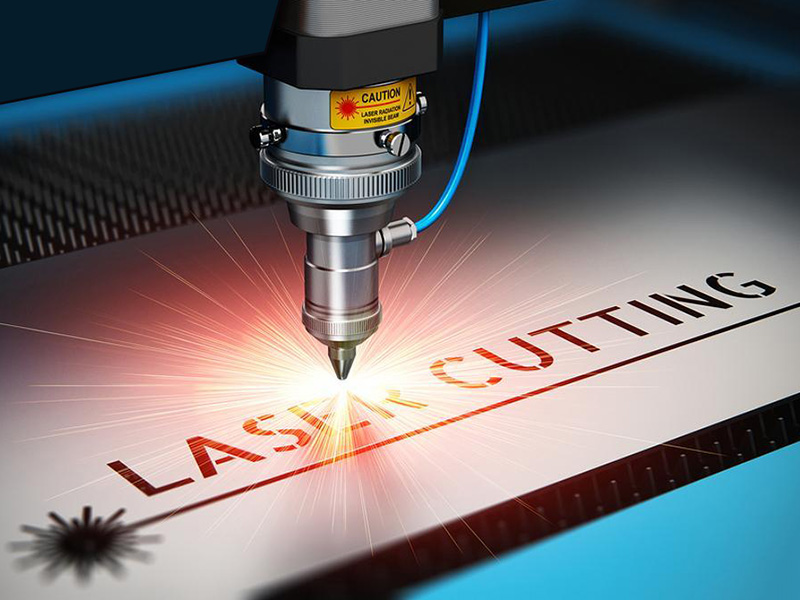
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for laser cutting machine description
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right laser cutting machine can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially when navigating the diverse markets of Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam. Laser cutting machines are essential tools that utilize high-powered laser beams to cut, engrave, or etch a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. Understanding the intricacies of these machines—from their operational technologies to their applications across different industries—is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of laser cutting machines, exploring the various types available, their specific applications, and the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers. Additionally, it covers critical aspects such as cost analysis and operational efficiency, ensuring that buyers can weigh their options effectively. By providing actionable insights and detailed comparisons, this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence. Whether you are looking to enhance manufacturing capabilities or streamline production processes, understanding the nuances of laser cutting technology is imperative for achieving your business objectives.
Understanding laser cutting machine description Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser | Uses a gas mixture; ideal for cutting non-metal materials. | Woodworking, textiles, acrylics | Pros: Versatile for various materials. Cons: Less effective for metals compared to fiber lasers. |
| Fiber Laser | Utilizes fiber optics; excellent for metal cutting. | Aerospace, automotive, and metal fabrication | Pros: High cutting speed and efficiency. Cons: Higher initial investment cost. |
| Nd:YAG Laser | Solid-state laser; suitable for engraving and cutting. | Jewelry making, medical devices | Pros: Good for precision work. Cons: Limited to thinner materials. |
| Hybrid Laser | Combines CO2 and fiber technologies; versatile application. | Diverse industries including signage and packaging | Pros: Flexible for both metal and non-metal materials. Cons: Complexity may require specialized training. |
| Ultrafast Laser | Produces very short pulses; ideal for intricate designs. | Electronics, medical devices, and fine art | Pros: High precision with minimal thermal damage. Cons: Typically more expensive and requires specific applications. |
What Are the Characteristics of CO2 Laser Cutting Machines?
CO2 lasers are recognized for their ability to cut a wide range of non-metal materials, including wood, plastics, and textiles. They operate using a gas mixture that generates a powerful beam, making them suitable for applications in woodworking and signage. When considering a CO2 laser, businesses should evaluate the types of materials they will primarily work with, as this technology excels in non-metals but may not perform as well with metals.
How Do Fiber Laser Cutting Machines Stand Out?
Fiber lasers are distinguished by their use of fiber optics to deliver laser energy, making them particularly effective for cutting metals. They are known for their speed and efficiency, which can significantly enhance productivity in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing. Buyers should consider the long-term operational costs and the potential for reduced maintenance compared to CO2 lasers, as fiber lasers typically have a longer lifespan.
What Are the Benefits of Nd:YAG Laser Cutting Technology?
Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) lasers are solid-state lasers that are primarily used for engraving and cutting thinner materials. They are favored in industries such as jewelry making and medical device manufacturing due to their precision. When purchasing Nd:YAG lasers, B2B buyers should assess the thickness of the materials they intend to process, as this type is limited to less robust applications.
Why Consider Hybrid Laser Cutting Machines?
Hybrid lasers combine the strengths of CO2 and fiber laser technologies, allowing for versatility in cutting both metal and non-metal materials. This adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of industries, including packaging and signage. Buyers should weigh the complexity of operating hybrid systems against their increased flexibility, as these machines may require more specialized training for effective use.
What Are the Applications of Ultrafast Laser Cutting Machines?
Ultrafast lasers produce short pulses that minimize thermal damage, making them ideal for intricate designs in sensitive applications such as electronics and fine art. Their high precision allows for detailed work without affecting the surrounding material. However, the cost of ultrafast lasers can be higher, which makes them more suitable for specialized industries that require advanced technology. B2B buyers should consider their specific application needs and budget constraints when evaluating this option.
Key Industrial Applications of laser cutting machine description
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of laser cutting machine description | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Cutting of precision metal components | Enhances production efficiency and reduces material waste | Machine power, cutting speed, and compatibility with materials |
| Aerospace | Fabrication of complex structural parts | Ensures high accuracy and lightweight components | Regulatory compliance, precision requirements, and material types |
| Automotive | Production of intricate designs and parts | Improves design flexibility and quick prototyping capabilities | Scalability, software integration, and after-sales support |
| Construction | Custom steel and metal fabrication | Speeds up project timelines and reduces labor costs | Size and capacity of the machine, as well as local material sourcing |
| Electronics | Cutting and engraving of circuit boards | Increases production accuracy and allows for intricate designs | Precision specifications and compatibility with electronic materials |
How is Laser Cutting Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, laser cutting machines are employed to produce precision metal components essential for various applications. By utilizing laser technology, manufacturers can achieve intricate cuts with minimal waste, significantly enhancing efficiency. Buyers should consider machine power and cutting speed, as well as the compatibility of the laser cutter with different materials, to ensure optimal performance for their specific production needs.
What Role Does Laser Cutting Play in Aerospace?
The aerospace industry relies on laser cutting for the fabrication of complex structural parts, such as airframes and engine components. The precision of laser cutting allows for lightweight designs that meet stringent safety and performance standards. International buyers in this sector must focus on regulatory compliance, precision requirements, and the types of materials used, as these factors are critical for maintaining quality and safety in aerospace applications.
How is Laser Cutting Beneficial in Automotive Production?
In the automotive sector, laser cutting machines are essential for creating intricate designs and parts, such as brackets and panels. This technology not only enhances design flexibility but also allows for rapid prototyping, enabling manufacturers to bring products to market faster. Buyers should prioritize scalability, software integration, and robust after-sales support when sourcing laser cutting machines, ensuring they can adapt to changing production demands.
Why is Laser Cutting Important for Construction?
Laser cutting plays a vital role in the construction industry, particularly for custom steel and metal fabrication. This technology accelerates project timelines and reduces labor costs by streamlining the cutting process. Buyers should evaluate the size and capacity of the laser cutting machine to match their project requirements, along with the availability of local material sourcing to minimize delays and additional costs.
How Does Laser Cutting Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics, laser cutting and engraving are used for producing circuit boards and intricate designs that require high precision. The ability to create detailed features without damaging surrounding areas significantly improves production accuracy. Buyers in this field need to focus on the precision specifications of the laser cutting machine and its compatibility with various electronic materials to ensure high-quality outputs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘laser cutting machine description’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Material Compatibility Assessment
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with determining which materials their laser cutting machines can effectively process. With a diverse range of materials available—such as metals, plastics, and wood—buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by the technical specifications and limitations associated with each material type. For instance, a manufacturer may invest in a CO2 laser cutting machine, only to discover later that it’s not suitable for the specific metal thickness they require, leading to costly production delays and wasted resources.
The Solution:
To overcome this challenge, buyers should prioritize conducting thorough research on the material compatibility of their chosen laser cutting machine before making a purchase. This can be achieved by consulting the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines, which typically include a list of materials and their respective thicknesses that can be processed. Additionally, buyers can reach out to industry experts or suppliers for recommendations based on their specific applications. It’s also beneficial to request samples or demonstrations to see how the laser cutter performs on various materials. This proactive approach will not only ensure that the right equipment is selected but also enhance operational efficiency by reducing trial-and-error in production.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Understanding of Software Requirements
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter issues related to the software needed for operating laser cutting machines. The process involves generating G-code through CAD/CAM software, which can be a significant hurdle for companies without the necessary technical expertise or resources. For instance, a small fabrication shop might invest in advanced laser cutting technology but struggle to produce the required design files, ultimately leading to underutilization of the equipment and missed business opportunities.
The Solution:
To effectively address this pain point, businesses should invest in training for their staff on the specific software used with their laser cutting machines. This could involve enrolling in workshops or online courses focused on CAD and CAM systems relevant to their operations. Additionally, companies should consider partnering with software vendors who offer comprehensive support and resources, including tutorials and troubleshooting assistance. By enhancing their team’s proficiency in software operation, businesses can maximize the utilization of their laser cutting equipment, streamline production processes, and reduce dependency on external services for design file generation.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Processes
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges related to the operational costs associated with running laser cutting machines. Inefficient processes, such as excessive material waste or prolonged machine downtimes due to improper setup, can significantly inflate production costs. For example, a company might find that its laser cutting operations are not as cost-effective as anticipated because of frequent adjustments and maintenance needs, leading to frustration and financial strain.
The Solution:
To mitigate these issues, buyers should implement best practices for operational efficiency. This includes conducting regular maintenance on laser cutting machines to ensure optimal performance and prevent unexpected downtimes. Additionally, investing in advanced monitoring tools can provide real-time insights into machine performance, allowing for proactive adjustments and minimizing material waste. Companies should also analyze their cutting processes to identify areas for improvement, such as optimizing cutting speeds and adjusting power settings based on material thickness and type. By focusing on operational excellence, businesses can significantly reduce costs and enhance the profitability of their laser cutting operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for laser cutting machine description
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Laser Cutting Machines?
Laser cutting technology is widely utilized across various industries, and the choice of material significantly influences the performance and application of laser cutting machines. Understanding the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for different materials is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Laser Cutting Applications?
Steel is one of the most commonly cut materials using laser technology. Its properties, such as high strength and durability, make it suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive and structural components. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Steel offers excellent durability and strength, which translates to longer-lasting products. It is also relatively cost-effective, particularly in bulk purchases.
Cons: The manufacturing complexity can increase with the thickness of the steel, requiring more powerful laser systems. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings for specific applications.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media, including automotive parts and structural frameworks, but its weight can be a consideration in design.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, particularly concerning corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Laser Cutting Processes?
Aluminum is another popular material for laser cutting due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It is often used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods.
Pros: Aluminum’s low weight contributes to reduced transportation costs and easier handling. Its corrosion resistance is advantageous for outdoor applications.
Cons: Aluminum can be more expensive than steel, and its thermal conductivity can lead to challenges in cutting, requiring adjustments in laser settings.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in the aerospace sector, but its higher cost can be a limiting factor for some projects.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like JIS for aluminum specifications is essential, particularly for industries with strict quality requirements.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastics in Laser Cutting?
Plastics, including acrylic and polycarbonate, are frequently used in laser cutting for signage, packaging, and various consumer products. Their versatility and ease of cutting make them attractive options.
Pros: Plastics are generally less expensive than metals and can be cut quickly with minimal waste. They also offer a wide range of colors and finishes.
Cons: Plastics can be less durable than metals and may not withstand high temperatures, limiting their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: The compatibility of plastics with various design applications, such as promotional materials and displays, is significant, but their lower durability can be a drawback.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of material certifications and compliance with local regulations regarding plastic usage, especially in packaging applications.
How Does Wood Compare in Laser Cutting Applications?
Wood is a traditional material used in laser cutting, particularly for decorative items, furniture, and architectural elements. Its natural properties offer unique aesthetic advantages.
Pros: Wood is widely available and relatively inexpensive. It can be cut and engraved with high precision, allowing for intricate designs.
Cons: Wood is susceptible to warping and can be affected by moisture, which may impact the final product’s quality. Additionally, the cutting process can produce smoke and residue that require proper ventilation.
Impact on Application: Wood is suitable for artistic applications but may not be ideal for high-stress environments due to its physical limitations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider local wood regulations and sustainability certifications, especially in regions with strict environmental standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Laser Cutting
| Material | Typical Use Case for laser cutting machine description | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Automotive and structural components | High strength and durability | Corrosion susceptibility | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive lightweight parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and thermal cutting issues | High |
| Plastics | Signage and packaging | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable and temperature sensitive | Low |
| Wood | Decorative items and furniture | Aesthetic appeal and availability | Susceptible to warping and moisture | Low |
By understanding these materials and their implications for laser cutting applications, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and industry standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for laser cutting machine description
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Laser Cutting Machines?
The manufacturing process of laser cutting machines is a complex procedure that involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product meets the stringent requirements of precision engineering and quality assurance.
How is Material Prepared for Laser Cutting Machines?
The first step in manufacturing a laser cutting machine is material preparation. This includes selecting high-quality raw materials such as steel, aluminum, and specialized optics. The choice of materials is crucial, as they must withstand high temperatures and pressures generated during laser operations.
Once selected, materials undergo cutting and machining processes to achieve the desired dimensions. This might involve the use of CNC machines for precision cutting. The prepared materials are then cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect the machine’s performance.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Laser Cutting Machine Manufacturing?
The forming stage typically involves the fabrication of various components, including the frame, laser resonator, and motion systems. Techniques such as welding, bending, and milling are employed to shape these components into functional parts.
For instance, the frame of a laser cutting machine must be robust enough to handle vibrations and mechanical stresses during operation. Welding is often used to join metal pieces, ensuring structural integrity. Additionally, advanced techniques like laser sintering may be used for creating complex geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve.
How Are Laser Cutting Machines Assembled?
Assembly is where all the prepared and formed components come together. This stage requires skilled technicians who follow detailed assembly instructions to ensure that every part fits perfectly.
Key elements such as the laser source, optics, and CNC controls are integrated during this phase. Calibration is critical to ensure that the laser aligns correctly with the cutting bed. This step often involves extensive testing to confirm that all systems work harmoniously, which is essential for achieving precise cutting results.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for Laser Cutting Machines?
The final stage, finishing, focuses on enhancing the durability and aesthetic appeal of the machine. This may include surface treatments such as painting, anodizing, or powder coating to protect against corrosion and wear.
Moreover, final inspections are conducted to ensure that all components meet quality specifications. This stage is crucial because even minor imperfections can significantly impact the machine’s performance and longevity.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Laser Cutting Machines?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of laser cutting machines. It encompasses a series of processes and standards designed to ensure that each machine meets international quality benchmarks.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that comply with internationally recognized standards such as ISO 9001. This certification indicates a commitment to quality management systems, ensuring consistent product quality and operational efficiency.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for compliance with European safety standards or API specifications for oil and gas applications can provide added assurance of quality. For buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, understanding these certifications can help navigate local regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining product quality throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter production to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help identify issues early, preventing defects from progressing to later stages.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough examination of the finished machine ensures it meets all performance and safety standards before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to strict quality control measures, B2B buyers should consider conducting audits and requesting detailed QC reports. Engaging third-party inspection services can also provide an unbiased assessment of a manufacturer’s quality practices.
Buyers should ask for evidence of compliance with quality standards, including documentation of inspections and testing results. This transparency helps build trust and ensures that the purchased machines will perform reliably in demanding industrial environments.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of laser cutting machines. These may include:
- Functional Testing: Verifying that all machine functions, including cutting speed and precision, meet specified standards.
- Safety Testing: Ensuring compliance with safety regulations to protect operators and prevent accidents.
- Durability Testing: Assessing how well the machine withstands prolonged usage under various conditions.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers, particularly from diverse regions like the Middle East, Africa, and Europe, should be cognizant of the varying quality control expectations and standards across different markets. For instance, while European standards may emphasize stringent safety protocols, buyers in other regions may prioritize cost-effectiveness and rapid delivery.
Understanding these nuances is essential for negotiating terms and ensuring that the final product aligns with local market demands and regulations. Engaging local representatives or consultants can also help navigate these complexities and facilitate smoother transactions.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with laser cutting machines can significantly enhance the purchasing decisions of B2B buyers. By considering these factors, buyers can ensure they invest in reliable, high-quality machinery that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘laser cutting machine description’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring laser cutting machines. With the increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries, understanding the key elements in selecting the right machine is critical. This guide will help you navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring that you make informed decisions tailored to your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential before starting your search for a laser cutting machine. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will be cutting (e.g., metal, plastic, wood), the maximum thickness of these materials, and the desired cutting speed. This clarity will help you focus on machines that meet your specific operational requirements.
Step 2: Research Different Laser Cutting Technologies
Understanding the various types of laser cutting technologies available—such as CO2, fiber, and Nd:YAG—is vital. Each technology has its unique advantages and limitations regarding material compatibility, cutting speed, and operational costs. Familiarizing yourself with these differences will enable you to select a machine that aligns with your production goals and budget.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it’s crucial to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries. Look for suppliers that have a proven track record of reliability and customer satisfaction, as this can significantly impact your machine’s operational success.
Step 4: Check for Compliance and Certifications
Verify that the laser cutting machines and suppliers comply with international safety and quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or CE mark are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality and safety regulations. Ensuring compliance helps mitigate risks and ensures that your investment meets industry standards.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Training
Inquire about the after-sales support and training provided by the supplier. A reputable supplier should offer comprehensive training for your team and ongoing technical support. This service is crucial for maximizing the machine’s capabilities and minimizing downtime during operations.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Whenever possible, request demonstrations or trial periods before making a final decision. Observing the machine in action will provide insights into its performance, ease of use, and overall efficiency. This step can help you avoid costly mistakes by ensuring that the machine meets your operational standards.
Step 7: Compare Total Cost of Ownership
Finally, evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for each machine you are considering. This includes not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing operating costs, maintenance, and potential upgrades. A thorough TCO analysis will enable you to make a more informed financial decision that aligns with your long-term business objectives.
By following this checklist, you will be better equipped to source a laser cutting machine that meets your operational needs and supports your business growth effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for laser cutting machine description Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Laser Cutting Machine Sourcing?
When sourcing laser cutting machines, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. Common materials for laser cutting machines include high-grade steel and specialized optics for the laser itself. The cost varies based on the quality and the specific applications they are designed for.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing, assembling, and testing the laser cutting machines. Regions with higher labor costs, like Europe, may have a different pricing structure compared to countries in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and other operational costs incurred during production. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, making it crucial for buyers to assess suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the creation of molds and fixtures necessary for the production of laser cutting machines. Custom tooling can escalate costs, especially for specialized machines designed for unique applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are vital in ensuring that laser cutting machines meet industry standards. Higher QC costs can reflect in the final price but are often necessary for reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs should be considered, especially for international buyers. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) will dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact overall pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding typical margins in different regions can help in negotiating better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Laser Cutting Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of laser cutting machines, making it essential for buyers to recognize these when negotiating.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk can often lead to discounts. Suppliers may offer better pricing for larger orders, which can significantly reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized machines tailored to specific needs can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (like ISO standards) typically come with a premium price. However, investing in certified machines can lead to lower maintenance and operational costs in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a critical role. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, but they often provide better support and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. The terms determine the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, which can affect the total landed cost of the machine.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Laser Cutting Machine Purchases?
To maximize value when sourcing laser cutting machines, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Always approach negotiations with a clear understanding of the market price and the total cost of ownership (TCO). Leverage competitive quotes from different suppliers to enhance your bargaining position.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: TCO includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and expected lifespan. A cheaper machine might incur higher operating costs, making it less economical in the long term.
-
Consider Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Factors such as currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes can significantly impact costs. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should factor these into their budgets.
-
Research and Benchmark: Conduct thorough research to benchmark prices and specifications across different suppliers. This will help identify the best value for money.
-
Stay Informed on Trends: The laser cutting technology landscape is evolving rapidly. Staying updated on the latest advancements can provide insights into future pricing trends and potential cost savings.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for laser cutting machines can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. The costs discussed are indicative and may not reflect current market conditions. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their own market research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing laser cutting machine description With Other Solutions
When considering manufacturing solutions for cutting materials, it is crucial to evaluate various technologies to determine the best fit for specific business needs. Laser cutting machines are widely recognized for their precision and versatility, but alternatives may offer distinct advantages depending on the application. Below, we compare laser cutting machines with plasma cutting and waterjet cutting technologies, two viable alternatives in the market.
| Comparison Aspect | Laser Cutting Machine Description | Plasma Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, ideal for intricate designs | Fast cutting speed, good for thick materials | Excellent for various materials, no heat distortion |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, but low operational costs | Moderate initial costs, consumables needed | Higher operational costs, expensive equipment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and CAD software | Easier to operate, less training needed | More complex setup, requires water recycling systems |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required, sensitive optics | Moderate maintenance, consumables need replacement | High maintenance, water filtration systems need upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for detailed metal, plastic, and wood cutting | Best for thick metals and quick jobs | Versatile for materials like glass, ceramics, and metals |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Plasma Cutting?
Plasma cutting utilizes a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through materials. One of its primary advantages is speed; plasma cutters can operate much faster than laser cutters, making them suitable for high-volume production of thicker materials. However, while plasma cutting is efficient for thicker metals, it lacks the precision of laser cutting, which can be a significant drawback for applications requiring intricate designs. Additionally, the quality of the cut edge may not be as smooth, necessitating further finishing processes.
How Does Waterjet Cutting Compare?
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure jet of water mixed with abrasive materials to cut through various materials, including metals, plastics, and even stone. One of the standout features of waterjet technology is its ability to cut without generating heat, which prevents thermal distortion—a critical factor for sensitive materials. However, the initial investment and operational costs can be higher than laser cutting due to the complexity of the equipment and the need for water recycling systems. Waterjet cutting is also slower than laser cutting, making it less ideal for high-speed applications.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Cutting Solution?
Selecting the appropriate cutting technology involves evaluating the specific requirements of your manufacturing process. Laser cutting machines excel in precision and versatility for intricate designs, making them suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive. Plasma cutting is advantageous for rapid, heavy-duty tasks, while waterjet cutting offers versatility across various materials without heat distortion. B2B buyers should consider factors such as material type, production volume, cost constraints, and the required precision level when making their decision. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and limitations of each method will empower buyers to choose the best solution for their unique operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for laser cutting machine description
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Laser Cutting Machines?
When considering the purchase of a laser cutting machine, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for making informed decisions. Here are several essential properties to consider:
-
Material Compatibility
Laser cutting machines can process a variety of materials, including metals (like steel and aluminum), plastics, wood, and composites. The choice of material influences the machine’s design and capabilities. For B2B buyers, knowing the compatible materials is essential to ensure the machine meets specific production needs. -
Cutting Thickness
This specification indicates the maximum thickness of material the machine can cut effectively. Different laser technologies (CO2, Fiber, Nd:YAG) have varying capabilities in terms of thickness. Understanding the cutting thickness is critical for manufacturers as it affects the range of projects that can be undertaken, thus impacting operational efficiency and market competitiveness. -
Laser Power (Wattage)
The power of the laser, measured in watts, directly influences the cutting speed and quality. Higher wattage allows for faster cutting and the ability to process thicker materials. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate wattage is vital to balance production speed with operational costs. -
Precision and Tolerance
Precision refers to the accuracy of the cuts made by the laser, while tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from specified dimensions. High precision and tight tolerances are crucial in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where component fitment is critical. For businesses, investing in machines with superior precision can lead to reduced waste and improved product quality. -
Speed of Operation
Measured in inches per minute (IPM), this specification indicates how quickly the machine can cut through materials. Speed is a key factor for productivity and can significantly affect lead times. B2B buyers should evaluate their production schedules and choose a machine that aligns with their operational requirements. -
Software Compatibility
The ability to integrate with CAD/CAM software is essential for modern laser cutting machines. This compatibility allows for efficient design-to-production workflows. Businesses should consider the software ecosystem of the laser cutter to ensure seamless operations, particularly in industries where rapid prototyping and design iteration are common.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Laser Cutting Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for reliable suppliers of laser cutting machines or components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for businesses looking to optimize inventory costs and negotiate favorable purchasing agreements. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the context of laser cutting machines, submitting an RFQ can help buyers gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple vendors. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping and delivery obligations. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to manage logistics and costs effectively. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
This technology allows machines to be controlled via computer programming. In laser cutting, CNC systems enable precise control over the laser’s movements, which is vital for achieving the desired cutting patterns and efficiencies. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between the initiation of a process and its completion. In the context of laser cutting, it encompasses manufacturing time, delivery, and setup. Understanding lead times is essential for effective project management and client satisfaction.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting laser cutting machines, ultimately enhancing their operational capabilities and market positioning.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the laser cutting machine description Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing Laser Cutting Machine Descriptions?
The laser cutting machine sector is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for precision manufacturing, and the need for cost-effective production processes. Globally, industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are increasingly adopting laser cutting technology due to its ability to deliver high-quality finishes and intricate designs. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are particularly capitalizing on these advancements as they seek to enhance their manufacturing capabilities. For international B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
One notable trend is the shift towards automation and integration of Industry 4.0 principles. Laser cutting machines are now being equipped with smart technology that allows for real-time monitoring, data analytics, and connectivity with other manufacturing systems. This enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, making laser cutting an attractive option for manufacturers looking to optimize their processes. Moreover, with the rise of e-commerce and just-in-time manufacturing, buyers are increasingly interested in flexible sourcing options that can accommodate rapid changes in demand.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Laser Cutting Machines?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the sourcing of laser cutting machines. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. The laser cutting process, while efficient, can have environmental impacts, including energy consumption and waste generation. Therefore, companies are exploring options for energy-efficient machines that utilize less power while maintaining high performance.
Ethical sourcing is also crucial. Buyers are encouraged to assess the supply chain for transparency and adherence to environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of eco-friendly materials in machine manufacturing can guide sourcing decisions. Additionally, integrating ‘green’ technologies, such as laser machines that utilize renewable energy sources or produce minimal waste, is becoming a competitive advantage. This trend not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to environmentally conscious customers.
What Is the Evolution of Laser Cutting Technology in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of laser cutting technology has profoundly shaped the manufacturing landscape. Initially developed in the 1960s for industrial applications, the technology has undergone significant advancements. The introduction of computer numerical control (CNC) systems revolutionized the precision and repeatability of laser cutting.
As technology progressed, different types of lasers—such as CO2, fiber, and Nd:YAG—were developed, each offering unique benefits for various materials. In recent years, the convergence of laser cutting with digital technologies has paved the way for innovative applications across diverse industries. Today, laser cutting machines are not just tools for cutting; they are integrated into smart factories, where they contribute to automation, customization, and enhanced production capabilities.
This evolution is essential for B2B buyers to understand as they seek modern solutions that meet the demands of a rapidly changing market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of laser cutting machine description
-
How do I choose the right laser cutting machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right laser cutting machine involves assessing your specific requirements, such as the types of materials you will cut, thicknesses, and production volume. Consider the technology type (CO2, Fiber, Nd:YAG) based on your material preferences; for instance, fiber lasers are excellent for metals, while CO2 lasers excel in cutting non-metal materials. Evaluate machine specifications, including cutting speed, precision, and power, alongside your budget. Lastly, consider the manufacturer’s reputation and after-sales support for maintenance and troubleshooting. -
What are the key features to look for in a laser cutting machine?
Key features to consider include laser type and power, cutting area size, speed, and precision. Look for advanced CNC controls for ease of programming and operation. Ensure the machine has a reliable cooling system to maintain optimal performance during extended use. Additionally, consider safety features such as enclosed cutting areas and emergency stop buttons. Lastly, compatibility with CAD/CAM software can streamline your workflow by facilitating easy design imports. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering a laser cutting machine?
Lead times for laser cutting machines can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, model, and customization requirements. Standard models may have a lead time of 4 to 12 weeks, while custom solutions could take longer, potentially up to 6 months. It’s essential to communicate your timeline needs with suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure timely delivery. Always confirm the lead time during the ordering process and inquire about any potential delays. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) when sourcing laser cutting machines?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for laser cutting machines can vary by supplier and region. Many manufacturers may set MOQs based on production capabilities, with some offering single units, while others may require a minimum of three or more. For bulk orders, you might negotiate better pricing or terms. Always clarify MOQs before engaging in discussions to avoid misunderstandings and to ensure that your order aligns with your operational needs. -
How do I vet suppliers for laser cutting machines internationally?
To vet international suppliers, start by researching their market reputation and customer reviews. Check their certifications, such as ISO, which indicate quality assurance standards. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their experience with the supplier. Visit their facilities if possible or opt for virtual tours. Additionally, consider their after-sales support, warranty policies, and responsiveness to inquiries as indicators of reliability and professionalism. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted when purchasing laser cutting machines?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upon order confirmation (typically 30-50%) with the balance due prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms during negotiations, including any penalties for late payments. Always ensure that payment methods are secure, and consider using escrow services for large transactions to protect your investment. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from laser cutting machine suppliers?
Quality assurance measures should include comprehensive testing of the machine before shipment, including calibration and performance checks. Suppliers should provide documentation of these tests, including certification of compliance with international standards. Look for warranties that cover defects and consider suppliers who offer training on machine operation and maintenance. Regular maintenance support and availability of spare parts are also critical components of a robust quality assurance program. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing laser cutting machines?
When importing laser cutting machines, consider shipping methods, costs, and potential customs duties. Choose a logistics partner experienced in handling industrial equipment to ensure safe transport. Understand the import regulations in your country, including necessary documentation and compliance with local standards. Additionally, factor in lead times for customs clearance and delivery to avoid unexpected delays. It’s also prudent to have insurance coverage during transit to safeguard against damage or loss.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Laser Cutting Machine Description Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AMS – Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: ams-fa.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: A laser cutting machine is a powerful and versatile tool used across various industries to cut, engrave, or etch materials with precision and speed. It operates using focused laser beams generated by gas lasers (like CO2) or solid-state lasers (like fiber lasers). The process involves several steps: design and programming using CAD software, material preparation, laser setup, cutting, and finishin…
2. All3DP – Laser Cutters
Domain: all3dp.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: A laser cutter is a machine that uses a focused beam of light to cut or engrave materials. It operates by directing the laser beam onto the material, which is then melted, burned, or vaporized away. Laser cutters are commonly used for various applications, including woodworking, metal fabrication, and crafting. They can work with a wide range of materials such as wood, acrylic, leather, and metal….
3. Ametals – Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: ametals.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Laser cutting machines are a type of computer numerical control (CNC) machine used for high-speed cutting with extreme accuracy in sheet metal services. They operate by using a laser source that produces powerful, consistent light, which is focused and redirected to cut through various materials. The most common types of laser cutting machines are CO2 and fiber lasers. CO2 lasers are affordable an…
4. ADHMT – Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: adhmt.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Laser cutting machines utilize a high-power-density laser beam for cutting, engraving, and drilling materials with high precision and efficiency. They are essential in modern manufacturing, applicable in metalworking, artistic creation, and the medical field. Key components include a laser generator, optical system for focusing, and a CNC system for cutting path control. Major types include CO₂ la…
5. Trumpf – Laser Cutting Solutions
Domain: trumpf.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Laser cutting is a contact-free slitting process that can cut metallic and non-metallic raw materials of varying thicknesses, from 0.5 to over 30 millimeters. It utilizes a focused laser beam that heats the material to the point of melting or vaporization, allowing for precise cuts without wear on the tool or damage to the workpiece. The process is suitable for a wide range of materials, including…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for laser cutting machine description
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers Considering Laser Cutting Machines?
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, laser cutting machines stand out for their precision, versatility, and efficiency. These machines leverage advanced technologies such as CO2, Fiber, and Nd:YAG lasers, making them suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the specific applications and operational capabilities of these machines is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Strategic sourcing not only enhances cost-effectiveness but also ensures access to the latest technologies and support services. By collaborating with reputable suppliers, businesses can optimize their production processes, reduce lead times, and improve product quality. This is particularly vital in competitive markets where efficiency and innovation drive success.
How Can International Buyers Position Themselves for Future Opportunities?
As the demand for customized and high-precision components continues to rise, investing in advanced laser cutting technology can provide a significant competitive edge. Buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers who offer comprehensive training and support, ensuring that their teams are well-equipped to utilize these machines effectively.
Looking ahead, the integration of automation and AI in laser cutting processes will further enhance productivity and capabilities. Now is the time to explore these advancements and position your business for future growth in the global marketplace. Take action today to secure the best laser cutting solutions that meet your specific needs and drive your business forward.