Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lathe equipment
Navigating the global market for lathe equipment poses significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing high-quality machinery that meets specific operational needs. With an array of options available, from woodturning lathes to CNC-controlled models, the decision-making process can become overwhelming. This guide aims to streamline your purchasing journey by providing a thorough overview of the various types of lathe equipment, their applications, and essential accessories that enhance functionality.
In this comprehensive resource, you will find valuable insights on supplier vetting, pricing structures, and cost-saving strategies tailored for international buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia. By understanding the intricacies of lathe equipment—from standard features to advanced functionalities—you will be better equipped to make informed decisions that align with your operational goals and budget constraints.
Whether you are looking to expand your manufacturing capabilities or enhance your woodworking projects, this guide empowers you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the lathe equipment market confidently. With actionable insights and expert advice, you can optimize your sourcing strategy and achieve greater efficiency in your operations.
Understanding lathe equipment Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood Lathe | Designed for wood turning, features variable speed settings | Furniture making, artistic woodturning | Pros: User-friendly, versatile for various projects. Cons: Limited to softer materials. |
| Metal Lathe | Equipped for precision machining of metals, often CNC-capable | Aerospace, automotive parts manufacturing | Pros: High precision and durability. Cons: Higher initial investment and maintenance costs. |
| CNC Lathe | Computer-controlled for automated precision work | Mass production, complex geometries | Pros: Consistent quality, reduces labor costs. Cons: Requires skilled operators and software expertise. |
| Mini Lathe | Compact size, ideal for small projects and hobbyist applications | Prototyping, small part manufacturing | Pros: Space-efficient, cost-effective. Cons: Limited capacity and features compared to larger lathes. |
| Bench Lathe | Benchtop model, suitable for light-duty tasks | Small workshops, educational settings | Pros: Affordable, easy to use. Cons: Limited power and size for larger projects. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Wood Lathes for B2B Buyers?
Wood lathes are specifically engineered for turning wood, making them essential for industries focused on furniture production and artistic woodturning. These machines typically offer variable speed settings, allowing users to adjust the rotation based on the project requirements. When considering a wood lathe, B2B buyers should focus on the machine’s power, bed length, and available accessories, such as mobility kits and bed extensions, which can enhance operational flexibility.
How Do Metal Lathes Differ in Functionality and Application?
Metal lathes are robust machines designed for machining metal parts with high precision. They often feature advanced capabilities, including CNC technology, which allows for automated operations and complex part geometries. In B2B contexts, these lathes are invaluable in sectors like aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where precision is paramount. Buyers should evaluate the machine’s rigidity, tooling options, and software compatibility to ensure it meets their production needs.
What Advantages Do CNC Lathes Offer for Mass Production?
CNC lathes leverage computer programming to execute precise machining tasks automatically, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. They are capable of producing complex shapes with consistent quality, significantly reducing labor costs and time. B2B purchasers should consider factors such as machine compatibility with existing systems, ease of programming, and the availability of technical support when investing in CNC lathes.
Why Choose Mini Lathes for Prototyping and Small Projects?
Mini lathes are compact and designed for light-duty applications, making them suitable for hobbyists and prototyping in small workshops. They are cost-effective and space-efficient, allowing businesses to maintain flexibility without significant capital investment. However, B2B buyers should be aware of their limitations in terms of capacity and power, ensuring that the chosen model aligns with the scale of their projects.
What are the Benefits of Bench Lathes for Educational Settings?
Bench lathes are small, benchtop models ideal for light-duty tasks, often utilized in educational institutions and small workshops. They provide an affordable entry point for beginners looking to learn turning techniques. When considering a bench lathe, B2B buyers should assess the machine’s ease of use, safety features, and overall durability to ensure it meets the learning objectives of their programs.
Key Industrial Applications of lathe equipment
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lathe equipment | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of precision components | High precision and reliability in critical parts | Need for CNC lathes with advanced automation capabilities |
| Automotive | Production of engine components and shafts | Enhanced efficiency and reduced production costs | Focus on durable machines capable of handling metals |
| Woodworking | Crafting furniture and decorative items | Ability to create custom designs and high-quality finishes | Importance of versatility and ease of use for various wood types |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments and implants | Compliance with strict industry standards | Requirement for high-precision lathes and quality assurance processes |
| Oil & Gas | Manufacturing of valves and fittings | Reliability in harsh environments | Selection of lathes with corrosion resistance and heavy-duty performance |
How is Lathe Equipment Used in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, lathe equipment is crucial for producing precision components such as turbine blades, landing gear, and structural elements. These parts require extremely tight tolerances and high reliability due to safety standards. International buyers must consider CNC lathes that offer advanced automation and precision control to meet these stringent requirements. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers with a proven track record in aerospace applications can ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
What Role Does Lathe Equipment Play in Automotive Production?
Lathe equipment in the automotive sector is primarily used for machining engine components, shafts, and transmission parts. The ability to produce high volumes with consistent quality directly impacts production efficiency and cost savings. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing durable lathes capable of handling tough metals and high-speed operations. Furthermore, considering suppliers that offer comprehensive service and support can enhance operational uptime and efficiency.
How is Lathe Equipment Beneficial in Woodworking?
In woodworking, lathes are employed to craft furniture, decorative items, and custom wood pieces. They allow artisans to create intricate designs while ensuring a smooth finish. For international buyers, it’s essential to select versatile lathes that can accommodate various wood types and sizes. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who offer a range of accessories can enhance the lathe’s functionality, making it easier to adapt to different projects.
Why is Lathe Equipment Essential for Medical Device Manufacturing?
Lathe equipment is integral to the fabrication of surgical instruments and implants, where precision and quality are paramount. The medical industry is heavily regulated, requiring manufacturers to adhere to strict standards for safety and efficacy. Buyers must look for high-precision lathes equipped with quality assurance processes to ensure compliance. Furthermore, sourcing from suppliers with expertise in medical applications can provide added assurance of product reliability.
How is Lathe Equipment Used in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, lathe equipment is essential for manufacturing valves, fittings, and other components that must withstand harsh environmental conditions. The reliability of these parts directly affects operational safety and efficiency. Buyers should prioritize sourcing lathes that offer corrosion resistance and heavy-duty performance. Additionally, considering suppliers with experience in the oil and gas sector can ensure that the equipment meets industry-specific standards and requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘lathe equipment’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complexity in Lathe Equipment Selection
The Problem: For many B2B buyers, the selection of lathe equipment can be a daunting task. With a myriad of options available in the market, each varying in specifications, capabilities, and price points, it can be overwhelming to determine which machine is the best fit for specific production needs. Buyers often struggle with understanding the technical jargon associated with lathes, such as spindle speeds, horsepower, and bed lengths, leading to potential misalignment between the equipment chosen and the actual operational requirements of their businesses.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should begin by conducting a thorough needs assessment that includes a detailed analysis of their production processes. It is beneficial to consult with industry experts or suppliers who can provide guidance based on experience and application. Additionally, buyers should prioritize equipment demonstrations or trials to evaluate functionality in real-world scenarios. Utilizing comparison charts can also help distill complex specifications into more understandable formats, allowing for informed decision-making. Finally, engaging with a supplier that offers comprehensive after-sales support ensures that any further questions or operational challenges can be swiftly addressed.
Scenario 2: Managing Lathe Equipment Maintenance and Downtime
The Problem: Maintenance of lathe equipment is a critical concern for many businesses, particularly for those operating in high-demand environments. Unexpected breakdowns can lead to significant downtime, affecting productivity and potentially causing delays in fulfilling client orders. B2B buyers often find themselves without a clear maintenance schedule or lack the necessary knowledge to perform routine checks, resulting in reactive rather than proactive maintenance strategies.
The Solution: To address maintenance issues effectively, businesses should establish a structured maintenance program that includes regular inspections, lubrication schedules, and timely replacement of wear parts. This program should be documented and easily accessible to all relevant personnel. It is also advisable to invest in training sessions for staff to ensure they are equipped to identify potential issues before they escalate. Partnering with suppliers who offer maintenance services or support can provide an additional safety net. Additionally, leveraging technology such as predictive maintenance software can help monitor equipment conditions in real-time, allowing for timely interventions and minimizing downtime.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safety and Ergonomics in Lathe Operations
The Problem: Safety concerns are paramount in any manufacturing environment, and lathe operations are no exception. B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring that their employees operate machinery safely and efficiently. Poor ergonomics and inadequate safety measures can lead to workplace injuries, which not only affect employee morale but also result in costly compensation claims and reduced productivity.
The Solution: To enhance safety and ergonomics, businesses should invest in lathe equipment that incorporates safety features such as automatic shut-off mechanisms, emergency stops, and protective enclosures. Furthermore, it is crucial to provide ergonomic assessments of the workstations to ensure that all operators can work comfortably and safely. Training programs focused on safe operation practices and emergency protocols should be implemented as part of the onboarding process for new employees. Regular safety audits can help identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with industry safety standards. Lastly, fostering a culture of safety awareness encourages employees to proactively engage in safe practices, contributing to a more secure work environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lathe equipment
When selecting materials for lathe equipment, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and disadvantages in relation to specific applications. This analysis focuses on four common materials used in lathe manufacturing: cast iron, steel, aluminum, and composite materials. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact performance and suitability for various applications, especially for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Cast Iron for Lathe Equipment?
Cast iron is widely used in lathe construction due to its excellent vibration-damping properties and high wear resistance. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Cast iron also exhibits good corrosion resistance, although it may be prone to rust if not properly maintained.
Pros and Cons: Cast iron lathes are durable and stable, providing a solid foundation for precision machining. However, they can be heavy, which may complicate transportation and installation. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly due to the need for specialized molds.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is particularly compatible with ferrous and non-ferrous materials, making it a versatile choice for various turning operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards such as DIN or ASTM. The weight of cast iron may also influence shipping costs, which is a crucial factor for buyers in Africa and South America.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for Lathe Equipment?
Steel is another popular choice for lathe equipment due to its strength and versatility. It can be alloyed to enhance specific properties, such as hardness and corrosion resistance. Steel lathes can handle higher loads and are often used in more demanding applications.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its high tensile strength and durability, which allows for the machining of a wide range of materials. However, steel can be more expensive than cast iron and may require additional treatments to prevent corrosion.
Impact on Application: Steel lathes are well-suited for high-speed machining and can effectively process a variety of materials, including tough alloys.
Considerations for International Buyers: Steel’s compliance with international standards (like JIS) is essential for buyers in regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia. The potential for higher costs may also necessitate careful budgeting.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum in Lathe Equipment?
Aluminum is increasingly being utilized in the manufacturing of lathes due to its lightweight and excellent machinability. It offers good corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications where heat dissipation is critical.
Pros and Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easier to transport and install, which is beneficial for international buyers. However, aluminum is generally less durable than cast iron or steel and may not withstand heavy loads as effectively.
Impact on Application: Aluminum lathes are ideal for lighter machining tasks and are often used in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where weight is a critical factor.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the different grades of aluminum and their compliance with local standards. The lower durability may limit its application in heavy-duty scenarios.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Lathe Equipment Performance?
Composite materials, often a combination of polymers and reinforcing fibers, are becoming popular in lathe equipment due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. They can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements.
Pros and Cons: Composites offer excellent vibration damping and thermal stability, which can enhance machining precision. However, they can be more expensive to produce and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composite materials are suitable for high-performance applications, especially in industries where weight and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should verify the material specifications and compliance with relevant standards. The cost implications of advanced composites may also require careful financial planning.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Lathe Equipment
| Material | Typical Use Case for lathe equipment | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty machining | Excellent vibration damping | Heavy and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Steel | High-load applications | High tensile strength | More expensive and corrosion-prone | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machining | Lightweight and easy to handle | Less durable under heavy loads | Medium |
| Composite Materials | High-performance applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and requires specialized production | High |
This comprehensive analysis of material selection for lathe equipment provides international B2B buyers with critical insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific operational needs and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lathe equipment
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Lathe Equipment?
The manufacturing of lathe equipment involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. Each stage is designed to optimize the use of materials and the overall performance of the lathe.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality raw materials, typically metals such as cast iron, steel, or aluminum, are selected based on the desired characteristics of the lathe. These materials undergo cutting, milling, and grinding to achieve specific dimensions and surface finishes. The careful selection and preparation of materials not only enhance the durability and performance of the lathe but also influence its cost-effectiveness.
2. Forming Processes
Following material preparation, the forming processes come into play. Techniques such as casting, forging, and machining are commonly employed. For instance, cast iron components are often produced through sand casting, while precision parts may be machined using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology. This stage is crucial for shaping the lathe’s body, bed, and other structural components, ensuring they meet precise tolerances.
3. Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This stage often involves the use of fixtures and jigs to maintain accuracy during assembly. Key components such as the spindle, tailstock, and tool rest are carefully aligned to ensure smooth operation. Assembly is typically performed by skilled technicians who follow strict guidelines to maintain consistency and quality.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes that enhance both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the lathe. This can include surface treatments like painting, anodizing, or powder coating, as well as precision grinding to achieve the desired surface finish. Finishing not only improves the appearance of the lathe but also protects against corrosion and wear, thereby extending its lifespan.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Lathe Equipment Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of manufacturing lathe equipment, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. The QA process typically involves several checkpoints and standards.
Relevant International Standards for Lathe Equipment
For B2B buyers, understanding the quality standards that govern lathe manufacturing is essential. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system. It emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, which are critical in the B2B space. Other relevant certifications may include CE marking for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, and API standards for equipment used in the petroleum and natural gas industries.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in lathe manufacturing typically includes several key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers must provide documentation, including material certificates and compliance reports, to verify the quality of the materials.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various inspections are performed to ensure that components are being produced according to specifications. This may include measuring tolerances, checking surface finishes, and conducting functional tests.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the lathe undergoes a final inspection to verify that all components function correctly and meet the specified standards. This may include load testing, precision measurements, and visual inspections.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Lathe Equipment?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality and performance of lathe equipment. These methods help ensure that the equipment operates efficiently and meets the needs of end-users.
-
Dimensional Testing: This involves measuring the physical dimensions of components to ensure they meet specified tolerances. Tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are often used.
-
Functional Testing: Lathe equipment is subjected to operational tests to ensure all functionalities work as intended. This may include testing the speed, torque, and stability of the lathe during operation.
-
Durability Testing: To assess the longevity of the lathe, manufacturers may perform stress tests that simulate extended use. This helps identify potential weaknesses in the design or materials.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are several strategies to consider:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing practices, quality control processes, and adherence to international standards. This helps assess their capabilities and commitment to quality.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including inspection results and compliance certificates, can help buyers gauge the supplier’s quality management system. This documentation should clearly outline the procedures followed during manufacturing and testing.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can occur at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with required standards.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges regarding quality control. These may include:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations and standards for manufacturing equipment. Understanding these requirements is essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential legal issues.
-
Logistics and Transportation: The quality of lathe equipment can be compromised during transportation. Buyers should consider how suppliers package and ship equipment to minimize damage and maintain quality during transit.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: Effective communication is vital for ensuring that quality expectations are clearly understood. Buyers should establish open lines of communication with suppliers to address any concerns promptly.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in lathe equipment production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘lathe equipment’
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing and woodworking, sourcing lathe equipment requires a strategic approach to ensure quality, reliability, and value. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical specifications of the lathe equipment you need. Consider factors such as the type of materials you will be working with, the size and capacity of the lathe, and the specific features that are crucial for your operations. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure they can meet your requirements.
- Types of Lathes: Understand whether you need woodturning lathes, CNC lathes, or metal lathes based on your production needs.
- Capacity Requirements: Determine the maximum diameter and length of the workpieces you intend to turn.
Step 2: Set Your Budget and Pricing Strategy
Establish a budget that reflects the total cost of ownership, including purchase price, shipping, installation, and ongoing maintenance. While it may be tempting to opt for the cheapest option, consider the long-term value and potential hidden costs.
- Consider Total Cost: Factor in accessories and tooling that may be needed, which can significantly affect your overall investment.
- Pricing Trends: Research market prices for similar equipment to understand the price range and negotiate effectively.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can deliver quality products and services. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other businesses in your industry or region.
- Certifications and Compliance: Verify that the suppliers meet international quality standards and certifications relevant to your region.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty Options
Strong after-sales support can make a significant difference in your operational efficiency. Inquire about warranty terms, maintenance services, and availability of spare parts.
- Service Agreements: Consider suppliers that offer comprehensive service agreements to minimize downtime.
- Response Times: Evaluate how quickly a supplier can respond to service requests or equipment issues.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Trials
Whenever possible, request demonstrations or trial periods for the lathe equipment you are considering. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the machine’s performance and usability firsthand.
- Performance Testing: Observe how the lathe handles various materials and tasks to ensure it meets your operational needs.
- Operator Feedback: Involve your operators in the evaluation process to gather insights on usability and functionality.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Purchase
Once you have selected a supplier and equipment, engage in negotiations to finalize terms. Discuss payment options, delivery timelines, and installation support to ensure all parties are aligned.
- Contract Clarity: Ensure the contract clearly outlines all terms, including warranties, service agreements, and return policies.
- Logistics Coordination: Plan for transportation and installation logistics to avoid unexpected delays in production.
Step 7: Monitor and Evaluate Performance Post-Purchase
After acquiring the lathe equipment, continuously monitor its performance and maintenance needs. Regular evaluations will help you identify any issues early and optimize your operations.
- Performance Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the lathe’s efficiency and output quality.
- Feedback Loop: Create a feedback mechanism for operators to report on any operational challenges or equipment performance.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing lathe equipment, ensuring that they invest in machinery that meets their production needs effectively and efficiently.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lathe equipment Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Lathe Equipment Sourcing?
When sourcing lathe equipment, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials significantly affect the price. High-grade metals and specialized alloys used in manufacturing lathes can increase costs but enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and depend on the complexity of the equipment. Skilled labor is essential for precision manufacturing, which may be more expensive in developed regions compared to emerging markets.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, impacting the final price of the lathe.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are often overlooked but are critical in the production of custom lathe components. Specialized tools may be required for specific designs, affecting both lead times and pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the lathe meets industry standards incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are essential, especially for international buyers who need to comply with various certifications.
-
Logistics: Transporting lathe equipment can be costly, particularly for international shipping. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin to cover risks and profit. Understanding the margin expectations can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Lathe Equipment Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of lathe equipment, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers may offer better rates for larger orders, which can mitigate per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-built lathes tailored to specific needs generally come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the increased costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Equipment made from premium materials or that meets specific quality certifications (e.g., ISO standards) tends to be priced higher. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of quality over initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The shipping terms agreed upon can influence the final cost. Understanding Incoterms is vital for assessing who bears the cost and risk during transportation.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Lathe Equipment Procurement?
Navigating the cost landscape of lathe equipment procurement requires strategic approaches:
-
Negotiation: Leverage your position as a buyer by negotiating terms and prices. Highlighting long-term purchasing potential can incentivize suppliers to offer better rates.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the upfront price. Consider maintenance, operation costs, and potential downtime in your decision-making process.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect overall costs. Establishing a clear understanding of these factors can prevent unexpected expenses.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research and benchmark prices against multiple suppliers. This helps in identifying competitive pricing and understanding market trends.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to exclusive deals. Consistent communication and collaboration can be beneficial.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While indicative prices for lathe equipment can provide a helpful starting point, it is essential to note that actual costs may vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. Buyers should always confirm pricing with suppliers to ensure accuracy and alignment with their specific sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing lathe equipment With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Lathe Equipment for Precision Machining
In the realm of precision machining and woodturning, lathe equipment is a widely recognized solution for shaping materials. However, alternative methods and technologies exist that can achieve similar objectives, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. This analysis aims to provide B2B buyers with insights into these alternatives, allowing for informed decisions based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Lathe Equipment | CNC Machines | Hand Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for complex shapes | Extremely high precision and speed | Moderate precision; skill-dependent |
| Cost | Moderate to high ($5,000 – $10,000) | High initial investment ($20,000+) | Low cost ($50 – $500) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and training | Requires skilled operators and programming | Easy to use; minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | High maintenance; software updates required | Low maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Woodturning, metalworking | Mass production, complex designs | Simple tasks, repairs |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of CNC Machines as an Alternative to Lathe Equipment?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines offer an alternative to traditional lathe equipment, particularly for businesses focused on high-volume production. They provide exceptional precision and speed, making them ideal for complex designs and mass production. However, the initial investment is significantly higher, often exceeding $20,000, which may be prohibitive for smaller enterprises. Additionally, CNC machines require skilled operators who are familiar with programming and maintenance, adding to the overall complexity of implementation.
How Do Hand Tools Compare to Lathe Equipment for Crafting and Repairing?
Hand tools represent the most basic form of machining and can be a viable alternative for smaller projects or repairs. They are cost-effective, with prices ranging from $50 to $500, and typically require minimal training, making them accessible to a broader range of users. However, the precision of hand tools is largely dependent on the skill of the operator, which can lead to variability in results. Hand tools are best suited for simple tasks or one-off projects rather than large-scale production.
How Can a B2B Buyer Decide Between Lathe Equipment and Its Alternatives?
When considering the right solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific needs, production volume, and budget constraints. For businesses focused on high precision and mass production, investing in CNC machines may be beneficial despite the higher upfront costs. Conversely, companies looking for cost-effective solutions for smaller projects or repairs may find hand tools to be a more suitable option. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the balance between desired performance, available budget, and the operational capabilities of the workforce.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lathe equipment
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Lathe Equipment?
When selecting lathe equipment, understanding its technical specifications is vital for ensuring efficiency and quality in production processes. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade: The quality of materials used in lathe construction, such as cast iron or steel, impacts durability and performance. Higher-grade materials can withstand heavy use and resist wear, ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance costs. For B2B buyers, investing in lathes with superior material grades translates to lower total cost of ownership over time.
-
Tolerance: This refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and is crucial for precision machining. Tighter tolerances result in better fitting parts, which is essential for high-quality end products. In industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace and automotive, understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers select equipment that meets their production standards.
-
Horsepower (HP): The power rating of the lathe’s motor determines its capability to handle various materials and workloads. Higher horsepower allows for faster cutting speeds and the ability to work with tougher materials. B2B buyers should assess their production needs to ensure they select a lathe with adequate horsepower for their applications.
-
Swing Over Bed: This dimension indicates the maximum diameter of the workpiece that can be rotated on the lathe. It is essential for ensuring that the lathe can accommodate the size of the materials being processed. Buyers should match this specification to the size of their typical projects to avoid purchasing inadequate machinery.
-
Spindle Speed Range: The spindle speed affects the cutting rate and surface finish of the machined part. A wide range of spindle speeds allows for versatility in processing different materials. For B2B decision-makers, understanding the spindle speed capabilities helps in selecting lathes that can adapt to varying project requirements.
-
Bed Length: This specification impacts the maximum length of the workpiece that can be machined. Longer beds allow for larger projects, making this a critical factor for businesses that work with extensive materials. Buyers should consider their operational scope when evaluating bed length options.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand for Lathe Equipment?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication with suppliers and streamline procurement processes. Here are essential terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to source reliable components or machinery.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps B2B buyers plan their purchases effectively and can impact inventory management strategies.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): This is a document sent to suppliers to request price quotes for specific quantities of products. An RFQ is a vital tool for B2B buyers to compare pricing and terms from different manufacturers.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for managing logistics and delivery expectations.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and maintaining workflow efficiency.
-
Service Level Agreement (SLA): An SLA outlines the expected level of service between a supplier and a buyer, including delivery times, quality standards, and support. This agreement is important for ensuring that both parties have aligned expectations, contributing to smoother business operations.
By grasping these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring lathe equipment, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the lathe equipment Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Influencing the Lathe Equipment Market?
The lathe equipment market is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in manufacturing technology and the increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries. Key drivers include the rise of automation, which is enhancing production efficiency and reducing labor costs. Furthermore, the growing trend towards CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes is transforming traditional machining processes, allowing for greater accuracy and versatility in manufacturing.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as IoT (Internet of Things) integration and AI (Artificial Intelligence), are reshaping sourcing strategies in the lathe equipment sector. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring of operations, and improved supply chain management, which can significantly lower operational costs for international buyers. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional factors. For instance, European manufacturers are focusing on sustainability and energy efficiency, which is becoming a significant consideration for buyers. In contrast, emerging markets in Africa and South America are witnessing a surge in demand for affordable yet reliable lathe equipment, driving suppliers to offer cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Buying Decisions in the Lathe Equipment Sector?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority for businesses worldwide, including those in the lathe equipment sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the sourcing of materials can significantly influence purchasing decisions. B2B buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and reducing waste in their manufacturing processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are seeking suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and maintain transparency throughout their operations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for wood-based products are becoming essential in the procurement process, as they assure buyers of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing.
Moreover, the integration of ‘green’ technologies in lathe equipment is gaining traction. Buyers are increasingly looking for machines that not only meet their operational needs but also align with their corporate sustainability goals. Investing in such equipment can enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of Lathe Equipment Development in B2B Markets?
The evolution of lathe equipment has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations, where primitive lathes were used for crafting wooden objects. Over the centuries, the technology has advanced significantly, transitioning from manual lathes to sophisticated CNC systems that dominate today’s market.
In the 19th century, the industrial revolution catalyzed significant advancements in lathe technology, allowing for mass production and greater precision. The introduction of electric power in the early 20th century further revolutionized lathe operations, enabling faster and more efficient production processes. As we moved into the 21st century, the advent of digital technology and automation has created a paradigm shift in how lathe equipment is manufactured and utilized, leading to more innovative solutions for B2B buyers worldwide.
Understanding this historical context is essential for buyers as it helps frame the current landscape of lathe equipment and the ongoing technological advancements that continue to shape the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lathe equipment
-
How do I choose the right lathe equipment for my business needs?
Selecting the right lathe equipment involves assessing your specific production requirements. Consider factors such as the types of materials you’ll be working with, the volume of production, and the desired precision. Evaluate the lathe’s specifications, including motor power, swing capacity, and bed length. Additionally, consult with suppliers about customization options to better fit your operational needs. It’s advisable to request demonstrations or sample runs before finalizing your purchase to ensure the equipment meets your expectations. -
What is the best lathe for small to medium-sized woodworking projects?
For small to medium-sized woodworking projects, a benchtop lathe with a swing capacity of around 12-14 inches is often ideal. Models like the Robust Scout or Rikon 70-3040 offer versatility and ease of use, making them suitable for various turning tasks. Look for features such as variable speed control and sturdy construction. Ensure that the lathe can accommodate the size of projects you typically handle, and consider the availability of accessories like bed extensions for larger workpieces. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing lathe equipment internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of lathe equipment can vary significantly by supplier and region. Common terms include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%), with the balance due prior to shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before proceeding and consider using secure payment methods to mitigate risks. Ensure all terms are documented in a formal contract to protect both parties. -
How can I ensure the quality of lathe equipment from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Check for certifications and industry standards compliance, such as ISO 9001. Request product samples or visit the supplier’s facility if possible. Additionally, ask for references from other clients, particularly those in your industry. Establish clear quality assurance processes, including inspections upon delivery and during production, to maintain high standards throughout the manufacturing process. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lathe equipment?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lathe equipment vary by supplier and product type. Some manufacturers may offer flexibility for small businesses or first-time buyers, while others have strict MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with suppliers directly to negotiate terms. If MOQs are too high, consider forming partnerships with other businesses to pool orders or look for suppliers that specialize in lower-volume sales. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing lathe equipment?
Logistics are crucial when importing lathe equipment. Consider shipping methods, transit times, and potential customs duties or tariffs that may apply. Work with logistics partners experienced in international shipping to navigate regulations and ensure timely delivery. Additionally, ensure that the equipment is adequately packaged to prevent damage during transit. Track your shipment closely and maintain communication with your supplier to address any issues that may arise. -
Can lathe equipment be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for lathe equipment to meet specific applications. Customization can include modifications to the lathe’s size, features, or tooling to accommodate unique production processes. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and requirements to the supplier. Be aware that customized equipment may involve longer lead times and higher costs, so plan accordingly. -
What should I consider regarding after-sales support for lathe equipment?
After-sales support is vital for maintaining operational efficiency. Evaluate the supplier’s warranty and service policies, including the availability of spare parts and technical support. Ensure that the supplier provides comprehensive training for your team to operate the lathe effectively. Additionally, inquire about ongoing maintenance services and whether the supplier offers remote troubleshooting or on-site support. A reliable after-sales service can significantly enhance your investment in lathe equipment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Lathe Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Woodturners Wonders – Robust Scout 14” Benchtop Lathe
Domain: woodturnerswonders.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Robust Scout 14” Benchtop Lathe’, ‘price’: ‘$5,695.00’, ‘horsepower’: ‘1 HP’, ‘lead_time’: ‘8-16 weeks’}, {‘name’: ‘Robust Sweet 16 – Short Bed’, ‘price’: ‘$8,695.00’, ‘horsepower’: ‘1.5 HP’, ‘lead_time’: ‘8-16 weeks’}, {‘name’: ‘Robust Sweet 16 – Standard Bed’, ‘price’: ‘$8,795.00’, ‘horsepower’: ‘1.5 HP’, ‘lead_time’: ‘8-16 weeks’}, {‘name’: ‘Robust Sweet 16 – Long Bed’, ‘price’: ‘$8,…
2. Woodturners Catalog – Woodturning Lathe Accessories
Domain: woodturnerscatalog.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Woodturners Catalog – Woodturning Lathe Accessories, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Knuth – Lathe Tools and Accessories
Domain: knuth.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Lathe Tools and Accessories include turning and drilling tools essential for conventional and CNC-controlled lathes. The product range features high-quality tools and accessories that enhance production quality while saving time and costs. Key offerings include:
– Centers for lathes with various specifications:
– Live Center MT 2: SKU 106745, Length: 4.92in, Center Ø: 0.87in
– Live Center MT …
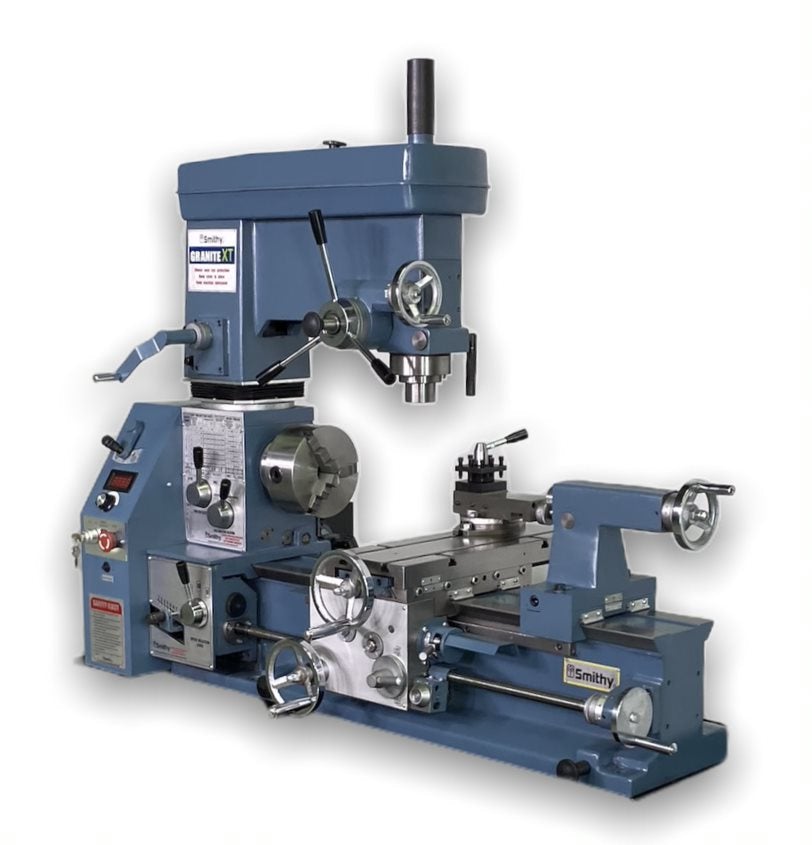
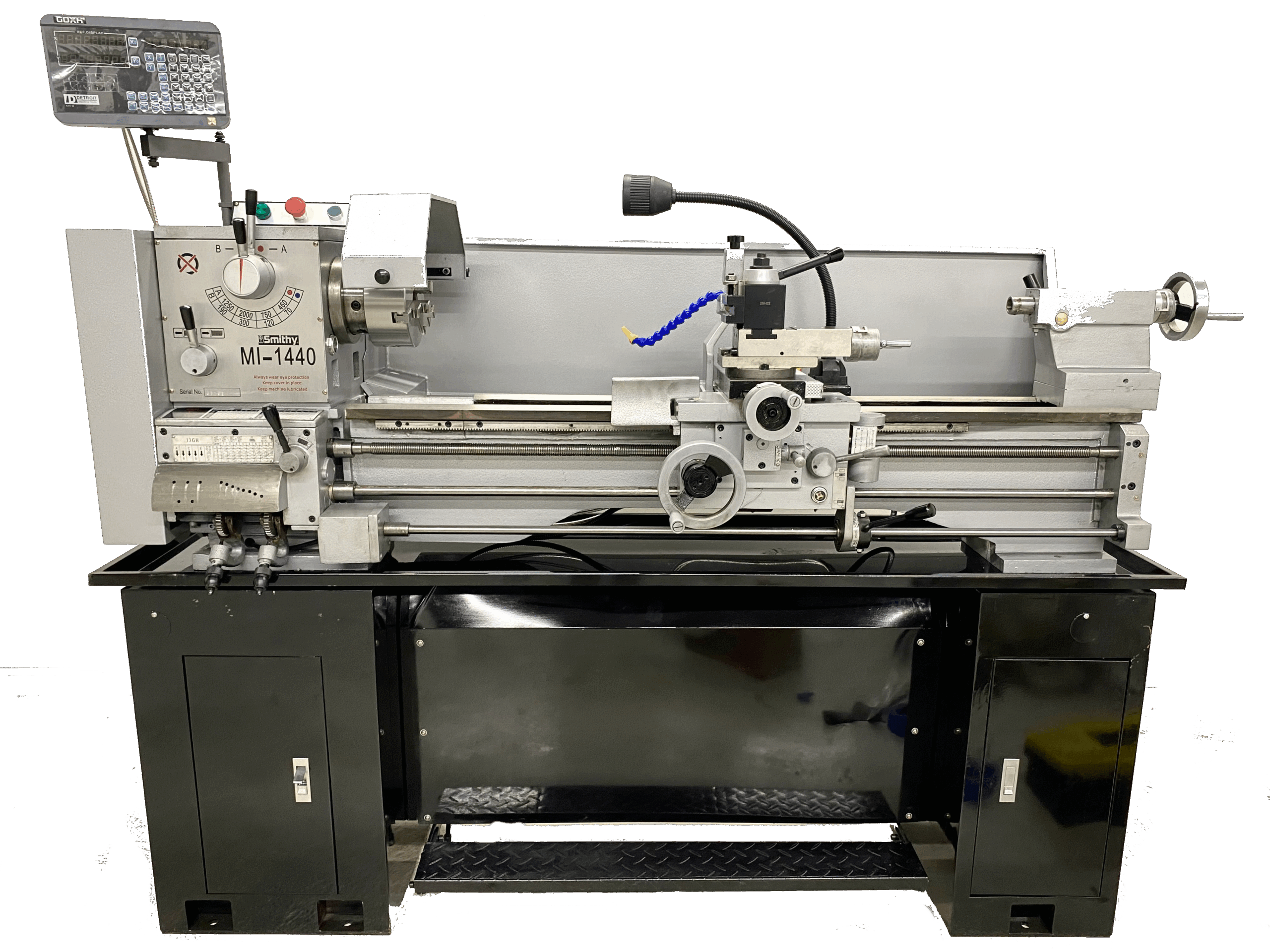
4. Smithy – Premium Mill Drill Lathe Combo Machines
Domain: smithy.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Smithy Machine Tools offers premium mill drill lathe combo machines, including models such as Granite XT 3-in-1 Mill-Turn, MI-1337L, MI-1440 Lathe, MI-329M, and 409 PRO Milling Machine. The company provides various accessories and support resources, including operations manuals, technical support, and financing options. They also offer a 90-day hands-on trial and discounts for military and educati…
5. Grizzly – Metal Lathes
Domain: grizzly.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: This company, Grizzly – Metal Lathes, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Grainger – Lathe Machines
Domain: grainger.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, Grainger – Lathe Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. CLIMAX – Portable Lathes
Domain: climaxportable.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Lathes: CLIMAX portable lathes are designed for various applications including cutting O-ring grooves, repairing turbine spindles, and fixing out-of-round gear seat areas. They can re-turn shafts and roll journals from 1.5 inches to 24 inches (38 to 610 mm). Some models operate in tight quarters with a radial clearance of 7 inches (177.8 mm). Pneumatic power is standard, with optional electric pow…
8. Acme Tools – Lathe Machines
Domain: acmetools.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: This company, Acme Tools – Lathe Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lathe equipment
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of lathe equipment is pivotal for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their manufacturing capabilities. As the demand for precision and efficiency grows, investing in high-quality lathes and accessories can significantly impact production quality and operational costs. Key considerations include understanding the specific needs of your projects, evaluating the total cost of ownership, and selecting suppliers that offer reliable customer support and timely delivery.
International buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that provide comprehensive solutions, including a range of customizable lathe options and essential accessories. By leveraging strategic sourcing, companies can not only improve their operational efficiency but also gain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Looking ahead, the lathe equipment market is expected to evolve with advancements in technology and increased demand for automation. It is crucial for businesses to stay informed about these trends and adapt their sourcing strategies accordingly. We encourage you to engage with reputable suppliers, explore innovative solutions, and invest in lathe equipment that aligns with your long-term business goals. Your success in this dynamic market begins with informed and strategic sourcing decisions.