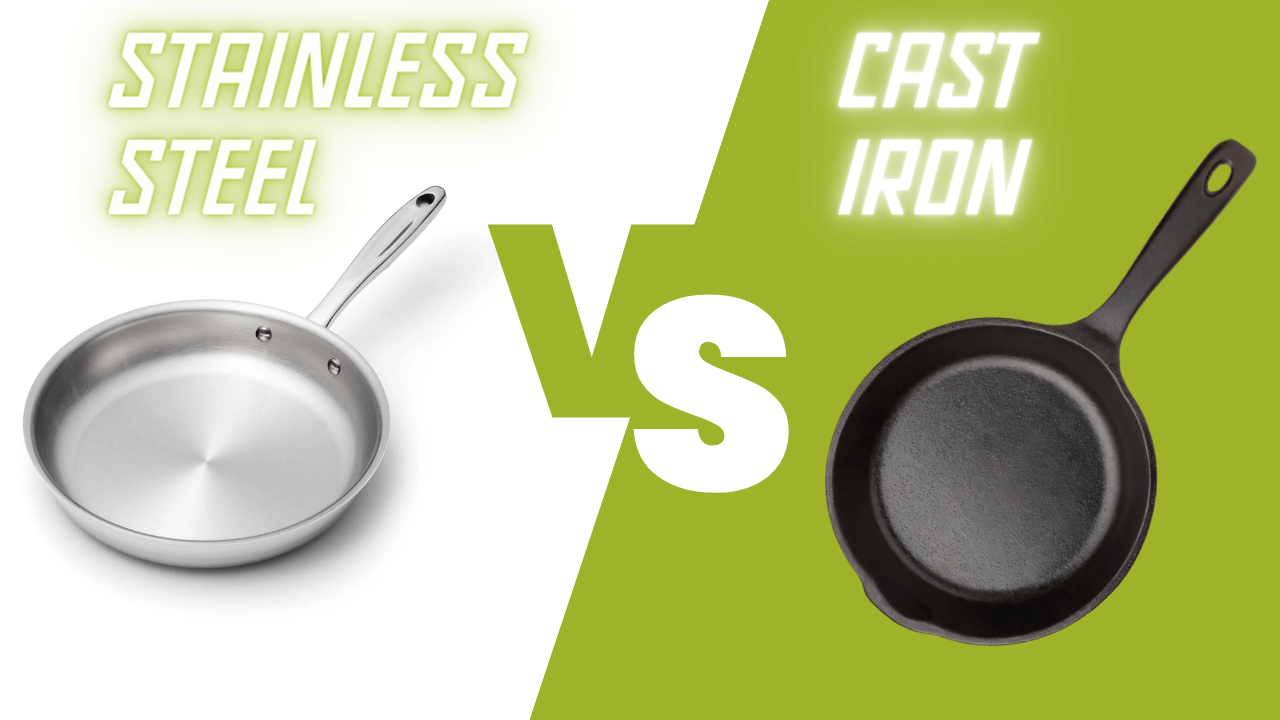
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is cast iron better than stainless steel
In the quest to determine whether cast iron is better than stainless steel, B2B buyers face a significant challenge: making informed sourcing decisions that align with their specific culinary needs and operational requirements. Both materials offer unique advantages, but understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right cookware that enhances performance and durability in various cooking environments. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of cast iron and stainless steel, covering key factors such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost implications.
By examining the benefits and limitations of each material, this resource empowers international B2B buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Germany and Vietnam)—to navigate the complexities of their cookware options. Whether your focus is on the exceptional heat retention of cast iron or the versatility and ease of maintenance offered by stainless steel, this guide aims to provide actionable insights. Armed with this knowledge, decision-makers can confidently procure the best cookware solutions that not only meet their culinary standards but also enhance operational efficiency and longevity in their kitchens.
Understanding is cast iron better than stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Cast Iron | Heavyweight, exceptional heat retention, requires seasoning | Restaurants, catering, outdoor cooking | Pros: Durable, long-lasting, excellent heat retention. Cons: Heavy, requires maintenance, not ideal for acidic foods. |
| Enameled Cast Iron | Coated with enamel, non-reactive, easier to clean | Bakeries, gourmet cooking | Pros: Easy to clean, versatile with acidic foods. Cons: Can chip, generally more expensive than traditional. |
| Stainless Steel | Lightweight, non-reactive, quick heat responsiveness | Commercial kitchens, food processing | Pros: Versatile, easy to maintain, good heat control. Cons: Poor heat retention compared to cast iron, can warp under high heat. |
| Hybrid Cast Iron | Moderate weight, retains benefits of cast iron | High-end restaurants, specialty dishes | Pros: Easier to handle, combines benefits of both materials. Cons: Higher cost, may not be as durable as traditional cast iron. |
| Stainless Clad | Multi-layer construction for even heating | Professional kitchens, catering | Pros: Excellent heat distribution, durable, induction-compatible. Cons: Heavier than standard stainless, can be pricier. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Traditional Cast Iron Cookware?
Traditional cast iron cookware is renowned for its durability and excellent heat retention, making it a staple in both home and commercial kitchens. Its heavyweight design allows for even heat distribution, which is ideal for slow-cooking and frying. However, it requires regular seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface and to prevent rust. B2B buyers should consider the maintenance aspect, as well as the cookware’s weight, which can impact handling in busy kitchen environments.
How Does Enameled Cast Iron Differ from Traditional Cast Iron?
Enameled cast iron features a glossy, protective enamel coating that makes it non-reactive and easier to clean than traditional cast iron. This type is particularly suitable for cooking acidic foods without the risk of damaging the seasoning. Enameled cast iron is favored in bakeries and gourmet cooking settings where presentation is key. Buyers should weigh the benefits of ease of maintenance against the higher price point and potential for chipping.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for B2B Applications?
Stainless steel cookware is lightweight and versatile, making it ideal for fast-paced commercial kitchens. Its non-reactive surface allows for a wide range of cooking applications, including those involving acidic ingredients. The quick heat responsiveness is a significant advantage for chefs who need to adjust temperatures rapidly. However, buyers should note that stainless steel does not retain heat as well as cast iron, which may be a consideration for certain cooking methods.
What Are the Advantages of Hybrid Cast Iron Cookware?
Hybrid cast iron cookware offers a balance between the weight of traditional cast iron and the ease of handling found in stainless steel. This type retains the heat retention qualities of cast iron while being lighter and easier to maneuver. It’s particularly suited for high-end restaurants that require both performance and ease of use. However, the higher cost may deter some buyers, and its long-term durability compared to traditional cast iron should be considered.
How Does Stainless Clad Cookware Enhance Cooking Performance?
Stainless clad cookware combines multiple layers of metals to enhance heat distribution and responsiveness, making it a preferred choice in professional kitchens. Its durability and compatibility with induction cooktops make it a versatile option for various cooking styles. B2B buyers should consider the investment in stainless clad cookware, as it often comes at a premium price but offers superior cooking performance and longevity compared to standard stainless steel.
Key Industrial Applications of is cast iron better than stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is cast iron better than stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Cookware for industrial kitchens and food manufacturing | Exceptional heat retention and durability enhance cooking efficiency | Supplier reliability, availability of enameled options, and price stability |
| Construction and Heavy Industry | Machinery components and tools | High strength and wear resistance lead to reduced downtime and maintenance costs | Material certifications, sourcing from local suppliers to reduce costs, and weight considerations |
| Agriculture | Equipment for food storage and preservation | Cast iron’s durability and non-reactive properties ensure long-lasting storage solutions | Compliance with health and safety regulations, sourcing for specific climates, and bulk purchasing options |
| Hospitality | Cookware for restaurants and catering services | The ability to handle high temperatures and provide consistent cooking results enhances food quality | Supplier reputation, ease of maintenance, and adaptability to diverse cuisines |
| Energy and Utilities | Heat exchangers and industrial piping systems | Superior heat retention and resistance to thermal cycling improve energy efficiency | Sourcing for specific industry standards, availability of customized solutions, and long-term cost analysis |
How is Cast Iron Better Than Stainless Steel in Food Processing?
In the food processing sector, cast iron cookware is favored for its exceptional heat retention and durability. Industrial kitchens benefit from its ability to maintain consistent temperatures during cooking, which is crucial for quality control in food manufacturing. Buyers in this sector should consider sourcing enameled cast iron options to prevent rust and enhance ease of cleaning, while also ensuring that suppliers can reliably deliver high volumes to meet operational demands.
What are the Benefits of Using Cast Iron in Construction and Heavy Industry?
Within construction and heavy industry, cast iron is utilized for machinery components and tools due to its high strength and wear resistance. This material significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs, making it an economically viable choice for businesses. When sourcing cast iron, companies should prioritize suppliers that provide material certifications and consider local sourcing to mitigate transportation costs, especially in regions like Africa and South America.
Why Choose Cast Iron for Agricultural Equipment?
In agriculture, cast iron is commonly used for food storage and preservation equipment. Its durability and non-reactive properties ensure that stored food remains uncontaminated, which is essential for maintaining quality. International buyers must ensure compliance with local health and safety regulations and consider sourcing options that cater to specific climate conditions, such as humidity, which can affect product longevity.
How Does Cast Iron Enhance Hospitality Operations?
For the hospitality industry, cast iron cookware offers the ability to withstand high temperatures and deliver consistent cooking results, which is vital for restaurants and catering services. This reliability enhances food quality and customer satisfaction. Buyers should focus on suppliers with a solid reputation and consider the ease of maintenance of cast iron products, especially in high-volume kitchen environments.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Energy and Utilities?
In the energy and utilities sector, cast iron is used for heat exchangers and industrial piping systems due to its superior heat retention and resistance to thermal cycling. This property improves energy efficiency, which is increasingly important in today’s environmentally conscious market. When sourcing cast iron for these applications, businesses should focus on suppliers that offer customized solutions and adhere to industry standards to ensure optimal performance and compliance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is cast iron better than stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Dilemma of Versatility in Diverse Culinary Operations
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those managing commercial kitchens or restaurants, often face the challenge of selecting cookware that meets a wide array of culinary needs. For example, a buyer may need equipment that performs well for both high-heat applications, such as searing meats, and low, slow cooking methods, like braising. The confusion arises when trying to determine whether cast iron or stainless steel is the more versatile option, as both materials have distinct advantages and drawbacks.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should assess their specific cooking requirements and consider the versatility of each material. Stainless steel is renowned for its quick heat responsiveness and adaptability to various recipes, including those involving acidic ingredients. Therefore, for operations that require rapid temperature adjustments and a broad range of cooking techniques, stainless steel cookware should be prioritized. Conversely, for tasks that involve prolonged cooking times at high temperatures—such as roasting or baking—cast iron’s superior heat retention and even cooking surface make it an excellent choice. Buyers should consider investing in a combination of both materials, utilizing stainless steel for versatility and cast iron for its durability in specific applications.
Scenario 2: The Weight and Maneuverability Challenge
The Problem: In fast-paced commercial kitchens, the weight of cookware can significantly impact efficiency. Many buyers find that traditional cast iron cookware is often too heavy, making it cumbersome to handle, particularly during busy service times. This can lead to fatigue among kitchen staff and a decrease in overall productivity, ultimately affecting service quality and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: Buyers should look for lightweight alternatives or hybrid options that combine the benefits of cast iron with improved maneuverability. For instance, investing in enameled cast iron or cast iron cookware designed with ergonomic handles can alleviate some of the weight challenges without sacrificing the advantages of cast iron. Additionally, stainless steel cookware generally offers a lighter weight, making it easier to manage during high-volume cooking. By carefully selecting cookware that balances weight and functionality, kitchens can enhance workflow efficiency while maintaining high standards in food preparation.
Scenario 3: The Maintenance and Care Conundrum
The Problem: Maintenance is a crucial consideration for B2B buyers when selecting between cast iron and stainless steel. Many buyers encounter confusion regarding the care requirements for each type of cookware. Cast iron, while durable, requires a specific seasoning process to maintain its non-stick properties, which can be time-consuming. Conversely, while stainless steel is often marketed as low-maintenance, it can still require regular cleaning to prevent discoloration and maintain appearance.
The Solution: To effectively manage maintenance, buyers should implement a structured care protocol for each type of cookware. For cast iron, staff should be trained on the proper seasoning techniques and cleaning methods to ensure longevity and optimal performance. This includes avoiding soap and harsh scrubbing, instead opting for gentle cleaning tools and methods. For stainless steel, using specialized cleaning agents designed to remove stains and restore shine can significantly reduce maintenance time. Furthermore, incorporating staff training sessions on care practices can empower kitchen teams, ensuring that all cookware, regardless of material, remains in top condition and contributes to the overall efficiency of the culinary operation.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is cast iron better than stainless steel
Analyzing Cast Iron and Stainless Steel for B2B Applications
When evaluating whether cast iron is better than stainless steel, it is essential to analyze the key properties, advantages, and disadvantages of each material from a B2B perspective. This analysis will help international buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
What Are the Key Properties of Cast Iron?
Cast iron is an alloy primarily composed of iron, carbon, and silicon. It is known for its excellent heat retention and distribution properties, making it ideal for slow-cooking methods. Cast iron cookware can withstand temperatures up to 1500°F, which is advantageous for high-heat cooking. However, it is susceptible to rusting if not properly seasoned or maintained, and its weight can be a disadvantage in terms of maneuverability.
Pros:
– Exceptional durability and longevity, often lasting generations.
– Naturally non-stick when seasoned properly.
– Excellent heat retention, ideal for slow cooking.
Cons:
– Heavy and cumbersome, making it less suitable for high-speed applications.
– Requires regular maintenance to prevent rust.
– Not ideal for cooking acidic foods in unfinished cast iron, which can damage the seasoning.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare?
Stainless steel is a versatile material made from iron, chromium, and nickel, which provides it with corrosion resistance and a non-reactive surface. It is lightweight and responds quickly to temperature changes, making it suitable for a wide range of cooking techniques. Stainless steel cookware typically features multiple layers to enhance heat conductivity, which can improve cooking performance.
Pros:
– Lightweight and easy to handle, suitable for fast-paced cooking environments.
– Non-reactive, allowing for the cooking of acidic foods without flavor alteration.
– Durable and resistant to rust and staining.
Cons:
– Poor heat retention compared to cast iron, which may affect cooking consistency.
– Higher manufacturing complexity due to layered construction, leading to increased costs.
– May warp under extreme heat if not properly constructed.
What Are the Implications for Specific Applications?
When considering the application of these materials, cast iron is particularly well-suited for slow-cooking, braising, and baking, where heat retention is paramount. Conversely, stainless steel excels in environments requiring quick temperature adjustments, such as sautéing and stir-frying.
For international B2B buyers, understanding local compliance and standards is crucial. For instance, buyers in Europe may need to adhere to DIN standards, while those in the U.S. might follow ASTM standards. Additionally, buyers should consider the availability of replacement parts and maintenance services in their region, which can influence the long-term costs associated with each material.
Summary Table of Material Comparison
| Material | Typical Use Case for is cast iron better than stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Slow cooking, baking, braising | Excellent heat retention and durability | Heavy, requires maintenance to prevent rust | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Sautéing, stir-frying, high-heat cooking | Lightweight and versatile | Poor heat retention, higher manufacturing costs | High |
This detailed analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the considerations for choosing between cast iron and stainless steel in B2B applications. By understanding the properties, pros and cons, and implications for specific applications, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is cast iron better than stainless steel
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Processes for Cast Iron and Stainless Steel Cookware?
The manufacturing processes for cast iron and stainless steel cookware differ significantly, reflecting their unique properties and intended uses. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed decisions about which material best suits their needs.
Material Preparation: How Are the Raw Materials Sourced and Prepared?
For cast iron production, the primary raw materials include iron, carbon, and alloying elements such as silicon and manganese. The iron is sourced from iron ore, which is then melted in a furnace. The carbon content is added to achieve the desired properties of the alloy, typically around 2-4% carbon for cast iron.
In contrast, stainless steel is made primarily from iron, chromium, and nickel. The chromium content (at least 10.5%) is essential for corrosion resistance, while nickel adds to the material’s toughness and workability. The steel is produced in electric arc furnaces or induction furnaces, where the metals are melted together and then cast into molds.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape the Cookware?
The forming process for cast iron involves pouring the molten metal into sand molds to create various cookware shapes, such as skillets and Dutch ovens. Once cooled, the cast iron pieces are removed from the molds, often requiring additional machining to ensure a smooth finish and precise dimensions.
For stainless steel, the forming process typically employs methods such as deep drawing, spinning, or stamping. These techniques allow for the creation of complex shapes while maintaining the integrity of the material. The stainless steel is often layered (3-ply, 5-ply) during this process, enhancing heat distribution and durability.
Assembly and Finishing: How Are the Products Completed and Prepared for Sale?
Once formed, cast iron cookware may undergo several finishing processes, including polishing and seasoning. Seasoning involves applying a layer of oil and heating the cookware to create a natural non-stick surface. Enameled cast iron requires an additional step where a vitreous enamel coating is applied and fused to the cast iron surface, providing a colorful and durable finish.
For stainless steel cookware, finishing can include polishing to a mirror finish, bead blasting for a matte surface, or applying a protective coating. The assembly of multi-ply stainless steel cookware also involves welding or bonding layers together to enhance performance.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Cast Iron and Stainless Steel Cookware?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing process to ensure the final products meet industry standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be aware of the key QA practices relevant to cast iron and stainless steel cookware.
What International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
International standards, such as ISO 9001, are essential for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer has established processes for consistently producing products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe indicate compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For cookware, adherence to FDA regulations in the United States and similar standards in other regions is also crucial for ensuring food safety.
What Are the Critical Checkpoints in the Quality Control Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process. Suppliers must provide certification for materials used in cookware production, ensuring they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, random samples may be taken to verify that production adheres to established guidelines. This step often involves visual inspections and measurements to detect any deviations from specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all quality standards. This may include functional testing, where cookware is tested for heat retention, non-stick properties, and durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. Audits can reveal insights into a supplier’s commitment to quality and areas for improvement.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide transparency regarding their QC processes. These reports may include results from testing, certifications, and any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors to evaluate products before shipment can provide an additional layer of assurance. These inspectors can verify that products meet specified quality and safety standards, reducing the risk of receiving subpar goods.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations regarding cookware safety and quality. Understanding these regulations is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties.
-
Cultural Expectations: Buyers may have specific cultural preferences related to cookware, such as preferences for non-toxic materials or traditional cooking methods. Suppliers should be prepared to meet these expectations while adhering to quality standards.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Challenges: Ensuring quality throughout the supply chain can be challenging, particularly with long lead times and multiple handling stages. B2B buyers should work closely with suppliers to establish robust logistics processes that prioritize quality at every step.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for both cast iron and stainless steel cookware, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right products but also fosters stronger relationships with suppliers committed to maintaining high-quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is cast iron better than stainless steel’
Introduction
When deciding between cast iron and stainless steel cookware for your business, understanding the distinct advantages and limitations of each material is essential. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers, enabling informed sourcing decisions based on specific needs, operational contexts, and product requirements.
Step 1: Assess Your Cooking Needs
Begin by identifying the primary cooking methods and recipes you will use. Consider whether your operations require high heat retention for slow cooking or quick heat responsiveness for sautéing. This assessment will help you determine which material aligns best with your culinary applications.
- High-Heat Cooking: Opt for cast iron if you need cookware that can withstand extreme temperatures.
- Versatility: Choose stainless steel for its adaptability across a variety of cooking techniques and ingredient types.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Outline the technical requirements for your cookware, including size, weight, and material composition. Each specification will influence the performance and usability of the cookware in your kitchen.
- Weight Considerations: If staff will frequently handle the cookware, consider lighter stainless steel options for ease of use.
- Material Properties: Ensure the chosen material can handle the specific dishes you plan to prepare without compromising quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Credentials
Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. This step is crucial to ensure that the cookware you source meets industry standards and quality expectations.
- Certifications: Look for suppliers with relevant certifications, such as ISO or food safety compliance, to guarantee product quality.
- Supplier Reputation: Research reviews and testimonials from other buyers, particularly those in your region or industry, to gauge reliability.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before committing to a bulk order, request samples of both cast iron and stainless steel cookware. Testing samples in your kitchen will provide firsthand experience with their performance and durability.
- Practical Application: Use the samples to prepare a range of dishes, assessing heat retention, non-stick properties, and ease of cleaning.
- Durability Assessment: Check for any signs of wear or damage after regular use to evaluate long-term viability.
Step 5: Analyze Cost vs. Value
Evaluate the cost of procurement against the expected lifespan and performance of each cookware type. While stainless steel may have a lower initial cost, cast iron’s longevity could provide better long-term value.
- Initial Investment: Factor in the upfront costs of each material, including potential discounts for bulk orders.
- Lifecycle Cost: Consider maintenance costs, such as seasoning for cast iron or potential replacements for stainless steel, to determine overall value.
Step 6: Consider Maintenance Requirements
Understand the maintenance demands associated with each cookware type. Cast iron requires regular seasoning, while stainless steel is generally low-maintenance.
- Ease of Care: Assess your team’s capacity for maintaining cast iron cookware versus the straightforward cleaning and care required for stainless steel.
- Operational Impact: Evaluate how maintenance requirements will affect kitchen efficiency and staff training.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision Based on Comprehensive Analysis
With all considerations taken into account, make a well-informed decision that aligns with your operational needs and budget. Document your findings and rationale for future reference and to guide subsequent purchases.
- Decision-Making Process: Ensure that all stakeholders are involved in the final decision to foster buy-in and support.
- Future Planning: Consider how this decision fits into your long-term kitchen strategy and equipment upgrades.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is cast iron better than stainless steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Cast Iron and Stainless Steel Cookware?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing cast iron versus stainless steel cookware, several critical components come into play. Understanding these can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Materials:
The primary material cost differs significantly between cast iron and stainless steel. Cast iron is typically less expensive per unit due to its simpler production process, involving the melting of iron and pouring it into molds. Stainless steel, on the other hand, involves multiple layers of metals, including chromium and nickel, which can increase costs. Buyers should consider the long-term value of these materials; while cast iron may have a lower initial price, its longevity can offset higher upfront costs over time.
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead:
Labor costs can vary depending on the region and production method. Cast iron production is often more labor-intensive due to the need for careful molding and finishing. Conversely, stainless steel cookware can be produced on more automated lines, potentially reducing labor costs. However, the precision required in stainless steel manufacturing may require skilled labor, impacting overall costs.
Tooling and Quality Control (QC):
The tooling costs for both materials can be significant. Cast iron requires specific molds, which can be expensive, especially for custom shapes or sizes. Stainless steel production benefits from standardized tooling but may incur additional QC costs due to the complexity of ensuring even heat distribution and finish quality.
Logistics and Margin:
Logistics costs can be influenced by the weight and shipping requirements of each material. Cast iron is heavier, which can lead to higher shipping costs, particularly for international buyers. Stainless steel is generally lighter, allowing for more cost-effective shipping solutions. Margins will vary based on supplier pricing strategies and market demand, with stainless steel often commanding higher margins due to its perceived value and versatility.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Cookware?
Several factors can influence pricing in the B2B market for both cast iron and stainless steel cookware.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ):
Higher volume purchases often lead to significant discounts. Suppliers may offer lower prices per unit for larger orders, making it essential for buyers to negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs.
Specifications and Customization:
Customization requests can lead to higher costs. Standard products are generally cheaper, while unique designs or specifications may necessitate additional tooling and labor, thus increasing the price.
Material Quality and Certifications:
The quality of materials, including certifications for food safety and manufacturing standards, can impact pricing. Buyers should be aware that sourcing from suppliers who offer certified materials may incur higher costs but will ensure compliance with international standards.
Supplier Factors and Incoterms:
The choice of supplier can significantly affect costs. Established suppliers with a reputation for quality may charge premium prices. Additionally, understanding Incoterms is crucial, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can influence overall costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Cookware?
B2B buyers should consider several strategies to optimize their sourcing decisions.
Negotiation Strategies:
Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing. Buyers should be prepared with market research and competitor pricing to leverage in discussions. Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can also result in more favorable terms.
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Buyers should evaluate the TCO, which includes not only the purchase price but also maintenance, durability, and lifecycle costs. Cast iron, for example, may require more maintenance but can last generations, making it cost-effective over time.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers:
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to account for currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Engaging with local suppliers or those familiar with regional markets can provide insights that lead to better deals.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for cast iron and stainless steel cookware can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Therefore, it is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is cast iron better than stainless steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Cast Iron and Stainless Steel Cookware
When considering cookware options, the debate between cast iron and stainless steel often leads to inquiries about other viable alternatives. Each material has its unique benefits and drawbacks, but there are additional solutions worth evaluating. This section will compare cast iron and stainless steel against two alternatives: non-stick cookware and carbon steel.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Is Cast Iron Better Than Stainless Steel | Non-Stick Cookware | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent heat retention, versatile use | Quick heating, easy release | Good heat conduction, durable |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower | Moderate |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires seasoning for optimal use | Ready to use, minimal prep | Requires seasoning, similar to cast iron |
| Maintenance | High maintenance for traditional cast iron | Low maintenance | Moderate, requires proper care |
| Best Use Case | Searing, frying, baking | Everyday cooking, eggs, pancakes | Stir-frying, sautéing, high-heat cooking |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Non-Stick Cookware?
Non-stick cookware has gained popularity for its ease of use, especially in commercial kitchens. The primary advantage is its ability to provide a smooth cooking surface that requires minimal oil, making it ideal for health-conscious cooking. Additionally, non-stick pans heat up quickly and allow for easy food release, which can significantly reduce cooking and cleaning time. However, the downside includes a shorter lifespan compared to cast iron and stainless steel, especially when exposed to high heat or metal utensils, which can scratch the surface.
What Makes Carbon Steel a Viable Alternative?
Carbon steel cookware shares many characteristics with cast iron, including excellent heat retention and the ability to develop a natural non-stick surface with proper seasoning. It is lighter than cast iron, making it easier to handle, which is particularly beneficial in fast-paced kitchen environments. Carbon steel is also highly responsive to heat changes, allowing for precise cooking control. However, similar to cast iron, it requires seasoning and maintenance to prevent rust, which may deter some users looking for a low-maintenance option.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Cookware Solution?
When selecting cookware for commercial applications, B2B buyers must consider the specific needs of their kitchen environment. Cast iron is ideal for high-heat cooking and offers unparalleled durability, while stainless steel provides versatility and quick heat responsiveness. Non-stick cookware is perfect for everyday tasks requiring minimal cleanup, and carbon steel offers a middle ground with excellent heat retention and lighter weight. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, so it’s crucial for buyers to evaluate their cooking style, maintenance preferences, and budget to make an informed decision that aligns with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is cast iron better than stainless steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cast Iron and Stainless Steel?
When evaluating whether cast iron or stainless steel is better suited for your business needs, understanding their critical technical properties is essential. Here are some vital specifications:
1. Material Composition
- Cast Iron: Primarily composed of iron with a high carbon content (2-4%). This composition contributes to its excellent heat retention and durability, making it suitable for high-heat cooking.
- Stainless Steel: An alloy that typically includes iron, chromium (at least 10.5%), and often nickel. The chromium provides corrosion resistance, while the nickel enhances strength and ductility. This composition makes stainless steel versatile and easy to maintain.
2. Heat Conductivity and Retention
- Cast Iron: Known for its superior heat retention, cast iron cookware can hold heat for extended periods, which is advantageous for slow cooking and baking. However, it has slower heat-up times compared to stainless steel.
- Stainless Steel: While it can be less efficient in retaining heat, stainless steel cookware often incorporates conductive metals (like copper) to improve heat distribution and responsiveness. This feature allows for quick adjustments in cooking temperatures, crucial in high-paced kitchen environments.
3. Weight and Maneuverability
- Cast Iron: Generally heavier than stainless steel, which can be cumbersome for some users, especially in commercial settings where equipment is frequently moved.
- Stainless Steel: Typically lighter, facilitating ease of handling during cooking and cleaning. This property is particularly beneficial in restaurants and catering operations.
4. Durability and Lifespan
- Cast Iron: With proper care, cast iron cookware can last for generations. Its durability is often passed down through families, making it a reliable long-term investment.
- Stainless Steel: Also durable but may not match the lifespan of well-maintained cast iron. However, it is resistant to rust, staining, and corrosion, which makes it a practical choice for everyday use.
5. Maintenance Requirements
- Cast Iron: Requires seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface and prevent rust. This process can be labor-intensive and may not be ideal for all users.
- Stainless Steel: Generally low maintenance, requiring only basic cleaning. Its non-reactive surface allows for a wide range of cooking applications, including acidic foods.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Cast Iron and Stainless Steel?
Understanding industry jargon can help facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
- Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the cookware industry, an OEM might produce cast iron or stainless steel cookware for various brands.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
- The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For cookware, MOQs can significantly affect procurement strategies and inventory management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
- A document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products. An RFQ is critical when comparing the costs of cast iron versus stainless steel cookware.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
- A set of predefined international rules published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for negotiating shipping and delivery terms for cookware imports.
5. Lead Time
- The time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the cookware market, lead times can vary significantly between cast iron and stainless steel products, affecting inventory turnover and production schedules.
6. Certification Standards
- Standards such as ISO or ASTM that ensure the quality and safety of cookware products. Familiarity with these certifications can help buyers assess the reliability of suppliers and the suitability of materials for their intended use.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting between cast iron and stainless steel cookware, aligning their choices with operational needs and customer preferences.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is cast iron better than stainless steel Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing the Choice Between Cast Iron and Stainless Steel?
In the cookware market, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the debate between cast iron and stainless steel is increasingly significant. One of the primary drivers is the growing consumer preference for durable, long-lasting kitchenware that can withstand high temperatures and diverse cooking methods. Cast iron is revered for its heat retention and durability, making it a staple in both home and professional kitchens. Conversely, the versatility and lightweight nature of stainless steel appeal to a broader range of culinary applications, especially in fast-paced environments such as restaurants.
Additionally, technological advancements are shaping sourcing trends. Manufacturers are increasingly utilizing innovative production techniques to enhance the performance of both materials. For instance, the introduction of hybrid cast iron cookware combines the benefits of traditional cast iron with the lighter weight and ease of use found in stainless steel. This trend is particularly appealing to international B2B buyers looking for versatile products that cater to diverse cooking styles.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional cooking traditions and the growing interest in sustainability. As consumers become more aware of the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions, they are inclined to choose products that align with eco-friendly practices. This shift is prompting suppliers to highlight sustainable sourcing and production processes in their marketing strategies.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the Cookware Industry?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the cookware industry, particularly for B2B buyers seeking to align with ethical sourcing practices. The environmental impact of cookware production can be significant, with factors such as energy consumption and raw material extraction playing a crucial role. Cast iron, for instance, has a longer lifespan than many alternatives, which can mitigate its environmental footprint over time. Its durability allows for generations of use, making it a sustainable choice when considering the lifecycle of cookware.
On the other hand, stainless steel’s recyclability is a strong advantage in terms of sustainability. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to ethical supply chains, including the responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade standards are becoming essential for manufacturers looking to appeal to conscious buyers.
Moreover, the trend towards ‘green’ certifications is gaining traction, with many companies seeking to achieve sustainability credentials that resonate with eco-aware consumers. This demand for transparency in sourcing practices is reshaping the competitive landscape, encouraging suppliers to invest in environmentally friendly materials and processes.
What Is the Historical Context of Cast Iron and Stainless Steel Cookware?
The evolution of cookware materials is rooted in centuries of culinary tradition. Cast iron cookware has been in use for thousands of years, with its origins tracing back to ancient China. Its ability to retain heat and provide even cooking has made it a favorite among chefs and home cooks alike. In contrast, stainless steel emerged in the early 20th century, developed as a response to the need for durable, non-reactive cookware that could withstand the rigors of modern cooking.
The historical significance of these materials informs current market dynamics, as many buyers value the authenticity and heritage associated with cast iron while simultaneously appreciating the modernity and convenience of stainless steel. Understanding this evolution allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on both the performance characteristics of these materials and their historical context. As the market continues to evolve, the interplay between tradition and innovation will remain a defining factor in the choice between cast iron and stainless steel cookware.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is cast iron better than stainless steel
-
How do I determine whether to choose cast iron or stainless steel for my business needs?
When deciding between cast iron and stainless steel, consider the specific cooking applications and durability required for your business. Cast iron is ideal for high-heat cooking and retains heat exceptionally well, making it suitable for slow-cooked dishes. However, it requires more maintenance and is heavier. Stainless steel, on the other hand, is versatile, lightweight, and resistant to rust, making it easier to handle and clean. Assess your culinary needs, kitchen setup, and staff capabilities to make an informed decision. -
What are the advantages of using cast iron cookware in a professional kitchen?
Cast iron cookware is favored for its exceptional heat retention and even cooking capabilities, which are crucial for dishes requiring consistent temperature control. It is also highly durable and can last for generations with proper care, reducing long-term replacement costs. Additionally, when seasoned correctly, cast iron provides a natural non-stick surface, enhancing cooking efficiency. This can be particularly advantageous in environments that prioritize both quality and cost-effectiveness. -
What benefits does stainless steel cookware offer for commercial use?
Stainless steel cookware is known for its durability, non-reactive surface, and low maintenance requirements, making it a staple in many commercial kitchens. It heats up quickly and responds well to temperature changes, allowing for precise cooking control. Its lightweight nature facilitates easy handling, which is essential in fast-paced kitchen environments. Furthermore, stainless steel does not rust or stain easily, ensuring a longer lifespan and maintaining a professional appearance. -
How can I vet suppliers for cast iron and stainless steel cookware?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry through reviews and testimonials. Request samples of their products to assess quality firsthand, and inquire about their manufacturing processes to ensure they meet international standards. Verify their certifications, such as ISO or food safety compliance, and evaluate their ability to provide customization options that suit your specific needs. Finally, consider their communication responsiveness and logistics capabilities for timely deliveries. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cast iron and stainless steel cookware?
MOQs can vary widely depending on the supplier and product type. For cast iron cookware, MOQs may range from 100 to 500 units due to the casting process involved. Stainless steel cookware, being lighter and more versatile, may have lower MOQs, often starting at around 50 to 200 units. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that suit your business volume. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing cookware internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly among suppliers. Common arrangements include a deposit (often 30% to 50%) upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or before shipping. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit for larger orders, providing added security. Always clarify payment terms and conditions before finalizing contracts, and consider using escrow services for added protection in international transactions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my cookware orders?
To ensure quality assurance, establish clear specifications and standards for the cookware you require. Request detailed product documentation, including material certifications and testing results. Consider conducting factory audits or hiring third-party inspection services to verify manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Additionally, include QA clauses in your contracts that outline penalties for non-compliance, ensuring accountability from suppliers. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing cookware?
When importing cookware, factor in shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Select reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling cookware to ensure safe transport. Understand the import duties and taxes applicable in your country, as they can impact overall costs. Also, consider warehousing solutions if you anticipate large shipments, ensuring you have adequate storage and distribution capabilities upon arrival.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Is Cast Iron Better Than Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Cookware Comparison
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Cast Iron: Heavier, requires more maintenance, can develop a non-stick surface over time, good for searing, retains heat longer. Carbon Steel: Similar maintenance to cast iron, used frequently by some users. Stainless Steel: Easier maintenance, magnetic for induction heating, often preferred for first cookware sets.
2. Made In – Cast Iron Cookware
Domain: madeincookware.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Cast Iron:
– Material: Alloy of carbon and iron
– Heat Resistance: Withstands up to 1500F
– Non-Stick Surface: Naturally non-stick when seasoned or enameled
– Durability: Can last lifetimes with proper care, less likely to warp from heat
– Use Cases: Excellent for braising, searing, baking; not ideal for acidic foods in unfinished cast iron
– Cleaning: Enameled cast iron is easy to clean; un…
3. GreenPan – Key Cookware Collections
Domain: greenpan.us
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel vs. Cast Iron: Starring Bobby Flay by GreenPan. Bobby Flay by GreenPan offers cookware, cutlery, and more for professional results at home. Key product collections include the Valencia Pro Collection, The Stanley Tucci™ Collection, and the Spectra Collection. Notable products include the Valencia Pro Ceramic Nonstick 19-Piece Cookware Set, Spectra Thermobond Hybrid Ceramic Nonstick…
4. TVWBB – Cast Iron and Stainless Steel Grates
Domain: tvwbb.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Cast Iron Grates: Porcelain Enameled Cast Iron (PECI) grates hold and retain heat very well, sear effectively, and are warrantied for the same duration as stainless steel. Stainless Steel Grates: Hold heat well, sear well, and have a premium look and finish. Both types of grates can perform well over many years, and the choice between them is based on personal preference.
5. 360 Cookware – Stainless Steel & Cast Iron Essentials
Domain: 360cookware.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Cookware Types: Stainless Steel, Cast Iron
Key Features:
– Stainless Steel: Non-reactive, versatile, ready to use out of the box, can create a non-stick surface with proper heating and oiling, suitable for acidic foods, good for searing and frying, can be oven-safe.
– Cast Iron: Requires seasoning for non-stick surface, high maintenance, reacts with acidic foods, retains flavors from previous mea…
6. Well-Trained Mind – Cast Iron Cookware
Domain: forums.welltrainedmind.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, Well-Trained Mind – Cast Iron Cookware, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Thinkitchen – Stainless Steel and Cast Iron Cookware
Domain: thinkitchen.in
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Cookware:
– Material: Blend of iron, carbon, and chromium
– Pros: Durable, non-reactive, low maintenance, aesthetic appeal
– Cons: Poor heat retention, uneven heat distribution, food sticking
– Market Value: Expected to reach $3.8 billion by 2026
Cast Iron Cookware:
– Material: Cast from molten iron
– Pros: Excellent heat retention, naturally non-stick when seasoned, unmatc…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is cast iron better than stainless steel
In the ongoing debate of cast iron versus stainless steel, it is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate the unique advantages of each material in the context of their specific operational needs. Cast iron excels in heat retention and durability, making it ideal for slow cooking and high-heat applications, while stainless steel offers versatility and lightweight convenience for fast-paced environments.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in aligning these materials with the requirements of your culinary operations. By carefully assessing factors such as weight, maintenance needs, and heat responsiveness, businesses can optimize their kitchenware investment for maximum efficiency and longevity.
As international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe look to enhance their culinary offerings, understanding the distinct benefits of cast iron and stainless steel can lead to more informed purchasing decisions. Embrace this opportunity to refine your kitchen arsenal and elevate your culinary capabilities. Explore your options today and select the cookware that best complements your culinary vision and operational demands.