Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for injection molding cost estimator
In the complex world of global manufacturing, accurately estimating the costs associated with injection molding can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. As companies seek to optimize production and control expenditures, leveraging an effective injection molding cost estimator becomes essential. This guide delves into the multifaceted nature of injection molding, examining the various types of molds, materials, and processes involved, while also addressing applications across diverse industries.
From low-volume 3D printed molds to high-capacity steel tooling, understanding the cost implications of each choice is crucial for making informed procurement decisions. Additionally, this guide offers practical insights into supplier vetting, ensuring that businesses can identify reliable partners who meet quality and compliance standards. By breaking down the components of injection molding costs—including equipment expenses, labor, and material prices—this resource empowers buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Vietnam and Germany, to navigate their specific market challenges effectively.
With a comprehensive approach, this guide not only facilitates a clearer understanding of injection molding costs but also equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to drive profitability and efficiency in their manufacturing operations. Whether you are exploring initial project feasibility or seeking to optimize existing processes, this guide serves as your roadmap to successful injection molding procurement.
Understanding injection molding cost estimator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Injection Molding Estimator | Utilizes industry averages for cost estimation based on part geometry and material type. | High-volume production of standard plastic parts | Pros: Quick estimates, easy to use. Cons: May not account for specific project nuances. |
| Feature-Based Injection Molding Estimator | Focuses on part features and complexity, providing a detailed breakdown of costs. | Custom parts with unique geometries | Pros: Detailed insights, tailored to specific needs. Cons: More complex to use. |
| Tooling Cost Estimator | Concentrates on the costs associated with mold creation and maintenance. | Industries requiring precise mold specifications | Pros: Accurate mold cost analysis. Cons: May overlook other production costs. |
| Low-Volume Injection Molding Estimator | Designed for smaller production runs, often using 3D printed molds. | Prototyping and low-volume production | Pros: Cost-effective for small batches. Cons: Limited durability of molds. |
| Automated Injection Molding Estimator | Integrates automation and machine specifications to provide real-time cost analysis. | Large-scale manufacturing and automation setups | Pros: Real-time data, efficient for large volumes. Cons: Requires advanced knowledge. |
What are the Characteristics of Standard Injection Molding Estimators?
Standard injection molding estimators provide a quick overview of costs based on established industry averages. These tools typically require input on basic geometrical features and materials, making them user-friendly for businesses looking for general cost insights. They are particularly suitable for high-volume production runs, where the costs can be evenly distributed across thousands of parts. However, while they offer speed and simplicity, they may not account for unique project specifications, which could lead to discrepancies in actual costs.
How Do Feature-Based Injection Molding Estimators Work?
Feature-based injection molding estimators delve deeper into the specifics of part design, focusing on features such as complexity, dimensions, and material types. This detailed approach allows for more accurate cost predictions, especially for custom parts that do not conform to standard designs. They are ideal for B2B buyers needing precise estimates for unique components. However, the complexity of these estimators may pose a challenge for users unfamiliar with injection molding specifics, requiring a steeper learning curve.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Tooling Cost Estimators?
Tooling cost estimators are essential for understanding the financial implications of mold design and manufacturing. These estimators focus on the intricacies involved in creating molds, which are often the largest upfront costs in injection molding projects. They are highly valuable for industries that require precision molds for complex parts. Nevertheless, while they provide accurate mold cost assessments, they might not consider other production costs, which can lead to an incomplete financial picture.
When to Use Low-Volume Injection Molding Estimators?
Low-volume injection molding estimators are tailored for projects with smaller production needs, often utilizing 3D printed molds. This approach is particularly beneficial for prototyping or limited runs, allowing companies to test designs without significant investment. While these estimators are cost-effective for small batches, the durability of the molds may be limited, making them less suitable for long-term production needs.
How Do Automated Injection Molding Estimators Benefit Large-Scale Manufacturing?
Automated injection molding estimators leverage advanced technology to provide real-time cost analysis based on machine specifications and operational data. They are designed for large-scale manufacturing environments where efficiency and accuracy are paramount. These tools allow manufacturers to optimize production costs dynamically. However, they may require a higher level of expertise and understanding of automated systems, which can be a barrier for some B2B buyers.
Key Industrial Applications of injection molding cost estimator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Injection Molding Cost Estimator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of interior and exterior plastic components | Reduces manufacturing costs while ensuring high precision and quality | Understanding local regulations, material requirements, and production capacity |
| Consumer Electronics | Manufacturing of housings and components for devices | Streamlines the design-to-production process, enabling faster time-to-market | Compatibility with existing supply chains and technology standards |
| Medical Devices | Creation of precision parts for diagnostic and therapeutic equipment | Ensures compliance with stringent quality standards and lowers costs | Certification of materials and processes, especially for international markets |
| Packaging | Development of custom containers and packaging solutions | Enhances product protection and branding while minimizing waste | Material sourcing and sustainability practices, especially in emerging markets |
| Industrial Equipment | Fabrication of durable components for machinery | Improves reliability and performance, reducing downtime and costs | Access to skilled labor and technology for complex mold designs |
How is the Injection Molding Cost Estimator Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, the injection molding cost estimator plays a crucial role in determining the feasibility of producing various plastic components, such as dashboards, panels, and bumpers. By analyzing the costs associated with tooling and materials, manufacturers can make informed decisions about production volumes and materials. This is particularly important for international buyers from regions like Africa and Europe, where varying regulatory standards and material availability can impact the overall cost structure.
What Benefits Does the Injection Molding Cost Estimator Provide for Consumer Electronics?
For the consumer electronics industry, the estimator aids companies in calculating the costs of producing housings, buttons, and other intricate components. This process helps businesses optimize their designs for manufacturability while keeping production costs low. International buyers must consider factors such as technology compatibility and supply chain logistics, especially in regions like South America where infrastructure may vary.
How Does the Injection Molding Cost Estimator Facilitate Medical Device Manufacturing?
In medical device manufacturing, precision is paramount. The injection molding cost estimator assists in evaluating the costs of producing complex parts that meet stringent regulatory standards. This tool enables manufacturers to balance quality with cost-efficiency, essential for international buyers who need to ensure compliance with local regulations in diverse markets like the Middle East and Europe.
Why is the Injection Molding Cost Estimator Important for Packaging Solutions?
The packaging industry benefits from the injection molding cost estimator by enabling the design and production of custom packaging solutions that enhance product protection and aesthetic appeal. By accurately estimating costs, businesses can minimize waste and optimize material usage. Buyers in emerging markets must focus on sustainability and local material sourcing to ensure competitiveness.
How Can the Injection Molding Cost Estimator Enhance Industrial Equipment Manufacturing?
For industrial equipment manufacturers, the cost estimator is vital in assessing the production of durable components used in machinery. It helps in understanding the cost implications of different materials and tooling methods, ensuring that production remains efficient. International buyers should evaluate the availability of skilled labor and advanced technology to meet the demands of complex mold designs, particularly in regions with varying levels of industrial development.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘injection molding cost estimator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unclear Cost Breakdown for Injection Molding Projects
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find themselves overwhelmed by the complexity of cost structures associated with injection molding. They often struggle to understand how various factors—like mold design, material choice, and production volume—affect the overall cost. This lack of clarity can lead to underestimating project budgets, resulting in financial strain and project delays. Buyers may also face difficulties in comparing estimates from different suppliers without a clear understanding of what each cost component entails.
The Solution: To address this challenge, it is essential to utilize an injection molding cost estimator that offers a detailed breakdown of costs. Buyers should prioritize tools that provide customizable input options for factors such as material types, mold complexity, and production quantities. By inputting specific parameters, buyers can receive a more accurate estimate that reflects their unique project requirements. Additionally, it’s beneficial to request explanations from suppliers regarding their cost components, ensuring that buyers understand each aspect of the estimate. Engaging in discussions with suppliers can also uncover potential areas for cost savings, such as alternative materials or more efficient production processes.
Scenario 2: Variability in Manufacturing Costs Across Regions
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter significant variability in injection molding costs based on geographical location. For example, manufacturers in Africa might face different material and labor costs compared to those in Europe or South America. This regional disparity can lead to confusion when trying to source competitive pricing and may result in unforeseen expenses that can derail project timelines and budgets.
The Solution: To navigate these regional differences effectively, buyers should leverage global injection molding cost estimators that incorporate localized cost data. These estimators can help buyers understand the specific cost implications of sourcing materials and labor in their chosen region. Furthermore, establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions can provide a comparative analysis of costs and capabilities. Buyers should also consider conducting market research to gain insights into prevailing local costs and industry standards. This approach not only aids in accurate budgeting but also allows for better negotiation with suppliers by understanding the market landscape.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Estimating Tooling Costs for Complex Designs
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges B2B buyers face is estimating tooling costs accurately, especially for complex part designs. Many buyers underestimate these costs, which can account for a substantial portion of the overall injection molding budget. This miscalculation often arises from a lack of understanding of the tooling process and the impact of design intricacies on manufacturing costs.
The Solution: To overcome this pain point, buyers should engage with injection molding cost estimators that feature advanced tooling cost breakdowns. When using these tools, buyers should focus on providing detailed specifications for their designs, including dimensions, material selections, and any unique features that may complicate the mold creation. Additionally, collaborating closely with mold makers during the design phase can help identify potential cost-saving measures and alternatives before production begins. Participating in design reviews and utilizing 3D modeling tools can also aid in visualizing complex designs, making it easier to estimate tooling costs accurately. By proactively addressing tooling expenses, buyers can enhance their budgeting accuracy and ensure smoother project execution.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for injection molding cost estimator
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Injection Molding?
When selecting materials for injection molding, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the properties of the materials, their suitability for specific applications, and compliance with regional standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in injection molding: ABS, Polypropylene (PP), Polycarbonate (PC), and Nylon (PA).
How Does ABS Perform in Injection Molding Applications?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a widely used thermoplastic known for its strength and impact resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 80°C and is resistant to many chemicals, making it suitable for various applications, including automotive parts and consumer goods.
Pros: ABS is relatively inexpensive and easy to mold, allowing for complex shapes and designs. It offers good durability and can be finished with various surface treatments.
Cons: However, ABS has lower heat resistance compared to other materials, which may limit its use in high-temperature applications. Additionally, it can be prone to stress cracking under certain conditions.
Impact on Application: ABS is compatible with a wide range of media, making it a versatile choice for many industries. However, its limitations in temperature resistance should be considered when designing products for high-heat environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM for safety and performance. In Europe, DIN standards may apply, particularly for automotive applications.
What Advantages Does Polypropylene Offer for Injection Molding?
Polypropylene (PP) is another popular thermoplastic, known for its excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. It can handle temperatures up to 100°C and is often used in packaging, automotive components, and household goods.
Pros: PP is lightweight, cost-effective, and has a low density, which can reduce shipping costs. It also exhibits good fatigue resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated flexing.
Cons: The main drawback is its lower impact strength compared to ABS, which may not make it suitable for high-stress applications. Additionally, PP can be challenging to bond with adhesives due to its non-polar nature.
Impact on Application: PP’s chemical resistance makes it suitable for applications involving exposure to solvents and acids. However, its lower strength limits its use in structural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with JIS standards in Japan or ASTM in the United States is crucial for ensuring product quality. Buyers should also consider local recycling regulations, as PP is highly recyclable.
Why Choose Polycarbonate for High-Performance Applications?
Polycarbonate (PC) is known for its high impact resistance and transparency, making it suitable for applications like safety glasses, electronic housings, and automotive components. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C.
Pros: PC is exceptionally durable and offers excellent optical clarity, which is beneficial for applications requiring visibility. It also has good dimensional stability.
Cons: However, PC can be more expensive than other thermoplastics, and its susceptibility to UV degradation can limit its outdoor applications unless treated.
Impact on Application: PC is ideal for applications requiring high strength and transparency, such as lenses and protective covers. Its performance in high-temperature environments is also a significant advantage.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe may need to adhere to REACH regulations regarding chemical safety. In the Middle East, understanding local standards for electrical components is vital.
What Are the Benefits of Using Nylon in Injection Molding?
Nylon (Polyamide, PA) is a strong, versatile thermoplastic known for its excellent wear resistance and mechanical properties. It can handle temperatures up to 120°C and is often used in automotive, electrical, and industrial applications.
Pros: Nylon offers high tensile strength and is resistant to abrasion, making it suitable for moving parts and gears. It also has good chemical resistance.
Cons: Its moisture absorption can lead to dimensional changes, which may affect precision in certain applications. Additionally, it can be more costly than other materials.
Impact on Application: Nylon’s strength and durability make it suitable for high-stress applications, but its moisture sensitivity must be considered, particularly in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ISO standards is often required for industrial applications. Buyers should also be aware of local manufacturing capabilities to ensure quality and consistency.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Injection Molding
| Material | Typical Use Case for injection molding cost estimator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Automotive parts, consumer goods | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Lower heat resistance | Low |
| Polypropylene | Packaging, automotive components | Lightweight and chemical resistant | Lower impact strength | Low |
| Polycarbonate | Safety glasses, electronic housings | High durability and clarity | UV degradation susceptibility | High |
| Nylon | Gears, industrial components | High strength and wear resistance | Moisture absorption issues | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions in their injection molding projects, ensuring compliance and suitability for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for injection molding cost estimator
What Are the Main Stages of the Injection Molding Manufacturing Process?
Injection molding is a widely adopted manufacturing process for producing plastic parts, characterized by its efficiency and ability to create complex geometries. The process can be broken down into several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Injection Molding?
The first step in the injection molding process involves the preparation of the raw materials, typically thermoplastics like ABS, PS, or PP. The plastic pellets are dried to remove moisture, which is critical to ensure high-quality parts. Moisture in the pellets can lead to defects such as bubbles or surface imperfections in the final product. After drying, the pellets are fed into an injection molding machine where they are heated until they melt into a viscous liquid.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming. The molten plastic is injected into a precisely designed mold at high pressure. The choice of molding technique can vary based on the complexity of the part and the volume of production. Common techniques include:
- Single-Cavity Molds: Used for lower production volumes, allowing for flexibility and reduced costs.
- Multi-Cavity Molds: Designed for high-volume production, these molds can produce multiple parts in a single cycle, thus optimizing efficiency and reducing per-part costs.
- Hot Runner Systems: These systems keep the plastic in a molten state within the mold, reducing waste and cycle time.
After injection, the material cools and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold.
What Happens During the Assembly and Finishing Processes?
Following the forming stage, parts may undergo assembly if they consist of multiple components. This may involve manual assembly or automated processes, depending on the complexity and volume of parts. After assembly, finishing processes such as trimming, polishing, and coating may be applied to enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of the parts. Techniques like ultrasonic welding or laser engraving can also be utilized for more intricate designs.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Injection Molding?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the injection molding process to ensure that the final products meet industry standards and customer specifications. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, while industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for the European market or API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications may be required based on the application of the molded parts.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Injection Molding?
Quality control (QC) in injection molding typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting the raw materials before they enter the production process. Testing for material properties and verifying certifications are essential steps.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the molding process, operators monitor various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cycle time. Statistical process control (SPC) techniques can be employed to detect variations and ensure consistency.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once parts are produced, they undergo final inspections and testing. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests to ensure they meet the required specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from international suppliers, verifying the quality control processes of potential partners is vital. Here are several strategies to ensure supplier quality:
What Steps Can Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits can provide insights into a manufacturer’s quality assurance processes. Buyers can assess the supplier’s facilities, equipment, and adherence to quality standards. An audit checklist may include:
- Review of quality management systems and certifications.
- Evaluation of equipment calibration and maintenance records.
- Observation of production processes and employee training programs.
How Important Are Quality Assurance Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Requesting quality assurance reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC measures and outcomes. These reports should detail any non-conformities and corrective actions taken. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. These inspections may occur at various stages of production, ensuring compliance with agreed specifications before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing from international suppliers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of several nuances:
- Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Different regions may have varying interpretations of quality. It’s essential for buyers to communicate their specific requirements clearly and ensure that suppliers understand the expectations.
- Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks such as damage during transit. Buyers should discuss how suppliers handle packaging and logistics to mitigate these risks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have different regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with both local and international regulations relevant to their products.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of the injection molding manufacturing process and its quality assurance practices is vital for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains. By familiarizing themselves with the manufacturing stages, implementing robust QC measures, and verifying supplier practices, buyers can significantly reduce risks and enhance product quality. This proactive approach not only fosters stronger supplier relationships but also ensures that the final products meet the high standards expected in today’s competitive global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘injection molding cost estimator’
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of injection molding cost estimation is vital for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their manufacturing processes. This guide provides a practical checklist to help you efficiently source an injection molding cost estimator, ensuring you understand the costs involved and make informed decisions that align with your business goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements of your project, including part geometry, material types, and production volumes. This step is crucial because the accuracy of your cost estimate heavily relies on detailed specifications. Providing precise information allows estimators to calculate costs that reflect your project’s unique needs.
Step 2: Identify Your Budget Constraints
Establish a clear budget for your injection molding project. Understanding your financial limitations helps narrow down options and facilitates discussions with potential suppliers. Consider not only the initial costs but also long-term expenses such as maintenance and material procurement.
Step 3: Research Available Cost Estimators
Explore various injection molding cost estimation tools available in the market. Look for online platforms that offer user-friendly interfaces and customizable features, allowing you to input specific parameters related to your project. A comprehensive cost estimator should provide insights into tooling costs, material costs, and production costs.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the capabilities of potential suppliers who provide cost estimation services. Inquire about their experience in your industry and their familiarity with your specific requirements. This evaluation is essential to ensure that the supplier can deliver accurate and relevant estimates based on your project’s needs.
- Request Samples or Case Studies: Ask for previous estimates or projects similar to yours to gauge the supplier’s proficiency.
- Check References: Reach out to previous clients to understand their experiences and satisfaction levels.
Step 5: Verify Technological Competence
Ensure that the supplier utilizes advanced technology in their estimation process. Modern software solutions can significantly improve the accuracy and speed of cost estimations. Look for suppliers who use updated tools that can simulate various manufacturing scenarios and provide real-time data.
Step 6: Confirm Transparency in Pricing
Seek suppliers who offer transparent pricing structures with no hidden fees. A reliable cost estimator should break down costs into clear categories, such as tooling, materials, and labor. Transparency builds trust and allows you to understand exactly what you are paying for.
Step 7: Assess Post-Estimation Support
Consider the level of support provided after the estimation process. A good supplier should offer assistance in interpreting estimates and provide guidance on optimizing costs. This ongoing support can be invaluable, particularly if adjustments are needed during the manufacturing phase.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the procurement of an injection molding cost estimator, ensuring that you select a solution that meets your needs and helps streamline your manufacturing processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for injection molding cost estimator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Injection Molding?
When estimating costs for injection molding, several critical components contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary cost drivers include:
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts costs. Thermoplastics such as ABS, PP, and PS are commonly used, with prices fluctuating based on market conditions. Specialty materials or reinforced composites will elevate costs due to their unique properties.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs represent one of the most significant fixed expenses in injection molding. The complexity of the mold design, the material used (e.g., aluminum vs. steel), and the method of creation (CNC machining, EDM, or 3D printing) all influence tooling costs. These can range from a few hundred dollars for low-volume molds to over $100,000 for complex, high-volume applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with machine operation, setup, and maintenance. Automation trends are decreasing labor intensity, but skilled operators remain essential, especially for complex projects.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, facility costs, and administrative expenses. Overhead can vary widely depending on the geographical location of the manufacturer and their operational efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet specified tolerances and quality standards incurs additional costs. QC processes can include material testing, inspection during production, and final audits, which are crucial for industries requiring certifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are particularly relevant for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms can significantly influence overall logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins typically range from 10% to 30%, depending on the market, competition, and the unique value proposition of the supplier. Understanding these margins can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Injection Molding Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in injection molding, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
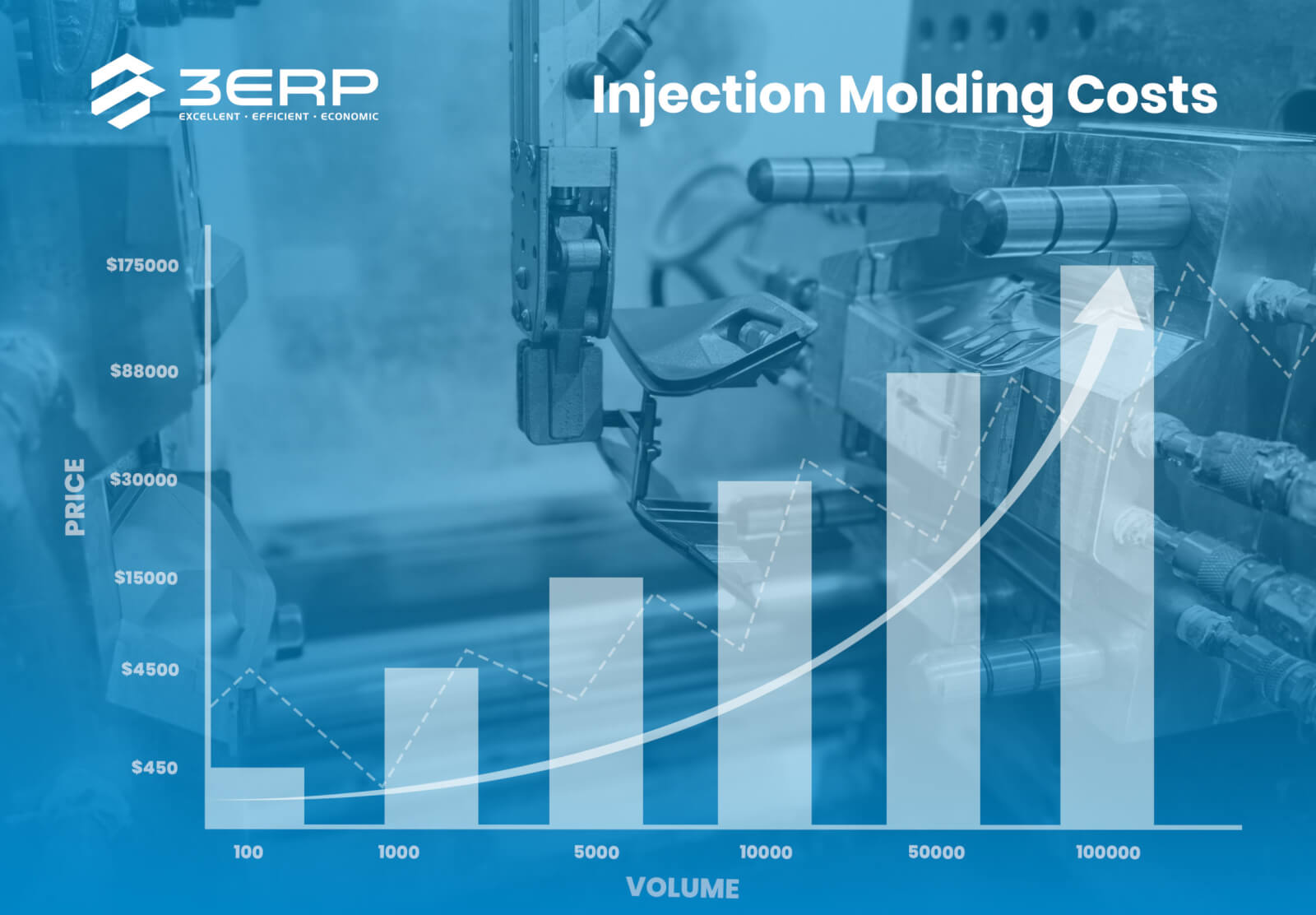
Volume/MOQ: The quantity of parts ordered directly affects cost per unit. Higher volumes generally lead to lower costs per part due to the distribution of fixed costs over a larger production run.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications can increase both tooling and production costs. Buyers should provide detailed specifications to receive accurate estimates.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material not only impacts the initial cost but also affects durability and performance, which can influence long-term costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Industries such as automotive and medical require stringent quality standards. Parts that need specific certifications may incur higher costs due to additional testing and compliance measures.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can influence pricing. It’s beneficial to consider suppliers with established track records in similar projects.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions as they define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact total costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Injection Molding?
To ensure cost-efficiency in injection molding projects, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing structures and potential discounts for larger orders. Transparency about budget constraints can lead to mutually beneficial agreements.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial pricing, consider long-term costs associated with maintenance, replacement, and potential operational efficiencies. A slightly higher initial investment may yield significant savings over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: For international buyers, being aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions can aid in better budgeting and negotiations.
-
Engage Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from several suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify competitive pricing. It also allows buyers to compare capabilities and reliability.
-
Plan for Volume: If feasible, consolidate orders to achieve better pricing. This approach can significantly reduce per-unit costs and improve supplier relationships.
Disclaimer on Pricing Estimates
It’s important to note that the costs and pricing discussed are indicative and may vary based on specific manufacturer practices, geographical factors, and market conditions. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and request detailed quotes tailored to their unique projects.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing injection molding cost estimator With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions for Injection Molding Cost Estimation
In the realm of manufacturing, particularly for plastic parts, choosing the right cost estimation method is crucial for optimizing budgets and enhancing production efficiency. While the injection molding cost estimator offers a comprehensive approach to understanding costs, various alternatives also exist that may cater to specific business needs. This analysis provides a comparison of the injection molding cost estimator against two viable alternatives: manual cost estimation and 3D printing cost estimation.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Injection Molding Cost Estimator | Manual Cost Estimation | 3D Printing Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy with data-driven insights | Variable accuracy depending on expertise | Moderate accuracy; relies on model quality |
| Cost | Generally low with free or subscription models | Potentially high if hiring experts | Varies widely; low for prototyping, high for production |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly online tools available | Time-consuming; requires expertise | Simple for prototyping; complex for production |
| Maintenance | Minimal; requires updates based on market changes | None; relies on user knowledge | Regular updates needed for software and hardware |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production with detailed part specifications | Small projects or custom parts needing expert insight | Rapid prototyping and low-volume runs |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Manual Cost Estimation?
Manual cost estimation involves calculating costs based on historical data, expert opinions, and industry standards. The primary advantage of this method is its flexibility. Businesses can tailor estimates to their unique specifications and production conditions. However, this approach can be highly variable in accuracy, heavily reliant on the estimator’s expertise, and often time-consuming. For companies in regions where skilled labor is scarce, such as parts of Africa or South America, this method may not be the most efficient.
How Does 3D Printing Cost Estimation Compare?
3D printing cost estimation offers a modern alternative for businesses looking to prototype or produce small batches of parts. This method is particularly advantageous for rapid prototyping, as it allows for quick iterations and adjustments without the need for extensive tooling costs. However, while initial costs for prototyping can be low, scaling up production can become expensive, especially for complex designs. Additionally, the accuracy of cost estimates can vary based on the quality of the 3D model and the printing technology used. This method is ideal for companies in Europe or the Middle East focusing on innovation and quick turnaround times but may not suit high-volume production needs.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate cost estimation method, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific production needs, budget constraints, and the complexity of the parts involved. For high-volume production with intricate designs, the injection molding cost estimator is likely the most effective option due to its accuracy and efficiency in cost breakdowns. Conversely, for smaller projects or rapid prototyping, manual estimation or 3D printing may offer the flexibility and speed required. Ultimately, the decision should align with the overall business strategy, market conditions, and the technical capabilities of the organization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for injection molding cost estimator
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Injection Molding Cost Estimation?
Understanding the technical properties associated with injection molding is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of plastic or composite used in the injection molding process. Common materials include ABS, Polycarbonate (PC), and Polypropylene (PP). Each material has distinct properties, such as strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance. The choice of material affects not only the cost but also the performance of the final product. For instance, selecting a high-grade material might increase initial costs but can result in better durability and a longer product lifespan, which is a significant consideration for OEMs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the molded part. It is expressed as a range (e.g., ±0.01mm) and is critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assembly. Tight tolerances can increase tooling costs and manufacturing complexity, but they are essential for applications requiring precision, such as in automotive or aerospace sectors. Buyers need to understand the tolerance levels needed for their specific applications to avoid costly reworks.
3. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time it takes to complete one injection molding cycle, including injection, cooling, and ejection. Shorter cycle times lead to higher production efficiency and lower per-part costs. However, achieving reduced cycle times often requires advanced machinery and optimized processes. Understanding cycle time is essential for buyers to estimate production capacity and timelines accurately, which can impact inventory management and delivery schedules.
4. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and quality of the final product’s surface. Common finishes include matte, glossy, or textured. The desired surface finish affects both the mold design and the post-processing requirements, which can add to overall costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their surface finish requirements to ensure that the final product meets their aesthetic and functional expectations.
5. Draft Angle
Draft angle is the angle that is added to the vertical walls of a mold to facilitate the easy removal of the molded part. A proper draft angle reduces wear on the mold and minimizes defects in the finished product. Understanding the required draft angle is crucial for cost estimation, as it can influence mold design complexity and manufacturing costs.
What Are Common Terms Used in Injection Molding Cost Estimation?
Familiarity with industry terminology can help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of injection molding. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the injection molding context, OEMs often specify the design and material requirements for parts they need. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure that their parts meet the necessary specifications and quality standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In injection molding, MOQs can vary significantly based on tooling and production costs. Buyers should consider MOQs when planning their production volumes to ensure they meet their budget and inventory needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a detailed quote for specific products or services. This process is critical in injection molding for obtaining accurate cost estimates based on material, labor, and tooling requirements. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ can lead to more competitive pricing and better supplier relationships.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaging in cross-border transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thus impacting overall costs.
5. Tooling Cost
Tooling cost refers to the expenses associated with creating the molds used in the injection molding process. These costs can vary widely based on the complexity of the design and the materials used. Understanding tooling costs is vital for buyers, as they often represent the most significant upfront investment in injection molding projects.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes, ensuring they achieve optimal results from their injection molding projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the injection molding cost estimator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Injection Molding Cost Estimators?
The injection molding cost estimator sector is experiencing a transformative phase driven by technological advancements, global market shifts, and evolving buyer needs. One of the most significant drivers is the growing demand for customized, high-quality plastic parts across various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and healthcare. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek competitive advantages, they are increasingly relying on accurate cost estimation tools to evaluate production feasibility and budget constraints.
Emerging trends in this sector include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in cost estimation software. These technologies enhance the accuracy of cost predictions by analyzing vast datasets that reflect real-time market conditions. Moreover, there is a notable shift toward digital platforms that offer comprehensive online estimators, allowing buyers to customize inputs based on part geometry, material costs, and production volume. This shift not only streamlines the procurement process but also facilitates quicker decision-making.
Additionally, international buyers are becoming more conscious of supply chain transparency and the implications of sourcing decisions. With the rise of global trade tensions and regional economic fluctuations, companies are evaluating local versus offshore manufacturing options. This trend underscores the importance of understanding local market dynamics, including labor costs, material availability, and regulatory considerations, which can significantly impact overall project costs.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence Injection Molding Cost Estimators?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point for B2B buyers in the injection molding sector. The environmental impact of plastic production and disposal has prompted businesses to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. As a result, ethical sourcing has gained importance, with companies looking for partners that can demonstrate responsible material sourcing and manufacturing processes.
Buyers are now more inclined to work with suppliers who have obtained ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or certifications for using recycled materials. These certifications not only reflect a commitment to sustainability but can also enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
Moreover, the use of biodegradable materials and innovative recycling technologies is becoming a competitive advantage. By leveraging sustainable materials in the injection molding process, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and potentially lower costs associated with waste management and compliance with environmental regulations. As a result, integrating sustainability into cost estimators is essential for businesses looking to align their operations with modern environmental standards while maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
How Has the Injection Molding Cost Estimator Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the injection molding cost estimator sector mirrors advancements in manufacturing technology and shifts in global market demands. Initially, the estimation process relied heavily on manual calculations and basic spreadsheets, which often led to inaccuracies and inefficiencies. However, with the advent of computer-aided design (CAD) software and digital tools, the industry saw a significant transformation.
In recent years, the introduction of advanced cost estimation platforms has further streamlined this process. These platforms enable real-time cost analysis by integrating various parameters such as material prices, production techniques, and machine costs. This evolution has not only improved accuracy but has also enhanced the ability of international B2B buyers to make informed decisions quickly.
Additionally, the rise of globalization and the expansion of supply chains have prompted buyers to seek more sophisticated solutions that consider multiple factors affecting cost, including geopolitical risks and regional economic conditions. Today, the focus is not just on cost minimization but also on value creation through strategic partnerships and sustainable practices, marking a significant shift in the landscape of the injection molding cost estimator sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of injection molding cost estimator
-
How do I calculate the total cost of injection molding?
To calculate the total cost of injection molding, consider three main components: tooling costs, material costs, and production costs. Tooling costs refer to the expenses associated with creating the mold, which can vary significantly based on complexity and material. Material costs depend on the type of plastic used, while production costs include labor, machine operation, and overhead. Using a cost estimator can streamline this process by allowing you to input specific parameters, such as part geometry and production volume, to generate a detailed cost breakdown. -
What is the best way to estimate injection molding costs for my project?
The best way to estimate injection molding costs is to utilize an online cost estimator designed for this purpose. These tools require you to input key variables, including part dimensions, material type, and expected production volume. They provide a comprehensive cost analysis, including tooling, material, and production costs. Additionally, consulting with experienced manufacturers can provide valuable insights tailored to your specific project requirements and help refine your estimates. -
What factors should I consider when selecting a supplier for injection molding?
When selecting a supplier for injection molding, consider their experience, quality certifications, and production capabilities. Evaluate their portfolio for similar projects and client testimonials to gauge reliability. It’s also essential to assess their communication practices and responsiveness, as these can significantly impact project success. Furthermore, inquire about their ability to meet your specific needs regarding customization, lead times, and minimum order quantities (MOQs) to ensure alignment with your business goals. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for injection molding?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for injection molding can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the part. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 100 units for low-volume production to several thousand units for high-volume runs. Discussing your specific project requirements with potential suppliers is crucial, as many may offer flexibility or alternative solutions, such as using 3D printed molds for lower quantities, which can help reduce initial investment costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in injection molding projects?
To ensure quality assurance in injection molding projects, establish clear specifications and standards for your parts upfront. Work closely with your supplier to implement rigorous QA processes, including regular inspections and testing of prototypes before full-scale production. Request documentation of their quality control measures, such as ISO certifications, and consider utilizing third-party inspection services for additional assurance. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks associated with defects and ensures that the final products meet your quality expectations. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with injection molding suppliers?
Payment terms for injection molding suppliers can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (usually 30-50% of the total cost) followed by the balance upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer payment plans based on milestones in the production process. It’s essential to discuss and negotiate payment terms during the initial discussions to ensure clarity and avoid potential misunderstandings later in the project. -
How do international trade regulations affect injection molding sourcing?
International trade regulations can significantly impact injection molding sourcing, particularly concerning tariffs, customs duties, and compliance with local laws. Buyers must be aware of import/export regulations in their home country and the supplier’s country, as these can affect overall costs and lead times. Additionally, understanding trade agreements that may apply can help minimize tariffs and facilitate smoother transactions. Engaging with trade experts or consultants can provide valuable insights into navigating these complexities effectively. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for injection molding shipments?
Logistics considerations for injection molding shipments include shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance processes. Choose a shipping method that balances cost and delivery speed based on your project timeline. It’s crucial to plan for potential delays in customs by ensuring all documentation is accurate and complete. Additionally, consider the supplier’s location relative to your operations, as this can affect shipping costs and delivery times. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can also help streamline the process and mitigate risks associated with international shipping.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Injection Molding Cost Estimator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CustomPartNet – Injection Molding Cost Estimator
Domain: custompartnet.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Injection Molding Cost Estimator, Features: Rapid tooling options, Material options (e.g., Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)), Basic shapes (Cube, Cylinder, Disk, Hollow box, Hollow tube, Sheet, Sphere), Containers and covers (Caps, Enclosures, Liquid containers, Panels, Storage containers), Fasteners (Clamps, Connectors, Inserts, Spacers, Threaded fasteners), Interfaces (Handles, Pedals, Swit…
2. Reddit – Product Specifications
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Dimensions: 330.0×330.0×150.0 mm; Weight: approximately 0.5 kg; Manufacturing cost: $6.85 per part; Tooling cost: $15,760; Estimated cost per part for 8000 units: around $9.
3. ULProspector – CostMate® Injection Molding Calculator
Domain: ulprospector.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: CostMate® is an injection molding calculator designed to help accurately estimate the cost of producing injection molded parts. Key features include: monthly and annual subscriptions, profit calculation based on total quote price or actual costs, the ability to add material quantities, profit, and material cost per lb, report generation for material price, machine and secondary costs, and total qu…
4. TruMould – Instant Injection Molding Quotes
Domain: app.trumould.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Instant Injection Molding Quotes Online, Free Cost Estimator, Capabilities include Injection Mold, Insert Molding, Thin Wall Injection Molding, Over Molding, Plastic Parts Manufacturing. Features include On Demand Injection Molding, Clean room injection molding, various mold types (Stack Mold, Family Mold, Hot Runner Mold, 3 Plate Mold, 2 Plate Mold). Quoting process involves uploading .STEP or .S…
5. In3DTEC – Injection Molding Insights
Domain: in3dtec.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Injection molding is a manufacturing technique favored for mass production of plastic parts. Key factors affecting injection molding costs include: 1. Part Costs: Influenced by part size, complexity, and design for manufacturability (DFM). 2. Tooling Costs: Determined by mold manufacturing process (3D printing, CNC machining, EDM machining), mold material (aluminum or steel), mold complexity, and …
6. IDSys – Injection Molding Cost Estimator
Domain: idsys.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Injection Molding Part Cost Calculator: A tool to estimate manufacturing costs for plastic injection molded parts. Key features include:
– Estimates total costs for budgetary purposes during project planning and part design.
– Simplified for quick ballpark cost determination, focusing on material and processing costs.
– Factors affecting costs: number of inserts, post-decorating operations, CNC…
7. Phas – Injection Molding Essentials
Domain: phas.io
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Injection molding is a manufacturing process for mass production of plastic parts with consistent quality and precision. Key components influencing costs include: 1. Material Costs: The cost of plastic resin varies by type and affects overall expenses. 2. Tooling Costs: Involves mold creation, influenced by complexity and material choice. 3. Production Time: Cycle time impacts labor and machine co…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for injection molding cost estimator
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Injection Molding Cost Estimation?
In conclusion, leveraging a comprehensive injection molding cost estimator is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their manufacturing processes. Understanding the various cost drivers—such as mold complexity, material selection, and production volume—enables informed decision-making that can significantly reduce overall expenses. By strategically sourcing suppliers and technologies, companies can access competitive pricing and innovative solutions tailored to their specific needs.
The value of strategic sourcing extends beyond immediate cost savings; it fosters long-term partnerships and enhances supply chain resilience. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize collaboration with reputable manufacturers who can deliver quality and efficiency, especially as global market dynamics continue to evolve.
As you navigate the complexities of injection molding, consider utilizing advanced cost estimation tools to forecast expenses accurately. Engaging with industry experts and exploring diverse sourcing options will empower your business to remain competitive in a fast-paced marketplace. Take the next step towards optimizing your production capabilities—start evaluating your injection molding needs today and embrace the potential for growth and innovation.