Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lathe metal turning tools
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing high-quality lathe metal turning tools presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The complexities of global supply chains, fluctuating prices, and diverse regional standards can make the procurement process daunting, especially for those operating in emerging markets like Africa and South America, as well as established economies in Europe and the Middle East. This guide aims to demystify the landscape of lathe metal turning tools by providing a comprehensive overview of various tool types, their applications, and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
Buyers will gain insights into the latest trends in tooling technology and materials, which are critical for ensuring precision and efficiency in manufacturing operations. We will also delve into cost factors, helping you understand pricing structures and budget considerations that can influence your purchasing decisions. Additionally, this guide will equip you with actionable strategies to effectively evaluate suppliers, ensuring that you select partners who can meet your quality and service expectations.
By empowering B2B buyers with knowledge and resources, this guide facilitates informed purchasing decisions that drive productivity and competitiveness in your operations. Whether you’re based in Brazil, Germany, or elsewhere, understanding the nuances of lathe metal turning tools will enhance your ability to navigate the global market with confidence and clarity.
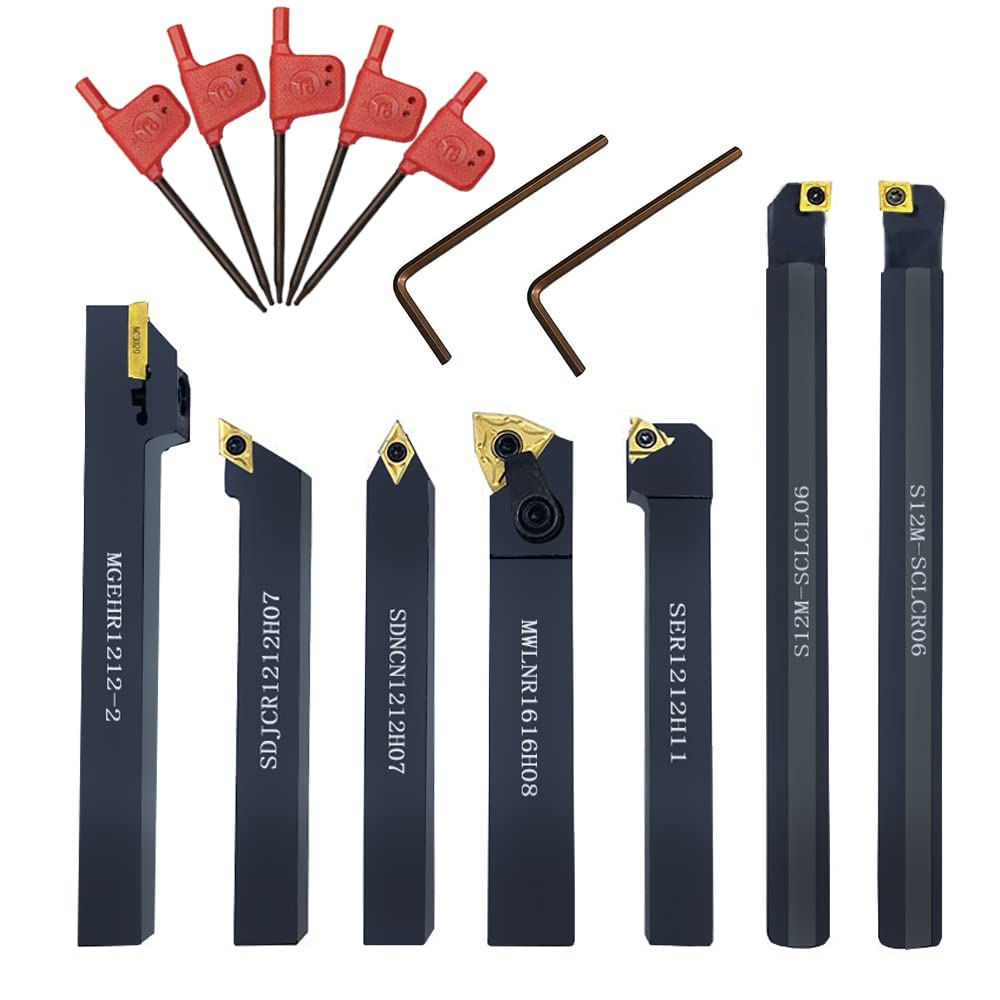
Understanding lathe metal turning tools Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turning Tools | Designed for shaping and finishing cylindrical workpieces. | Automotive, Aerospace, General Manufacturing | Pros: Versatile for various materials; Cons: Requires skill for optimal use. |
| Boring Bars | Used for enlarging existing holes with precision. | Tooling, Aerospace, Energy | Pros: High accuracy; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Grooving Tools | Ideal for creating narrow grooves and recesses. | Electronics, Automotive | Pros: Efficient for detailed work; Cons: May require frequent tool changes. |
| Threading Tools | Specifically designed for cutting threads on workpieces. | Plumbing, Manufacturing | Pros: Essential for threaded components; Cons: Specialized use may limit versatility. |
| Insert Tools | Utilize replaceable cutting inserts for various operations. | General Manufacturing, Aerospace | Pros: Cost-effective with reduced downtime; Cons: Inserts can wear out quickly in harsh conditions. |
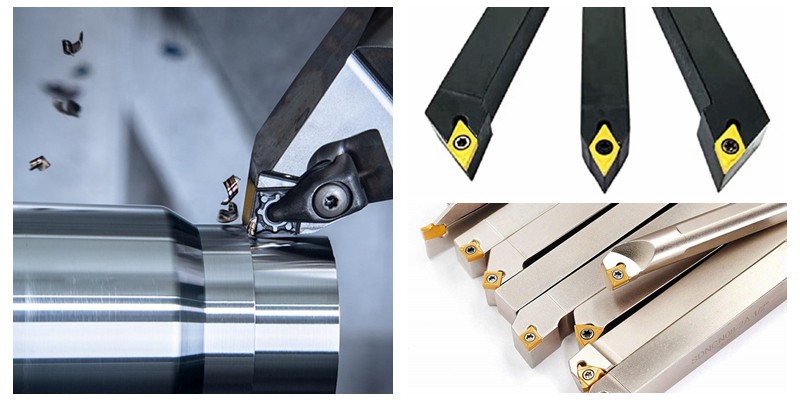
What Are Turning Tools and Their B2B Relevance?
Turning tools are essential for shaping and finishing cylindrical workpieces, making them indispensable in sectors such as automotive and aerospace. These tools can work with a variety of materials, including metals and plastics, allowing manufacturers to produce precise components. When purchasing turning tools, buyers should consider factors like the material compatibility, tool geometry, and the required finish quality, as these aspects can significantly impact production efficiency.
How Do Boring Bars Enhance Precision in Metalworking?
Boring bars are specialized tools used to enlarge existing holes with a high degree of accuracy. They are particularly useful in industries like tooling and aerospace, where precision is critical. When selecting boring bars, B2B buyers should evaluate the bar length, diameter, and the type of inserts used, as these factors influence the tool’s performance and longevity. Investing in quality boring bars can lead to improved production rates and reduced rework costs.
Why Are Grooving Tools Essential for Detailed Work?
Grooving tools are designed to create narrow grooves and recesses in various materials, making them vital for applications in electronics and automotive sectors. Their ability to perform detailed work efficiently is a significant advantage. Buyers should consider the tool’s width, geometry, and material compatibility when making a purchase. While grooving tools can enhance precision, they may require frequent changes, impacting overall workflow.
What Makes Threading Tools Crucial in Manufacturing?
Threading tools are specifically engineered for cutting threads on workpieces, a necessity in plumbing and manufacturing. These tools ensure that components fit together securely, which is essential for product integrity. When purchasing threading tools, buyers should focus on thread pitch, depth, and the tool’s compatibility with different materials. While they are indispensable for threaded components, their specialized nature may limit their application in broader contexts.
How Do Insert Tools Improve Efficiency in Production?
Insert tools are characterized by their use of replaceable cutting inserts, allowing for versatility in various operations. They are widely utilized across general manufacturing and aerospace industries, providing cost-effective solutions with reduced downtime. Buyers should assess the insert material, geometry, and the tool holder’s compatibility before making a purchase. Although insert tools can quickly wear out in harsh conditions, their efficiency and adaptability can lead to significant savings in operational costs.
Key Industrial Applications of lathe metal turning tools
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lathe metal turning tools | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision manufacturing of engine components | Ensures high performance and reliability of vehicles | Quality of materials, precision tolerances, lead times |
| Aerospace | Fabrication of aircraft parts | Reduces weight and enhances fuel efficiency | Certification standards, material certifications, delivery schedules |
| Oil & Gas | Production of drilling equipment | Increases operational efficiency and safety | Durability of tools, resistance to corrosion, supplier reliability |
| Medical Devices | Creation of surgical instruments and implants | Supports patient safety and compliance with regulations | Sterilization capabilities, precision machining, regulatory compliance |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of components for electronic devices | Enhances product performance and reduces defects | Precision machining capabilities, material specifications, scalability |
How Are Lathe Metal Turning Tools Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, lathe metal turning tools are crucial for the precision manufacturing of engine components such as crankshafts, camshafts, and pistons. These components require high tolerances to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The use of advanced CNC lathe tools allows manufacturers to produce intricate designs and maintain consistency across mass production. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality tooling that meets automotive standards is essential to avoid production delays and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
What Role Do Lathe Tools Play in Aerospace Applications?
Lathe metal turning tools are instrumental in the aerospace industry, where they are used to fabricate lightweight yet strong components for aircraft. This includes parts like turbine housings and landing gear. The precision afforded by CNC turning tools helps reduce weight, which is critical for fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance. Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, must consider sourcing tools that meet stringent aerospace certification standards, ensuring both quality and reliability in their manufacturing processes.
How Are Lathe Tools Essential in Oil & Gas Production?
In the oil and gas sector, lathe metal turning tools are utilized in the production of drilling equipment and components such as valves and fittings. The durability and resistance to harsh environments provided by high-quality turning tools are essential for maintaining safety and efficiency in operations. For businesses in the Middle East, where oil extraction is a primary industry, sourcing tools that can withstand extreme conditions while providing precise machining is vital for minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Why Are Lathe Tools Important for Medical Device Manufacturing?
The medical device industry relies heavily on lathe metal turning tools for the creation of surgical instruments and implants. Precision is paramount, as these tools must meet strict regulatory standards to ensure patient safety. Manufacturers must consider the sterilization capabilities of the tools and their ability to produce components that comply with health regulations. For international buyers, particularly in regions with emerging medical markets, understanding the specific requirements for materials and machining processes is crucial for successful sourcing.
How Do Lathe Tools Contribute to Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, lathe metal turning tools are used to create components such as housings and connectors that require precise dimensions for optimal functionality. The accuracy of machining directly influences the performance of electronic devices, making high-quality lathe tools essential. Buyers, especially from South America, need to prioritize suppliers who can provide precision machining capabilities and adhere to specific material specifications to ensure product integrity and reduce defect rates in their electronics.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘lathe metal turning tools’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Tool for Specific Materials
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in selecting the appropriate lathe metal turning tools for specific materials. For instance, a manufacturer might be working with a variety of metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, or brass, each requiring different types of tooling. Without proper guidance, they risk investing in tools that either underperform or lead to excessive wear, resulting in increased costs and production downtime. This scenario is particularly prevalent among companies in emerging markets where access to expert knowledge and resources is limited.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of the materials they work with and the corresponding tooling requirements. Begin by referencing material-specific tooling guides from reputable suppliers, which detail the recommended insert geometries and coatings for various materials. For example, carbide inserts may be ideal for aluminum, while coated inserts can enhance performance on tougher materials like stainless steel. Additionally, consider reaching out to manufacturers for expert consultations or webinars that can provide insights tailored to your specific needs. This proactive approach not only ensures better tool selection but also optimizes machining processes, ultimately improving productivity and reducing costs.
Scenario 2: Frequent Tool Failures Leading to Production Delays
The Problem: Frequent tool failures can severely disrupt production schedules and impact overall operational efficiency. Buyers might encounter scenarios where tools break or wear out unexpectedly, leading to costly downtime and delays in fulfilling orders. This issue can be particularly acute in industries with tight deadlines and high-volume production, such as automotive or aerospace manufacturing, where every minute of lost time translates to significant financial losses.
The Solution: Implementing a robust tool monitoring and maintenance program can significantly mitigate the risk of unexpected tool failures. Invest in tool wear measurement technology that allows operators to track the condition of tools in real-time, identifying wear patterns before they lead to failure. Additionally, establish a preventive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and timely replacements of worn tools. Training staff on proper handling and storage techniques can also extend the lifespan of the tools. By fostering a culture of proactive maintenance and utilizing technology, businesses can enhance tool reliability and minimize disruptions, ensuring smoother operations.
Scenario 3: Limited Availability of Quality Tools in Local Markets
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, often struggle with limited access to high-quality lathe metal turning tools. Local suppliers may offer only a narrow range of products, which may not meet the quality standards required for precision machining. This limitation can lead to subpar production quality, increased waste, and ultimately, customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should explore strategic partnerships with established global suppliers who can provide a wider selection of high-quality tools. This could involve setting up direct import agreements or utilizing e-commerce platforms specializing in industrial tools. Additionally, joining industry associations can provide valuable networking opportunities and insights into reliable suppliers. Conducting thorough research and leveraging online reviews can also help in identifying reputable vendors. By broadening their sourcing strategies, companies can access a diverse array of quality lathe tools that enhance production capabilities and ensure consistent output quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lathe metal turning tools
When selecting materials for lathe metal turning tools, several factors come into play, including performance characteristics, manufacturing complexity, and cost. This guide will analyze four common materials used in the production of lathe tools: High-Speed Steel (HSS), Carbide, Cobalt, and Ceramic. Each material has unique properties that impact their suitability for various applications, especially in the context of international B2B markets.
What are the Key Properties of High-Speed Steel (HSS) for Lathe Tools?
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is renowned for its ability to withstand high temperatures without losing hardness. This property makes HSS ideal for high-speed machining applications. It typically has a temperature rating of around 600°C and offers good corrosion resistance. HSS tools can be sharpened easily, allowing for extended tool life and versatility in various machining processes.
Pros: HSS tools are less expensive than carbide and can be ground to a fine edge. They are suitable for a wide range of materials, including steel and aluminum.
Cons: However, HSS tools wear out faster than carbide tools and may not perform well in high-volume production settings due to their lower durability.
Impact on Application: HSS is compatible with a wide range of materials, making it a versatile choice for general machining tasks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards for tool hardness and performance. HSS tools often meet ASTM standards, which are widely recognized.
How Does Carbide Compare as a Material for Lathe Tools?
Carbide tools are made from tungsten carbide, a material known for its hardness and wear resistance. Carbide tools can withstand temperatures exceeding 1000°C, making them suitable for high-speed machining and heavy-duty applications. They typically exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, which is crucial when working with abrasive materials.
Pros: The primary advantage of carbide is its exceptional durability, leading to longer tool life and reduced downtime for replacements.
Cons: The main drawback is the higher cost compared to HSS, and carbide tools are more brittle, making them susceptible to chipping under shock loads.
Impact on Application: Carbide is ideal for machining hard materials like stainless steel and titanium, which are commonly used in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
Considerations for International Buyers: In Europe, particularly Germany, compliance with DIN standards for tool materials is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of carbide tools in local markets, as they may require specific inserts or holders.
What Advantages Does Cobalt Bring to Lathe Tool Manufacturing?
Cobalt is often added to HSS to enhance its hardness and wear resistance. Cobalt tools can operate at higher temperatures than standard HSS, making them suitable for more demanding machining tasks. They typically have a temperature rating of around 700°C.
Pros: Cobalt tools offer a good balance between cost and performance, making them suitable for medium to high-volume production.
Cons: However, they are not as hard as carbide, which limits their application in extremely high-speed operations.
Impact on Application: Cobalt is particularly effective for machining tough materials, including high-strength alloys.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with relevant standards, such as JIS in Japan, to ensure the quality and performance of cobalt tools.
How Do Ceramic Tools Fit into the Lathe Tool Material Landscape?
Ceramic tools are made from advanced ceramic materials, providing excellent hardness and wear resistance. They can operate at temperatures exceeding 1200°C, making them suitable for high-speed machining of hard materials.
Pros: The primary advantage of ceramic tools is their ability to maintain sharpness over extended periods, reducing the need for frequent tool changes.
Cons: However, ceramic tools are brittle and can fracture under impact, limiting their use in applications where shock loads are common.
Impact on Application: Ceramic tools are ideal for machining hardened steels and other difficult-to-machine materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of the specific handling requirements for ceramic tools, as they may require specialized toolholders and setups.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Lathe Metal Turning Tools
| Material | Typical Use Case for lathe metal turning tools | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSS | General machining tasks | Cost-effective and easy to sharpen | Lower durability compared to carbide | Low |
| Carbide | High-speed machining, heavy-duty applications | Exceptional durability and wear resistance | Higher cost and brittleness | High |
| Cobalt | Medium to high-volume production | Good balance of cost and performance | Not as hard as carbide | Medium |
| Ceramic | Machining hardened steels | Maintains sharpness longer | Brittle and prone to fracture | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their lathe metal turning tools based on specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lathe metal turning tools
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Lathe Metal Turning Tools?
Manufacturing lathe metal turning tools involves a series of precise and methodical processes aimed at achieving high-quality end products. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Lathe Metal Turning Tools?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This typically involves selecting high-grade materials, such as high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide, known for their durability and ability to maintain sharpness. The raw materials are then cut into manageable sizes and subjected to treatments like annealing or hardening to enhance their mechanical properties.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
After preparation, the next stage is forming, where the raw material is shaped into the desired tool geometry. Techniques such as forging, machining, or grinding are utilized, depending on the tool type and specifications. For instance, forging is often used to create rough shapes, while precision machining and grinding refine the dimensions and surface finish. Advanced methods, including CNC machining, ensure high precision and repeatability, which is critical for performance in industrial applications.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Tool Manufacturing?
Once the components are formed, assembly takes place. This may involve attaching various parts, such as tool holders and inserts, to create a complete tool unit. The assembly process must ensure that all components fit together seamlessly to maintain tool balance and functionality. Techniques such as laser welding or adhesive bonding might be employed for robust connections, depending on the design requirements.
What Finishing Processes Are Critical for Quality?
Finishing processes are essential in achieving the final specifications of lathe tools. Common practices include surface treatment, coating, and polishing. Coatings such as titanium nitride (TiN) or aluminum titanium nitride (AlTiN) are applied to enhance wear resistance and reduce friction. Polishing improves surface smoothness, which is crucial for effective cutting performance and longevity. The combination of these finishing techniques not only enhances the tool’s functional properties but also its aesthetic appeal.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Tool Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of manufacturing lathe metal turning tools, ensuring that products meet both safety and performance standards. Key international standards include ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems, and specific industry standards such as CE marking for compliance within Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
The quality control process typically involves several critical checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage examines the raw materials upon receipt, ensuring they meet specified requirements before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring occurs during manufacturing to detect and correct any issues in real-time. This might involve measuring dimensions, checking tolerances, and assessing surface finish at various stages.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, tools undergo rigorous testing and inspection to verify they meet all specifications before shipping. This includes functional tests, durability assessments, and visual inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control practices through several methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports and compliance certifications, can provide insights into the supplier’s QA practices.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the products before shipment ensures an unbiased assessment of quality.
What Are the Common Testing Methods for Lathe Metal Turning Tools?
Testing methods for lathe tools vary based on the intended application and performance criteria. Common tests include:
- Hardness Testing: Ensures the tool material can withstand operational stresses without deforming.
- Tensile Testing: Measures the material’s strength and ductility, essential for determining how the tool will perform under load.
- Cutting Tests: Practical assessments simulate real-world conditions to evaluate tool performance, wear rates, and cutting efficiency.
How Do QC and Certification Nuances Affect International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding QC and certification nuances is crucial, especially when sourcing from different regions. Certifications such as ISO 9001 are universally recognized, but regional standards may vary. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while companies in the Middle East may require adherence to local standards.
Buyers from Africa and South America should be particularly vigilant about understanding these differences, as compliance can impact import regulations and market acceptance. It is advisable to engage suppliers with a proven track record in international markets to ensure smooth transactions and product acceptance.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for lathe metal turning tools are integral to delivering high-performance products. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that uphold rigorous quality standards, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes in their respective industries.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘lathe metal turning tools’
When sourcing lathe metal turning tools, it’s essential for B2B buyers to follow a structured approach. This guide serves as a practical checklist to streamline your procurement process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific requirements for the lathe tools you need. This includes determining the types of materials you will be working with (e.g., steel, aluminum), the dimensions of the tools, and any special features required (such as coatings or insert types). Clearly defined specifications help in narrowing down suppliers and ensuring compatibility with your existing machinery.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of lathe metal turning tools. Utilize online resources, trade directories, and industry forums to compile a list of vendors. Pay attention to their reputation, product range, and customer reviews. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for your sourcing decisions and helps avoid suppliers with poor service or product quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify that your potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and quality standards in place. Look for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Checking these credentials ensures that the tools meet international standards and reduces the risk of receiving subpar products.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the lathe tools you intend to purchase. Testing samples will allow you to evaluate their performance, durability, and compatibility with your machines. This hands-on approach helps in making an informed decision and can highlight any potential issues before committing to a larger order.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
After evaluating the tools, compare pricing among your selected suppliers. Look beyond just the cost; consider the value offered, including warranty, after-sales support, and bulk order discounts. Clarifying payment terms upfront, including deposits and payment methods, can prevent misunderstandings later on and enhance your cash flow management.
Step 6: Inquire About Lead Times and Delivery Options
Timing is critical in manufacturing. Confirm the lead times for production and delivery with your chosen suppliers. Understand their shipping options, including international logistics if you’re sourcing from overseas. This information helps in planning your production schedules and ensures that you receive your tools when needed.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Finally, establish clear communication channels with your supplier. Regular updates regarding your order status, delivery tracking, and customer service should be easily accessible. Strong communication can foster a better relationship, ensuring swift resolutions to any potential issues that may arise during the procurement process.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source lathe metal turning tools, ensuring that they meet operational needs while optimizing costs and timelines.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lathe metal turning tools Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of lathe metal turning tools is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis breaks down the cost components, identifies price influencers, and offers practical tips for effective sourcing.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Lathe Metal Turning Tools?
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. High-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and ceramic are common materials for lathe tools. Each has different price points and performance characteristics. For instance, carbide tools, while more expensive, offer longer tool life and better performance, which may justify the higher initial investment.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the total price. In countries with higher wage standards, such as Germany, the labor component will be more substantial compared to regions with lower labor costs, like parts of Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling and Quality Control (QC): Investment in advanced tooling and strict QC measures ensures high product quality but adds to the overall cost. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against potential savings from cheaper alternatives.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on distance, shipping method, and customs duties. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on competition, product exclusivity, and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Lathe Metal Turning Tools?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider their production needs and negotiate MOQs that balance cost with inventory management.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom tools or those with specific features may command a premium price. Buyers must assess whether the added cost aligns with their operational requirements.
-
Quality and Certifications: Tools that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) may be priced higher. However, they often provide greater reliability and reduced risk of failure.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and history of performance can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived value and trustworthiness.
-
Incoterms: Different shipping terms can significantly impact total costs. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) helps buyers anticipate additional expenses.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If planning to make a large purchase, negotiate for discounts based on volume. Suppliers are often willing to lower prices to secure larger orders.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the lifespan, maintenance costs, and performance of tools. A cheaper tool may result in higher TCO due to frequent replacements or poor performance.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to understand market pricing. This provides leverage during negotiations and helps identify the best overall value.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should account for currency fluctuations, import taxes, and tariffs, which can affect the final price.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Suppliers may offer loyalty discounts or favorable payment terms to long-term clients.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the cost structure, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing lathe metal turning tools. By considering these factors, buyers can optimize their procurement processes and enhance their operational efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing lathe metal turning tools With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Lathe Metal Turning Tools
In the realm of metalworking and manufacturing, lathe metal turning tools are a staple for shaping and finishing components. However, various alternative technologies and methods exist that can achieve similar outcomes, each offering unique advantages and challenges. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their production processes, reduce costs, or improve efficiency.
Comparison of Lathe Metal Turning Tools and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Lathe Metal Turning Tools | CNC Machining Tools | Manual Machining Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for cylindrical parts | Excellent for complex shapes | Moderate precision, dependent on skill |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing costs for tooling | Higher initial costs; lower ongoing costs | Low initial costs; labor-intensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; setup time can be lengthy | Requires programming knowledge; setup can be complex | Simple tools; minimal training required |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required for tools and machine | Less frequent maintenance; advanced systems | High maintenance; tool wear is significant |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for mass production of uniform parts | Best for custom, intricate designs | Suitable for small batches or prototypes |
Analyzing CNC Machining Tools as an Alternative
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining tools represent a significant advancement over traditional lathe metal turning tools. These machines offer high precision and can produce complex geometries that lathe tools may struggle with. However, they require a higher initial investment and a skilled operator familiar with programming. On the maintenance front, CNC machines generally require less frequent attention compared to lathe tools, but when they do require service, it can be more complex and costly. In terms of best use, CNC machining shines in applications where intricate designs and high-volume production are necessary.
Evaluating Manual Machining Techniques
Manual machining techniques, including hand lathes and milling, are another alternative to lathe metal turning tools. These methods are often less expensive to acquire and can be implemented with basic training, making them accessible for small workshops or prototyping environments. However, the precision and consistency of manual techniques can be significantly lower than both lathe and CNC options, and they are highly dependent on the operator’s skill level. Additionally, manual machining is labor-intensive, which can increase production time and costs for larger runs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate metalworking solution, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including the complexity of the parts being produced, budget constraints, and available workforce skills. Lathe metal turning tools remain a robust choice for uniform parts, while CNC machining tools are ideal for intricate designs and high production rates. Manual machining techniques can serve small-scale needs effectively but may not meet the demands of high-volume production. Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific operational goals, production volumes, and resource availability within the organization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lathe metal turning tools
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Lathe Metal Turning Tools?
Understanding the essential technical properties of lathe metal turning tools is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in lathe tools significantly impacts their performance and durability. Common materials include high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and cobalt. HSS tools are favored for their toughness and resistance to wear, while carbide tools offer superior hardness and cutting performance, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Selecting the right material grade ensures that tools can withstand specific machining processes and materials, thus optimizing operational efficiency. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In lathe turning, maintaining tight tolerances is essential for achieving high-quality finishes and ensuring parts fit together correctly. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels helps in assessing the precision required for their specific applications, which can affect product quality and manufacturing costs. -
Coating Type
Tool coatings, such as TiN (Titanium Nitride) or TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride), enhance the performance of cutting tools by reducing friction, improving wear resistance, and extending tool life. Buyers should consider coating types based on their specific machining needs, as this can lead to lower operational costs and improved productivity. -
Shank Size and Configuration
The shank size determines compatibility with various lathe machines. Standard sizes are typically measured in inches or millimeters, and configurations can vary (e.g., square or round). Ensuring that the shank size matches the lathe tool holder is critical for optimal tool performance and stability during operation. -
Insert Type and Geometry
Inserts play a vital role in the efficiency of turning operations. Different geometries (e.g., sharp, rounded, or flat) and insert types (e.g., threading, grooving) are designed for specific cutting tasks. B2B buyers must align their choice of inserts with the materials they will be machining to achieve the desired cutting action and surface finish. -
Cutting Speed and Feed Rate
These parameters dictate the operational efficiency of lathe turning tools. Cutting speed refers to the speed at which the tool engages the workpiece, while feed rate is the distance the tool advances during each revolution. Optimizing these settings can lead to improved productivity, reduced wear on tools, and enhanced surface finish quality.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Lathe Metal Turning Tool Procurement?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some common trade terms relevant to lathe metal turning tools:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for specific tool specifications or quality assurance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess the feasibility of bulk purchasing, which can lead to cost savings but may also require larger capital investment upfront. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers. It is essential for B2B transactions, enabling buyers to compare pricing, terms, and conditions before making purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, ensuring a smooth procurement process. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to delivery. It is crucial for buyers to understand lead times to manage inventory and production schedules effectively. -
Supplier Certification
This refers to the process by which a supplier is evaluated and approved based on specific standards (e.g., ISO certifications). Supplier certification assures buyers of the quality and reliability of the tools they are purchasing.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they select the right lathe metal turning tools for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the lathe metal turning tools Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for Lathe Metal Turning Tools?
The lathe metal turning tools sector is experiencing significant growth driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and an increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries. Key global drivers include the rising automation in manufacturing processes, which enhances productivity and efficiency. Moreover, the expansion of industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, particularly in emerging markets in Africa and South America, is driving demand for high-quality lathe tools.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing are primarily influenced by technological innovations, including the adoption of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology, which allows for greater precision and efficiency in metal turning operations. Suppliers are increasingly focusing on digital platforms to streamline procurement processes, providing buyers with easy access to a wide range of products. International B2B buyers are also looking for suppliers who offer customized solutions and quick turnaround times, enhancing their operational agility.
Furthermore, the emphasis on quality and durability in tooling is leading to a shift towards advanced materials and coatings that extend tool life. As buyers become more discerning, they are seeking suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to quality assurance and continuous improvement.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing for Lathe Metal Turning Tools?
Sustainability is becoming an integral aspect of sourcing strategies in the lathe metal turning tools sector. As environmental concerns rise globally, businesses are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of their supply chains. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and energy consumption in their manufacturing processes.
The importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. Companies are seeking to partner with suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing practices and can provide evidence of compliance with environmental regulations. This includes certifications that indicate sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications that highlight the use of eco-friendly materials.
Moreover, the shift towards circular economy principles is prompting manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products. This includes using recyclable materials for lathe tools and designing products that can be easily reconditioned or repurposed. For international buyers, especially those in Europe and the Middle East, aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance their brand image and meet regulatory requirements.
What Is the Historical Context of Lathe Metal Turning Tools in B2B Markets?
The evolution of lathe metal turning tools dates back to the early days of machining, where manual lathes were the primary tools used for shaping materials. The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point, introducing mechanization and leading to the development of more sophisticated lathes. Over time, advancements in materials science and engineering have transformed lathe tools into highly specialized instruments designed for precision and efficiency.
The introduction of CNC technology in the late 20th century revolutionized the sector, enabling automated control of lathe operations, which drastically improved productivity and accuracy. Today, lathe metal turning tools are at the forefront of manufacturing technology, continually evolving to meet the demands of modern industries.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is crucial. It provides insights into the advancements that have shaped current market offerings and highlights the importance of innovation in selecting suppliers who can meet the evolving needs of their businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lathe metal turning tools
-
1. How do I select the right lathe metal turning tools for my projects?
Selecting the right lathe metal turning tools involves understanding your specific machining requirements, such as material type, desired finish, and tolerances. Consider the tool geometry, insert type, and coating that best suits your application. Additionally, consult with suppliers who can provide insights based on their experience and customer feedback. It’s often beneficial to request samples or trial runs to ensure compatibility with your machinery and production goals. -
2. What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers of lathe metal turning tools?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Evaluate their product range, quality certifications, and manufacturing processes. Additionally, inquire about their ability to meet your specific requirements, such as customization options, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and delivery times. A reliable supplier should also provide transparent communication and strong after-sales support. -
3. What is the importance of minimum order quantities (MOQ) in sourcing lathe tools?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) are crucial as they impact your inventory management and cash flow. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. When sourcing lathe tools, negotiate MOQs that align with your production needs without overcommitting resources. Understanding MOQs can help you maintain flexibility in inventory while ensuring you have the necessary tools for your operations. -
4. How can I ensure the quality of lathe metal turning tools before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request product samples or specifications from potential suppliers. Look for certifications like ISO or similar quality assurance standards that indicate a commitment to quality. Additionally, review third-party testing results and customer testimonials. Establish a clear quality assurance process that includes inspections upon delivery to verify that the tools meet your standards before they are put into use. -
5. What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of lathe tools?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from upfront payments to net 30 or net 60 days after delivery. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or flexible financing options for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms before placing an order to avoid misunderstandings. Building a solid relationship with your supplier may also lead to more favorable payment conditions over time. -
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing lathe tools?
When importing lathe tools, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery times. Ensure that your supplier provides the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and certificates of origin. Evaluate logistics partners to find reliable shipping options that align with your budget and timeline. It’s also wise to factor in potential tariffs or taxes that may apply to your imports. -
7. Can lathe metal turning tools be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for lathe metal turning tools to meet specific application needs. Customization can include tool geometry, material selection, and coating types tailored to your machining requirements. Discuss your needs with the supplier early in the process to explore available options and any associated costs or lead times. Customized tools can enhance performance and improve machining efficiency. -
8. What are the common applications for lathe metal turning tools in various industries?
Lathe metal turning tools are widely used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Common applications include shaping, threading, and boring components from materials such as steel, aluminum, and plastics. Understanding the specific needs of your industry can help you select the right tools that improve productivity and precision in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Lathe Metal Turning Tools Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Little Machine Shop – Cutting Tools for Lathes
Domain: littlemachineshop.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Cutting Tools for Lathes include various types of tools designed for machining operations on lathes. These tools are essential for shaping, cutting, and finishing materials such as metal and plastic. The product range typically includes high-speed steel (HSS) tools, carbide inserts, and specialized tooling for specific applications. Key features may include durability, precision, and compatibility…
2. Tormach – CNC Lathe Tooling
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Tormach – CNC Lathe Tooling, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Grizzly – Cutting Tools & Tooling
Domain: grizzly.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: Cutting Tools & Tooling from Grizzly Industrial includes a wide range of products such as: CNC Cutting Tools & Tooling, Boring Bars, Clamping Kits, Collets, End Mills, Inserts, Lathe Centers, Lathe Chucks, Live Centers, Rotary Burrs, Rotary Tables, Slitting Saws, Spiral Cutterheads, Tap & Die Sets, and various tooling accessories. The product categories also feature router bits, shaper cutters, an…
4. KBC Tools – Lathe Tooling Solutions
Domain: kbctools.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Tool Posts and Lathe Tooling from KBC Tools & Machinery includes a variety of products designed to enhance productivity and versatility in lathe operations. Key categories include: Grinding Carriers (12), Lathe Accessories (6), Lathe and Expanding Mandrels (53), Lathe Dogs (12), Quick Change Tool Holders (248), Quick Change Tool Post Sets (18), Quick Change Tool Posts (24), Radius Tools (6), Rocke…
5. Reddit – HSS Tooling Essentials
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. HSS (High-Speed Steel) tooling: Recommended for beginners due to its ease of sharpening and versatility. Start with pre-ground profiles that can be trimmed to length. 2. HSS stock: For those interested in grinding their own tools. 3. Pedestal grinder: Necessary for sharpening HSS tools. 4. Center gage: Useful for setting tool heights and angles. 5. Indicator with a magnetic base: For precise me…
6. The Woodturning Store – Wood Turning Tools
Domain: thewoodturningstore.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Wood Turning Tools available at The Woodturning Store include a variety of categories such as Traditional Tools, CryoCut Series, Signature Series, and more. Specific tools offered include Bowl Gouges, Parting Tools, Scrapers, Skew Chisels, Spindle Gouges, and Bead Forming Tools. The store also features sets, replacement cutters, and accessories. Additionally, there are various brands available inc…
7. Dorian – 3/4 SCLCR Boring Bar
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Brands mentioned: Dorian, Kennametal, Hertel, Iscar, Seco, Mitsubishi, ZCC-CT, Sandvik, Pramet. Price examples: Dorian 3/4″ SCLCR boring bar – $151; Chinese generic tooling – $6 + $6 shipping; ZCC-CT 1″ WNMG holder – $30. Quality considerations: Generic Chinese tools may require deburring and quality control; name brands like Iscar and Sandvik offer better support and quality. User experiences: Do…
8. Accusize – Indexable Carbide Turning Tools
Domain: accusizetools.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Indexable Turning Tools: 41 products available. Key products include: 7 Pc/Set Indexable Carbide Turning Tools ($127.04), M35 Cobalt Lathe Tool Bits for Heavy Cuts ($2.85), Positive Stop Adjustable Blades for Self-Lock Cut-Off Inserts ($30.66), 5 PCS Indexable Turning Tool Set ($38.70), 8 pcs H.S.S. Tool Bit Set ($48.19), SVJB R/L Toolholders with VBMT Inserts ($26.28), SCLC R/L Toolholders for CC…
9. Wayken – Lathe Cutting Tools
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Lathe cutting tools are categorized into four main categories: 1) Based on Material: High-speed Steel (HSS), Carbide, Diamond, Cubic Boron Nitride; 2) Based on Operations: Turning tools (Rough and Finish), Chamfering tools, Thread Cutting tools, Facing tools, Forming tools, Grooving tools, Boring tools, Knurling tools; 3) Based on Structure: Single Body tools, Welding lathe cutting tools, Clamp la…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lathe metal turning tools
In navigating the competitive landscape of lathe metal turning tools, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse range of tooling options—from inserts to specialized tool holders—companies can make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Leveraging insights into supplier capabilities and market trends allows buyers to negotiate better terms and cultivate long-term partnerships.
Moreover, as global demand for precision machining continues to rise, the importance of sourcing high-quality tools from reputable manufacturers cannot be overstated. Buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize suppliers who not only deliver exceptional products but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and innovation.
Looking ahead, the landscape of lathe tooling will undoubtedly evolve, driven by advancements in technology and changing market needs. International buyers are encouraged to stay agile, continuously reassessing their sourcing strategies to capitalize on new opportunities. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive support and expertise can significantly impact productivity and profitability. Embrace the future of machining by investing in strategic sourcing today.