Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for kovar alloy
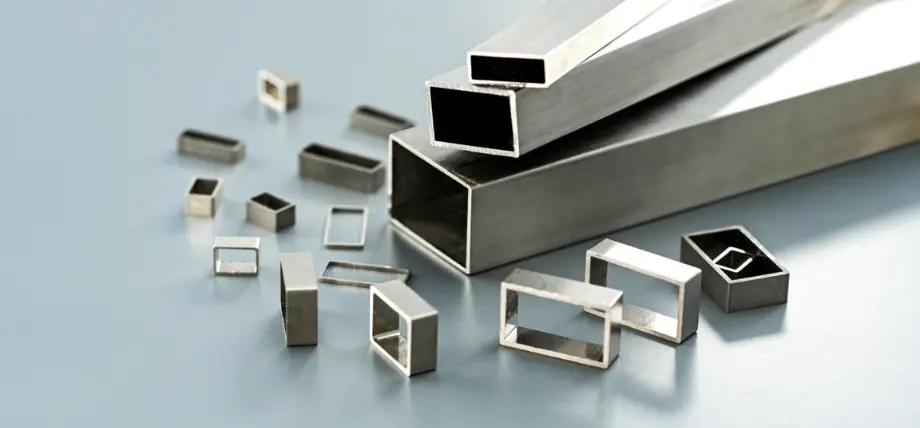
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing Kovar alloy can pose challenges for international B2B buyers, especially when consistent quality and specific thermal properties are critical for manufacturing processes. Kovar, a vacuum-melted iron-nickel-cobalt alloy, is renowned for its low thermal expansion characteristics, making it essential in applications ranging from microwave tubes to satellite propulsion systems. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the diverse types of Kovar alloy, its myriad applications, and crucial factors to consider while sourcing—from supplier vetting to cost analysis.
For B2B buyers navigating markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, making informed purchasing decisions hinges on a deep understanding of Kovar’s unique attributes. This guide empowers stakeholders by highlighting effective strategies for evaluating suppliers, ensuring quality production, and aligning thermal expansion needs with product specifications. Additionally, we delve into emerging trends that impact Kovar alloy sourcing, equipping you with the insights needed to enhance your procurement strategies. With actionable information at your fingertips, you’ll be well-prepared to harness the advantages of Kovar alloy and drive success in your industry. Let’s navigate this complex market together and unlock the potential of this specialty alloy.
Understanding kovar alloy Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kovar 29 | High nickel content (29%); excellent thermal expansion matching | Electronics (IC packaging), aerospace | Pros: Excellent thermal expansion match; good machinability. Cons: Higher cost compared to standard alloys. |
| Kovar 17 | Lower nickel content (17%); better magnetic properties | Telecommunications, microwave applications | Pros: Improved magnetic performance; lower cost. Cons: Less thermal expansion consistency. |
| Kovar 45 | Enhanced hardness and strength properties; developed for high-stress applications | Defense, medical devices | Pros: Increased durability; suitable for high-stress applications. Cons: More complex processing requirements. |
| Kovar 25 | Balanced properties between Kovar 17 and Kovar 29 | Automotive sensors, precision instruments | Pros: Versatile; good balance of machinability and performance. Cons: May not excel in niche applications focused on extreme properties. |
| Kovar LT | Low thermal expansion variant; tailored for specific applications | Optical systems, specialized sensors | Pros: Tailored properties for precision applications; low thermal drift. Cons: Requires specialized processing; may have limited availability. |
What Are the Characteristics of Kovar 29 Alloy?
Kovar 29 is a leading variant known for its high nickel content of 29%. This composition facilitates an exceptional thermal expansion coefficient that closely matches materials like borosilicate glass, making it ideal for electronic applications, particularly in integrated circuit packaging. Buyers should consider that while Kovar 29 provides excellent machinability and robustness, it typically comes at a higher price point, making it a significant investment for manufacturers requiring precision and reliability.
How Does Kovar 17 Differentiate Itself?
Kovar 17 stands out with its reduced nickel composition of 17%, enhancing its magnetic properties. This variant is particularly valuable in telecommunications and microwave applications, where magnetic performance is paramount. Though it offers a more economical option compared to its high-nickel counterparts, purchasing agents must be aware of its less consistent thermal expansion characteristics, potentially limiting its application in highly sensitive environments.
Why Is Kovar 45 Preferred in High-Stress Applications?
Kovar 45 is engineered for applications that face significant stress, characterized by enhanced hardness and tensile strength. It is often deployed in rough environments, such as defense and medical devices, where durability is crucial. While its high-stress suitability is a considerable advantage, manufacturers should account for the more complex processing requirements that may necessitate specialized tooling or techniques.
What Makes Kovar 25 a Versatile Option?
Kovar 25 strikes a balance between the properties of Kovar 17 and Kovar 29, offering versatility across multiple applications including automotive sensors and precision instruments. Its balanced performance makes it a strategic choice for buyers pursuing multiple use cases without extreme specialization. However, it is essential to note that Kovar 25 might not be the best solution for applications demanding specialized thermal or magnetic attributes.
When to Choose the Low Thermal Expansion Variant, Kovar LT?
Kovar LT is tailored for precision applications requiring minimal thermal drift, particularly in optical systems and specialized sensors. This low expansion variant ensures optimal performance in environments where thermal fluctuations are inevitable. Potential buyers should be prepared to manage the specialized processing it demands and understand its specific application suitability, which may limit its widespread use.
Key Industrial Applications of kovar alloy
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Kovar Alloy | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Sealing components for transistors and diodes | Enables reliable hermetic seals, ensuring long-term performance | Require consistent thermal expansion rates and precise machining capabilities. |
| Aerospace and Defense | Components in satellite propulsion systems | Guarantees durability and performance in extreme conditions | Focus on supplier certifications for aerospace-grade materials. |
| Automotive | Glass-to-metal seals in automotive sensors | Enhances reliability and reduces risk of failure under stress | Demand traceability and testing for high-stress applications. |
| Medical Devices | Encapsulation of electronic components in medical instruments | Ensures biocompatibility and reliability in critical devices | Must adhere to stringent medical standards and regulations. |
| Telecommunications | Metal end caps for microwave and communication tubes | Improves signal integrity and operational efficiency | Specify matching thermal properties with ceramic components for optimal performance. |
What Are the Key Applications of Kovar Alloy in Electronics?
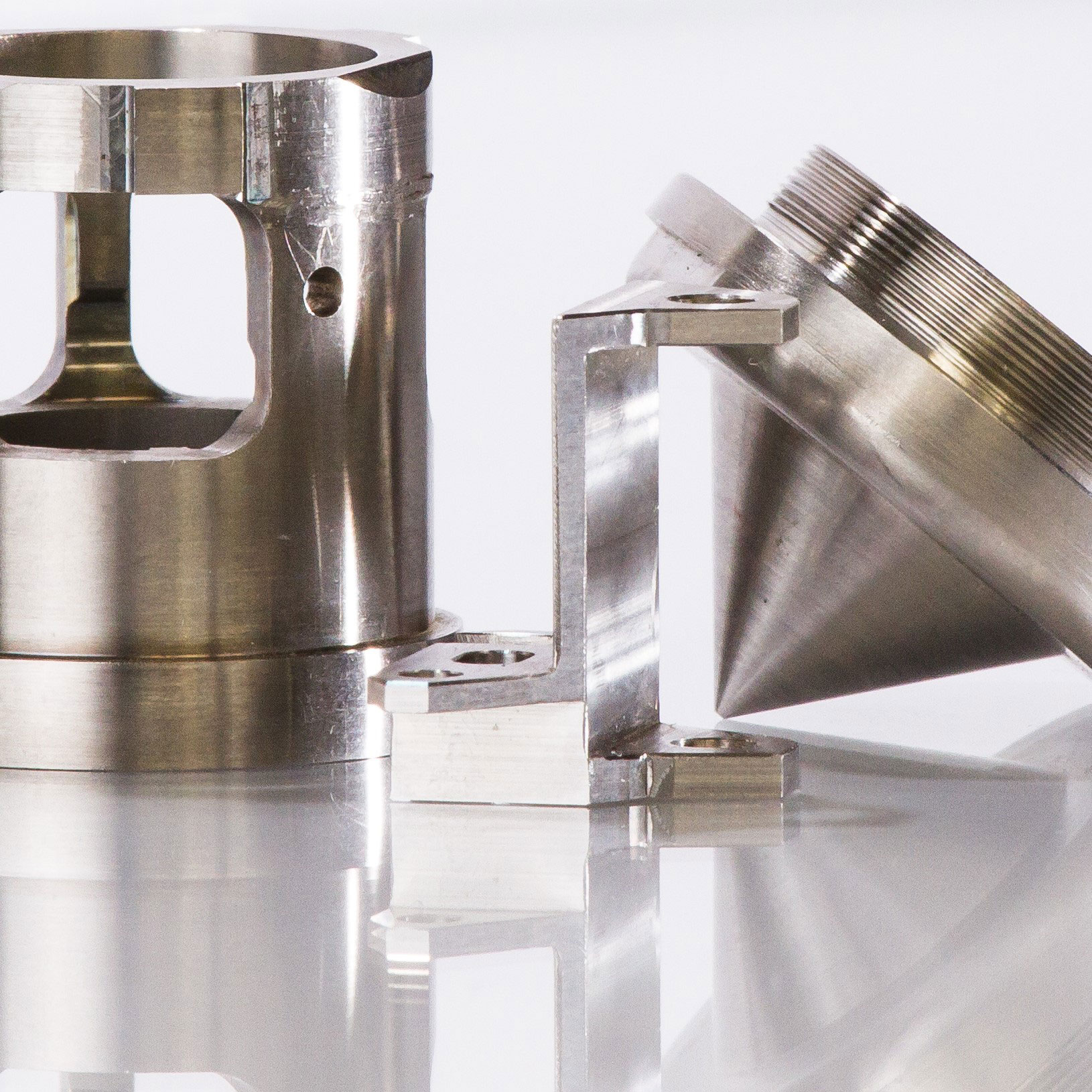
Kovar alloy is predominantly utilized in the electronics industry for hermetic sealing of transistors and diodes. Its low thermal expansion coefficient makes it compatible with various glass types, ensuring long-term reliability. Buyers in this sector should source Kovar that adheres to strict manufacturing standards to prevent thermal mismatch and ensure durability in high-performance applications.
How Is Kovar Alloy Leveraged in Aerospace and Defense?
In aerospace, Kovar is critical for components within satellite propulsion systems. Its resilience to fluctuations in temperature and pressure is paramount for functionality in extreme environments. International buyers must emphasize suppliers who are certified for aerospace-grade materials to meet the rigorous standards of safety and performance required in this sector.
What Role Does Kovar Play in the Automotive Industry?
Kovar is increasingly used in automotive sensors, where glass-to-metal seals are essential for durability and performance. These sensors must withstand harsh conditions, making Kovar’s reliable sealing properties invaluable. When sourcing Kovar for automotive applications, buyers should ensure traceability and testing for high-stress scenarios to mitigate risks of component failure.
Why Is Kovar Preferred in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device sector, Kovar alloy is used to encapsulate electronic components in instruments requiring biocompatibility and reliability. Its ability to be molded into complex geometries while retaining thermal properties is crucial for device functionality. Buyers must prioritize compliance with medical standards and regulations, ensuring that the materials used do not pose health risks.
How Does Kovar Alloy Enhance Telecommunications Equipment?
Kovar is utilized in telecommunications for metal end caps in microwave and communication tubes, where it improves signal integrity and operational efficiency. Ensuring that Kovar components match the thermal properties of ceramic parts is vital for optimal performance. B2B purchasers should focus on specifications and mechanical properties to guarantee high-quality output that meets industry standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘kovar alloy’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Proper Sourcing Challenges in Kovar Alloy Procurement
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties when trying to source high-quality Kovar alloy due to inconsistent supplier standards and varying product specifications. This inconsistency can lead to challenges in meeting project deadlines, as batch variations might compromise the material’s critical properties, such as thermal expansion rates. Buyers from industries such as aerospace or medical devices face the additional burden of stringent regulatory compliance, making it essential that the Kovar they procure meets precise specifications consistently.
The Solution: To tackle this sourcing challenge, it is crucial for buyers to vet suppliers rigorously. Begin by requesting detailed material certification to ensure that the Kovar alloy meets the necessary ASTM standards, such as ASTM F-15. Engage with suppliers that can provide thorough documentation of their quality control processes. Look for companies that perform comprehensive in-house testing, including thermal expansion measurement and tensile strength analysis, adhering strictly to uniform composition limits. Establishing long-term partnerships with a reliable supplier who understands your specific application needs can also reduce variability in quality across different orders, providing peace of mind throughout the production timeline.
Scenario 2: Difficulties in Machining Kovar Alloy Components
The Problem: Machining Kovar alloy presents significant challenges due to its unique properties, which may lead to excessive tool wear, warping, or difficulty in achieving the desired precision. Buyers often face frustration when the machined parts do not meet specifications or when production processes slow down due to the need for adjustments, leading to increased costs and project delays.
The Solution: To effectively machine Kovar alloy, it is vital to employ the right tooling, speeds, and feeds tailored to its specific characteristics. Use carbide tools specifically designed for difficult-to-machine materials, ensuring they are well-maintained and sharp. A recommended approach is to use a high-speed steel (HSS) or cobalt-based tool for turning operations, alongside appropriate coolant to manage heat and friction. Create a comprehensive machining guideline that outlines optimal feed rates (approximately 0.010″ to 0.012″ per revolution) and temperature management techniques during the cutting process. Investing in quality tooling and providing thorough training for machinists can help overcome these challenges, thus improving both efficiency and output quality.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compatibility in Glass and Metal Sealing Applications
The Problem: A common concern for B2B buyers using Kovar in glass-to-metal sealing applications is ensuring compatibility with the sealing materials, such as borosilicate glass. If the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of Kovar does not perfectly match that of the sealing glass, the final product may suffer from stress fractures or premature failure, ultimately affecting reliability and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To ensure optimal compatibility, it is essential to conduct comprehensive thermal expansion testing as part of the design phase. Create detailed specs that define the desired thermal expansion characteristics of both materials being sealed. Work with a supplier that provides Kovar alloy with a known CTE that closely aligns with that of the glass or ceramic components. A proactive approach includes collaborative testing of prototypes to identify any potential mismatch before full-scale production begins. Consider integrating a secondary layer or oxide coating on the Kovar to enhance the sealing surfaces further. Conducting trials and focusing on achieving the right combination of materials will mitigate compatibility issues, thus promoting longer-lasting and reliable products crucial in sectors like aerospace and telecommunications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for kovar alloy
What are Common Alternatives to Kovar Alloy?
When considering materials for high-precision applications, Kovar alloy is often compared with various alternatives. Here, we will analyze several common materials based on key properties and advantages and disadvantages, focusing on aspects pertinent to B2B buyers.
How Does Invar Compare to Kovar Alloy?
Key Properties: Invar, an iron-nickel alloy, boasts a very low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), typically around 1.2 x 10^-6/°C. It is specifically designed to maintain dimensional stability when subjected to temperature variations.
Pros & Cons: Invar excels in applications where thermal expansion needs to be minimized, making it a favorite in precision instruments and aerospace components. However, its corrosion resistance is relatively low compared to Kovar, necessitating protective coatings in harsh environments. Additionally, Invar can be more expensive and may have a more complex manufacturing process due to its specific heat treatment needs.
Impact on Application: Invar is suitable for temperature-sensitive measuring devices, optical equipment, and aerospace components, where precision is crucial. It is commonly used in international markets, and compliance with ASTM standards is essential for ensuring quality.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with strict aerospace standards, such as Europe or the Middle East, should be aware of certification processes needed for Invar. Understanding local certifications will help expediate compliance and procurement procedures.
What About Molybdenum as a Kovar Alternative?
Key Properties: Molybdenum offers high melting points (around 2620°C) and exceptional strength under extreme temperatures. It has good resistance to corrosion, particularly in high-temperature environments.
Pros & Cons: Its significant high-temperature strength makes Molybdenum ideal for aerospace and military applications. However, it can be expensive and challenging to machine compared to Kovar, requiring specialized tools. The need for high manufacturing complexity limits its mass production feasibility.
Impact on Application: Molybdenum is often utilized in high-temperature furnaces and components that experience extreme thermal environments. Its susceptibility to oxidation can limit its application in certain media within industrial processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Firms in Latin America looking to procure Molybdenum for their operations must consider import tariffs and the additional costs incurred due to its processing complexities. Knowledge of DIN and JIS standards is critical for compliance.
Is Stainless Steel a Viable Alternative to Kovar Alloy?
Key Properties: Stainless steel, known for its good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, has a variable CTE depending on the alloy. The most common types have a CTE in the range of 16 to 20 x 10^-6/°C.
Pros & Cons: A major advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, which makes it suitable for various applications. However, it doesn’t match Kovar’s CTE closely, which is essential for glass sealing applications. Additionally, it is often more difficult to achieve tight tolerances in machining.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for a wide array of industries, including food processing and medical devices, but may not suit precision applications involving glass-to-metal seals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM or ISO standards is crucial for international buyers, particularly in Europe and Asia. Familiarity with local regulations regarding stainless steel can aid in smoother procurement processes.
How Does Glass Ceramics Compare to Kovar Alloy?
Key Properties: Glass ceramics are materials engineered to possess both glass and ceramic properties, making them ideal for thermal expansion compatibility with metals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of glass ceramic is its exceptional thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. However, it is generally more fragile and can be challenging to integrate in manufacturing processes where mechanical strength is needed.
Impact on Application: Glass ceramics are widely used in electronics and insulators due to their thermal properties. Specific compatibility with metals like Kovar can enhance product durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers from Africa and South America, understanding the interplay between glass ceramics and metals like Kovar is essential for ensuring effective design and manufacturing processes. Regulatory compliance unique to their local markets will also be crucial.
Summary of Material Alternatives to Kovar Alloy
| Material | Typical Use Case for Kovar Alloy | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invar | Precision instruments | Very low thermal expansion | Limited corrosion resistance and high cost | High |
| Molybdenum | Aerospace components | Excellent high-temperature strength | More expensive and difficult to machine | High |
| Stainless Steel | Various industrial applications | Good durability and corrosion resistance | Higher CTE, challenging tolerance requirements | Medium |
| Glass Ceramics | Electronics and insulators | Exceptional thermal stability | Fragility and integration issues with manufacturing | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with insightful comparisons to assist in strategic material selection, particularly in international contexts. Understanding the unique properties, advantages, and considerations for each option will facilitate informed decisions for their specific needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for kovar alloy
Kovar alloy manufacturing and quality assurance processes are critical for ensuring the performance and reliability of components used in demanding applications across various sectors, such as telecommunications, medical devices, and aerospace. Understanding these processes can significantly aid B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions. This overview provides insights into the typical manufacturing stages, key techniques employed, and the necessary quality control (QC) measures that should be in place.
What Are the Main Stages of the Kovar Alloy Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing process for Kovar alloy involves several key stages, including material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How Is Kovar Alloy Initially Processed?
In the initial phase, high-purity iron, nickel, and cobalt are selected based on stringent quality criteria. The chosen materials undergo vacuum melting to achieve a uniform chemical composition tailored to incorporate specific thermal expansion properties. The advantage of vacuum melting is that it minimizes contamination and facilitates the production of fine-grained metal with enhanced mechanical properties. This method also allows the manufacturer to control the alloy’s final properties closely, which is essential for applications requiring low thermal expansion.
What Techniques Are Used to Form Kovar Alloy?
Once the alloy is prepared, forming techniques such as deep drawing, stamping, and machining are employed. These methods allow the alloy to be shaped into precise components. Deep drawing is particularly common for producing complex geometries, while machining is often utilized for achieving tight tolerances. Careful control of temperature during forming is crucial, as Kovar is also sensitive to heat treatment; overheating can lead to oxidation, which may adversely affect the metal’s properties.
How Is Assembly Handled in Kovar Alloy Manufacturing?
The assembly stage typically involves the integration of Kovar components with other materials, often glass or ceramics, due to its compatibility in thermal expansion. Technical expertise is required to ensure that these materials are compatible for hermetic sealing applications, which are common in devices like semiconductors and microwave tubes. The components are carefully cleaned and may undergo surface treatments to enhance bonding capabilities with the sealing materials.
What Finishing Processes Ensure Quality in Kovar Alloy Products?
Finishing processes include precise machining to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finishes, followed by cleaning to remove any debris or contaminants. This stage may involve various methods, such as acid pickling or ultrasonication. Surface treatment techniques might also be implemented to improve oxidation resistance or lubrication for further processing.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Kovar Alloy Quality Assurance?
To ensure Kovar alloy products meet the highest safety and performance standards, adherence to international standards is essential. ISO 9001 serves as a baseline certification for quality management systems applicable to manufacturers across various industries. Furthermore, industry-specific regulations such as CE marking for equipment sold in the European market or compliance with API specifications for aerospace components must be observed.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Should Be Established for Kovar Alloy Production?
Implementing effective QC checkpoints at different manufacturing stages is critical.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints?
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials such as iron, nickel, and cobalt are evaluated for compliance with specified chemical compositions and mechanical properties.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring during production processes ensures part dimensional accuracy and consistency of material properties. Key tests conducted during IPQC may include thermal expansion measurements and mechanical property assessments.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo extensive testing, including integrity checks (e.g., hermetic seals) and material property verification (tensile strength and thermal conductivity).
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Kovar Alloy Quality Assessment?
A variety of testing methods are employed to guarantee the integrity and performance of Kovar products. These typically include:
- Metallography: Examines the microstructure to ensure appropriate grain size and distribution.
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluates tensile strength, hardness (via Rockwell or Brinell methods), and ductility.
- Thermal Testing: Measures the coefficient of thermal expansion to confirm compliance with specifications.
- Hermeticity Testing: For applications involving seals, tests such as the Leak Test and Helium Leak Detection are crucial to ensure there are no breaches in the materials.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier QC Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to assess the quality standards of their suppliers.
What Verification Methods Are Available?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities allows buyers to observe QC practices in real-time and evaluate the effectiveness of processes and certifications.
- Review of Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide periodic quality assurance reports detailing their testing methods and results for transparency.
- Third-Party Inspection: Enlisting independent inspection services can offer unbiased validation of a supplier’s claims regarding quality control and compliance with industry standards.
What Unique QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, especially those sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, nuances such as local regulatory requirements and import/export compliance certifications become critical. Adherence to local standards, while ensuring compatibility with international norms, may require coordinating efforts with suppliers to bridge language barriers, cultural differences, or varying compliance expectations.
In summary, understanding Kovar alloy’s manufacturing processes and the associated quality assurance measures can equip international B2B buyers with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions. By focusing on specifications, pursuing reliable suppliers, and navigating the complexities of international compliance, businesses can secure high-quality Kovar alloy products tailored to their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘kovar alloy’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring Kovar alloy effectively, this guide offers a comprehensive checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. Kovar alloy is invaluable for its unique thermal properties, making it a go-to option for specialized applications. Use this checklist to ensure you cover all necessary steps for successful procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical to ensure that the supplied Kovar alloy meets the performance needs of your applications. Specify the required chemical composition, mechanical properties, and any pertinent dimensional tolerances. This clarity will help suppliers tailor their offerings to your specific requirements.
Step 2: Research and Select Reputable Suppliers
Identifying reputable suppliers is essential for securing high-quality Kovar alloy. Utilize online directories and industry databases to compile a list of potential vendors. Prioritize companies with a solid track record in producing alloy materials, and check for established certifications such as ISO 9001 or relevant industry standards, which indicate quality management practices.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing a supplier, it’s vital to verify their certifications to ensure compliance with international standards. Certifications not only reflect the quality controls in place during production but also reassure you about their capability to meet your specifications consistently. Request copies of certifications and inquire about their testing methods.
Step 4: Request Sample Materials for Testing
Securing material samples for testing is a proactive way to evaluate the quality of Kovar alloy. By conducting your own evaluations, such as verifying thermal expansion properties and mechanical performance, you can ascertain if the alloy aligns with your application needs. This step minimizes risks associated with quality discrepancies post-purchase.
Step 5: Discuss Pricing, Volume Discounts, and Payment Terms
Engaging in open discussions regarding pricing is crucial to align expectations between your business and the supplier. Inquire about bulk purchase discounts, as well as various payment terms available. Understanding the pricing structure upfront can also help you manage budgets effectively and prevent unexpected cost escalations.
Step 6: Understand Logistics and Shipping Arrangements
Clarify the logistics involved in the procurement process, including delivery timelines and shipping costs. Timely delivery is essential to keep your production schedule on track, especially for projects with tight deadlines. Discuss responsibility for insurance during transport, and confirm the shipping methods that best suit your operational needs.
Step 7: Review and Finalize the Contract Terms
Before finalizing the purchase, thoroughly review all contract terms, including warranties and service agreements related to Kovar alloy. Make sure that all agreements regarding return policies, defect handling, and post-purchase support are clearly articulated. This helps mitigate future disputes and aligns expectations between both parties effectively.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a well-organized procurement process for Kovar alloy, maximizing both quality and efficiency while minimizing risks and uncertainties.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for kovar alloy Sourcing
What Are the Primary Cost Components for Sourcing Kovar Alloy?
When evaluating the cost structure of sourcing Kovar alloy, several fundamental components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
Materials: The primary cost driver is often the raw materials. Kovar’s unique composition demands high-purity iron, nickel, and cobalt, all of which are subject to market fluctuations. As a specialty alloy, its price can be significantly higher than standard metals.
Labor: Skilled labor required for machining Kovar can drive costs upward. The alloy is difficult to work with, necessitating experienced machinists familiar with advanced tooling and precise engineering methods.
Manufacturing Overhead: Costs related to the facilities, utilities, and operational processes play a crucial role. Kovar’s production involves stringent quality controls and specialized processes that can increase overhead costs.
Tooling: Given Kovar’s properties, specific tooling is necessary for effective machining. The choice of tooling materials and the maintenance of these tools can impact overall costs.
Quality Control: Rigorous QC measures are essential in Kovar production to ensure consistent properties. This aspect is non-negotiable for many applications across industries like aerospace and electronics.
Logistics: Transporting Kovar alloy adds another layer of cost, particularly for international buyers. Expenses here can be affected by factors such as distance, mode of transport, and shipping regulations.
Margin: Finally, the supplier’s margin is influenced by their operational strategy, market position, and the unique attributes of the Kovar they supply.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Kovar Alloy Sourcing?
A variety of factors contribute to the pricing of Kovar alloy, including volume requirements, specifications, material quality, supplier reliability, and logistics.
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often have minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can influence per-unit pricing. Larger orders typically benefit from reduced costs due to economies of scale.
Specs/Customization: Customized specifications for Kovar alloy, such as varying dimensions or mechanical properties, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly understand their requirements to avoid costly modifications after an order is initiated.
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of Kovar alloy, including certifications like ASTM specifications, significantly affects its cost. Superior quality often comes at a premium, which is justified in applications that face stringent performance expectations.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and capabilities of the supplier can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more, but often provide better support, reliability, and assurances of quality.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for estimating total costs. These terms play a key role in determining who bears the costs and responsibilities associated with transportation, insurance, customs clearance, and delivery.
What Tips Can Enhance Your Cost-Effectiveness in Buying Kovar Alloy?
For international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency.
Negotiation Skills: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can yield better pricing and service terms. Be prepared to negotiate on the volume, delivery timings, and payment terms.
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): TCO goes beyond the initial purchase price and includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Assessing TCO can inform more strategic sourcing decisions that align with long-term business goals.
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Variability in currency exchange rates, geopolitical factors, and import tariffs can affect the pricing of Kovar alloy. Keeping abreast of these trends will enable better forecasting and budgeting.
Regular Market Analysis: Monitoring the commodity prices for cobalt and nickel, as well as changes in global demand for Kovar, will assist in making informed purchasing decisions. Resources like industry reports and supplier insights can be invaluable.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for Kovar alloy can fluctuate widely based on several factors outlined above. For accurate quotations and up-to-date price ranges, engaging directly with suppliers is recommended.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing kovar alloy With Other Solutions
When considering manufacturing processes that require high thermal stability and precision, choosing the right material is crucial. Kovar alloy, known for its unique thermal expansion properties and mechanical strength, has several alternatives that may fit specific applications. Below, we explore viable alternatives to Kovar alloy, assessing their characteristics across several factors.
| Comparison Aspect | Kovar Alloy | Invar Alloy | Molybdenum Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent thermal stability, low thermal expansion coefficient, high machinability. | Very low thermal expansion, maintaining dimensional stability over varying temperatures. | High melting point, excellent strength at high temperatures, good thermal conductivity. |
| Cost | Moderate to high cost due to specialized manufacturing. | Generally higher than Kovar; premium pricing for finely controlled alloy. | Higher than Kovar, often price-prohibitive for large-scale applications. |
| Ease of Implementation | Good machinability, facilitating complex designs; requires specific toolings. | More difficult to machine; requires specialized tools and setups. | Typically challenging to machine; requires careful processing to avoid deformation. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; stable and reliable in performance. | Low maintenance but sensitive to fabrication quality and heat treatment. | Requires regular monitoring at high temperatures; subject to oxidation without protection. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for electronic components, glass/metal seals, and hermetic packages. | Best suited for precision optical instruments and components requiring exceptional stability. | Perfect for aerospace and high-temperature applications, such as components in reactors. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Invar Alloy?
Invar alloy, an iron-nickel alloy, is recognized for its incredibly low thermal expansion, making it ideal for applications where stability across variable temperatures is paramount. One of its notable strengths is its ability to maintain dimensions, which is essential in precision instruments such as measuring devices and optical components. However, the challenges of machining Invar can lead to higher production costs and require specialized tools, making it less accessible for some manufacturers compared to Kovar.
How Does Molybdenum Alloy Compare to Kovar Alloy?
Molybdenum is known for its high melting point and excellent high-temperature performance. This makes it suitable for extreme conditions, including aerospace applications and components within nuclear reactors where thermal resistance is vital. Despite its robust properties, Molybdenum’s high cost and difficulties in machining can limit its use to niche applications where performance justifies the cost. In contrast, Kovar offers a more balanced solution for a wider array of electronic and hermetic applications due to its ease of fabrication.
Choosing the Right Material: What Should B2B Buyers Consider?
When faced with the choice between Kovar alloy and its alternatives, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific application demands, including thermal requirements, cost constraints, and mechanical properties. If precision and low thermal expansion are crucial, Invar might be the best option. For high-temperature scenarios, Molybdenum may be the better fit, albeit at a higher cost and with machining challenges. Kovar, with its balanced performance and versatility, often strikes the ideal balance for many industrial applications, especially in electronics and sealing technologies. By weighing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for kovar alloy
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Kovar Alloy That Impact Purchase Decisions?
Kovar alloy, classified as UNS #K94610, is a vacuum melted iron-nickel-cobalt alloy noted for its low thermal expansion and precise mechanical properties. Understanding its technical specifications is critical for international B2B buyers, particularly in industries requiring stringent performance standards. Here are some key properties to consider:
-
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE): Kovar’s CTE typically ranges from 4.9 to 6.2 x 10^-6 /°C. This property allows Kovar to expand and contract similarly to glass and ceramics, making it ideal for sealed applications. B2B buyers must ensure the CTE aligns with the specifications of glass or ceramic components to avoid stress fractures in assemblies.
-
Mechanical Strength: With a tensile strength of approximately 517 MPa and a hardness rating of 68 on the Rockwell B scale, Kovar demonstrates impressive mechanical resilience, crucial for high-stress applications like electronic packaging and aerospace components. Evaluating the specific mechanical properties can help buyers identify suitable grades for their projects without compromising performance.
-
Thermal Conductivity: Kovar exhibits thermal conductivity of about 17 W/m·K, allowing efficient heat dissipation in electronic devices. For B2B buyers in the electronics sector, this quality is paramount to ensuring that heat-sensitive components stay within operational temperature limits.
-
Manufacturing Tolerances: This alloy can be machined to precise tolerances due to its workability, enabling the manufacturing of complex geometries. Understanding tolerance levels is vital for B2B buyers aiming for high accuracy in applications, as deviations can lead to function failures in end-use products.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Familiarize Themselves With?
Navigating the purchase process involves understanding commonly used trade terms. Here are essential terminologies related to Kovar that B2B buyers should grasp:
-
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM): An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of Kovar, understanding OEM relationships is crucial for sourcing components that fit seamlessly into larger systems like defense electronics or medical devices.
-
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): This term indicates the smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. For Kovar, MOQs can significantly affect pricing and procurement strategies, especially for smaller companies or those entering new markets where usage volume is uncertain.
-
Request for Quote (RFQ): An RFQ is a document submitted to suppliers asking for pricing information based on specific requirements. Crafting an accurate RFQ for Kovar not only expedites the procurement process but also ensures prospective suppliers understand the project’s technical and commercial needs.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce to clarify shipping responsibilities between buyers and sellers. For buyers of Kovar, understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) will clarify shipping costs and liability.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving it. In the context of Kovar, lead times can be influenced by material availability and production schedules. Buyers must factor these into project timelines to avoid delays in product launches.
Familiarity with these specifications and terms not only empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions but also ensures a smoother purchasing process, ultimately yielding better operational outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the kovar alloy Sector
Global Kovar Alloy Market Overview & Key Trends
The Kovar alloy market is witnessing significant growth, driven by its unique properties that make it suitable for various high-tech applications across multiple sectors. The low expansion characteristics of Kovar, which aligns its thermal expansion with materials like borosilicate glass, are critical in industries ranging from electronics to aerospace. The increasing demand for miniaturization of devices is pushing manufacturers to seek materials that can maintain integrity under varying temperatures, further bolstering the demand for Kovar.
Emerging trends highlight a shift towards automation and digitalization in sourcing practices. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies allows buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to enhance procurement efficiency. Modern supply chain solutions that utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning are optimizing inventory management and forecasting, aligning procurement strategies with real-time market dynamics. Additionally, increased collaboration among international suppliers is fostering innovative solutions and accelerating the delivery of Kovar products to global markets, notably benefiting regions with burgeoning tech industries.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape is evolving as new entrants leverage lower production costs while maintaining quality. Buyers from diverse regions, especially Brazil and Vietnam, are increasingly prioritizing not just cost but also the reliability of their suppliers, encouraging vendors to refine their quality assurance processes.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
In today’s environmentally conscious market, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount for B2B buyers in the Kovar alloy sector. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of sourcing decisions, driving a demand for more eco-friendly practices throughout the supply chain. Manufacturers are now adopting sustainable practices to limit carbon footprints and reduce waste during production processes.
Ethical supply chains are gaining traction as consumers increasingly prefer businesses that support responsible sourcing. Factors such as fair labor practices and adherence to environmental regulations are prominent among international buyers from regions like the Middle East and Africa. As a result, alloy suppliers are encouraged to obtain ‘green’ certifications that can showcase their commitment to sustainability.
Kovar alloy, being recyclable, presents a unique opportunity for sustainable procurement. The existence of ‘green’ labels could enhance buyer confidence and satisfaction, making it preferable for companies looking to partner with socially and environmentally responsible suppliers. By prioritizing these ethical sourcing practices, organizations not only cater to consumer demand but also contribute to long-term sustainability in the Kovar alloy market.
Brief Evolution/History of Kovar Alloy
Kovar alloy was developed in the mid-20th century, primarily to address the challenges of achieving stable hermetic seals for electronic devices. Over decades, its application has expanded beyond electronics to critical fields such as aerospace and telecoms. The alloy’s thermal expansion properties aligned closely with various substrates made Kovar a go-to material for harsh environments, especially where temperature fluctuations occur.
As globalization took hold, the production of Kovar transitioned toward more advanced manufacturing techniques, including vacuum melting methods that ensure a high degree of purity and consistency. This evolution enabled producers to meet expanding global demands and address the particular needs of emerging markets in regions like South America and Southeast Asia. Today, Kovar remains a pivotal material in cutting-edge technologies, offering a broader scope for innovation and application across multiple sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of kovar alloy
-
How do I ensure the quality of Kovar alloy for my application?
To ensure the quality of Kovar alloy, request material certification and detailed specifications from suppliers. Be sure to inquire about the alloy’s chemical composition and physical properties, as these can significantly affect performance in applications like hermetic sealing with glass or ceramics. Additionally, consider asking for samples prior to bulk orders to evaluate machining characteristics and surface finishes. Collaborating with well-established suppliers who adhere to relevant industry standards, such as ASTM specifications, will also help in securing reliable quality. -
What is the best Kovar alloy for extremely tight tolerance applications?
When precision is paramount, Kovar 29 (often referred to simply as Kovar) is the preferred choice due to its well-controlled coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that closely matches materials like borosilicate glass. This alloy is particularly beneficial in high-tech applications like integrated circuits and aerospace components. Ensure that the supplier employs strict quality controls during manufacturing to achieve optimal dimensional accuracy and surface finish, which are critical for tight tolerance applications. -
How can I efficiently source Kovar alloy internationally?
Efficiently sourcing Kovar alloy internationally involves identifying reputable suppliers with experience in exporting to your region. Use platforms like industry trade shows and online B2B marketplaces to gather insights and initiate contact. Conduct thorough vetting, including checking references and previous client feedback. Evaluate potential suppliers’ logistical capabilities, certifications, and compliance with relevant trade regulations. Establish reliable communication channels and be clear about your requirements to streamline the procurement process. -
What should I consider when discussing Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) with suppliers?
When discussing MOQ with Kovar alloy suppliers, consider your project requirements, budget, and storage capabilities. Many suppliers offer flexible MOQ options depending on the specific alloy form and quantity. However, high-demand periods may increase MOQs, so it’s advisable to cultivate a relationship with your supplier, potentially allowing for negotiations on minimums that accommodate your needs. Additionally, ordering larger quantities can often reduce the per-unit cost, providing better overall value. -
What payment terms are typically available for international orders of Kovar alloy?
Payment terms for international Kovar alloy orders can vary significantly from supplier to supplier. Common terms include options like partial upfront payment, Letter of Credit (LC), or Open Account terms for established relationships. It’s essential to clarify these terms during contract negotiations to ensure mutual understanding. Be mindful of currency fluctuations, and consider securing a fixed exchange rate if applicable to safeguard against potential cost changes during the transaction process. -
How do I vet potential suppliers of Kovar alloy?
Vetting suppliers of Kovar alloy involves assessing their industry experience, certifications, and reputation. Begin by reviewing their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Requesting references or case studies from previous clients can provide insights into reliability and capability. Investigate their compliance with international standards, and ensure they have a solid logistical framework for timely delivery. A visit to the production facility, if feasible, can further enhance your confidence in their operational capabilities. -
What logistics challenges should I anticipate when importing Kovar alloy?
Logistics challenges when importing Kovar alloy may include customs clearance delays, shipping costs, and potential damage during transport. It’s crucial to work closely with suppliers and freight forwarders who are experienced in handling metal shipments. Ensure proper packaging that minimizes risk during transit and verify all customs documentation ahead of shipping. Establish clear timelines for delivery and consider potential tariffs that could impact final costs to avoid unanticipated budget overruns. -
How can customization options for Kovar alloy affect pricing and delivery timelines?
Customization options for Kovar alloy, such as specific geometries, dimensions, and surface treatments, can significantly influence both pricing and delivery timelines. Custom orders often require additional processing time and resources, leading to higher production costs. Engage suppliers early in the design phase to discuss specifications, as this allows for shared insights that may optimize both the ordering process and costs. Clear communication of your requirements will help suppliers provide realistic timelines and pricing estimates.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Kovar Alloy Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carpenter Technology – Kovar UNS #K94610
Domain: carpentertechnology.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Kovar UNS #K94610 is a vacuum melted, iron-nickel-cobalt, low expansion alloy. Its chemical composition is controlled within narrow limits to ensure precise uniform thermal expansion properties. It serves as a glass and ceramic sealing alloy, with extensive quality controls employed during its manufacture for uniform physical and mechanical properties, facilitating ease in deep drawing, stamping, …
2. Hightemp Metals – Kovar Alloy
Domain: hightempmetals.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Hightemp Metals – Kovar Alloy, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Mindrum – Kovar Alloy Solutions
Domain: mindrum.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Kovar is an Iron-Nickel-Cobalt alloy known for a similar coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) to borosilicate glass and other optical materials, facilitating glass-to-metal bonds. Density: 8.35 g/cm^3, Hardness: Rockwell B 68, Tensile Strength: 517 MPa, Modulus of Elasticity: 138 GPa, Poisson’s Ratio: 0.317, CTE: 4.9 – 6.2 x 10^-6/°C, Thermal Conductivity: 17 W/m K, Specific Heat: 460 J/kg*K. Ap…
4. City Special Metals – Kovar Alloy
Domain: cityspecialmetals.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Kovar is a controlled expansion alloy made of Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt, patented in 1936. It has low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) below the Curie point (435°C or 815ºF) and is used for hermetic sealing and glass-to-metal bonded assemblies. Applications include electronics (lightbulb ends, microwave tubes, x-ray tubes, and integrated circuit packages), aerospace (radar systems, satellites…
5. Efineametals – Kovar® ASTM F15 Properties
Domain: efineametals.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: ASTM F15 – Kovar® Typical Properties & Standards – Pernifer® 2918, Dilver® P1, Nilo® K. Key data points to guide customers in their assessment of Kovar®, ASTM F15 Alloy properties including mean coefficient of thermal expansion.
6. Aircraft Materials – Kovar / Nilo K Alloy K
Domain: aircraftmaterials.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: {“Product_Name”:”Kovar / Nilo K / Alloy K”,”UNS_Code”:”K94610″,”ASTM_Standard”:”F15″,”Chemical_Composition”:{“Ni”:”29.0%”,”Fe”:”53.0%”,”Co”:”17.0%”,”C”:”0.04 max”,”Mn”:”0.50 max”,”Si”:”0.20″,”Al”:”0.10 max”,”Cr”:”0.20 max”,”Mg”:”0.10 max”,”Zr”:”0.10 max”,”Ti”:”0.10 max”,”Cu”:”0.20 max”,”Mo”:”0.20 max”},”Density”:”8.36 g/cm3″,”Mechanical_Properties”:{“Condition”:”Annealed”,”Yield_Strength”:”49,000 …
7. Carpenter – Kovar® Alloy
Domain: matweb.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Carpenter Kovar® Alloy”, “description”: “Glass and Ceramic Sealing Alloy”, “categories”: [“Metal”, “Electronic/Magnetic Alloy”, “Ferrous Metal”, “Superalloy”], “tensile_hardness_data”: “Data provided by Carpenter Technology Corporation. Tensile and hardness data for samples annealed 1830°F (999°C) 30 min. then furnace cooled.”, “properties”: {“density”: {“metric”: “8.36 g/cc”, “e…
8. Columbia Metals – Alloy K (Kovar®)
Domain: columbiametals.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Alloy K (Kovar®) is an iron-nickel-cobalt alloy with a controlled chemical composition for precise thermal expansion and mechanical characteristics. It is ideal for high integrity glass-to-metal and ceramic-to-metal seals and is used in applications requiring resistance to thermal shock. Common uses include hermetic seals for Pyrex or borosilicate glasses, alumina-type ceramics, transistors, diode…
9. Azom – Super Alloy KOVAR
Domain: azom.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Super Alloy KOVAR (UNS K94610) is an iron-based alloy containing nickel (29%) and cobalt (17%). This super alloy is designed for high-temperature applications, providing low and uniform thermal expansion properties. Physical properties include a density of 8.3 g/cm³ and a melting point of 1449°C (2640°F). Mechanical properties are as follows: tensile strength of 518 MPa (75 ksi), yield strength of…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for kovar alloy
As the global demand for technologically advanced materials continues to rise, Kovar alloy stands out for its unique properties, particularly its precise thermal expansion matching that of glass and ceramics. This compatibility is vital for applications across diverse industries, from aerospace to medical devices. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the advantages of Kovar can enhance sourcing strategies, ensuring access to high-quality components that meet strict manufacturing specifications.
Strategic sourcing of Kovar not only guarantees consistency in product performance but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers. Leveraging Kovar’s machinability and adaptability allows companies to innovate rapidly, responding effectively to market changes and technological advancements. By fostering relationships with manufacturers who specialize in this alloy, businesses can optimize production processes and reduce costs while maintaining superior quality.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to actively seek out suppliers who can demonstrate expertise in Kovar alloy applications. By doing so, companies are better positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities and trends, ensuring sustained growth and competitiveness in their respective markets. Engage today with trusted Kovar suppliers to explore the full potential of this exceptional alloy.