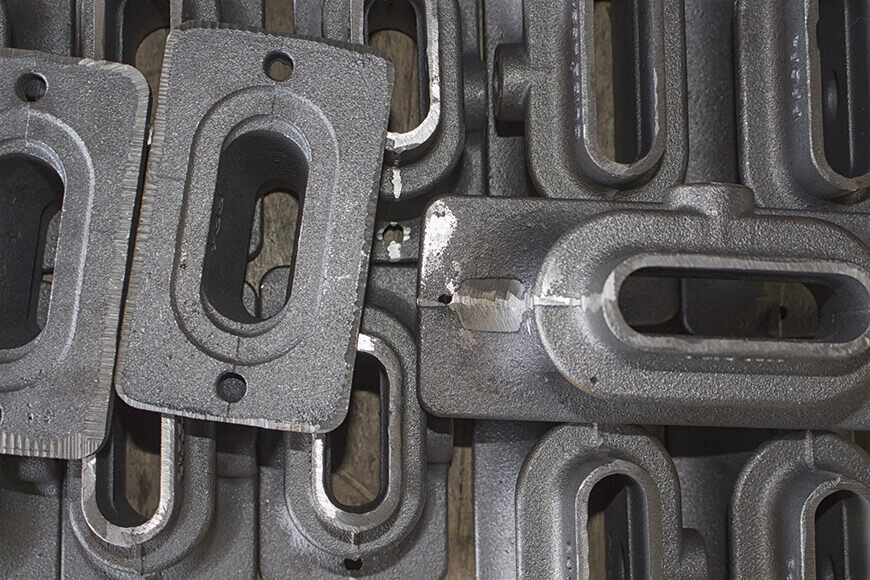
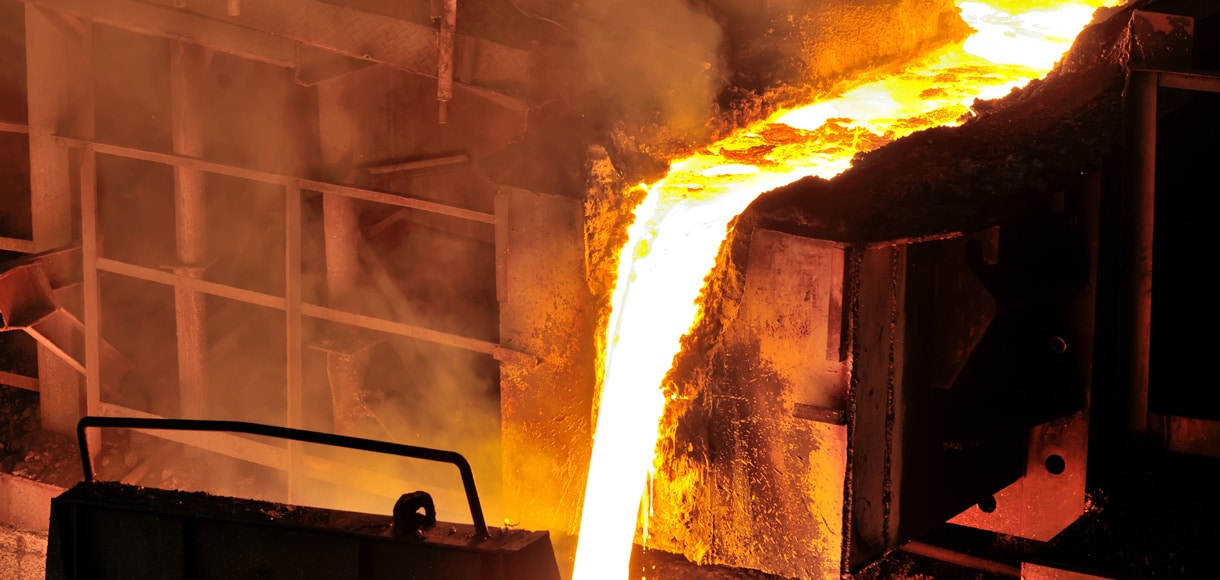
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for iron and steel casting
In today’s dynamic global market, sourcing iron and steel casting materials can present a myriad of challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the intricate balance of cost, performance, and reliability, making informed decisions is crucial for manufacturers and procurement professionals. This guide delves deep into the world of iron and steel casting, exploring essential topics such as the distinctions between cast iron and cast steel, their respective applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting processes.
Buyers will gain insights into the diverse types of castings available—from gray iron to ductile iron and various steel alloys—each tailored for specific industrial uses. Understanding these materials’ mechanical properties, including their strength, machinability, and impact resistance, enables businesses to select the right components for their projects. Additionally, the guide addresses cost considerations, helping buyers navigate pricing structures and potential savings.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and strategies, this comprehensive resource empowers them to make confident purchasing decisions. Whether you are in Brazil, Nigeria, or elsewhere, understanding the complexities of iron and steel casting is essential for achieving operational excellence and maintaining a competitive edge in your industry.
Understanding iron and steel casting Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gray Cast Iron | High carbon content (>2%), excellent machinability, good vibration damping | Engine blocks, machine frames, decorative items | Pros: Cost-effective, excellent for intricate designs; Cons: Low tensile strength, brittle under high stress |
| Ductile Iron | Enhanced ductility and toughness, lower carbon content than gray iron | Automotive components, pressure pipes, valves | Pros: Higher strength and impact resistance; Cons: More expensive than gray iron, requires careful processing |
| Malleable Iron | Heat-treated gray iron, improved ductility and strength | Agricultural equipment, fittings, and hardware | Pros: Good wear resistance and toughness; Cons: More complex production process, can be costlier |
| Carbon Steel Castings | Lower carbon content (<2%), high tensile strength and durability | Heavy machinery, structural components, pressure vessels | Pros: Superior strength and flexibility; Cons: More challenging to cast, higher production costs |
| Alloy Steel Castings | Tailored chemical composition, can withstand extreme conditions | Aerospace, oil and gas, high-pressure applications | Pros: Customizable properties for specific needs; Cons: Higher costs, requires precise metallurgy management |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Gray Cast Iron for B2B Buyers?
Gray cast iron is characterized by its high carbon content, typically over 2%, which grants it excellent machinability and good vibration damping properties. This material is particularly suited for applications requiring intricate designs and stable performance, such as engine blocks and machine frames. B2B buyers should consider gray cast iron for projects where cost-effectiveness is crucial, but they must be aware of its limitations in tensile strength and potential brittleness under high-stress conditions.
How Does Ductile Iron Compare in Terms of Strength and Applications?
Ductile iron, with its enhanced ductility and toughness, is a variant that features lower carbon content than gray iron. This material excels in applications that demand high strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for automotive components and pressure pipes. Buyers should note that while ductile iron offers superior mechanical properties, it generally comes at a higher cost and requires careful processing to maintain its advantages.
What are the Advantages of Malleable Iron for Industrial Applications?
Malleable iron is produced through the heat treatment of gray iron, resulting in improved ductility and strength. This type of iron is particularly useful in agricultural equipment and various fittings. B2B buyers should consider malleable iron when durability and wear resistance are essential, but they must also factor in the more complex production process that can lead to higher costs.
Why Choose Carbon Steel Castings for Heavy-Duty Uses?
Carbon steel castings, which contain less than 2% carbon, are recognized for their high tensile strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy machinery and structural components. Buyers in industries requiring robust performance under dynamic loads, such as construction and manufacturing, should prioritize carbon steel. However, the challenges associated with casting this material and the higher production costs must be taken into account.
What Benefits Do Alloy Steel Castings Offer for Specialized Industries?
Alloy steel castings are distinguished by their tailored chemical composition, allowing them to withstand extreme conditions. They find applications in aerospace and oil and gas industries, where performance is critical. Buyers should appreciate the customizable nature of alloy steel castings, which can be adapted to specific needs, but they must also be prepared for the higher costs and the necessity of precise metallurgy management to achieve the desired outcomes.
Key Industrial Applications of iron and steel casting
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of iron and steel casting | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine Blocks and Cylinder Heads | High strength and durability ensure reliable vehicle performance | Quality certifications, alloy specifications, and lead times |
| Construction | Structural Components (Beams, Columns) | Enhanced load-bearing capacity and safety in infrastructure | Compliance with local building codes and material standards |
| Oil & Gas | Valve Bodies and Pump Casings | Resistance to harsh conditions improves operational efficiency | Material compatibility with specific fluids and temperatures |
| Heavy Machinery | Gearboxes and Transmission Housings | Improved performance under high-stress conditions | Customization options and dimensional accuracy |
| Agriculture | Plow and Harrow Components | Durability and resistance to wear in tough farming conditions | Supplier reliability and after-sales support |
How is Iron and Steel Casting Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, iron and steel casting is crucial for manufacturing engine blocks and cylinder heads. These components require high strength and durability to withstand extreme conditions, such as high temperatures and mechanical stress. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing castings that meet stringent quality certifications is vital. Additionally, understanding alloy specifications can significantly impact performance and longevity.
What Role Does Iron and Steel Casting Play in Construction?
Structural components like beams and columns made from iron and steel casting are essential in construction projects, providing the necessary load-bearing capacity and safety. These castings are designed to meet specific regulatory standards, which vary by region. Buyers must ensure compliance with local building codes and material standards, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, where regulations can be stringent. This compliance not only ensures safety but also enhances the project’s overall credibility.
How is Iron and Steel Casting Beneficial in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, iron and steel casting is extensively used for producing valve bodies and pump casings. These components must resist harsh environmental conditions, including high pressures and corrosive substances. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing materials that are compatible with specific fluids and can withstand extreme temperatures is critical. Ensuring that suppliers can provide these specifications will enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
What are the Advantages of Iron and Steel Casting in Heavy Machinery?
Heavy machinery relies on iron and steel casting for critical components like gearboxes and transmission housings. These parts must perform reliably under high-stress conditions, and their casting allows for precise design and durability. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer customization options and ensure dimensional accuracy, especially in regions like Brazil, where heavy machinery is vital for infrastructure development. This focus can lead to improved performance and reduced maintenance costs.
How Does Iron and Steel Casting Support Agricultural Equipment?
In agriculture, iron and steel casting is used to produce components such as plows and harrows. These parts must exhibit durability and resistance to wear due to the challenging conditions they face in the field. For international buyers, evaluating supplier reliability and after-sales support is essential to ensure that their agricultural equipment remains operational. This focus on quality and support can lead to enhanced productivity and reduced operational disruptions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘iron and steel casting’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Selection Challenges for High-Stress Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the daunting task of selecting the right material for their projects, particularly when it comes to high-stress applications like structural components or heavy machinery. The differences between cast iron and cast steel can be subtle but significant. Buyers may struggle to understand the impact of carbon content on mechanical properties, leading to potential failures if the wrong material is chosen. This is especially critical in industries such as construction and mining, where performance and safety are paramount.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific mechanical properties required for their applications. Begin by conducting a thorough analysis of the operational environment, including temperature variations, load requirements, and potential impact stresses. Once these factors are identified, consult with material specialists or foundries that can provide expert insights into the best material options. When specifying materials, ensure to communicate the required tensile strength, ductility, and impact resistance levels. Utilizing advanced material selection software can also aid in comparing the properties of different alloys. This proactive approach not only helps in choosing the right material but also fosters a collaborative relationship with suppliers, enhancing product reliability and safety.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Production Delays Due to Quality Control Issues
The Problem: Quality control is a critical concern in iron and steel casting, particularly for international B2B buyers who may be sourcing from multiple regions. Delays caused by subpar casting quality can lead to significant project setbacks, increased costs, and strained supplier relationships. Issues such as internal voids, shrinkage, and inconsistent cooling rates can compromise the integrity of cast components, leading to costly rework or replacements.
The Solution: To address these quality control challenges, buyers should establish clear quality standards and inspection protocols with their suppliers before production begins. Implementing a stringent qualification process for foundries, including on-site audits and inspections, can help ensure that they adhere to industry standards. Additionally, consider using non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing to evaluate the integrity of castings before they are shipped. This proactive approach not only reduces the risk of production delays but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers who are committed to quality.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost Efficiency in a Competitive Market
The Problem: In a competitive B2B landscape, managing costs while maintaining quality is a significant pain point for buyers in the iron and steel casting industry. Fluctuating raw material prices and increased labor costs can squeeze margins, making it challenging to provide competitive pricing to end customers. Buyers often struggle with balancing cost-efficiency and the need for high-performance materials, which can lead to tough decisions that compromise quality.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs, buyers should adopt a strategic sourcing approach. This includes building long-term relationships with multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and a consistent supply chain. Additionally, consider leveraging technology such as predictive analytics to forecast material price fluctuations and adjust procurement strategies accordingly. Collaborating with suppliers on cost-saving initiatives—such as bulk purchasing agreements or exploring alternative materials that meet performance requirements—can also provide significant savings. By focusing on strategic partnerships and data-driven decision-making, buyers can achieve cost efficiency without sacrificing quality, positioning themselves favorably in the market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for iron and steel casting
What Are the Key Properties of Cast Iron in B2B Applications?
Cast iron is a popular choice in iron and steel casting due to its excellent casting properties and vibration damping capabilities. Typically containing over 2% carbon, cast iron exhibits good machinability and moderate wear resistance, making it suitable for applications like engine blocks, machine frames, and architectural components. Its ability to absorb vibrations makes it advantageous for precision machinery, reducing wear and extending the lifespan of moving parts.
However, cast iron has limitations, particularly in tensile strength and elongation, which can restrict its use in high-stress applications. The brittleness of cast iron can lead to fractures under sudden impacts, making it less suitable for dynamic load-bearing applications. For international buyers, understanding regional preferences for cast iron grades is essential, as standards vary. Compliance with ASTM, DIN, or JIS standards will be crucial for ensuring product quality and reliability.
How Does Cast Steel Compare in Terms of Performance and Cost?
Cast steel, typically containing less than 2% carbon, is renowned for its superior tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for high-stress applications such as structural supports, mining equipment, and heavy-duty machinery. The ability to modify the metallurgy and heat treatment of cast steel allows for tailored mechanical properties, enhancing its versatility across various industries.
Despite its advantages, cast steel can be more complex and costly to manufacture compared to cast iron. The pouring process requires careful attention due to its lower fluidity and higher shrinkage rates, leading to increased production costs. For international buyers, understanding the specific mechanical properties required for their applications is vital, as well as ensuring compliance with international standards for quality assurance.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Ductile Iron?
Ductile iron, also known as spheroidal graphite iron, offers a unique combination of strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. With a microstructure that enhances toughness, ductile iron can replace carbon steel in many applications, particularly in pressure pipes and automotive components. Its ability to withstand high levels of stress and strain makes it suitable for applications requiring durability.
However, ductile iron can be more expensive than traditional cast iron and may require more complex manufacturing processes. For buyers in emerging markets, the initial investment in ductile iron castings can be a consideration, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs due to lower maintenance and replacement rates. Compliance with local and international standards is also essential to ensure product reliability and performance.
Why Choose Malleable Iron for Specific Applications?
Malleable iron, which is produced by heat-treating white cast iron, is known for its excellent ductility and toughness. This material is often used in applications that require good machinability and resistance to wear, such as automotive parts and agricultural equipment. Malleable iron’s ability to withstand deformation under stress makes it a preferred choice for components that undergo significant mechanical loads.
On the downside, malleable iron may not offer the same level of impact resistance as cast steel, which can limit its use in high-impact applications. For international buyers, understanding the specific applications and mechanical requirements is crucial, as well as ensuring that the material meets relevant industry standards for quality and safety.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Iron and Steel Casting
| Material | Typical Use Case for iron and steel casting | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Engine blocks, machine frames | Excellent vibration damping | Low tensile strength and brittleness | Medium |
| Cast Steel | Structural supports, mining equipment | Superior tensile strength and impact resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
| Ductile Iron | Pressure pipes, automotive components | High strength and ductility | More expensive than traditional cast iron | Medium to High |
| Malleable Iron | Automotive parts, agricultural equipment | Good machinability and wear resistance | Lower impact resistance than cast steel | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various casting materials, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for iron and steel casting
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Iron and Steel Casting?
The manufacturing process for iron and steel casting involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets specific mechanical and aesthetic requirements. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Iron and Steel Casting?
Material preparation is the foundation of any successful casting operation. This stage involves the selection of raw materials, which typically include ferrous metals such as pig iron, scrap iron, and steel. The materials are melted in a furnace, with temperatures reaching approximately 2300°F for iron and 2600°F for steel.
In addition to selecting the appropriate base metals, alloying elements such as carbon, silicon, and manganese may be added to achieve desired mechanical properties. For example, cast iron generally contains over 2% carbon, while cast steel contains 0.1% to 0.5%. The quality of the raw materials directly impacts the integrity of the final casting.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Iron and Steel Castings?
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This is primarily done using either sand casting or investment casting methods.
-
Sand Casting: This is the most common method for both iron and steel castings. Molds are made using sand mixed with a binder, and the molten metal is poured into these molds. Sand casting is particularly favored for its versatility and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for large and complex shapes.
-
Investment Casting: Also known as lost-wax casting, this method is used for intricate designs and provides a high level of dimensional accuracy. It involves creating a wax pattern coated with a ceramic shell, which is then heated to remove the wax before pouring the molten metal.
After the metal is poured, it cools and solidifies, forming the desired shape. Cooling rates vary significantly between iron and steel, with iron typically cooling more uniformly due to its lower shrinkage rates.
How Are Iron and Steel Castings Assembled and Finished?
Post-casting, the components may require assembly, especially if they are part of a larger system or machinery. This may involve welding, bolting, or other joining techniques, depending on the design specifications.
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the surface quality and performance of the castings. Techniques such as grinding, machining, and shot blasting are commonly employed to achieve the desired finish. For example, cast iron is often easier to machine due to its graphite structure, while steel may require more effort and specialized tools due to its toughness.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Iron and Steel Casting?
Quality assurance is paramount in iron and steel casting, ensuring that the final products meet both international standards and customer specifications. Key quality control measures include adherence to international standards like ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications such as CE marking or API standards.
What Are the Main Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards. Any non-compliant materials are rejected or sent back.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various inspections are conducted to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pouring conditions, and mold integrity. This is essential for identifying issues early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the casting is complete, a thorough inspection is carried out. This includes visual inspections, dimensional checks, and mechanical testing to confirm that the product meets all specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to evaluate the quality of castings:
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and dye penetrant testing are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the casting.
-
Destructive Testing: Mechanical tests, such as tensile strength tests and impact tests, are conducted on samples to determine material properties.
-
Chemical Analysis: Spectrometric methods are often used to verify the chemical composition of the metal, ensuring it meets the required standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from international suppliers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify quality control practices.
What Audits and Reports Should Be Requested?
Buyers should request regular quality control reports from suppliers, detailing the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. Additionally, buyers can conduct audits of the manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of quality control measures.
How Important Is Third-Party Inspection?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an additional layer of assurance regarding the quality of castings. These independent inspections can validate the findings of the supplier’s internal quality checks and offer an unbiased assessment of compliance with relevant standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential.
Buyers should be aware of varying standards and regulations that may apply in different regions. For instance, European suppliers may adhere to CE marking requirements, while suppliers from other regions might follow different local standards. Buyers should also consider cultural differences in business practices and communication styles, which can impact the effectiveness of quality assurance processes.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for iron and steel casting is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the reliability and performance of their sourced products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘iron and steel casting’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in effectively procuring iron and steel castings. By following this checklist, buyers can navigate the complexities of material selection, supplier evaluation, and quality assurance to ensure they receive products that meet their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your castings, including material type (cast iron or cast steel), dimensions, tolerances, and mechanical properties. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for your sourcing process. Buyers should consider the application of the castings—whether they require high strength, impact resistance, or vibration dampening features.
- Material Type: Decide between cast iron and cast steel based on their distinct properties.
- Mechanical Properties: Specify requirements such as tensile strength, ductility, and wear resistance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in iron and steel castings. Look for manufacturers with a strong reputation in the industry, and consider their experience in your specific sector. A well-established supplier is likely to have the necessary capabilities and resources to meet your demands.
- Industry Experience: Check how long the supplier has been in the business.
- Product Range: Ensure the supplier offers a variety of casting options that fit your specifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications and adhere to industry standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management, which is critical for ensuring consistent production quality.
- Quality Management Systems: Look for suppliers with established quality control processes.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure they meet international standards relevant to your industry.
Step 4: Request and Review Samples
Before making a large order, request samples of castings that meet your specifications. This allows you to assess the quality of the product firsthand and verify that it meets your technical requirements. Pay attention to the finish, dimensions, and any specific properties stated in your specifications.
- Sample Evaluation: Check for defects, dimensional accuracy, and overall quality.
- Performance Testing: If applicable, conduct tests to evaluate mechanical properties.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Delivery Logistics
Engage in discussions about production lead times and delivery logistics with potential suppliers. Understanding the timeline is crucial for your project planning and can impact your overall operations. Be clear about your delivery deadlines and any potential penalties for delays.
- Production Capacity: Ensure the supplier can meet your order volume within your timeline.
- Shipping Options: Discuss logistics and shipping arrangements, especially for international orders.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, enter into negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and warranty agreements. Transparent discussions can help establish a mutually beneficial relationship and prevent misunderstandings in the future.
- Payment Terms: Clarify terms such as deposits, installment payments, and payment methods.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure there is a clear warranty policy for the castings to protect your investment.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Set up a communication plan to maintain ongoing dialogue with your supplier throughout the production and delivery process. Regular updates can help address any issues promptly and foster a strong working relationship.
- Point of Contact: Identify a dedicated contact person for both parties.
- Communication Frequency: Agree on how often you will check in on production progress.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing process for iron and steel castings, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for iron and steel casting Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Iron and Steel Casting?
When sourcing iron and steel castings, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant factor, influenced by the type of metal (cast iron vs. cast steel), carbon content, and quality. Prices can vary based on market conditions and availability, especially for specialty alloys.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ based on the complexity of the casting process. Skilled labor is required for intricate designs, leading to higher labor costs. In regions like Africa and South America, labor rates may be lower, potentially reducing overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. The efficiency of the foundry and its technology can significantly impact overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs encompass the creation of molds and patterns. Custom designs require more investment, which is often amortized over the production volume. Buyers should consider the scale of production when evaluating tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is crucial, particularly for applications requiring high reliability. QC processes may include inspections, testing, and certifications, all contributing to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on the distance from the supplier, chosen Incoterms, and the volume of the order. Efficient logistics planning can mitigate costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover risks and business expenses. This margin can vary based on market competition and the supplier’s reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Iron and Steel Casting Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of iron and steel castings:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications or unique designs can increase costs due to the additional time and resources required for production.
-
Materials: The choice between cast iron and cast steel, as well as the specific grades and alloys, can drastically affect pricing. For instance, high-grade ductile iron may command a premium over standard gray iron.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific certifications (like ISO or ASTM standards) may incur additional costs, impacting the overall price.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s experience, technology, and location can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices but provide better reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can affect the overall cost of acquisition. For instance, terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) may result in higher upfront costs compared to EXW (Ex Works), where the buyer assumes more responsibility.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Iron and Steel Castings?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse international markets, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiation: Be prepared to negotiate terms and prices. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide leverage during discussions.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime. This comprehensive view can help in selecting the most cost-effective option.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and regional market conditions that may affect pricing. Engage with local experts or consultants to navigate these complexities effectively.
-
Volume Commitments: Consider consolidating orders to meet MOQ requirements and secure better pricing. Long-term contracts can also lead to favorable terms.
-
Supplier Assessment: Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers, focusing on their capabilities, quality history, and financial stability. A reliable supplier can mitigate risks and ensure consistent quality.
In conclusion, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of iron and steel casting is critical for making informed sourcing decisions. By focusing on these components and influencers, international B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of the market, ultimately leading to more strategic procurement outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing iron and steel casting With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Iron and Steel Casting
In the realm of manufacturing and construction, the choice of materials and methods is critical. Iron and steel casting have long been preferred for their strength and versatility, but several alternative solutions also provide viable options for various applications. This analysis compares iron and steel casting with other methods, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Iron And Steel Casting | Additive Manufacturing | Forging |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, good ductility; excellent vibration dampening (cast iron) | Highly customizable; excellent for complex geometries | Exceptional strength and toughness; good for high-stress applications |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower long-term cost for mass production | Higher upfront costs due to technology and materials | Typically higher costs due to labor and energy requirements |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized molds and facilities; longer lead times | Relatively easy to implement with the right technology; shorter lead times for prototypes | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor; longer setup time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance if designed properly; susceptible to corrosion (iron) | Minimal maintenance; however, parts may need post-processing | Low maintenance but requires regular inspections for wear |
| Best Use Case | Heavy machinery, automotive components, structural applications | Prototyping, custom parts, low-volume production | Aerospace, automotive, and high-performance applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Pros and Cons of Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has gained traction for its ability to create complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve. The primary advantage is its customization capabilities, allowing manufacturers to produce unique parts without the need for extensive tooling. This method also results in shorter lead times, making it ideal for prototyping and low-volume production runs. However, the initial investment in additive manufacturing technology can be high, and the materials used may not always match the mechanical properties of cast iron or steel, particularly in high-stress applications.
How Does Forging Compare to Casting?
Forging is a traditional method that involves shaping metal using compressive forces, resulting in parts with exceptional strength and toughness. It is particularly suited for high-stress applications, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. The downside is that forging typically requires more energy and labor, leading to higher production costs compared to casting. Additionally, the setup time for forging can be lengthy, as it necessitates specialized dies and equipment. However, forged parts often exhibit superior performance characteristics, making them a preferred choice for critical applications.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right manufacturing method depends on various factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and production volume. Iron and steel casting offer a robust solution for many applications, particularly where strength and durability are paramount. However, alternatives like additive manufacturing and forging may provide better results in specific scenarios, such as custom parts or high-performance applications. B2B buyers should carefully assess their unique requirements and consider how each option aligns with their operational goals to make an informed choice.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for iron and steel casting
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Iron and Steel Casting?
Understanding the technical properties of iron and steel casting is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Below are some critical specifications that define the performance and suitability of these materials for various applications.
1. Carbon Content
The carbon content in cast iron and steel is a pivotal factor influencing their mechanical properties. Cast iron typically contains over 2% carbon, contributing to its excellent machinability and vibration-damping characteristics. In contrast, cast steel usually has a carbon content of 0.1% to 0.5%, which enhances its tensile strength and impact resistance. For buyers, selecting the appropriate carbon content can significantly affect the durability and functionality of the final product.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures a material’s ability to withstand tension without breaking. Steel castings generally exhibit superior tensile strength compared to cast iron, making them suitable for high-stress applications such as structural components and heavy machinery. B2B buyers should prioritize tensile strength when sourcing materials for applications that experience dynamic loads or impacts.
3. Ductility
Ductility refers to a material’s ability to deform under tensile stress without fracturing. Cast iron tends to be more brittle, while cast steel offers greater ductility, making it less prone to sudden failure under stress. This property is crucial for applications requiring resilience and flexibility, particularly in sectors like automotive and aerospace.
4. Machinability
Machinability indicates how easily a material can be machined to achieve desired specifications. Cast iron typically offers better machinability due to its graphite microstructure, which allows for easier cutting and shaping. Understanding machinability is vital for buyers concerned with production efficiency and cost-effectiveness, as materials that are harder to machine can lead to higher tooling costs and longer lead times.
5. Impact Resistance
Impact resistance is the ability of a material to absorb energy during a sudden force or shock without fracturing. Steel castings excel in this area, making them ideal for applications that require durability under high-impact conditions, such as mining equipment or construction machinery. Buyers should consider impact resistance when evaluating materials for high-stress environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Iron and Steel Casting?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the iron and steel casting market. Below are some common trade terms that buyers should know.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand, as it can significantly impact inventory management and procurement strategies, especially in markets with varying demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific products or services. This term is important for buyers looking to compare costs and secure the best deals in the market, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities, ensuring smoother transactions.
5. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is a process used to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material. It can improve strength, hardness, and ductility, making it a critical consideration for buyers aiming to enhance material performance in specific applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their investment in iron and steel casting meets their operational needs and expectations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the iron and steel casting Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Shaping the Iron and Steel Casting Market?
The global iron and steel casting market is experiencing significant transformation, driven by several key factors. First, the ongoing industrialization in emerging economies, particularly in Africa and South America, is increasing demand for durable and efficient materials in sectors such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. Countries like Brazil and Nigeria are investing heavily in infrastructure development, creating a robust demand for cast iron and steel components.
Technological advancements in manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing and automation, are revolutionizing the production landscape. These innovations enhance precision and reduce waste, making sourcing more efficient for international buyers. Furthermore, the trend towards customized solutions is gaining traction; suppliers are increasingly offering tailored products to meet specific application needs, thereby enhancing competitiveness.
Market dynamics are also influenced by fluctuating raw material costs and supply chain disruptions. Buyers must navigate these challenges by establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide consistent quality and pricing. Additionally, the push for digital transformation in procurement processes is gaining momentum, with platforms facilitating easier access to suppliers and real-time data analytics for informed decision-making.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in Iron and Steel Casting?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration for international B2B buyers in the iron and steel casting sector. The environmental impact of metal casting processes, particularly concerning emissions and waste, necessitates a shift towards more sustainable practices. Suppliers who adopt eco-friendly manufacturing methods, such as using recycled materials or implementing energy-efficient technologies, are increasingly favored by conscientious buyers.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses seek to ensure that their supply chains align with their corporate social responsibility goals. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with certifications that demonstrate commitment to ethical practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or Fair Trade certifications. These certifications not only reflect a supplier’s dedication to sustainability but also enhance brand reputation and consumer trust.
The trend toward ‘green’ materials is gaining traction, with innovations in alloy compositions that reduce the carbon footprint. By collaborating with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, buyers can contribute to a circular economy while ensuring compliance with emerging regulations on carbon emissions.
How Has the Iron and Steel Casting Industry Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the iron and steel casting industry is marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in market demand. Historically, iron casting has its roots in ancient civilizations, where artisans crafted functional and decorative items. The Industrial Revolution catalyzed mass production techniques, leading to the establishment of foundries and the modern casting processes we see today.
As industries grew, the demand for more durable and versatile materials led to the development of various iron and steel alloys, enhancing performance characteristics for specific applications. The introduction of computerized systems and automation in recent decades has further refined production efficiency and quality control.
Today, the focus is on not just meeting performance standards but also addressing environmental concerns and ethical sourcing, reflecting a holistic approach to manufacturing in the iron and steel casting sector. This historical context underscores the need for international buyers to stay informed about ongoing innovations and best practices to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of iron and steel casting
-
How do I choose between cast iron and cast steel for my application?
Choosing between cast iron and cast steel depends on the specific requirements of your application. Cast iron, with its higher carbon content, offers excellent machinability and vibration dampening, making it ideal for components like engine blocks and machine frames. In contrast, cast steel is preferred for high-stress applications due to its superior tensile strength and impact resistance. Evaluate the mechanical properties needed, such as tensile strength, ductility, and wear resistance, alongside cost considerations to make the best choice for your needs. -
What are the key benefits of using iron castings in my projects?
Iron castings, particularly gray and ductile iron, provide several advantages. They excel in vibration dampening, making them suitable for machinery and automotive applications. Their casting properties allow for intricate designs without the need for extensive machining. Additionally, gray iron is cost-effective for lower-stress applications, while ductile iron offers enhanced strength and ductility, broadening its usability in structural and automotive components. Assess your project’s requirements to leverage these benefits effectively. -
What factors should I consider when vetting international suppliers of iron and steel castings?
When vetting international suppliers, prioritize their experience, production capabilities, and certifications. Request samples and review their quality assurance processes to ensure they meet your specifications. It’s crucial to check their compliance with international standards, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, assess their capacity for customization, lead times, and responsiveness to inquiries. A reliable supplier should also provide references from previous clients, allowing you to gauge their reputation in the industry. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for iron and steel castings?
Minimum order quantities for iron and steel castings vary by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred kilograms to several tons, depending on the complexity and cost of production. Suppliers may offer lower MOQs for standard products or larger quantities for custom designs. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly and negotiate terms that align with your project scale, ensuring cost-effectiveness while meeting production requirements. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of iron and steel castings?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers but often include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer partial payment upon order confirmation and the balance upon shipment. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Evaluate the supplier’s financial stability and consider using escrow services for high-value transactions, ensuring protection for both parties during the payment process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in my iron and steel castings?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes, including inspection reports and material certifications. Many reputable suppliers use advanced testing methods, such as non-destructive testing (NDT), to assess the integrity of castings. Establish clear specifications and tolerances in your purchase order, and consider onsite inspections during production. Regular communication with the supplier throughout the manufacturing process can also help address any quality concerns promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing castings internationally?
When sourcing castings internationally, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a logistics partner experienced in handling heavy industrial goods to ensure safe transportation. Factor in potential delays due to customs clearance and plan for contingencies. Also, assess the supplier’s ability to provide proper packaging to prevent damage during transit. Clear communication regarding delivery schedules is vital to align with your project timelines. -
What customization options are available for iron and steel castings?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including design modifications, material specifications, and surface treatments. You can often specify dimensions, weight, and performance characteristics tailored to your application. Discuss your requirements early in the procurement process to explore available options. Some suppliers may also provide assistance with design optimization, helping you achieve the best balance between functionality and cost.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Iron And Steel Casting Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HSCast – Steel Casting Solutions
Domain: hscast.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Steel casting involves pouring molten steel into a mold to create complex shapes for various industries including agriculture, construction, automobile, aviation, gas and oil, mining, and marine. It is used for heavy-duty components in construction and mining equipment, railroad cars, pumps and valves, and heavy trucks. Common materials used in steel casting include steel and iron, with other meta…
2. Quaker City Castings – Steel Castings
Domain: quakercitycastings.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Steel Castings: Made from carbon steel and alloy steel with carbon content of 2% or lower. Highly-strength material suitable for critical engineering applications. Mechanical properties can be adjusted through metallurgy and heat treatments. Ideal for high tensile stress and dynamic load requirements, especially in pressure vessel castings for low or high temperature conditions. Iron Castings: Inc…
3. Sinoway Industry – Cast Iron and Cast Steel Solutions
Domain: sinowayindustry.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Cast iron and cast steel are both iron-carbon alloys with different chemical compositions. Cast iron has a carbon content of 2% or more, while cast steel has less than 2%. Key types of cast iron include: 1. Grey iron (2.7% to 4.0% carbon, flaky graphite, good shock absorption), 2. White iron (low carbon, high hardness, brittle), 3. Malleable cast iron (good plasticity and toughness), 4. Ductile ir…
4. U.S. Casting Company – Steel and Iron Castings
Domain: uscastingco.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: U.S. Casting Company specializes in steel and iron castings, including carbon and low alloy steel, grey and ductile iron. They offer castings in weights ranging from 10 to 8,000 pounds and provide a variety of flask sizes to meet customer needs. The company has two electric induction furnaces with a melting capacity of 6,200 pounds per hour. They focus on consistent melting practices and regular t…
5. Bernier Inc – Iron and Steel Castings
Domain: bernierinc.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Iron and steel castings are produced by pouring molten iron into a vessel to create desired shapes. Common ferrous metals include grey iron, ductile iron, steel, and malleable iron. The market includes various product forms such as pipes and tubes, plates and sheets, and semi-finished cast products. The plates and sheets segment holds a significant share. Key applications include automotive, const…
6. Ferralloy – Steel Castings & Cast Irons
Domain: ferralloy.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Steel Castings: Formed by pouring molten steel into a mold, offering high strength, ductility, and toughness. Used in industries such as food processing, electronics, oil and gas, railroad, construction, drilling, transportation, and mining. Cast Irons: Better corrosion resistance than steel, often cheaper due to lower material costs, energy, and labor. Easier to cast with less shrinkage compared …
7. Reddit – Steel Casting Discussion
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around casting steel, particularly for someone new to metalworking who is interested in making metal parts using casts from 3D printed models. Key points include: 1. Steel has a high melting point, making it challenging to melt at home compared to metals like aluminum or bronze. 2. Specialized equipment and techniques are required to cast steel safely, including a controlle…
8. GMI Insights – Iron & Steel Casting Market
Domain: gminsights.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Iron & Steel Casting Market Size: USD 162.68 billion in 2023, projected 3.8% CAGR from 2024 to 2032. Key materials: Iron (USD 128.67 billion in 2023) and Steel. Key processes: Sand Casting (USD 83.72 billion in 2023, 3.7% CAGR) and Die Casting. Applications include Automotive, Industrial Machinery, Pipe, Fittings & Valves, Power & Electrical, and Sanitary. Trends include environmentally friendly p…
9. Iron Foundry – Galvanized Cast Iron Truck Brackets
Domain: iron-foundry.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Galvanized Cast Iron Truck Brackets’, ‘material’: ‘ductile cast iron GGG50’, ‘process’: ‘automatic molding’, ‘features’: ‘machined and hot dip galvanized coating’}, {‘name’: ‘Axle Support Brackets’, ‘material’: ‘ductile cast iron GGG40’, ‘process’: ‘green sand casting’, ‘features’: ‘black electrophoresis coating, machined by client’}, {‘name’: ‘Gray Cast Iron Manifolds’, ‘material’: ‘gr…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for iron and steel casting
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing in Iron and Steel Casting?
In the competitive landscape of iron and steel casting, understanding the nuances between cast iron and cast steel is crucial for international buyers. Cast iron, with its superior machinability and vibration dampening properties, is ideal for components requiring stability and precision, such as engine blocks and machine frames. Conversely, cast steel offers enhanced tensile strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for high-stress applications like structural supports and heavy machinery.
Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in optimizing supply chains, enabling businesses to balance cost and performance effectively. By leveraging local and global suppliers, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they secure the best materials for their specific needs.
How Can Buyers Prepare for Future Trends in Iron and Steel Casting?
As the industry evolves, the demand for innovative materials and sustainable practices will continue to rise. International buyers should remain agile and informed about market trends, technological advancements, and regulatory changes affecting iron and steel casting. Engaging in partnerships and collaborations with trusted suppliers can foster resilience and adaptability in their operations.
Invest in strategic sourcing today to secure a competitive edge in the dynamic world of iron and steel casting.