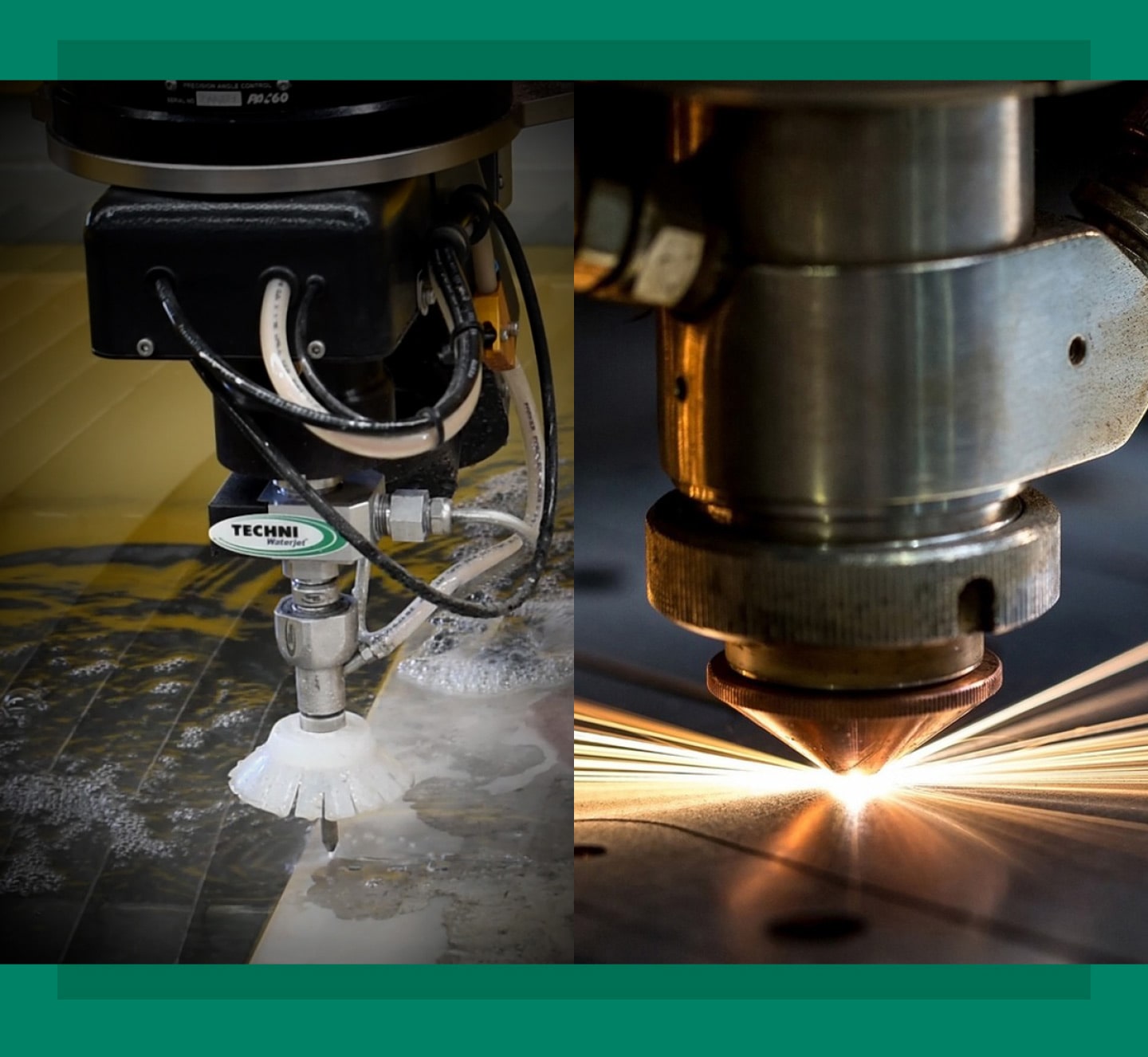
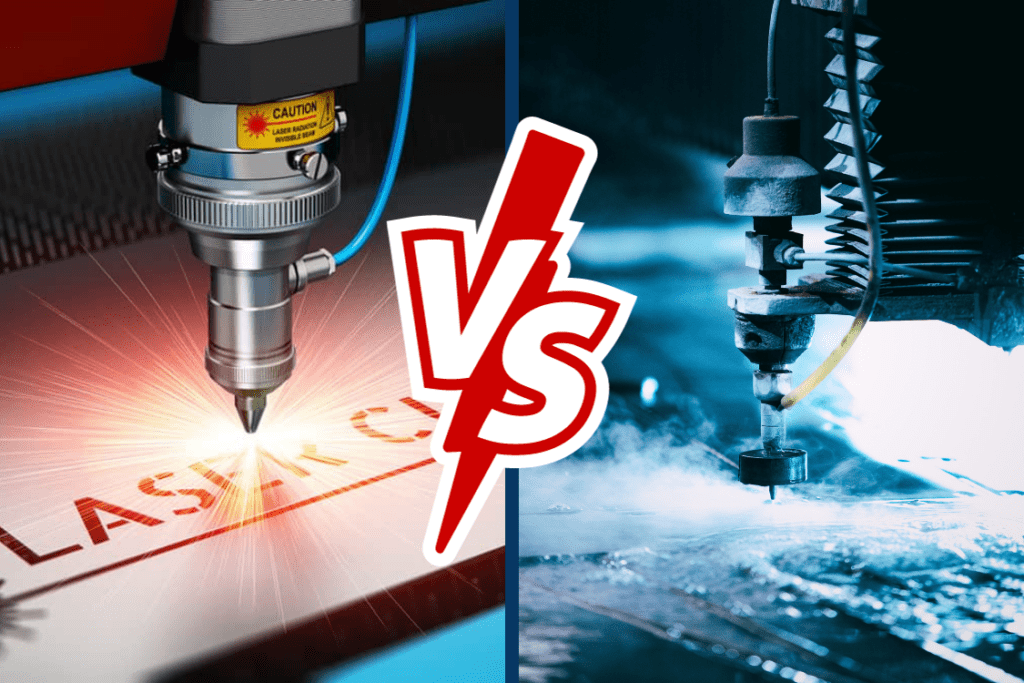
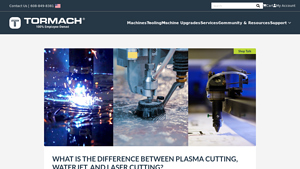
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for laser cutting vs water jet
In the competitive landscape of modern manufacturing, choosing the right cutting technology—be it laser cutting or waterjet cutting—can present a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. This guide is designed to simplify the sourcing process, providing insights into the strengths and limitations of each method. With applications spanning diverse industries, understanding the nuances of laser cutting and waterjet cutting is crucial for making informed decisions that align with specific project requirements and material considerations.
This comprehensive guide delves into critical aspects such as material compatibility, precision levels, operational costs, and supplier vetting processes. By exploring the distinct characteristics of laser and waterjet cutting, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in manufacturing hubs like Germany and Saudi Arabia—will gain valuable knowledge to effectively assess their options.
Arming yourself with this information not only enhances your purchasing strategy but also ensures that you select the most suitable technology for your operational needs. Whether you prioritize speed, precision, or material versatility, this guide will empower you to navigate the global market confidently, ultimately leading to more efficient production processes and better overall outcomes for your business.
Understanding laser cutting vs water jet Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Cutting | Utilizes a CO2 gas laser, ideal for non-metal materials. | Signage, woodworking, and textiles. | Pros: Fast cutting, excellent for intricate designs. Cons: Limited thickness, potential for hazardous fumes. |
| Fiber Laser Cutting | Employs a fiber optic laser, effective for metals and reflective materials. | Aerospace, automotive, and metal fabrication. | Pros: High speed, energy-efficient, minimal maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment, may require specialized training. |
| Waterjet Cutting | Uses high-pressure water, suitable for thick and heat-sensitive materials. | Stone, glass, and thick metals. | Pros: No heat distortion, can cut very thick materials. Cons: Slower than laser cutting, higher maintenance needs. |
| Abrasive Waterjet Cutting | Combines water with abrasive materials for cutting hard substances. | Heavy machinery, aerospace components. | Pros: Effective for hard materials, clean cuts. Cons: Higher operational costs, potential for abrasive wear. |
| Pure Waterjet Cutting | Pure water stream cutting, ideal for softer materials and food applications. | Food processing, rubber, and plastics. | Pros: Environmentally friendly, no heat generation. Cons: Slower cutting speed, less precise than lasers. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of CO2 Laser Cutting?
CO2 laser cutting is particularly effective for non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, and textiles. It operates using a gas laser, producing high-quality cuts with intricate details. B2B buyers in industries like signage and woodworking benefit from its speed and precision. However, the process is limited in terms of material thickness and can produce hazardous fumes, necessitating good ventilation and safety measures. Buyers should consider the type of materials they work with and the potential need for fume extraction systems.
How Does Fiber Laser Cutting Stand Out in Metal Applications?
Fiber laser cutting is known for its efficiency and speed, particularly when working with metals and reflective materials. This technology uses a fiber optic laser, making it suitable for industries such as aerospace and automotive where precision is critical. Its energy-efficient design reduces operational costs over time, though the initial investment may be higher. Buyers should assess their production volume and the types of metals processed to determine if the benefits justify the cost.
What Makes Waterjet Cutting Ideal for Thick and Heat-Sensitive Materials?
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure water stream, making it an excellent choice for cutting thick materials such as stone and glass without generating heat. This feature prevents thermal distortion, which is crucial for precision applications in industries like architecture and construction. While it provides clean cuts and can handle significant thickness, the process is generally slower compared to laser cutting. B2B buyers should evaluate their project timelines and the types of materials they need to cut when considering this option.
Why Choose Abrasive Waterjet Cutting for Hard Materials?
Abrasive waterjet cutting combines water with abrasives to effectively cut through hard materials like metals and ceramics. This method is particularly beneficial in sectors such as heavy machinery and aerospace, where tough materials are common. While it delivers clean cuts and can handle complex shapes, operational costs can be high due to abrasive wear. Buyers should analyze their production needs and budget to determine if this cutting method aligns with their manufacturing goals.
What are the Benefits of Pure Waterjet Cutting for Soft Materials?
Pure waterjet cutting utilizes only water to cut softer materials, making it suitable for applications in the food industry, rubber, and plastics. This method is environmentally friendly, generating no heat and minimizing waste. However, it operates at a slower speed and may not achieve the same level of precision as laser cutting. B2B buyers should consider their material types and production requirements to decide if pure waterjet cutting meets their operational needs effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of laser cutting vs water jet
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Laser Cutting vs Water Jet | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision cutting of lightweight components | Reduces weight while maintaining structural integrity, enhancing fuel efficiency. | Need for high precision and compliance with strict safety regulations. |
| Automotive | Fabrication of metal parts and panels | Faster production times and reduced material waste, leading to cost savings. | Consideration of material compatibility and thickness requirements. |
| Construction | Cutting of tiles, glass, and metals | Enables intricate designs and efficient material usage in architecture. | Environmental impact and waste management solutions are critical. |
| Electronics | PCB manufacturing and enclosures | High precision cutting enhances functionality and reliability of components. | Sourcing of materials that meet electrical standards and certifications. |
| Art and Design | Custom signage and artistic installations | Unique designs that attract customers and enhance brand visibility. | Flexibility in design and material choice is essential for creativity. |
How is Laser Cutting Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, laser cutting is employed for the precision fabrication of lightweight components such as brackets and frames. This technique allows manufacturers to create intricate designs that meet stringent safety standards while minimizing weight. The ability to cut materials with high precision ensures that parts fit perfectly within assembly specifications, thus enhancing overall aircraft performance. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with industry certifications and provide detailed documentation on material properties and cutting tolerances.
What Role Does Water Jet Cutting Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Water jet cutting is increasingly utilized in the automotive sector for fabricating metal parts and panels. This method allows for the efficient cutting of thick materials without generating heat, which can lead to warping or thermal stress. As a result, manufacturers can achieve cleaner cuts and reduce the need for extensive post-processing. Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should consider the total cost of ownership, including machine maintenance and the availability of water jet technology, which may vary by region.
Why is Water Jet Cutting Essential in Construction?
In the construction industry, water jet cutting is ideal for processing materials such as tiles, glass, and metals. It enables contractors to create detailed designs that are essential for modern architecture. The absence of heat during the cutting process ensures that materials retain their integrity, preventing cracks and imperfections. For international buyers, sourcing water jet cutting services requires an understanding of local environmental regulations and waste management practices, as these can significantly impact project timelines and costs.
How Does Laser Cutting Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics, laser cutting is critical for the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and enclosures. The precision offered by laser cutting ensures that components fit together seamlessly, which is vital for the reliability of electronic devices. Buyers should seek suppliers who can provide high-quality materials that meet international electrical standards, ensuring that the final products are both functional and compliant. Additionally, understanding the lead times and technology capabilities of suppliers in different regions can aid in effective project management.
What Benefits Does Laser Cutting Offer to the Art and Design Sector?
In the art and design sector, laser cutting is used to create custom signage and unique artistic installations. This method allows artists and designers to explore intricate patterns and shapes that would be difficult to achieve through traditional cutting methods. For businesses in this sector, sourcing laser cutting services requires flexibility in material choices and design capabilities. International buyers should also consider the supplier’s ability to handle varying project scales and timelines to meet creative demands effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘laser cutting vs water jet’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Choosing Between Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting for Specific Materials
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion when selecting between laser cutting and waterjet cutting for specific projects, particularly when dealing with diverse materials. For instance, a manufacturer looking to cut a mix of acrylic and rubber components may struggle to understand the implications of using one method over the other. Laser cutting excels with materials like acrylic due to its speed and precision but could cause melting or burning with softer materials like rubber. Conversely, while waterjet cutting can handle rubber without damaging it, it may not deliver the same efficiency or quality on acrylic.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this dilemma, buyers should conduct a thorough material compatibility analysis. Create a detailed list of all materials involved in the project and consult with cutting service providers about their capabilities. Many companies offer sample cutting services where you can test both methods on small pieces before making a full commitment. Additionally, leverage CAD software to simulate cuts and visualize potential outcomes for both laser and waterjet techniques. By understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each method, manufacturers can optimize their choice based on material properties and project requirements, ensuring high-quality results without unnecessary costs.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Limitations in Precision and Thickness
The Problem: Precision and thickness limitations can be a significant concern for B2B buyers when selecting cutting methods. For example, a company specializing in intricate metal parts may find that while laser cutting offers excellent precision, it can only effectively cut materials up to a certain thickness. On the other hand, waterjet cutting can handle thicker materials but may not achieve the same fine tolerances. This can lead to frustration and potential delays in production schedules if the wrong method is selected.
The Solution: To address these limitations, buyers should focus on understanding the specific requirements of their projects, including tolerances and thicknesses. It is beneficial to categorize projects based on their precision needs and material thickness. For components requiring high precision with thinner materials, laser cutting is ideal. In contrast, for projects involving thicker materials where precision is slightly less critical, waterjet cutting should be considered. Consulting with a machining specialist can provide insights into the best practices for each method. Furthermore, utilizing advanced technologies like CNC machining in conjunction with laser or waterjet cutting can enhance precision, enabling manufacturers to meet strict tolerances while optimizing their production processes.
Scenario 3: Managing Costs and Maintenance for Long-Term Projects
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are concerned about the long-term costs associated with both laser cutting and waterjet cutting, particularly regarding equipment maintenance and operational expenses. A company may invest heavily in either cutting technology but later discover that ongoing maintenance, energy costs, and material waste exceed their budget. This is especially critical for businesses operating in regions like Africa or South America, where operational budgets are often constrained.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs, buyers should consider the total cost of ownership for both technologies, including initial investment, maintenance, and operational costs. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive cost breakdowns can help in understanding the long-term financial implications. Additionally, it’s advisable to establish a preventive maintenance schedule to mitigate unexpected breakdowns and extend the life of the machinery. For companies focused on high-volume production, investing in automation can significantly reduce labor costs and improve efficiency. Finally, consider sourcing materials that optimize the chosen cutting method to minimize waste, which can further enhance cost-effectiveness. By adopting a holistic view of costs and maintenance, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals while ensuring high-quality production outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for laser cutting vs water jet
What Materials Are Best for Laser Cutting vs. Water Jet Cutting?
When selecting materials for laser cutting and waterjet cutting, understanding the properties and applications of each material is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials: steel, acrylic, wood, and rubber, focusing on their suitability for each cutting method.
How Does Steel Perform in Laser Cutting and Water Jet Cutting?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its strength and durability, with a high-temperature resistance that makes it suitable for various industrial applications. It can withstand significant pressure and is resistant to corrosion, especially when treated.
Pros & Cons: Laser cutting offers high precision and speed for steel, producing clean edges with minimal post-processing. However, it may struggle with very thick steel (over 40 mm) and can be more expensive due to the energy required. Water jet cutting can handle thicker steel (up to 300 mm) without heat-affected zones, which preserves the material’s integrity. However, it is slower and less precise than laser cutting.
Impact on Application: Steel is widely used in construction, automotive, and manufacturing. The choice between cutting methods affects the final product’s strength and finish.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers from regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia may prioritize precision and finish quality, while those in Africa and South America might focus on cost and thickness capabilities.
What About Acrylic as a Material Choice?
Key Properties: Acrylic is lightweight, transparent, and has good weather resistance. It can be easily molded and shaped, making it popular for signage and displays.
Pros & Cons: Laser cutting acrylic provides excellent edge quality and speed, with minimal waste. However, it can produce harmful fumes and is sensitive to heat, which may lead to melting or warping. Water jet cutting is slower and less effective for acrylic, but it avoids heat-related issues.
Impact on Application: Acrylic is often used in signage, displays, and protective barriers. The choice of cutting method can significantly affect clarity and finish.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with safety standards related to fumes and waste disposal, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
How Does Wood Compare for Laser Cutting and Water Jet Cutting?
Key Properties: Wood is a versatile material with varying densities and grain patterns. It is generally lightweight and has good thermal insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: Laser cutting wood is fast and produces clean cuts with intricate designs. However, it can char the edges and create smoke. Water jet cutting is slower but avoids burning, making it suitable for applications where aesthetics are critical.
Impact on Application: Wood is commonly used in furniture, cabinetry, and decorative items. The choice of cutting method can influence the final appearance and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding sourcing and sustainability is vital, especially in regions focused on environmental conservation.
Is Rubber a Suitable Material for These Cutting Techniques?
Key Properties: Rubber is flexible, durable, and has excellent shock absorption properties. It is resistant to wear and tear, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: Laser cutting can be challenging due to the melting and burning of rubber, which can compromise the cut quality. Water jet cutting is more effective, producing clean cuts without heat damage. However, it may be slower and more costly.
Impact on Application: Rubber is used in seals, gaskets, and cushioning materials. The choice of cutting method can affect the performance and longevity of the final product.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of rubber and compliance with local material standards, particularly in regions where specific grades are mandated.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cutting Techniques
| Material | Typical Use Case for laser cutting vs water jet | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, automotive parts | High precision and speed | Limited thickness capacity | High |
| Acrylic | Signage, displays | Excellent edge quality | Produces harmful fumes | Medium |
| Wood | Furniture, cabinetry | Fast and intricate cuts | Can char edges | Low |
| Rubber | Seals, gaskets | Clean cuts without heat | Slower and potentially costlier | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for laser cutting vs water jet
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Processes of Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting?
Both laser cutting and waterjet cutting involve several stages that ensure the effective transformation of raw materials into finished products. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their supply chains and ensure quality.
1. Material Preparation
The initial stage involves selecting and preparing the right materials. For laser cutting, materials such as metals, plastics, and wood are commonly used. Waterjet cutting, on the other hand, can handle a broader range of materials, including thicker metals and stone. Accurate material selection is vital, as different materials require different cutting parameters.
- Laser Cutting: Materials are typically flat sheets that need to be cleaned and, if necessary, treated to remove any contaminants.
- Waterjet Cutting: Materials may also require cleaning, but they can be more varied in thickness and type. The waterjet process can cut materials up to 300 mm thick, which makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
2. Forming
In this stage, the actual cutting process occurs. Both techniques utilize computer-aided design (CAD) to ensure precision.
- Laser Cutting: A high-powered laser beam is focused on the material, melting or burning through it. This process can be very fast, with cutting speeds reaching up to 70 inches per minute for thin materials. It is important to note that laser cutting generates heat, which can affect certain materials adversely.
- Waterjet Cutting: In contrast, waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure water stream, often mixed with abrasives for harder materials. The cutting speed is generally slower, ranging from 1 to 20 inches per minute for thicker materials, but it does not introduce heat, making it ideal for materials that are sensitive to temperature changes.
3. Assembly
After cutting, some projects may require assembly. This stage can involve welding, bonding, or mechanical fastening, depending on the design specifications.
- Laser Cutting: The precision of laser cutting often means that the pieces fit together more accurately, reducing the need for extensive adjustments during assembly.
- Waterjet Cutting: While waterjet cutting also offers precision, the nature of the cut may require additional finishing processes to ensure that the pieces align correctly.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves any additional processing required to prepare the product for delivery.
- Laser Cutting: This may include secondary operations such as polishing, painting, or applying protective coatings. The clean edges produced by laser cutting typically require less finishing work.
- Waterjet Cutting: Often results in a smooth finish, but may still require post-processing for certain applications, particularly if tight tolerances are necessary.
What Are the Quality Assurance Protocols for Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in manufacturing, ensuring that products meet specified standards and customer expectations. For both laser cutting and waterjet cutting, international and industry-specific standards guide the QA process.
International Standards and Industry-Specific Certifications
B2B buyers should be aware of the relevant international standards that govern quality assurance in manufacturing.
- ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Companies that adhere to ISO 9001 demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant for European markets, CE marking indicates that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For buyers in the oil and gas sector, API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications are crucial, ensuring products meet specific quality and safety requirements.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Implementing a robust quality control (QC) system involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. Effective IQC can prevent costly production delays and ensure that only high-quality materials are used.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This stage includes monitoring the manufacturing process itself. For laser cutting and waterjet cutting, this may involve checking cutting parameters and inspecting the quality of the cuts during production.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After manufacturing, FQC involves a thorough inspection of the finished product against specifications. This can include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control practices. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
1. Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits allow buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems. During an audit, buyers can evaluate compliance with international standards and identify any areas for improvement.
2. Request Quality Control Reports
Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports, testing results, and compliance certifications. This transparency is crucial for building trust and ensuring product quality.
3. Utilize Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These agencies can conduct inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process, offering additional assurance to buyers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional compliance requirements is essential:
- Cultural Differences: Buyers should be aware of varying cultural attitudes toward quality and compliance. For instance, European manufacturers may prioritize stringent compliance with environmental regulations, while Middle Eastern suppliers may focus on durability and reliability.
- Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations that may affect manufacturing processes. For example, certain countries have specific standards for materials used in construction or automotive applications.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Ensure that suppliers maintain transparency throughout the supply chain, including sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution. This can help mitigate risks associated with quality control and compliance.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for laser cutting and waterjet cutting is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, companies can make informed decisions that enhance product quality, reduce waste, and ultimately improve customer satisfaction.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘laser cutting vs water jet’
To assist B2B buyers in navigating the decision-making process between laser cutting and water jet cutting, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to ensure informed procurement. Each step is designed to help you evaluate your options based on your specific project requirements and supplier capabilities.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your project requirements. Identify the materials you intend to cut, the thickness of these materials, and the desired precision levels. Specifications will guide your choice between laser cutting and water jet cutting, as each technique excels in different areas.
- Material Types: Determine if your materials are heat-sensitive or require a cold cutting process.
- Thickness: Consider the maximum thickness you need to cut, as water jet cutting can handle thicker materials.
Step 2: Assess Your Budget Constraints
Establish a budget that accommodates not just the cutting services but also any associated costs such as shipping and potential post-processing. Understanding the financial implications will help narrow your supplier options effectively.
- Cost Comparison: Compare the cost of laser cutting vs. water jet cutting based on the thickness and type of materials.
- Long-term Investment: Consider the potential longevity and maintenance costs of the machinery involved in the cutting process.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to ensure they meet your requirements. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry and region.
- Certifications and Compliance: Verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications for quality and safety standards.
- References and Case Studies: Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality of service.
Step 4: Request Sample Cuts
Before finalizing a supplier, request sample cuts of your specified materials. This will provide insight into the precision and quality of their work.
- Material Testing: Ensure the samples reflect the actual materials and thicknesses you plan to use.
- Performance Evaluation: Analyze the samples for cut quality, edge smoothness, and dimensional accuracy.
Step 5: Understand Lead Times and Capacity
Inquire about the lead times for production and the supplier’s capacity to handle your order size. This is particularly important if you have strict deadlines.
- Production Capacity: Ensure the supplier can meet your volume needs without compromising quality.
- Delivery Timelines: Discuss delivery options and timelines to avoid potential project delays.
Step 6: Review Maintenance and Support Services
Investigate the maintenance requirements and support services offered by your chosen supplier. This is crucial for ensuring consistent performance over time.
- Maintenance Protocols: Understand how often the cutting equipment needs maintenance and what that entails.
- Support Availability: Check if the supplier provides ongoing support, including troubleshooting and repairs.
Step 7: Finalize Contractual Terms
Once you’ve selected a supplier, carefully review and negotiate the contract terms. Ensure that all specifications, lead times, and costs are clearly outlined to prevent misunderstandings later.
- Clear Deliverables: Define the exact deliverables, including quality standards and timelines.
- Payment Terms: Agree on payment terms that align with your budget and cash flow requirements.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when choosing between laser cutting and water jet cutting, ensuring their projects meet the necessary specifications while also aligning with budgetary constraints.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for laser cutting vs water jet Sourcing
When evaluating the cost structure and pricing for laser cutting versus waterjet cutting, it is essential to understand the various cost components involved in each process. Both technologies have their unique pricing structures influenced by multiple factors.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting?
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts costs. Laser cutting is generally more suited for metals, plastics, and wood, while waterjet cutting excels with thicker materials and composites. The price of raw materials can vary widely depending on market conditions and geographical location.
-
Labor: Labor costs include the wages for machine operators and technicians. Laser cutting often requires less skilled labor due to its automated processes, while waterjet cutting may necessitate more skilled operators to manage the complexities of abrasive materials and water pressures.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with running the machinery, including energy consumption and maintenance. Laser cutting machines, while generally faster, may require more frequent maintenance on optics, leading to potential downtime costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the expense of maintaining and replacing cutting heads and other equipment. Waterjet cutting may incur higher tooling costs due to the wear and tear from abrasive materials, whereas laser cutting primarily focuses on lens and mirror maintenance.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of the cuts can involve additional costs for inspections and testing. Laser cutting typically offers higher precision, which may reduce the need for extensive QC measures compared to waterjet cutting.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the weight and dimensions of the cut parts. Waterjet-cut parts, especially when thicker, may be heavier and thus incur higher shipping fees.
-
Margin: Suppliers will mark up prices based on their operational costs, market demand, and competition. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers negotiate better margins.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting Costs?
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider consolidating orders to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized cuts or intricate designs may incur additional costs. Clear specifications can help suppliers provide more accurate quotes.
-
Material Choices: The type and thickness of material chosen will affect pricing. Some materials are more expensive and may require specific cutting techniques.
-
Quality Certifications: Parts requiring certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may lead to higher costs due to the additional processes involved in ensuring compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and capabilities of the supplier can significantly influence pricing. Local suppliers may offer lower logistics costs, but international suppliers might provide better technology or pricing models.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms can help buyers manage costs related to transportation, insurance, and duties. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the final price significantly.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting?
-
Negotiate with Suppliers: Building strong relationships and negotiating terms can lead to better pricing and flexibility in orders.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price and evaluate long-term costs, including maintenance, waste disposal, and potential downtime.
-
Research Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Understanding local market conditions in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can offer insights into better sourcing strategies. Currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local regulations can all impact final pricing.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers allows for better comparison and can highlight cost discrepancies.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for laser cutting and waterjet cutting can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. The figures provided are indicative and should be confirmed with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing laser cutting vs water jet With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Cutting Technologies
In the realm of industrial manufacturing, selecting the appropriate cutting technology is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and achieving desired outcomes. While laser cutting and waterjet cutting are two leading methods, there are alternative solutions that may also meet specific operational needs. This analysis compares these two technologies against other viable alternatives, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Laser Cutting Vs Water Jet | Plasma Cutting | CNC Milling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High speed and precision; ideal for thin materials. | Fast cutting; effective on metals but less precise than laser. | Versatile; good for complex shapes but slower than laser. |
| Cost | $8,000 – $250,000 for machines; lower operational cost for thin materials. | $30,000 – $150,000; cost-effective for thick materials. | $5,000 – $100,000; varies with complexity and tooling. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; CAD integration necessary. | Easier setup; often requires less operator training. | More complex setup; operator expertise needed for programming. |
| Maintenance | Moderate; lenses and mirrors need regular cleaning. | Low; fewer wear parts, but consumables can add up. | High; regular maintenance required for moving parts and tooling. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for intricate designs in materials like acrylic and metal under 40mm. | Best for thick metals; effective for quick cuts in fabrication. | Suitable for detailed work on a variety of materials, including metals and plastics. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting utilizes a high-temperature plasma arc to cut through electrically conductive materials, such as steel and aluminum. Its primary advantage is speed; plasma cutters can operate at several inches per minute, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. However, the precision is generally lower than that of laser cutting, with cut tolerances around 1mm. Plasma cutting is also less effective on non-conductive materials and may create a rougher edge that requires additional finishing work.
CNC Milling
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling involves rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. This method excels in creating complex shapes and can be used on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. While CNC milling provides excellent precision and flexibility, it is typically slower than both laser and waterjet cutting. The initial setup costs can also be high due to the need for specific tooling and machinery, and ongoing maintenance can be labor-intensive.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cutting Technology for Your Needs
When selecting a cutting technology, B2B buyers must consider the specific requirements of their operations, including the materials being processed, the desired precision, and budget constraints. Laser cutting is often the preferred choice for intricate designs and thin materials, while waterjet cutting shines with thicker, more brittle materials. Alternatives like plasma cutting and CNC milling offer their own unique benefits and drawbacks. By assessing these factors, businesses can identify the cutting solution that best aligns with their production goals and operational capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for laser cutting vs water jet
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting?
When considering laser cutting and waterjet cutting for industrial applications, several technical properties are crucial for B2B buyers. Understanding these specifications will help in selecting the right method for specific projects.
1. Material Thickness and Compatibility
Laser cutting typically excels with materials up to 30-40 mm thick, while waterjet cutting can handle materials as thick as 300 mm. The choice of cutting technique heavily depends on the material type and thickness required for the project. For example, laser cutting is ideal for metals, plastics, and wood, while waterjet cutting is preferred for thicker materials like stone and rubber. Understanding these limits allows businesses to optimize production efficiency and reduce costs.
2. Tolerance and Precision
Laser cutting offers a high degree of precision, often achieving tolerances as tight as 0.15 mm. Waterjet cutting, in contrast, typically maintains tolerances around 0.5 mm. High precision is essential for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where even minor deviations can lead to significant operational issues. Buyers should evaluate the required tolerances for their projects to select the appropriate cutting technology.
3. Speed of Operation
In terms of speed, laser cutting generally operates at 20-70 inches per minute, significantly faster than waterjet cutting, which operates at about 1-20 inches per minute for materials under one inch thick. Faster cutting speeds can lead to increased productivity and lower labor costs, making it a vital consideration for manufacturers aiming to meet tight deadlines.
4. Waste and Byproducts
Laser cutting produces minimal waste and is less likely to generate hazardous byproducts compared to waterjet cutting, which may require waste disposal for used abrasives. This environmental consideration is increasingly important for businesses focusing on sustainability. Companies should assess their waste management capabilities and environmental policies when choosing between the two methods.
5. Operating Costs
The cost of laser cutting machines can range from $8,000 to $250,000, while waterjet cutting machines typically start around $60,000 and can go up to $450,000. Although waterjet cutting may be more cost-effective for thick materials, the initial investment is higher. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational expenses, is crucial for budget-conscious buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Laser and Waterjet Cutting?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some critical terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to source components or machinery for their operations.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for businesses to ensure they meet suppliers’ requirements while managing inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. This process is essential for comparing offers and ensuring competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses navigate shipping logistics and costs effectively.
5. CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
CAD refers to software used to create precision drawings or technical illustrations. Understanding CAD is crucial for ensuring compatibility with cutting technologies and optimizing design processes.
6. Abrasive Waterjet Cutting
This term refers to a waterjet cutting process that incorporates abrasive materials to enhance cutting capabilities, especially for harder materials. Recognizing the distinction between pure waterjet and abrasive waterjet cutting can help buyers select the appropriate technique for their specific needs.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting between laser cutting and waterjet cutting for their manufacturing needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the laser cutting vs water jet Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Laser Cutting vs. Waterjet Sector?
The global market for laser cutting and waterjet cutting technologies is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing processes and the increasing demand for precision cutting across various industries. Key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are leveraging these technologies to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. In regions like Africa and South America, the adoption of these cutting methods is accelerating due to the expansion of manufacturing capabilities and infrastructure improvements.
International B2B buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, are increasingly focused on sourcing technologies that offer not only speed and accuracy but also versatility across materials. Laser cutting is favored for its rapid processing speeds and precision, making it ideal for thinner materials like plastics and metals. Conversely, waterjet cutting is gaining traction for its ability to handle thicker materials without generating heat, making it suitable for cutting complex shapes in materials such as stone and ceramics. Emerging trends indicate a growing integration of automation and IoT technologies, which enhance machine capabilities and facilitate real-time monitoring, thus improving supply chain efficiency.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Sourcing Decisions in Laser Cutting and Waterjet Technologies?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor for B2B buyers when selecting laser cutting and waterjet technologies. As businesses increasingly prioritize environmental impact, there is a rising demand for eco-friendly manufacturing practices. Waterjet cutting, known for its minimal material waste and lack of hazardous emissions, is often perceived as a more sustainable option. This method uses high-pressure water, which can be recycled, reducing the need for additional resources.
Conversely, while laser cutting generates waste materials, advancements in technology are leading to more efficient processes that minimize waste production. Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining importance, prompting companies to seek suppliers with transparent supply chains and certifications that align with environmental standards. B2B buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers who offer ‘green’ certifications and use sustainable materials, as this not only enhances their brand image but also meets the growing consumer demand for responsible manufacturing.
What Is the Evolution of Laser Cutting and Waterjet Technologies in the B2B Context?
The evolution of laser cutting and waterjet technologies has been marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to meet the demands of various industries. Laser cutting emerged in the 1960s, initially utilized for industrial applications, but has since evolved to include advanced features such as fiber optics and improved software integration, allowing for greater precision and efficiency.
On the other hand, waterjet cutting gained traction in the 1980s, primarily for its ability to cut materials without thermal damage. The integration of abrasive materials into the process has expanded its application to thicker and harder materials. Both technologies have undergone significant advancements, including automation and digital integration, which are crucial for modern manufacturing. As a result, B2B buyers today benefit from a plethora of options that cater to diverse cutting needs, making informed sourcing decisions essential for competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of laser cutting vs water jet
-
How do I choose between laser cutting and waterjet cutting for my project?
When deciding between laser cutting and waterjet cutting, consider the material type and thickness. Laser cutting excels with metals, plastics, and thin materials (up to 30-40 mm) due to its speed and precision. In contrast, waterjet cutting is ideal for thicker materials (up to 300 mm) and is effective for soft materials that could melt under laser heat. Additionally, evaluate the desired finish quality and any specific tolerances needed for your application to make an informed choice. -
What types of materials can be cut using laser cutting vs. waterjet cutting?
Laser cutting is suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, acrylic, wood, and cardboard. However, it struggles with reflective materials and heat-sensitive substances. Waterjet cutting, on the other hand, can handle various materials like metals, plastics, glass, and ceramics, including those that are too soft for laser cutting. If your project involves diverse materials, waterjet cutting might provide more versatility. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers for laser cutting or waterjet cutting services?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience and expertise in the specific cutting technology you require. Request samples of previous work to evaluate quality and precision. Additionally, consider their certifications, production capacity, lead times, and customer testimonials. Transparency in pricing, communication, and support for international shipping can also indicate a reliable partner for your project. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) typically required for laser cutting and waterjet cutting services?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of your project. Laser cutting services may have lower MOQs, especially for simpler cuts or prototypes, while waterjet cutting services might require higher MOQs due to longer setup times. Always inquire directly with potential suppliers to understand their specific MOQ policies and negotiate terms that fit your needs. -
What payment terms are standard when sourcing cutting services internationally?
Payment terms can differ between suppliers and regions. Common practices include upfront deposits (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after quality inspection. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 payment terms, especially for established relationships. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. -
How does quality assurance work in laser cutting and waterjet cutting processes?
Quality assurance is crucial in both processes to ensure precision and customer satisfaction. Suppliers often employ a combination of in-process inspections, dimensional checks, and final quality assessments. Request details about their QA protocols, including any certifications like ISO 9001. Additionally, ask about their ability to accommodate custom specifications and how they handle defects or discrepancies in delivered products. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing laser cutting or waterjet cutting services?
Logistics play a significant role in international sourcing. Consider the supplier’s location and its impact on shipping costs and delivery times. Evaluate their experience with customs and import regulations in your country. It’s also wise to discuss packaging methods to ensure that your products arrive safely. Establish clear communication channels for tracking shipments and addressing any potential delays. -
Can I customize my designs for laser cutting and waterjet cutting projects?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options for both laser and waterjet cutting. You can provide your designs in CAD format, and suppliers can often accommodate specific dimensions, shapes, and finishes. Discuss any particular requirements or modifications you may need, and ensure that the supplier can meet your expectations. Clear communication about your design intent will help achieve the desired outcome.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Laser Cutting Vs Water Jet Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – CNC Milling vs. Laser Cutting
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC Milling: Allows cutting in multiple planes depending on the number of axes; can cut overhangs and bore holes; generally takes longer than laser cutting and waterjet; cheaper to buy, maintain, and operate; more complex parts are machined; limited by tool radius for inner corners. Laser Cutting: More accurate than waterjet; suitable for flat materials; can cause warping in low heat deflection pl…
2. Sculpteo – Laser Cutting vs Waterjet Cutting
Domain: sculpteo.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Laser Cutting vs Waterjet Cutting Comparison:
1. **Cutting Techniques**:
– Laser Cutting: Can engrave and cut materials.
– Waterjet Cutting: Only cuts materials.
2. **Material Compatibility**:
– Laser Cutting: Cuts a wide range of materials including plastics, glass, wood, and metals (stainless steel, aluminum, mild steel).
– Waterjet Cutting: Can cut all materials, including thicker…
3. Dahlstrom – Waterjet Cutting Solutions
Domain: blog.dahlstromrollform.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Waterjet Cutting: Uses high-pressure water streams mixed with abrasive particles; generally more expensive due to component wear and consumables; operating costs range from $15-$30 per hour; lower up-front machine cost; cleanup is extensive; cutting speed typically up to 20″ per minute; accuracy within +/- 0.02 inches; versatile, can cut almost any material. Laser Cutting: Utilizes a focused beam …
4. Practical Machinist – Waterjet Cutting Insights
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Waterjet cutting is typically more expensive than laser cutting, with costs reported to be 3-4 times higher for certain parts made from mild steel, 1/2″ thick. Waterjet machines require significant maintenance due to wear on nozzles and pumps, and they consume a large amount of electricity. Common waterjet pumps range from 30-60HP, with some capable of cutting materials up to 8″ thick at speeds of…
5. Tormach – 1300PL Plasma Table
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Plasma Cutting: Uses electricity and compressed gases to cut conductive materials like steel or aluminum. It creates a large heat-affected zone and is less accurate than laser or waterjet cutting but offers speed, flexibility, and lower operational costs. Tormach 1300PL Plasma Table starts at under $16,000.
Waterjet Cutting: Utilizes high-pressure water and an abrasive (typically garnet) to cut …
6. Techni Waterjet – Waterjet Cutting Solutions
Domain: techniwaterjet.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Waterjet Cutting: Versatile, can cut virtually any material using pressurized water, often with abrasives like Garnet and Aluminum Oxide. Materials include metals (Aluminum, Brass, Carbon Steel, etc.), composites (Aero Fiber, Carbon Fiber), naturals (Ceramic, Quartz), plastics (Acrylic, PVC), and more. Can cut materials up to 6″ (150mm) thick. Safety benefits include no heat-affected zone, no toxi…
7. Flow Waterjet – High-Pressure Cutting Solutions
Domain: flowwaterjet.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Waterjet technology uses high-pressure streams of water to cut through a wide range of materials, including thick, thin, soft, or hard materials. It operates at 60,000 psi and can cut through gaskets, foam, soft plastics, and rubber. When sand is added for abrasive waterjet cutting, it can cut through almost any material, including metal and stone. Waterjet cutting is accurate, capable of cutting …
8. Xometry – Cutting Solutions
Domain: xometry.pro
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Choosing between laser, plasma, or waterjet cutting for stainless steel components involves considering factors such as material thickness, precision requirements, and production volume. Laser cutting offers high precision and is suitable for thin materials, while plasma cutting is effective for thicker materials but may have rougher edges. Waterjet cutting is versatile and can handle various mate…
9. BladeForums – Laser vs Waterjet Cutting
Domain: bladeforums.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The discussion compares laser cutting and waterjet cutting for mid-tech projects, highlighting key differences in edge finish, kerf, heat affected zones, and cost. Waterjet cutting does not leave a heat affected zone and provides a cleaner edge finish, while laser cutting is faster but may leave a heat affected zone and slag. Waterjet machines can have issues with kerf and precision, especially wi…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for laser cutting vs water jet
In navigating the decision between laser cutting and waterjet cutting, international B2B buyers must consider key factors including material compatibility, precision, speed, and operational costs. Laser cutting excels in speed and precision for thinner materials, making it ideal for industries requiring intricate designs. In contrast, waterjet cutting offers versatility for thicker materials without heat distortion, catering well to sectors like metalworking and stone fabrication.
Strategic sourcing is essential for optimizing production processes and aligning with the specific needs of your business. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each cutting technology, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
As global markets evolve, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for precision manufacturing techniques will only increase. Embracing innovative cutting technologies will position your business for future growth. Evaluate your specific requirements, engage with suppliers, and leverage the benefits of both laser and waterjet cutting to stay competitive in the international landscape. The future of manufacturing is bright—seize the opportunity to elevate your operations today.