Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Laser Cutting Vs Cnc Router
Precision Fabrication Pathway Selection at Honyo Prototype
When selecting between laser cutting and CNC routing for your next fabrication project, understanding the fundamental process capabilities is critical for achieving optimal part quality, material integrity, and cost efficiency. Laser cutting excels in high-speed processing of thin sheet materials, particularly metals and acrylics, leveraging thermal energy to vaporize material along a defined path. However, inherent limitations exist including heat-affected zones that can alter material properties, restricted capability with highly reflective or thick materials, and kerf widths that limit intricate feature resolution.
CNC routing fundamentally differs by mechanically removing material using rotating cutting tools, enabling cold machining that preserves material characteristics. This method delivers superior dimensional accuracy for complex 3D geometries, tight tolerances down to ±0.001 inches, and exceptional surface finishes across an expansive material spectrum—from engineering plastics and composites to aluminum and steel alloys. At Honyo Prototype, our advanced 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC machining centers are engineered to handle prototyping through low-volume production with rigorous process control and first-article inspection.
The following comparison highlights key technical differentiators for informed decision-making:
| Parameter | Laser Cutting | Honyo CNC Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | Limited (typically <25mm) | Extensive (up to 500mm+) |
| Kerf Width | 0.1–0.5mm (thermal spread) | Tool-dependent (as low as 0.5mm) |
| Tolerance | ±0.1–0.2mm | ±0.001–0.005mm standard |
| Material Types | Metals, acrylics, wood | Metals, plastics, composites, wood, foam |
| Thermal Impact | Significant HAZ | None (cold process) |
| 3D Geometry | Not feasible | Full capability |
For projects demanding micron-level precision, complex contours, or material-sensitive applications, Honyo’s CNC machining services provide the definitive solution. We integrate rapid engineering feedback, stringent quality protocols, and flexible capacity to accelerate your development timeline without compromising integrity. Streamline your procurement process immediately—leverage our Online Instant Quote system to receive validated pricing and lead times in under 90 seconds, backed by our engineering team’s expertise to optimize manufacturability from your initial design upload.
Technical Capabilities
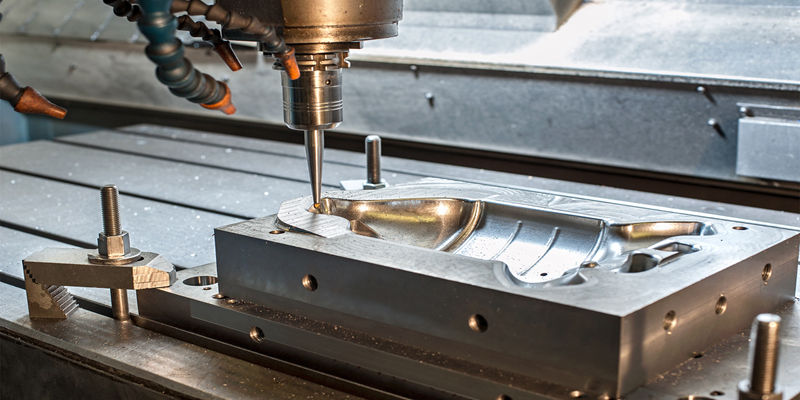

Laser cutting and CNC routing serve distinct roles in precision manufacturing, particularly when compared to advanced CNC machining processes such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling, as well as CNC turning. While laser cutting and CNC routing are effective for 2D profiling and material removal in softer materials, they lack the precision, multi-axis capability, and tight tolerance control of full CNC milling and turning systems.
Below is a comparative technical specification table highlighting key differences in capabilities, especially with respect to multi-axis machining, tight tolerances, and material compatibility (Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon).
| Feature | Laser Cutting | CNC Router | 3/4/5-Axis CNC Milling | CNC Turning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | 2D profile cutting via focused laser beam | 2.5D to 3D contouring and routing using rotating bit | Multi-directional material removal with high precision | Cylindrical part generation via rotating workpiece |
| Axis Capability | Typically 2-axis (X, Y) | 3-axis standard; 4/5-axis possible with upgrades | Full 3-axis; 4-axis (rotary A); 5-axis (A+B or A+C) | 2-axis (X, Z); multi-axis turning centers with Y/C/B axes |
| Material Compatibility | Metals (thin Al, Steel), Plastics (ABS, Nylon) | Wood, Plastics (ABS, Nylon), non-ferrous metals (soft Al) | Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon, composites, titanium | Aluminum, Steel, brass, plastics (ABS, Nylon) |
| Tolerance Capability | ±0.1 mm – ±0.2 mm (thermal effects) | ±0.05 mm – ±0.1 mm (depends on rigidity) | ±0.005 mm – ±0.025 mm (tight tolerance achievable) | ±0.005 mm – ±0.01 mm (high repeatability) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth cut edge, possible dross on metals | Good on plastics; tool marks on metals | Excellent; fine finishes with proper tooling | Excellent; fine finishes with proper speed/feed |
| Tooling / Cutting Method | Non-contact laser beam | Spinning end mill or router bit | High-speed end mills, ball nose, face mills | Turning inserts (carbide, ceramic) |
| Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) | Yes (especially in metals) | Minimal (mechanical process) | Minimal (controlled cutting) | Minimal (controlled cutting) |
| Ideal Use Cases | Sheet metal cutting, engraving, rapid prototyping | Woodworking, plastic fabrication, mold patterns | Aerospace, medical, high-precision components | Shafts, pins, threaded parts, rotational geometries |
| Limitations | Poor for thick metals; HAZ; no undercut capability | Limited rigidity for steel; not for hardened materials | Higher cost; complex programming | Limited to axisymmetric geometries |
| Multi-Axis Complexity | Not applicable | Limited; 4/5-axis uncommon and less rigid | High; complex contours, undercuts, angled features | High in multi-tasking lathes (with milling) |
Notes on Material Suitability:
Aluminum: Machinable well in all processes except laser cutting of thick sections (>6 mm), where thermal distortion may occur.
Steel: Laser cutting feasible for thin sheets; CNC milling and turning preferred for structural or high-tolerance steel parts.
ABS & Nylon: Easily processed via laser cutting and CNC routing; CNC milling used for tight-tolerance prototypes or end-use parts.
For applications requiring tight tolerances, complex 3D geometry, or high repeatability in engineering-grade materials, 3/4/5-axis CNC milling and CNC turning are superior to both laser cutting and CNC routing. Laser cutting excels in speed and cost for 2D sheet processing, while CNC routing is optimal for non-metal fabrication and large-scale prototyping.
From CAD to Part: The Process

Honyo Prototype Laser Cutting vs CNC Router Process Workflow
Honyo Prototype employs a standardized digital workflow for both laser cutting and CNC routing services, ensuring precision and efficiency from design to delivery. The process begins when a client uploads a CAD file to our secure portal. Our system automatically validates file integrity and compatibility, confirming support for industry-standard formats like DXF, DWG, and STEP. This initial step ensures geometric accuracy and prevents downstream errors.
The uploaded CAD file enters our AI-driven quoting engine, which analyzes key parameters including material type, thickness, part complexity, and quantity. For laser cutting, the AI prioritizes factors such as kerf width, thermal distortion risks, and edge quality requirements. For CNC routing, it evaluates toolpath complexity, spindle speed constraints, and fixturing needs. The quote generated includes process-specific cost drivers, such as laser power consumption for reflective metals or CNC tool wear for abrasive composites. Lead times are dynamically calculated based on machine availability and material procurement.
During Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis, our engineering team conducts a technical review to validate process suitability. Laser cutting is recommended for thin-gauge sheet metal (≤25mm mild steel, ≤12mm aluminum) and non-reflective plastics requiring clean 2D profiles, while CNC routing is advised for thicker substrates, 3D contouring, or materials prone to laser-induced melting (e.g., PVC, polycarbonate). Critical checks include minimum feature sizes—laser cutting typically supports 0.5mm internal radii versus CNC’s 3mm tool diameter limitation—and heat-affected zone assessment for welded assemblies. If conflicts arise, we provide actionable redesign suggestions via our client portal.
Production execution follows strict process protocols. Laser cutting utilizes fiber-optic systems with nitrogen assist gas for oxide-free stainless steel edges or compressed air for cost-effective mild steel cuts. CNC routing employs automated tool changers with carbide-tipped bits optimized for material hardness, applying adaptive clearing strategies to minimize vibration in delicate features. Both processes undergo real-time in-process inspection: laser systems verify focal point accuracy via capacitive height sensors, while CNC machines use probe routines to confirm dimensional compliance mid-run. All operations adhere to ISO 2768-mK geometric tolerances unless tighter specifications are requested.
Final delivery includes comprehensive documentation. Parts ship with first-article inspection reports detailing critical dimensions measured via CMM or optical comparators, along with material certification. Laser-cut components receive edge quality validation per ASTM E3, while CNC-routed parts include surface roughness reports (Ra values). Standard lead time is 3–5 business days post-DFM approval, with expedited options available.
Process Capability Comparison
| Parameter | Laser Cutting | CNC Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Max Material Thickness | 25mm mild steel / 12mm aluminum | 100+mm (material-dependent) |
| Primary Materials | Sheet metal, acrylic, wood | Wood, composites, thick metals |
| Typical Tolerance | ±0.1mm | ±0.05mm |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, dross-free (with assist gas) | Requires post-processing for burrs |
| Feature Limitation | Kerf width (0.1–0.5mm) | Tool diameter (≥3mm standard) |
| Optimal Use Case | High-speed 2D profiles, thin sheets | 3D contours, thick materials |
This integrated workflow ensures clients receive the optimal manufacturing solution based on technical merit, not process preference. Our DFM stage is pivotal in selecting between laser and CNC methods, eliminating assumptions through data-driven analysis of the specific part geometry and functional requirements. All production data is logged for traceability, supporting continuous improvement in future iterations.
Start Your Project
Considering your project requirements, understanding the differences between laser cutting and CNC routing is essential for optimizing precision, material compatibility, and production efficiency. Laser cutting excels in high-precision cuts for thin materials like sheet metal, acrylic, and plastics, using a focused laser beam for clean, detailed results. It’s ideal for intricate designs and fast turnaround. On the other hand, CNC routing offers greater versatility with thicker materials—wood, aluminum, composites—and supports 3D profiling, making it suitable for complex geometries and structural components.
Each method has distinct advantages depending on material type, tolerances, and volume. To determine the best solution for your application, consult with our manufacturing team.
For expert guidance tailored to your design and material needs, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. Our production facility is based in Shenzhen, enabling rapid prototyping and scalable manufacturing with strict quality control.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.