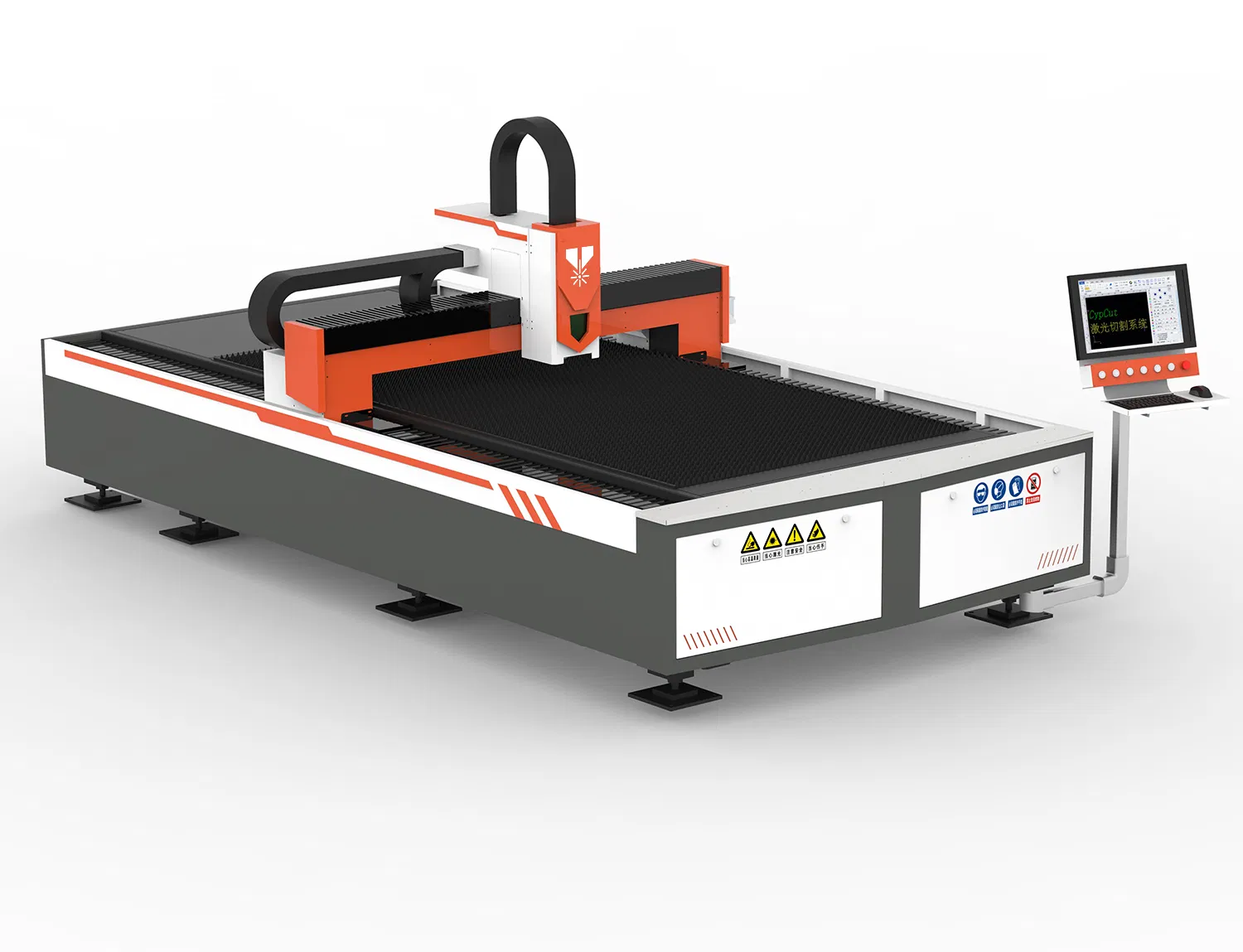
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for laser milling machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing a reliable laser milling machine can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying technological advancements, material compatibility, and application-specific demands, understanding the nuances of laser milling technology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of laser milling machines, covering essential aspects such as the different types available, their diverse applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting.
As international buyers navigate the complexities of the global market, they face the challenge of aligning their operational needs with the right equipment. This comprehensive resource aims to empower businesses by providing detailed insights into cost factors, technological innovations, and market trends. By highlighting practical solutions and expert advice, this guide serves as a critical tool for making educated investment choices, ensuring that organizations can leverage the full potential of laser milling technology to enhance productivity and drive growth. Whether you are looking for a compact desktop model or a high-capacity industrial machine, understanding these elements will enable you to choose a laser milling machine that meets your specific requirements and budget.
Understanding laser milling machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Milling Machines | Utilizes CO2 gas; ideal for non-metal materials; versatile cutting and engraving capabilities. | Signage, crafting, and woodworking. | Pros: Excellent for organic materials; cost-effective. Cons: Limited metal cutting capabilities. |
| Fiber Laser Milling Machines | Uses fiber optics for precision; excels in cutting metals; high-speed operation. | Industrial metal fabrication and automotive parts. | Pros: High efficiency on metals; lower operational costs. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| UV Laser Milling Machines | Shorter wavelength for high precision; ideal for delicate materials; minimal heat impact. | Electronics, medical devices, and fine jewelry. | Pros: Excellent detail; minimal thermal damage. Cons: Limited materials compatibility. |
| Desktop Laser Milling Machines | Compact design; user-friendly; suitable for small businesses and hobbyists. | Small-scale production, prototyping, and personalization. | Pros: Affordable; space-efficient. Cons: Limited cutting area and power. |
| Hybrid Laser Milling Machines | Combines CO2 and fiber technology; versatile for various materials. | Custom manufacturing and specialized applications. | Pros: Dual functionality; adaptable to different projects. Cons: Complexity in operation. |
What are CO2 Laser Milling Machines and Their B2B Relevance?
CO2 laser milling machines are primarily designed for cutting and engraving non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, and leather. These machines utilize CO2 gas to generate the laser beam, making them versatile for a wide range of applications, especially in signage and crafts. B2B buyers should consider their material needs and whether they require a machine that can handle metals, as CO2 machines have limitations in that area. They offer a cost-effective solution for businesses focused on organic materials, but potential buyers should weigh the trade-off in metal cutting capabilities.
How Do Fiber Laser Milling Machines Benefit Industrial Applications?
Fiber laser milling machines are renowned for their efficiency and precision in cutting metals, making them a staple in industrial applications like automotive parts and metal fabrication. These machines leverage fiber optics to produce a high-energy beam, allowing for rapid cutting speeds and reduced operational costs. B2B buyers in heavy manufacturing should prioritize fiber lasers for their ability to handle a variety of metals, including stainless steel and aluminum. Although they require a higher initial investment, the long-term savings and productivity gains can justify the cost.
What Sets UV Laser Milling Machines Apart for Specific Industries?
UV laser milling machines are characterized by their short wavelength, which enables them to achieve high precision on delicate materials without causing thermal damage. This makes them ideal for applications in electronics, medical devices, and fine jewelry. B2B buyers should consider the specific materials they plan to work with, as UV lasers have limited compatibility compared to CO2 and fiber lasers. Their ability to produce intricate designs with minimal heat impact can be a significant advantage in sectors where detail and quality are paramount.
What Advantages Do Desktop Laser Milling Machines Offer to Small Businesses?
Desktop laser milling machines provide a compact and user-friendly solution for small businesses and hobbyists. These machines are ideal for small-scale production, prototyping, and personalized items, making them popular among entrepreneurs entering the custom manufacturing market. While they are generally more affordable and space-efficient, B2B buyers should be aware of their limitations in cutting area and power. These machines are suitable for businesses that prioritize versatility and ease of use but may not be ideal for high-volume industrial applications.
Why Consider Hybrid Laser Milling Machines for Custom Manufacturing?
Hybrid laser milling machines combine the capabilities of CO2 and fiber technologies, making them adaptable for various materials, from metals to non-metals. This versatility is particularly beneficial for custom manufacturing and specialized applications where material requirements may vary from project to project. B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of operation and maintenance, as hybrid systems can be more intricate than single-technology machines. However, the dual functionality can provide significant advantages for businesses looking to expand their service offerings.
Key Industrial Applications of laser milling machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of laser milling machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High accuracy and reduced waste in complex parts | Certification for aerospace standards, precision requirements |
| Automotive | Custom tooling and prototyping | Faster development cycles and reduced lead times | Material compatibility, machine scalability |
| Electronics | PCB and micro-component fabrication | Enhanced precision and efficiency in intricate designs | Source for specific laser types and software compatibility |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instrument production | High precision and ability to work with biocompatible materials | Compliance with medical regulations, material sourcing |
| Jewelry and Fashion | Custom engraving and cutting | Unique, personalized products that enhance brand value | Design software compatibility, material versatility |
How is a laser milling machine used in the aerospace industry?
In the aerospace sector, laser milling machines are instrumental in manufacturing precision components such as turbine blades and structural parts. These machines enable manufacturers to achieve high accuracy while minimizing material waste, which is crucial in an industry where both performance and cost-efficiency are paramount. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the milling machines meet rigorous aerospace standards and possess the necessary certifications for reliability and safety.
What role does laser milling play in automotive custom tooling and prototyping?
For automotive manufacturers, laser milling machines facilitate the creation of custom tooling and prototypes with remarkable speed and accuracy. This technology allows for rapid iteration of designs, reducing the overall development cycle and accelerating time-to-market. When sourcing, businesses should prioritize machines that offer flexibility in material compatibility and scalability to accommodate varying production volumes.
How does laser milling benefit the electronics industry?
In the electronics industry, laser milling machines are utilized for fabricating printed circuit boards (PCBs) and micro-components. The precision offered by these machines is critical for intricate designs that require tight tolerances. International buyers need to consider the specific laser types that can handle the delicate materials often used in electronics, as well as the software compatibility for design and manufacturing processes.
Why is laser milling essential for medical device production?
Laser milling machines are vital in producing surgical instruments and medical devices, where precision and biocompatibility are essential. These machines can work with a variety of materials, ensuring that devices meet stringent regulatory standards. Buyers in this sector must focus on compliance with medical regulations and ensure the sourcing of high-quality materials that are suitable for medical applications.
How does laser milling enhance customization in jewelry and fashion?
In the jewelry and fashion industries, laser milling machines are employed for custom engraving and cutting, enabling the creation of unique, personalized products. This capability not only enhances brand value but also meets the growing consumer demand for bespoke items. When sourcing, businesses should look for machines that offer versatility in materials and compatibility with design software, ensuring they can meet diverse customer needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘laser milling machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Material Compatibility and Performance
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges when it comes to the material compatibility of laser milling machines. For instance, a manufacturer in the automotive sector might require precise cuts on various materials such as aluminum, steel, or plastics. However, if their chosen laser milling machine is not designed to handle a diverse range of materials, it can lead to inefficiencies, wasted materials, and increased operational costs. This situation is particularly concerning for businesses that need to pivot quickly between different projects and materials.
The Solution: To ensure that the laser milling machine meets diverse material requirements, buyers should conduct thorough research and assessments before making a purchase. This includes reviewing the specifications of different models to confirm their cutting capabilities on various materials. It’s advisable to select machines that offer versatile material handling, such as those capable of processing both metals and non-metals. Additionally, working closely with suppliers to obtain detailed information on material compatibility and performance ratings can prevent costly errors. Implementing a trial period, if possible, can also help businesses gauge the machine’s effectiveness with their specific materials before finalizing the investment.
Scenario 2: Complexity in Operation and User Training
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the complexity involved in operating laser milling machines. Many models come with advanced software and functionalities that can be overwhelming for new users, leading to increased downtime and mistakes. For example, a small business owner might invest in a state-of-the-art machine only to find that their staff struggles to utilize it effectively, resulting in delayed production schedules and lost revenue.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize laser milling machines that come with user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training resources. Before purchasing, it’s beneficial to inquire about the availability of training programs, both online and in-person, provided by the manufacturer. Engaging with vendors that offer dedicated customer support and detailed user manuals can also enhance the learning curve. Furthermore, establishing a designated training period for staff, where they can familiarize themselves with the machine’s features and functionalities, will lead to more efficient operation and better outcomes in production.
Scenario 3: High Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs
The Problem: The initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs of laser milling machines can be daunting for B2B buyers, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises. A business may be hesitant to invest in a high-end machine due to budget constraints, fearing that the costs associated with repairs, parts replacement, and operational inefficiencies will overshadow the benefits of the machine.
The Solution: To navigate the financial aspects of acquiring a laser milling machine, businesses should consider models that offer a balance between cost and performance. Buyers should look for machines with a proven track record of reliability and lower maintenance requirements. Additionally, negotiating with suppliers for warranty options and maintenance packages can provide peace of mind. It’s also wise to explore financing options that can spread the costs over time, making the initial investment more manageable. Implementing a preventative maintenance schedule will help in extending the machine’s lifespan and reducing unexpected repair costs, ultimately leading to a more sustainable investment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for laser milling machine
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Laser Milling Machines?
When selecting materials for laser milling machines, it is essential to consider their properties, performance characteristics, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: acrylic, wood, stainless steel, and aluminum. Each material has unique attributes that can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of laser milling operations.
How Does Acrylic Perform in Laser Milling Applications?
Acrylic is a popular choice for laser milling due to its excellent optical clarity and versatility. It typically has a temperature rating of around 80°C and is resistant to UV light, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. The material is relatively easy to cut and engrave, producing clean edges without the need for post-processing.
Pros: Acrylic is lightweight, cost-effective, and offers a wide range of colors and finishes, enhancing design possibilities. Its durability against weathering makes it suitable for signage and display applications.
Cons: While acrylic is durable, it can be prone to scratching and may not withstand high-impact forces. Additionally, it can emit harmful fumes when cut, necessitating proper ventilation and safety measures.
Impact on Application: Acrylic is ideal for applications requiring aesthetic appeal, such as awards, signage, and decorative items. Its compatibility with various laser milling machines allows for intricate designs and custom shapes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local safety standards regarding fume emissions and consider the material’s availability in their region. In Europe, for instance, adherence to REACH regulations is vital.
What Are the Advantages of Using Wood in Laser Milling?
Wood is a traditional material favored for its natural beauty and versatility. It has a wide range of temperature ratings depending on the type, typically around 60-70°C. Wood is biodegradable and can be sourced sustainably, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Pros: Wood offers excellent engraving quality and can be easily cut into intricate designs. It is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a popular choice for custom products and crafts.
Cons: Variability in wood density can affect cutting consistency, and certain types may warp or splinter during processing. Additionally, wood can be susceptible to moisture, which may limit its applications in humid environments.
Impact on Application: Wood is commonly used in furniture, decorative items, and crafts. Its ability to absorb stains and finishes allows for a wide range of aesthetic possibilities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regional preferences for specific wood types and any associated regulations regarding sustainable sourcing, especially in regions like Europe where such standards are stringent.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Laser Milling?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. It typically has a high-temperature rating, making it suitable for applications that require heat resistance. The material can be laser cut with precision, allowing for intricate designs and robust end products.
Pros: Stainless steel’s durability and resistance to corrosion make it ideal for industrial applications, including automotive and aerospace components. It also offers a sleek finish that enhances aesthetic appeal.
Cons: The primary drawback of stainless steel is its higher cost compared to non-metal materials. Additionally, cutting thicker gauges can require more powerful laser systems, increasing operational costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for applications in harsh environments, including medical devices and kitchenware, where hygiene and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN for material specifications. Understanding local market demands for stainless steel products is also crucial.
What Makes Aluminum a Preferred Material in Laser Milling?
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent thermal conductivity, making it a popular choice for various applications. It typically has a temperature rating of around 120°C and is resistant to corrosion, particularly when anodized.
Pros: Aluminum is versatile and can be easily machined, providing high precision in laser milling. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in the aerospace industry.
Cons: While aluminum is generally cost-effective, certain alloys can be expensive. Additionally, it may require specialized laser settings to achieve optimal cutting results, which can complicate the milling process.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics due to its strength-to-weight ratio and aesthetic finish.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of specific aluminum alloys and ensure compliance with local manufacturing standards. Understanding the regional market for aluminum products can also provide insights into demand.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Laser Milling Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for laser milling machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic | Signage, awards, decorative items | Excellent optical clarity and versatility | Prone to scratching and harmful fumes | Low |
| Wood | Furniture, crafts, decorative items | Easy to cut and engrave, biodegradable | Variability in density and moisture issues | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial components, medical devices | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and requires powerful lasers | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics | Lightweight and high precision | Some alloys can be expensive, specialized settings needed | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for laser milling machine
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Laser Milling Machines?
The manufacturing process of laser milling machines is a multi-faceted endeavor that requires precision engineering and meticulous attention to detail. Typically, this process can be broken down into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
1. Material Preparation:
The first step involves sourcing high-quality materials suitable for laser milling machines. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys. Suppliers often conduct thorough inspections of raw materials to ensure they meet specific mechanical properties and quality standards. Proper material selection is critical, as it directly affects the machine’s performance and longevity.
2. Forming:
In this stage, the raw materials undergo various forming processes such as cutting, bending, and machining. Advanced CNC machines are often utilized for precision cutting, ensuring that all components are fabricated to exact specifications. Techniques such as laser cutting and waterjet cutting may be employed to create intricate shapes and designs that are essential for the machine’s functionality.
3. Assembly:
Once the components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. Skilled technicians assemble the machine by integrating various parts, such as the laser source, motion systems, and cooling systems. This stage often requires careful alignment and calibration to ensure optimal performance. Automated assembly systems may be used alongside manual labor to enhance efficiency and maintain quality.
4. Finishing:
The final stage includes surface treatment processes, such as polishing, anodizing, or coating, which enhance the machine’s durability and aesthetic appeal. Quality checks are performed throughout this stage to ensure that the finished product meets industry standards and customer specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Laser Milling Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process for laser milling machines, ensuring that each unit meets stringent performance and safety standards. Key aspects of quality assurance include adherence to international standards, implementation of rigorous inspection checkpoints, and the use of various testing methods.
1. International and Industry-Specific Standards:
Manufacturers often comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking (for European markets) and API (for oil and gas sectors) may be required. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to quality and safety, which is essential for B2B buyers.
2. Quality Control Checkpoints:
Quality control is typically segmented into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections occur during the manufacturing process to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed machine undergoes a thorough inspection and testing to ensure it operates within desired parameters.
3. Common Testing Methods:
Testing methods may include functional tests, stress tests, and performance evaluations. For instance, laser power output, cutting speed, and precision are often assessed to ensure that the machine meets performance expectations. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods may also be employed to evaluate the integrity of welds and joints without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are several actionable strategies:
1. Supplier Audits:
Conducting on-site audits can provide valuable insights into a manufacturer’s quality control processes. This involves examining their facilities, quality management systems, and adherence to industry standards. Audits can help identify potential risks and ensure that the supplier’s practices align with your quality expectations.
2. Quality Control Reports:
Requesting detailed quality control reports can provide transparency regarding the manufacturing process. These reports should outline the results of inspections, testing methods used, and any corrective actions taken. Regular updates on quality metrics can also help in assessing ongoing supplier performance.
3. Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of assurance. These organizations can conduct independent evaluations of the manufacturing process and the final product, ensuring that it meets required standards and specifications. This is particularly beneficial for buyers who may not have the resources to conduct extensive audits themselves.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality control in international trade can present unique challenges for B2B buyers. Understanding these nuances can facilitate smoother transactions and better product quality.
1. Variability in Standards:
Different countries may have varying quality standards and regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific requirements of their target market to ensure compliance. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while buyers in the Middle East might focus on local standards.
2. Cultural and Language Differences:
Cultural nuances can influence communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should ensure clear communication regarding quality standards, specifications, and expectations. Utilizing bilingual staff or translators can help bridge language barriers and enhance understanding.
3. Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations:
Quality control does not end at manufacturing; it extends to logistics and supply chain management. Buyers should assess the reliability of suppliers in terms of delivery timelines and product integrity during transit. Establishing clear agreements regarding packaging and handling can further mitigate risks.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with laser milling machines is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, implementing rigorous quality control measures, and verifying supplier practices, buyers can ensure they are investing in high-quality machinery that meets their operational needs. As global trade continues to evolve, maintaining a proactive approach to quality assurance will be vital for success in the competitive landscape of laser milling technology.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘laser milling machine’
Introduction
Sourcing a laser milling machine is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance your manufacturing capabilities. This guide provides a practical checklist to help international B2B buyers effectively navigate the procurement process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget.
1. Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider factors such as the materials you will be working with (e.g., metals, plastics, wood), desired cutting speeds, and the thickness of materials. This clarity will help you identify machines that meet your operational requirements.
2. Step 2: Research Machine Types and Features
Different laser milling machines offer varying capabilities and features. Familiarize yourself with CO2 and fiber lasers, understanding their specific advantages—CO2 lasers are typically better for non-metals, while fiber lasers excel in cutting metals. Review features such as work area size, power output, and cooling mechanisms, which can greatly impact performance.
3. Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Look for established manufacturers with a track record of reliability and quality. Request company profiles, client testimonials, and case studies relevant to your industry. This step is vital in ensuring that the supplier can meet your needs and provide ongoing support.
4. Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the laser milling machines you are considering comply with international safety and quality standards. Look for certifications such as ISO and CE, which indicate adherence to industry regulations. Compliance is crucial not only for operational safety but also for legal considerations in your region.
5. Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
A strong after-sales support system is essential for the longevity and efficiency of your laser milling machine. Inquire about the warranty period, technical support availability, and the ease of obtaining spare parts. A reliable support system can minimize downtime and ensure smooth operations.
6. Step 6: Request Demonstrations or Samples
Whenever possible, request a demonstration of the laser milling machine or sample work from the supplier. This firsthand experience allows you to evaluate the machine’s performance and suitability for your specific applications. Pay attention to the quality of cuts, speed, and user interface during the demonstration.
7. Step 7: Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Finally, compare pricing across different suppliers while considering the total cost of ownership. Look beyond the initial purchase price; factor in maintenance costs, energy consumption, and potential upgrades. Additionally, explore financing options that may be available to help manage your budget effectively.
By following these steps, you can streamline the sourcing process for a laser milling machine and ensure that your investment aligns with your business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for laser milling machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Laser Milling Machines?
When sourcing laser milling machines, it’s crucial to understand the various cost components involved. These typically include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials used in manufacturing the machine, such as metals and components, can significantly affect pricing. High-quality materials may increase initial costs but can enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled technicians and engineers involved in the manufacturing and assembly processes. Regions with higher labor costs may result in increased machine prices.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, thereby affecting the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can add to the cost. The complexity of the tooling required for specialized features often translates to higher pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that machines meet specified standards. The investment in QC can raise costs but is essential for ensuring reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, especially for international buyers, can vary widely based on distance, shipping methods, and import duties. Understanding these logistics is vital for accurate cost forecasting.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin on top of their costs. This margin can vary based on market competition and the perceived value of the machine.
What Influences the Pricing of Laser Milling Machines?
Several factors can influence the pricing structure of laser milling machines:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to volume discounts. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help in negotiating better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can significantly impact the price. Machines tailored to specific applications or industries usually come at a premium.
-
Materials Used: The type of materials chosen (e.g., high-grade steel versus standard steel) can affect both cost and performance. Premium materials often justify higher prices due to enhanced longevity and capability.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines that comply with international standards and certifications (like ISO) may command higher prices but offer assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer better support and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for international transactions. They define shipping responsibilities and costs, affecting the overall price.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Laser Milling Machines?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective sourcing strategies can lead to significant savings:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Leverage multiple quotes to enhance your bargaining position.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional differences in pricing. Local market conditions, tariffs, and exchange rates can significantly influence overall costs.
-
Research Supplier Background: Verify suppliers’ credentials and reviews. Choosing a reputable supplier can mitigate risks associated with quality and service.
-
Plan for Logistics: Account for shipping times and costs in your purchasing decision. Effective logistics planning can prevent unexpected delays and expenses.
Conclusion
Sourcing laser milling machines requires a comprehensive understanding of the cost components and pricing influencers. By employing strategic negotiation tactics and considering the total cost of ownership, international buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their business needs. Always remember that indicative prices can vary based on market conditions, so continuous market research is essential for maintaining cost-efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing laser milling machine With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Laser Milling Machines
In the realm of precision manufacturing and material processing, laser milling machines offer distinct advantages, yet they are not the only option available to businesses. Understanding alternative technologies can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs, budget constraints, and specific application requirements. Below, we explore two viable alternatives to laser milling: CNC milling machines and waterjet cutting systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Laser Milling Machine | CNC Milling Machine | Waterjet Cutting System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, intricate designs; best for metals and non-metals | Excellent for complex shapes; good for hard materials | Versatile; excellent for thick materials without heat-affected zones |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; lower operating costs | Moderate initial investment; higher operational costs | High initial investment; variable operating costs depending on water and abrasives |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; software training needed | Established technology; relatively easy to learn | Requires technical knowledge for setup; software can be complex |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; regular lens cleaning | Moderate maintenance; regular tool changes | High maintenance; pump and nozzle upkeep required |
| Best Use Case | Detailed engraving, cutting of diverse materials | Machining metals, plastics, and wood with complex shapes | Cutting thick materials like metals and stones, with no thermal distortion |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Milling Machines
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling machines are a popular alternative that provides precision machining capabilities for a wide range of materials. They excel in creating complex geometries and are particularly effective for metalworking. The initial investment is moderate compared to laser milling machines, but operational costs can rise due to tool wear and replacement. CNC milling requires skilled operators familiar with G-code programming, but many businesses find the learning curve manageable. These machines are best suited for applications where detailed machining of hard materials is required.
Waterjet Cutting Systems
Waterjet cutting systems utilize high-pressure water, often mixed with abrasives, to cut through materials. This technology is particularly advantageous for thicker materials and applications where heat distortion must be avoided, making it ideal for cutting metals, glass, and stone. While the initial setup costs can be high, the versatility of waterjet systems allows them to handle a variety of materials. However, they may require more maintenance due to the complexity of the pumps and nozzles. The operational costs can vary significantly based on water usage and the type of abrasives employed. Waterjet cutting is best used in industries where material thickness and precision are critical, such as aerospace and architectural applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the most appropriate manufacturing solution depends on various factors, including the materials you work with, the complexity of designs, your budget, and your operational capabilities. Laser milling machines stand out for their precision and versatility, particularly in applications requiring detailed engraving and cutting of diverse materials. However, CNC milling machines and waterjet cutting systems offer compelling alternatives depending on specific manufacturing needs. It is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate these factors carefully, considering both the short-term and long-term implications of their investment to ensure they choose the right technology that aligns with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for laser milling machine
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a Laser Milling Machine?
Understanding the technical specifications of a laser milling machine is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key properties that should be considered:
1. Material Compatibility
Laser milling machines can process a diverse range of materials, including metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and brass, as well as non-metals such as wood, acrylic, and plastics. The ability to work with various materials allows businesses to expand their product offerings and cater to different industries, from aerospace to custom signage.
2. Cutting Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the precision of the cuts made by the laser milling machine, typically measured in microns. A tight tolerance (e.g., ±0.01 mm) is essential for applications requiring high precision, such as aerospace components or intricate designs. Understanding the machine’s tolerance capabilities helps buyers determine if it meets their production standards and quality requirements.
3. Laser Power Output
The power output of a laser (measured in watts) significantly affects its cutting speed and material thickness capabilities. Higher wattage machines can cut through thicker materials at faster speeds. For instance, a 100W CO2 laser can cut acrylic and wood efficiently, while a fiber laser is preferred for metal cutting. Selecting the right power output is critical for achieving the desired production efficiency and quality.
4. Work Area Size
The size of the work area determines the maximum dimensions of the material that can be processed. Machines come in various sizes, from compact desktop models suitable for small projects to large industrial units capable of handling extensive sheets. Businesses must assess their project requirements to choose a machine that fits their operational space and production needs.
5. Speed of Operation
Cutting speed is a vital specification, often measured in inches per minute (IPM). The speed at which a laser milling machine can operate depends on various factors, including material type and thickness. Higher speeds translate to increased productivity, making it essential for businesses aiming to optimize their manufacturing processes.
6. Cooling Systems
Effective cooling systems, such as water or air cooling, are crucial for maintaining the laser’s operational temperature and prolonging its lifespan. A well-designed cooling system can prevent overheating, which is essential for consistent performance and precision during prolonged operations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Laser Milling Machines?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for navigating the procurement process and ensuring smooth transactions. Here are several common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of laser milling machines, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality suppliers and ensure they receive genuine parts and support.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost. Understanding the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases and avoid overstocking or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is essential for comparing costs and evaluating different suppliers, enabling informed decision-making in the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, which is vital for international trade.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for businesses to manage production schedules and meet customer demands, especially in industries with tight deadlines.
6. Service Level Agreement (SLA)
An SLA outlines the expected service standards between a provider and a customer. For laser milling machines, SLAs may include maintenance schedules, response times for support, and warranty terms, ensuring that buyers receive the necessary support to keep their operations running smoothly.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make better-informed decisions when investing in laser milling machines, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the laser milling machine Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics Driving the Laser Milling Machine Sector?
The laser milling machine sector is experiencing robust growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and the increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries. Key factors propelling this market include the rise of automation and Industry 4.0, which emphasizes the integration of smart technology in manufacturing processes. This shift is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where the push for efficiency and productivity is paramount.
Emerging trends in sourcing reveal a growing preference for hybrid machines that combine laser milling capabilities with other processes, such as cutting and engraving. This multifunctionality not only reduces operational costs but also maximizes space in manufacturing facilities. Furthermore, as businesses adapt to fluctuating supply chains and economic uncertainties, there is a noticeable trend toward local sourcing of machinery, which enhances supply chain resilience and reduces lead times.
International buyers are also increasingly prioritizing vendors that offer comprehensive support and training for their laser milling machines, ensuring a seamless integration into existing workflows. This trend is particularly evident in regions like Vietnam and Germany, where technical expertise is critical for leveraging the full capabilities of advanced machinery. Overall, the laser milling machine market is set to evolve continuously, influenced by technological innovations and changing buyer preferences.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Laser Milling Machine Market?
As global awareness of environmental issues rises, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become central tenets for B2B buyers in the laser milling machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are now more inclined to partner with manufacturers that prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as using sustainable materials and adopting energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical supply chains are gaining traction, with businesses seeking transparency in sourcing practices. This includes ensuring that the materials used in laser milling machines, such as metals and composites, are obtained from responsible suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ credentials are becoming essential for manufacturers aiming to attract international buyers.
Moreover, the trend toward recycling and the use of biodegradable materials is influencing product designs. Buyers are increasingly considering suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through their product offerings and corporate practices. This shift not only meets regulatory requirements but also aligns with the values of consumers and businesses increasingly focused on sustainability.
What is the Brief Evolution of Laser Milling Machines in the B2B Context?
The evolution of laser milling machines can be traced back to the early days of laser technology in the 1960s, initially used for cutting and engraving. Over the decades, advancements in laser technology, optics, and automation have transformed these machines into sophisticated tools capable of intricate milling tasks. The introduction of computer numerical control (CNC) systems in the 1980s revolutionized precision manufacturing, allowing for greater control and versatility.
In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has further enhanced the capabilities of laser milling machines, enabling predictive maintenance and improved operational efficiency. As industries demand more complex designs and faster production times, the laser milling machine has solidified its role as an indispensable asset in modern manufacturing. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with current technological capabilities and market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of laser milling machine
-
How do I choose the right laser milling machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right laser milling machine involves assessing your specific application requirements, such as material type, thickness, and desired precision. Consider the machine’s specifications, including its work area size, cutting speed, and power output. Additionally, evaluate the versatility of the machine in handling different materials, such as metals and non-metals. It’s also beneficial to consult with suppliers for recommendations based on your industry and production goals, ensuring that the machine aligns with your operational capabilities and budget constraints. -
What are the key features to look for in a laser milling machine?
When selecting a laser milling machine, focus on key features such as laser type (CO2 vs. fiber), cutting area dimensions, and maximum material thickness it can handle. Look for advanced technology like hybrid servo motors for enhanced speed and precision, as well as integrated cooling systems for prolonged operation. Compatibility with various software for design and operation is also crucial, as is the machine’s energy efficiency and ease of maintenance. Lastly, consider customer support and warranty options offered by the manufacturer. -
What materials can I process with a laser milling machine?
Laser milling machines can process a wide range of materials, including various metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium, as well as non-metals like acrylic, wood, leather, and plastics. The specific capabilities depend on the machine’s laser type and power output. For businesses looking to diversify their production, choosing a machine with versatile material compatibility can enhance operational efficiency and open new market opportunities. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering a laser milling machine?
Lead times for ordering a laser milling machine can vary significantly based on the supplier, machine specifications, and customization requirements. Generally, standard models may have a lead time of 4-8 weeks, while customized solutions can take 12 weeks or longer. It’s important to communicate your timeline needs with suppliers early in the purchasing process to ensure that the delivery aligns with your production schedules. -
How do I vet suppliers of laser milling machines for international trade?
Vetting suppliers for international trade involves assessing their reputation, certifications, and compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients and review case studies relevant to your industry. Verify their manufacturing capabilities, quality assurance processes, and after-sales support. Engaging in direct communication, visiting their facility if possible, and reviewing their financial stability can further ensure they are a trustworthy partner for your business. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for laser milling machines?
Minimum order quantities for laser milling machines can vary by supplier and machine type. Some manufacturers may offer machines with no MOQ for standard models, while custom solutions might require higher quantities to justify production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as many are willing to negotiate MOQs based on your business requirements and long-term partnership potential. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a laser milling machine?
Payment terms for laser milling machine purchases typically range from full upfront payment to installment plans, depending on the supplier’s policies and the machine’s cost. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation (usually 20-50%), with the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms in advance and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment, especially for international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my laser milling machine?
Ensuring quality assurance for your laser milling machine involves several steps. First, request detailed specifications and quality certifications from the supplier, such as ISO 9001. Inquire about their QA processes, including testing procedures and inspections during manufacturing. Once the machine is delivered, conduct a thorough inspection and performance test to verify its functionality against the agreed specifications. Establishing a warranty and maintenance agreement can also safeguard your investment and ensure ongoing performance standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Laser Milling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Boss Laser – 2kw AccuCut
Domain: shop.bosslaser.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Laser Machines – Boss Laser offers a variety of laser cutting, engraving, and marking machines including CO2 Lasers, UV & Fiber Laser Markers, and Industrial Fiber Cutters. Key products include the 2kw AccuCut priced at $57,997, and various models from the LS-Series, HP-Series, FC-Series, FM-Series, and UV-Series. The machines can cut and engrave a wide range of materials such as acrylic, aluminum…
2. Full Spectrum Laser – Laser Cutting and Engraving Machines
Domain: fslaser.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Top Laser Cutting and Laser Engraving Machines from Full Spectrum Laser. Key product categories include:
– Muse Series Lasers:
– Muse Desktop UV Lasers
– Muse 1064nm Fiber Desktop Lasers
– Muse Desktop CO2 Lasers
– UNMEI P-Series Lasers:
– P-Series 20×12
– P-Series 24×16
– P-Series 36×24
– P-Series 48×36
– MC Series Lasers:
– 1064nm Galvo Fiber Marking Lasers
– 1064nm…
3. STYLECNC – CO2 Laser Engraver
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Affordable CNC Laser Cutter Engraving Machines for Sale – STYLECNC offers a variety of CNC laser machines including CO2 laser cutters, fiber laser cutting machines, hybrid laser cutting systems, and laser marking machines. Key products include: 1. STJ1390: CO2 laser engraver (60W-180W) for wood, fabric, leather, glass, acrylic, paper, plastic, stone, priced at $3,500 – $5,500. 2. STJ9060: Entry-le…
4. Kern Laser Systems – OptiFlex CO2 Laser Cutter
Domain: kernlasers.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Kern Laser Systems offers a range of large format laser cutting and engraving systems, including: 1. OptiFlex: Most popular CO2 laser cutter and engraver, ideal for processing metal, acrylic, wood, textiles, and foam with high-speed engraving capabilities. 2. LaserCELL: Complete laser engraving and cutting machine with a fully enclosed design for safety, suitable for high-traffic areas. 3. FiberCE…
5. Wattsan – Laser Machines
Domain: wattsan.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: This company, Wattsan – Laser Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Trotec Laser – Laser Machines
Domain: troteclaser.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Trotec Laser offers a range of laser machines including:
– Laser Cutter: Suitable for all levels of expertise, ideal for cutting various materials.
– Laser Engraver: Machines designed for both simple and complex engravings.
– Laser Marker: High-performance lasers for marking parts.
– Industrial Solutions: High-speed marking machines for seamless production.
– Speedy Series: High-performance l…
7. OneLaser – Best Laser Engraving Cutting Machines
Domain: 1laser.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 6 Best Laser Engraving Cutting Machines from OneLaser: 1. ONELASER XRF Desktop Laser with 38W RF Metal Tube – Sale Price: From $4,295.00 (Regular Price: $5,999.00) 2. ONELASER “HYDRA 9” High-Performance CO2 Cabinet Dual-Laser System (100W DC Glass Tube/38W RF Metal Tube Hybrid) – Sale Price: From $6,995.00 (Regular Price: $9,999.00) 3. ONELASER XT Desktop Laser with 55W Glass Tube – Sale Price: Fr…
8. JustLaser – Laser Cutting Solutions
Domain: justlaser.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Laser Cutting Instead of CNC Milling: Benefits include no maintenance costs, precise edges, maximum cleanliness, no fixing necessary, no material wear, easy integration into work processes, and high efficiency. JustLaser offers various laser machines such as JustMark Laser Marker, JustLaser Large Laser Cutter, JustCut Metal-Laser Cutter, and JustLaser Laser Engraver. Applications include cutting a…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for laser milling machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, strategic sourcing of laser milling machines is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The versatility and precision offered by modern laser milling technology can significantly enhance production capabilities, enabling businesses to work with a wide array of materials, from metals to non-metals.
Investing in high-quality laser milling machines not only streamlines operations but also provides a pathway to cater to diverse market demands, including personalized products and bespoke manufacturing solutions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a strong commitment to innovation, quality, and customer support, ensuring a reliable partnership that enhances their operational efficiency.
As you consider your sourcing strategy, remember that the right laser milling machine can transform your production processes, offering both immediate and long-term benefits. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your capabilities and stay ahead in your industry. Explore options, compare technologies, and choose wisely to position your business for success in the evolving global market. Your investment today can pave the way for tomorrow’s growth and competitiveness.