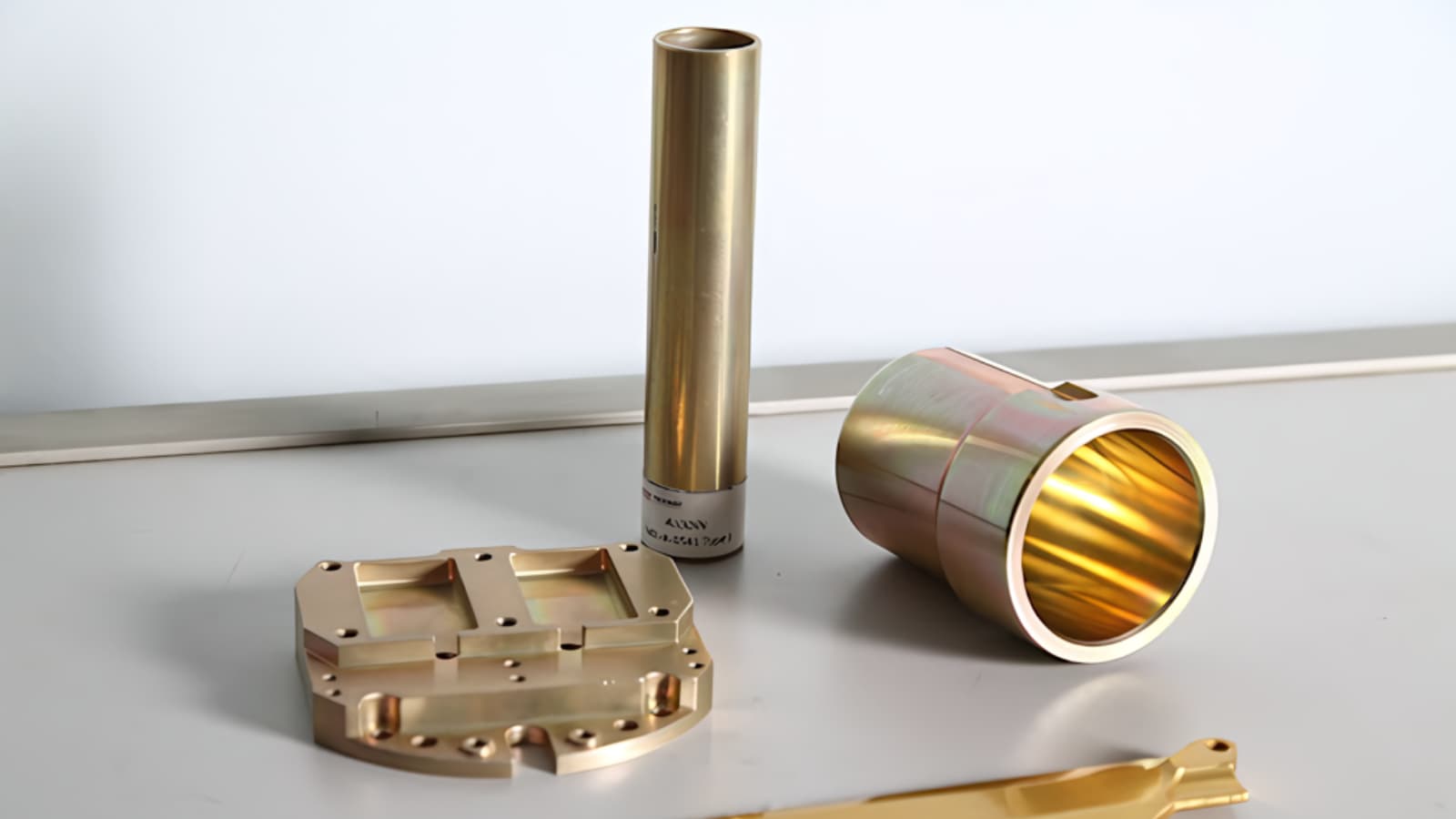
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is alodine conductive
In the competitive landscape of international manufacturing, understanding whether Alodine is conductive presents a critical challenge for B2B buyers. With a growing demand for materials that not only resist corrosion but also maintain electrical integrity, companies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Brazil) are seeking reliable solutions. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of Alodine coatings, exploring their conductivity properties, applications, and how they compare to other surface treatments.
Throughout this guide, we will cover essential aspects such as the different types of Alodine coatings, their specific applications in various industries, and key factors to consider when vetting suppliers. Additionally, we will address the cost implications of sourcing Alodine-treated components, helping you make informed decisions that balance performance with budgetary constraints.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights into the conductive properties of Alodine, this guide aims to empower organizations to enhance their procurement strategies and ensure that they invest in materials that meet their operational needs. Whether you are involved in aerospace, automotive, or electronics, understanding the role of Alodine coatings in your applications can lead to improved product performance and longevity.
Understanding is alodine conductive Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1A Alodine | Thicker coating, high corrosion resistance | Aerospace, automotive | Pros: Excellent corrosion protection; Cons: Lower electrical conductivity. |
| Class 3 Alodine | Thinner coating, allows for electrical conductivity | Electrical components, heat sinks | Pros: Better conductivity; Cons: Reduced corrosion resistance compared to Class 1A. |
| Chem Film | Transparent finish, versatile for various metals | Marine equipment, electronic housings | Pros: Aesthetic appeal; Cons: May require additional coatings for optimal performance. |
| Alodine 1200 | High thermal conductivity, designed for extreme conditions | Military, aerospace, industrial machinery | Pros: Superior thermal management; Cons: May be more expensive than standard options. |
| Alodine 600 | Designed for aluminum alloys, enhanced adhesion properties | Medical devices, precision tooling | Pros: Improved paint adhesion; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
What are the Characteristics of Class 1A Alodine Coatings?
Class 1A Alodine coatings are characterized by their thicker application, which provides significant corrosion resistance, making them ideal for industries where durability is paramount, such as aerospace and automotive. These coatings create a robust barrier against environmental factors, but this thickness comes at the expense of electrical conductivity. Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, as this type is suited for environments where corrosion is a major concern, but not where electrical conductivity is critical.
How Does Class 3 Alodine Differ from Other Types?
Class 3 Alodine coatings are thinner, allowing aluminum substrates to maintain their inherent electrical conductivity. This feature makes them suitable for applications involving electrical components and heat sinks, where grounding is essential. While they offer less corrosion resistance than Class 1A coatings, their conductivity can be a decisive factor for businesses focused on electrical performance. Buyers should weigh the need for conductivity against the potential for corrosion in their specific applications.
What Makes Chem Film a Versatile Choice?
Chem Film, or chromate conversion coating, is distinguished by its transparent finish and compatibility with various metals, including aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. This versatility allows it to be used in diverse applications, from marine equipment to electronic housings. While it enhances the aesthetic appeal of parts, buyers should note that it may require additional protective coatings to ensure optimal performance in harsh environments. The choice of Chem Film is ideal for businesses that prioritize both appearance and performance.
Why Consider Alodine 1200 for High-Performance Applications?
Alodine 1200 coatings are specifically designed for applications requiring high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for military, aerospace, and industrial machinery. This type excels in extreme conditions, providing effective thermal management, which is crucial in high-performance environments. However, the cost may be higher than standard options, so buyers should assess whether the added benefits justify the investment for their specific applications.
What Are the Advantages of Alodine 600 for Medical Devices?
Alodine 600 coatings are tailored for aluminum alloys and offer enhanced adhesion properties, making them particularly effective in medical devices and precision tooling. This type not only improves paint adhesion but also contributes to the overall durability of the components. While its application may be limited to specific sectors, the advantages in performance and longevity make it a valuable option for businesses in the medical and precision engineering fields. Buyers should consider the compatibility of Alodine 600 with their materials and processes to maximize its benefits.
Key Industrial Applications of is alodine conductive
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is alodine conductive | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Electrical grounding of aircraft components | Ensures safety and compliance with aviation standards | Certification to MIL-DTL-5541 Class 3 standards |
| Automotive | Coating for electrical connectors and wiring harnesses | Enhances durability and reduces corrosion risks | Compatibility with various metals and environmental conditions |
| Telecommunications | Coating for circuit boards and heat sinks | Improves thermal management and electrical performance | Need for reliable suppliers with international shipping capabilities |
| Marine | Protection of electrical components in harsh marine environments | Extends equipment life and reduces maintenance costs | Resistance to saltwater corrosion and environmental certifications |
| Medical Devices | Coating for components requiring electrical connectivity | Meets stringent hygiene and safety standards | Compliance with medical regulations and biocompatibility testing |
How is Alodine Conductive Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, Alodine conductive coatings are critical for ensuring electrical grounding of aircraft components. This application is vital for safety, as it helps prevent electrical faults that could compromise flight operations. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that their Alodine coatings meet the MIL-DTL-5541 Class 3 standards, which guarantee low electrical resistance while providing adequate corrosion protection. Sourcing from certified suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with these standards is essential for maintaining safety and performance in aerospace applications.
What Role Does Alodine Conductive Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, Alodine coatings are used on electrical connectors and wiring harnesses to enhance durability and protect against corrosion. Given the challenging environments that vehicles operate in, these coatings provide a reliable solution to maintain electrical conductivity and prevent failures. Buyers must consider the compatibility of Alodine coatings with various metals and their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and humidity. Sourcing from manufacturers with a proven track record in automotive applications can ensure product reliability and longevity.
How Does Alodine Conductive Benefit Telecommunications Equipment?
The telecommunications sector utilizes Alodine conductive coatings for circuit boards and heat sinks, which are critical for managing thermal performance and ensuring effective electrical connectivity. This application enhances the reliability of communication equipment, especially in regions with varying climatic conditions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that can provide coatings with consistent quality and the ability to withstand environmental stressors. Additionally, sourcing from companies that offer rapid international shipping is advantageous for maintaining production timelines.
Why is Alodine Conductive Important for Marine Equipment?
In marine applications, Alodine coatings protect electrical components from the corrosive effects of saltwater and harsh environmental conditions. This application is vital for extending the lifespan of equipment and reducing maintenance costs, which can be particularly high in marine operations. Buyers should seek coatings that meet specific resistance requirements to saltwater corrosion and consider suppliers with certifications for marine-grade applications. Ensuring that the coatings are durable and effective under marine conditions is crucial for operational efficiency.
What are the Key Considerations for Alodine Conductive in Medical Devices?
In the medical device industry, Alodine conductive coatings are applied to components that require reliable electrical connectivity while meeting stringent hygiene and safety standards. This application is essential for devices that operate in sterile environments, where contamination can pose serious risks. Buyers must focus on sourcing from manufacturers who comply with medical regulations and can provide biocompatibility testing results. Ensuring the coatings are suitable for repeated sterilization processes is another critical consideration for maintaining the integrity of medical devices.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is alodine conductive’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Electrical Conductivity in Critical Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics often face challenges when ensuring that the aluminum components meet stringent electrical conductivity standards. For instance, a manufacturer may need to source aluminum parts that are not only corrosion-resistant but also retain their electrical conductivity to ensure proper grounding. If the Alodine coating is not applied correctly, the conductivity might not meet the required specifications, which can lead to failures in critical applications and potential safety hazards.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is essential to specify the application of Alodine according to the MIL-DTL-5541 Class 3 standard. This class allows for a thinner coating that facilitates better electrical conductivity while still offering adequate corrosion resistance. When sourcing Alodine-coated components, request documentation that confirms compliance with this standard. Additionally, consider working closely with suppliers who can provide detailed information on the coating thickness and surface preparation methods, as these directly impact conductivity. Conducting tests to measure electrical resistance after coating can further validate that the components meet operational requirements before they are deployed in critical systems.
Scenario 2: Addressing Corrosion Resistance Versus Conductivity Trade-offs
The Problem: A common dilemma for B2B buyers is balancing the need for corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity in aluminum components. For example, a company might find that while Class 1A coatings offer superior corrosion protection, they significantly reduce the electrical conductivity necessary for applications like heat sinks in electronic devices. This trade-off can lead to difficult decisions that affect the overall performance and longevity of products.
The Solution: To navigate this trade-off effectively, it is crucial to adopt a dual-coating strategy. Begin with a Class 3 Alodine coating that maintains electrical conductivity, especially for parts that require grounding. For components exposed to harsh environments, consider applying an additional protective layer, such as a polymer or epoxy, that can withstand corrosion without compromising conductivity. It’s advisable to conduct a thorough analysis of the operational environment to determine the most suitable combination of coatings. Engaging with a coatings specialist can help tailor a solution that meets specific performance requirements while maintaining durability.
Scenario 3: Understanding Surface Preparation for Optimal Conductivity
The Problem: Many buyers underestimate the importance of surface preparation before applying Alodine coatings. Inadequate preparation can lead to inconsistent results, affecting both the aesthetic quality and the electrical properties of the coated parts. A manufacturer may receive components that look good on the surface but fail to deliver the necessary conductivity due to improper surface roughness or contaminants that interfere with the coating process.
The Solution: To ensure optimal conductivity, buyers should prioritize proper surface preparation techniques such as cleaning, degreasing, and surface profiling. It is essential to specify that suppliers utilize methods that enhance surface roughness, as a slightly roughened surface can create micro-breaks in the Alodine coating, allowing for better conductivity. Additionally, implementing a quality control process that includes testing for surface cleanliness and roughness before coating can help mitigate potential issues. Buyers should request detailed reports on the surface preparation procedures and consider conducting independent tests to verify that the components meet conductivity requirements prior to application. This proactive approach not only improves performance but also enhances the reliability of the final product.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is alodine conductive
What Are the Key Properties of Alodine Coating for Conductivity?
Alodine, a type of chromate conversion coating, is primarily applied to aluminum alloys to enhance their corrosion resistance while maintaining electrical conductivity. The key properties of Alodine coatings include their thin application thickness, typically ranging from 0.00001 to 0.00004 inches. This minimal thickness allows the underlying aluminum to retain its electrical conductivity, particularly when applied according to Class 3 of the MIL-DTL-5541 standard. The surface roughness of the aluminum substrate also plays a crucial role in conductivity, as a rougher surface can enhance the electrical connection.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Alodine Coating?
The advantages of Alodine coatings are significant for B2B applications. They provide excellent corrosion resistance, which is vital for industries facing harsh environmental conditions. The coating is also lightweight, ensuring that the structural integrity of the aluminum components is not compromised. Furthermore, Alodine coatings are cost-effective, requiring minimal maintenance and reapplication over several years.
However, there are limitations to consider. Class 3 coatings, while conductive, offer less corrosion resistance compared to thicker Class 1A coatings. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can increase if the surface preparation is not adequately managed, as a clean and properly finished surface is essential for optimal coating performance.
How Does Alodine Coating Impact Specific Applications?
Alodine coatings are particularly beneficial in applications requiring electrical grounding or thermal conductivity, such as in aerospace, automotive, and electronic components. The coatings can withstand various media, including moisture and chemicals, making them suitable for marine environments and other corrosive settings. For international buyers, it is important to ensure that the Alodine coatings meet local compliance standards, such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS, which can vary significantly across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Alodine Coating?
For international B2B buyers, understanding local regulations and standards is crucial. In regions like Saudi Arabia and Brazil, compliance with local environmental regulations regarding chromate usage may be necessary. Additionally, buyers should consider the availability of suppliers who can provide consistent quality and adhere to international standards. The choice of Alodine coating should also align with the specific needs of the application, factoring in the environmental conditions and the expected lifespan of the coated components.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alodine Conductivity
| Material | Typical Use Case for is alodine conductive | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Excellent corrosion resistance | Less corrosion resistance than thicker coatings | Medium |
| Zinc Alloys | Marine applications, fasteners | Good corrosion resistance | Limited electrical conductivity compared to aluminum | Low |
| Magnesium Alloys | Lightweight structures, automotive parts | Lightweight and strong | Susceptible to corrosion in harsh environments | Medium |
| Cadmium Plated | Electrical connectors, aerospace | High electrical conductivity | Environmental concerns due to toxicity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of Alodine conductive coatings, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is alodine conductive
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Alodine Coatings?
The manufacturing process for Alodine coatings involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the required specifications for conductivity and corrosion resistance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing from suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Is the Base Metal Treated Before Coating?
Material preparation is a vital first step in the Alodine coating process. It typically involves cleaning and surface conditioning the aluminum alloy substrate. Manufacturers may employ techniques such as ultrasonic cleaning or alkaline cleaning to remove oils, dirt, and oxides. This ensures that the surface is free of contaminants, which could impede the adhesion of the Alodine coating.
Surface roughness also plays a crucial role in the coating’s effectiveness. A roughened surface can enhance electrical conductivity by allowing breaks in the coating, which facilitates better contact with the aluminum substrate. Thus, achieving the correct surface finish is essential for maximizing the performance of the Alodine coating.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming and Applying Alodine Coatings?
The forming stage often involves shaping the aluminum parts through various manufacturing processes such as machining, stamping, or extrusion. Once the components are shaped, the application of the Alodine coating can take place. This is typically done through immersion, spray, or brush-on methods.
The specific technique chosen depends on the part’s size, complexity, and the desired thickness of the coating. For electrically conductive applications, it is essential to apply a Class 3 Alodine coating as specified under the MIL-DTL-5541 standard. This ensures that the coating is thin enough to allow the underlying aluminum to retain its electrical conductivity while still providing adequate corrosion resistance.
What Are the Finishing Steps for Alodine Coated Products?
After the Alodine coating is applied, the parts undergo a finishing stage that may include rinsing, drying, and curing. Curing is particularly important as it helps the coating achieve its desired hardness and durability. The thickness of the Alodine coating typically ranges from 0.00001 to 0.00004 inches, which is minimal but effective for protecting the substrate without adding significant weight.
The final inspection of the coated parts is essential to ensure they meet quality standards before they are dispatched to customers. This includes visual inspections and, where necessary, further testing to confirm that the coatings meet specified electrical resistance values.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Alodine Coating Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for Alodine coatings, particularly given the international standards that apply to this type of product. Manufacturers must adhere to various quality control (QC) protocols to ensure that their coatings meet the necessary specifications for conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Which International Standards Govern Alodine Coating Quality?
The ISO 9001 standard is commonly adopted in the manufacturing industry to ensure consistent quality management processes. However, for Alodine coatings specifically, adherence to industry-specific standards such as MIL-DTL-5541 is essential. This standard outlines the requirements for chemical conversion coatings on aluminum alloys, including conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Additionally, other certifications like CE marking or API standards may apply depending on the industry and application of the coated parts. Buyers should inquire about these certifications when evaluating potential suppliers.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Alodine Coating Process?
Quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
-
IQC: This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. It ensures that only materials meeting specified quality criteria are used in production.
-
IPQC: During the production process, various parameters such as coating thickness, surface finish, and conductivity are monitored. This helps to identify any issues early on, allowing for corrective actions to be taken before the final product is completed.
-
FQC: Final inspections are conducted to verify that the finished products conform to the required specifications. This may include electrical resistance testing to ensure the coatings meet the Class 3 standard.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Verify Alodine Coating Quality?
To ensure that Alodine coatings meet performance specifications, several testing methods are employed. Common tests include:
-
Electrical Resistance Testing: This assesses the conductivity of the coated parts to ensure they meet the required resistance levels (0.005 – 0.010 ohms per square inch).
-
Corrosion Testing: Salt spray tests and other accelerated corrosion tests are performed to evaluate the longevity and protective capabilities of the Alodine coating.
-
Adhesion Testing: This verifies that the coating adheres properly to the substrate, ensuring durability and effectiveness.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take a proactive approach to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. This can include:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to review manufacturing practices, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their QC processes, including test results and certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certification for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements that affect product compliance.
Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards that may apply to Alodine-coated products. Additionally, they should ensure that their suppliers are capable of meeting both international and regional standards to avoid potential compliance issues.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with Alodine coatings is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality, conductive coatings that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is alodine conductive’
Introduction
In the realm of manufacturing and engineering, ensuring that your aluminum components are protected against corrosion while maintaining electrical conductivity is essential. Alodine coatings, also known as chromate conversion coatings, serve this dual purpose effectively. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers to navigate the procurement process of Alodine coatings, ensuring they meet specific conductivity and performance standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Identify the specific requirements for electrical conductivity, such as compliance with Class 3 of the MIL-DTL-5541 standard, which mandates a resistance of no more than 0.005 – 0.010 ohms per square inch. Understanding the thickness and surface roughness needed for your application will also help narrow down your options.
Step 2: Research the Different Alodine Products
Not all Alodine coatings are created equal; they come in various formulations tailored for different applications. Investigate the properties of Class 1A versus Class 3 coatings, as each offers different balances of corrosion resistance and conductivity. This knowledge will enable you to select a product that best fits your operational needs and budget.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to conduct thorough evaluations. Request detailed company profiles, product data sheets, and case studies to understand their capabilities and expertise. Engage with references from similar industries or geographic regions to gauge their reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that align with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific military standards for coatings indicate a commitment to quality and reliability. This step is vital to mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and ensure that your products meet the required specifications.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the Alodine coating for testing. Conduct conductivity tests and evaluate the coating’s performance in your specific environment. This practical assessment will provide insight into how well the product meets your expectations for electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as corrosion resistance.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and conditions. Discuss pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty options to ensure that you receive the best value. Clear agreements on these aspects will help avoid misunderstandings and foster a strong working relationship.
Step 7: Plan for Long-Term Maintenance
Consider the long-term implications of your Alodine coating choice. Discuss with your supplier about maintenance schedules and reapplication intervals to maximize the lifespan and effectiveness of the coating. Understanding these factors can lead to better asset management and reduced long-term costs associated with corrosion damage.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement of Alodine coatings, ensuring they select products that meet both their technical needs and operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is alodine conductive Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Alodine Conductive Coatings?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing Alodine conductive coatings, several key components come into play. The material costs primarily depend on the type of chromate conversion chemicals used and the base aluminum alloys. Quality materials, especially those that meet the MIL-DTL-5541 standards, can be more expensive but are essential for ensuring the desired conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Labor costs encompass the workforce required for coating application, which can vary significantly based on location and labor rates. The manufacturing overhead includes operational costs such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. These overheads can fluctuate based on the production scale and location of the manufacturing facility.
Tooling costs refer to the equipment and machinery necessary for the coating process. This includes plating tanks and automated systems which can enhance efficiency. Additionally, quality control (QC) is crucial in maintaining standards, and this can add to the overall cost due to the need for rigorous testing and certification processes.
Finally, logistics costs must be considered, especially for international shipments, which can include customs duties and insurance. Suppliers typically add a margin to cover these costs and ensure profitability.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Alodine Coating Costs?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of Alodine coatings. Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) are critical; larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Customization specifications, such as specific thicknesses or additional properties (like thermal conductivity), can also impact pricing.
The choice of materials affects cost, with high-quality or specialty chemicals driving prices higher. Additionally, the quality and certifications required for specific industries (e.g., aerospace or automotive) can necessitate more expensive processes, influencing the final price.
Supplier factors, including their reputation, experience, and geographical location, can also play a role. Suppliers in regions with higher operational costs may charge more. Finally, the use of specific Incoterms can affect the total landed cost, as they determine who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs duties.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies are vital to achieving cost efficiency. Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is essential; this includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, reapplication, and potential downtime costs associated with the coating.
Buyers should leverage their purchasing power, especially when ordering in bulk, to negotiate better terms. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to favorable pricing and priority service. It’s also beneficial to solicit multiple quotes to compare offers and identify competitive pricing.
Additionally, discussing the possibility of cost-sharing initiatives for quality certifications or bulk purchasing agreements can be advantageous. Buyers should also be aware of the pricing nuances related to international shipping, as costs can vary significantly based on the Incoterms chosen and the specific logistics involved.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding Pricing Nuances in Different Regions?
When sourcing Alodine conductive coatings, buyers should consider regional pricing nuances. For example, import tariffs and local regulations can affect the final cost in countries like Brazil or Saudi Arabia. Understanding these regional dynamics is crucial for accurate budgeting.
Furthermore, currency fluctuations can impact costs, especially for long-term contracts. Buyers should consider locking in prices or negotiating terms that mitigate the risks associated with currency volatility.
Lastly, buyers should stay informed about market trends and technological advancements, as these can lead to shifts in pricing structures. Awareness of new developments in coating technologies or changes in raw material availability can provide leverage during negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for Alodine conductive coatings can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The figures provided in this analysis are indicative and should be used as a guideline. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate and current pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is alodine conductive With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives for Alodine Coating
When considering protective coatings for aluminum alloys, electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and application methods are critical factors that influence decision-making. While Alodine, a chromate conversion coating, is well-regarded for its properties, exploring alternative solutions can help buyers identify the best fit for their specific applications. This analysis compares Alodine with two viable alternatives: anodizing and powder coating, each with unique characteristics and advantages.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | ‘Is Alodine Conductive’ | Anodizing | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High electrical conductivity; corrosion resistant | Excellent corrosion resistance; non-conductive | Good corrosion resistance; can be conductive with additives |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial costs | Generally lower than anodizing |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple application process | Requires specialized equipment | Easy to apply, requires curing |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, long-lasting | Requires periodic inspection | Durable, minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Electrical components needing grounding | Aerospace and automotive applications | General-purpose applications, decorative finishes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that transforms the surface of aluminum to increase its thickness and improve corrosion resistance. It provides a hard, protective layer that can be dyed for aesthetic purposes. However, anodized surfaces are typically non-conductive, making them less suitable for applications requiring electrical grounding. The initial costs are higher due to the need for specialized equipment and facilities. Anodizing is best for industries like aerospace and automotive, where durability and resistance to wear are paramount.
Powder Coating
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder that is then cured under heat to form a hard finish. This method can provide good corrosion resistance and a variety of aesthetic options. While standard powder coatings are non-conductive, formulations with conductive additives can meet specific electrical requirements. The application process is relatively straightforward, and it is often more cost-effective than anodizing. However, powder-coated surfaces may require more maintenance in harsh environments compared to Alodine coatings, especially if scratches occur.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right coating solution involves evaluating specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance expectations. Alodine offers excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it a strong candidate for applications where grounding is essential. Anodizing provides superior surface hardness and aesthetic options but lacks conductivity, while powder coating offers versatility and cost-effectiveness but may require careful selection of formulations for conductive needs. B2B buyers should assess their unique application scenarios, considering factors such as environmental conditions, performance requirements, and cost-effectiveness to make an informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is alodine conductive
What are the Key Technical Properties of Alodine Coatings for Electrical Conductivity?
When evaluating Alodine coatings for their conductive properties, several technical specifications are crucial for B2B buyers to understand. These properties not only determine the performance of the coating but also its suitability for specific applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
1. Coating Thickness
Alodine coatings, particularly those classified under Class 3 of the MIL-DTL-5541 standard, typically range from 0.00001 to 0.00004 inches in thickness. This minimal thickness allows aluminum to maintain its inherent electrical conductivity, which is vital for components requiring grounding or electrical connections. Understanding the correct thickness is essential for ensuring that the coating provides adequate protection without compromising conductivity.
2. Electrical Resistance
For Class 3 Alodine coatings, the electrical resistance should not exceed 0.005 – 0.010 ohms per square inch under nominal pressure conditions (200 psi). This specification is critical for applications where low resistance is necessary to prevent overheating and ensure efficient electrical performance. Buyers should prioritize coatings that consistently meet these resistance thresholds.
3. Surface Roughness
The surface finish of the aluminum substrate prior to coating significantly impacts the conductivity of the Alodine layer. Rougher surfaces allow for better electrical contact due to micro-breaks in the coating, enhancing conductivity. Conversely, smoother surfaces may lead to higher resistance. B2B buyers should consider surface preparation techniques that optimize conductivity while maintaining corrosion resistance.
4. Corrosion Resistance
While Class 3 coatings provide superior electrical conductivity, they offer less corrosion resistance than thicker alternatives like Class 1A. However, they still present a reliable barrier against environmental factors that could lead to corrosion. For businesses operating in harsh conditions, understanding the trade-off between conductivity and corrosion protection is essential for long-term equipment reliability.
5. Thermal Conductivity
In addition to electrical conductivity, Alodine coatings also exhibit thermal conductivity, making them suitable for applications like heat sinks. This dual functionality can enhance the performance of electronic components, allowing buyers to streamline their supply chain by sourcing coatings that meet multiple operational requirements.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Alodine Conductivity?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common trade terms relevant to Alodine coatings and their applications:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEMs are companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the relationship between OEMs and Alodine coatings is crucial for buyers who require specific standards for their components.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for B2B buyers as it affects inventory levels and cost structures. Knowing the MOQ for Alodine coatings can help businesses plan their purchasing strategy effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. When requesting quotes for Alodine coatings, it is essential to provide detailed specifications to ensure accurate pricing and compliance with required standards.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions involving Alodine coatings, especially for international buyers looking to import products.
5. Passivation
Passivation refers to a chemical treatment process that creates a protective layer on metal surfaces to prevent corrosion. In the context of Alodine coatings, passivation enhances corrosion resistance while maintaining conductivity, making it a relevant term for buyers focused on durability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding the procurement of Alodine coatings, ensuring they meet both performance and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is alodine conductive Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Alodine Conductive Coatings?
The global market for Alodine conductive coatings is driven by increasing demands for corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, seek reliable solutions, several key trends are emerging. First, the shift toward lightweight materials is prompting manufacturers to use aluminum alloys more frequently, making Alodine coatings essential for maintaining conductivity while ensuring corrosion protection.
Moreover, advancements in coating technologies are leading to the development of more efficient application processes, reducing lead times and costs for buyers. The rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) is also influencing sourcing strategies, as manufacturers increasingly rely on data-driven insights to optimize their production and maintenance schedules. This trend underscores the importance of selecting suppliers that not only provide high-quality coatings but also leverage technology for improved service delivery.
In addition, geopolitical factors are reshaping sourcing dynamics. For instance, trade agreements and tariffs can impact the availability and pricing of Alodine coatings. Buyers must stay informed about regional regulations and standards, such as the MIL-DTL-5541, to ensure compliance and quality assurance in their procurement processes.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Alodine Conductive Coatings Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the Alodine coatings sector. The environmental impact of chemical treatments, including chromate conversion coatings, necessitates a focus on ethical sourcing and the adoption of greener alternatives. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate responsible practices, such as using low-impact chemicals and sustainable manufacturing processes.
The significance of certifications cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers with recognized ‘green’ certifications that validate their commitment to environmental stewardship. Such certifications can include ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or other industry-specific certifications that emphasize sustainable practices.
Additionally, the push for circular economy principles is influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are looking for suppliers that offer recyclable or biodegradable materials, which can enhance the sustainability profile of their products. By aligning with ethical suppliers, businesses not only mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance but also strengthen their brand reputation in a market increasingly driven by corporate social responsibility.
What Is the Evolution and Historical Context of Alodine Conductive Coatings in B2B Applications?
The development of Alodine conductive coatings can be traced back to the need for effective corrosion protection in aerospace and military applications during the mid-20th century. Initially, chromate conversion coatings were developed to enhance the durability of aluminum alloys used in aircraft, ensuring that these materials could withstand harsh environmental conditions without compromising structural integrity.
Over the decades, the application of Alodine coatings has expanded significantly. Today, they are utilized in a wide array of industries, including automotive, marine, and electronics, due to their ability to provide both corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. The evolution of these coatings has been marked by technological advancements that enhance application efficiency and performance, making them a go-to solution for manufacturers seeking reliable and effective protection for their aluminum components.
As global markets continue to evolve, the demand for innovative and sustainable solutions will likely drive further advancements in Alodine coating technologies, ensuring that they remain a relevant and essential component in modern manufacturing processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is alodine conductive
-
How does Alodine affect the electrical conductivity of aluminum parts?
Alodine, specifically when applied as a Class 3 chemical conversion coating per MIL-DTL-5541 standards, enhances the electrical conductivity of aluminum. This is achieved because the coating is thin enough to allow the underlying aluminum to maintain its conductive properties. It is crucial to note that the coating itself is not conductive; rather, it preserves the aluminum’s conductivity while offering some corrosion resistance. This makes Alodine suitable for applications where both grounding and electrical performance are essential. -
What applications benefit from the use of Alodine coatings?
Alodine coatings are widely used in industries where aluminum parts require both corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Common applications include aerospace components, electrical enclosures, and heat sinks. These coatings help prevent corrosion while ensuring that electrical components remain grounded. Additionally, Alodine is suitable for marine equipment and automotive parts, where exposure to harsh environments is prevalent. -
What factors influence the conductivity of Alodine coatings?
The conductivity of Alodine coatings is influenced by several factors, including the coating thickness and the surface roughness of the aluminum substrate. Thinner Class 3 coatings enhance conductivity but offer less corrosion protection compared to thicker coatings. Moreover, a rougher surface finish can improve conductivity due to the presence of breaks in the coating, while highly polished surfaces may reduce conductivity by providing fewer breaks. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for Alodine coatings?
The minimum order quantity for Alodine coatings can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, suppliers may set an MOQ based on production capabilities and customer requirements. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. For large-scale projects, some suppliers may offer flexibility, allowing you to negotiate quantities that align with your production schedule. -
How should I vet suppliers for Alodine coatings?
When sourcing Alodine coatings, vet suppliers by assessing their certifications, quality assurance processes, and industry experience. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications, as this indicates adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, request samples or trial orders to evaluate the quality of their coatings firsthand. Engaging in discussions regarding their production methods and customer support can also provide insights into their reliability and service quality. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international B2B transactions involving Alodine coatings?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary by supplier and region. Common terms include payment in advance, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., 30 or 60 days). It’s essential to clarify payment options before finalizing agreements, as well as any potential fees associated with international transactions. Establishing clear terms can help mitigate risks and ensure a smoother procurement process. -
What quality assurance measures should I consider when sourcing Alodine coatings?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing Alodine coatings. Ensure that the supplier conducts rigorous testing and quality checks throughout the coating process. Inquire about their compliance with industry standards, such as MIL-DTL-5541, and request documentation of their quality control procedures. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer warranties or guarantees on their coatings, as this indicates confidence in their product quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing Alodine coatings?
When importing Alodine coatings, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Ensure that your supplier provides reliable shipping options and can meet your delivery timelines. Familiarize yourself with the import regulations in your country, including any necessary documentation and duties. Engaging a logistics partner experienced in international trade can help streamline the process and ensure compliance with local laws.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Is Alodine Conductive Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Best Technology Inc – Alodine Coatings
Domain: besttechnologyinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Alodine coatings, also known as chromate conversion coatings, provide electrical conductivity for aluminum parts when applied according to Class 3 of the MIL-DTL-5541 standard. Class 3 coatings are thinner than Class 1A, offering less corrosion resistance but better electrical conductivity. The coating itself is not conductive; rather, the thinness allows the aluminum to retain its conductivity. S…
2. Namf – Alodine Coating
Domain: namf.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Alodine coating is a type of chromate conversion coating applied to aluminum and other metals to protect against corrosion. It is known for its higher corrosion resistance compared to aluminum oxide coatings. Key features include:
– Thickness: 0.00001 to 0.00004 inches, maintaining the weight of the equipment.
– Application: Can be used on aluminum alloys, zinc, magnesium, cadmium, and other met…
3. Gabrian – Alodine Finish
Domain: gabrian.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Alodine finish is a type of conversion coating for aluminum parts that creates a thin protective film to prevent corrosion and can be used as a primer for painting. It is often referred to as chromate conversion coating or chem film. The Alodine® product is a registered trademark of Henkel, Inc., with similar products available from other companies like Iridite 14-2®. The process is governed by st…
4. ChemProcessing – Chemfilm/Alodine
Domain: chemprocessing.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Chemfilm/Alodine is a chemical conversion coating used to passivate aluminum, providing corrosion protection and serving as a base for organic coatings without altering dimensions. It can be applied by dipping, spraying, or brushing and is suitable for repairing minor damage to anodized surfaces (up to 5% of surface area per MIL-A-8625). Chemfilm is preferred for spaceflight applications due to it…
5. Henkel – Alodine 1201 Chromate Conversion Coating
Domain: chemical-supermarket.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Henkel Alodine 1201 Chromate Conversion Coating”, “Price”: “$34.95”, “Chemical Name”: “Alodine 1201 Conversion Coating”, “Synonyms”: “Chromate Conversion Coating”, “Description”: “Alodine® 1201 is a chemical treatment process for aluminum that provides corrosion protection and surface preparation for paint and adhesives. It contains hexavalent chromium and is designed to prevent …
6. Finishing.com – Electrically Conductive Coatings
Domain: finishing.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Electrically conductive coatings for aluminum include Iridite and Alodine, both of which are chemical conversion coatings and not scratch resistant. Alternatives suggested include electroless nickel, which is electrically conductive and scratch resistant, and anodizing with chromate conversion coating for areas requiring conductivity. Alodine is noted to be a class 3 option for corrosion protectio…
7. Valence Surface Tech – Alodine Coating
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Alodine coating, also known as chromate conversion coating, is a chemical treatment process primarily used on aluminum and its alloys, but can also be applied to other metals like steel, magnesium, and copper. It involves applying a chromic acid-based chemical compound that reacts with the metal surface to form a protective, corrosion-resistant film. This film prevents oxidation and enhances paint…
8. VansAirForce – Alodine Treatment
Domain: vansairforce.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Alodine is a chemical treatment used for aluminum surfaces to provide corrosion protection. It is available in different classes: Class 1A offers maximum corrosion protection and is non-conductive, while Class 3 provides less protection and is conductive. The treatment is often used in aviation for components exposed to ethanol-laced fuel, such as fuel tanks and aluminum fuel tubing. Alodine is pr…
9. Tuofa CNC Machining – Alodine and Anodizing Finishes
Domain: tuofa-cncmachining.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Alodine and anodize are two types of finishing for aluminum. Alodine, also known as chromate conversion or chemical film, is a chemical process that creates a protective thin film of chromium over aluminum surfaces. It is economical, retains electrical and thermal conductivity, and has a lifespan of decades, but has lower durability and corrosion resistance compared to anodizing. Anodizing is an e…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is alodine conductive
In conclusion, Alodine coatings, particularly Class 3 chemical conversion coatings, provide a unique balance of electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making them an excellent choice for various applications in sectors such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. By understanding the nuances of Alodine’s conductivity—where surface roughness and coating thickness play critical roles—international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Strategic sourcing of Alodine coatings not only enhances product longevity but also contributes to cost efficiency by reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement. As industries increasingly prioritize durability and functionality, leveraging Alodine’s properties will be pivotal in achieving sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to explore partnerships with reliable suppliers who can deliver high-quality Alodine solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operational efficiency and product reliability—invest in Alodine coatings today for a more resilient tomorrow.