Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is cnc a good career
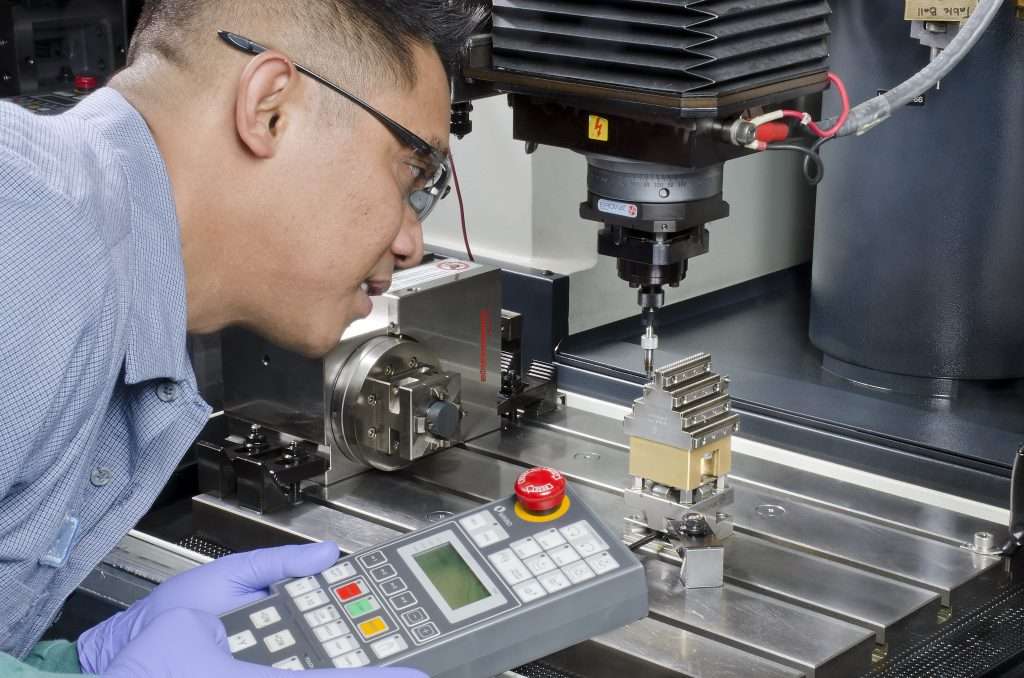
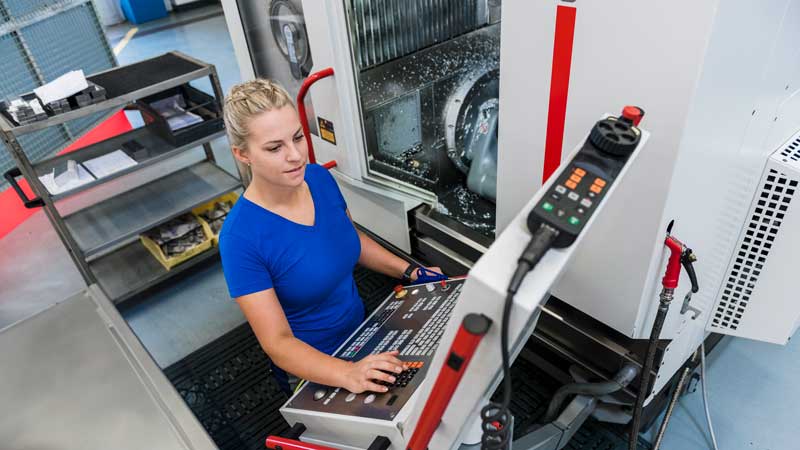
CNC machining represents a robust career path that is increasingly appealing to a diverse workforce worldwide. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, the demand for skilled CNC machinists is surging. However, many international B2B buyers face challenges in understanding the full scope of this career, including its applications, growth potential, and the necessary skill sets required for success. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing these concerns and equipping buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about investing in CNC machining talent.
Within this guide, we will explore various facets of a career in CNC machining, including the different types of CNC technologies, their applications across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices, and effective strategies for vetting suppliers. Additionally, we will delve into the cost considerations associated with CNC education and training, ensuring that B2B buyers can identify the most cost-effective pathways for sourcing skilled professionals. By offering actionable insights and expert analysis, this guide empowers buyers to navigate the complexities of the CNC job market, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and competitiveness in the global landscape.
Understanding is cnc a good career Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level CNC Machinist | Requires minimal experience; hands-on training available. | General manufacturing, small-scale production. | Pros: Low entry barrier; immediate job opportunities. Cons: Limited specialization; potential for lower pay. |
| Advanced CNC Technician | In-depth knowledge of CNC programming and machine operation. | Aerospace, automotive, medical device manufacturing. | Pros: Higher salaries; complex problem-solving skills. Cons: Requires extensive training; higher responsibility. |
| CNC Programmer | Focus on writing and optimizing CNC machine code. | Custom manufacturing, prototyping, and tooling. | Pros: High demand for programming skills; creative role. Cons: Requires continual learning; can be isolating. |
| CNC Setup Specialist | Specializes in machine setup and configuration. | High-volume production runs, assembly lines. | Pros: Critical role in efficiency; steady demand. Cons: Physically demanding; requires precision and attention to detail. |
| CNC Operations Manager | Oversees CNC operations and team management. | Large-scale manufacturing, production facilities. | Pros: Leadership opportunities; strategic influence. Cons: High-pressure environment; requires management skills. |
What Are the Characteristics of Entry-Level CNC Machinists?
Entry-level CNC machinists are typically individuals who have recently graduated from technical schools or vocational programs. They usually require minimal experience and receive hands-on training in various manufacturing environments. This role is suitable for those looking to start a career in machining without the burden of significant educational debt. B2B buyers seeking entry-level machinists benefit from a readily available workforce, though they may encounter varying skill levels and limited specialization in this category.
How Do Advanced CNC Technicians Differ from Entry-Level Roles?
Advanced CNC technicians possess a deeper understanding of CNC programming and machine operation, often requiring several years of experience or specialized training. They are essential in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision is critical. For B2B buyers, hiring advanced technicians means investing in skilled labor capable of handling complex tasks, albeit at a higher salary range. However, the investment pays off in terms of reduced errors and increased efficiency, making them a valuable asset.
What Role Do CNC Programmers Play in Manufacturing?
CNC programmers focus on writing and optimizing the code that directs CNC machines. This role is crucial in custom manufacturing and prototyping, where adaptability and creativity are paramount. B2B buyers benefit from programmers who can innovate and enhance production processes. However, the role can be isolating, and continual learning is necessary to keep up with technological advancements. As such, companies must consider the long-term commitment to professional development for their programming staff.
Why Are CNC Setup Specialists Important?
CNC setup specialists are responsible for the initial configuration and setup of CNC machines before production runs. They play a critical role in ensuring efficiency and precision in high-volume production environments. B2B buyers rely on setup specialists to minimize downtime and maximize output. However, the role can be physically demanding and requires a keen eye for detail. Companies must weigh the benefits of hiring specialized setup personnel against the physical and mental demands of the job.
What Are the Responsibilities of CNC Operations Managers?
CNC operations managers oversee the entire CNC machining process, including team management and production schedules. They are vital in large-scale manufacturing settings, where strategic planning and leadership are essential. For B2B buyers, hiring an operations manager can significantly improve production efficiency and team dynamics. However, this position comes with high pressure and necessitates strong management skills, making it crucial to choose candidates with proven leadership experience.
Key Industrial Applications of is cnc a good career
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is cnc a good career | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High-quality, reliable parts crucial for safety and performance | Skilled machinists with experience in aerospace standards and certifications |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments | Ensures accuracy and reliability in life-saving equipment | Compliance with strict regulatory requirements and quality control measures |
| Automotive | Production of engine components | Enhances efficiency and performance of vehicles | Access to advanced CNC technology and skilled labor for complex parts |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of circuit boards and housings | Supports the rapid production of high-tech devices | Need for precision and rapid prototyping capabilities to meet market demands |
| Oil and Gas | Creation of specialized machinery parts | Increases operational efficiency and safety in extraction processes | Understanding of harsh environmental conditions and material specifications |
How CNC Machining Benefits the Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, CNC machining plays a critical role in the production of precision components, such as turbine blades and structural parts. The demand for high-quality, reliable parts is paramount, as they directly impact safety and performance. International buyers in this industry must prioritize sourcing skilled machinists who are familiar with aerospace standards and certifications, ensuring that all components meet stringent regulations. This focus on quality not only enhances operational efficiency but also builds trust with end-users, ultimately leading to increased market share.
The Role of CNC Machining in Medical Device Manufacturing
CNC machining is essential in the medical device industry, where the fabrication of surgical instruments and implants requires utmost precision. The ability to produce accurate and reliable components can mean the difference between life and death. Buyers in this sector must consider suppliers who adhere to strict regulatory requirements, including ISO certifications and quality control measures. By investing in skilled CNC machinists who understand these complexities, companies can ensure that their products meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
Enhancements in Automotive Production Through CNC Machining
The automotive industry leverages CNC machining for the production of various engine components, enhancing both efficiency and vehicle performance. As the automotive market evolves with a focus on sustainability and innovation, the need for skilled machinists who can operate advanced CNC machinery is critical. International buyers should seek out suppliers that offer a combination of cutting-edge technology and a skilled workforce capable of producing complex parts. This approach not only reduces production costs but also accelerates time-to-market for new vehicle models.
Advancements in Electronics Manufacturing with CNC Machining
In electronics, CNC machining is vital for the production of circuit boards and housings, where precision is crucial. The rapid pace of technological advancements demands quick turnaround times and the ability to prototype new designs efficiently. Businesses should look for CNC machining services that offer rapid prototyping capabilities and a deep understanding of the specific requirements of electronic components. By partnering with skilled machinists, companies can ensure that they remain competitive in a fast-evolving market.
CNC Machining’s Impact on the Oil and Gas Sector
CNC machining is increasingly important in the oil and gas industry, particularly for creating specialized machinery parts that withstand harsh environmental conditions. These components must meet rigorous performance specifications to ensure safety and efficiency during extraction processes. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing from suppliers that understand the unique challenges of oil and gas operations. This includes familiarity with material specifications and the ability to produce durable components that can endure extreme conditions, ultimately enhancing operational reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is cnc a good career’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Skills Gap in CNC Machining
The Problem: Many businesses are struggling to find skilled CNC machinists, which hampers their production capabilities. The demand for CNC machining expertise is growing, but educational institutions often fail to provide adequate training aligned with industry needs. As a result, B2B buyers face delays in project timelines and increased operational costs due to the inability to hire qualified personnel.
The Solution: Companies should actively engage with local technical schools and vocational training programs to develop tailored apprenticeship initiatives. By collaborating with educational institutions, businesses can help shape curricula that meet their specific skill requirements. Offering internships and hands-on training opportunities not only helps students gain real-world experience but also creates a pipeline of talent ready to enter the workforce. Furthermore, investing in ongoing training for existing employees can enhance skills and improve retention rates, ensuring a more stable workforce in the long run.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Perception Challenges of CNC Careers
The Problem: A significant barrier to attracting new talent in CNC machining is the lack of understanding and appreciation for the profession. Many potential candidates perceive CNC machining as a mundane or unskilled job, which deters them from considering it as a viable career option. This perception is particularly prevalent in regions where traditional manufacturing jobs have declined, leading to a shortage of new entrants into the field.
The Solution: B2B buyers can tackle this issue by launching awareness campaigns that highlight the innovative and rewarding aspects of CNC machining. Utilizing social media, industry events, and partnerships with influencers can help change the narrative. Success stories of current machinists—emphasizing their career growth, financial stability, and the creativity involved in the job—can effectively draw interest. Additionally, companies can offer open house events or workshops to provide firsthand experiences of CNC machining, allowing potential candidates to engage with the technology and understand the value of the profession.
Scenario 3: Addressing Job Satisfaction and Retention Issues
The Problem: High turnover rates in CNC machining roles are a major concern for many manufacturers. Employees often leave for better opportunities or due to job dissatisfaction stemming from repetitive tasks and lack of career advancement. This not only disrupts production but also incurs significant costs related to recruitment and training new hires.
The Solution: To enhance job satisfaction and improve retention rates, companies should implement structured career development plans that provide clear pathways for advancement. This includes offering continuous education programs, mentorship opportunities, and performance incentives tied to skill development. Encouraging machinists to diversify their skill sets—such as programming, quality control, and management—can lead to a more engaged workforce. Additionally, creating a positive workplace culture that recognizes achievements and fosters teamwork can significantly boost morale and encourage long-term commitment to the company.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is cnc a good career
What Are the Key Materials for CNC Machining Careers?
In the CNC machining industry, the selection of materials is crucial for ensuring product performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials can significantly impact a machinist’s career trajectory and the overall success of manufacturing operations. Below are analyses of four prevalent materials used in CNC machining, tailored for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: A Versatile Choice for CNC Machining
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum lies in its ease of machining, which allows for high-speed production and intricate designs. However, it can be more expensive than other materials like steel, and its lower strength-to-weight ratio may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in automotive and aerospace components, where weight reduction is critical. Its compatibility with various media, including water and oil, makes it a preferred choice in many industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with international standards like ASTM and ISO. Additionally, sourcing aluminum from local suppliers can mitigate costs associated with import tariffs.
Steel: The Backbone of CNC Machining
Key Properties: Steel boasts high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to deformation. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The strength of steel is its main advantage, providing longevity and reliability in demanding environments. On the downside, steel can be challenging to machine, requiring specialized tools and longer processing times, which may increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is widely used in manufacturing machinery, automotive parts, and structural components. Its compatibility with harsh environments makes it suitable for applications in industries like construction and oil and gas.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like South America and Europe, adherence to standards such as DIN and JIS is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of local steel suppliers to reduce lead times.
Plastics: The Lightweight Alternative
Key Properties: Plastics are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be easily molded into complex shapes. They generally have lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastics is their versatility and lower cost, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, they may not be as durable as metals and can degrade under UV exposure or extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are commonly used in consumer products, medical devices, and electronic housings. Their compatibility with various chemicals makes them ideal for applications in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should consider local regulations regarding plastic materials and their environmental impact. Compliance with standards such as ASTM can also influence material selection.
Titanium: The Premium Choice for Specialized Applications
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It is lightweight yet incredibly strong, making it ideal for specialized applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of titanium is its performance in demanding environments, such as aerospace and medical applications. However, it is one of the most expensive materials to machine, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Titanium is commonly used in aerospace components, medical implants, and high-performance automotive parts. Its biocompatibility makes it particularly valuable in medical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the high costs associated with titanium and ensure compliance with industry-specific standards. Sourcing titanium from reputable suppliers is crucial to maintaining quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machining Careers
| Material | Typical Use Case for is cnc a good career | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and easy to machine | Higher cost compared to steel | Medium |
| Steel | Machinery and structural components | High strength and durability | Difficult to machine | Medium |
| Plastics | Consumer products and medical devices | Versatile and cost-effective | Less durable than metals | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical applications | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High machining costs | High |
This material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers considering a career in CNC machining, emphasizing the importance of material properties, applications, and regional compliance. Understanding these factors can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is cnc a good career
What Are the Key Stages in CNC Manufacturing Processes?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining involves a series of meticulously planned stages, each crucial for transforming raw materials into high-precision components. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers and quality products.
1. Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Handled?
Material preparation is the first step in the CNC machining process. This stage involves selecting appropriate materials—often metals like aluminum, steel, or titanium, as well as plastics. Suppliers must ensure that the materials meet specific industry standards and specifications.
- Material Inspection: Before use, materials undergo rigorous quality checks, including dimensional verification and chemical composition analysis. This ensures that the raw materials can withstand the operational demands of the final product.
- Cutting and Shaping: Depending on the requirements, materials are cut to size using saws or shears. This step reduces waste and prepares the material for the subsequent forming processes.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used in CNC Machining?
The forming stage is where CNC machines come into play. Utilizing computer-controlled tools, the forming process can include milling, turning, drilling, and grinding.
- Milling: This involves rotating cutting tools to remove material from the workpiece, creating complex shapes and features. CNC milling machines can operate on multiple axes, allowing for intricate designs.
- Turning: In this process, the workpiece rotates while a cutting tool moves along its length. This is particularly useful for producing cylindrical parts.
- Drilling and Grinding: Drilling creates holes, while grinding ensures the precision and smoothness of surfaces. Both processes are essential for achieving the desired tolerances and finishes.
3. Assembly: How Are Parts Integrated?
Once individual components are machined, they may require assembly. This stage can involve:
- Sub-assembly: Parts are initially assembled into smaller units, which are then integrated into the final product.
- Joining Techniques: Techniques such as welding, adhesive bonding, or mechanical fastening may be employed, depending on the application and material properties.
Effective assembly processes are critical, as they directly affect the functionality and reliability of the final product.
4. Finishing: What Are the Final Touches Applied?
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional qualities of the machined parts. Common finishing techniques include:
- Anodizing: Often used for aluminum parts, anodizing improves corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Polishing and Coating: These processes enhance the surface appearance and can provide additional protective layers.
- Quality Checks: At this stage, components undergo final inspections to ensure they meet specified tolerances and surface finishes.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into CNC Machining?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in CNC machining, ensuring that products meet industry standards and customer expectations. Implementing robust QA processes helps minimize defects and enhance customer satisfaction.
1. What Are the Relevant International Standards for CNC Machining?
To ensure consistent quality, many CNC machining companies adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001. This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that can enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking signifies compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: In the oil and gas industry, API standards ensure that products meet rigorous safety and quality benchmarks.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are vital throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the machining process helps identify issues early, reducing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished products undergo thorough inspections to confirm they meet all specifications.
3. What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality and performance of CNC-machined components:
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers and micrometers, dimensional checks ensure that parts conform to specified tolerances.
- Material Testing: Techniques like tensile testing and hardness testing assess the mechanical properties of materials.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection can identify internal defects without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is critical to ensuring reliable product quality. Here are several strategies:
1. What Role Do Audits and Reports Play?
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their QA processes and adherence to standards. Buyers should request:
- Quality Management System (QMS) Documentation: This includes details on how the supplier implements QA processes.
- Audit Reports: These documents highlight past inspections and compliance with industry standards.
2. How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can be critical, especially for international transactions, as they ensure compliance with local and international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers operating across different regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances:
- Regulatory Differences: Each region may have unique regulatory requirements, necessitating thorough research to ensure compliance.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context can facilitate better communication and collaboration with suppliers.
- Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks; therefore, working with suppliers experienced in global logistics can mitigate potential issues.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the CNC manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these key areas, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and ensure the delivery of high-quality products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is cnc a good career’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers considering the procurement of CNC machinists or CNC machining services. Understanding the nuances of this career can aid in making informed decisions about hiring skilled labor or investing in CNC technology.
Step 1: Assess Your Business Needs
Before diving into the CNC machining sector, identify your specific business requirements. Determine the types of parts you need, the complexity of designs, and the production volume. A clear understanding of these factors will help you find the right machinists or services that can meet your demands effectively.
- Consider the industry: Different sectors may require varying levels of precision and technology.
- Evaluate volume: High-volume production may necessitate advanced CNC capabilities.
Step 2: Define the Skill Set Required
CNC machining is diverse, encompassing various skills from programming to operating complex machinery. Clearly outline the skill set necessary for your projects.
- Programming proficiency: Look for machinists familiar with CAD/CAM software.
- Experience level: Determine if you need entry-level machinists or seasoned professionals.
Step 3: Verify Training and Certification
Ensure that potential machinists or suppliers have relevant training and certifications. This step is crucial for maintaining quality and safety standards in production.
- Look for industry certifications: Certifications from recognized organizations can indicate a commitment to best practices.
- Evaluate training programs: Check if they have undergone continuous education in the latest CNC technologies.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers before entering a contract. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from similar industries to gauge their reliability and expertise.
- Ask for client testimonials: Positive feedback from previous clients can provide insight into their performance.
- Review past projects: Assess their experience in delivering projects that align with your needs.
Step 5: Inquire About Technology and Equipment
Understanding the technology and equipment used by your potential suppliers is vital for ensuring they can meet your quality and efficiency standards.
- Check machinery capabilities: Ensure they use modern CNC machines that can handle your specific requirements.
- Ask about software tools: Familiarity with the latest CAD/CAM software can enhance productivity and precision.
Step 6: Assess Job Security and Growth Potential
Consider the job security and growth potential of CNC machinists in your region. A stable workforce can lead to reduced turnover and better continuity in production.
- Research local demand: High demand for CNC machinists can indicate a robust labor market.
- Evaluate training opportunities: Suppliers that invest in ongoing training for their machinists are likely to have a more skilled and stable workforce.
Step 7: Understand the Cost Structure
Lastly, grasp the cost implications of hiring CNC machinists or outsourcing CNC machining services. A clear understanding of pricing can help you budget effectively.
- Request detailed quotes: Ensure you understand all components of pricing, including materials and labor.
- Compare with industry standards: Benchmark costs against industry averages to ensure competitiveness.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions about sourcing CNC machining services or hiring skilled machinists, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and product quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is cnc a good career Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Machining Careers?
When evaluating the costs associated with a career in CNC machining, several critical components come into play:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant factor in CNC machining. High-quality metals and composites are often required, and prices can fluctuate based on market demand and availability. For international buyers, understanding local sourcing options can help mitigate costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in CNC machining, and labor costs can vary significantly by region. In areas like Africa and South America, labor may be less expensive compared to Europe, but the availability of skilled machinists can influence overall costs. Investing in training programs can enhance skill levels and improve productivity.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility costs, and equipment maintenance. The overhead can differ based on the manufacturing environment, impacting overall profitability. Shops in regions with higher energy costs or stringent regulations may see increased overhead.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and machinery can be substantial. Depending on the complexity of the parts being produced, the need for specialized tools may arise. High-precision tools can offer better longevity and performance but come at a premium price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet required specifications is crucial in CNC machining. The costs associated with QC processes, including inspections and certifications, can add to the overall expense. This is particularly relevant for industries with stringent regulatory requirements, such as aerospace and medical devices.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs for materials and finished products can vary widely. Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing these costs effectively, especially when sourcing materials internationally.
-
Margin: The desired profit margin can affect pricing strategies. A balance must be struck between competitive pricing and ensuring adequate profit to sustain operations.
What Influences Pricing in CNC Machining Careers?
Several factors can influence pricing in the CNC machining industry:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating MOQs can be beneficial for international buyers looking to maximize cost-efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts require additional design work and may incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly communicate specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the need for specific certifications can significantly impact costs. For instance, aerospace-grade materials will generally command a higher price.
-
Supplier Factors: Relationships with suppliers can lead to favorable pricing. Long-term partnerships often result in better negotiation power and lower costs.
What Are the Best Practices for International B2B Buyers in CNC Machining?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your understanding of local market conditions to negotiate better pricing. Building rapport with suppliers can also yield discounts or favorable terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial price. This includes considering maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of how local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and tariffs can affect pricing. This knowledge is critical when sourcing from multiple regions.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and cost requirements. Utilize industry networks and forums to gather insights on supplier reliability.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices in the CNC machining industry can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers should conduct detailed market research and consult with multiple suppliers to gain a clear understanding of the pricing landscape relevant to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is cnc a good career With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Career Paths
When considering career options in the manufacturing sector, CNC machining stands out due to its robust demand and growth potential. However, it is essential to evaluate other viable career paths that may also align with your skills and interests. This analysis will compare CNC machining with two alternative solutions: traditional manufacturing roles and automation engineering. By examining these options, B2B buyers can make informed decisions about career investments that best suit their business needs and workforce development goals.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Is CNC A Good Career | Traditional Manufacturing Roles | Automation Engineering |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High demand and job security | Moderate demand, variable security | High demand, growing field |
| Cost | Low entry cost (technical training) | Low entry cost (apprenticeships) | Higher cost (degree required) |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick training available | On-the-job training prevalent | Requires formal education |
| Maintenance | Ongoing skill development needed | Skill refreshers occasionally | Continuous learning essential |
| Best Use Case | Precision manufacturing | General manufacturing tasks | Designing automated systems |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Manufacturing Roles
Traditional manufacturing roles encompass a range of positions from assembly line work to quality control. These roles typically require less specialized training than CNC machining and can be filled by a broader pool of candidates. The primary advantage is the relatively low barrier to entry, allowing for quick staffing solutions. However, the job security in these positions can be less stable compared to CNC machining due to automation trends that threaten repetitive tasks. Workers may also face a more monotonous work environment, which can lead to lower job satisfaction and higher turnover rates.
Automation Engineering
Automation engineering focuses on designing, implementing, and maintaining automated systems and machinery. This field is rapidly growing due to the increasing demand for efficiency in manufacturing processes. While it offers high performance and job security, entering this field often requires a formal degree in engineering, which can lead to higher upfront costs in terms of education. Automation engineers are integral in shaping the future of manufacturing; however, they may face a steep learning curve as technology continues to evolve. This path is best suited for individuals who are mechanically inclined and have a strong interest in technology and innovation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Career Path
For B2B buyers exploring workforce development solutions, the choice between CNC machining and its alternatives hinges on specific business needs and strategic goals. CNC machining offers a strong balance of job security, low entry costs, and hands-on creativity, making it an attractive option for many. Traditional manufacturing roles can provide flexibility and lower costs but may lack the stability and satisfaction found in CNC careers. On the other hand, automation engineering presents exciting opportunities for innovation and efficiency, albeit with higher educational requirements. Ultimately, understanding these alternatives allows organizations to align their hiring and training strategies with the demands of the market and the capabilities of their workforce.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is cnc a good career
What Are the Key Technical Properties for CNC Machining Careers?
When considering a career in CNC machining, understanding essential technical properties is crucial for both potential machinists and B2B buyers in the manufacturing sector. Here are several critical specifications that define the CNC machining landscape:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of materials based on their mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. Common materials used in CNC machining include aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. Understanding material grades is vital for B2B buyers as it directly impacts product durability and performance, influencing both manufacturing costs and end-product quality. -
Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension, crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly. In CNC machining, tight tolerances (often in the range of ±0.001 inches) can mean the difference between a functioning assembly and a failed product. For businesses, knowing the required tolerances for their components can help in sourcing the right machinist and ensuring that the final product meets quality standards. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish pertains to the texture and smoothness of a machined part’s surface. Different applications may require specific surface finishes (e.g., rough, polished, or anodized). This property is important for B2B companies as it can affect the part’s functionality, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to wear and corrosion. -
Machining Speed
Machining speed is the rate at which a CNC machine operates, typically measured in surface feet per minute (SFM). Higher machining speeds can lead to increased productivity but may also require careful management of tool wear and heat generation. Understanding machining speeds is vital for decision-makers who aim to optimize production efficiency while maintaining quality. -
Tooling Options
The choice of tooling, including cutters, drills, and inserts, can significantly affect the machining process. Tooling options must align with the material and desired tolerances. For B2B buyers, being aware of tooling compatibility can lead to better procurement strategies and cost management, ensuring that the manufacturing process remains efficient.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Machining?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication within the CNC machining field. Here are some common terms that buyers and professionals should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help businesses identify reliable suppliers and ensure that the components meet specific quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to understand, as it can affect inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses negotiate better terms with suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In CNC machining, RFQs help buyers gather competitive pricing and assess suppliers’ capabilities, enabling informed decision-making. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks associated with the transportation of goods, thereby minimizing misunderstandings. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In CNC machining, lead times can vary based on complexity and volume. Understanding lead times is critical for B2B buyers to manage project timelines effectively and ensure timely delivery of essential components.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, businesses can make informed decisions about entering the CNC machining industry, whether as a career path or as a strategic component of their supply chain.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is cnc a good career Sector
What are the Global Drivers Influencing CNC Machining Careers?
The CNC machining sector is witnessing robust growth, driven by a combination of technological advancements and the increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries. Key markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are experiencing a notable shift towards automation and digitalization. As global supply chains recover and evolve post-pandemic, businesses are investing heavily in CNC technology to enhance productivity and efficiency. This shift is further fueled by the rising need for skilled labor, as many countries face a shortage of qualified machinists.
Emerging B2B technology trends, such as the integration of AI and machine learning in CNC processes, are redefining operational capabilities. These technologies not only streamline production but also enhance the skill set required for machinists, making the profession more appealing to younger generations. International buyers are encouraged to consider partnerships with educational institutions to develop tailored training programs that address local skill gaps. By fostering talent through apprenticeships and technical training, companies can ensure a steady supply of skilled machinists, essential for maintaining competitive advantage in the global market.
How Does Sustainability Impact the CNC Machining Industry?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly crucial in the CNC machining sector. As global awareness of environmental issues rises, businesses are compelled to adopt sustainable practices. This includes the implementation of energy-efficient machinery and the utilization of eco-friendly materials in production processes. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 or adherence to environmentally friendly practices.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications is not just a trend; it is becoming a prerequisite for many companies looking to improve their corporate responsibility profile. By sourcing from CNC machining providers that focus on reducing waste and energy consumption, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and align with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. Additionally, companies that embrace sustainability often benefit from cost savings in the long term, as they optimize resource use and reduce overhead associated with waste management.
What is the Historical Context of CNC Machining as a Career?
CNC machining has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed to enhance precision in manufacturing, CNC technology has transformed from simple numerical control systems to sophisticated computerized machines capable of executing complex designs with high accuracy. This evolution has not only improved manufacturing efficiency but has also expanded career opportunities in the sector.
Historically, CNC machining was often seen as a niche skill; however, as industries diversified and technological advancements proliferated, the role of CNC machinists has become vital. Today, machinists are integral to various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. The evolution of this career path reflects broader trends in workforce development, emphasizing the importance of technical training and ongoing education. As the industry continues to innovate, the demand for skilled machinists will only increase, further solidifying CNC machining as a viable and rewarding career choice.
Conclusion
In summary, the CNC machining sector offers a promising career path characterized by job security, competitive salaries, and opportunities for advancement. As global markets continue to evolve, the integration of sustainable practices and advanced technologies will shape the future of this industry, making it an attractive option for both current and prospective workers. B2B buyers should actively engage with educational and training institutions to cultivate a skilled workforce that meets the demands of this dynamic field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is cnc a good career
-
How do I evaluate if CNC machining is a suitable career for my region?
Evaluating CNC machining as a career in your region involves analyzing local demand for skilled machinists, available training programs, and industry growth projections. Research labor market reports and industry forecasts specific to your area. Engage with local manufacturing associations to gain insights into job openings and salary expectations. Additionally, consider the technological advancements in your region’s manufacturing sector, as areas investing in automation and precision engineering may present more opportunities for CNC professionals. -
What is the average salary for CNC machinists in emerging markets?
Salaries for CNC machinists can vary significantly across emerging markets. In regions like Africa and South America, entry-level CNC machinists may earn between $15 to $25 per hour, depending on local demand and industry standards. Conversely, in more developed markets like Europe, salaries can range from €30,000 to €50,000 annually. Always consider the cost of living and the availability of skilled labor, as these factors greatly influence salary structures in different regions. -
What training and qualifications are necessary to become a CNC machinist?
To become a CNC machinist, candidates typically need a high school diploma or equivalent, followed by specialized training in machining technology. Many vocational schools and community colleges offer programs that include hands-on training with CNC machines. Certifications from recognized bodies, such as the National Institute for Metalworking Skills (NIMS), can enhance employability. Continuous professional development is also crucial, as technology in CNC machining evolves rapidly, requiring machinists to stay updated with the latest techniques and software. -
How can I assess the quality of CNC machining suppliers for my business?
Assessing the quality of CNC machining suppliers involves a thorough vetting process. Start by reviewing their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples of their work to evaluate precision and finish quality. Additionally, check customer testimonials and case studies to gauge their reliability and service levels. Establishing clear communication and understanding their production capabilities, including lead times and flexibility, is also essential for ensuring they meet your business needs. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing CNC machining services?
When sourcing CNC machining services, consider customization options such as materials used, machining processes (e.g., milling, turning), and design specifications. Discuss tolerances, surface finishes, and post-processing services like anodizing or plating that may enhance the final product. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s capability to handle prototypes and small batch runs, as this flexibility can be vital for adapting to your specific project requirements. -
What are common payment terms in international CNC machining contracts?
Common payment terms in international CNC machining contracts can vary based on the supplier and the nature of the order. Typically, terms may include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon completion or delivery of the order. Some suppliers may offer payment upon receipt of goods or after a quality inspection. It’s crucial to negotiate clear payment terms and conditions to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How do logistics and shipping affect CNC machining projects?
Logistics and shipping play a critical role in CNC machining projects, particularly in international trade. Factors such as lead times, shipping costs, and customs regulations can impact delivery schedules and overall project timelines. When sourcing CNC services, discuss the supplier’s logistics capabilities, including their experience with international shipping and handling of customs documentation. Additionally, consider the distance from the supplier to your location and the potential for delays, as these can affect your supply chain efficiency. -
What are the key factors influencing job security for CNC machinists?
Job security for CNC machinists is influenced by several key factors, including industry demand, technological advancements, and skill levels. As industries increasingly adopt automation and advanced manufacturing technologies, skilled CNC machinists who can operate and program these machines will be in high demand. Additionally, geographic location plays a role; regions with a strong manufacturing base often provide more stable employment opportunities. Continuous skill development and adaptability to new technologies are essential for maintaining long-term job security in this evolving field.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Is Cnc A Good Career Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CNC Careers – Balancing Rewards and Challenges
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: A career in CNC can be rewarding but also stressful and monotonous. CNC machinists often feel underpaid for their contributions, with many earning around $20 an hour despite the work being valued at $40 an hour. The job involves solving problems and creating things, which can be fulfilling for those who enjoy challenges. Some individuals have reported significant salary increases, with one example…
2. Indeed – Machinist Career Insights
Domain: indeed.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Indeed – Machinist Career Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Wisconsin Metal Tech – CNC Machining Services
Domain: wisconsinmetaltech.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Services including Stainless Steel Machining, Shaft Turning, Swiss Machining, Vertical Milling, Y-axis Horizontal Milling, Gun Drilling, 5-Axis Horizontal Machining, Centerless Grinding, Bar Grinding, Infeed Grinding, Thru-Feed Grinding. Materials supplied include various grades of Stainless Steel (17-4, 303, 304, 316, 410, 416, 420, 440) and 4140 Steel. Processing and Finishing serv…
4. Jetcrafted – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: jetcrafted.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining is a process that uses Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines to shape or fabricate parts from various materials. CNC machinists operate these machines, interpreting design files (CAD/CAM), setting up and calibrating machines, and ensuring precision in production. Key responsibilities include understanding machine components, processes like milling, turning, and drilling, and main…
5. Randstad USA – CNC Machinist Career Overview
Domain: randstadusa.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC machinist career overview: A CNC machinist operates CNC machinery in factories, starting as a CNC machine operator. Responsibilities include loading raw materials, monitoring machine operations, making adjustments, and ensuring precise tool creation. Average salary ranges from $40,000 to $60,000 per year, with a mean of $48,510. Salary influenced by education, experience, industry, and geograp…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is cnc a good career
Why Should International B2B Buyers Consider CNC Machining Careers?
CNC machining represents a robust career path characterized by high demand, financial stability, and opportunities for creative problem-solving. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the strategic value of CNC machinists is crucial. As the manufacturing sector continues to evolve, the need for skilled CNC professionals is projected to grow, ensuring job security and competitive salaries that often exceed traditional roles.
Investing in CNC machining talent not only supports the production of high-quality components across various industries—such as aerospace, automotive, and medical technology—but also fosters innovation within your supply chain. The versatility of CNC skills allows for seamless transitions across sectors, empowering businesses to adapt to market shifts and technological advancements.
As you explore partnerships in CNC machining, consider the long-term benefits of nurturing a skilled workforce. By prioritizing strategic sourcing in this domain, you position your organization to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market. Embrace the future of manufacturing and unlock the potential that CNC machining offers for your business growth and operational excellence.