Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for kovar metal
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing Kovar metal can present unique challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This iron-nickel-cobalt alloy is renowned for its exceptional thermal expansion properties, making it indispensable in applications requiring glass-to-metal seals, such as electronics and aerospace. However, understanding the nuances of Kovar’s specifications, applications, and procurement processes is critical for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of Kovar metal, including its types, mechanical and thermal properties, and diverse applications across industries such as transportation, defense, and medical technology. We will also explore effective strategies for supplier vetting, ensuring quality control, and cost management, which are vital for maximizing your investment. By equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the Kovar metal market, this guide empowers you to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with your operational needs and enhance your competitive advantage.
Whether you are in Brazil seeking reliable suppliers or in Nigeria looking for cost-effective options, this guide serves as your go-to resource for understanding Kovar metal and optimizing your supply chain. Prepare to unlock new opportunities and streamline your procurement process with actionable insights tailored for your region’s unique market dynamics.
Understanding kovar metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kovar 29 | 29% Nickel content, excellent thermal expansion properties | Electronics, hermetic sealing, aerospace | Pros: High thermal stability; Cons: Higher cost |
| Kovar 17 | 17% Cobalt content, optimized for magnetic applications | Medical devices, telecommunications | Pros: Superior magnetic properties; Cons: Limited availability |
| Kovar 36 | Tailored for low expansion; specific CTE for ceramics | Glass-to-metal seals, optical devices | Pros: Excellent compatibility with glass; Cons: Specialized machining required |
| Kovar 42 | Enhanced workability and machining capabilities | Defense, automotive applications | Pros: Easier to machine; Cons: Slightly lower thermal resistance |
| Kovar 50 | High corrosion resistance and mechanical strength | Industrial applications, power tubes | Pros: Durable under harsh conditions; Cons: May require specific sourcing |
What are the Characteristics of Kovar 29 Alloy?
Kovar 29 is characterized by its 29% nickel content, which grants it exceptional thermal expansion properties, closely matching those of certain glasses. This makes it ideal for applications requiring hermetic sealing, particularly in electronics and aerospace industries. When purchasing Kovar 29, buyers should consider its thermal stability and ability to maintain structural integrity under varying temperatures, though they should also be prepared for a higher price point compared to alternatives.
How Does Kovar 17 Differ in Terms of Magnetic Properties?
Kovar 17 features a cobalt content of 17%, enhancing its magnetic properties, making it suitable for medical devices and telecommunications equipment. Its ability to retain magnetic characteristics at lower temperatures is advantageous in applications where precision is critical. Buyers should evaluate their specific magnetic requirements, as the availability of Kovar 17 may be limited, potentially affecting lead times and costs.
Why is Kovar 36 Preferred for Glass-to-Metal Sealing?
Kovar 36 is specifically tailored for low expansion, with a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that aligns well with ceramics and glass. This alloy is frequently used in glass-to-metal seals, particularly in optical devices where precision is paramount. When considering Kovar 36, buyers should prioritize its compatibility with their glass materials, understanding that specialized machining processes may be necessary to achieve desired tolerances.
What Makes Kovar 42 a Good Choice for Automotive Applications?
Kovar 42 stands out due to its enhanced workability and machining capabilities, making it a preferred choice in the automotive and defense sectors. It offers a balance between performance and ease of manufacturing, which can result in lower production costs. Buyers should assess the trade-off between ease of machining and thermal resistance, as Kovar 42 may not match the thermal properties of other Kovar variants.
How Does Kovar 50 Perform in Harsh Environments?
Kovar 50 is notable for its high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications, including power tubes. Its durability ensures longevity in harsh environments, which is a significant advantage for buyers in sectors requiring reliable materials. However, sourcing Kovar 50 may involve specific suppliers, necessitating careful planning and procurement strategies.
Key Industrial Applications of kovar metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Kovar Metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Hermetic seals for electronic components | Ensures reliability and longevity in sensitive devices | Quality certifications and thermal expansion matching |
| Aerospace | Components in satellite propulsion systems | High performance in extreme environments | Supplier reliability and material traceability |
| Medical Devices | Packaging for sensitive medical equipment | Protects against contamination and ensures device integrity | Compliance with medical standards and certifications |
| Telecommunications | Microwave tubes and transistors | Enhanced signal integrity and reduced interference | Precision machining capabilities and thermal properties |
| Automotive | Seals in high-temperature applications | Improved durability and performance in harsh conditions | Material cost and availability in specific regions |
How is Kovar Metal Used in Electronics and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the electronics industry, Kovar is primarily utilized for hermetic seals in devices like transistors and diodes. Its coefficient of thermal expansion closely matches that of glass, enabling reliable glass-to-metal seals that prevent moisture ingress and enhance device longevity. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, ensuring the supplier can meet stringent quality certifications is crucial to maintain the integrity of sensitive components.
What Role Does Kovar Play in Aerospace Applications?
Kovar is essential in aerospace applications, particularly in satellite propulsion systems. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and maintain structural integrity under pressure makes it ideal for components that operate in harsh environments. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing from suppliers with proven reliability and traceability to ensure compliance with aerospace standards.
How is Kovar Metal Utilized in Medical Devices?
In the medical device sector, Kovar is often used in the packaging of sensitive equipment to ensure contamination-free environments. Its robust sealing capabilities protect against environmental factors that could compromise device functionality. Buyers, especially in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil, must consider compliance with medical device standards and the supplier’s ability to deliver high-quality materials.
Why is Kovar Important in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, Kovar is used in microwave tubes and transistors to enhance signal integrity and reduce interference. Its thermal properties are critical for maintaining performance in varying temperatures. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers that offer precision machining capabilities to achieve the tight tolerances necessary for these applications.
How Does Kovar Benefit Automotive Applications?
Kovar is increasingly being employed in automotive applications, particularly for seals designed to withstand high temperatures. Its durability enhances performance and longevity in challenging conditions, such as engine compartments. Buyers should consider the material’s cost-effectiveness and availability in their respective regions to ensure timely procurement without compromising quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘kovar metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Consistent Thermal Expansion Properties
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the challenge of sourcing Kovar metal that consistently meets the required thermal expansion properties. This inconsistency can lead to issues in applications that require precise thermal management, such as in electronics or aerospace components. If the Kovar used does not match the thermal expansion coefficient of the materials it bonds with, such as borosilicate glass, it can lead to stresses and potential failures, resulting in costly rework or product recalls.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should prioritize sourcing Kovar from reputable manufacturers who adhere to strict quality control processes. When specifying Kovar, clearly communicate the required thermal expansion characteristics and any specific manufacturing processes that the alloy must undergo. Engaging with suppliers who can provide detailed technical data sheets and certifications will ensure that the material meets the necessary specifications. Additionally, consider conducting thermal expansion tests on samples before full-scale implementation to verify compatibility with mating materials.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Machining Kovar Metal
The Problem: Machining Kovar can present significant difficulties due to its specific properties, which can lead to tool wear and increased production costs if not handled correctly. B2B buyers often find that standard machining practices do not yield the desired precision or surface finish, leading to delays in production schedules and potential quality issues in the final products.
The Solution: To effectively machine Kovar, it is crucial to implement specialized techniques tailored to its characteristics. Buyers should invest in high-quality cutting tools designed for machining Kovar, such as carbide tools, and maintain them in excellent condition to avoid tool wear. Additionally, employing advanced cooling techniques, like using coolant solutions specifically formulated for Kovar, can help manage heat generation and prevent warpage. Partnering with experienced machinists familiar with Kovar’s properties can further enhance the machining process, ensuring high-quality outputs that meet tight tolerances.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Effective Sealing in Applications
The Problem: Many industries, including medical and aerospace, require Kovar metal to create hermetic seals with glass or ceramic materials. Buyers may find it challenging to achieve reliable sealing due to improper preparation of Kovar parts, leading to leaks and compromised integrity of the final assembly. This issue can result in significant operational risks and financial losses, especially in critical applications.
The Solution: To ensure effective sealing, buyers should follow precise preparation protocols for Kovar alloy components. Parts must be properly degreased and annealed in a controlled hydrogen atmosphere to prevent carbon contamination, which can hinder sealing performance. It is advisable to work closely with suppliers who can provide guidance on the ideal heating temperatures and times for annealing, as well as the necessary cooling processes. Additionally, conducting regular quality checks on the sealing process, including pressure tests, will help identify any potential issues before full-scale production, ensuring that the final products maintain their integrity and reliability in demanding applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for kovar metal
What are the Key Properties of Kovar Metal?
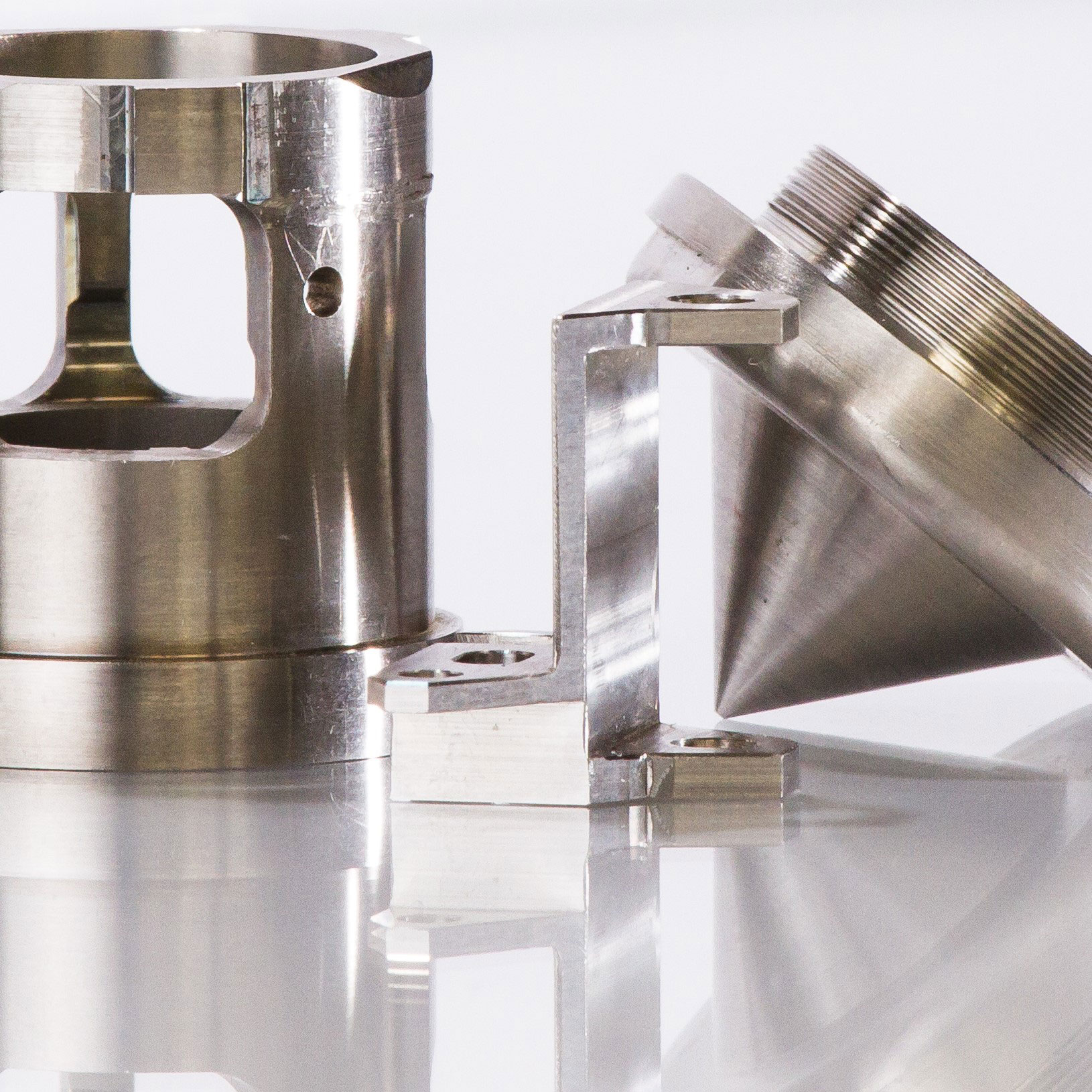
Kovar is an iron-nickel-cobalt alloy known for its unique thermal expansion characteristics that closely match those of borosilicate glass and other optical materials. Its chemical composition is tightly controlled, ensuring uniform thermal expansion properties, which is critical in applications requiring glass-to-metal seals. Kovar exhibits excellent mechanical properties, including a tensile strength of approximately 517 MPa and a hardness rating of 68 on the Rockwell B scale. Its low thermal conductivity (around 17 W/m K) and specific heat capacity (460 J/kg*K) make it suitable for high-temperature applications.
What are the Pros and Cons of Using Kovar Metal?
The advantages of Kovar include its excellent thermal expansion compatibility with various materials, making it ideal for applications in electronics, aerospace, and medical devices. Its machinability is relatively good compared to other specialty alloys, which can lead to lower manufacturing costs. However, Kovar is not without its drawbacks. It can be more expensive than standard metals, and its manufacturing complexity may pose challenges, especially for intricate designs. Additionally, while Kovar is durable, it may not be the best choice in corrosive environments without proper surface treatments.
How Does Kovar Metal Impact Specific Applications?
Kovar’s properties make it highly suitable for applications such as hermetic seals in electronic components, where maintaining a tight seal under varying temperatures is essential. Its compatibility with glass and ceramics allows for reliable sealing in devices like power tubes, microwave tubes, and integrated circuits. However, international buyers must consider the specific media compatibility, as Kovar may not perform well in environments with aggressive chemicals unless adequately protected.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Kovar Metal?
For international buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to be aware of compliance with local and international standards such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS. These standards often dictate the quality and performance requirements for materials used in specific applications. Additionally, buyers should consider the availability of Kovar in their regions, as sourcing may vary significantly. Economic factors, including currency fluctuations and import duties, can also affect the overall cost and feasibility of using Kovar in their projects.
Summary of Material Selection for Kovar Metal
| Material | Typical Use Case for Kovar Metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kovar | Hermetic seals in electronic components | Excellent thermal expansion compatibility | Higher cost compared to standard metals | Medium |
| Borosilicate Glass | Sealing with Kovar in electronic devices | Good thermal stability and transparency | Brittle and prone to breakage under stress | Medium |
| Molybdenum | High-temperature applications | Exceptional strength at elevated temperatures | Very high cost and difficult to machine | High |
| Aluminum Nitride | Substrates in electronic packaging | Excellent thermal conductivity and insulation | More expensive than Kovar and less compatible with glass | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers considering Kovar metal for their applications. Understanding the material’s properties, advantages, and limitations will help in making informed decisions that align with project requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for kovar metal
What Are the Key Stages in Kovar Metal Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process for Kovar metal involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the alloy’s unique properties are preserved and enhanced. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Kovar Metal Production?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-purity iron, nickel, and cobalt, which are vacuum melted to form Kovar. The vacuum melting process is crucial as it minimizes contamination and allows for precise control over the chemical composition. The alloy’s properties, such as its low thermal expansion, are dependent on maintaining tight tolerances on the composition—typically consisting of approximately 29% nickel, 17% cobalt, and the balance iron, with strict limits on impurities like carbon and silicon.
Once the alloy is melted, it is cast into various forms, including bars, strips, and billets. These forms are then subjected to further processing, such as forging or rolling, to achieve the desired dimensions and mechanical properties. The controlled environment during melting and casting is essential for ensuring uniformity and consistency in the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Kovar Metal?
Forming Kovar involves techniques such as deep drawing, stamping, and machining. Each of these processes requires specialized equipment and expertise due to the alloy’s unique characteristics. For instance, deep drawing is often used to produce complex shapes, while stamping is suitable for flat components. Machining is critical for achieving tight tolerances necessary for high-performance applications, such as those found in electronics and aerospace.
To facilitate these processes, the alloy is often heat-treated to optimize its workability. Proper heat treatment can enhance the material’s ductility, making it easier to shape without cracking. Additionally, the use of suitable lubricants during machining can reduce friction and heat generation, which are common causes of warpage and dimensional inaccuracies.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Kovar Metal Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of Kovar metal manufacturing, ensuring that the end products meet international standards and customer specifications.
What International Standards Govern Kovar Metal Quality?
For B2B buyers, compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is vital. This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for oil and gas applications may also apply, depending on the intended use of the Kovar products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications before being used in production. This includes testing for chemical composition and physical properties.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, processes are monitored to ensure adherence to defined standards. This may involve regular sampling and testing of the alloy’s properties at various stages of production.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, Kovar products undergo thorough testing to verify that they meet all required specifications. Common tests include mechanical property assessments (e.g., tensile strength, hardness), thermal expansion measurements, and non-destructive testing techniques.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Kovar Metal?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of Kovar metal, including:
-
Mechanical Testing: To evaluate properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility, mechanical testing is performed using standardized methods (e.g., ASTM E8).
-
Thermal Expansion Testing: The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is critical for applications where Kovar is bonded to glass or ceramics. Testing is typically conducted using dilatometry to measure changes in dimensions with temperature fluctuations.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or eddy current testing can identify internal defects without damaging the product, ensuring reliability in critical applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure product reliability.
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Buyers should request detailed quality control reports that outline the supplier’s adherence to relevant standards and the results of their testing procedures. This may include:
-
Audit Reports: Regular audits by third-party organizations can provide an independent assessment of the supplier’s QMS and compliance with industry standards.
-
Certificates of Compliance: Suppliers should provide certificates that affirm their products meet specified standards, such as ISO 9001 or other relevant certifications.
-
Traceability Documentation: This includes records that trace the material back to its source, ensuring that all components meet the necessary specifications and quality requirements.
What Are the QC Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that can vary by region. For example, certain markets may have additional regulatory requirements that must be met for Kovar products, especially in medical or aerospace applications. Understanding these nuances can help buyers select suppliers that can meet their specific needs while ensuring compliance with local regulations.
By thoroughly evaluating the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of Kovar metal suppliers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that mitigate risks and ensure the reliability of their products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘kovar metal’
In the competitive landscape of international B2B procurement, sourcing Kovar metal requires a strategic approach. This guide will assist buyers in identifying the necessary steps to ensure a successful procurement process, focusing on the unique properties and applications of Kovar, which make it a critical material for various industries.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications for Kovar is the first step in the sourcing process. Consider factors such as the required dimensions, thermal expansion characteristics, and mechanical properties like tensile strength and hardness. These details will help narrow down suppliers who can meet your specific needs, ensuring compatibility with your application.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers specializing in Kovar metal. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in producing high-quality Kovar and check their industry certifications. Focus on suppliers that provide detailed product specifications and have experience with similar applications in your region.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your choice, verify the certifications and quality control processes of potential suppliers. Ensure they comply with relevant industry standards, such as ASTM specifications. This step is vital as it guarantees that the material meets the necessary performance and safety requirements for your specific applications.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of Kovar metal for testing. Evaluate the samples against your defined specifications to assess their physical and mechanical properties. This hands-on assessment will help you determine the material’s suitability for your application and avoid costly errors down the line.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from your selected suppliers to compare pricing and payment terms. Look beyond the initial cost and consider factors such as lead times, shipping costs, and potential discounts for bulk orders. Understanding the total cost of ownership is essential for budgeting and ensuring that you receive the best value for your investment.
Step 6: Assess Supplier Communication and Support
Effective communication is crucial in the procurement process. Evaluate how responsive and supportive each supplier is during your inquiries. A supplier that provides clear answers and demonstrates a willingness to assist can significantly enhance your procurement experience and ensure smoother transactions.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After making your selection, aim to build a long-term relationship with your chosen supplier. Continuous engagement can lead to better pricing, priority service, and tailored solutions as your needs evolve. Consider regular reviews and feedback sessions to ensure ongoing alignment and to foster a collaborative partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for Kovar metal, ensuring they procure high-quality materials that meet their technical and operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for kovar metal Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components for Kovar Metal Sourcing?
When sourcing Kovar metal, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: Kovar is a specialized alloy, primarily composed of iron, nickel, and cobalt. The price of these raw materials fluctuates based on market conditions, availability, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should be aware that Kovar’s unique properties make it more expensive than standard metals.
-
Labor: The manufacturing process for Kovar involves skilled labor, particularly in machining and forming due to its specialized nature. Labor costs can vary significantly by region, with higher costs in developed countries compared to emerging markets like Brazil or Nigeria.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. For Kovar, which requires precise manufacturing techniques, overhead can be substantial, impacting the overall cost.
-
Tooling: The production of Kovar parts may require specialized tooling, which can be a significant upfront investment. Tooling costs will vary based on the complexity of the parts being produced and the technology used.
-
Quality Control (QC): Given Kovar’s applications in critical sectors like aerospace and medical devices, rigorous quality control measures are necessary. This adds to the cost but is essential for ensuring compliance with industry standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping Kovar internationally involves additional costs such as freight, insurance, and customs duties. The logistics cost can be influenced by the chosen Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding transportation and risk.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Kovar Metal Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of Kovar metal:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to the need for specialized processes or materials. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of Kovar and any certifications (e.g., ASTM standards) can significantly affect pricing. Higher quality materials typically command a premium.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge more than newer or less experienced suppliers. Evaluating supplier reputation and reliability is crucial for long-term partnerships.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and risk allocation. Understanding these terms can lead to more favorable pricing and delivery terms.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Kovar Metal Pricing?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Buyers should engage in open discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can lead to more favorable pricing.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Assessing the total cost of ownership (TCO) is vital. This includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime costs associated with the use of Kovar parts.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East may face unique challenges such as currency fluctuations and import duties. Being aware of these factors can aid in budgeting and financial planning.
-
Keep an Eye on Market Trends: Staying informed about market trends in raw materials and Kovar pricing can provide leverage during negotiations. This knowledge can help buyers make timely purchasing decisions.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Remember About Kovar Metal Pricing?
While sourcing Kovar metal can be complex due to its specialized nature, a thorough understanding of cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies can empower buyers to make informed decisions. Always consider the total cost of ownership and the specific needs of your application to achieve the best value. As prices can vary widely, it’s advisable to seek multiple quotes and conduct a thorough supplier evaluation to ensure quality and reliability.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing kovar metal With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Kovar Metal: A Comparative Analysis
When evaluating materials for specialized applications, particularly those requiring a specific coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), it’s essential to consider viable alternatives to Kovar metal. While Kovar is known for its unique thermal properties and excellent workability, other materials can also meet specific project needs. This analysis presents a comparison of Kovar against two alternatives: Invar and Molybdenum.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Kovar Metal | Invar | Molybdenum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent CTE match for glass/ceramics; good mechanical properties | Very low CTE; ideal for precision instruments | High melting point; excellent strength at high temperatures |
| Cost | Moderate cost; more affordable than Molybdenum | Generally lower than Kovar; cost-effective for large-scale production | Higher cost due to mining and processing complexities |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively easy to machine; requires specialized techniques | Easy to machine; can be welded | Difficult to machine; requires specific tooling |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; stable properties | Low maintenance; very stable over time | Moderate maintenance; can oxidize at high temperatures |
| Best Use Case | Glass-to-metal seals, electronics | Precision instruments, measuring devices | Aerospace, high-temperature applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Invar
Invar is an iron-nickel alloy characterized by its exceptionally low coefficient of thermal expansion. This makes it suitable for applications requiring high precision, such as measuring devices and scientific instruments. One of its primary advantages is cost-effectiveness for larger production runs, as it is generally cheaper than Kovar. Additionally, Invar is easy to machine and can be welded, facilitating diverse manufacturing processes. However, it does not possess the same mechanical strength as Kovar and may not be suitable for applications involving high mechanical stress.
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a refractory metal known for its high melting point and strength at elevated temperatures. It is often used in aerospace applications and environments where materials are subjected to extreme conditions. Molybdenum is highly resistant to wear and corrosion, making it an excellent choice for demanding applications. However, it is significantly more expensive than both Kovar and Invar, and its machining can be challenging, requiring specialized tooling and techniques. This can lead to higher production costs and longer lead times, making it less ideal for projects with tight deadlines.
Making the Right Choice: How to Select the Best Material for Your Needs
When selecting the right material for a specific application, B2B buyers should carefully consider the unique requirements of their projects. Factors such as performance under thermal stress, cost implications, ease of machining, and maintenance needs play a crucial role in decision-making. Kovar is a preferred choice for applications involving glass-to-metal seals due to its excellent thermal expansion properties and workability. However, alternatives like Invar and Molybdenum may be more suitable depending on the specific technical requirements and budget constraints. Evaluating these aspects in relation to project goals will lead to a well-informed decision that aligns with operational needs and financial considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for kovar metal
Kovar metal, an iron-nickel-cobalt alloy, is highly regarded in various industries for its unique thermal expansion properties and versatility. Understanding its essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section provides valuable insights into the key specifications and common jargon associated with Kovar metal.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Kovar Metal?
-
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
Kovar exhibits a coefficient of thermal expansion ranging from 4.9 to 6.2 x 10^-6/°C, which closely matches that of borosilicate glass and other optical materials. This property is vital for applications requiring glass-to-metal seals, ensuring minimal thermal stress and preventing cracking during temperature fluctuations. For buyers, selecting Kovar can enhance product reliability in high-performance environments. -
Tensile Strength
Kovar has a tensile strength of approximately 517 MPa, making it suitable for applications that demand durability and resistance to deformation under stress. This strength is particularly important for components used in aerospace, medical devices, and electronics, where structural integrity is paramount. Understanding tensile strength helps buyers assess the suitability of Kovar for specific applications. -
Hardness
The hardness of Kovar is measured at 68 on the Rockwell B scale. This property indicates its resistance to wear and abrasion, essential for components subjected to mechanical wear in industrial settings. Buyers should consider hardness when evaluating the longevity and performance of Kovar parts in demanding applications. -
Thermal Conductivity
Kovar’s thermal conductivity is approximately 17 W/m·K, allowing for efficient heat transfer in electronic and thermal management applications. This characteristic is crucial for ensuring that components operate within safe temperature limits, which can prolong their lifespan. Buyers should assess thermal conductivity to optimize the thermal performance of their systems. -
Density
With a density of 8.35 g/cm³, Kovar is relatively dense compared to other alloys. This property influences the weight and balance of components, which is particularly significant in aerospace and automotive applications. Understanding density assists buyers in determining the material’s impact on overall product design and performance. -
Magnetic Properties
Kovar retains magnetic properties at temperatures below its Curie point. This feature is essential for applications in electronics and telecommunications, where magnetic interactions are crucial. Buyers should consider magnetic properties when selecting materials for sensitive electronic components.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Kovar Metal?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of Kovar, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality components for their products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For Kovar metal, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for businesses looking to minimize costs while ensuring they meet production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products, including Kovar. This process is critical for buyers seeking competitive pricing and understanding the market landscape. It facilitates informed decision-making and negotiation. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping and delivery terms. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for buyers dealing with Kovar suppliers across borders, as it clarifies who bears costs and risks at various stages of transportation. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the Kovar market, understanding lead times is vital for planning production schedules and ensuring timely project completion. -
Certification
Certification indicates that a material meets specific industry standards or regulations. For Kovar, certifications may include compliance with ASTM specifications or other quality assurance standards. Buyers should prioritize certified materials to ensure reliability and performance in their applications.
By familiarizing themselves with these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding the procurement of Kovar metal, optimizing their supply chain and product development processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the kovar metal Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Trends Influencing the Kovar Metal Market?
The global market for Kovar metal is primarily driven by its unique thermal expansion properties, which make it indispensable in applications requiring precise glass-to-metal seals. Industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics are increasingly adopting Kovar due to its compatibility with various glass and ceramic materials. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for advanced materials in telecommunications and electronic components is rising, propelling the need for Kovar. Emerging technologies, particularly in the field of semiconductors and satellite communications, are creating new avenues for Kovar applications, thus expanding its market reach.
Furthermore, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming sourcing trends. International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for procurement, enabling them to streamline their supply chains and enhance transparency. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in developing markets, such as Nigeria and Brazil, where digital infrastructure is improving. Sustainability considerations are also influencing sourcing decisions, as companies seek suppliers who adhere to ethical and environmentally friendly practices.
How Can B2B Buyers Address Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Kovar Metal Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the procurement of Kovar metal, as businesses recognize the environmental impact of their supply chains. The mining and processing of the raw materials used in Kovar production can lead to significant ecological footprints. Consequently, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, including waste reduction and responsible sourcing of raw materials.
Ethical sourcing involves ensuring that the suppliers adhere to labor standards and environmental regulations. Buyers should look for suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety), which indicate compliance with international sustainability standards. Additionally, the growing trend of using recycled materials in the production of Kovar can further enhance the sustainability profile of procurement activities, offering buyers a more eco-friendly alternative.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Kovar Metal’s Development?
Kovar metal, a low expansion alloy composed primarily of iron, nickel, and cobalt, was first developed in the mid-20th century to meet the specific thermal expansion needs of glass and ceramic materials. Its unique properties, particularly its thermal expansion coefficient, were tailored to match that of borosilicate glass, making it an ideal candidate for applications in electronics and hermetic sealing technologies. Over the decades, Kovar has found its way into critical applications, from aerospace components to medical devices, cementing its status as a vital material in various high-tech industries.
As the demand for precision and reliability in technological applications continues to grow, Kovar’s role is likely to expand, making it a focal point for B2B buyers seeking materials that meet stringent performance criteria.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of kovar metal
-
How do I ensure the quality of Kovar metal before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of Kovar metal, request detailed specifications and certifications from suppliers, such as ASTM compliance. It’s beneficial to ask for material test reports, including mechanical and thermal properties, to verify they meet your project requirements. Conducting a supplier audit or visiting their manufacturing facility can also provide insights into their quality control processes. Establishing a clear communication line with the supplier for ongoing quality assurance during production is crucial. -
What is the best application for Kovar metal in electronics?
Kovar metal is ideal for applications requiring hermetic sealing, particularly in electronic components like microwave tubes, transistors, and integrated circuits. Its low thermal expansion coefficient closely matches that of borosilicate glass, making it suitable for glass-to-metal seals. This characteristic is essential in devices subjected to varying temperatures, ensuring durability and performance. For high-tech applications, Kovar’s excellent mechanical properties make it a preferred choice for reliable and efficient operation. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for Kovar metal?
Minimum order quantities for Kovar metal can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from 100 kg to 500 kg, depending on the manufacturer and specific product form. Custom orders may have different MOQs based on the complexity and processing requirements. Always clarify MOQs during initial discussions with suppliers to ensure alignment with your project needs and budget. Negotiating terms can sometimes lead to lower MOQs, especially for long-term partnerships. -
How can I customize Kovar metal for specific applications?
Customization of Kovar metal can be achieved by working closely with your supplier to specify the desired dimensions, surface treatments, and mechanical properties. Discuss the thermal and mechanical requirements of your application to ensure the alloy’s properties are tailored accordingly. Many suppliers offer machining services and can produce parts to your exact specifications, including tight tolerances and complex geometries. It’s advisable to provide detailed drawings and technical requirements to facilitate the customization process. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Kovar metal internationally?
Payment terms for sourcing Kovar metal can vary significantly based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include upfront payment, 30% deposit with the balance upon delivery, or net 30/60 days after invoice. For international transactions, consider using letters of credit to mitigate risks. Always negotiate terms that are mutually beneficial and ensure you understand any additional costs related to shipping, duties, or taxes that may affect the final price. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing Kovar metal?
When importing Kovar metal, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Ensure your supplier provides accurate shipping documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance. It’s important to understand tariffs or duties applicable in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Collaborating with a freight forwarder experienced in handling specialty metals can streamline the logistics process and help manage risks associated with international shipping. -
How do I vet potential suppliers of Kovar metal?
To vet potential suppliers, research their industry reputation through reviews, testimonials, and case studies. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service quality. Evaluate their production capabilities, quality control processes, and certifications to ensure they meet international standards. Additionally, visiting the supplier’s facility can provide valuable insights into their operations and commitment to quality, helping you make an informed decision. -
What are the key thermal properties of Kovar metal that I should consider?
Kovar metal is renowned for its low thermal expansion coefficient, which closely matches that of borosilicate glass and other materials used in electronics. Typically, its coefficient of thermal expansion ranges from 4.9 to 6.2 x 10^-6/°C. This property is crucial for applications requiring thermal stability under varying conditions. Additionally, Kovar exhibits good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for heat-sensitive applications, thus ensuring reliable performance in diverse environments.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Kovar Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carpenter Technology – Kovar UNS #K94610
Domain: carpentertechnology.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Kovar UNS #K94610 is a vacuum melted, iron-nickel-cobalt, low expansion alloy with a controlled chemical composition to ensure precise uniform thermal expansion properties. It is used as a glass and ceramic sealing alloy, manufactured with extensive quality controls to guarantee uniform physical and mechanical properties for ease in deep drawing, stamping, and machining. Type Analysis: Carbon (Max…
2. Hightemp Metals – Kovar® Alloy
Domain: hightempmetals.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Kovar® is a registered trademark of Carpenter Technology Corporation. It is a vacuum melted, iron-nickel-cobalt, low expansion alloy with controlled chemical composition for precise thermal expansion properties. Key elements include: Carbon (max 0.02), Nickel (29.0), Iron (balance), Silicon (max 0.20), Manganese (max 0.30), Cobalt (17.0). Applications include hermetic seals with Pyrex glasses, pow…
3. City Special Metals – Kovar Alloys
Domain: cityspecialmetals.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Kovar is a controlled expansion alloy made up of Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt, originally patented in 1936. It can be fabricated into various parts such as plates, round bars, sheets, coils, wires, and tubes. Kovar is best known for its low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE), which is below the Curie point (435°C or 815ºF), making it expand and contract similarly to hard/borosilicate glass or cera…
4. Mindrum – Kovar Alloy
Domain: mindrum.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Kovar”, “type”: “Iron-Nickel-Cobalt alloy”, “key_properties”: {“coefficient_of_thermal_expansion”: “4.9 – 6.2 (1 x 10^-6/°C)”, “density”: “8.35 g/cm^3”, “hardness”: “68 (Rockwell B)”, “tensile_strength”: “517 MPa”, “modulus_of_elasticity”: “138 GPa”, “poisson_ratio”: “0.317”, “thermal_conductivity”: “17 W/m K”, “specific_heat”: “460 J/kg*K”}, “applications”: [“satellite propulsion system…
5. ESPI Metals – Kovar Alloy
Domain: espimetals.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {‘name’: ‘Kovar’, ‘type’: ‘iron-nickel-cobalt alloy’, ‘applications’: ‘suitable for uses requiring matched-expansion seal between metal and glass parts, widely used in electronics industry for glass-to-metal seals in devices like power tubes and x-ray tubes’, ‘typical_analysis’: {‘Ni’: ’29’, ‘Co’: ’17’, ‘Fe’: ‘Balance’, ‘Si’: ‘0.10’, ‘Mn’: ‘0.30’, ‘C’: ‘0.02 maximum’}, ‘typical_physical_properties…
6. Prototek – Kovar Alloy
Domain: prototek.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Kovar is a special metal alloy primarily composed of 29% nickel, 17% cobalt, and 54% iron. It is known for its unique properties, including: 1. Thermal Expansion: Expands and contracts at the same rate as borosilicate glass, making it ideal for creating strong seals between metal and glass. 2. Corrosion Resistance: Resists rust and corrosion, ensuring durability in harsh environments. 3. Precision…
7. Digital Fire – Kovar Metal Alloy
Domain: digitalfire.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Kovar metal is a nickel-cobalt alloy that is thermally compatible with borate glazes, allowing it to be glazed and fired like pottery at cone 05-06. It has a thermal expansion that can match borosilicate glass, maintaining bond integrity over a wide range of temperatures. The metal-to-glass bond is achieved through a thin layer of cobalt or nickel oxide. Common hobby ceramic glazes for cone 05-06 …
8. Kryton Metals – Kovar Alloy
Domain: blog.krytonmetals.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Kovar is an iron-nickel-cobalt alloy designed to have thermal expansion properties similar to borosilicate glass, allowing for tight mechanical joints between materials over a wide temperature range. It is used in applications such as light bulbs, vacuum tubes, aerospace sensors, and scientific research equipment. Key advantages of Kovar include low magnetic interference, thermal stability, and du…
9. Kovar® – ASTM F15 Alloy Properties
Domain: efineametals.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Kovar® | ASTM F15 Alloy Properties: Typical properties and standards include mean coefficient of thermal expansion. Kovar® is also known as Pernifer® 2918, Dilver® P1, and Nilo® K. The properties of Kovar® are critical for evaluating its suitability for various applications.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for kovar metal
As the demand for precision-engineered components continues to rise across various sectors, Kovar metal stands out as a critical material for applications that require stable thermal expansion properties. Its unique composition allows it to be an ideal choice for glass-to-metal seals and electronic packaging, making it invaluable in industries such as aerospace, defense, and medical technology. The strategic sourcing of Kovar not only ensures access to high-quality materials but also promotes cost efficiency through careful supplier selection and relationship management.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing reliable supply chains for Kovar is essential. Engaging with manufacturers who offer robust quality controls and technical expertise will enhance product reliability and performance. As new applications for Kovar continue to emerge, now is the time to invest in strategic partnerships that can support innovation and growth in your projects.
Looking ahead, the evolving landscape of technology and manufacturing presents abundant opportunities for businesses that prioritize quality sourcing of Kovar. By aligning with reputable suppliers and leveraging Kovar’s unique properties, you can position your company for success in an increasingly competitive market.