Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial chrome plating
In an increasingly competitive global marketplace, sourcing reliable industrial chrome plating services poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers. The durability, wear resistance, and corrosion protection offered by hard chrome plating make it a preferred choice for various applications, from aerospace components to heavy machinery. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource to navigate the complex landscape of industrial chrome plating, detailing the types of plating available, their specific applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—will find valuable insights on cost factors, quality standards, and environmental regulations that influence the chrome plating industry. By equipping decision-makers with actionable knowledge and strategies, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product longevity.
Whether you are looking to repair worn components or improve the performance of new parts, understanding the intricacies of industrial chrome plating is essential. The information provided herein not only highlights the advantages of various plating processes but also offers practical tips for ensuring compliance with international standards, ultimately helping businesses achieve their goals while mitigating risks associated with sourcing and procurement.
Understanding industrial chrome plating Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Chrome Plating | High hardness (HRC 65-70), excellent wear resistance | Aerospace, automotive, manufacturing | Pros: Exceptional durability, corrosion resistance. Cons: Higher initial costs. |
| Decorative Chrome Plating | Aesthetic finish, lower thickness | Consumer goods, automotive trim | Pros: Enhanced appearance, lower cost. Cons: Limited functional benefits. |
| Electroless Nickel Plating | Uniform coating, good corrosion resistance | Electronics, aerospace, automotive | Pros: Excellent coverage on complex shapes. Cons: Less hardness compared to hard chrome. |
| Flash Chrome Plating | Very thin layer, quick application | Tools, components requiring light coating | Pros: Cost-effective, fast turnaround. Cons: Limited wear resistance. |
| Chrome Plated Bars | Induction hardened, consistent properties | Hydraulic rods, machinery components | Pros: Improved impact resistance, uniform quality. Cons: Limited to specific sizes and shapes. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Hard Chrome Plating?
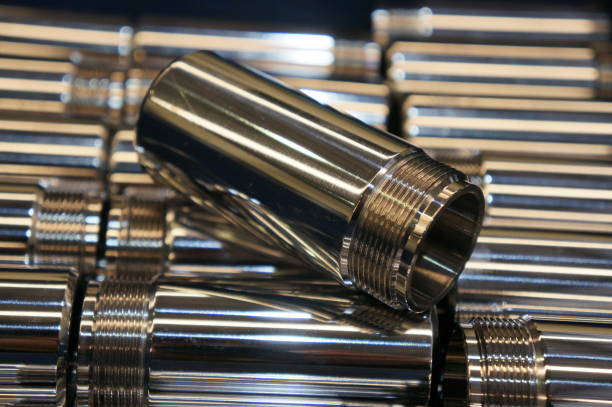
Hard chrome plating is renowned for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for components subjected to high friction and severe mechanical stress. With a hardness rating of HRC 65-70, it is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing sectors where durability is paramount. Buyers should consider the initial investment against the longevity and performance benefits, especially in environments prone to corrosion and wear.
How Does Decorative Chrome Plating Differ from Other Types?
Decorative chrome plating focuses on enhancing the aesthetic appeal of products rather than providing functional benefits. This type typically involves a thinner layer of chrome, making it suitable for consumer goods and automotive trim. While it offers a shiny, attractive finish at a lower cost, buyers should note that it lacks the robust wear and corrosion resistance found in hard chrome plating, limiting its application in more demanding environments.
What Are the Advantages of Electroless Nickel Plating?
Electroless nickel plating is characterized by its uniform coating, which is applied without the use of electrical current. This technique is particularly effective for complex geometries, ensuring complete coverage. It is widely used in electronics and aerospace applications due to its good corrosion resistance. Buyers should weigh the benefits of uniformity and protection against the lower hardness compared to hard chrome, depending on their specific application needs.
When Should You Consider Flash Chrome Plating?
Flash chrome plating involves applying a very thin layer of chrome, making it a cost-effective solution for components that require minimal wear resistance. This type is often used for tools and components that do not undergo heavy wear. While it offers a quick turnaround and lower costs, buyers should be cautious about its limited durability and suitability for high-stress applications.
What Are the Key Benefits of Chrome Plated Bars?
Chrome plated bars are typically induction hardened to enhance their impact resistance and durability. They are used in applications such as hydraulic rods and machinery components where consistent properties are crucial. Buyers should appreciate the uniform quality and reliability of these products, although they may be limited in terms of size and shape flexibility. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will guide you in making the right choice.
Key Industrial Applications of industrial chrome plating
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industrial chrome plating | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Engine components and landing gear | Enhanced wear resistance and longevity in extreme conditions | Compliance with aerospace specifications (e.g., AMS2406) |
| Automotive | Cylinder bores and piston rods | Improved durability and performance of engine components | Availability of large-scale plating capabilities |
| Oil & Gas | Drill bits and downhole tools | Increased lifespan in abrasive environments | Ability to handle large and complex geometries |
| Manufacturing Machinery | Hydraulic cylinders and molds | Reduced friction and wear, leading to lower maintenance costs | Precision in achieving tight tolerances |
| Construction Equipment | Excavator and loader components | Enhanced corrosion resistance in harsh environments | Consistency in quality and turnaround time |
How is Industrial Chrome Plating Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, industrial chrome plating is vital for enhancing the durability of engine components and landing gear. The extreme conditions faced by these parts necessitate high wear resistance and longevity, which chrome plating provides. Buyers in this industry must ensure their suppliers comply with strict aerospace specifications, such as AMS2406, to guarantee quality and performance. International buyers, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe, should prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in meeting these demanding standards.
What Role Does Chrome Plating Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, industrial chrome plating is extensively used for cylinder bores and piston rods, where it significantly improves the components’ durability and performance. The plating process enhances wear resistance and reduces friction, contributing to better fuel efficiency and longer engine life. When sourcing chrome plating services, automotive manufacturers should look for suppliers with large-scale capabilities to handle mass production and ensure uniform quality across components, especially when sourcing from regions like Africa and South America.
How Does Chrome Plating Benefit Oil & Gas Industry Tools?
For the oil and gas industry, chrome plating is applied to drill bits and downhole tools to extend their lifespan in abrasive environments. The enhanced hardness and wear resistance of chrome-plated tools lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime. Buyers must consider suppliers that can manage large and complex geometries, as many tools in this sector have intricate designs. Additionally, sourcing from local suppliers can mitigate logistical challenges often faced in remote locations.
Why is Industrial Chrome Plating Important for Manufacturing Machinery?
Manufacturing machinery, such as hydraulic cylinders and molds, benefits greatly from industrial chrome plating, which reduces friction and wear. This leads to lower maintenance costs and improved operational efficiency. Buyers should seek suppliers capable of achieving precision in tight tolerances, as this is crucial for the performance of machinery components. Suppliers with a robust quality assurance process are essential, particularly for international buyers from diverse regions, to ensure reliability and consistency.
What Advantages Does Chrome Plating Offer Construction Equipment?
In construction equipment, chrome plating is used on components like excavators and loaders to enhance corrosion resistance in harsh environments. This protection is vital for maintaining equipment performance and reducing replacement costs. When sourcing chrome plating for construction equipment, businesses should prioritize suppliers known for their consistency in quality and timely delivery. International buyers, especially in regions facing extreme weather conditions, should also consider the supplier’s capacity to handle large volumes while maintaining high standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘industrial chrome plating’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Corrosion Resistance in Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as oil and gas, mining, or marine often face significant challenges with corrosion resistance when it comes to metal components. In these environments, equipment is subjected to extreme conditions, leading to rapid deterioration. Buyers frequently find that standard coatings do not provide the necessary protection, resulting in costly repairs and operational downtime.
The Solution: To combat corrosion effectively, buyers should prioritize sourcing industrial chrome plating that specifically offers enhanced corrosion resistance. When selecting a chrome plating provider, it’s crucial to inquire about the specific formulations and processes they employ. Look for companies that utilize proprietary plating solutions and advanced filtration systems to maintain the integrity of the plating bath. Additionally, specifying thicker chrome layers can provide extra durability. Regular maintenance and inspections of the plated components will also help identify any early signs of wear, allowing for timely interventions before significant damage occurs.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality Across Batch Orders
The Problem: B2B buyers often report issues with inconsistent quality in chrome-plated products, particularly when ordering large batches. Variability in coating thickness, finish quality, and adherence can lead to discrepancies in performance, affecting the reliability of the final product. This inconsistency can hinder production schedules and erode trust in supplier relationships.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should establish clear specifications and standards before placing orders. Engaging with suppliers who have a well-documented quality assurance process can mitigate these issues. Request detailed information about their plating techniques, including the use of advanced monitoring systems that control plating parameters throughout the process. Furthermore, consider implementing a pre-production sample approval process, allowing for the evaluation of a small batch before full-scale production. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues early, ensuring that the final products meet the required specifications.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Meeting Tight Tolerances for Precision Components
The Problem: Industries such as aerospace and automotive often require components that must meet stringent tolerances and specifications. B2B buyers face difficulties when chrome plating services cannot accommodate these precise requirements, leading to delays and additional costs associated with rework or sourcing alternative suppliers.
The Solution: Buyers should focus on partnering with chrome plating providers that specialize in precision plating techniques. When sourcing suppliers, inquire specifically about their capabilities in handling complex geometries and tight tolerances. Look for companies that utilize state-of-the-art equipment and have a robust engineering team that can design custom fixturing. Additionally, buyers should communicate their tolerance requirements clearly and request that the supplier provides a detailed plan for achieving these specifications. Regular communication throughout the plating process can help ensure that any adjustments needed to maintain tolerances are made promptly, ultimately saving time and resources.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial chrome plating
What Are the Common Materials Used for Industrial Chrome Plating?
When selecting materials for industrial chrome plating, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications. The following analysis covers four common materials used in hard chrome plating: steel, aluminum, titanium, and brass.
How Does Steel Perform in Chrome Plating Applications?
Steel is one of the most widely used substrates for hard chrome plating due to its strength and versatility. Key properties include high tensile strength, good machinability, and excellent wear resistance. Steel components can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Pros: Steel offers exceptional durability and can be plated to enhance its surface hardness, providing significant wear and corrosion resistance. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: While steel is robust, it is susceptible to rust if not properly coated. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity increases with the need for precise machining before plating.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media, including hydraulic fluids and chemicals, making it ideal for industrial machinery and automotive applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A532 for wear-resistant steel and DIN 17100 for structural steel is crucial. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that suppliers meet these specifications.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer in Chrome Plating?
Aluminum is another popular substrate for chrome plating, known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It has a lower density compared to steel, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
Pros: Aluminum provides excellent corrosion resistance and is non-magnetic, which can be beneficial in specific electronic applications. It also has good thermal conductivity.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of aluminum is its lower strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, the plating process can be more complex due to aluminum’s oxide layer.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in aerospace and automotive industries, where reducing weight is critical. Its compatibility with various environmental conditions enhances its application range.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM B633 for electroplated coatings and ensure that suppliers can meet these requirements.
How Does Titanium Compare as a Substrate for Chrome Plating?
Titanium is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, making it a premium choice for chrome plating in specialized applications.
Pros: Titanium’s durability and resistance to extreme environments make it suitable for aerospace, marine, and medical applications. It also has a high melting point, which allows it to perform well under elevated temperatures.
Cons: The primary drawback is the high cost of titanium, which can be prohibitive for some applications. Additionally, the complexity of machining titanium can lead to increased manufacturing time and costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is often used in applications requiring high performance, such as aerospace components and medical implants, where reliability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with aerospace standards like AMS 2488 for titanium plating is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure their suppliers are familiar with these specifications.
What Role Does Brass Play in Chrome Plating Applications?
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is often used in decorative chrome plating due to its aesthetic appeal and good machinability.
Pros: Brass offers excellent corrosion resistance and is relatively easy to machine, allowing for intricate designs. The aesthetic finish of chrome plating enhances its visual appeal.
Cons: While brass is suitable for low-stress applications, it is not as durable as steel or titanium and may not withstand high wear conditions. Its susceptibility to dezincification can also limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Brass is commonly used in plumbing fixtures, decorative hardware, and electrical components, where appearance and moderate strength are required.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM B36 for brass and ensure that their suppliers adhere to these guidelines, particularly in the Middle East and Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Industrial Chrome Plating
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial chrome plating | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Industrial machinery components | Exceptional durability | Susceptible to rust | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and machining complexity | High |
| Brass | Decorative hardware and plumbing fixtures | Aesthetic appeal | Lower durability and wear resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials commonly used in industrial chrome plating, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial chrome plating
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Industrial Chrome Plating?
The manufacturing process of industrial chrome plating is a multi-step procedure that ensures the application of a durable, high-performance coating on various metal substrates. This process can be broken down into several critical stages:
Material Preparation: Why Is It Crucial for Successful Chrome Plating?
Before any plating can occur, the base material must be meticulously prepared. This stage involves cleaning the substrate to remove any contaminants, such as grease, oil, or rust, that could compromise the plating adhesion. Common cleaning methods include chemical degreasing, ultrasonic cleaning, and abrasive blasting.
Once cleaned, the material is often subjected to an acid etch to further enhance surface roughness, promoting a better bond between the substrate and the chrome layer. Depending on the desired outcome, this preparation phase may also include surface treatments like anodizing for aluminum parts, which helps improve corrosion resistance.
What Techniques Are Used During the Forming and Assembly Stages?
In many cases, the components to be plated are manufactured through processes such as machining, casting, or forging. Proper forming ensures that the parts meet the precise tolerances required for effective chrome plating.
Assembly, when applicable, involves the integration of multiple components before plating, especially for complex parts such as hydraulic cylinders or automotive components. By ensuring all parts fit together correctly, manufacturers can avoid potential issues with plating uniformity and performance.
How Is the Finishing Stage Conducted in Chrome Plating?
The finishing stage is where the actual chrome plating occurs. Industrial hard chrome plating is typically performed using an electroplating process, where a direct current is passed through a chromium electrolyte solution, depositing a layer of chromium onto the prepared surface.
The thickness of the chrome layer can vary based on application requirements, ranging from 0.0002 inches to over 0.020 inches. The controlled environment during plating, including temperature and pH levels, is crucial to achieving a consistent and high-quality finish.
Post-plating, components often undergo polishing to enhance the surface finish. This polishing process is vital for applications requiring aesthetic considerations or where a low coefficient of friction is essential for functionality.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Industrial Chrome Plating?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the industrial chrome plating process, ensuring that all products meet specified performance and safety standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 set the framework for quality management systems in manufacturing. Compliance with these standards indicates that a supplier has established processes for maintaining consistent product quality.
Industry-specific standards may also apply, such as CE marking for products sold within the European Economic Area, or API standards for parts used in the oil and gas industry. Understanding these standards can help B2B buyers ensure that their suppliers are adhering to best practices.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects and ensure compliance with specifications. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line. Any non-compliant materials are rejected to prevent further issues.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the plating process is vital. Parameters such as plating thickness, temperature, and chemical concentrations must be regularly checked to ensure uniformity and quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once plating is complete, final inspections are conducted. This may involve visual inspections, dimensional checks, and tests for adhesion, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Procedures?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control measures:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help ensure compliance with both international standards and company-specific requirements. Audits can be scheduled or surprise visits to gauge the effectiveness of QC processes.
-
Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can provide insights into the supplier’s testing methods and results. Look for documentation that outlines their processes and any corrective actions taken in response to defects.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality practices. These inspections can validate compliance with industry standards and provide additional assurance of product quality.
What Are the Challenges and Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are unique challenges and considerations when sourcing industrial chrome plating services.
How Do Regional Regulations Impact Chrome Plating?
Different regions have varying regulations regarding environmental standards, particularly concerning the use of hazardous materials and waste disposal. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with local laws, such as those enforced by the EPA in the U.S. or similar regulatory bodies in other countries.
What Are the Nuances of Certification and Compliance for Global Trade?
Certifications can vary significantly by region and industry. Buyers should verify that suppliers possess the necessary certifications for the markets they intend to serve. For example, suppliers targeting the European market should be familiar with REACH regulations, which govern the registration, evaluation, and authorization of chemicals.
How Can Buyers Navigate Language and Cultural Barriers?
Effective communication is essential when dealing with international suppliers. Buyers should consider working with suppliers that have experience exporting to their region and can provide documentation in the appropriate language. Utilizing local representatives or consultants can also help bridge cultural differences and facilitate smoother transactions.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for industrial chrome plating, ultimately ensuring the reliability and performance of their products in demanding applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘industrial chrome plating’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of industrial chrome plating services can be complex, especially for B2B buyers in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide offers a comprehensive checklist to ensure that you make informed decisions when sourcing chrome plating services, enhancing the durability and performance of your components.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of successful sourcing. This includes determining the thickness of the chrome layer, the substrate material, and the specific properties required, such as hardness and corrosion resistance. Clearly defined requirements help suppliers understand your needs, ensuring they can provide accurate quotes and solutions tailored to your application.
- Considerations:
- What types of metal substrates will be plated?
- Are there specific industry standards or certifications that must be met?
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers with a solid reputation in industrial chrome plating. Look for companies with extensive experience and a proven track record in your industry. Online reviews, testimonials, and case studies can provide insight into their capabilities and reliability.
- Key Actions:
- Utilize platforms like LinkedIn or industry-specific forums to gather information.
- Seek recommendations from industry peers or trade associations.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Verify that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and comply with industry standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific aerospace and military specifications (like AMS2406) indicate a commitment to quality and reliability. Compliance ensures that the plating process meets safety and environmental regulations, which is particularly critical in international trade.
- What to Check:
- Are the suppliers certified for the specific applications you require?
- Do they follow environmentally responsible practices?
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes from each. Ensure that the quotes include all costs associated with the plating process, such as setup fees, material costs, and lead times. Comparing multiple quotes helps you understand the market rate and assess the value offered by each supplier.
- Comparison Points:
- Are the quotes itemized for transparency?
- How do the lead times compare across suppliers?
Step 5: Assess Quality Control Processes
Inquire about the quality control measures each supplier implements during the plating process. Understanding their quality assurance protocols will help ensure that the final products meet your specifications consistently. Look for suppliers who utilize advanced monitoring systems and regular testing of their plating baths.
- Quality Indicators:
- Do they conduct regular inspections and tests on plated components?
- What is their process for addressing defects or issues?
Step 6: Evaluate Production Capabilities
Consider the production capabilities of each supplier, including their capacity to handle your volume requirements. This is particularly important if you anticipate scaling up production in the future. Suppliers should have the necessary equipment and facilities to meet your needs efficiently.
- Key Questions:
- Can they accommodate large orders or unique geometries?
- Do they have the facilities to handle specific surface finishes you require?
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Effective communication is critical throughout the sourcing process. Choose suppliers who are responsive and willing to provide support during and after the procurement process. Establishing clear channels for communication can help resolve issues quickly and ensure a smooth partnership.
- Communication Considerations:
- What methods do they use for updates and problem-solving?
- Are they open to providing ongoing support and consultation as needed?
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing industrial chrome plating services, ensuring they select a supplier that meets their technical and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial chrome plating Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Industrial Chrome Plating?
When sourcing industrial chrome plating services, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality of the chromium used is paramount. High-purity chromium results in better surface finishes and durability, impacting overall costs. Additionally, the substrate material being plated can also affect pricing, particularly if specialized metals like titanium or aluminum are involved.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for precise electroplating processes. The complexity of the job, including the need for custom fixturing or unique geometries, can drive labor costs higher.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Advanced filtration systems and environmental compliance measures add to overhead, particularly in regions with strict regulations.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specific projects, especially when dealing with unique or complex components. This initial investment can significantly impact the overall cost, particularly for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are crucial in chrome plating to ensure adherence to specifications and prevent defects. This involves additional labor and equipment costs but is essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling can vary based on the size and weight of the plated components, as well as the distance to the buyer. International shipments may incur additional tariffs and customs duties, affecting the total landed cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s positioning in the market.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Industrial Chrome Plating?
Several factors influence the pricing of industrial chrome plating, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Specific requirements, such as thickness and finish type, can affect pricing. Customized solutions generally incur higher costs due to additional labor and material requirements.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., aerospace or military standards) can drive costs up. Buyers must weigh the need for compliance against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with advanced capabilities may charge more but often deliver higher quality and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk, which can significantly influence the total cost.
What Are the Best Tips for Buyers Looking to Optimize Costs in Chrome Plating?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, optimizing costs requires strategic planning:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always engage in negotiation. Suppliers may have room to adjust pricing, especially for large orders or long-term contracts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on initial costs, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, durability, and potential rework costs associated with the plated components. This approach can lead to more cost-effective purchasing decisions in the long run.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the fluctuations in raw material prices, which can affect plating costs. Stay informed about market trends and seasonal demand variations.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into future pricing trends or new technologies.
-
Consider Local Sourcing: When possible, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, ultimately impacting the total cost more favorably.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of cost components and pricing influencers in industrial chrome plating, actual prices can vary widely based on specific requirements, geographic location, and market conditions. Buyers are encouraged to request quotes tailored to their unique needs to ensure accurate budgeting.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing industrial chrome plating With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Industrial Chrome Plating
In the realm of surface finishing and protective coatings, industrial chrome plating stands out due to its robust performance characteristics. However, various alternative solutions are available that may suit specific applications or requirements better. This section will compare industrial chrome plating against alternatives such as electroless nickel plating and thermal spray coatings, highlighting their respective advantages and limitations.
| Comparison Aspect | Industrial Chrome Plating | Electroless Nickel Plating | Thermal Spray Coatings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High hardness (HRC 65-70), excellent wear and corrosion resistance. | Good corrosion resistance and uniform coating. | Versatile, can coat complex geometries; excellent wear resistance. |
| Cost | Moderate to high; cost-effective for large-scale production. | Generally lower than chrome plating; costs vary based on thickness. | Can be high, depending on materials and application methods. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise; longer lead times. | Easier to apply on various geometries; no external power source needed. | Requires skilled operators; setup can be complex. |
| Maintenance | Minimal; durable but can wear over time. | Moderate; susceptible to pitting under severe conditions. | Moderate; coating may require periodic inspection and maintenance. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-wear, high-precision components in automotive and aerospace. | Suitable for components requiring uniform coverage and corrosion resistance, such as valves and pumps. | Best for heavy-duty applications, such as marine and industrial machinery where impact resistance is critical. |
Understanding Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless nickel plating offers a viable alternative to industrial chrome plating, particularly when uniformity and corrosion resistance are priorities. This process uses a chemical reduction reaction to deposit nickel onto a substrate without the need for an electric current. The resulting coating is generally thinner than chrome but provides excellent corrosion protection and can be applied to complex shapes. However, it may not achieve the same level of hardness as chrome plating, which could be a drawback in high-wear applications.
Evaluating Thermal Spray Coatings
Thermal spray coatings are another alternative that can provide a high level of wear resistance and protection. This method involves melting powdered materials and spraying them onto a substrate, creating a thick layer of coating. Thermal spray coatings are particularly advantageous for components that experience high impact or thermal stress. While they can be applied to a wide variety of materials, the complexity of the application process and the need for skilled technicians can make this solution more challenging to implement compared to chrome plating.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a surface finishing solution, B2B buyers must consider specific application requirements, such as performance criteria, cost constraints, and the complexity of implementation. Industrial chrome plating is optimal for applications demanding high hardness and wear resistance, especially in sectors like aerospace and automotive. However, for projects where uniformity or impact resistance is more critical, electroless nickel or thermal spray coatings may present better options. Ultimately, the choice should align with both the technical specifications of the components involved and the operational budget, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial chrome plating
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Industrial Chrome Plating?
Understanding the essential technical properties of industrial chrome plating is crucial for B2B buyers who need to make informed purchasing decisions. Below are some critical specifications relevant to this process:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the substrate material that will be plated. Common substrates include steel, aluminum, and titanium. The choice of material grade affects the bonding strength and durability of the chrome layer. For buyers, selecting the appropriate substrate is vital for ensuring that the finished product meets the required performance standards and longevity.
2. Plating Thickness
Plating thickness is a key specification that dictates the durability and performance of the chrome layer. Typical thickness ranges from 0.0002 inches to 0.020 inches or more, depending on application requirements. A thicker coating generally provides better wear and corrosion resistance, which is essential for industrial applications. Buyers should specify their desired thickness to ensure optimal performance in their operational environments.
3. Hardness Rating (HRC)
The hardness of chrome plating is usually measured on the Rockwell scale (HRC), with values often ranging from HRC 65 to HRC 70. A higher hardness rating means improved wear resistance, making it suitable for components subjected to high friction or mechanical stress. This property is particularly important for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where component failure can have significant repercussions.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance indicates how well the chrome plating can withstand environmental factors that may lead to rust or degradation. This property is critical for components used in harsh conditions, such as marine or chemical applications. Buyers should assess the environmental factors their products will face and choose plating that offers adequate protection.
5. Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction measures the resistance between two surfaces in contact. A low coefficient is desirable in applications involving sliding motion, as it reduces wear and energy consumption. Understanding this property allows buyers to select chrome plating solutions that enhance the efficiency and lifespan of their components.
6. Bond Strength
Bond strength refers to the adhesion of the chrome layer to the substrate. Strong bond strength ensures that the plating will not chip or peel under stress. This property is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the component over time, especially in high-performance applications.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies in Industrial Chrome Plating?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication and negotiation between buyers and suppliers. Here are several important terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of chrome plating, OEMs often require specific plating specifications to meet their product standards. Understanding OEM requirements is essential for buyers to ensure compliance and quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell. This term is significant for buyers as it can affect pricing and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and determining the feasibility of large-scale orders.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers use to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. Crafting a thorough RFQ ensures that buyers receive accurate and competitive pricing, streamlining the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for buyers to avoid misunderstandings regarding shipping, insurance, and risk management.
5. Electroplating
Electroplating is the process of depositing a layer of metal onto a surface using electrical current. This term is fundamental in chrome plating, as it outlines the method used to apply the chrome layer. Buyers should be aware of the electroplating techniques used by suppliers to ensure quality and compliance with industry standards.
6. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the final texture and appearance of the plated surface, which can vary from matte to polished. This characteristic not only affects aesthetics but can also impact performance characteristics such as corrosion resistance. Buyers should specify their surface finish requirements to achieve the desired functionality and look for their products.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the industrial chrome plating Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Shaping the Industrial Chrome Plating Market?
The industrial chrome plating market is experiencing robust growth driven by several key factors. First, the increasing demand for durable and corrosion-resistant materials across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, is propelling the need for hard chrome plating. This process enhances the longevity and performance of components, making it particularly attractive for industries that operate in harsh environments.
Technological advancements in electroplating processes are also influencing market dynamics. Innovations such as proprietary plating solutions and improved monitoring systems ensure higher quality and consistency in chrome plating. International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer tailored solutions to meet specific engineering challenges. Furthermore, the rise of automated manufacturing processes is creating a demand for chrome-plated components that can withstand rigorous operational demands.
Emerging trends like the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies into manufacturing processes are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that leverage smart technologies for better efficiency, reduced lead times, and enhanced quality control. As businesses in the Middle East and Europe continue to adopt these technologies, they create a competitive landscape that encourages innovation and collaboration among suppliers and manufacturers.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Becoming Central in Industrial Chrome Plating?
The environmental impact of industrial processes, including chrome plating, has led to a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing in B2B transactions. The chrome plating process, while effective, can produce hazardous waste and emissions if not managed properly. Consequently, buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to stringent environmental regulations and demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers, particularly in regions where environmental regulations are tightening. Suppliers that implement ‘green’ practices, such as using low-emission plating solutions and recycling waste materials, are gaining a competitive edge. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming essential criteria for suppliers seeking to attract international buyers, particularly in Europe and North America.
Moreover, the introduction of alternative materials and processes that reduce the environmental footprint of chrome plating is gaining traction. For instance, suppliers exploring the use of electroless nickel plating or other eco-friendly coatings can position themselves favorably in the market. As sustainability becomes a key purchasing criterion, B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship.
What Is the Historical Context of Industrial Chrome Plating That Affects Current B2B Dynamics?
Industrial chrome plating has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed as a decorative finish, it quickly gained popularity in industrial applications due to its exceptional hardness, durability, and corrosion resistance. Over the decades, technological advancements have improved the electroplating process, allowing for more precise control over thickness and surface quality.
The transition from decorative to functional applications has reshaped the market, with hard chrome plating becoming a standard in critical industries such as aerospace and automotive. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers today, as understanding the historical context of chrome plating can provide insights into the reliability and performance standards expected in modern applications.
As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about historical trends can help international buyers make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that not only meet current standards but also have a proven track record in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial chrome plating
-
How do I ensure the quality of industrial chrome plating?
To guarantee high-quality industrial chrome plating, it is crucial to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to recognized industry standards and certifications, such as ASTM and military specifications. Request documentation of their quality assurance processes, including inspection and testing protocols. It is also beneficial to visit their facilities if possible, or seek third-party reviews and testimonials from existing clients. Additionally, inquire about their plating technology and techniques, such as the use of reverse osmosis water and advanced filtration systems, which can significantly impact the final product’s quality. -
What is the best chrome plating specification for my application?
The best chrome plating specification depends on the specific requirements of your application. Common specifications include AMS2406 for aerospace components, ASTM B650 for engineering coatings, and MIL-C-23422 for military applications. Assess factors such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability to determine the appropriate specification. Consulting with your plating supplier can provide valuable insights, as they can recommend the most suitable options based on your operational conditions and performance expectations. -
How can I customize chrome plating services to meet my needs?
Customization in chrome plating services can include variations in coating thickness, surface finish, and specific substrate materials. Discuss your project requirements in detail with potential suppliers, including the desired aesthetic finish (e.g., matte or polished), application environment, and performance characteristics. Many suppliers also offer tailored solutions for unique geometries and specialized coatings, so it’s essential to communicate your specifications clearly to achieve optimal results. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for industrial chrome plating?
Minimum order quantities for industrial chrome plating can vary significantly among suppliers. Some may have MOQs as low as a few pieces for specialized projects, while others may require larger batch sizes to maintain cost-effectiveness. When sourcing suppliers, clarify their MOQ policies and explore the potential for flexibility, especially if you are a new buyer or testing a new product line. This can help you gauge supplier responsiveness and willingness to accommodate smaller orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing chrome plating services?
Payment terms for chrome plating services can differ based on supplier policies and the scale of your order. Common terms may include upfront deposits (often 30-50%), progress payments during production, or payment upon completion and delivery. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and budget constraints. Additionally, consider discussing options for letters of credit or payment via secure platforms to mitigate risks, especially for international transactions. -
How do I vet potential chrome plating suppliers for international trade?
Vetting potential chrome plating suppliers involves thorough research and due diligence. Start by checking their business credentials, certifications, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your region or industry. Utilize platforms like LinkedIn to review their company profiles and employee expertise. If possible, conduct site visits or audits to evaluate their production capabilities and quality control processes. Engaging with local trade associations can also provide insights into reliable suppliers in your target markets. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing chrome-plated products?
When importing chrome-plated products, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with hazardous materials, as chrome plating involves chemicals that may require special handling. Ensure your supplier provides proper documentation, including certificates of conformity and safety data sheets. Additionally, plan for potential delays at customs and consider insurance for high-value shipments to mitigate risks associated with loss or damage during transit. -
What are common issues faced in chrome plating, and how can they be resolved?
Common issues in chrome plating include poor adhesion, uneven coating thickness, and surface imperfections. To resolve these problems, ensure proper substrate preparation, including cleaning and surface treatment before plating. Communicate closely with your supplier regarding any specific challenges you face in your application, as they may recommend adjustments in their plating processes or material treatments. Regular quality checks during production can also help catch and correct issues early, minimizing defects in the final product.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Industrial Chrome Plating Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. U.S. Chrome – Hard Chrome Plating Services
Domain: uschrome.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Hard Chrome Plating – U.S. Chrome offers over 80 years of experience in chromium electroplating services. Key features include:
– Increased hardness of HRC 65-70
– Excellent sliding wear resistance
– Great abrasion resistance
– Low coefficient of friction
– Excellent release properties
– Enhanced corrosion resistance
– High heat mitigation
– Superior bond strength to base metal
– Large ha…
2. HCS Plating – Hard Chrome Plating Solutions
Domain: hcsplating.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Hard chrome plating increases hardness, durability, and corrosion resistance of surfaces, providing a shiny and smooth finish that is easier to clean. It is suitable for harsh environments and can extend the wear life of base materials by 2 to 10 times. The process typically takes up to a day and is applicable to various metals including stainless steel, copper, and brass. Common applications incl…
3. Industrial Chrome Plating – Hard Chrome Solutions
4. Swanson Industries – Industrial Chrome Plating
Domain: swansonindustries.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Swanson’s industrial chrome plating provides corrosion resistance and increased surface hardness for hydraulic cylinder components. Key features include:
– Extensive experience in design, manufacture, and utilization of industrial hard chrome.
– Ability to repair large components with precision hard chrome.
– Capable of precise chrome plating and polishing or heavy chrome plating of several thousa…
5. Chrome Plating – Quality Control Challenges
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Industrial chrome plating process; issues with pin-head and smaller imperfections (nodules) on chrome plating; need for de-plating and rework; daily chemistry testing of chrome baths; aim for plating thickness of 50 to 55 microns (acceptable down to 48 microns); materials being plated include 316 stainless steel and cast or ductile iron; use of hull cells for evaluating plating bath performance; b…
6. Industrial Plating – Hard Chrome Plating Services
Domain: industrialplating.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Industrial Hard Chrome Plating Services provide a layer of chromium applied to metal parts through electroplating. Key benefits include: abrasion resistance, wear protection, mold release, repair of score marks, correction of grinding errors, and customizable thickness from 0.0001″ to over 0.040″. Applications include rolls, tooling, dies, guides, mandrels, screens, shafts, and sleeves. The servic…
7. Caswell Inc. – Hard Chrome Plating Kits
Domain: caswellplating.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Hard Chrome Plating Kits from Caswell Inc. are designed for electroplating applications, providing a durable and corrosion-resistant finish. These kits include all necessary components for hard chrome plating, ensuring high-quality results for various metal surfaces. Ideal for industrial and commercial use, they cater to professionals looking to enhance the longevity and appearance of their metal …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial chrome plating
As the industrial chrome plating market continues to evolve, the importance of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. Buyers must prioritize sourcing partners that offer not only high-quality chrome plating services but also innovative solutions that enhance durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance of components. Understanding the unique benefits of hard chrome plating—such as its ability to extend the lifespan of machinery and improve operational efficiency—can significantly impact your procurement strategies.
For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the selection of reliable suppliers with proven expertise is crucial. This involves evaluating their capabilities in handling diverse substrates, maintaining compliance with industry specifications, and employing advanced technologies for consistent quality.
Looking ahead, the demand for industrial chrome plating is set to grow as industries increasingly seek sustainable and cost-effective solutions. By aligning your sourcing strategies with trusted partners who prioritize innovation and quality, you can secure a competitive edge in your market. Now is the time to engage with leading chrome plating suppliers to enhance your operational resilience and drive long-term success.