Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial machine parts
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing high-quality industrial machine parts poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The complexities of navigating global supply chains, ensuring product compatibility, and managing costs can overwhelm even the most seasoned procurement professionals. This guide is designed to demystify the landscape of industrial machine parts, offering a comprehensive overview of various types, applications, and essential considerations for sourcing effectively.
From buffing and grinding machines to hydraulic presses and metal fabrication equipment, the diversity of industrial machine parts can be daunting. This guide explores critical aspects such as supplier vetting, quality assurance, and cost management strategies, equipping international buyers with the tools necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. With insights tailored specifically for markets in Brazil, Nigeria, and beyond, this resource empowers businesses to streamline their procurement processes and enhance operational efficiency.
By understanding the nuances of the global market for industrial machine parts, buyers can mitigate risks associated with sourcing and ensure they are investing in reliable, high-performance equipment. This guide serves as a strategic companion, helping businesses navigate the complexities of procurement while capitalizing on opportunities for growth and innovation.
Understanding industrial machine parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buffing & Grinding Machines | Used for polishing and shaping materials; includes various wheel types. | Metalworking, automotive, woodworking | Pros: Enhances surface finish; versatile. Cons: Requires skilled operators; maintenance-intensive. |
| Milling Machines | Employs rotary cutting tools to shape and add features to workpieces. | Aerospace, automotive, manufacturing | Pros: High precision; adaptable to various materials. Cons: High initial investment; needs regular calibration. |
| Hydraulic Presses | Utilizes hydraulic force for shaping, flattening, and stamping. | Metal fabrication, automotive, plastics | Pros: Powerful and efficient; minimal manual effort. Cons: Space-intensive; potential for hydraulic leaks. |
| Industrial Sewing Machines | Designed for heavy fabrics; includes walking foot and serger types. | Textiles, upholstery, leather goods | Pros: High-speed production; durable. Cons: Specialized parts may be costly; requires operator training. |
| Waterjet Cutting Machines | Uses high-pressure water streams for cutting; suitable for intricate designs. | Aerospace, automotive, stone cutting | Pros: No heat-affected zone; versatile materials. Cons: Higher operational costs; requires water management. |
What Are Buffing & Grinding Machines and Their B2B Relevance?
Buffing and grinding machines are essential in metalworking and fabrication processes, known for their ability to enhance surface finishes and shape materials. These machines come equipped with various wheel types tailored for specific applications, from sharpening edges to polishing surfaces. For B2B buyers, the versatility of these machines allows for a broad range of uses in industries such as automotive and woodworking. However, they necessitate skilled operators for optimal performance and can be maintenance-intensive, which is a crucial consideration in budgeting and workforce training.
How Do Milling Machines Benefit Different Industries?
Milling machines are vital tools in various sectors, including aerospace and automotive, for their ability to create complex shapes and features with high precision. Utilizing rotary cutting tools, they can handle a wide range of materials, making them adaptable for different manufacturing needs. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and ongoing calibration needs, as these machines require regular maintenance to ensure accuracy. Investing in a milling machine can significantly enhance production capabilities but requires careful consideration of operational costs and workforce expertise.
What Are the Advantages of Hydraulic Presses in Manufacturing?
Hydraulic presses are powerful machines that apply significant force to shape, flatten, or stamp materials, making them indispensable in metal fabrication and the automotive industry. Their efficiency and minimal manual effort required for operation make them appealing to B2B buyers looking to improve productivity. However, potential hydraulic leaks and the need for adequate space can pose challenges. Buyers should weigh these factors against the significant advantages of increased production speed and reduced labor costs.
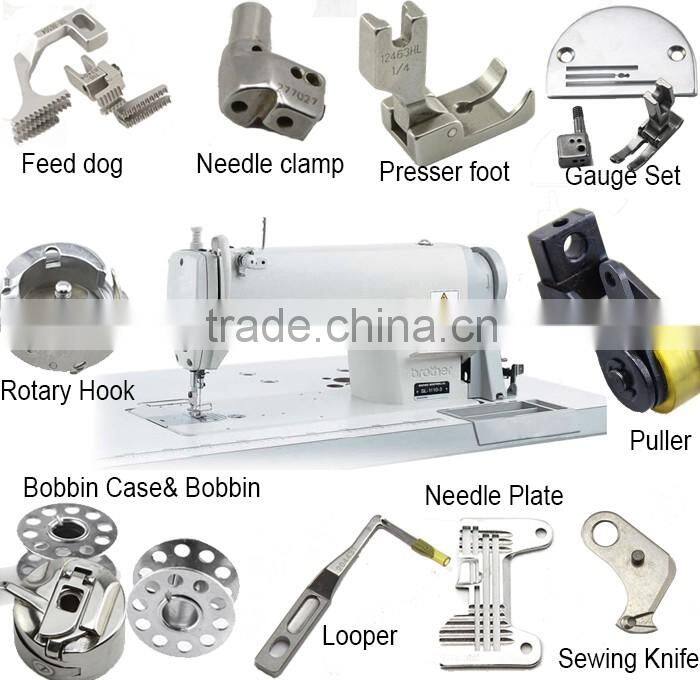
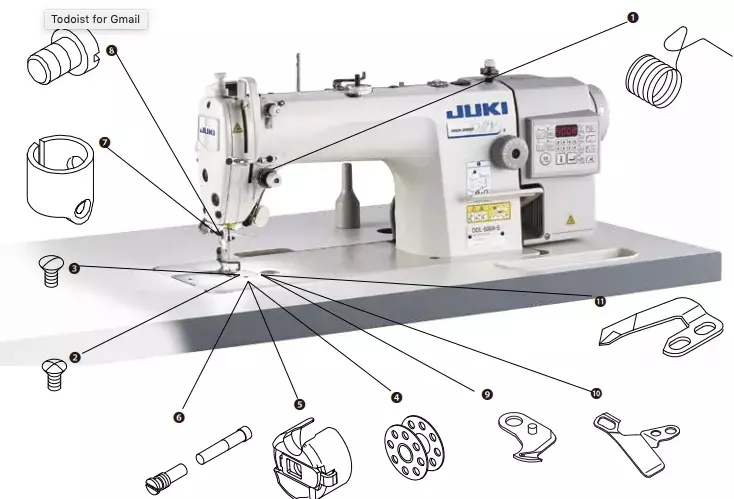
Why Are Industrial Sewing Machines Important for Textile Production?
Industrial sewing machines are designed for high-volume production, particularly in textiles and upholstery. Models such as walking foot machines and sergers are built to handle heavy fabrics, ensuring durability and speed in manufacturing. B2B buyers in the textile industry must consider the specialized parts and potential costs associated with maintenance, alongside the need for operator training to maximize efficiency. These machines are crucial for businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge in fast-paced production environments.
What Makes Waterjet Cutting Machines a Unique Option?
Waterjet cutting machines stand out due to their ability to cut a wide variety of materials without creating a heat-affected zone, making them ideal for intricate designs in sectors like aerospace and stone cutting. Their versatility allows B2B buyers to explore a range of applications, but operational costs can be higher compared to traditional cutting methods. Additionally, effective water management is essential to ensure sustainability and efficiency in operations. Understanding these dynamics is vital for businesses considering waterjet technology for their manufacturing processes.
Key Industrial Applications of industrial machine parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industrial machine parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Metal fabrication and machining | Enhanced precision and efficiency in production | Quality certifications, local availability, lead times |
| Textile and Apparel | Industrial sewing machine components | Improved production speed and quality | Compatibility with existing machines, durability |
| Construction and Heavy Equipment | Hydraulic presses and leveling components | Increased safety and operational effectiveness | Load capacity, material specifications, service support |
| Food and Beverage | Processing machinery parts for food packaging | Compliance with safety standards and reduced waste | Regulatory compliance, hygiene standards, sourcing reliability |
| Automotive | Engine components and assembly line machinery | Streamlined production and reduced downtime | OEM specifications, warranty terms, after-sales support |
How Are Industrial Machine Parts Utilized in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, industrial machine parts such as milling machines and hydraulic presses are critical for metal fabrication and machining. These components enhance precision and efficiency, allowing manufacturers to produce high-quality parts with minimal waste. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that offer quality certifications and local availability to ensure timely delivery and compliance with industry standards, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where logistics can be challenging.
What Role Do Industrial Sewing Machine Parts Play in Textile and Apparel Production?
In the textile and apparel industry, components like presser feet, needles, and bobbins for industrial sewing machines significantly boost production speed and quality. These parts ensure that stitching is consistent and durable, which is vital for maintaining product integrity. B2B buyers need to consider the compatibility of these parts with their existing machinery and the durability of materials, especially when sourcing from international suppliers in Europe or the Middle East.
How Are Industrial Machine Parts Used in Construction and Heavy Equipment?
Hydraulic presses and leveling components are essential in the construction and heavy equipment sectors, where they facilitate shaping and assembling materials safely and efficiently. These machine parts contribute to increased safety and operational effectiveness on job sites. When sourcing these components, businesses should focus on load capacity, material specifications, and the availability of service support, particularly in developing markets where equipment reliability is crucial.
What Are the Applications of Industrial Machine Parts in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, machine parts used in processing and packaging machinery must comply with stringent safety and hygiene standards. This ensures that products are safe for consumption while minimizing waste during production. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that understand regulatory compliance and can provide parts that meet hygiene standards, especially in regions with varying regulations like Africa and South America.
How Do Automotive Applications Benefit from Industrial Machine Parts?
In the automotive industry, components such as engine parts and assembly line machinery are vital for streamlining production and reducing downtime. These industrial machine parts enhance the overall efficiency of manufacturing processes. Buyers should consider OEM specifications, warranty terms, and after-sales support when sourcing parts, as these factors can significantly impact the long-term performance and reliability of automotive manufacturing operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘industrial machine parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Supply Chain Disruptions Impacting Production Timelines
The Problem: In the fast-paced world of industrial manufacturing, timely access to machine parts is crucial. Many B2B buyers face significant challenges when suppliers experience delays due to global supply chain disruptions. This can lead to halted production lines, missed deadlines, and increased operational costs. For instance, a manufacturer in Brazil might rely on specific hydraulic press components that are suddenly backordered, causing a ripple effect throughout their production schedule. These delays not only impact immediate operations but can also tarnish relationships with customers who expect timely delivery of finished products.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions, B2B buyers should establish strong relationships with multiple suppliers, both local and international. Diversifying the supplier base can provide alternative options when one source faces delays. Additionally, investing in inventory management systems can help track lead times and reorder levels effectively. Buyers should also consider engaging in proactive communication with suppliers to gain insights into potential disruptions and plan accordingly. By maintaining a buffer stock of critical components and using predictive analytics to forecast demand, businesses can better prepare for unexpected shortages and keep production flowing smoothly.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing Compatible Parts Across Different Machinery Brands
The Problem: Many industrial operations utilize machinery from various manufacturers, leading to challenges in sourcing compatible machine parts. A B2B buyer in Nigeria might find themselves in a bind when a specific part for a lathe from one brand is incompatible with another brand’s specifications, leading to downtime and frustration. The lack of standardization in parts can complicate maintenance and repair efforts, resulting in lost productivity and increased costs.
The Solution: To address compatibility issues, buyers should invest time in understanding the specifications and standards of the machinery they operate. Creating a detailed inventory of existing equipment and its parts can help in identifying compatible components from different manufacturers. Utilizing online catalogs and databases that offer cross-reference capabilities for machine parts can also streamline the sourcing process. Furthermore, establishing partnerships with suppliers who specialize in multi-brand compatibility can provide buyers with tailored solutions that ensure they have the right parts on hand when needed. This approach not only improves maintenance efficiency but also reduces overall operational costs.
Scenario 3: Lack of Knowledge on Proper Installation and Maintenance of Machine Parts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties not just in procuring parts, but also in the installation and ongoing maintenance of those components. For example, a manufacturing facility in Europe may purchase a new milling machine but lacks the in-house expertise to properly install and calibrate the machine parts. This can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased wear and tear, and ultimately higher costs due to improper functioning of the equipment.
The Solution: To overcome this knowledge gap, it is essential for buyers to invest in training and support services when procuring industrial machine parts. Many suppliers offer installation guides, training sessions, or even on-site support to ensure proper setup and maintenance of equipment. Buyers should take advantage of these resources to empower their teams with the knowledge they need. Additionally, forming a relationship with a trusted maintenance service provider can provide ongoing support and troubleshooting assistance. By prioritizing proper installation and regular maintenance, businesses can enhance equipment longevity and performance, leading to reduced downtime and cost savings in the long run.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial machine parts
When selecting materials for industrial machine parts, several factors come into play, including performance characteristics, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the production of industrial machine parts, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Steel for Industrial Machine Parts?
Steel is a widely used material in industrial applications due to its excellent mechanical properties. It exhibits high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for parts that must withstand significant stress and wear. Steel also has good temperature resistance, allowing it to perform well in high-heat environments. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can be a drawback unless it is treated or alloyed.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of steel is its strength and versatility, which makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from structural components to precision parts. On the downside, the cost of high-quality steel can be considerable, and its weight may impact the overall design and efficiency of machinery.
Impact on Application:
Steel’s compatibility with various media, including oils and greases, makes it a preferred choice in many industrial settings. However, specific applications may require stainless steel or other alloys to enhance corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local steel standards and certifications, such as ASTM or EN. Compliance with these standards can affect both the quality and marketability of the end product.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Industrial Machine Parts?
Aluminum is known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making it ideal for applications where weight savings are critical. It also has good thermal and electrical conductivity, which is beneficial in specific machinery applications.
Pros and Cons:
The key advantage of aluminum is its low density, which can lead to energy savings in transport and operation. However, aluminum may not be as strong as steel, limiting its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, the manufacturing processes for aluminum can be more complex and costly.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum’s resistance to oxidation makes it suitable for parts exposed to moisture or corrosive environments. However, it may not perform well in high-temperature applications without alloying.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, such as the Middle East, aluminum parts may be preferred. Buyers should ensure that the aluminum grades meet international standards like JIS or ASTM.
What are the Benefits of Using Plastics in Industrial Machine Parts?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics like polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in industrial applications due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. They can also be molded into complex shapes, offering design flexibility.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of plastics is their resistance to corrosion and chemicals, making them suitable for various environments. However, they generally have lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which can limit their use in high-load applications. Additionally, the thermal stability of plastics can vary significantly based on the type.
Impact on Application:
Plastics are often used in applications where electrical insulation is required or where weight is a concern. They are compatible with various media, but their performance can degrade under extreme temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific plastic grades and their compliance with international standards, especially in regions like Europe, where regulations on material safety are stringent.
How Does Cast Iron Perform as a Material for Industrial Machine Parts?
Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and good machinability, making it suitable for parts that experience high friction and wear. It can withstand high temperatures and has good damping properties, which can reduce vibration.
Pros and Cons:
The main advantage of cast iron is its durability and ability to absorb shock, making it ideal for heavy machinery components. However, it is relatively brittle compared to other materials, which can lead to cracking under extreme stress.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is commonly used in applications such as engine blocks and machine bases, where strength and stability are crucial. Its compatibility with lubricants and oils enhances its performance in mechanical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should consider the availability of specific grades of cast iron and their compliance with local standards, as this can impact the manufacturing process and final product quality.
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial machine parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, precision parts | High strength and versatility | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components, heat exchangers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Plastics | Insulating parts, lightweight applications | Corrosion-resistant and flexible | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Cast Iron | Engine blocks, machine bases | Excellent wear resistance | Brittle under extreme stress | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial machine parts
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Industrial Machine Parts?
The manufacturing of industrial machine parts is a complex process that involves several critical stages. Each stage requires precise execution to ensure that the final product meets the necessary specifications and quality standards.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in manufacturing industrial machine parts is material preparation. This involves selecting the right materials based on the part’s application and the desired mechanical properties. Common materials include metals like steel, aluminum, and alloys, as well as plastics and composites for specific applications.
Once selected, raw materials undergo various processes such as cutting, shearing, and deburring to achieve the required dimensions and surface finishes. Techniques like laser cutting and waterjet cutting are often employed for their precision and ability to handle complex geometries. B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust material selection and preparation protocols to avoid material-related failures in the final products.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Industrial Parts?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming, where the raw materials are shaped into the desired forms. Several techniques are commonly utilized:
- Machining: This includes processes such as milling, turning, and drilling, where rotary tools are used to remove material and create precise shapes and features.
- Casting: Metal is poured into a mold to create complex shapes, which is particularly useful for parts that require intricate designs.
- Forging: This technique involves shaping metal using compressive forces, enhancing the material’s strength through work hardening.
- Welding and Fabrication: These methods join different parts together, creating assemblies that are often stronger than the individual components.
Understanding these techniques allows B2B buyers to assess whether a supplier has the appropriate capabilities for their specific needs.
Assembly: How Are Different Components Joined Together?
The assembly stage is crucial for creating the final product. It involves fitting together various parts and components, which may have been manufactured separately. This can include processes like:
- Mechanical Assembly: Utilizing fasteners such as bolts and screws.
- Adhesive Bonding: Using adhesives for parts where welding or mechanical fastening is impractical.
- Quality Checks During Assembly: Implementing checks at various points ensures that components fit correctly and function as intended.
B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly techniques employed by their suppliers, as this can significantly affect the durability and performance of the final product.
Finishing: What Processes Enhance the Quality and Appearance of Parts?
Finishing processes are employed to enhance the surface quality and performance of industrial machine parts. These may include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as anodizing, plating, and powder coating protect against corrosion and improve aesthetics.
- Polishing and Grinding: These processes achieve desired surface finishes, which can be critical for certain applications.
- Inspection: Final inspections often occur after finishing to ensure that parts meet the required specifications.
Buyers should confirm that suppliers have established finishing protocols to ensure the longevity and functionality of the parts.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Processes in Industrial Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of industrial machine parts. It ensures that products meet both international standards and specific customer requirements.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Several international standards govern quality assurance in manufacturing:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system, focusing on consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For parts used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
Buyers should verify that their suppliers adhere to these standards to ensure product quality and safety.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential for identifying defects and ensuring compliance with specifications. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This occurs when raw materials are received. Suppliers should inspect materials for defects or inconsistencies.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections ensure that processes remain within specified tolerances.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The last stage of inspection, where finished parts are thoroughly tested and verified against specifications.
B2B buyers should request documentation of these QC processes to assess supplier reliability.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of industrial machine parts, including:
- Dimensional Inspection: Measuring parts against specifications using tools like calipers and micrometers.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection detect internal defects without damaging the parts.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that parts perform as intended under operational conditions.
B2B buyers should understand the testing methods used by their suppliers to gauge the reliability of the products.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality assurance practices of suppliers is crucial for minimizing risks. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can help buyers assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications can provide insight into a supplier’s adherence to standards and practices.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality assurance processes.
Understanding these verification methods can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions and mitigate potential risks in their supply chain.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, B2B buyers should be aware of various nuances related to quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Attitudes towards quality and compliance can vary significantly across regions. Understanding these differences can aid in negotiations and expectations management.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have unique regulations regarding manufacturing and quality assurance. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with local regulations in addition to international standards.
- Supply Chain Complexity: International sourcing often involves multiple suppliers and logistical challenges. Establishing clear communication and documentation protocols is essential for maintaining quality throughout the supply chain.
By being aware of these nuances, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of international sourcing more effectively, ensuring that they receive high-quality industrial machine parts.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘industrial machine parts’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of industrial manufacturing, sourcing machine parts efficiently is essential for operational success. This practical sourcing guide outlines a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procuring industrial machine parts. By following these steps, you can ensure that your sourcing process is thorough, effective, and aligned with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline the technical requirements of the machine parts you need. This includes dimensions, materials, tolerances, and performance standards. A well-defined specification will not only streamline the sourcing process but also minimize the risk of receiving incorrect or subpar parts.
- Consider specific applications: Identify how each part will be used within your machinery to ensure compatibility.
- Document standards: Reference industry standards or certifications that the parts must meet.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct comprehensive research to identify suppliers that specialize in the type of machine parts you require. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry publications to compile a list of potential vendors.
- Leverage networks: Engage with industry contacts or join forums to gather recommendations on reputable suppliers.
- Evaluate geographical considerations: Consider suppliers in regions with established logistics and trade agreements to enhance delivery efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; seek third-party evaluations.
- Assess experience and specialization: Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in providing machine parts relevant to your industry.
- Inquire about quality control processes: Ensure they adhere to quality standards and certifications, such as ISO 9001.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotes for the machine parts you need. Compare not only pricing but also the terms of delivery, payment options, and warranty policies.
- Look for transparency: Ensure that quotes break down costs (e.g., unit price, shipping, taxes) for clearer comparison.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Evaluate long-term costs associated with each supplier, including maintenance and support services.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
It is essential to confirm that your chosen supplier meets all relevant industry certifications and regulatory requirements. This step helps mitigate risks associated with quality and compliance.
- Check for international standards: Ensure suppliers hold certifications recognized in your target markets, such as CE marking in Europe or ANSI standards in the U.S.
- Review compliance with local regulations: Particularly in regions like Africa and South America, ensure adherence to local manufacturing standards.
Step 6: Conduct a Trial Order
Before placing a large order, conduct a trial order to evaluate the supplier’s reliability and the quality of the machine parts. This step allows you to assess their production capabilities and service levels firsthand.
- Monitor delivery timelines: Evaluate whether the supplier meets promised delivery dates and communicates effectively during the process.
- Inspect product quality: Thoroughly inspect the trial order to ensure it meets your specified standards and requirements.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Once you have successfully sourced machine parts, aim to build a long-term relationship with your supplier. Strong partnerships can lead to better pricing, priority service, and collaborative problem-solving.
- Communicate regularly: Maintain open lines of communication to address any issues and share feedback.
- Explore opportunities for joint ventures: Consider collaborating on product development or improvements to enhance mutual benefits.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for industrial machine parts, ensuring they find reliable suppliers that meet their technical and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial machine parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Industrial Machine Parts?
When sourcing industrial machine parts, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the overall cost. High-quality metals or specialized composites may come at a premium but can enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the machining processes involved. Skilled labor is essential for precision manufacturing, particularly in custom parts.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient operations can help minimize these expenses.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are incurred for the creation of molds, dies, and fixtures required for production. These costs can be substantial, especially for custom parts.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that the parts meet specified standards and certifications. This may involve additional testing and inspection costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary dramatically based on the origin of the parts and the destination. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties play a crucial role.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding this can aid in negotiating better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Industrial Machine Parts Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of industrial machine parts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to better pricing due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing, where per-unit costs decrease with increased quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts generally command higher prices due to the complexity of design and manufacturing. Clear communication of specifications can minimize revisions and associated costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only impacts the initial cost but also the longevity and maintenance requirements of the parts. Premium materials may reduce total cost of ownership over time.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts that require specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) typically cost more due to the additional compliance processes involved. Buyers must weigh the benefits of certified parts against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and reliability can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while new entrants may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. Costs can vary significantly based on whether the seller or buyer assumes responsibility for shipping and insurance.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
Negotiating effectively is key to securing favorable pricing and terms in industrial machine parts sourcing. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Before entering negotiations, conduct thorough research on market prices and competitor offerings. This information will empower you to negotiate from a position of strength.
-
Leverage Volume: If possible, consolidate orders to achieve higher volumes. This not only reduces costs but also strengthens your negotiating position.
-
Explore Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When discussing pricing, factor in the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. This broader perspective can justify a higher upfront cost if long-term savings are evident.
-
Be Transparent About Budgets: Sharing your budget constraints with suppliers can foster collaboration and lead to creative solutions that satisfy both parties.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Be mindful of cultural differences, especially when dealing with suppliers from diverse regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East. Understanding local business practices can enhance rapport and negotiation outcomes.
Why Is It Important to Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various pricing nuances that can impact their sourcing decisions. Factors such as currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions can affect the final price. Additionally, understanding the local supply chain dynamics in regions like Brazil and Nigeria can help buyers make informed decisions and mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for industrial machine parts can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always request updated quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any purchasing agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing industrial machine parts With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Industrial Machine Parts
In the industrial landscape, the choice of machinery components is critical for optimizing production and ensuring efficiency. While traditional industrial machine parts serve their purpose well, it’s essential to evaluate alternative solutions that may offer enhanced performance, cost-effectiveness, or ease of implementation. This analysis will compare industrial machine parts with two viable alternatives: modular automation systems and 3D printing technologies.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Industrial Machine Parts | Modular Automation Systems | 3D Printing Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and durability | Flexible and scalable production | Customization capabilities |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Higher initial setup costs; lower long-term operational costs | Variable costs based on design complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Established processes; requires trained personnel | Complex integration with existing systems | Requires design expertise and specialized software |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to ensure longevity | Low maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Minimal maintenance; dependent on material quality |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty applications requiring reliability | High-volume production with frequent changes | Prototyping and small-batch production with customization |
Evaluating Modular Automation Systems
Modular automation systems are designed for flexibility and scalability, allowing manufacturers to adapt their production lines quickly to changing demands. These systems integrate various automated components that can be reconfigured as needed.
Pros: Modular systems can significantly reduce downtime during reconfiguration and are ideal for environments where product lines frequently change. They also promote efficiency through automation, potentially reducing labor costs.
Cons: The initial setup costs can be prohibitive, particularly for smaller manufacturers. Furthermore, integrating these systems with existing machinery may require significant technical expertise and time, posing a challenge for companies that lack specialized staff.
Analyzing 3D Printing Technologies
3D printing has emerged as a powerful alternative for creating industrial components. This technology allows for the on-demand production of parts, reducing the need for inventory and enabling rapid prototyping.
Pros: The most significant advantage of 3D printing is its customization capability, which allows manufacturers to create unique parts tailored to specific applications. It also minimizes waste and can lower production costs for low-volume runs.
Cons: However, the cost of 3D printing can vary widely based on the complexity of the design and the materials used. Additionally, the technology may not yet match the strength and durability of traditional machine parts, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between industrial machine parts, modular automation systems, and 3D printing technologies, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and production goals. If high precision and durability are paramount, traditional machine parts may be the best choice. Conversely, if flexibility and customization are key, exploring modular systems or 3D printing could yield better long-term benefits. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial machine parts
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Industrial Machine Parts?
Understanding the technical properties of industrial machine parts is crucial for international buyers, especially when ensuring compatibility, performance, and longevity. Here are several key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the type and quality of materials used in manufacturing machine parts, such as steel, aluminum, or polymers. Each material has unique properties that influence strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. For example, high-grade stainless steel is often preferred for its resistance to rust and wear, making it ideal for parts exposed to harsh environments. Selecting the right material grade can significantly impact the operational efficiency and lifespan of machinery.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance denotes the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In machine parts, tight tolerances are critical for ensuring proper fit and function. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.01 mm indicates that the actual measurement can vary by this amount from the specified dimension. Understanding tolerances is essential for B2B buyers as it directly affects assembly processes, performance, and the potential need for rework or adjustments.
3. Hardness
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation, particularly permanent indentation. Common scales include Rockwell and Brinell. Parts made from harder materials are typically more durable and wear-resistant, making hardness a vital specification for components like gears and bearings. Buyers should consider hardness ratings to ensure parts can withstand operational stresses without failure.
4. Surface Finish
Surface finish pertains to the texture and quality of a part’s surface, which can affect its performance and aesthetic appeal. Common finishes include polished, anodized, or coated surfaces. A smooth finish can reduce friction and wear, while certain coatings can enhance corrosion resistance. Understanding surface finish specifications helps buyers select parts that meet both functional and visual standards.
5. Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum load a machine part can safely support without failure. This specification is particularly important for components like bearings and supports, which bear significant operational stresses. Knowing the load capacity ensures that parts can handle the intended operational loads, preventing premature wear or catastrophic failure.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Industrial Machine Parts Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for navigating the procurement process and ensuring effective communication. Here are some common terms used in the industrial machine parts sector:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For B2B buyers, sourcing from OEMs often guarantees compatibility and quality, as these parts are designed specifically for certain machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for buyers, particularly in budgeting and inventory management. It also impacts the ability to test new products or parts without committing to large quantities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit pricing and other information on specific products or services. This process helps buyers compare costs and terms from different vendors, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, thereby reducing the risk of misunderstandings in global trade.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is vital for project planning and ensuring that production schedules are met without delays.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of technical properties and trade terminology is essential for B2B buyers in the industrial machine parts sector. By grasping these concepts, buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they procure the right parts for their operational needs while optimizing costs and efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the industrial machine parts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Industrial Machine Parts Sector?
The industrial machine parts sector is experiencing a transformative phase, driven by globalization, technological advancements, and changing consumer demands. Key drivers include the rise of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies, which emphasize smart manufacturing and connectivity. This shift is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where there is an increasing emphasis on efficiency and productivity. Emerging technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data analytics are reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling businesses to optimize their supply chains and enhance decision-making processes.
Furthermore, the demand for customized solutions is on the rise. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer tailored machine parts that meet specific operational needs. This trend is fueled by the diverse industrial landscapes in regions such as Brazil and Nigeria, where local manufacturers require parts that cater to unique production processes. Additionally, the growing emphasis on digital procurement platforms is revolutionizing how B2B buyers source machine parts. These platforms facilitate easier access to suppliers, real-time inventory management, and streamlined order processes, ultimately enhancing procurement efficiency.
Another notable trend is the increasing importance of supply chain resilience. Recent global disruptions, such as those caused by the pandemic, have highlighted vulnerabilities in sourcing practices. Consequently, buyers are now prioritizing partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate reliability and flexibility in their operations. This focus on resilience is reshaping buyer-supplier relationships, leading to more strategic alliances that prioritize mutual growth and sustainability.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing B2B Practices in the Industrial Machine Parts Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount considerations for B2B buyers in the industrial machine parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has prompted companies to adopt more sustainable practices, focusing on reducing carbon footprints and minimizing waste. As a result, buyers are increasingly demanding machine parts that are produced with environmentally friendly materials and processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now scrutinizing their suppliers’ practices, looking for transparency regarding labor conditions, sourcing methods, and environmental compliance. This shift is particularly significant in regions like Africa and South America, where ethical considerations can directly influence purchasing decisions. Companies that prioritize ethical sourcing not only enhance their brand reputation but also foster trust among consumers and stakeholders.
Moreover, certifications for sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 or LEED, are gaining traction. Buyers are more inclined to partner with suppliers who hold these certifications, as they signify a commitment to environmental stewardship. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recycled metals or biodegradable components, is becoming a competitive differentiator in the market. By aligning with sustainability goals, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also appeal to a growing base of environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of the Industrial Machine Parts Sector’s Evolution?
The evolution of the industrial machine parts sector has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in manufacturing paradigms. Initially, the sector was characterized by manual processes and limited machinery, which constrained production capabilities. However, the advent of the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century heralded a new era of mechanization, enabling mass production and the development of specialized machine parts.
As industries grew, so did the complexity of machinery, leading to the emergence of specialized suppliers focused on manufacturing specific components. The late 20th century saw the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) technologies, which revolutionized the precision and efficiency of manufacturing processes. This technological leap not only increased production rates but also allowed for greater customization in machine parts, catering to the diverse needs of global markets.
Today, the sector stands at the intersection of traditional manufacturing and digital innovation. As B2B buyers increasingly seek efficiency, customization, and sustainability, the historical context of the industrial machine parts sector provides valuable insights into the ongoing evolution of sourcing trends and market dynamics. This legacy continues to shape the future of industrial manufacturing, driving the sector towards greater resilience and adaptability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial machine parts
-
How do I choose the right industrial machine parts for my production needs?
Selecting the appropriate industrial machine parts involves understanding your specific operational requirements. Start by analyzing the machinery you have and the tasks it performs. Consider factors such as compatibility, the material of the parts, and their specifications. Engage with suppliers who can provide detailed product information and support. Additionally, assess the performance and durability of the parts through reviews or case studies from similar industries. -
What are the best practices for vetting suppliers of industrial machine parts?
To effectively vet suppliers, begin by researching their reputation in the market. Look for certifications, industry experience, and customer testimonials. Request samples or conduct site visits to evaluate their production capabilities and quality control processes. Ensure they have a robust logistics system for timely delivery and can provide after-sales support. Establishing communication to discuss your needs can also reveal their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate. -
What customization options are available for industrial machine parts?
Many suppliers offer customization options tailored to your specific requirements. This may include modifications to dimensions, materials, or features of the parts. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly and check if the supplier has the capabilities to meet them. Be aware that customized parts may have different lead times and costs, so it’s advisable to discuss these aspects upfront to avoid surprises. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for industrial machine parts?
The MOQ for industrial machine parts varies widely by supplier and product type. Some suppliers may have flexible MOQs, while others may require larger orders to maintain cost efficiency. When sourcing, inquire about MOQs early in the negotiation process to ensure they align with your purchasing capabilities. If your needs are lower than the MOQ, discuss potential alternatives, such as consolidating orders with other buyers. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing industrial machine parts?
Payment terms can differ significantly among suppliers, often influenced by your relationship with them and the order size. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days, requiring payment within that timeframe after delivery. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or require partial upfront payments for larger orders. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before placing an order to ensure they fit your cash flow management strategy. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for industrial machine parts?
To ensure quality, work with suppliers who follow strict quality control processes and are certified to industry standards, such as ISO 9001. Request documentation such as inspection reports or certificates of compliance for the parts. Conduct your inspections upon receipt to verify that the products meet your specifications. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate transparency in their quality assurance practices. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing internationally?
When sourcing industrial machine parts internationally, consider shipping methods, costs, and delivery timelines. Understand the customs regulations in both the exporting and importing countries to avoid delays. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide reliable logistics solutions. Additionally, factor in the potential for tariffs and taxes, which could impact your overall costs. -
How can I handle potential disputes with suppliers effectively?
To manage disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements, including specifications and timelines. If a dispute arises, address it promptly and professionally, seeking a resolution that is fair to both parties. Consider involving a neutral third party for mediation if necessary. Building a strong relationship with your suppliers can also minimize the risk of disputes and facilitate smoother negotiations in the future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Industrial Machine Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Grainger – Machinery & Tools
Domain: grainger.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, Grainger – Machinery & Tools, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Industrial Equipment Parts – Quality Components
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Store Name: industrial-equipment-parts
Feedback: 100% positive feedback
Items Sold: 86K
Followers: 1.4K
Categories: Business & Industrial, Light Equipment & Tools, Heavy Equipment, Parts & Attachments, Hydraulics, Pneumatics, Pumps & Plumbing, Electrical Equipment & Supplies, Material Handling, Industrial Automation & Motion Controls, Cleaning & Janitorial Supplies, Agriculture & Forestry, Test, M…
3. Gold Star Tool – Replacement Sewing Machine Parts
Domain: goldstartool.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Replacement sewing machine parts for various brands including Singer, JUKI, Consew, Pegasus, and more. Key product categories include: sewing machine essentials, needles, bobbin cases, needle plates, sewing machine feet, loopers, knives, oils, lubricants, cutting supplies, and various sewing notions. Specific parts listed include needle clamps, screws, tension filters, belts, pulleys, gears, and b…
4. TechSew – Industrial Sewing Machine Parts
Domain: techsew.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Industrial Sewing Machine Parts & Supplies including: Needles, Bobbins, Presser Feet, Bobbin Cases, Needle Plates, Rotary and Shuttle Hooks, Attachments and Folders, Sewing Accessories, Feed-Dogs, Tension Parts, Oil, Seam Guides, Lamps, V Belts, Sewing Thread, Motors, Leathercraft Tools & Supplies, Cutting & Skiving Tools, Leather Kits, Dyes & Liquids, Fabric Cutters, and Replacement Parts. Specif…
5. Elesa – Standard Machine Parts
Domain: elesa.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Elesa – Standard Machine Parts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. WAWAK – Replacement Sewing Machine Parts
Domain: wawak.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Replacement Sewing Machine Parts at WAWAK, Fast, Free Shipping over $99 or Flat Rate $5.95, Customer Service 1-800-331-7600, Categories include Thread, Zippers, Sewing Needles, Sewing Machine Parts & Accessories, Garment Construction, and more. Thread options by Brand, Material, Use, and Weight. Zippers available in various materials and styles. Sewing Machine Parts include Bobbins, Feed Dogs, Nee…
7. Mechanical Power – Industrial Machinery Parts
Domain: mechanicalpower.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Industrial machinery parts supplied by Mechanical Power include: Bearings (Agricultural-bearings, Cam-type-bearings, Slewing bearing rings, Linear bearings), Precision Castings, High Pressure Nozzles, Hydraulic Cylinders, Hydraulic Fittings, Hydraulic Seals, Plastic Molded Parts, Bushings, Clutch assemblies, CNC Machining, Extrusions, Fasteners, Forging, Gearboxes, Chains, Pulleys, Rod-End Bearing…
8. CutSew – Industrial Sewing Machine Parts
Domain: cutsew.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Industrial Sewing Machine Parts including: Belts, Bobbin Winders, Feed Dogs, Feedrail, Feet, Foot & Knee Lifters, Gaskets, Knives, Loopers, Needle Bars, Needle Plates, Screws, Spare Parts Kits, Springs, Thread Stands, Sewing Kits, Sewing Machine Oil, Industrial Thread (Nylon, Polyester, Monofilament, Upholstery, Leather), Bobbins (Prewound), and more. Brands include Juki, Brother, Consew, Groz-Bec…
9. Industrial Sewing Machine – Essential Parts & Schematics
Domain: industrialsewingmachineman.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Industrial Sewing Machine Parts, Schematics, JUKI Machine Schematics, Juki Parts Search, Automatic Reverse Feed Components, Belt Cover & Bobbin Components, Cobra Commercial Sewing Machine Needles, Driving Shaft Components, Feed Mechanism Components, Feed Rocker Mechanism Components, Frame & Cover Components, Hand Lifter Components, Hand Wheels, Industrial Bobbin Cases, Industrial Bobbins, Industri…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial machine parts
In navigating the complexities of sourcing industrial machine parts, buyers must prioritize strategic approaches that align with their operational goals. The diverse range of machinery—ranging from milling machines to hydraulic presses—highlights the necessity of understanding specific needs and selecting suppliers that offer quality, reliability, and comprehensive support. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, organizations can not only enhance cost efficiency but also ensure a steady supply of critical components, thus minimizing downtime and fostering innovation.
Moreover, international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must remain agile in their sourcing strategies. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who understand regional market dynamics can lead to advantageous partnerships that drive long-term growth.
As we look ahead, the importance of integrating technology and data analytics into the sourcing process will continue to grow, enabling businesses to make informed decisions. Now is the time for B2B buyers to explore new suppliers, engage in collaborative partnerships, and invest in solutions that will propel their operations forward. Embrace the future of strategic sourcing to unlock new opportunities in the industrial machine parts market.