tools. Originally designed as a simple support mechanism for long workpieces, the tailstock has transformed into a sophisticated component that integrates advanced features such as adjustable spindles and locking mechanisms.
In the early days, tailstocks were primarily made of cast iron, focusing on basic functionality. Over time, advancements in materials science have introduced stronger and lighter materials, enhancing durability and precision. The introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology has further revolutionized tailstock design, allowing for greater accuracy and repeatability in machining processes.
Today, the lathe tailstock is not only a support tool but also a crucial element in various machining operations, including drilling and milling. Its evolution reflects the broader trends in manufacturing, emphasizing precision, efficiency, and sustainability—key factors that international B2B buyers must consider when sourcing lathe parts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lathe parts tailstock
-
How do I solve issues with a malfunctioning tailstock?
A malfunctioning tailstock can often be resolved by first inspecting the tailstock spindle and handwheel for any signs of wear or damage. Ensure that the locking mechanisms are functioning correctly, as improper locking can lead to misalignment during operations. If the problem persists, consider checking for any debris or foreign objects that may be obstructing movement. In cases where parts are damaged, sourcing quality replacement parts from reputable suppliers is essential. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for troubleshooting specific issues. -
What is the best tailstock option for precision machining?
For precision machining, look for tailstocks that feature a non-rotating spindle and a high-quality handwheel for fine adjustments. Tailstocks equipped with live centers or high-precision drill chucks are ideal, as they provide greater accuracy and stability. Consider tailstocks that offer graduated scales for easy positioning and those that allow for easy locking to maintain alignment during operation. Brands with a proven reputation for quality and durability in the machining industry are often the best choice. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing tailstock parts internationally?
When sourcing tailstock parts internationally, it is crucial to evaluate the quality of the parts, the reliability of the supplier, and their compliance with international standards. Look for suppliers who provide detailed product specifications and certifications. Additionally, consider the logistics involved, including shipping costs and delivery times. It’s also advisable to check the supplier’s reputation by reading reviews and asking for references from other buyers. A good communication channel is essential for addressing any issues that may arise during the procurement process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for tailstock parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for tailstock parts can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific components being ordered. Generally, MOQs can range from a few pieces to several hundred units. For bulk buyers, negotiating MOQs can be beneficial, especially if you require customized components. Always inquire about the possibility of lower MOQs for trial orders or sample parts, as this can help mitigate risks associated with new suppliers. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing lathe tailstock parts?
Payment terms for purchasing lathe tailstock parts can vary by supplier, but commonly accepted terms include upfront payment, partial payment before shipping, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, it is advisable to use secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect both parties. Always clarify the payment terms in advance and ensure they are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure the quality of tailstock parts from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of tailstock parts, request certifications and quality assurance documentation from the supplier. Look for suppliers who adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001. Consider ordering samples to evaluate the quality firsthand before committing to larger orders. Additionally, establishing a good communication channel with the supplier can help address any quality concerns promptly and effectively. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing tailstock parts?
When importing tailstock parts, consider factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Research the best shipping methods for your needs—air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for bulk orders but takes longer. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance. It’s also wise to partner with logistics providers experienced in international shipping to avoid delays and ensure compliance with local regulations. -
Are there customization options available for tailstock parts?
Many suppliers offer customization options for tailstock parts to meet specific operational requirements. Customizations can include alterations in dimensions, materials, or additional features tailored to your machining processes. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and requirements to the supplier. Be aware that custom orders may come with higher costs and longer lead times, so it’s essential to factor this into your planning. Always confirm the feasibility of customization with the supplier before placing an order.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Lathe Parts Tailstock Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Axminster – Mini Faceplate
Domain: thewoodturningstore.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: This company, Axminster – Mini Faceplate, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Little Machine Shop – Mini Mill
Domain: littlemachineshop.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Product ID: 4791, Product Name: Mini Mill, Description: A compact and versatile milling machine designed for small-scale machining tasks, Features: Variable speed control, digital readout, and a sturdy construction, Dimensions: 30″ x 30″ x 60″, Weight: 150 lbs, Power: 1 HP, Voltage: 110V, Applications: Ideal for hobbyists, small workshops, and educational purposes.
3. Sherline – Tailstock Assembly
Domain: sherline.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Tailstock Assembly – Sherline Products
Options: Inch, Metric
SKU: N/A
Category: Replacement Parts
Related Products:
– Tailstock Assembly w/ Zero Adjustable Handwheel (Pricing available on product page)
– 3/8″ Drill Chuck with Two Arbors – $78.43
– Live Center – $48.27
– WW Collet to 5/8″ Adapter (Pricing available on product page)
Part No. Description Quantity:
– 32140 10-32 x 1/2″ Cup Point S…
4. ToolNotes – Tailstock Components
Domain: toolnotes.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Tailstock Components include: 1. Tailstock – Slides along the bedways, supports long workpieces, can be fitted with a drill chuck for holemaking operations. 2. Tailstock Spindle – Non-rotating, has a tapered hole for tooling, can be extended/retracted with a handwheel, locked in place with a spindle lock, typically graduated for rough positioning. 3. Tailstock Handwheel – Used to extend/retract th…
5. Lathe – Tailstock and Turret Parts
Domain: store.lathe.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Tailstock and Turret Parts:
– Tailstock Screw: $134.75, $142.75, $148.00, $156.75, $240.75
– Binding Lever: $64.00
– Screw Retainer: $84.50
– Tailstock Quill (1-1/8 Dia): $286.75
– Binding Plug: $47.25
– Dauber: $44.75
– Hex Nut: $34.75
– Tailstock Quill (1-3/8 Dia): $465.00
– Tailstock Quill, #3MT (1-3/8 Dia): $472.50
– Tailstock Quill Key: $25.75
– Tailstock Stud: $23.25
– Tailstock Wrench: $44….
6. Taig Tools – 1150 Drilling Tailstock
Domain: taigtools.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “1150 Drilling Tailstock”, “price”: “$47.70”, “description”: “Drilling tailstock, lever operated 5/8\” off set with dead center, 3/8-24 thd for drill chucks”, “sku”: “1150”, “categories”: [“General Parts”, “Parts & Accessories”]}
7. VEVOR – Metal Lathe 7 x 12 Inch
Domain: vevor.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Shop the Best Selection of lathe tailstock parts Products | VEVOR US. Categories include Machining, Metal Lathe, and various lathe accessories. Products available include: VEVOR Metal Lathe 7 x 12 Inch, Precision Mini Metal Lathe 2250 RPM 400W Variable Speed, Woodworking Lathe 1.5 HP 16 x 40 in, Woodworking Lathe 1 HP 12 x 18 in, VEVOR 7″X14″ Mini Precision Wood Lathe 550W, Metal Lathe 8 x 16 in 5…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lathe parts tailstock
In today’s global marketplace, strategic sourcing of lathe parts tailstock is vital for enhancing manufacturing efficiency and operational reliability. By understanding the various components—such as tailstock assemblies, spindles, and handwheels—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their production needs. The importance of sourcing high-quality parts cannot be overstated, as they directly influence the precision and longevity of lathe operations.
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to engage with reputable suppliers who can offer tailored solutions, competitive pricing, and reliable delivery. Emphasizing quality and compatibility with existing machinery will not only streamline operations but also reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Looking forward, the demand for precision-engineered lathe parts will continue to grow, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies. As you explore sourcing options, consider building long-term partnerships with suppliers who understand your specific requirements and can provide ongoing support. This proactive approach will ensure that your operations remain at the forefront of the industry, enabling you to seize new opportunities in an increasingly competitive landscape.