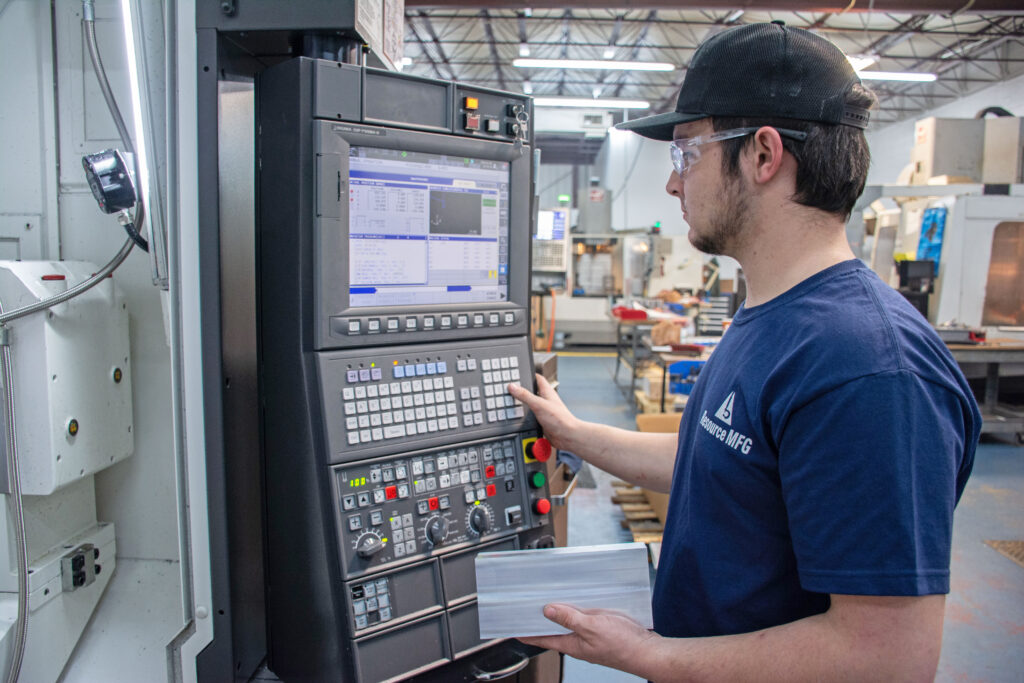
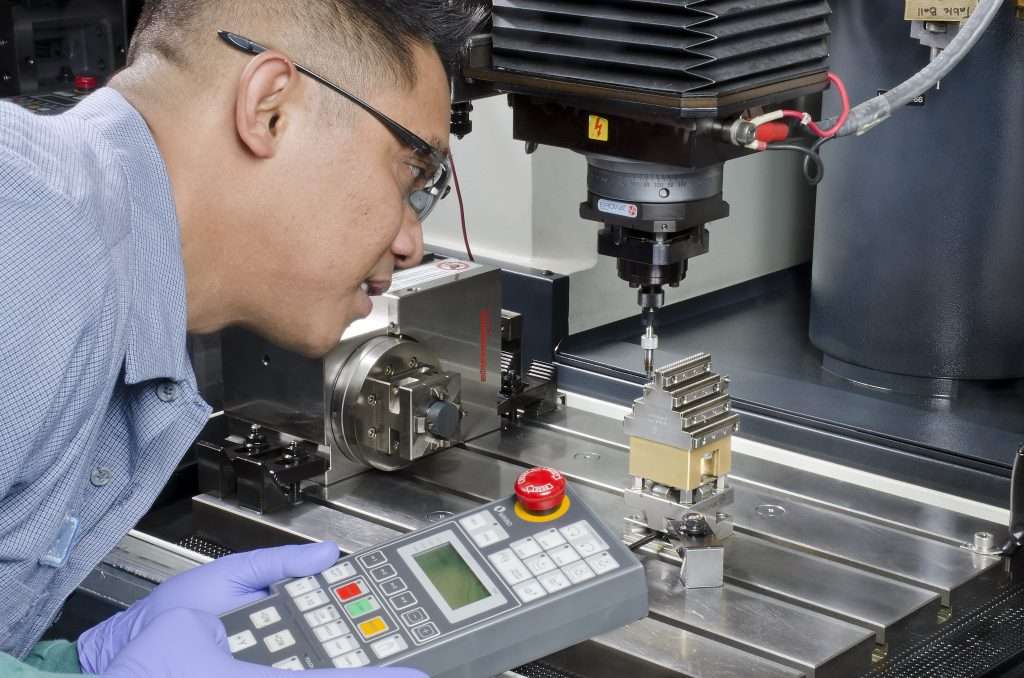
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is cnc machinist a good career
In an era where precision and efficiency are paramount, the question arises: Is CNC machinist a good career choice for those seeking stability and growth? As global manufacturing continues to evolve, the demand for skilled CNC machinists is surging, presenting a significant challenge for businesses in sourcing qualified talent. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of CNC machining, exploring various types of machinists, their applications across diverse industries, and the critical factors influencing supplier selection and cost.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets such as Nigeria and Germany—understanding the intricacies of CNC machining careers is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By examining the landscape of CNC machining, this guide equips business leaders with actionable insights into workforce trends, training requirements, and the long-term viability of CNC machinist roles.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing skilled professionals in this field, you will discover how to leverage this knowledge not only to enhance operational efficiency but also to ensure sustained competitive advantage in the global market. Join us as we explore why investing in CNC machinists is not just a good career choice, but a strategic imperative for your business’s success.
Understanding is cnc machinist a good career Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional CNC Machinist | Operates standard CNC machines, focused on metalworking. | Aerospace, automotive, and general manufacturing. | Pros: Established industry; Cons: May require higher initial training costs. |
| 5-Axis CNC Machinist | Utilizes advanced machines for complex geometries. | Aerospace, medical devices, and high-precision industries. | Pros: High precision; Cons: Equipment is costly and requires advanced skills. |
| Swiss CNC Machinist | Specializes in Swiss-style lathes for small, intricate parts. | Medical devices, watchmaking, and electronics. | Pros: High demand for precision; Cons: Limited to specific industries. |
| CNC Programmer | Focuses on writing and optimizing machine code. | Any industry using CNC machining. | Pros: Versatile skill set; Cons: May require ongoing education to keep up with technology. |
| CNC Setup Technician | Prepares machines and tools for production runs. | Manufacturing sectors requiring batch production. | Pros: Critical for efficiency; Cons: May face pressure for quick setups. |
What Are the Characteristics of a Traditional CNC Machinist?
Traditional CNC machinists typically work with standard CNC machines, primarily focusing on metalworking processes. They are essential in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where precision and reliability are crucial. B2B buyers should consider the training and certification requirements for machinists, as the initial investment in skilled labor can impact overall production efficiency and product quality. However, the established nature of this role means a steady supply of qualified candidates.
How Does a 5-Axis CNC Machinist Differ from Traditional Roles?
A 5-axis CNC machinist operates advanced machinery capable of creating complex geometries, significantly enhancing production capabilities. This specialization is particularly relevant in high-precision sectors such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in 5-axis technology against the higher costs associated with both equipment and skilled labor. The potential for increased product complexity and reduced production times can justify these investments.
What Are the Unique Aspects of Swiss CNC Machining?
Swiss CNC machinists focus on using Swiss-style lathes, which are designed for producing small, intricate parts with high precision. This specialization is critical in industries like medical device manufacturing and electronics, where detail and accuracy are paramount. B2B buyers should consider the niche nature of Swiss machining, as it may limit the versatility of machinists. However, the demand for such precision work often leads to higher margins in specialized markets.
Why Is CNC Programming a Valuable Skill for B2B Buyers?
CNC programmers are responsible for writing and optimizing the code that runs CNC machines. Their role is crucial across all industries that utilize CNC technology, making it a versatile career path. Buyers should recognize the importance of ongoing education and training for programmers, as software and technology evolve rapidly. Investing in skilled programmers can lead to improved efficiency and reduced downtime, making it a worthwhile consideration for businesses.
What Role Does a CNC Setup Technician Play in Manufacturing?
CNC setup technicians prepare machines and tools for production runs, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently. Their role is vital in manufacturing sectors where batch production is common. For B2B buyers, understanding the significance of having skilled setup technicians can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced lead times. However, the pressure for quick setups can be a challenge, necessitating strong problem-solving skills and adaptability in the workforce.
Key Industrial Applications of is cnc machinist a good career
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is cnc machinist a good career | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Manufacturing precision components for aircraft | Ensures safety and performance in flight operations | Need for skilled machinists familiar with aerospace standards and materials. |
| Automotive | Production of engine parts and chassis components | Enhances vehicle performance and reliability | Demand for CNC machinists with experience in high-volume production and quality control. |
| Medical Devices | Creation of surgical instruments and implants | Guarantees high precision and compliance with health regulations | Requires machinists knowledgeable about biocompatible materials and regulations. |
| Energy | Fabrication of components for power generation systems | Supports efficient and reliable energy production | Sourcing machinists with expertise in machining durable materials suitable for high-stress environments. |
| Electronics | Production of intricate parts for devices and machinery | Facilitates innovation and technological advancement | Need for machinists skilled in micro-machining and working with advanced materials. |
How Do CNC Machinists Contribute to the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, CNC machinists are crucial for manufacturing precision components, such as turbine blades and fuselage parts. Their expertise ensures that parts meet strict safety and performance standards, which is paramount in aviation. For international B2B buyers, sourcing skilled machinists who understand aerospace specifications and can work with advanced materials is essential. This guarantees not only compliance with regulations but also enhances the overall quality and reliability of aircraft components.
What Role Do CNC Machinists Play in the Automotive Sector?
CNC machinists in the automotive industry are responsible for producing critical engine parts, transmission components, and chassis elements. Their work directly impacts vehicle performance and safety, making their role vital. For businesses in Africa, South America, and Europe, finding CNC machinists with experience in high-volume production and quality assurance is key. This ensures that the manufactured parts are not only cost-effective but also meet the rigorous standards of the automotive market.
How Are CNC Machinists Essential in the Medical Device Industry?
In the medical device sector, CNC machinists create highly precise surgical instruments and implants, which must adhere to strict health regulations. Their ability to work with biocompatible materials is essential for ensuring patient safety and device efficacy. International buyers must consider sourcing machinists who are well-versed in medical manufacturing standards to maintain compliance and ensure high-quality production. This is particularly important in regions with stringent health regulations, making skilled machinists a valuable asset.
Why Are CNC Machinists Important in Energy Production?
CNC machinists play a significant role in fabricating components for power generation systems, including turbines and generators. Their work supports efficient and reliable energy production, which is critical in today’s energy landscape. For businesses in developing regions, sourcing machinists with experience in machining durable materials that can withstand high-stress environments is vital. This ensures that energy components are not only functional but also long-lasting, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
How Do CNC Machinists Impact the Electronics Sector?
In the electronics industry, CNC machinists are tasked with producing intricate parts for devices ranging from smartphones to industrial machinery. Their skills facilitate innovation and the development of advanced technologies. For international B2B buyers, it is important to source machinists skilled in micro-machining and familiar with advanced materials. This expertise allows companies to stay competitive by producing high-quality electronic components that meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is cnc machinist a good career’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Skills Gap in CNC Machining
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in manufacturing sectors, face a significant challenge in finding qualified CNC machinists. The skills gap is a prevalent issue, as there is a growing demand for skilled workers who can operate and program CNC machines effectively. This can lead to project delays, increased operational costs, and difficulty in meeting production deadlines, ultimately affecting profitability. For companies in regions like Africa and South America, where technical education may not be as advanced, sourcing skilled labor can be even more challenging.
The Solution: To address this skills gap, companies should consider investing in partnerships with local technical schools and vocational training centers. By collaborating on curriculum development and offering internships or apprenticeships, businesses can help shape a workforce that meets their specific needs. Additionally, companies should provide in-house training programs that allow current employees to upskill, focusing on the latest CNC technologies and practices. This proactive approach not only enhances the skill level of the workforce but also creates a loyal employee base that is invested in the company’s success.
Scenario 2: Evaluating Career Longevity and Job Security in CNC Machining
The Problem: B2B buyers often express concerns about the longevity and job security of CNC machinists, particularly in fluctuating economies. They worry that investing in training and onboarding CNC machinists may not yield a long-term return if the industry experiences downturns or technological advancements lead to job automation. This uncertainty can hinder investment decisions and workforce planning.
The Solution: To alleviate these concerns, companies should conduct thorough market research to understand the growth trajectory of the CNC machining sector in their respective regions. Highlighting the resilience of CNC machining careers, especially during economic downturns, can be a powerful selling point. Additionally, businesses should consider diversifying their operations to include multiple sectors (e.g., aerospace, automotive, medical devices) that require CNC machining services. This diversification not only provides stability but also opens up new revenue streams, making the investment in CNC machinists more appealing.
Scenario 3: Attracting and Retaining Talent in a Competitive Market
The Problem: Attracting and retaining skilled CNC machinists can be particularly challenging in competitive job markets. Companies often struggle with high turnover rates, which disrupt operations and increase hiring costs. This issue is exacerbated in regions like Europe, where skilled labor is in high demand, leading to bidding wars for talent.
The Solution: To create a compelling workplace for CNC machinists, organizations should focus on building a robust employee value proposition. This includes offering competitive salaries, comprehensive benefits, and opportunities for professional development. Implementing mentorship programs and clear career advancement paths can significantly enhance job satisfaction and retention. Furthermore, fostering a positive workplace culture that values innovation and creativity can make a significant difference. By actively promoting these initiatives, companies can position themselves as employers of choice in the CNC machining industry, reducing turnover and improving operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is cnc machinist a good career
What Are the Key Materials Used in CNC Machining and Their Implications for Career Viability?
CNC machining is a versatile field that utilizes various materials to create precision components for diverse industries. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials can significantly impact the effectiveness of a CNC machinist’s work, thereby influencing career prospects in this domain. Here, we analyze four common materials used in CNC machining: aluminum, steel, titanium, and plastics.
How Does Aluminum Perform in CNC Machining Applications?
Aluminum is one of the most widely used materials in CNC machining due to its lightweight and excellent machinability. Key properties include a low density, high corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. These characteristics make aluminum suitable for applications in the aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods sectors.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive and easy to machine, which allows for quick production cycles. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in aircraft components.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it may not withstand high-temperature applications as effectively as other metals. Its softness can also lead to wear on cutting tools, increasing manufacturing costs over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a variety of media, including air and water, but may not be suitable for high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, especially in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local suppliers for cost-effective sourcing.
What Are the Advantages of Using Steel in CNC Machining?
Steel is another prevalent material in CNC machining, known for its strength and versatility. Key properties include high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures.
Pros: Steel’s durability makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications, including automotive and industrial machinery. It also offers excellent dimensional stability, which is crucial for precision machining.
Cons: The main drawback is its weight, which can be a disadvantage in applications where lightweight materials are preferred. Additionally, steel can be more challenging to machine, leading to higher tooling costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and gases, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international quality standards is critical, especially in sectors like aerospace and defense. Buyers should also be aware of the varying grades of steel and their specific applications.
Why Is Titanium a Preferred Material for Certain CNC Machining Applications?
Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Key properties include high tensile strength, low density, and excellent biocompatibility, making it popular in aerospace and medical applications.
Pros: Titanium’s strength allows for thinner components without compromising structural integrity, which is advantageous in aerospace engineering. Its corrosion resistance also extends the lifespan of machined parts.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of titanium is its high cost and challenging machinability, which can lead to increased manufacturing time and expenses.
Impact on Application: Titanium is suitable for high-performance applications, including those exposed to harsh environments, such as marine and chemical processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding compliance with ASTM standards is crucial, especially in the medical and aerospace sectors. Buyers should also consider sourcing from specialized suppliers familiar with titanium machining.
How Do Plastics Compare in CNC Machining?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and acrylic, are increasingly used in CNC machining due to their versatility and ease of machining. Key properties include lightweight, good chemical resistance, and ease of fabrication.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be machined quickly, making them ideal for prototyping and low-volume production runs. Their lightweight nature also makes them suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
Cons: Plastics generally lack the strength and durability of metals, which may limit their use in high-stress applications. They can also be sensitive to temperature changes, affecting dimensional stability.
Impact on Application: Plastics are compatible with various media, but their performance can be compromised in high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local and international standards is essential, especially in consumer goods. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of plastic materials and explore sustainable options.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machinists
| Material | Typical Use Case for is CNC machinist a good career | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less effective in high-temperature applications | Low |
| Steel | Industrial machinery, automotive parts | High strength and durability | Heavier and more challenging to machine | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and challenging machinability | High |
| Plastics | Prototyping, consumer goods | Cost-effective and versatile | Limited strength and temperature sensitivity | Low |
Understanding these materials and their implications can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions about CNC machining applications, ultimately enhancing the career prospects of CNC machinists in various regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is cnc machinist a good career
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes in CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a sophisticated manufacturing method that employs computerized controls to operate machine tools. The process is divided into several key stages, each critical to ensuring precision and quality in the final product.
How is Material Prepared for CNC Machining?
The first step in CNC machining is material preparation, which involves selecting the appropriate raw material based on the specifications of the final product. Common materials include metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics and composites.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes cutting, shaping, or sizing to fit the dimensions required for machining. This may involve sawing, shearing, or other processes to ensure that the workpiece is ready for the CNC machine. Proper material preparation is crucial, as any inaccuracies at this stage can lead to costly errors downstream in the manufacturing process.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in CNC Machining?
The next phase is forming, where the CNC machine performs operations such as milling, turning, drilling, and grinding. Each of these techniques serves a specific purpose:
- Milling: Removes material using rotary cutters and is ideal for creating complex shapes and features.
- Turning: Involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool is applied to shape it, commonly used for cylindrical parts.
- Drilling: Creates holes in the material, essential for assembly and fastening.
- Grinding: Provides finishing touches to achieve tight tolerances and a smooth surface finish.
Each operation requires precise programming and setup to ensure the final dimensions meet specifications.
How is Assembly Conducted in CNC Machining?
After the individual components are machined, assembly becomes the next critical step. This stage may involve fitting together multiple machined parts, which can include welding, fastening, or other joining methods.
In some cases, CNC machining can be integrated with robotic systems for automated assembly, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Ensuring that all components fit together seamlessly is essential for the functionality and durability of the final product.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed in CNC Machining?
Finishing techniques are applied to enhance the appearance and performance of the machined parts. Common finishing processes include anodizing, painting, and surface polishing. These processes not only improve the aesthetic quality but also increase corrosion resistance and surface durability.
Finishing is often the last step before the product is packaged and shipped. Ensuring high-quality finishes can significantly impact customer satisfaction and product longevity.
How Does Quality Assurance Work in CNC Machining?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in CNC machining to ensure that products meet established standards and specifications. Various international standards and industry-specific certifications guide these QA processes.
What International Standards Are Relevant for CNC Machining?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. It sets out criteria for ensuring that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements while enhancing customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for the oil and gas sector are also crucial. These certifications help buyers verify that suppliers adhere to high-quality manufacturing practices.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) in CNC machining typically involves several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before machining begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps catch deviations early, preventing further production of defective parts.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo thorough inspection and testing to confirm they meet all quality standards before shipping.
These checkpoints form a comprehensive quality management system that minimizes errors and ensures product integrity.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of machined parts. Common techniques include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers to verify that parts meet specified dimensions.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection to detect internal flaws without damaging the part.
- Functional Testing: Assessing whether the finished product performs as intended in real-world applications.
These methods provide valuable data that can be used for continuous improvement in manufacturing processes.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is critical.
What Are Effective Strategies for Supplier Audits and Reports?
Conducting regular audits of suppliers is an effective way to assess their quality control processes. Buyers should request detailed reports on the supplier’s quality management system, including their certifications, inspection results, and compliance with international standards.
During audits, buyers can evaluate the supplier’s facilities, observe their manufacturing processes, and review their quality documentation. This hands-on approach helps ensure that suppliers maintain high standards of quality.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These independent organizations can conduct inspections and audits to verify that suppliers comply with relevant standards and specifications.
Third-party inspections are particularly valuable for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site evaluations. They can offer peace of mind and ensure that products sourced from suppliers meet the necessary quality criteria.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate additional complexities when dealing with quality control across borders. Different countries may have varying standards and regulations, making it crucial to understand these differences.
For example, while ISO certifications are globally recognized, compliance with local regulations may vary significantly. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific requirements of the countries they are sourcing from and ensure that their suppliers are compliant.
Additionally, cultural differences in business practices may affect quality control processes. Establishing clear communication and expectations with suppliers can help bridge these gaps and ensure quality standards are consistently met.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in CNC machining is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers who uphold the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is cnc machinist a good career’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to equip B2B buyers with essential steps to evaluate the career prospects of CNC machinists. As the demand for skilled machinists continues to rise globally, understanding the nuances of this profession can help organizations make informed decisions about workforce development and training investments.
Step 1: Identify Industry Needs
Understanding the specific needs of your industry is crucial. Different sectors, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing, have varying requirements for CNC machinists. Assess your operational demands to determine the skill sets and experience levels necessary for your organization.
- Consider sector-specific skills: Some industries may require specialized knowledge in materials or compliance with stringent regulations.
- Anticipate future trends: Stay informed about technological advancements that may affect machining processes and workforce requirements.
Step 2: Evaluate Training Programs
Investing in training programs for CNC machinists can significantly enhance your workforce’s capabilities. Look for accredited vocational schools or technical colleges that offer CNC machining courses.
- Check curriculum relevance: Ensure the program includes hands-on training with current machinery and software.
- Assess partnerships: Programs that collaborate with local manufacturers often provide students with real-world experience, which is invaluable.
Step 3: Assess Career Advancement Opportunities
CNC machinists often seek positions that offer growth potential. Evaluate your organization’s capacity for career progression within your machining department.
- Promote continuous learning: Establish pathways for machinists to advance their skills through ongoing training and certifications.
- Foster a supportive environment: Cultivate a culture that encourages innovation and problem-solving, which can enhance job satisfaction and retention.
Step 4: Benchmark Salaries and Benefits
Competitive compensation packages are essential to attract and retain skilled CNC machinists. Research industry standards for salaries and benefits in your region.
- Consider geographic variations: Salary expectations can vary widely depending on location, so factor this into your budgeting.
- Include non-monetary benefits: Offering flexible working hours, health benefits, and opportunities for professional development can enhance your appeal as an employer.
Step 5: Engage with Industry Associations
Connecting with industry associations can provide valuable insights into the CNC machining landscape. These organizations often offer resources, networking opportunities, and industry reports.
- Participate in events: Attend conferences and workshops to meet potential hires and gain insights into best practices.
- Leverage resources: Utilize available research and tools to stay updated on industry trends and workforce challenges.
Step 6: Implement Recruitment Strategies
Develop a targeted recruitment strategy to attract qualified CNC machinists. Use job boards, social media, and industry-specific platforms to reach potential candidates.
- Highlight unique selling points: Clearly communicate what sets your organization apart, such as advanced technology or a strong company culture.
- Utilize employee referrals: Current employees can be a great resource for finding skilled candidates who may fit well within your organization.
Step 7: Monitor Workforce Performance
Once you have onboarded CNC machinists, continuously monitor their performance and satisfaction. Regular feedback loops can help identify areas for improvement and enhance overall productivity.
- Set clear performance metrics: Establish KPIs that align with your organizational goals and regularly review them.
- Encourage open communication: Foster a culture where employees feel comfortable sharing their challenges and successes, which can lead to improvements in both morale and output.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively assess and enhance the career prospects of CNC machinists within their organizations, ultimately leading to a more skilled and motivated workforce.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is cnc machinist a good career Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Machinist Sourcing?
When considering the sourcing of CNC machinists, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The type of materials used in CNC machining significantly impacts costs. Common materials like aluminum and steel are generally less expensive than specialized alloys or composites. The choice of material not only affects the direct costs but also influences the machining complexity and time required, which can escalate overall expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the region and the machinist’s skill level. In developed markets like Germany, salaries can range between €40,000 to €60,000 annually, while in emerging markets like Nigeria, skilled machinists may earn significantly less. Additionally, ongoing training and skill development are crucial to maintain competitiveness, which adds to labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with running a machining operation, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Understanding local overhead rates is vital for international buyers, as these can vary dramatically between countries.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are often overlooked but can be substantial. Custom tooling, especially for specialized parts, can require significant upfront investment. Buyers should consider whether existing tooling can be utilized or if new tooling is necessary, as this can impact the overall cost structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Effective QC processes are essential in CNC machining to ensure precision and compliance with specifications. Investing in robust QC systems can lead to higher initial costs but may reduce long-term expenses related to rework and scrap.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and customs duties, particularly for international transactions. Buyers should factor in these costs when evaluating suppliers from different regions.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on competition and the unique value proposition they offer. Buyers should engage in negotiations to ensure they receive a fair price that reflects the quality and service provided.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Machinist Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC machining services, including volume and minimum order quantities (MOQs), specifications and customization, materials used, quality certifications, and supplier-related factors.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities that align with their production needs to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom parts with unique specifications may incur higher costs due to increased labor and material requirements. Clear communication of specifications can prevent misunderstandings and cost overruns.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: The choice of materials can directly impact costs. Additionally, parts that require specific certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may lead to higher prices due to added compliance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices, but this often translates into lower risk and better outcomes.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international buyers to avoid unexpected costs related to shipping, insurance, and responsibilities during transport.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Negotiating CNC Machinist Costs?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost-efficiency strategies can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Building a long-term relationship can lead to better pricing and service over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as lead times, potential for delays, and the quality of the finished product, which can all affect overall costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations and economic conditions in the supplier’s country, as these can influence pricing. Understanding local market dynamics can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to benchmark prices and services against competitors. This insight can help in making informed decisions and identifying the best value.
-
Continuous Assessment: Regularly assess supplier performance and pricing structures to ensure competitiveness and quality are maintained over time.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing in the CNC machining industry can fluctuate based on a variety of factors, including market demand, raw material availability, and labor costs. The figures provided are indicative and should be verified with current market conditions and specific supplier quotes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is cnc machinist a good career With Other Solutions
Exploring Career Alternatives to CNC Machinist
In the rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, professionals often seek viable career paths that not only promise job security but also align with their skills and interests. While a career as a CNC machinist offers numerous benefits, including high demand and competitive salaries, it’s essential to compare this option with other alternatives. This analysis examines two potential career paths: Additive Manufacturing Technician and Industrial Automation Specialist.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Is CNC Machinist A Good Career | Additive Manufacturing Technician | Industrial Automation Specialist |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High demand in various sectors | Growing demand in niche markets | High demand across industries |
| Cost | Low entry cost (technical training) | Moderate cost (specialized training) | High cost (engineering degree) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical training | Requires knowledge of 3D printing | Requires extensive technical knowledge |
| Maintenance | Moderate (machine upkeep) | Low (software updates) | High (system maintenance) |
| Best Use Case | Precision parts manufacturing | Prototyping and custom parts | Automation of production processes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Additive Manufacturing Technician
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is a burgeoning field with applications across various industries, including aerospace, healthcare, and consumer products. As an Additive Manufacturing Technician, one would be responsible for operating 3D printers, designing prototypes, and ensuring the production of high-quality parts.
Pros: The demand for skilled technicians is rapidly increasing, particularly in sectors focused on innovation and customization. Additionally, entry into this field often requires less formal education compared to CNC machining, making it accessible for those with a passion for technology.
Cons: While the initial investment in training can be lower, specialized knowledge in software and materials is crucial, which may require further investment. Moreover, the job may be less stable in certain regions compared to CNC machining, which has a broader application.
Industrial Automation Specialist
Industrial Automation Specialists focus on the design, implementation, and maintenance of automated systems in manufacturing environments. This role typically requires a strong background in engineering or computer science, making it one of the more technical career paths.
Pros: This career offers high earning potential and job security, as companies increasingly rely on automation to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. The skills gained in this role are transferable across various industries, providing flexibility in career choices.
Cons: The path to becoming an Industrial Automation Specialist often involves significant educational investment, including a degree in engineering. Additionally, the complexity of the systems involved can lead to a steep learning curve, which may deter some potential candidates.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Career Path
When evaluating career options, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs, including industry demands, personal interests, and educational background. While a career as a CNC machinist offers immediate job opportunities and stability, alternatives like Additive Manufacturing Technician and Industrial Automation Specialist present unique advantages and challenges. Ultimately, the decision should align with the individual’s career goals and the evolving landscape of the manufacturing industry, ensuring a fulfilling and secure professional future.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is cnc machinist a good career
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for CNC Machinists?
CNC machining is a critical element in modern manufacturing, and understanding its technical properties is vital for B2B decision-makers. Here are key specifications that define the quality and precision of CNC machined components:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of material used in the machining process, such as aluminum, steel, or plastic. Each material grade possesses unique properties that affect machinability, strength, and application suitability. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is essential to ensure product durability and performance, especially in industries like aerospace or automotive where safety and reliability are paramount. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in a dimension of a part. It is crucial for ensuring that components fit together accurately. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.01 mm indicates that the actual dimension can vary by that amount without compromising functionality. In B2B contexts, tighter tolerances often lead to higher manufacturing costs, so understanding the balance between cost and precision is vital for procurement decisions. -
Surface Finish
This specification describes the texture and quality of the part’s surface after machining. Surface finishes can range from rough to polished and can significantly affect factors such as wear resistance and aesthetic appeal. For companies in sectors like consumer electronics, where appearance matters, specifying a particular surface finish can enhance product value and marketability. -
Machining Speed
Machining speed refers to the rate at which the CNC machine can cut through materials, usually measured in inches per minute (IPM). Faster machining speeds can lead to increased productivity but may require more advanced machines and tooling. For B2B buyers, understanding machining speeds can help in evaluating production timelines and costs, particularly in high-volume manufacturing environments. -
Tooling Type
The type of tooling used—such as end mills, drills, or lathes—affects both the machining process and the final product. Different tools are suited for specific operations and materials. For businesses, selecting the right tooling type can optimize production efficiency and product quality, making it a critical aspect of CNC machining procurement.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to CNC Machining?
Familiarity with industry terminology can greatly enhance communication and decision-making in CNC machining. Here are some commonly used trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In CNC machining, OEMs are often the end-users who require custom machined components. Understanding the OEM landscape helps B2B buyers identify potential partners for collaboration and sourcing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and production planning. Knowing the MOQ can help companies avoid excess stock and optimize their cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. In CNC machining, an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and capabilities from various suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thus influencing the total cost of procurement. For B2B buyers, understanding Incoterms is essential for managing logistics and ensuring smooth transactions. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the technology used to control machine tools via computers. This term is fundamental in the industry, as it distinguishes traditional machining from modern automated processes. Understanding CNC technology helps B2B buyers assess the capabilities and efficiencies of potential machining partners.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions about entering the CNC machining sector, ensuring they select the right partners and materials for their manufacturing needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is cnc machinist a good career Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing CNC Machinist Careers?
The global CNC machining market is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by advancements in technology, increasing automation, and a rising demand for precision manufacturing. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of CNC machinists cannot be overstated. As industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices expand, the need for skilled machinists who can operate complex CNC machines is becoming critical.
One key trend is the growing integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, which includes IoT, AI, and advanced robotics in manufacturing processes. This transition is not just about efficiency; it also enhances the quality of produced parts, thereby reducing waste and operational costs. Additionally, there is a noticeable shift towards sourcing from local suppliers to mitigate supply chain disruptions, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic. Countries like Germany are leading in this regard, focusing on advanced manufacturing hubs, while regions in Africa and South America are emerging as potential centers for CNC machining due to lower labor costs and untapped talent.
Moreover, as the skill gap widens, companies are increasingly investing in training programs and partnerships with educational institutions to nurture the next generation of CNC machinists. This trend not only enhances workforce readiness but also ensures a sustainable pipeline of talent that can adapt to evolving technologies and market needs.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the CNC Machinist Career Landscape?
Sustainability is becoming an essential consideration for B2B buyers in the CNC machining sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, leading many companies to prioritize ethical sourcing and green manufacturing practices. For CNC machinists, this translates into the adoption of sustainable materials and eco-friendly machining techniques that minimize waste and energy consumption.
The push for ‘green’ certifications is particularly relevant as companies seek to align their operations with global sustainability goals. Certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, can enhance a company’s reputation and marketability. B2B buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, making it imperative for machinists and manufacturers to adopt practices that align with these expectations.
Furthermore, the circular economy is influencing how materials are sourced and utilized in CNC machining. This approach emphasizes reusing and recycling materials, which not only reduces environmental impact but can also lead to cost savings. As buyers in regions like Europe and South America become more environmentally conscious, the demand for CNC machinists skilled in sustainable practices will likely continue to rise.
What is the Evolution of CNC Machining and Its Impact on Career Opportunities?
CNC machining has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, the process was limited to simple tasks, but advancements in computer technology have transformed CNC machines into sophisticated tools capable of executing complex designs with high precision. This evolution has opened up diverse career opportunities for CNC machinists, allowing them to work across various sectors, from aerospace to consumer electronics.
As CNC technology continues to advance, the skill set required for machinists is also evolving. Today’s machinists need to be proficient in software programming and digital technologies, in addition to traditional machining skills. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities; while it may require additional training, it also allows machinists to enhance their career prospects significantly.
In summary, the CNC machining sector is not only a promising career path due to its growth and job security but also a dynamic field that adapts to technological advancements and sustainability initiatives. For international B2B buyers, understanding these market dynamics is crucial for making informed decisions in sourcing CNC machining services and products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is cnc machinist a good career
-
How do I determine if CNC machining is a good career choice for my country?
To assess whether CNC machining is a viable career choice in your country, analyze the local manufacturing landscape and employment trends. Look for growth in industries that utilize CNC machining, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. Additionally, consider the demand for skilled machinists, which can be gauged through job postings and industry reports. Engaging with local vocational training institutions can also provide insight into the skills and certifications in demand, helping you make an informed decision. -
What are the salary expectations for CNC machinists in different regions?
Salary expectations for CNC machinists vary significantly across regions. In Europe, for example, CNC machinists can earn between €30,000 and €50,000 annually, depending on experience and industry. In Africa and South America, salaries may be lower but are often balanced by lower living costs. It’s crucial to research local salary benchmarks and consider the cost of living when evaluating job offers. Engaging with local industry associations can also provide valuable insights into competitive salaries. -
What skills are essential for a successful CNC machinist career?
Successful CNC machinists should possess a combination of technical skills and soft skills. Key technical skills include proficiency in CNC programming, machine setup, and maintenance, as well as a solid understanding of CAD/CAM software. Soft skills such as problem-solving, attention to detail, and effective communication are equally important. Continuous learning and adaptability to new technologies are essential in this rapidly evolving field, ensuring machinists remain competitive and valuable to employers. -
How can I vet potential CNC machining suppliers for quality assurance?
When vetting CNC machining suppliers, prioritize their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request samples of previous work to assess their machining capabilities and attention to detail. Additionally, consider their production capacity, lead times, and ability to meet your specific requirements. Establishing clear communication and requesting references from other clients can also help you gauge their reliability and service quality. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing CNC machining services?
Customization options in CNC machining can include material selection, part design modifications, and surface finishes. It’s essential to communicate your specific requirements to potential suppliers, including tolerances, dimensions, and any special treatments needed for your products. Inquire about the supplier’s capabilities for prototyping and iterative design processes, as these can significantly enhance the final product’s quality and functionality. A supplier that offers flexibility in customization can better meet your unique needs. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC machining services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC machining services can vary widely based on the supplier’s capabilities and the complexity of the parts being manufactured. Some suppliers may have an MOQ of a few pieces for simple components, while others may require larger quantities for complex parts to justify production setup costs. When sourcing suppliers, inquire about their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that align with your project requirements, ensuring they can accommodate your production needs without excessive costs. -
What payment terms are common in international CNC machining contracts?
Payment terms in international CNC machining contracts typically include options such as upfront deposits, progress payments, or full payment upon delivery. Common terms might involve a 30% deposit before production starts, with the balance due upon completion or delivery. It’s crucial to establish clear payment schedules to mitigate risks for both parties. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods and trade finance options to protect your investment and ensure smooth transactions across borders. -
How does logistics impact the sourcing of CNC machining services?
Logistics plays a critical role in sourcing CNC machining services, affecting both cost and delivery timelines. Factors to consider include shipping methods, customs regulations, and the geographical location of suppliers. Efficient logistics management can minimize lead times and reduce shipping costs, which is vital for maintaining competitiveness in the market. Collaborating with suppliers who have robust logistics capabilities and experience in international shipping can enhance your sourcing strategy and ensure timely delivery of your products.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Is Cnc Machinist A Good Career Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CNC Machinists – Career Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: A career in CNC can be rewarding but also stressful and monotonous. CNC machinists often feel underpaid, with many contributing $40 an hour worth of work but earning only $20. The job involves solving problems and creating things from scratch, which can be challenging. Salaries can be high for skilled individuals, with some earning over $95k or even $120k, especially with overtime. Experience and …
2. Indeed – Machinist Career Insights
Domain: indeed.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Indeed – Machinist Career Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Randstad USA – CNC Machinist Career
Domain: randstadusa.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC machinist career combines technical expertise with practical skills. Responsibilities include operating CNC machinery, loading raw materials, monitoring operations, making adjustments, and ensuring precise tool creation. Average salary ranges from $40,000 to $60,000 per year, with a mean of $48,510. Salary influenced by education, experience, industry, and geographic location. Opportunities fo…
4. Wisconsin Metal Tech – CNC Machining Services
Domain: wisconsinmetaltech.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Services including Stainless Steel Machining, Shaft Turning, Swiss Machining, Vertical Milling, Y-axis Horizontal Milling, Gun Drilling, 5-Axis Horizontal Machining, Centerless Grinding, Bar Grinding, Infeed Grinding, Thru-Feed Grinding. Materials supplied include various grades of Stainless Steel (17-4, 303, 304, 316, 410, 416, 420, 440) and 4140 Steel. Processing and Finishing serv…
5. JetCrafted – Precision CNC Machining
Domain: jetcrafted.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining is a process that uses Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines to shape or fabricate parts from various materials. CNC machinists operate these machines, interpreting design files (CAD/CAM), setting up and calibrating machines, and ensuring precision in production. Key responsibilities include understanding machine components, processes like milling, turning, and drilling, and main…
6. Practical Machinist – CNC Technician Course
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC Machinist Technician course: 9 months duration, 5 days a week, 5 hours a day.
7. Facebook – Machinist Insights
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Machinist Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is cnc machinist a good career
Why Consider CNC Machinist Careers for Future Growth?
In summary, pursuing a career as a CNC machinist presents a compelling opportunity for both individuals and businesses alike. The demand for skilled machinists is soaring globally, driven by the essential role they play in diverse industries, from automotive to aerospace. With competitive salaries and job security, CNC machining offers a pathway to financial stability without the burden of significant student debt. Moreover, the profession encourages creativity and problem-solving, appealing to those who thrive in dynamic work environments.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in CNC machining capabilities can enhance operational efficiency and product quality. As the industry evolves, staying ahead through strategic sourcing of skilled machinists and advanced technology will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Looking forward, the prospects for CNC machinists are bright, with continuous growth anticipated in the sector. Now is the time to consider how integrating skilled CNC professionals into your workforce can drive innovation and success in your manufacturing processes. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your operations by investing in this vital talent pool.