Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Is Cast Steel Magnetic
Understanding Cast Steel Magnetism and Precision Manufacturing Requirements
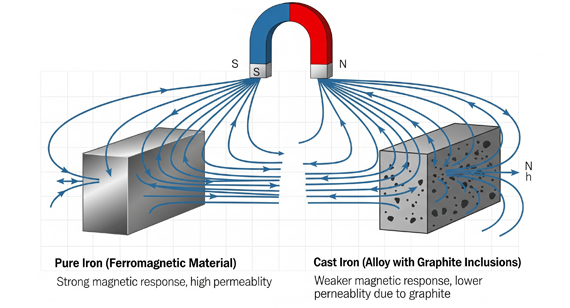
The question of whether cast steel is magnetic requires careful material science analysis, as magnetic properties depend on alloy composition, microstructure, and heat treatment. While most carbon and low-alloy cast steels exhibit ferromagnetism due to their ferritic or martensitic phases, austenitic stainless steel castings (e.g., CF-8M) are typically non-magnetic. This distinction is critical for applications in electromagnetic systems, sensors, or industrial machinery where magnetic permeability directly impacts performance. At Honyo Prototype, we recognize that material behavior must align precisely with functional demands, especially when final part geometry and surface integrity influence magnetic response.
Integrating Material Expertise with Advanced CNC Machining
Honyo Prototype delivers mission-critical CNC machining services for cast steel and other magnetic alloys, ensuring dimensional accuracy and material integrity for demanding applications. Our multi-axis milling and turning capabilities maintain tight tolerances (±0.005mm) while preserving the metallurgical properties essential for magnetic performance. Whether producing sensor housings, motor components, or hydraulic manifolds, we optimize machining parameters to prevent thermal or mechanical distortion that could alter magnetic characteristics. Every process is validated through in-house metrology, including coordinate measuring machines and material certification documentation.
Accelerate Your Development Cycle with Seamless Quoting
For engineering teams prioritizing speed without compromising technical rigor, Honyo Prototype’s Online Instant Quote system provides immediate pricing and lead time estimates for CNC-machined cast steel components. Upload your CAD file, specify material grades (e.g., ASTM A216 WCB or custom magnetic alloys), and receive a manufacturability assessment within minutes. This integration of material science insight and digital procurement efficiency ensures your prototypes or low-volume production parts meet both magnetic and geometric requirements on schedule. Partner with us to transform complex material challenges into precision-engineered solutions.
Technical Capabilities
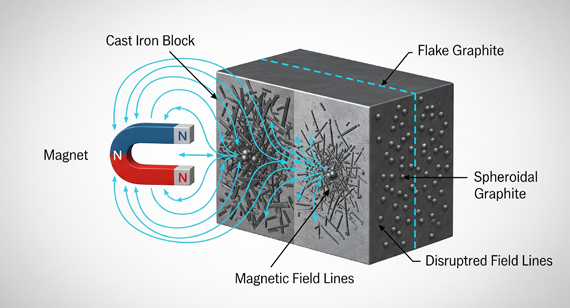
Cast steel is inherently magnetic due to its ferromagnetic properties, primarily resulting from its iron content and microstructure. This characteristic is critical when considering fixturing, tooling, and handling during precision machining operations such as 3/4/5-axis milling and turning. Magnetic workholding solutions—such as magnetic chucks or fixtures—are effective only with ferromagnetic materials like cast steel, enhancing rigidity and reducing setup time. However, non-ferrous and non-metallic materials such as aluminum, ABS, and nylon require alternative workholding methods due to their non-magnetic nature.
The following table outlines the technical considerations for various materials in high-precision machining environments, focusing on magnetic properties, machinability in multi-axis systems, and suitability for tight tolerance applications:
| Material | Magnetic? | Suitable for 3/4/5-Axis Milling | Suitable for Turning | Typical Tolerance Range (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Steel | Yes | Yes | Yes | ±0.01 to ±0.05 | Excellent for magnetic fixturing; good dimensional stability; moderate machinability; requires robust tooling due to hardness |
| Aluminum (e.g., 6061, 7075) | No | Yes | Yes | ±0.005 to ±0.025 | High machinability; lightweight; ideal for complex 5-axis parts; requires non-magnetic fixturing (vises, vacuum, mechanical) |
| ABS | No | Yes (with care) | Limited | ±0.05 to ±0.1 | Thermoplastic; prone to melting or burring; low thermal resistance; used for prototypes; non-magnetic; requires gentle cutting parameters |
| Nylon | No | Yes (with specialized tools) | Yes | ±0.05 to ±0.15 | Low friction, high toughness; prone to deformation under heat; requires sharp tools and cooling; non-magnetic; used in low-wear components |
Key Technical Notes:
Cast steel’s magnetic nature allows for efficient and repeatable fixturing in automated and high-accuracy environments, especially beneficial in 3/4/5-axis milling where complex geometries demand stable workholding. In tight tolerance applications (±0.01 mm), thermal stability and material homogeneity are critical—cast steel provides this, though post-casting stress relieving may be required.
Aluminum, while non-magnetic, remains a top choice for high-speed, tight-tolerance milling due to its excellent thermal conductivity and machinability. ABS and nylon, though less precise, are commonly used in prototype and non-structural applications, where magnetic properties are irrelevant but dimensional stability and fixturing design are still important.
For optimal performance in multi-axis systems, material selection must balance magnetic characteristics, thermal behavior, and mechanical stability to achieve tight tolerances consistently.
From CAD to Part: The Process

Honyo Prototype confirms that standard carbon and low-alloy cast steels exhibit ferromagnetic properties due to their iron-based crystalline structure. This characteristic is systematically evaluated within our integrated workflow to ensure material suitability for the client’s functional requirements. Below is a precise explanation of how magnetic property validation is embedded within our core process sequence.
Upon CAD model upload, our system captures all geometric and metadata inputs. While the initial AI Quote phase primarily assesses dimensional complexity, volume, and surface finish for cost estimation, it also cross-references any declared material specifications against our internal material database. If the client specifies a steel grade (e.g., ASTM A27 WCB), the AI flags standard magnetic behavior as an inherent property but does not perform granular material analysis at this stage.
The critical evaluation occurs during Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis. Here, our engineering team conducts a rigorous material properties review. For cast steel components, we:
Verify the exact alloy grade against ASTM, SAE, or ISO standards to confirm ferritic/martensitic phase composition.
Assess whether residual magnetism could impact downstream processes (e.g., welding, machining) or end-use performance (e.g., interference with sensors).
Document magnetic characteristics in the DFM report, noting exceptions such as austenitic stainless steels (e.g., CF8M) which may be non-magnetic.
Recommend material substitutions if magnetic properties conflict with functional requirements.
Production execution strictly adheres to the validated DFM parameters. Material certification from our foundry partners includes magnetic permeability test data where relevant. For mission-critical applications, optional post-cast magnetic particle inspection (MPI) is performed per ASTM E709 to detect surface discontinuities that could affect magnetic flux paths.
Delivery encompasses comprehensive documentation. Material test reports (MTRs) explicitly state magnetic properties, including Brinell hardness correlations where applicable. Final inspection records confirm dimensional compliance while validating that magnetic behavior aligns with the approved DFM scope.
The following table details phase-specific actions regarding cast steel magnetism validation:
| Process Phase | Action Regarding Magnetic Properties | Output Verification |
|---|---|---|
| CAD Upload | Captures declared material grade from client metadata | Material grade logged in project file |
| AI Quote | Flags standard magnetic behavior based on declared grade; highlights non-standard alloys | Preliminary material suitability note in quote |
| DFM Analysis | Validates grade-specific magnetic properties against standards; assesses functional impact; documents exceptions | Formal DFM report with magnetic property certification |
| Production | Enforces material certification with magnetic test data; performs MPI if specified | MTRs with permeability/hardness data; MPI reports |
| Delivery | Includes magnetic property confirmation in final documentation package | Signed MTRs and inspection records in delivery dossier |
This structured approach ensures magnetic properties are not an afterthought but a controlled variable from quotation through delivery. Honyo Prototype guarantees that all cast steel components meet the magnetic performance criteria defined during DFM, eliminating ambiguity for applications requiring precise electromagnetic characteristics. Clients receive full traceability from raw material certification to final part validation.
Start Your Project

If you need to determine whether cast steel is magnetic for your application, our engineering team at Honyo Prototype can provide technical guidance and material testing support. Cast steel typically exhibits magnetic properties due to its ferromagnetic microstructure, but specific alloying elements and heat treatment can influence its magnetic response. For precise material characterization or custom prototyping needs, contact Susan Leo directly at [email protected]. Our manufacturing facility is located in Shenzhen, enabling rapid turnaround for samples and production runs.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.