Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is cnc machining a good career
As the global demand for precision manufacturing continues to rise, many international businesses are left grappling with the question: Is CNC machining a good career choice for their workforce? This guide delves into the multifaceted world of CNC machining, providing essential insights for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam. We explore various types of CNC machining roles, applications across industries, and the critical considerations for sourcing skilled machinists.
In navigating the complexities of the CNC machining market, this guide offers a comprehensive overview of the key factors influencing career viability and business success. From understanding the skills required and the training pathways available to evaluating potential suppliers and the costs involved, our resource equips decision-makers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
Moreover, as industries evolve and technology advances, the CNC machining field presents numerous opportunities for growth and innovation. By investing in this sector, businesses not only enhance their production capabilities but also secure a skilled workforce poised to tackle the challenges of modern manufacturing. Join us as we explore the dynamic landscape of CNC machining and uncover the pathways to a successful career in this essential industry.
Understanding is cnc machining a good career Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level CNC Machinist | Requires minimal experience; typically involves basic operations | General manufacturing, assembly plants | Pros: Quick to hire, lower training costs Cons: Limited skill set, potential for higher turnover |
| Advanced CNC Machinist | Involves complex programming and setup; requires specialized training | Aerospace, automotive, medical devices | Pros: High precision work, better problem-solving skills Cons: Higher salary expectations, longer training period |
| CNC Programmer | Focuses on writing and optimizing machine code; strong software skills | Custom part manufacturing, prototyping | Pros: High demand for skilled programmers Cons: Requires continuous learning and adaptation |
| CNC Setup Technician | Specializes in setting up machines and tools for production runs | Job shops, production facilities | Pros: Critical role in production efficiency Cons: Can be physically demanding, requires attention to detail |
| CNC Maintenance Technician | Ensures machines are operational and performs troubleshooting | Manufacturing plants, maintenance services | Pros: Essential for minimizing downtime Cons: Requires technical expertise, potential for on-call hours |
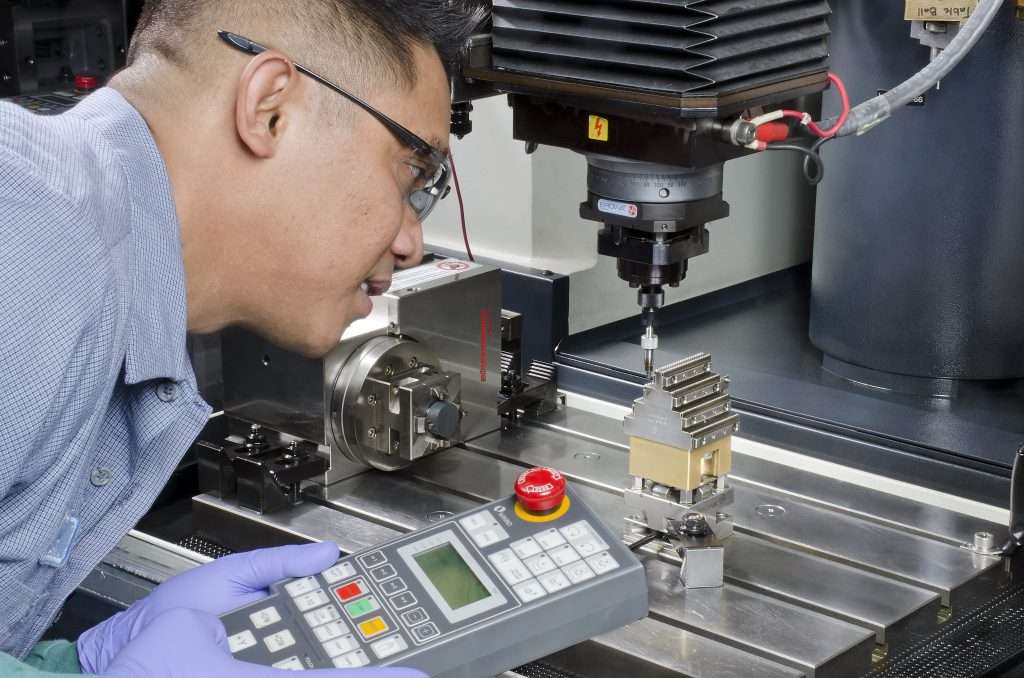
What Are the Characteristics of Entry-Level CNC Machinists?
Entry-level CNC machinists are typically fresh graduates from vocational schools or technical programs. They handle basic machining tasks under supervision, allowing them to gain hands-on experience. This role is suitable for businesses looking to fill positions quickly with cost-effective labor. However, buyers should be aware of the potential for high turnover and the limited skill set of these workers, which can impact production quality.
Why Choose Advanced CNC Machinists for Specialized Projects?
Advanced CNC machinists possess specialized training and experience in operating complex machinery. They excel in precision tasks and problem-solving, making them ideal for industries like aerospace and medical devices where accuracy is paramount. Companies investing in advanced machinists should consider the higher salary expectations and the need for ongoing training to keep up with technological advancements.
How Do CNC Programmers Contribute to Manufacturing Efficiency?
CNC programmers focus on developing the software that drives CNC machines, making them vital for custom manufacturing and prototyping. Their expertise in coding and machine optimization can significantly enhance production efficiency and reduce waste. B2B buyers should prioritize CNC programmers for projects requiring high customization, keeping in mind the necessity for continuous skill development to stay current with evolving technologies.
What Role Do CNC Setup Technicians Play in Production?
CNC setup technicians are responsible for preparing machines for production runs, ensuring that tools and settings are optimized for efficiency. They are crucial in reducing machine downtime and maintaining production flow in job shops and larger manufacturing facilities. While their role is essential, it can be physically demanding, and buyers should ensure that these technicians have the necessary skills and attention to detail to maintain high-quality standards.
Why Are CNC Maintenance Technicians Essential for Operations?
CNC maintenance technicians play a critical role in keeping machinery operational and minimizing downtime through regular maintenance and troubleshooting. Their expertise is indispensable in manufacturing environments where machine reliability directly impacts productivity. Businesses should consider the technical skills required for this role and the potential need for on-call hours, which can affect labor costs and scheduling flexibility.
Key Industrial Applications of is cnc machining a good career
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is CNC machining a good career | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Manufacturing precision components for aircraft and spacecraft | Enhanced safety and performance through high-quality parts | Certification standards, material specifications, and lead times |
| Automotive | Producing engine components and chassis parts | Improved efficiency and reliability of vehicles | Supplier reliability, technology integration, and cost-effectiveness |
| Medical Devices | Creating components for surgical instruments and implants | High precision and compliance with health regulations | Quality assurance processes, regulatory compliance, and traceability |
| Electronics | Machining housings and parts for consumer electronics | Faster time-to-market and innovation in product design | Flexibility in production volume, material compatibility, and rapid prototyping |
| Oil and Gas | Fabricating equipment for drilling and extraction | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Local sourcing options, logistical considerations, and environmental regulations |
How is CNC Machining Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, CNC machining is vital for manufacturing precision components essential for aircraft and spacecraft. These components must meet stringent safety and performance standards, making skilled CNC machinists indispensable. The ability to produce parts with high accuracy directly impacts flight safety and operational efficiency. International buyers must consider sourcing from certified suppliers that adhere to rigorous quality control and material specifications to ensure compliance with industry regulations.
What Role Does CNC Machining Play in the Automotive Sector?
CNC machining is integral to the automotive industry, where it is used to produce critical engine components and chassis parts. The precision afforded by CNC technology leads to improved vehicle performance and reliability, which are essential in a highly competitive market. For businesses looking to source these components, considerations include supplier reliability, integration of advanced manufacturing technologies, and cost-effectiveness to maintain competitive pricing while ensuring quality.
How Does CNC Machining Benefit Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical devices sector, CNC machining is employed to create intricate components for surgical instruments and implants. The need for high precision and adherence to health regulations makes skilled machinists crucial in this field. International buyers must prioritize suppliers with robust quality assurance processes and compliance with regulatory standards to ensure that the products meet necessary health and safety guidelines, thus mitigating risks associated with medical device manufacturing.
Why is CNC Machining Important in Electronics Manufacturing?
The electronics industry relies heavily on CNC machining for producing housings and components for consumer electronics. This application allows for rapid prototyping and innovation, enabling companies to bring products to market faster. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the flexibility of production volumes, compatibility of materials, and the ability to adapt to rapid changes in design specifications, ensuring that suppliers can meet evolving market demands.
How Does CNC Machining Enhance Operations in the Oil and Gas Industry?
CNC machining is critical in the oil and gas industry for fabricating equipment used in drilling and extraction processes. The precision and durability of machined components contribute to increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime, which are vital in this sector. Buyers should focus on local sourcing options to mitigate logistical challenges and ensure compliance with environmental regulations, as these factors can significantly impact project timelines and costs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is cnc machining a good career’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Long-Term Viability of CNC Machining Careers
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in regions such as Africa and South America are concerned about the sustainability of CNC machining careers. Given the rapid technological advancements and changing market dynamics, there’s a fear that CNC machinists may face job obsolescence. This uncertainty can hinder companies from investing in training programs or encouraging employees to pursue this career path, as they worry about the long-term return on investment.
The Solution: To address these concerns, companies should focus on building partnerships with educational institutions that offer CNC machining programs. By actively participating in curriculum development, businesses can ensure that training aligns with current industry standards and technological trends. Furthermore, establishing internship and apprenticeship opportunities can provide hands-on experience, allowing potential machinists to adapt to evolving technologies. Regularly assessing market needs and skill gaps can also help organizations identify areas for targeted training, ensuring that CNC machinists remain competitive and relevant in the job market.
Scenario 2: Recruitment and Skill Shortage Challenges
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, are often confronted with a shortage of skilled CNC machinists. Despite the growing demand for precision manufacturing, the industry struggles to attract young talent. This shortage can lead to increased operational costs, delays in production, and ultimately a negative impact on profitability.
The Solution: To combat this skill gap, companies should implement comprehensive recruitment strategies that appeal to younger demographics. This can include engaging with local schools and vocational training centers to introduce CNC machining as a viable career option. Offering competitive wages, benefits, and opportunities for career advancement will make the profession more attractive. Additionally, companies can utilize social media and digital marketing campaigns to highlight the creative and problem-solving aspects of CNC machining, showcasing success stories of current employees to inspire potential recruits. Investing in ongoing training and upskilling programs for existing employees can also help bridge the skills gap, allowing companies to cultivate a more knowledgeable workforce.
Scenario 3: The Physical and Mental Demands of CNC Machining
The Problem: B2B buyers might overlook the physical and mental demands that come with a career in CNC machining. Many potential candidates, especially those in regions with evolving job markets, may not realize the intricacies involved in operating CNC machinery, which can lead to burnout or high turnover rates. This oversight can affect workforce stability and production consistency.
The Solution: Companies should prioritize creating a supportive work environment that addresses both the physical and mental health of their CNC machinists. Implementing ergonomic assessments of workstations can reduce physical strain and enhance productivity. Additionally, establishing mentorship programs can help new machinists adapt to the demands of the job, providing them with the necessary support to thrive. Regular workshops on stress management and mental health awareness can foster a culture of well-being, encouraging machinists to voice concerns and seek help when needed. By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can improve retention rates and maintain a more stable and effective workforce.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is cnc machining a good career
What Materials Are Commonly Used in CNC Machining for Career Opportunities?
When considering a career in CNC machining, understanding the materials that machinists typically work with is crucial. Different materials present unique properties, advantages, and challenges that can influence both the manufacturing process and the final product. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in CNC machining, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: The Versatile Lightweight
Key Properties:
Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperatures and is non-magnetic, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is lightweight and easy to machine, which reduces manufacturing complexity. However, it can be more expensive than some other materials and may not be suitable for high-stress applications due to its lower tensile strength compared to steel.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications as well.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for aluminum alloys. Understanding the specific alloy requirements for different applications is essential.
Steel: The Strong Contender
Key Properties:
Steel offers high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to deformation. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, making it a preferred choice for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons:
While steel is highly durable and versatile, it is heavier and can be more challenging to machine compared to aluminum. The manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application:
Steel is commonly used in construction, automotive, and machinery applications where strength is paramount. Its ability to withstand harsh conditions makes it a reliable choice for critical components.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the various grades of steel and their compliance with international standards. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality steel that meets local regulations can be a challenge.
Plastics: The Lightweight Alternative
Key Properties:
Plastics, such as ABS and Nylon, are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be easily molded into complex shapes. They have good electrical insulation properties and can handle moderate temperatures.
Pros & Cons:
Plastics are generally less expensive and easier to machine than metals. However, they may not offer the same level of strength or heat resistance, limiting their use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Plastics are widely used in consumer products, electronics, and automotive components where weight savings and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the environmental impact of plastic materials and ensure compliance with regulations regarding plastic use in their respective regions. Understanding local preferences for recyclable materials can also influence purchasing decisions.
Titanium: The Premium Choice
Key Properties:
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength, low density, and high corrosion resistance. It can withstand extreme temperatures and is non-toxic, making it suitable for medical applications.
Pros & Cons:
While titanium offers superior performance, it is also one of the most expensive materials to machine. The complexity of working with titanium requires specialized tools and techniques, increasing manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is commonly used in aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance automotive applications where strength and weight are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should be aware of the high costs associated with titanium and ensure that their suppliers meet stringent quality standards. Compliance with international aerospace or medical device regulations is crucial for successful procurement.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for is cnc machining a good career | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower tensile strength than steel | Medium |
| Steel | Construction, heavy machinery | High strength and durability | Heavier and more complex to machine | Medium to High |
| Plastics | Consumer products, electronics | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Limited strength and heat resistance | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical devices | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | High cost and machining complexity | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is cnc machining a good career
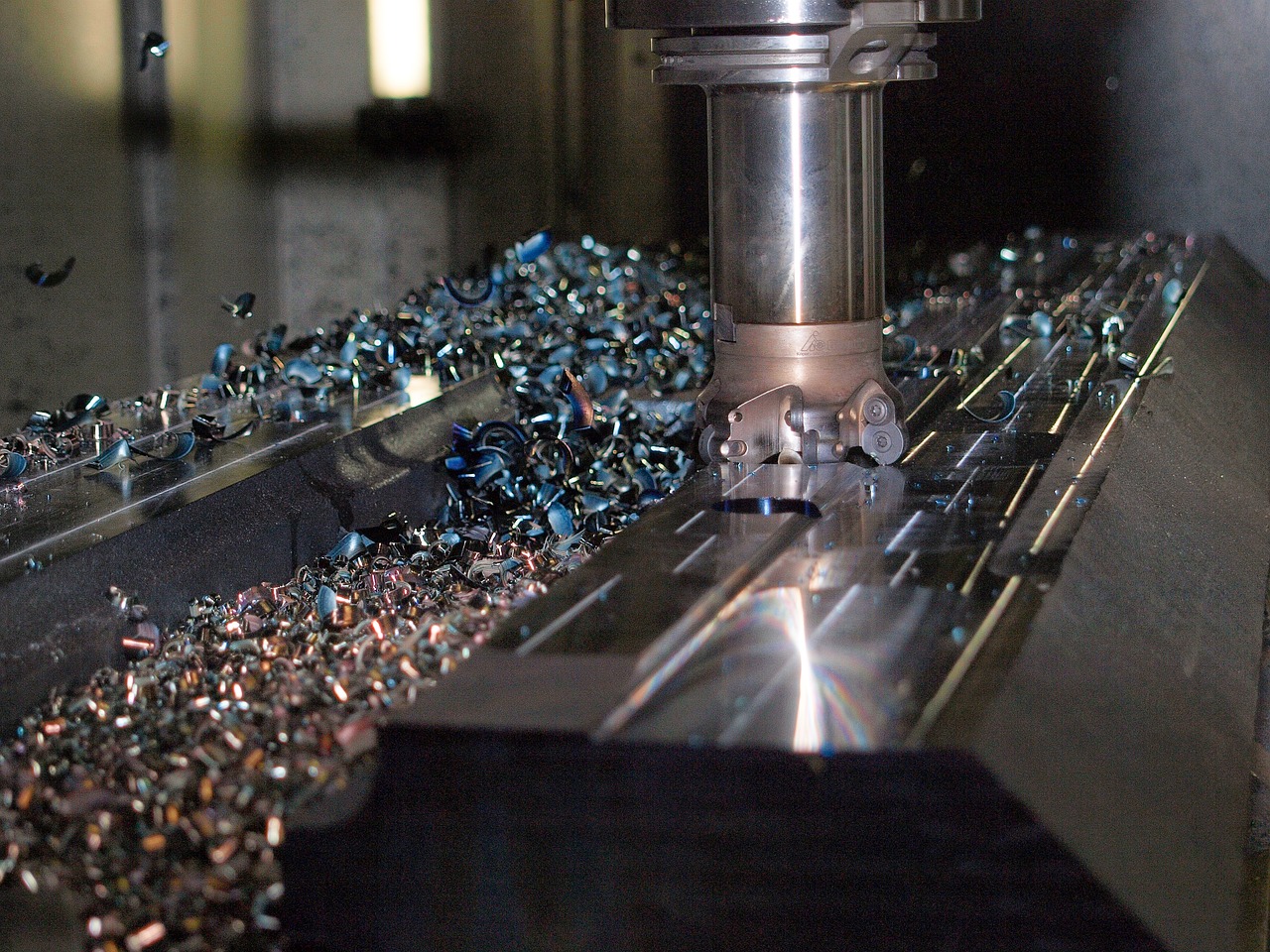
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes in CNC Machining?
CNC machining is an intricate process that combines advanced technology with skilled craftsmanship to produce high-precision parts. Understanding the key stages of the manufacturing process is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and efficiency in their supply chains.
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Machining?
-
Material Preparation
The first step in the CNC machining process involves selecting the appropriate raw materials based on the desired properties of the final product. Common materials include metals such as aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics and composites. Material preparation may also include cutting the raw materials into manageable sizes, cleaning, and inspecting for defects. -
Forming
In this stage, CNC machines perform the actual machining operations, which can include milling, turning, drilling, and grinding. Each technique is chosen based on the part’s design specifications:
– Milling involves removing material from a workpiece using rotary cutters, allowing for complex shapes and features.
– Turning is performed on a lathe, where the workpiece is rotated against a stationary cutting tool to create cylindrical parts.
– Drilling creates holes in the material, essential for assembly and functionality.
– Grinding finishes the surface of a part to achieve tight tolerances and a smooth finish. -
Assembly
After individual components are machined, they may need to be assembled into larger systems or products. This can involve fastening, welding, or bonding parts together, depending on the application. Precision during assembly is critical to ensure the integrity of the final product. -
Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the appearance and functionality of the machined parts. Techniques such as anodizing, plating, or painting may be employed to improve corrosion resistance, wearability, and aesthetics. Finishing processes can also involve additional machining operations to meet specific surface requirements.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Machining?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to CNC machining, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications. A robust QA process involves several checkpoints and testing methods to maintain high-quality output.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for CNC Machining?
For B2B buyers, understanding the quality standards applicable to CNC machining is vital. Key international standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable to any organization, regardless of size or industry. Certification to ISO 9001 indicates a commitment to consistent quality and continuous improvement.
-
CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking demonstrates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For industries like oil and gas, the American Petroleum Institute (API) sets specific standards that machining processes must adhere to, ensuring safety and reliability in critical applications.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Machining?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the machining process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During machining, operators conduct regular checks to monitor dimensions and tolerances, ensuring compliance with specifications as the work progresses.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the machining process is complete, final inspections are performed to verify that the finished products meet all quality and specification requirements.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in CNC Machining?
To ensure that machined parts meet quality standards, several testing methods can be employed:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM), dimensional inspections verify that parts conform to specifications.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and dye penetrant testing assess the integrity of materials without causing damage.
-
Functional Testing: This involves testing the final product in real-world conditions to ensure it performs as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are actionable steps to ensure compliance and quality:
-
Audits: Conduct on-site audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This provides insight into their adherence to standards and practices.
-
Quality Reports: Request detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers. These should include results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC, along with any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to evaluate the quality of products before shipment. This adds an extra layer of assurance regarding compliance with specifications.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances when it comes to quality control and certification:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific standards and certifications. Understanding these can help buyers ensure that products meet local regulations.
-
Documentation Requirements: Ensure that suppliers provide all necessary documentation, such as certificates of compliance, test reports, and material safety data sheets (MSDS).
-
Cultural Considerations: Be aware of cultural differences that may affect communication and expectations regarding quality and delivery. Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance collaboration and quality assurance.
Conclusion
CNC machining represents a dynamic and essential field within modern manufacturing, characterized by rigorous processes and stringent quality control measures. For B2B buyers, understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance is crucial for making informed decisions. By leveraging international standards, implementing robust QC measures, and verifying supplier practices, businesses can ensure they are sourcing high-quality components that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is cnc machining a good career’
Introduction
This guide is designed for B2B buyers interested in exploring CNC machining as a viable career path for their workforce. It outlines essential steps to assess the potential of CNC machining within your organization, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and strategic goals.
Step 1: Identify Your Workforce Needs
Understanding your current and future workforce requirements is crucial. Evaluate the specific skills and competencies needed for CNC machining roles in your organization. Consider factors such as production volume, technological advancements, and the complexity of parts being manufactured. This assessment will help you determine the number of skilled machinists required to meet your operational goals.
Step 2: Research Educational and Training Programs
Explore local and international training programs that specialize in CNC machining. Look for institutions that offer hands-on experience, apprenticeships, and certifications recognized in the industry. It’s important to ensure that these programs align with your company’s technological needs and the specific machinery you utilize.
- Consider partnerships with technical schools or universities for tailored training programs.
- Evaluate the curriculum to ensure it covers essential areas such as programming, setup, and operation of CNC machines.
Step 3: Analyze Job Market Trends
Stay informed about the job market dynamics for CNC machinists in your region. Research salary ranges, job availability, and the overall demand for skilled workers. Understanding these trends will help you gauge the competitiveness of your compensation packages and the feasibility of attracting top talent.
- Utilize job boards and industry reports to gather relevant data.
- Network with industry associations to gain insights into emerging trends.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Candidates
When sourcing CNC machinists, establish a robust evaluation process. Assess candidates not only on technical skills but also on their problem-solving abilities and adaptability. Given the technological advancements in CNC machining, it’s essential to find individuals who are eager to learn and grow within the field.
- Conduct practical assessments to test candidates’ abilities in real-world scenarios.
- Consider personality fit within your company culture, as collaboration is often key in manufacturing environments.
Step 5: Develop a Competitive Compensation Package
Craft a compensation package that reflects the market demand for CNC machinists. This should include competitive salaries, benefits, and opportunities for professional development. A well-structured compensation plan can enhance employee retention and attract skilled workers.
- Incorporate performance bonuses or profit-sharing options to motivate employees.
- Offer continued education incentives to support skill development.
Step 6: Implement Retention Strategies
Once you have sourced skilled CNC machinists, focus on retention strategies to maintain a stable workforce. Create a positive work environment that encourages growth, innovation, and job satisfaction. Regular feedback, recognition programs, and opportunities for advancement can significantly reduce turnover rates.
- Conduct employee surveys to gather insights on job satisfaction.
- Establish mentorship programs to foster skill development and career growth.
Step 7: Monitor Industry Developments
Finally, keep abreast of technological advancements and industry shifts in CNC machining. This ongoing research will allow you to adapt your workforce strategy and training programs accordingly. Staying ahead of trends will ensure your organization remains competitive in an evolving manufacturing landscape.
- Follow industry publications and attend trade shows to network and gather knowledge.
- Invest in continuous learning for your employees to keep their skills relevant.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can effectively assess and enhance their approach to integrating CNC machining into their workforce strategy, ensuring they remain competitive and equipped for future challenges.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is cnc machining a good career Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Machining Careers?
When evaluating the costs associated with CNC machining as a career, several key components must be considered:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials can significantly impact the overall expense of CNC machining projects. High-quality metals, plastics, and composites can vary in price based on market demand, availability, and sourcing location. B2B buyers should be aware that materials sourced from different regions may incur additional costs due to tariffs or shipping fees, particularly when importing to regions like Africa or South America.
-
Labor: The wages for CNC machinists can vary greatly depending on the region and skill level. In developed markets, skilled machinists command higher salaries due to demand. Conversely, in emerging markets, labor costs may be lower, but this often correlates with varying skill levels. Companies looking to hire CNC machinists should consider the long-term implications of labor costs, including training and retention.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with running a CNC machining operation, such as utilities, rent, and administrative salaries. Efficient overhead management can lead to significant cost savings. Buyers should analyze the overhead structures of potential suppliers to ensure they are getting competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The investment in tooling can be substantial, as specialized tools may be required for different machining operations. The costs of these tools should be factored into the overall pricing model, especially for custom or specialized projects. Understanding the life cycle and replacement costs of tooling is essential for accurate budgeting.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the precision and quality of machined parts is critical in CNC machining. Implementing effective quality control measures may increase upfront costs, but they can significantly reduce the risk of defects and rework, ultimately leading to cost savings in the long run.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting materials and finished products can be substantial, especially in international trade. B2B buyers should consider logistics costs when sourcing from different regions, as these can vary widely based on distance, transportation modes, and customs regulations.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin on top of their costs to ensure profitability. Understanding the typical margins in the CNC machining industry can aid buyers in negotiating better terms.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider?
Several factors can influence pricing in the CNC machining sector:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volume orders often result in discounted pricing due to economies of scale. B2B buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom projects may carry higher costs due to the need for specialized tooling or processes. Clear communication of specifications can help mitigate unexpected costs.
-
Material Selection: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Buyers should weigh the benefits of high-performance materials against their cost implications.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts requiring specific certifications or quality assurances can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their services, while newer suppliers may offer lower prices to attract business.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade is vital for international buyers. Incoterms dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can all impact the final cost.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in CNC Machining?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always discuss pricing with multiple suppliers to understand the market rate. Leverage volume commitments for better pricing.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, tooling, and training. TCO can reveal better overall value.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be mindful of fluctuating exchange rates and their impact on pricing. Currency volatility can affect the total cost significantly.
-
Research Local Markets: Understanding regional manufacturing capabilities can help buyers find cost-effective solutions. Emerging markets may offer competitive pricing due to lower labor costs.
-
Focus on Long-Term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and collaboration on future projects.
Conclusion
CNC machining presents a viable and lucrative career opportunity, especially in regions experiencing industrial growth. Understanding the cost components and pricing influencers is essential for B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. By applying strategic insights, buyers can optimize their procurement processes, ensuring they achieve the best value in their CNC machining investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is cnc machining a good career With Other Solutions
Exploring Career Alternatives in Precision Manufacturing
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, exploring various career options is essential for professionals and companies alike. CNC machining is a notable career path, but it’s beneficial to compare it with other viable alternatives in the field of precision manufacturing. Here, we examine CNC machining against two alternatives: Additive Manufacturing and Traditional Machining.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Is CNC Machining A Good Career | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Traditional Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and efficiency | Excellent for complex geometries | Reliable for large volumes |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial setup | Lower material waste; variable costs | High due to tooling and setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical training | Easier for rapid prototyping | Steep learning curve |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Low maintenance for printers | High maintenance for machines |
| Best Use Case | Mass production of parts | Custom parts and small batches | High-volume, less complex parts |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, offers a unique approach to creating parts layer by layer. It excels in producing complex geometries that are challenging for CNC machining. The initial investment in 3D printing technology can be lower than CNC, especially for prototyping. However, the cost of materials can vary significantly based on the type of filament or resin used. While the ease of implementation is a plus, particularly for rapid prototyping, the performance may not match the precision of CNC machining for high-volume production. This method is best suited for industries requiring customization, such as medical devices or aerospace components.
Traditional Machining
Traditional machining encompasses processes such as milling, turning, and grinding, which have been foundational in manufacturing. While it provides reliability and a proven track record for mass production, the initial setup costs can be high, and tooling changes are often necessary for different jobs. The learning curve for traditional machining can be steep, requiring skilled labor to operate effectively. Maintenance can also be demanding, as these machines often require regular servicing. Traditional machining is ideal for high-volume production of less complex parts, making it a staple in industries like automotive manufacturing.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Career Path
When considering career options in precision manufacturing, B2B buyers and professionals must evaluate their specific needs and the context of their operations. CNC machining offers a blend of high precision and job security, making it a strong contender for those seeking stable employment. In contrast, additive manufacturing provides flexibility and innovation, particularly for custom projects, while traditional machining is best for high-volume production. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the industry, the complexity of the parts required, and the long-term career aspirations of the individual. Assessing these factors will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and workforce development strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is cnc machining a good career
What Are the Key Technical Properties in CNC Machining for Career Consideration?
When evaluating CNC machining as a career, understanding the technical properties that define the industry is crucial. These properties not only influence the quality of machined parts but also impact job security and growth potential for machinists. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should be aware of:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of a material, such as steel, aluminum, or plastic, that determines its properties and suitability for various applications. For machinists, knowing the material grade is vital as it affects machining parameters, including tool selection and machining speed. High-quality materials lead to better end products, which in turn can enhance a machinist’s reputation and job security. -
Tolerance
Tolerance is the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in manufacturing. It is critical in CNC machining, where precision is paramount. Understanding tolerance levels can help machinists produce parts that meet stringent industry standards, essential for sectors like aerospace and medical devices. High tolerance capabilities often lead to higher demand for skilled machinists, as companies seek to maintain quality in competitive markets. -
Surface Finish
This property defines the texture and quality of a machined surface, which can influence both aesthetic appeal and functionality. Different machining processes yield various surface finishes, from rough to mirror-like. A machinist’s ability to achieve specific surface finishes can set them apart in the job market, offering opportunities in specialized sectors where appearance and performance are critical. -
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time taken to complete a machining operation, from setup to final inspection. Reducing cycle time without compromising quality is a key focus in modern manufacturing. Machinists who can optimize cycle times using advanced techniques or technologies are highly valued, as they contribute to increased productivity and cost savings for employers. -
Machining Strategy
This term refers to the approach taken to manufacture a part, including tool paths and machining sequences. A well-defined machining strategy can enhance efficiency and reduce material waste. For machinists, understanding various strategies can provide a competitive edge and broaden their skill set, allowing for versatility across different manufacturing environments.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in CNC Machining?
In addition to technical properties, familiarity with industry terminology is essential for B2B buyers and decision-makers in CNC machining. Here are some common terms that define the landscape:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the role of OEMs is crucial for machinists as they often work closely with them to meet specific requirements, ensuring that the parts produced align with the final product’s standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For CNC machining, this term is significant as it impacts inventory management and production planning. Buyers need to be aware of MOQs to effectively manage costs and ensure that they are not overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer requesting a quote from suppliers for specific products or services. For CNC machining, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and capabilities among different machinists, helping them make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms
Short for International Commercial Terms, Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for machinists and buyers alike, as they clarify the costs, risks, and logistics involved in shipping machined parts globally. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In CNC machining, shorter lead times can be a competitive advantage, allowing companies to respond quickly to market demands. Machinists who can deliver on tight deadlines are highly sought after, making this an important consideration for anyone looking to enter the field.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms provides a solid foundation for evaluating CNC machining as a career. It equips aspiring machinists and industry stakeholders with the knowledge necessary to navigate this dynamic field effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is cnc machining a good career Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting the CNC Machining Career Sector?
The CNC machining sector is witnessing a robust surge in demand, driven by a global shift towards advanced manufacturing technologies. This growth is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where the need for skilled CNC machinists is becoming increasingly critical. One of the primary drivers is the escalating requirement for precision engineering in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. As these sectors expand, they are investing in CNC machining capabilities to meet the rising standards of quality and efficiency.
Emerging technologies such as automation, Industry 4.0, and artificial intelligence are reshaping the landscape of CNC machining. These innovations not only enhance productivity but also reduce operational costs, making the sector more attractive to B2B buyers looking to optimize their supply chains. Additionally, the integration of smart manufacturing solutions allows for real-time monitoring and data analysis, which can lead to improved decision-making and reduced downtime. For international buyers, understanding these technological advancements is crucial for sourcing CNC machining services that align with their operational goals.
Furthermore, the global skills gap in CNC machining has intensified competition among manufacturers to attract and retain qualified machinists. This scarcity is prompting companies to invest in training programs and apprenticeship initiatives, creating a more skilled workforce. B2B buyers should leverage this trend by collaborating with suppliers who prioritize workforce development, ensuring they have access to high-quality machining services in the long term.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the CNC Machining Career Landscape?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming integral to the CNC machining sector, reflecting a broader shift in global manufacturing practices. As environmental concerns gain traction, companies are increasingly held accountable for their operational impact. This has led to a growing emphasis on sustainable machining practices, such as minimizing waste and utilizing eco-friendly materials. For B2B buyers, partnering with CNC machining firms that prioritize sustainability can enhance their brand reputation and align with corporate social responsibility goals.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, especially in a world where consumers are more informed and concerned about the origins of the products they purchase. Companies that adopt transparent sourcing practices and maintain ethical labor standards are likely to gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, selecting CNC machining partners who uphold these values is critical in mitigating risks and ensuring compliance with international regulations.
Moreover, certifications related to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 or green manufacturing certifications, are becoming increasingly relevant. B2B buyers should seek out CNC machining suppliers with these credentials, as they demonstrate a commitment to environmentally responsible practices. This not only supports a sustainable supply chain but also fosters innovation in machining techniques that can reduce environmental footprints.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Machining and Its Evolution in the B2B Sphere?
CNC machining has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1950s, transitioning from manual machining to highly automated processes. Initially developed to enhance precision and efficiency in manufacturing, CNC technology has undergone continuous refinement, leading to the sophisticated systems used today. This evolution has been marked by the integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software, which have revolutionized the way parts are designed and produced.
In the B2B context, the shift towards CNC machining has enabled manufacturers to respond rapidly to market demands and customize products to meet specific client needs. This adaptability has made CNC machining an essential component of modern manufacturing strategies, allowing businesses to remain competitive in an increasingly globalized economy. As companies continue to embrace digital transformation, the role of CNC machining is expected to expand further, solidifying its place as a cornerstone of effective manufacturing operations.
By understanding these market dynamics and trends, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their sourcing strategies in the CNC machining sector, ensuring they remain at the forefront of innovation and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is cnc machining a good career
-
How do I determine if CNC machining is a viable career path for my region?
To assess the viability of CNC machining as a career in your region, consider the local demand for skilled machinists. Research industry trends, job postings, and training programs available in your area. Engaging with local manufacturing associations can provide insights into the workforce needs and potential growth of CNC machining. Also, consider the economic stability of your region, as a growing manufacturing sector usually indicates a strong demand for CNC machinists. -
What skills are essential for success in CNC machining?
Successful CNC machinists need a blend of technical skills and soft skills. Technical skills include proficiency in operating CNC machines, understanding CAD/CAM software, and knowledge of machining processes. Soft skills such as problem-solving, attention to detail, and teamwork are equally important, as machinists often work in teams and must ensure precision in their work. Continuous learning and adaptability to new technologies are crucial for long-term success in this evolving field. -
What are the typical salary expectations for CNC machinists in different regions?
Salary expectations for CNC machinists can vary significantly by region due to factors such as demand, cost of living, and industry sector. In developed markets like Europe and North America, CNC machinists can earn between $40,000 to $70,000 annually, while in emerging markets such as those in Africa and South America, salaries may range from $20,000 to $40,000. Researching local salary benchmarks through job boards and industry reports can help you gauge fair compensation for machinists in your region. -
How do I vet suppliers for CNC machining services?
When vetting suppliers for CNC machining services, consider their experience, certifications, and customer reviews. Request samples of their previous work to assess quality and precision. Evaluate their production capabilities, lead times, and flexibility in handling custom orders. Additionally, understanding their quality assurance processes and compliance with international standards can provide confidence in their reliability and craftsmanship. -
What factors should I consider regarding minimum order quantities (MOQ) in CNC machining?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary based on the supplier and the complexity of the parts being produced. When negotiating MOQs, consider the cost-effectiveness of larger orders versus your actual needs. Assess whether the supplier can accommodate smaller runs, especially for prototypes or unique projects. Additionally, discuss any potential for scaling orders based on demand, which can help manage inventory and costs effectively. -
What payment terms are common in CNC machining contracts?
Payment terms in CNC machining contracts typically range from 30% upfront to 70% upon delivery or completion. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms for established clients. It’s important to clarify payment structures in advance to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using escrow services for larger projects to ensure both parties meet their obligations before final payments are released. -
How does quality assurance play a role in CNC machining?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in CNC machining to ensure that parts meet specified tolerances and standards. Suppliers should have established QA protocols, including regular inspections, testing, and documentation of processes. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality. As a buyer, insist on transparency regarding QA measures, and consider requesting inspection reports for critical components. -
What logistics considerations are important for international CNC machining projects?
Logistics play a crucial role in international CNC machining projects, including shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to handle shipping logistics efficiently and their experience with international clients. Discuss potential delivery timelines and any risks associated with customs delays. Understanding the import/export regulations in your country can also help prevent unforeseen challenges during the shipping process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Is Cnc Machining A Good Career Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Indeed – Machinist Career Insights
Domain: indeed.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Indeed – Machinist Career Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Wisconsin Metal Tech – CNC Machining Services
Domain: wisconsinmetaltech.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Services including Stainless Steel Machining, Shaft Turning, Swiss Machining, Vertical Milling, Y-axis Horizontal Milling, Gun Drilling, 5-Axis Horizontal Machining, Centerless Grinding, Bar Grinding, Infeed Grinding, Thru-Feed Grinding. Materials supplied include various grades of Stainless Steel (17-4, 303, 304, 316, 410, 416, 420, 440) and 4140 Steel. Processing and Finishing serv…
3. Randstad USA – CNC Machinist Overview
Domain: randstadusa.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC machinist career overview: A CNC machinist operates CNC machinery in factories, starting as a CNC machine operator. Responsibilities include loading raw materials, monitoring machine operations, making adjustments, and ensuring precise tool creation. Average salary ranges from $40,000 to $60,000 per year, with a mean of $48,510. Salary influenced by education, experience, industry, and geograp…
4. Practical Machinist – CNC Machining Insights
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC machining career insights, precision machining program at Ranken Technical College, learning manual machining, programming, CAD/CAM, average pay range of $25,000 to $70,000 per year, starting pay around $12/hour, potential to increase by $1/hour per year, higher pay with skills in programming and multi-axis CNC machines, advice to pursue engineering degree, importance of continuous learning an…
5. JetCrafted – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: jetcrafted.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining is a process that uses Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines to shape or fabricate parts from various materials. CNC machinists operate these machines, interpreting design files (CAD or CAM) to set up and calibrate the machines. Key responsibilities include understanding machine components, processes like milling, turning, and drilling, and maintaining tight tolerances and precis…
6. Total Aviation Staffing – CNC Machinist Opportunities
Domain: totalaviationstaffing.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: The job outlook for CNC lath and mill machinists is positive, with a projected 3% job growth rate from 2020 to 2030. Demand for skilled CNC machinists is driven by the need for precision manufacturing in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and electronics. CNC machinists operate and program CNC machines to produce precision parts. Qualifications include a high school diploma…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is cnc machining a good career
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global manufacturing, CNC machining emerges as a compelling career choice, particularly for international B2B buyers seeking skilled talent. The demand for CNC machinists is on the rise, driven by the industry’s increasing reliance on precision engineering across sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical technology. This demand translates into robust job security and competitive salaries, making it an attractive option for individuals looking to enter the workforce without the burden of extensive student debt.
Moreover, CNC machining offers diverse career paths, allowing professionals to pivot across various manufacturing sectors while continuously enhancing their skill sets. The hands-on nature of the job, coupled with the integration of cutting-edge technology, ensures that machinists are not only integral to the production process but also play a crucial role in driving innovation.
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in CNC machining talent can significantly enhance operational efficiency and product quality. As you consider your strategic sourcing decisions, recognize the immense potential within this field. Embrace the opportunity to cultivate a skilled workforce that will propel your business into the future of manufacturing.