Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is titanium better than aluminum
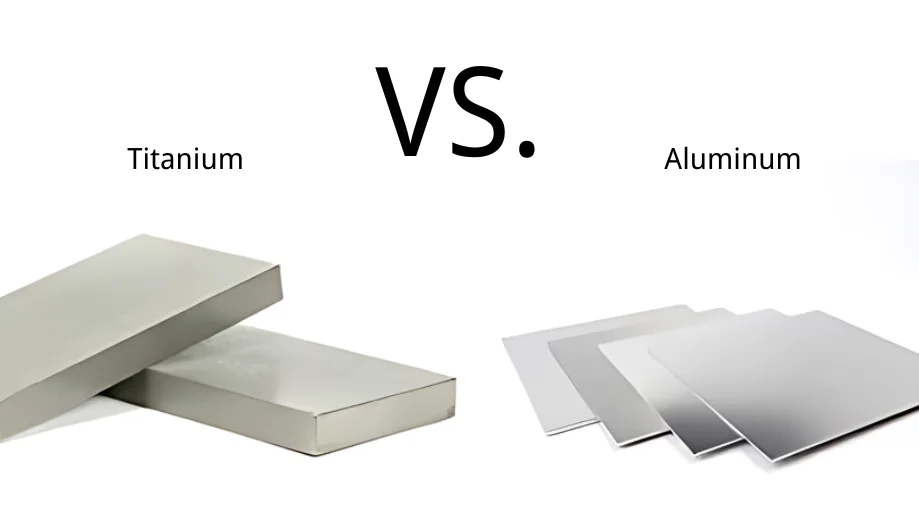
In the competitive landscape of international manufacturing, sourcing the right materials can be a daunting task, especially when weighing the advantages of titanium versus aluminum. Understanding whether titanium is better than aluminum for your specific applications is crucial for maximizing performance and cost-efficiency. This comprehensive guide delves into the properties, applications, and sourcing strategies for both metals, equipping B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
From aerospace and automotive industries to medical and consumer products, each metal offers unique advantages depending on the context of use. The guide also addresses critical aspects such as supplier vetting, material costs, and environmental considerations, ensuring that buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Brazil and Vietnam, can navigate the complexities of global sourcing effectively.
By examining the strengths and limitations of titanium and aluminum, this resource empowers decision-makers to choose the best material for their projects, ultimately driving innovation and competitive advantage. Whether you are looking for lightweight solutions, corrosion resistance, or thermal conductivity, this guide serves as your roadmap to mastering the selection process in the evolving global market.
Understanding is titanium better than aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Grade 2 | Excellent corrosion resistance, moderate strength | Aerospace, medical implants | Pros: Lightweight, biocompatible; Cons: Higher cost |
| 7075-T6 Aluminum | High strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance | Automotive, military applications | Pros: Cost-effective, lightweight; Cons: Less corrosion resistant than titanium |
| Anodized Aluminum | Enhanced surface durability, aesthetic finish | Consumer products, architecture | Pros: Corrosion-resistant, customizable; Cons: Limited high-temperature performance |
| Titanium Alloys | Superior strength and temperature resistance | Aerospace, high-performance engineering | Pros: High strength, excellent fatigue resistance; Cons: Expensive, difficult to machine |
| Aluminum Alloys | Versatile, lightweight, various grades available | Construction, transportation | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to work with; Cons: Lower strength compared to titanium |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Titanium Grade 2 for B2B Buyers?
Titanium Grade 2 is a commercially pure titanium known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and moderate strength. This makes it highly suitable for applications in the aerospace and medical fields, where durability and biocompatibility are crucial. For B2B buyers, the main considerations include its higher price point compared to aluminum and its lightweight nature, which can significantly reduce overall project weights. Its corrosion resistance also ensures longevity in harsh environments, making it a reliable choice for high-performance applications.
Why Choose 7075-T6 Aluminum for Cost-Effective Solutions?
7075-T6 aluminum is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio and good corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice in automotive and military applications. B2B buyers often gravitate towards this alloy due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication. However, it’s essential to note that while it is less expensive than titanium, it may not offer the same level of corrosion resistance, which could be a critical factor depending on the application. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their projects to determine if the trade-offs align with their operational goals.
How Does Anodized Aluminum Enhance Product Durability?
Anodized aluminum features an electrochemical process that enhances its surface durability and aesthetic appeal. This variation is widely used in consumer products and architectural applications, where a visually pleasing finish is often required. For B2B buyers, the anodization process provides added corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor or high-humidity environments. While anodized aluminum is versatile and customizable, buyers should consider its limitations in high-temperature applications, which may affect its suitability for certain projects.
What Advantages Do Titanium Alloys Offer for High-Performance Needs?
Titanium alloys are engineered to provide superior strength and temperature resistance, making them ideal for demanding applications in aerospace and high-performance engineering. B2B buyers should recognize that while these alloys offer significant performance benefits, they come at a premium price and can be challenging to machine. The high strength and fatigue resistance make them a valuable investment for projects where performance is critical, but buyers must weigh these benefits against the associated costs and manufacturing complexities.
Why Consider Aluminum Alloys for Versatile Applications?
Aluminum alloys are widely regarded for their versatility and lightweight properties, making them suitable for a range of applications, including construction and transportation. B2B buyers appreciate the ease of fabrication and lower costs associated with aluminum, which can lead to significant savings in large-scale projects. However, it is crucial to note that aluminum alloys may not provide the same strength levels as titanium, especially in high-stress applications. Buyers should assess their specific needs to determine the best alloy choice for their projects.
Key Industrial Applications of is titanium better than aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is titanium better than aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft Components | Enhanced strength-to-weight ratio improves fuel efficiency. | Certification of materials, compliance with aerospace standards. |
| Medical Devices | Surgical Implants | Superior biocompatibility reduces the risk of rejection. | Regulatory approvals, traceability of materials. |
| Automotive | High-Performance Components | Increased durability and performance in demanding conditions. | Cost vs. performance balance, availability of specific alloys. |
| Oil & Gas | Offshore Equipment | Corrosion resistance extends equipment lifespan. | Supplier reliability, material certifications for harsh environments. |
| Sports Equipment | High-End Gear (e.g., bicycles, golf clubs) | Lightweight and strong materials enhance performance. | Customization options, lead times for specialized manufacturing. |
How is Titanium Better than Aluminum in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, titanium is often preferred for aircraft components due to its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio. This property allows manufacturers to produce lighter aircraft that consume less fuel, thus reducing operational costs. Moreover, titanium’s excellent fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance make it ideal for components exposed to harsh environments. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing titanium requires understanding the necessary certifications and compliance with industry standards to ensure safety and performance.
What Advantages Does Titanium Offer in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device sector, titanium is widely used for surgical implants and prosthetics due to its superior biocompatibility. This characteristic significantly reduces the likelihood of rejection by the human body, making titanium the material of choice for long-term implants. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it’s crucial to consider regulatory approvals and the traceability of materials, as these factors are essential for compliance with health regulations and ensuring patient safety.
Why is Titanium Preferred Over Aluminum in Automotive High-Performance Components?
The automotive industry increasingly turns to titanium for high-performance components such as exhaust systems and suspension parts. The material’s durability and ability to withstand extreme conditions contribute to improved vehicle performance and longevity. However, buyers must weigh the cost against performance benefits when sourcing titanium, particularly in markets like Brazil and Vietnam, where budget constraints may be significant. Understanding the specific alloy requirements is also essential to meet performance expectations.
How Does Titanium’s Corrosion Resistance Benefit Oil & Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas sector, titanium’s exceptional corrosion resistance makes it a preferred material for offshore equipment, where exposure to saltwater and harsh chemicals is common. This property extends the lifespan of critical components, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. International B2B buyers need to ensure the reliability of suppliers and confirm that materials meet stringent certifications for use in harsh environments, particularly in regions with challenging operational conditions.
What Makes Titanium Ideal for High-End Sports Equipment?
Titanium is increasingly used in high-end sports equipment, such as bicycles and golf clubs, due to its lightweight and strength properties. These characteristics enhance performance, allowing athletes to achieve better results. Buyers in this sector should look for customization options and consider lead times for specialized manufacturing processes, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. Understanding market trends and consumer demands is also vital for aligning product offerings with customer expectations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is titanium better than aluminum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding Material Strength and Weight
The Problem: A common challenge for B2B buyers is the misconception that titanium is universally stronger and lighter than aluminum. This misunderstanding can lead to incorrect material selection for projects, resulting in structural failures or excessive costs. For instance, a manufacturing company in Brazil may opt for titanium components believing they would provide superior performance in their aerospace applications. However, they may not realize that certain aluminum alloys, such as 7075-T6, offer higher strength-to-weight ratios, making them more suitable for specific applications.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on the specific properties of various alloys. This involves not only understanding the basic characteristics of titanium and aluminum but also diving deeper into the specific grades and their mechanical properties. Engage with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and performance data for both materials. Utilize resources like material databases or consult with engineering experts to make informed decisions. Additionally, employing prototyping and testing phases can help validate material choices before full-scale production.
Scenario 2: Environmental and Cost Concerns
The Problem: Many international buyers face pressure to choose materials that align with sustainability goals and budget constraints. Titanium, while often marketed as a high-performance option, has a significantly higher carbon footprint compared to aluminum. Companies in regions like the Middle East or South America may struggle to justify the higher costs and environmental impact associated with titanium, especially when aluminum can meet their needs at a lower price point.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize a life-cycle analysis (LCA) when evaluating materials for their projects. This involves assessing not only the upfront costs but also the long-term environmental impact and sustainability of the materials. When sourcing materials, consider partnering with suppliers who are transparent about their production processes and environmental practices. Moreover, explore alternative aluminum alloys that provide high performance while being more eco-friendly. This approach not only helps in reducing costs but also aligns with corporate social responsibility goals.
Scenario 3: Sourcing Quality Materials and Reliable Suppliers
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the difficulty in sourcing high-quality titanium or aluminum materials from reliable suppliers. In regions like Africa and South America, the market can be fragmented, leading to challenges in finding vendors who provide consistent quality and compliance with industry standards. Inconsistent material quality can jeopardize project timelines and lead to costly rework.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this challenge, buyers should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record in the industry. This can be achieved by leveraging platforms that connect manufacturers with verified suppliers, such as Jiga. When sourcing materials, request certifications and test reports to ensure compliance with relevant standards. Additionally, consider implementing a supplier evaluation process that includes assessing their production capabilities, quality control measures, and customer feedback. By prioritizing reliable sourcing practices, businesses can mitigate risks and ensure the success of their projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is titanium better than aluminum
What Are the Key Properties of Titanium and Aluminum?
When evaluating titanium and aluminum for various applications, understanding their key properties is essential for making informed decisions. Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, high corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It is often used in aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance automotive components. In contrast, aluminum is lighter, more ductile, and has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including packaging, construction, and transportation.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Titanium and Aluminum?
Titanium Pros:
– Durability: Titanium has a higher tensile strength compared to aluminum, making it less prone to deformation under stress.
– Corrosion Resistance: It excels in harsh environments, including marine and chemical applications, due to its natural oxide layer.
– High-Temperature Performance: Titanium maintains its strength at elevated temperatures, which is crucial for aerospace and automotive applications.
Titanium Cons:
– Cost: Titanium is significantly more expensive to procure and process than aluminum, which can impact budget-sensitive projects.
– Manufacturing Complexity: The machining of titanium requires specialized tools and techniques, increasing production time and costs.
Aluminum Pros:
– Cost-Effectiveness: Aluminum is generally more affordable than titanium, making it a popular choice for mass-produced items.
– Ease of Fabrication: Aluminum is easier to work with, allowing for faster production cycles and reduced labor costs.
– Lightweight: With a lower density, aluminum is ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical.
Aluminum Cons:
– Lower Strength: Although aluminum alloys can be strong, they typically do not match the strength of titanium.
– Corrosion Vulnerability: While aluminum has good corrosion resistance, it can be less effective than titanium in extreme environments unless treated.
How Do Material Properties Impact Application Suitability?
The choice between titanium and aluminum significantly impacts application suitability. For instance, titanium’s high strength and corrosion resistance make it ideal for aerospace components, where performance under extreme conditions is essential. Conversely, aluminum’s lightweight and cost-effective nature make it suitable for consumer products like packaging and automotive parts, where performance requirements are less stringent.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Choosing Between Titanium and Aluminum?
International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider compliance with local standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS when selecting materials. Understanding the specific requirements for certifications, environmental regulations, and material properties is crucial. Additionally, buyers should evaluate the availability of suppliers and the logistical implications of sourcing materials from different regions.
Summary Table of Material Comparisons
| Material | Typical Use Case for is titanium better than aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Aerospace components, medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Packaging, automotive parts, construction | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Lower strength compared to titanium | Medium |
| Aluminum 7075-T6 | High-performance sports equipment, aircraft structures | High tensile strength and lightweight | Corrosion vulnerability without treatment | Medium |
| Titanium Grade 2 | Marine applications, chemical processing equipment | Superior corrosion resistance | More expensive and harder to machine | High |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the selection of titanium versus aluminum, allowing for informed decision-making tailored to specific industry needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is titanium better than aluminum
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Titanium and Aluminum?
When evaluating whether titanium is better than aluminum, understanding the manufacturing processes for each material is essential. The production of titanium and aluminum involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in determining the final quality and performance of the product.
How is Material Prepared for Titanium and Aluminum Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with sourcing the raw materials. Titanium typically comes from ore like rutile or ilmenite, which undergoes processes such as the Kroll process to extract the titanium metal. This process involves reducing titanium tetrachloride with magnesium in an inert atmosphere.
Aluminum, on the other hand, is primarily derived from bauxite ore. The Bayer process is used to refine bauxite into alumina, which is then smelted using the Hall-Héroult process to produce aluminum metal. Both materials require careful handling and storage to prevent contamination, which can affect their properties.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into desired forms. For titanium, common techniques include:
- Cold Working: This process involves deforming titanium at room temperature, enhancing its strength through strain hardening.
- Hot Working: Performed at elevated temperatures, hot working allows for better ductility, making it easier to form complex shapes without cracking.
Aluminum forming techniques often include:
- Extrusion: This method pushes aluminum through a die to create long shapes, ideal for various applications.
- Stamping and Forging: These processes involve shaping aluminum sheets or blocks using dies and hammers, respectively.
Understanding these techniques helps B2B buyers assess the capabilities of manufacturers and their suitability for specific projects.
How Are Products Assembled and Finished?
After forming, products undergo assembly. For titanium, this may involve techniques like welding or mechanical fastening. Given titanium’s unique properties, specialized welding techniques, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), are often employed to ensure strong joints without contamination.
Aluminum assembly may also use welding, but it can be more readily joined using rivets and adhesives due to its lower melting point. The finishing stage for both materials is crucial for enhancing performance and aesthetics. Common finishing processes include:
- Anodizing (for aluminum): This electrochemical process thickens the natural oxide layer, enhancing corrosion resistance and allowing for coloring.
- Surface Treatment (for titanium): Processes like shot peening or chemical cleaning improve fatigue resistance and surface integrity.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are in Place for Titanium and Aluminum?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in ensuring that the final products meet international standards and customer specifications. Various standards govern the QA processes for titanium and aluminum, including ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, and industry-specific certifications such as API for oil and gas applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are conducted to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that the products are meeting required specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, a comprehensive inspection is performed to verify that the finished products meet all standards and specifications.
Implementing these checkpoints helps minimize defects and ensure the reliability of the final product.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of titanium and aluminum products. Common testing methods include:
- Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile tests, hardness tests, and fatigue tests to determine the material’s strength, ductility, and durability.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection help identify internal defects without damaging the product.
- Chemical Analysis: This is performed to verify the elemental composition of the materials, ensuring they meet required standards.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods employed by suppliers to ensure that they meet industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control measures of suppliers is essential for mitigating risks. Here are several strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help assess their quality management systems and compliance with international standards.
- Requesting QC Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their QC processes, including test results and compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and product compliance.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various certification requirements. Understanding the nuances of certification helps ensure compliance with local and international regulations.
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific standards for manufacturing and quality assurance. Buyers must be aware of these to ensure compliance.
- Certification Validity: It’s essential to verify the validity of certifications claimed by suppliers. This can often be done through the certifying bodies.
- Language and Documentation: Ensure that all documentation is available in a language that all stakeholders can understand, facilitating smoother communication and compliance checks.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for titanium and aluminum is crucial for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions and select suppliers that meet their quality standards and project requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is titanium better than aluminum’
Introduction
This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in the process of evaluating whether titanium or aluminum is the better material for their specific applications. With both metals having distinct properties, understanding their differences and applications can lead to more informed purchasing decisions. Use this checklist to navigate the complexities of material selection and supplier procurement effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before delving into the procurement process, clearly outline your project requirements. Consider factors such as weight, strength, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and intended application. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for comparing the properties of titanium and aluminum relevant to your needs.
- Identify Key Properties: For instance, if weight is critical, aluminum might be preferable due to its lower density.
- Application Context: Determine the environment in which the material will be used, as this influences performance.
Step 2: Conduct a Cost Analysis
Evaluate the total cost implications of using titanium versus aluminum. While titanium often boasts superior strength and corrosion resistance, it typically comes with a higher price tag. Understanding the cost-benefit ratio will aid in making a financially sound decision.
- Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Value: Consider not just the upfront costs but also potential savings from durability and reduced maintenance.
- Market Prices: Research current market trends for both metals, as prices can fluctuate based on demand and availability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers to ensure they can meet your specific requirements and standards. A reliable supplier will provide quality materials that align with your technical specifications and budget.
- Request Documentation: Ask for certifications, quality assurance processes, and case studies relevant to your industry.
- Check References: Speak with other businesses that have sourced materials from the potential suppliers to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Assess Material Properties and Testing Standards
Investigate the material properties of both titanium and aluminum to ensure they meet your project requirements. Different alloys may offer varying strengths, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
- Understand Alloys: Familiarize yourself with the specific grades of titanium and aluminum that are best suited for your application.
- Testing Compliance: Ensure the materials comply with industry standards and have been tested for performance in conditions similar to those expected in your project.
Step 5: Consider Environmental Impact
Evaluate the environmental implications of sourcing either titanium or aluminum. Titanium generally has a higher carbon footprint during manufacturing compared to aluminum.
- Sustainability Practices: Assess whether suppliers implement sustainable practices in their production processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the materials meet any local or international environmental regulations.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of your agreement. This includes pricing, delivery timelines, payment terms, and any warranties or guarantees.
- Clarify Expectations: Clearly outline your expectations regarding quality and delivery to avoid future disputes.
- Include Contingencies: Discuss what happens in the event of delays or quality issues, ensuring you have a plan in place.
Step 7: Finalize and Place Your Order
After ensuring all terms are agreeable and you are confident in your supplier’s ability to meet your needs, finalize the order. Ensure that all documentation is accurate and complete.
- Double-Check Specifications: Review the order details to confirm they align with your original technical specifications.
- Establish Communication Channels: Set up regular check-ins with your supplier to monitor the progress of your order and address any potential issues early on.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the decision-making process regarding titanium versus aluminum with greater clarity and confidence.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is titanium better than aluminum Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Titanium and Aluminum?
When sourcing materials like titanium and aluminum, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The price of titanium is generally higher than aluminum due to its rarity and the complexity of extraction and processing. For instance, titanium’s average market price can be significantly influenced by global supply chain dynamics, while aluminum tends to be more stable and less expensive due to its abundant availability.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the region and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Titanium often requires specialized labor for machining and fabrication due to its unique properties, which can drive up costs. In contrast, aluminum fabrication processes are more standardized and widely understood, potentially leading to lower labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs encompass the indirect expenses incurred during production, such as utilities and facility maintenance. Titanium manufacturing typically incurs higher overhead due to the need for specialized equipment and safety measures, whereas aluminum manufacturing might benefit from more established processes, resulting in lower overhead.
-
Tooling: The tooling costs for titanium are higher due to the need for specific tools that can withstand its hardness and toughness. Conversely, aluminum tools are often more affordable and readily available, reducing initial investment costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the integrity and performance of titanium products involves rigorous QC processes, often leading to higher costs. Aluminum, while still requiring QC, generally has less stringent requirements, thus lowering overall costs.
-
Logistics: Logistics costs can vary significantly based on the weight and volume of materials. Aluminum’s lighter weight can result in lower shipping costs compared to titanium, which is denser and heavier, impacting transportation expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can fluctuate based on demand and material availability. Titanium suppliers may have higher margins due to the specialized nature of the product, while aluminum suppliers often operate on thinner margins due to increased competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions for Titanium and Aluminum?
Several factors can influence the pricing of titanium and aluminum, impacting B2B buyers’ sourcing strategies:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) and purchasing volume can significantly affect pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it more cost-effective for buyers to purchase in bulk.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products or specific alloys may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The grade of titanium or aluminum and the presence of certifications can influence pricing. Higher-grade materials with certifications will typically command premium prices due to their enhanced performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more, reflecting their quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers as they dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. These terms can affect overall costs and should be considered during negotiations.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Costs in International B2B Sourcing?
Negotiating costs effectively is vital for maximizing value when sourcing titanium and aluminum. Here are some tips for international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to benchmark prices and understand standard costs for titanium and aluminum. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and lifecycle costs, rather than just the upfront price. This approach can lead to better long-term decisions.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to negotiate volume discounts with suppliers. This strategy can significantly lower per-unit costs.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Trust and communication often result in favorable negotiations.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Understand the regional market dynamics, currency fluctuations, and tariffs that may affect prices. This awareness can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing for titanium and aluminum can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific project requirements. It is advisable for buyers to obtain multiple quotes and conduct due diligence before finalizing any sourcing agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is titanium better than aluminum With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Titanium and Aluminum: A Comparative Analysis
In the ever-evolving landscape of material science, businesses often face critical decisions regarding the selection of materials for their manufacturing processes. While titanium and aluminum are frequently compared, it’s essential to evaluate other viable alternatives that can meet specific project requirements. This analysis will delve into the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases of titanium and aluminum against two alternative materials: stainless steel and carbon fiber.
| Comparison Aspect | Is Titanium Better Than Aluminum | Stainless Steel | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio; excellent corrosion resistance | Strong and durable; good tensile strength | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio; high rigidity |
| Cost | Generally higher due to extraction and processing | Moderate; cost-effective for bulk applications | Higher initial cost; long-term savings due to durability |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized tools for fabrication | Widely available; easier to work with | Requires specific manufacturing techniques; less accessible |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to corrosion | Moderate; may require periodic maintenance to prevent rust | Very low maintenance; resistant to environmental factors |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance applications | Construction, automotive, and kitchenware | High-end sporting goods, automotive components, and aerospace |
Analyzing Stainless Steel as an Alternative to Titanium and Aluminum
Stainless steel is a popular alternative material known for its strength and durability. It offers good tensile strength, making it suitable for various applications, including construction and automotive parts. The cost of stainless steel is generally moderate, providing a cost-effective solution for bulk manufacturing. However, it does require periodic maintenance to prevent rust, especially in corrosive environments. Its ease of implementation is a significant advantage, as it is widely available and compatible with standard manufacturing processes.
Evaluating Carbon Fiber Against Titanium and Aluminum
Carbon fiber is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity, making it a compelling alternative in applications where weight savings are critical. Although the initial cost of carbon fiber is higher than that of aluminum or titanium, its long-term durability can lead to overall cost savings, particularly in high-performance sectors. However, carbon fiber requires specific manufacturing techniques, which can complicate its implementation. Maintenance is minimal, as carbon fiber is highly resistant to environmental factors, making it an attractive option for industries like aerospace and high-end sporting goods.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
When determining the best material for a project, B2B buyers should carefully consider the specific requirements of their applications. Titanium may be the ideal choice for projects requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, while aluminum can be a more cost-effective solution for less demanding applications. Alternatives like stainless steel and carbon fiber offer unique advantages, including ease of implementation and exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. By evaluating performance, cost, and maintenance needs, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is titanium better than aluminum
What Are the Critical Technical Properties to Consider When Comparing Titanium and Aluminum?
When evaluating titanium versus aluminum for specific applications, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are key specifications that every B2B buyer should consider:
1. Material Grades and Alloys
Both titanium and aluminum come in various grades and alloys, which significantly affect their performance characteristics. Titanium is commonly classified into grades (e.g., Grade 1, 2, 5) based on purity and alloying elements. Higher grades typically offer better strength and corrosion resistance. Aluminum also has multiple alloys, such as 6061, 7075, and 2024, each with distinct properties like strength, ductility, and weldability. Selecting the right grade is vital for ensuring that the material meets the specific requirements of your project.
2. Yield Strength
Yield strength refers to the maximum stress a material can withstand before it begins to deform permanently. Titanium generally has a higher yield strength than aluminum, making it suitable for high-stress applications. For example, Grade 5 titanium can have a yield strength of around 880 MPa, whereas 7075-T6 aluminum has a yield strength of about 570 MPa. Understanding yield strength is essential for applications in aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors, where material failure can have serious consequences.
3. Density
Density impacts the weight and strength-to-weight ratio of materials. Titanium has a density of about 4.5 g/cm³, making it significantly heavier than aluminum, which has a density of approximately 2.7 g/cm³. This difference is crucial for industries where weight reduction is a priority, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing. A lower density can lead to more efficient designs and better fuel economy.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Both titanium and aluminum exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, but their performance varies depending on the environment. Titanium is particularly resistant to harsh environments, including saltwater, making it ideal for marine applications. Aluminum can be anodized to enhance its corrosion resistance but may not perform as well in extreme conditions. B2B buyers must assess the operational environment to choose the right material.
5. Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Aluminum excels in thermal and electrical conductivity, with thermal conductivity values around 210 W/m·K, compared to titanium’s 17 W/m·K. This makes aluminum a preferred choice for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation, such as heat exchangers and electrical components. Buyers in electronics and HVAC industries should prioritize aluminum for such applications.
What Are the Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Relevant to Titanium and Aluminum?
Understanding trade terminology is essential for navigating the procurement process effectively. Here are some key terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components that are used in the manufacturing of another company’s end products. In the context of titanium and aluminum, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers gauge the quality and reliability of the materials being sourced.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers who need to ensure that their procurement aligns with budgetary and inventory considerations. Suppliers of titanium and aluminum may have varying MOQs based on the material grade and processing requirements.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers send to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. Including detailed specifications, such as material grade and quantity, can lead to more accurate and competitive quotes, facilitating better decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, delivery, and risk. Understanding these terms is vital for international transactions, particularly when sourcing titanium and aluminum from global suppliers. Key terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), which dictate who bears the costs and risks at various stages of shipment.
5. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. It is essential in manufacturing processes where precision is critical, especially when working with tight-fitting components in aerospace or automotive applications. Buyers must specify tolerances to ensure parts fit correctly and perform as intended.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when comparing titanium and aluminum for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is titanium better than aluminum Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in Titanium vs. Aluminum?
The global metals market is witnessing dynamic shifts as industries increasingly weigh the benefits of titanium versus aluminum. Key drivers include the growing demand for lightweight, high-strength materials across sectors like aerospace, automotive, and construction. Notably, titanium, while generally more expensive, offers superior corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratios, making it a preferred choice for high-performance applications. Conversely, aluminum remains attractive for its lower cost, ease of fabrication, and high thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring these properties.
Emerging technologies in sourcing are also influencing buyer decisions. Platforms that streamline procurement processes, such as Jiga, are gaining traction, allowing B2B buyers to access verified suppliers and receive competitive quotes quickly. This trend towards digital procurement is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where access to reliable suppliers can be challenging. Additionally, the rise of additive manufacturing (3D printing) is reshaping how both titanium and aluminum are sourced, with businesses increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer customized solutions tailored to specific project needs.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Choice Between Titanium and Aluminum?
Sustainability has become a critical factor in B2B sourcing decisions, influencing how international buyers approach the choice between titanium and aluminum. The environmental impact of material production is increasingly scrutinized, with titanium production typically having a larger carbon footprint—nearly four times that of aluminum. This discrepancy is pushing companies to evaluate not only the performance characteristics of the materials but also their environmental implications.
Ethical sourcing has emerged as a priority, with buyers seeking suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices and possess certifications for environmentally friendly materials. The demand for ‘green’ certifications is growing, as companies are held accountable for their supply chains’ ecological footprint. Buyers are advised to consider suppliers that prioritize responsible mining practices and those who can demonstrate a commitment to reducing waste and energy consumption during manufacturing processes. By selecting materials with lower environmental impacts, businesses can enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and partners.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Use of Titanium and Aluminum in Industry?
The use of titanium and aluminum in industrial applications has evolved significantly over the past century. Aluminum, first used in the late 19th century, gained popularity due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, making it a staple in aerospace and construction. Its versatility led to widespread adoption across various sectors.
Titanium, discovered in the early 18th century, was initially limited to niche applications due to its high cost and challenging workability. However, advancements in extraction and processing technologies in the mid-20th century opened up new possibilities, particularly in aerospace and military applications, where its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio became invaluable. As industries continue to innovate, both metals are likely to play crucial roles in future developments, with ongoing research aimed at improving their properties and reducing production costs. Understanding this historical context can help B2B buyers make informed decisions about material selection based on long-term trends and performance expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is titanium better than aluminum
-
How do I determine whether titanium or aluminum is more suitable for my project?
To ascertain the best material for your project, analyze key factors such as strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and cost. Titanium offers superior strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-stress environments, while aluminum is lighter and generally more cost-effective, suitable for applications where weight is a critical concern. Consider the specific requirements of your project, including mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, to make an informed decision. -
What are the main advantages of using titanium over aluminum?
Titanium boasts several advantages, including higher tensile strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and superior performance at elevated temperatures. Its durability makes it ideal for aerospace, medical, and high-performance applications. Additionally, titanium is biocompatible, making it suitable for medical implants. However, these benefits come at a higher price point, which is an essential consideration for budget-conscious projects. -
What are the cost implications of sourcing titanium versus aluminum?
Generally, titanium is more expensive than aluminum due to its extraction and processing costs. When budgeting for materials, consider not only the raw material costs but also factors such as machining, fabrication, and potential waste. While aluminum might offer lower upfront costs, the long-term performance benefits of titanium in specific applications may justify the investment. Evaluate your project’s lifecycle costs to make a comprehensive financial decision. -
How can I vet suppliers for titanium and aluminum materials?
When vetting suppliers, assess their certifications, quality assurance processes, and industry reputation. Request samples to evaluate material quality and conduct audits to understand their production capabilities. Additionally, check for compliance with international standards such as ISO or ASTM. Engaging with suppliers who have a proven track record in your industry can also provide insights into their reliability and service levels. -
What customization options should I consider when ordering titanium or aluminum products?
Customization options can significantly impact the performance and fit of your components. Inquire about the supplier’s ability to provide specific alloys, heat treatments, and surface finishes tailored to your project requirements. Discuss machining capabilities, tolerances, and design flexibility. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your needs within the required lead times to avoid delays in your production schedule. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for titanium and aluminum?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the material and product type. Generally, titanium may have higher MOQs due to its cost and processing complexities. Aluminum suppliers may offer more flexibility with lower MOQs, especially for common alloys. Always confirm MOQs during the sourcing process and consider consolidating orders to meet minimum requirements if necessary. -
What payment terms should I negotiate when sourcing metals internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on supplier policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or net payment within 30 to 90 days. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect both parties. Negotiating favorable payment terms can enhance cash flow and mitigate financial risks. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the sourcing of titanium and aluminum?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of materials. Consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs when sourcing internationally. Titanium, being denser and more expensive, may incur higher shipping costs compared to aluminum. Collaborating with logistics providers experienced in international shipping can help streamline the process, ensuring compliance and timely delivery to your location.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Is Titanium Better Than Aluminum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Aluminium vs. Titanium
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Aluminium vs. Titanium:
– Aluminium is cheaper and lighter for the same volume.
– Aluminium conducts heat better.
– Titanium has the highest strength per weight, potentially leading to lower weights for titanium items compared to aluminium.
– Concerns about non-stick coatings on aluminium pots, which may expose soft aluminium to food.
– Titanium products often considered overpriced; some manu…
2. Jiga – Titanium Solutions
Domain: jiga.io
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Titanium properties: exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, low density, high melting point, excellent heat and chemical resistance. Titanium applications: aircraft, rocket, satellite, engine components, artificial joints, dental implants, lightweight auto parts, sports equipment, chemical processing, marine industry. Aluminum properties: lightweight, corrosi…
3. Morsel’s Spork – Aluminum & Titanium Essentials
Domain: morselspork.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective, making it suitable for various applications. Titanium, while heavier and more expensive, offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures. Both materials have unique properties that make them ideal for specific uses, with aluminum being favored for its affordability and ease of manufacturing, while titani…
4. Wayken – Titanium and Aluminum Solutions
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Titanium and aluminum are both excellent metal options for manufacturing projects, each with distinct properties and applications.
**Elemental Composition:**
– Titanium: Composed mainly of titanium with elements like oxygen, nickel, nitrogen, iron, carbon, and hydrogen (0.013 to 0.5%).
– Aluminum: Primarily aluminum, with constituents including zirconium, zinc, chromium, silicon, magnesium, ti…
5. Apple – iPhone 15/16 Pro Aesthetic Preferences
Domain: forums.macrumors.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: User expresses a desire for an iPhone 15/16 Pro with blue aluminum and back glass instead of titanium. They dislike the titanium look and prefer the aesthetics of aluminum. Discussion includes the historical use of stainless steel in Pro models, with current rumors suggesting that the iPhone 17 Pro may revert to aluminum, while only the Pro Max will use titanium. Users reminisce about previous iPh…
6. Agood – iPhone 15 Series Features
Domain: agood.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The iPhone 15 series features a grade 5 titanium frame, which offers improved durability compared to traditional aluminium. Key advantages of titanium include its strength, lightweight nature, and resistance to corrosion. While aluminium is versatile and commonly used, it is softer and can be more easily scratched or dented. The transition to titanium also aligns with environmental considerations,…
7. SilverAnt Outdoors – Key Titanium Products
Domain: silverantoutdoors.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Aluminum vs Titanium – The Ultimate Guide | SilverAnt Outdoors. Key product details include: Titanium Rice Cooker, Ultralight 3-Piece Titanium Camping Cookware Set, Medium 2-Piece Titanium Pot & Pan Camping Cookware Set, Titanium Pot 750ml/25 fl oz with Lid and Bail Handle, Titanium 3-Piece Cutlery Set (Knife, Fork and Spoon), Long Handle Titanium Spork, Ultralight Titanium Chopsticks, Long Handle…
8. Snow Peak – 900 Pot Options
Domain: backpackinglight.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Snow Peak 900 pot, Aluminum option for $20, Titanium option for $25, Antigravity Gear (AGG) aluminum pot, Evernew 0.9 Liter titanium pot, GSI Outdoors aluminum pots, IMUSA pots, Hard Anodized (HA) aluminum pots from Antigravity Gear or Brasslite, Titan Kettle 4.2oz, AGG pot 5.0oz with lid and handle, both boil 2 cups of water in 5.5 minutes.
9. Titanium Processing Center – Titanium Products
Domain: titaniumprocessingcenter.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Titanium Products: Titanium Billet, Titanium Round Bar, Titanium Rod / Wire Rod, Titanium Plate, Titanium Sheet, Titanium Rec Bar, Titanium Pipe, Titanium Tube, Titanium Fittings. Other Services: Band Sawing, Waterjet Cutting, Plate Sawing, Shearing.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is titanium better than aluminum
When considering whether titanium or aluminum is the superior choice for your project, it’s essential to weigh the unique properties and applications of each metal. Titanium offers remarkable strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-stress environments. However, aluminum’s lightweight nature and superior thermal and electrical conductivity often make it a more practical and cost-effective option for many applications, particularly in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
Strategic sourcing plays a crucial role in navigating these material choices. By leveraging platforms that connect you with reliable suppliers, you can streamline procurement processes and ensure access to the best materials for your specific needs. Engaging with verified suppliers not only enhances your project outcomes but also fosters long-term partnerships that can adapt to evolving market demands.
As you move forward, consider the specific requirements of your projects and the regions you operate in—whether in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. Take advantage of local and international resources to optimize your sourcing strategy. Embrace the opportunity to innovate with the right materials, and let your choices propel your business to new heights in a competitive global market.