Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for laser cnc machine for metal
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing a laser CNC machine for metal can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Companies often grapple with the challenge of balancing cost-efficiency with advanced technology to meet their production needs. This guide aims to simplify that process by providing a comprehensive overview of the laser CNC machine market, including various types, applications, supplier vetting strategies, and cost considerations.
From understanding the advantages of fiber lasers over traditional CO2 models to exploring the latest innovations that enhance precision and efficiency, this guide equips buyers with the insights necessary to make informed decisions. Additionally, we delve into the operational benefits, such as reduced running costs and the potential for a quick return on investment, which can significantly impact a company’s bottom line.
By addressing common pain points and providing actionable intelligence, this guide serves as a valuable resource for businesses looking to invest in laser CNC machines. Whether you are in Vietnam, Brazil, or any other emerging market, our goal is to empower you with the knowledge to navigate the global market confidently and strategically, ensuring your investments align with your operational goals and industry demands.
Understanding laser cnc machine for metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Laser Cutting Machines | High efficiency, low operating costs, and excellent precision. | Automotive components, metal signage, and prototypes. | Pros: Fast cutting speeds, low maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| CO2 Laser Cutting Machines | Versatile for a range of materials, including non-metals. | Decorative items, packaging, and engraving. | Pros: Good for diverse applications. Cons: Less efficient for metals than fiber lasers. |
| Tube and Pipe Laser Cutters | Specialized for cutting metal tubes and profiles. | Structural components, furniture, and automotive parts. | Pros: Precise cuts for complex shapes. Cons: Limited to tube and pipe applications. |
| Hybrid Laser Cutting Systems | Combines fiber and CO2 technologies for versatile cutting. | Aerospace, jewelry, and intricate designs. | Pros: Flexibility in material types. Cons: More complex operation and maintenance. |
| Portable Laser Cutting Machines | Compact and mobile, ideal for on-site cutting. | Construction, repairs, and small-scale fabrication. | Pros: Easy transport and setup. Cons: Limited cutting power and sheet size. |
What Are Fiber Laser Cutting Machines and Their B2B Benefits?
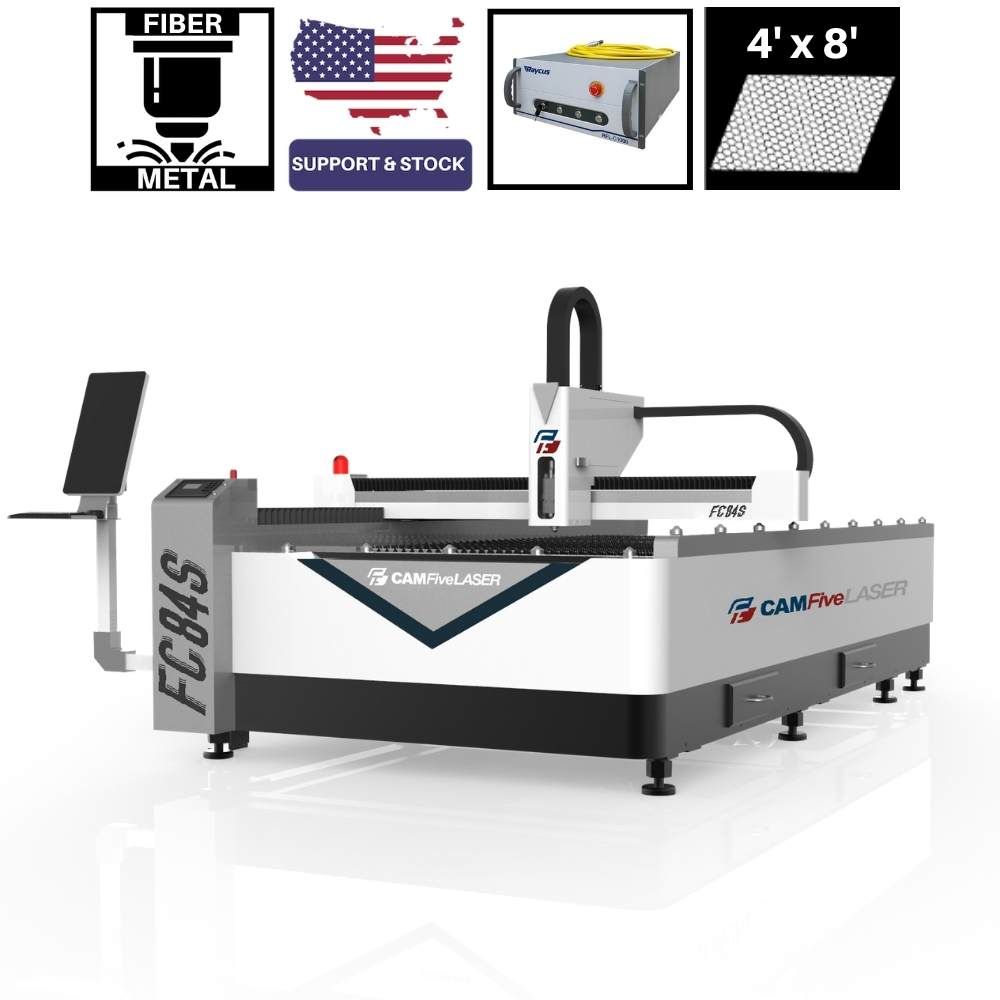
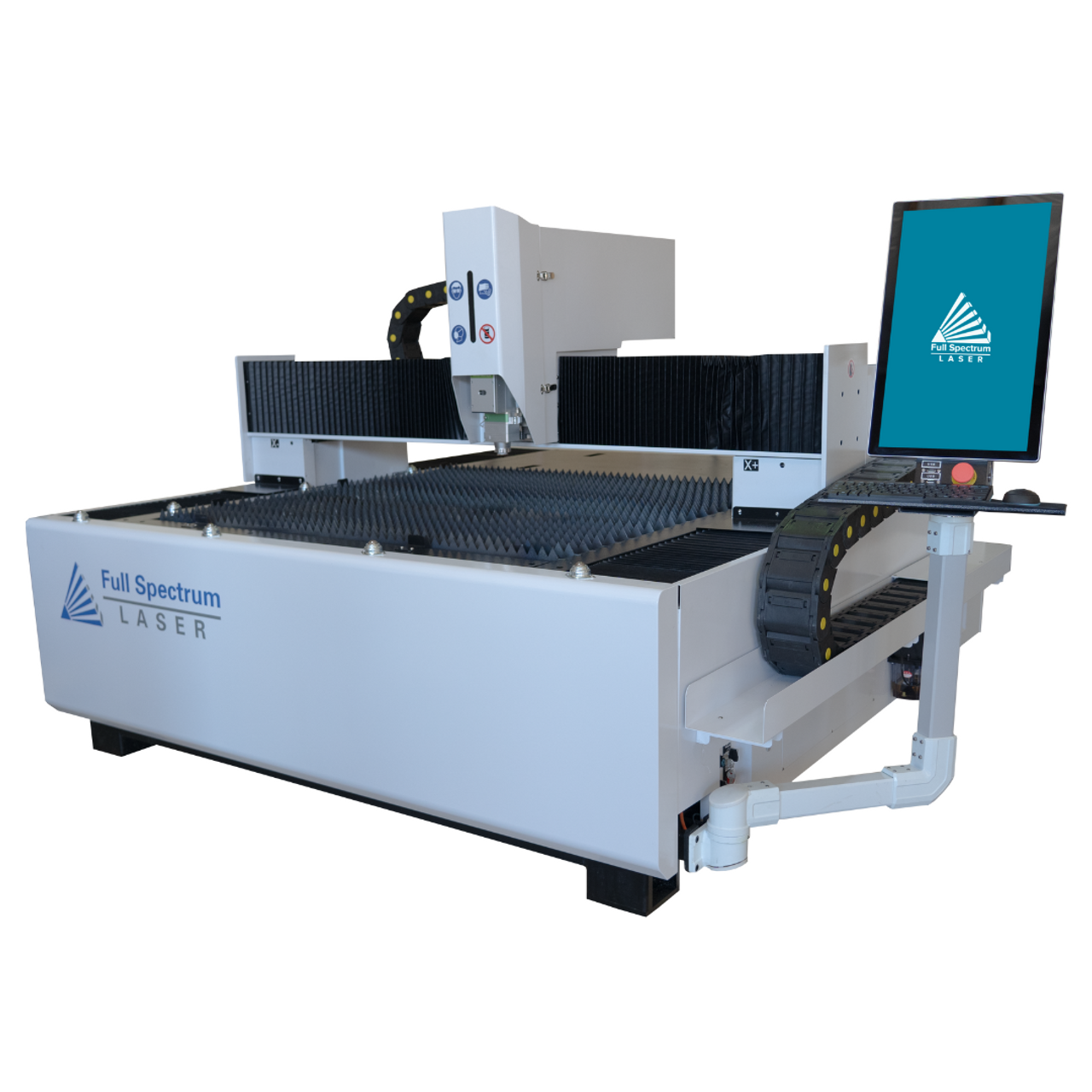
Fiber laser cutting machines are renowned for their high efficiency and precision, making them ideal for industries such as automotive and metal signage. They utilize solid-state lasers that offer lower operational costs due to their energy efficiency and longevity. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment versus the long-term savings on operational costs. These machines are particularly suitable for businesses looking for speed and high-quality cuts in thicker materials.
How Do CO2 Laser Cutting Machines Compare for B2B Applications?
CO2 laser cutting machines are highly versatile and can work with various materials, including plastics and wood, alongside metals. They are often used in decorative applications, packaging, and engraving due to their ability to produce intricate designs. For B2B buyers, the key consideration is the balance between versatility and cutting efficiency, especially when working primarily with metals. While they are suitable for lighter applications, businesses focused on metal fabrication may find fiber lasers more advantageous.
What Are the Advantages of Tube and Pipe Laser Cutters in B2B Settings?
Tube and pipe laser cutters are specialized systems designed to handle the unique challenges of cutting cylindrical materials. They are widely used in industries such as construction and automotive, where precise cuts are necessary for structural integrity. B2B buyers should evaluate their production needs against the capabilities of these machines, as they excel in creating complex profiles but are limited to specific applications.
Why Choose Hybrid Laser Cutting Systems for Diverse Needs?
Hybrid laser cutting systems combine the strengths of both fiber and CO2 lasers, allowing for flexibility across different materials and applications. This versatility makes them suitable for sectors like aerospace and jewelry, where intricate designs and various material types are common. Buyers should consider their production environment and the range of materials they work with when investing in a hybrid system, as it can streamline operations across multiple projects.
What Are the Key Considerations for Portable Laser Cutting Machines?
Portable laser cutting machines offer the advantage of mobility, making them perfect for on-site applications such as construction and repairs. While they are easy to transport and set up, buyers must weigh the limitations in cutting power and material thickness against the convenience they provide. These machines are best suited for small-scale operations that require quick setup and execution without the need for heavy, stationary equipment.
Key Industrial Applications of laser cnc machine for metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of laser cnc machine for metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Precision cutting of automotive panels and components | Improved accuracy and reduced material waste | Power requirements, cutting speed, and material compatibility |
| Aerospace | Fabrication of lightweight structural components | Enhanced performance and fuel efficiency | Certification standards, material types, and precision requirements |
| Metal Fabrication Services | Custom metal parts production | Rapid turnaround and lower operational costs | Machine size, versatility in cutting different metals, and maintenance support |
| Jewelry Manufacturing | Intricate designs for jewelry pieces | High precision and reduced post-processing needs | Laser power settings and software compatibility for design files |
| Construction and Architecture | Fabrication of metal frameworks and decorative elements | Cost-effective production and design flexibility | Material specifications, cutting thickness, and machine adaptability |
How is Laser CNC Machinery Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, laser CNC machines are crucial for cutting and shaping various components such as panels, frames, and brackets. The precision of laser cutting minimizes material waste and ensures that parts fit perfectly during assembly. This is particularly beneficial for manufacturers in Africa and South America, where reducing costs while maintaining quality is essential. Buyers should consider the machine’s power requirements and cutting speed to match their production needs effectively.
What Role Does Laser CNC Machinery Play in Aerospace Fabrication?
Aerospace manufacturers utilize laser CNC machines to fabricate lightweight structural components, which are vital for enhancing aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. The ability to cut complex shapes with high precision allows for innovative designs that meet stringent safety standards. International buyers in the Middle East and Europe must focus on sourcing machines that meet certification standards and can handle specific aerospace materials like titanium and aluminum.
How Do Metal Fabrication Services Benefit from Laser CNC Machines?
Metal fabrication services leverage laser CNC machines for producing custom parts rapidly and efficiently. The machines can handle various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, providing versatility for different client needs. For businesses in South America and Africa, this technology can significantly reduce operational costs and turnaround times. Key considerations for buyers include the machine’s size, versatility, and the availability of maintenance support to ensure ongoing productivity.
In What Ways is Laser CNC Machinery Used in Jewelry Manufacturing?
In jewelry manufacturing, laser CNC machines are employed to create intricate designs and detailed engravings on various metals. The precision cutting capabilities reduce the need for extensive post-processing, allowing jewelers to produce high-quality pieces quickly. Buyers in Europe and Asia should prioritize machines that offer adjustable power settings and compatibility with design software to streamline their production processes.
How is Laser CNC Machinery Transforming Construction and Architecture?
Laser CNC machines are increasingly used in the construction and architecture sectors for fabricating metal frameworks and decorative elements. The technology enables cost-effective production while allowing for complex designs that enhance aesthetic appeal. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East should focus on machines that can accommodate different material specifications and cutting thicknesses to meet diverse project requirements efficiently.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘laser cnc machine for metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Operating Costs and Low Efficiency
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are concerned about the high operating costs associated with running a laser CNC machine for metal. These costs can stem from energy consumption, maintenance, and the expense of outsourced cutting services. For businesses operating in regions with fluctuating energy prices or limited access to affordable materials, these factors can significantly impact profitability. Buyers may find themselves at a crossroads, needing to balance machine operation costs with the quality and speed of their production processes.
The Solution: To mitigate high operating costs, B2B buyers should consider investing in energy-efficient fiber laser CNC machines, which typically have lower energy consumption compared to traditional CO2 lasers. Machines like the Atlas Alloy Flatbed Fiber Laser, which operates at a lower power draw (less than 2kW) and utilizes inexpensive cutting gases such as nitrogen or oxygen, can reduce operational expenses significantly—sometimes costing as little as $0.25 per hour in gas and electricity. Additionally, buyers should prioritize machines with features like closed-loop servo motors for rapid, precise cutting, as these can enhance efficiency and reduce waste. Regular maintenance and using quality consumables can further minimize unexpected costs, ensuring that the machine operates at peak efficiency.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Material Compatibility
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in cutting different types of metals, especially when they deal with a diverse range of materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. A machine that excels at one material may struggle with another, leading to inconsistent quality and increased production times. This issue is particularly pressing for businesses in sectors like automotive manufacturing or custom fabrication, where precision and versatility are crucial.
The Solution: To address material compatibility challenges, buyers should look for laser CNC machines that offer a wide range of power options and advanced cutting capabilities. Machines like the Hytek Tools Fiber Laser, which can handle various metals and thicknesses, allow for greater flexibility in production. Buyers should also ensure that the machine is equipped with adjustable settings for speed and focus, enabling them to fine-tune the process for different materials. Additionally, investing in training for operators on how to adjust settings based on material type can lead to improved cutting quality and efficiency. Collaborating with suppliers who provide detailed material specifications and cutting recommendations can also facilitate better results.
Scenario 3: Limited In-House Expertise for Machine Operation
The Problem: Many companies encounter a skill gap when it comes to operating advanced laser CNC machines. With the rapid advancement of technology, operators may lack the necessary training to fully utilize the machine’s capabilities, which can lead to underperformance and suboptimal production outcomes. This is a common pain point for businesses in developing regions where access to technical training and resources is limited.
The Solution: To overcome the skills gap, companies should prioritize comprehensive training programs for their operators, emphasizing both machine operation and basic troubleshooting. Partnering with manufacturers that offer extensive training resources, including virtual demonstrations and hands-on workshops, can significantly enhance operator skill levels. Additionally, investing in user-friendly machines with intuitive software can help bridge the expertise gap, allowing operators to become proficient more quickly. Companies might also consider establishing mentorship programs where experienced operators can guide newer team members, fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Implementing these strategies will not only enhance productivity but also boost employee confidence and job satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for laser cnc machine for metal
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Laser CNC Machines for Metal?
When selecting materials for laser CNC machining, understanding their properties is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring compatibility with various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
Carbon Steel: A Versatile Choice for Laser Cutting
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and hardness, with a melting point around 1425-1540°C. It exhibits good machinability and weldability, making it a popular choice for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of carbon steel is a significant advantage, especially for structural applications. However, it is prone to corrosion, which may require additional treatment or coatings. The cost is relatively low compared to other metals, but its weight can complicate handling during manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications like automotive parts and construction materials. Its compatibility with laser cutting allows for precise shapes and designs, enhancing the end product’s functionality.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions such as Africa and South America should be aware of local standards like ASTM A36 for structural steel. Compliance with these standards ensures quality and safety in applications.
Stainless Steel: Corrosion Resistance and Aesthetic Appeal
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, offers excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance, with a melting point around 1400-1450°C.
Pros & Cons: Its durability and aesthetic appeal make stainless steel ideal for applications in food processing and medical devices. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be challenging to cut due to its toughness, which may increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in environments where hygiene is critical, such as kitchens and hospitals. The ability to achieve clean cuts with minimal burrs enhances its suitability for precision applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Understanding local regulations regarding food safety can also impact material selection.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Versatile
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, with a melting point around 660°C. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier handling and transportation, reducing overall costs. However, it is softer than steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, the cost can be moderate to high depending on the alloy used.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods. Its compatibility with laser cutting enables the production of intricate designs while maintaining structural integrity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Understanding the local market’s preference for aluminum alloys can also guide material selection.
Copper: High Conductivity for Specialized Applications
Key Properties: Copper has a melting point of around 1085°C and is known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. It is also resistant to corrosion in certain environments.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its conductivity, making it ideal for electrical applications. However, it is more expensive than other metals and can be challenging to cut due to its softness, which may result in increased manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Copper is frequently used in electrical components, plumbing, and heat exchangers. Its compatibility with laser cutting allows for precise fabrication of complex shapes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper can be essential for ensuring quality. Buyers should also consider the availability of copper in their region, as it may impact lead times and costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Laser CNC Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for laser cnc machine for metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive parts, construction materials | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, tougher to cut | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive, consumer goods | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Softer than steel, moderate cost | Med |
| Copper | Electrical components, plumbing | Excellent conductivity | Expensive, challenging to cut | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of common materials used in laser CNC machining, highlighting key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers. Understanding these factors can significantly enhance decision-making for B2B buyers across various regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for laser cnc machine for metal
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Laser CNC Machines for Metal?
Manufacturing a laser CNC machine for metal involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision, efficiency, and quality. Understanding these processes is vital for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for Laser CNC Machines?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, which includes sourcing high-quality metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. The choice of material directly impacts the machine’s cutting performance and durability. Suppliers typically conduct thorough inspections of incoming materials, checking for defects and verifying compliance with industry standards. This ensures that only the best materials are used in production, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Laser CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage involves forming. This process includes cutting, bending, and shaping the metal components that will make up the laser CNC machine. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are employed to achieve precise dimensions and intricate designs. The use of fiber lasers, known for their efficiency and accuracy, is increasingly common. They can cut through various metals with minimal kerf and heat-affected zones, resulting in cleaner edges and less material waste.
How Are Laser CNC Machines Assembled?
The assembly stage is where all the prepared components come together. Skilled technicians carefully assemble the laser CNC machine, paying close attention to alignment and fit. This stage often involves integrating various systems, including the laser source, control systems, and motion components. Manufacturers may use computer-aided design (CAD) software to guide the assembly process, ensuring that all parts are installed correctly and function as intended.
What Finishing Processes Are Implemented?
Finishing processes are critical for enhancing the performance and aesthetics of laser CNC machines. These processes may include surface treatment, painting, and powder coating to protect against corrosion and wear. Additionally, manufacturers often conduct final adjustments to ensure that the machine operates at optimal performance levels. This may involve calibrating the laser, testing the motion systems, and verifying cutting speeds.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Laser CNC Machines?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for laser CNC machines. It ensures that each machine meets rigorous performance and safety standards, which is particularly crucial for B2B buyers who rely on these machines for their operations.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered?
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer has established a robust quality management system, ensuring consistent product quality. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for safety and performance, and API standards for equipment used in oil and gas applications, are also important indicators of quality.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control in the manufacturing of laser CNC machines typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, incoming materials are inspected and tested to ensure they meet specified requirements before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This involves monitoring the manufacturing process itself. Technicians perform regular checks during forming and assembly to catch any defects early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the entire machine undergoes rigorous testing to verify that it meets all specifications and performance standards. This may include cutting tests, software validation, and safety inspections.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed?
Common testing methods for laser CNC machines include:
-
Cutting Tests: Evaluating the machine’s ability to cut through various metals at different speeds and thicknesses.
-
Functional Testing: Ensuring that all components, including the laser and motion systems, operate correctly.
-
Safety Inspections: Verifying that the machine complies with safety standards to protect operators and facilities.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial to ensuring a reliable partnership. Here are some strategies:
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Quality Verification?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. Buyers should request quality assurance reports, including details on testing procedures, inspection results, and compliance with international standards. A thorough audit can reveal a supplier’s commitment to quality and their ability to meet buyer expectations.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Trust?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance trust between B2B buyers and suppliers. These independent entities can conduct comprehensive evaluations of the manufacturing process, quality control measures, and the final product. Their unbiased assessments help buyers make informed decisions and mitigate risks associated with purchasing equipment from overseas.
What Are the Quality Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality certifications is essential. Different regions may have varying requirements for certifications, and compliance with local regulations is necessary for successful operations. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are familiar with the regulatory landscape in their specific region and can provide the necessary documentation.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for laser CNC machines for metal are intricate and critical to the success of the final product. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring they invest in machines that meet their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘laser cnc machine for metal’
Introduction
Sourcing a laser CNC machine for metal can be a complex process, especially for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help you navigate the procurement journey effectively. By following these steps, you will ensure that you select a machine that meets your operational needs and aligns with your business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin your search, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your laser CNC machine. This includes the types of metals you plan to cut, the thickness of the materials, and the size of the sheets you will be working with. Identifying these parameters will help you narrow down your options and ensure that the machines you consider can meet your production requirements.
- Material Types: Ensure the machine can handle the specific metals you work with, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or copper.
- Cutting Capacity: Specify the maximum thickness you need to cut for each material type to avoid underperformance.
Step 2: Research Available Technologies
Understanding the different types of laser technologies available is crucial. Common options include fiber lasers and CO2 lasers, each with unique advantages in terms of efficiency, speed, and cost. Researching these technologies will empower you to make informed decisions based on your specific cutting needs.
- Fiber Lasers: Typically offer higher cutting speeds and lower operational costs, making them suitable for thick metals.
- CO2 Lasers: Better for non-metal materials and intricate designs but may have higher running costs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This step is essential to ensure reliability and quality.
- Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and positive customer feedback.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers have relevant certifications that comply with international standards.
Step 4: Request Demonstrations and Samples
Once you have shortlisted potential machines, request live demonstrations or virtual showcases. Observing the machine in action will provide insights into its performance and capabilities. Additionally, inquire about the possibility of cutting sample materials to evaluate the quality of the cuts.
- Performance Metrics: Pay attention to cutting speed, precision, and kerf width during demonstrations.
- Sample Quality: Analyze the quality of the cuts, especially on the materials you typically use.
Step 5: Understand the Total Cost of Ownership
Assessing the total cost of ownership (TCO) is critical for long-term planning. This includes not only the initial purchase price but also maintenance, consumables, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs.
- Running Costs: Inquire about the cost of consumables, such as cutting gases and replacement parts.
- Energy Efficiency: Choose machines that offer low power consumption to reduce operational costs.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Support Services
A robust warranty and reliable support services are vital for minimizing operational disruptions. Ensure the supplier offers a comprehensive warranty on parts and labor, as well as ongoing technical support.
- Warranty Coverage: Look for warranties that cover critical components for at least one year.
- Technical Support: Confirm the availability of technical support and training resources to assist your team post-purchase.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Logistics
After selecting your machine and supplier, finalize the purchase agreement. Pay close attention to delivery timelines, installation requirements, and after-sales support. Understanding the logistics involved will help you plan your operations accordingly.
- Delivery Terms: Clarify shipping costs and timelines to avoid unexpected delays.
- Installation Support: Ensure that the supplier provides installation assistance to facilitate a smooth setup.
By following this checklist, you will be well-equipped to make an informed decision when sourcing a laser CNC machine for metal, ultimately enhancing your production capabilities and business efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for laser cnc machine for metal Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of laser CNC machines for metal cutting is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will delve into the key components of costs, the factors influencing pricing, and provide actionable tips for buyers navigating this complex market.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Laser CNC Machines?
The cost of laser CNC machines is determined by several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the manufacturing costs. High-quality components such as fiber lasers and precision machining parts often come at a premium, but they enhance the machine’s performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both the manufacturing and maintenance of these machines. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location and local wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for laser cutting can be expensive, and its costs should be factored into the overall pricing. The tooling needs may vary depending on the complexity and specificity of the laser cutting projects.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is essential for ensuring machine reliability and performance. Investing in quality assurance can elevate production costs but may lead to greater customer satisfaction and lower warranty claims.
-
Logistics: The shipping and handling of these machines, particularly for international buyers, can add significant costs. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties must be considered.
-
Margin: Finally, the profit margin that manufacturers or suppliers add to the overall cost can vary. It’s essential to understand how much markup is being applied to the base cost of the machine.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Laser CNC Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of laser CNC machines:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers may negotiate better pricing if they can commit to larger orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom machines or those with higher specifications typically carry a higher price tag. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Certifications: Machines made from premium materials or those that meet certain international certifications may be priced higher. However, such investments can lead to improved performance and durability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and financial stability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk, which can significantly impact total costs.
What Negotiation Strategies Can B2B Buyers Use to Ensure Cost-Efficiency?
B2B buyers should consider the following tips for effective negotiation and cost management:
-
Emphasize Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on the initial purchase price, evaluate the long-term costs, including maintenance, consumables, and operational efficiency. A higher upfront cost may be justified if the machine offers lower operating costs over time.
-
Compare Multiple Suppliers: Engaging multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. It allows buyers to compare prices, features, and warranties, helping them make an informed decision.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, potential tariffs, and local economic conditions that may affect pricing. Understanding these nuances can provide additional negotiation points.
-
Request for Detailed Quotations: Ask suppliers for a breakdown of costs to understand where savings can be made. This transparency can facilitate better negotiations and decision-making.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost and pricing analysis of laser CNC machines for metal cutting is essential for international B2B buyers. By grasping the key cost components, recognizing price influencers, and employing strategic negotiation tactics, buyers can secure favorable deals while ensuring they invest in the right equipment for their operational needs. As prices can vary widely, it’s crucial to approach the market with thorough research and a clear understanding of total ownership costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing laser cnc machine for metal With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of metal fabrication, B2B buyers often seek efficient and cost-effective solutions for their machining needs. While laser CNC machines for metal offer exceptional precision and versatility, it’s crucial to consider alternative technologies that may also meet specific operational requirements. This analysis examines two viable alternatives: plasma cutting and waterjet cutting, providing insights into their performance, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for various applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Laser CNC Machine for Metal | Plasma Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with kerf < 25um; suitable for a wide range of metals | Fast cutting speeds; good for thicker materials but less precise | Excellent precision; can cut thick materials; no heat-affected zone |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; low running costs (electricity and gas) | Lower initial cost; higher operating costs due to consumables | Higher initial cost; relatively high operating costs due to water and abrasives |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; software integration needed | Easier to set up; requires less technical expertise | More complex setup; requires water supply and drainage considerations |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and part replacements; lower long-term costs | Simple maintenance; consumables need frequent replacement | High maintenance due to pump systems; wear parts can be expensive |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for intricate designs, thin sheets, and high-quality finishes | Best for thicker metals and faster, less detailed cuts | Suitable for materials sensitive to heat or needing intricate cuts |
What Are the Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Plasma Cutting?
Plasma cutting is a popular alternative to laser CNC machines, particularly for thicker materials. The primary advantage of plasma cutting lies in its speed; it can cut through metal rapidly, making it an efficient choice for high-volume operations. However, the trade-off is precision; plasma cutting produces a wider kerf and may not achieve the same quality of finish as laser cutting. Additionally, while the initial investment is generally lower, the ongoing costs associated with consumables can add up quickly, impacting overall profitability.
How Does Waterjet Cutting Compare in Terms of Precision and Cost?
Waterjet cutting is another alternative that excels in precision and versatility. One of its most significant advantages is that it can cut through a wide variety of materials, including metals, glass, and ceramics, without introducing thermal stress. This results in no heat-affected zones, preserving the material’s structural integrity. However, the initial setup costs are relatively high, and operational costs can be substantial due to the need for water and abrasive materials. Furthermore, the complexity of the equipment may require more skilled operators compared to plasma cutting.
How Can B2B Buyers Make Informed Decisions on Metal Cutting Technologies?
Choosing the right solution for metal cutting depends on several factors, including the specific materials being processed, the desired precision, and the overall production volume. B2B buyers should assess their unique operational needs, considering both short-term costs and long-term operational efficiencies. For intricate designs and high-quality finishes, laser CNC machines may be the best choice. Conversely, for thicker materials requiring faster cuts, plasma or waterjet cutting might be more suitable. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis and evaluating technical support options can also aid in making an informed decision that aligns with business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for laser cnc machine for metal
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Laser CNC Machines for Metal?
When considering laser CNC machines for metal cutting, understanding the critical technical properties is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications:
1. Laser Power (Wattage)
The power of the laser, measured in watts (W), determines the cutting capacity of the machine. Common configurations range from 1,000W to 22,000W. Higher wattage allows for cutting thicker materials and achieving faster cutting speeds. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate power level is crucial for meeting production demands while optimizing energy consumption.
2. Material Compatibility
Laser CNC machines can cut various metals, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and even non-metal materials like plastics. Each material type has specific thickness limitations based on the machine’s laser power. Understanding material compatibility ensures that businesses can meet diverse project requirements without needing multiple machines.
3. Cutting Speed
Measured in meters per minute (m/min), cutting speed indicates how quickly a machine can process materials. For instance, a cutting speed of 25m/min is common in high-performance machines. Faster cutting speeds can significantly enhance productivity and reduce lead times, which is critical for businesses operating in competitive markets.
4. Positioning and Repeatability Accuracy
Positioning accuracy (typically within ±0.03mm) and repeatability accuracy (within ±0.02mm) are crucial for precision cutting applications. These specifications ensure that parts are manufactured to exact dimensions, minimizing waste and rework. For B2B buyers, high accuracy reduces costs associated with errors and enhances product quality.
5. Kerf Width
Kerf width refers to the width of the cut made by the laser, typically measured in micrometers (µm). A kerf of less than 25µm is ideal for intricate designs and tight tolerances. Understanding kerf width is essential for buyers looking to produce detailed components or assemblies where precision is paramount.
6. Cooling System
The cooling system, often a refrigerated water chiller, is vital for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and ensuring the longevity of the laser. Efficient cooling systems prevent overheating during prolonged use, which can lead to costly downtime and maintenance. Buyers should consider the cooling capabilities to ensure the machine can handle their production volumes.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Laser CNC Machines for Metal?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in B2B transactions. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM partnerships is crucial for buyers seeking reliable machinery and parts.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for budget-conscious buyers as it influences purchasing decisions, particularly for bulk orders.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process helps buyers evaluate potential suppliers and negotiate better deals.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Knowledge of Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, especially for international buyers navigating logistics and costs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and managing customer expectations.
6. Turnkey Solution
A turnkey solution refers to a complete package where a supplier provides everything needed for operation, from equipment to training. This term is significant for buyers looking for hassle-free procurement and integration.
In summary, understanding these technical properties and trade terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions regarding laser CNC machines for metal, ensuring they select the right equipment to meet their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the laser cnc machine for metal Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Laser CNC Machine for Metal Sector?
The laser CNC machine market for metal is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Factors such as the need for automation, cost reduction, and enhanced production efficiency are propelling the adoption of laser cutting technologies. International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly looking for high-performance machines that offer quick return on investment (ROI) and low operational costs. For instance, fiber laser machines, known for their energy efficiency and precision, are gaining traction due to their ability to cut a variety of metals with minimal waste.
Emerging trends include the integration of smart technologies such as IoT and AI into laser CNC machines, which enhance operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. Furthermore, as businesses pivot towards Industry 4.0, there is a growing emphasis on modular systems that allow for scalability and customization to meet specific production needs. International buyers should also be aware of the competitive landscape, as manufacturers are increasingly offering comprehensive service packages that include training, support, and maintenance to differentiate themselves in the market.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing Decisions for Laser CNC Machines?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions for laser CNC machines. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, and companies are seeking to minimize their carbon footprints. As a result, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainability through ethical sourcing practices and the use of ‘green’ materials. This includes sourcing machines that utilize energy-efficient technologies and recyclable components.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to sustainability standards can significantly influence purchasing decisions. Buyers should also consider the lifecycle impact of laser CNC machines, from production through to disposal, ensuring that their suppliers are not only compliant with environmental regulations but are also proactive in reducing waste and energy consumption. By aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals, companies can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Evolution of Laser CNC Technology and Its Impact on B2B Buyers?
The evolution of laser CNC technology has significantly transformed metal fabrication processes over the past few decades. Initially, laser cutting was a costly and complex technology, limited to specialized applications. However, advancements in fiber laser technology have made it more accessible and cost-effective, enabling widespread adoption across various industries. The introduction of high-powered fiber lasers has improved cutting speeds and precision, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
As laser CNC machines have evolved, so too have the capabilities and features available to B2B buyers. Modern machines offer enhanced automation, user-friendly interfaces, and integration with CAD/CAM software, streamlining the design-to-production workflow. This evolution not only facilitates faster turnaround times but also allows businesses to produce intricate designs that were previously unattainable. For international buyers, understanding this technological evolution is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of laser cnc machine for metal
-
How do I choose the right laser CNC machine for my metal cutting needs?
Selecting the right laser CNC machine involves assessing your specific requirements, including the types of metals you will cut, the thickness of the materials, and the volume of production. Consider factors such as laser power (measured in watts), cutting speed, and precision. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s size to ensure it accommodates your workspace and production demands. Research various brands and models, and consult with suppliers to understand the features that best match your operational needs. -
What is the best laser CNC machine for cutting stainless steel?
For cutting stainless steel, a fiber laser CNC machine is generally the best choice due to its efficiency and precision. Fiber lasers operate at a wavelength that is highly absorbed by metals, resulting in cleaner cuts and less heat distortion. Machines with higher wattage (2000W or more) are recommended for thicker stainless steel plates. Brands like Atlas Alloy and Hytek Tools offer models that excel in cutting stainless steel with minimal operational costs. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing a laser CNC machine internationally?
When sourcing a laser CNC machine internationally, consider factors such as supplier reputation, certifications, and experience in your specific market. Review the machine specifications to ensure they meet your production needs. Additionally, investigate the supplier’s warranty policies, after-sales support, and maintenance services. Understanding the import regulations and potential tariffs in your country is also crucial to avoid unexpected costs. -
What customization options are available for laser CNC machines?
Customization options for laser CNC machines can include adjustments in laser power, cutting bed size, and software features. Some manufacturers offer tailored solutions to fit unique production processes, such as specialized cutting heads or automated loading systems. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to explore the available customization options that can enhance your operational efficiency and meet your production goals. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for laser CNC machines?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for laser CNC machines can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific model. Some manufacturers may allow single-unit purchases, while others might require bulk orders to meet production efficiencies. It’s essential to communicate with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore potential discounts for larger orders, which can lead to better pricing and improved ROI. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a laser CNC machine?
Payment terms for purchasing a laser CNC machine typically vary by supplier. Common arrangements include a deposit (often 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms, including accepted currencies and methods (bank transfer, letter of credit, etc.), to ensure smooth transactions and avoid potential disputes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for my laser CNC machine?
To ensure quality assurance for your laser CNC machine, request detailed product specifications, certifications, and performance standards from the manufacturer. Conduct due diligence by reading reviews and testimonials from other buyers. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility to inspect the machine and its production processes. Implementing a thorough inspection upon delivery and maintaining regular maintenance checks will further ensure the machine operates at peak performance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a laser CNC machine?
Logistics considerations for importing a laser CNC machine include shipping methods, transportation costs, and estimated delivery timelines. Engage with freight forwarders experienced in heavy machinery to navigate customs and ensure compliance with import regulations in your country. Additionally, factor in insurance for the shipment to cover potential damages during transit. Clear communication with your supplier about logistics can help streamline the process and minimize delays.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Laser Cnc Machine For Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Hytek Tools – Fiber Laser Cutters
Domain: hytektools.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Fiber Laser Cutters from Hytek Tools include various models with different specifications and pricing:
1. 2025 FIBERTEK™ Model DE: 5×10, 2000w-30,000w, starting at $145,650.00
2. ROBOTUBE™ MODEL RT2: Fiber Laser Metal Tube Cutter, starting at $182,000.00
3. 2025 FIBERTEK™ MODEL SE: Fiber Laser 5×10, 2000W-12000W, starting at $122,000.00 (originally $144,000.00)
4. 2025 FIBERTEK™ MODEL D: Fiber…
2. CNC Laser Cutters – Key Product Details
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Key Product Details:
– Types of CNC Laser Cutters: Gas laser cutting, Crystal laser cutting, Fiber laser cutting.
– Brands Available: AMADA, MITSUBISHI, MAZAK, TRUMPF, BYSTRONIC, AP LAZER, BOSS LASER, LASERPRO, LVD STRIPPIT, TROTEC, BODOR, CINCINNATI, COHERENT, HK LASER & SYSTEMS, HYPERUSA, IPG PHOTONICS, NUKON, ROBOTEC, ROFIN.
– Models Listed: ENSIS 3015, FM-D, FO3015NT, LAP4836-1808W, ML3015LVPS…
3. Boss Laser – 2kw AccuCut
Domain: shop.bosslaser.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Laser Machines – Boss Laser offers a variety of laser cutting, engraving, and marking machines including CO2 lasers, UV lasers, and industrial fiber cutters. Key products include the 2kw AccuCut priced at $57,997, and various models from the LS-Series, HP-Series, FC-Series, FM-Series, and UV-Series. The machines can cut and engrave a wide range of materials such as acrylic, aluminum, brass, cardbo…
4. Hobbyist Laser Cutter – Aluminum Cutting Solutions
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Hobbyist/desktop laser cutter capable of cutting aluminum sheet metal from 24 gauge up to 16 gauge. Interested in cutting small simple shapes, perimeter cuts, scoring lines for bending, cutting out small holes, and engraving labels. Price range considered is under $1000 to under $2000. User has experience with 3D printing but no CNC machining experience.
5. ShopSabre – FiberSabre 2kW
Domain: shopsabre.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: {“CNC_Lasers”: {“FiberSabre_2kW”: {“description”: “Innovative Excellence: The USA-Made 220V Single-Phase Fiber Laser Machine”, “use”: “Commercial Use”, “precision”: “Ultimate Precision”, “starting_price”: “$64,995”}, “FiberSabre_6kW”: {“description”: “The next level solution for your American-made Fiber Laser needs.”, “use”: “Commercial Use”, “precision”: “Ultimate Precision”, “starting_price”: “$…
6. STYLECNC – ST-FC3015FM Sheet Metal Laser Cutter
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “ST-FC3015FM Sheet Metal Laser Cutter”, “Brand”: “STYLECNC”, “Laser Power Options”: [1500, 2000, 3000, 4000, 6000], “Table Size”: “1500x3000mm (5’x10′)”, “Max Cutting Speed”: “100 meters per minute”, “Material Thickness Range”: “1mm to 25mm”, “Laser Source Options”: [“Raycus”, “IPG”, “MAX”], “Standard Edition Price”: “$15,000”, “Pro Edition Price”: “$43,000”, “Warranty”: “One-Year…
7. MechMate – CNC Laser Cutting Machine for Metal
Domain: mechmate.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Laser Cutting Machine for Metal: A CNC laser cutting system for metal with high cutting quality, speed, precision, and efficiency. Suitable for various metal materials including stainless steel, carbon steel, electrical steel, galvanized steel, aluminum zinc plate, aluminum, aluminum alloy, titanium alloy, copper, brass, and iron. Power options range from 1,000W to 30,000W. Types of CNC laser cutt…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for laser cnc machine for metal
In today’s competitive landscape, investing in laser CNC machines for metal processing offers significant advantages for businesses looking to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. The strategic sourcing of these machines can lead to rapid returns on investment, particularly for firms in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By transitioning from outsourcing metal cutting services, companies can not only save on labor costs but also gain full control over production timelines and quality standards.
Key takeaways include the importance of selecting equipment that aligns with specific production needs, such as the ability to handle various metal types and thicknesses efficiently. Furthermore, understanding the energy consumption and maintenance requirements of different laser technologies can provide additional cost savings.
Looking forward, international B2B buyers are encouraged to explore the diverse offerings of laser CNC machines available in the market. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, companies can position themselves for success in an increasingly automated future, unlocking new opportunities for growth and innovation. Engage with suppliers to schedule demonstrations and gain deeper insights into how these advanced machines can transform your operations.