Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high precision cnc machine
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high precision CNC machines presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With increasing demands for accuracy and efficiency across various sectors—from aerospace to medical manufacturing—finding the right machine can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the global market for high precision CNC machines, providing an in-depth exploration of types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly in countries like Germany and Brazil, will find valuable insights tailored to their unique market dynamics. By understanding the nuances of CNC technologies and the various factors influencing purchasing decisions, buyers can confidently navigate their options.
The comprehensive scope of this guide empowers businesses to make informed choices, ultimately enhancing productivity and reducing operational risks. Whether you are looking to invest in advanced machining capabilities or optimize existing processes, this resource serves as a strategic tool to identify the best solutions for your manufacturing needs. From understanding the specifications of machines to evaluating supplier reliability, this guide is your roadmap to successful procurement in the high precision CNC machine market.
Understanding high precision cnc machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Machining | Utilizes high RPM spindles (up to 60,000 RPM), integrated linear scales for accuracy. | Aerospace, Medical Manufacturing, Job Shops | Pros: Faster production, high precision. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| 5-Axis CNC Machines | Allows for complex geometries and angles, enhancing flexibility in machining operations. | Jewelry, Aerospace, Custom Parts Manufacturing | Pros: Versatility in production. Cons: Complexity in programming. |
| Mini CNC Machines | Compact design for small-scale applications, often budget-friendly. | Research & Development, Educational Institutions | Pros: Space-efficient, cost-effective. Cons: Limited working area and capacity. |
| Laser CNC Machines | Employs laser technology for cutting and engraving, ideal for intricate designs. | Electronics, Jewelry, Aerospace Components | Pros: High precision and detail. Cons: Material limitations. |
| Multi-Tasking CNC Machines | Combines turning, milling, and drilling in one machine, optimizing workflow. | Automotive, Aerospace, General Manufacturing | Pros: Streamlined operations, reduced setup time. Cons: Higher maintenance needs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of High-Speed Machining CNC Machines?
High-speed machining (HSM) CNC machines are distinguished by their ability to achieve high spindle speeds, often exceeding 60,000 RPM. This capability allows for faster material removal rates and reduced cycle times, making them ideal for industries such as aerospace and medical manufacturing, where precision is paramount. Buyers should consider the machine’s rigidity and thermal stability, which are crucial for maintaining accuracy during high-speed operations.
How Do 5-Axis CNC Machines Enhance Manufacturing Flexibility?
5-axis CNC machines provide the ability to machine complex parts with intricate geometries and angles. This versatility is particularly beneficial in sectors like jewelry and aerospace, where customization is often required. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate the software compatibility and ease of use, as programming these machines can be more complex than traditional 3-axis systems.
Why Choose Mini CNC Machines for Small-Scale Applications?
Mini CNC machines are designed for compactness and affordability, making them suitable for research labs and educational institutions. They typically feature a smaller workspace but can deliver high precision for applications such as micromilling and prototyping. Buyers should assess the machine’s capabilities against their specific needs, especially regarding material types and the required level of precision.
What Are the Advantages of Laser CNC Machines?
Laser CNC machines utilize laser technology to achieve high precision in cutting and engraving, making them ideal for intricate designs in electronics and jewelry manufacturing. Their ability to work with a variety of materials enhances their appeal. However, potential buyers should consider the limitations regarding the thickness of materials that can be processed and the costs associated with laser maintenance.
How Do Multi-Tasking CNC Machines Streamline Operations?
Multi-tasking CNC machines integrate various machining processes—turning, milling, and drilling—into a single setup, significantly optimizing workflow. This feature is particularly valuable in industries like automotive and aerospace, where efficiency and precision are critical. Buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced setup times against the potential for increased complexity in maintenance and operation.
Key Industrial Applications of high precision cnc machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of High Precision CNC Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Aviation | Manufacturing of critical components such as turbine blades | Ensures high tolerance and reliability in mission-critical parts | Certification standards, material compatibility, precision requirements |
| Medical Manufacturing | Production of surgical instruments and implants | Enhances patient safety through precise manufacturing | Biocompatibility, regulatory compliance, high-volume capacity |
| Electronics | Fabrication of intricate circuit boards and enclosures | Improves product performance and reduces failure rates | Material types, lead times, and scalability of production |
| Jewelry | Creation of custom jewelry designs and components | Allows for intricate designs and high-quality finishes | Precision capabilities, tooling options, and software support |
| Automotive | Production of engine components and molds | Increases efficiency and reduces waste in production | Tolerance levels, material selection, and production volume |
How Are High Precision CNC Machines Used in Aerospace and Aviation?
In the aerospace sector, high precision CNC machines are pivotal for manufacturing critical components, including turbine blades and structural parts. These machines ensure that parts meet stringent tolerance levels, which is essential for performance and safety in aircraft. Buyers in this industry must consider certification standards, as well as the compatibility of materials used in high-stress environments. The ability to produce complex geometries with high reliability is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and safety.
What Role Do High Precision CNC Machines Play in Medical Manufacturing?
High precision CNC machines are integral to the medical manufacturing industry, particularly for the production of surgical instruments and implants. These machines enable the creation of components with exceptional accuracy, which is vital for patient safety. International buyers must prioritize biocompatibility and regulatory compliance when sourcing CNC equipment, as medical devices are subject to rigorous standards. Additionally, high-volume capacity is necessary to meet the demands of healthcare providers, making efficiency a key factor in purchasing decisions.
How Are High Precision CNC Machines Transforming Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, high precision CNC machines are utilized for fabricating intricate circuit boards and enclosures. The precision offered by these machines leads to improved product performance and reduced failure rates, which are critical in a market where reliability is paramount. Buyers should focus on the types of materials compatible with these machines and the lead times for production. Scalability is another important consideration, particularly for companies looking to expand their product lines or increase production volumes.
What Benefits Do High Precision CNC Machines Provide to the Jewelry Sector?
High precision CNC machines are widely used in the jewelry industry for creating custom designs and components. These machines allow jewelers to achieve intricate designs and high-quality finishes that are difficult to replicate manually. Buyers in this sector should evaluate the precision capabilities of the machines, as well as the tooling options available for various materials. Software support for design and manufacturing processes is also a critical factor, enabling jewelers to innovate while maintaining efficiency.
How Are High Precision CNC Machines Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, high precision CNC machines play a crucial role in the production of engine components and molds. These machines enhance efficiency and reduce waste during production, leading to cost savings and improved product quality. Buyers should consider the required tolerance levels and material selections, as well as the anticipated production volume. The ability to adapt and produce various components without significant downtime is also a key consideration for manufacturers looking to stay competitive in a fast-paced market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high precision cnc machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Inconsistent Part Quality
The Problem: Many B2B manufacturers face the challenge of producing parts with consistent quality and precision. In industries such as aerospace and medical manufacturing, even the slightest deviation in measurements can lead to significant issues, including part failures and safety hazards. This inconsistency often stems from outdated machinery, inadequate setup, or improper maintenance. Buyers may find themselves frustrated as they deal with increased scrap rates and rework costs, impacting their bottom line and reputation.
The Solution: To combat inconsistencies, investing in a high-precision CNC machine equipped with advanced features is essential. Look for machines that include integrated linear measuring systems for real-time feedback on precision. For instance, selecting a machine with a high-resolution measuring system can help maintain tolerances as tight as 4-5 microns. Additionally, implementing regular maintenance schedules and operator training on best practices can ensure that the machine operates at peak performance. Establishing a feedback loop between operators and engineers can further enhance quality control by identifying recurring issues and addressing them proactively.
Scenario 2: High Setup Times Affecting Productivity
The Problem: High setup times can severely hinder productivity, especially in environments where quick turnarounds are critical. B2B buyers often experience delays due to lengthy setup procedures when switching between different production runs or when adjusting machines for new components. This not only leads to wasted time but also increases labor costs and decreases overall efficiency.
The Solution: To reduce setup times, consider investing in CNC machines that come with automated tool changers and advanced software for job setup. Machines like the DATRON M10 Pro, which features an automatic tool changer and user-friendly control software, can drastically minimize the time spent on setups. Moreover, standardizing tools and fixtures can further streamline the process, allowing operators to quickly switch between tasks without extensive recalibration. Incorporating fixtures that are easy to adjust and utilizing CAD/CAM software for efficient programming can also help reduce setup times, enabling faster transitions between production runs.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Machining Complex Geometries
The Problem: As industries demand more intricate and complex designs, many manufacturers struggle to keep up with the machining capabilities of their current CNC equipment. High precision CNC machines that lack advanced features may not be able to produce complex geometries accurately, leading to increased design iterations and customer dissatisfaction. B2B buyers may find themselves at a competitive disadvantage if they cannot meet the evolving demands of their clients.
The Solution: To address the need for machining complex geometries, invest in a high-precision CNC machine with 5-axis capabilities. These machines allow for greater flexibility and precision when working on intricate designs, enabling manufacturers to create parts that would otherwise require multiple setups. When selecting a machine, ensure it comes with powerful software that supports advanced programming for 5-axis machining. Additionally, training operators in 5-axis machining techniques will maximize the capabilities of the equipment, ensuring that they can produce high-quality parts that meet client specifications. By embracing these advanced technologies, manufacturers can position themselves as leaders in innovation and quality within their respective markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high precision cnc machine
What Are the Key Materials for High Precision CNC Machines?
Selecting the right materials for high precision CNC machining is critical for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four commonly used materials in the context of high precision CNC machining, considering their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Versatile Choice
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating up to 600°C and can withstand moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easy to machine and transport, reducing overall manufacturing complexity. However, its lower hardness compared to other metals can lead to wear and tear, necessitating more frequent tool changes. While aluminum is relatively inexpensive, specific alloys can drive costs up.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of media, making it suitable for industries such as aerospace and automotive. Its corrosion resistance also makes it ideal for marine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN when sourcing aluminum. Additionally, the availability of specific alloys may vary by region, impacting lead times and costs.
Stainless Steel: The Durable Workhorse
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers exceptional corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,600°C) and pressures. Its mechanical properties make it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: While stainless steel is highly durable, its machining complexity is greater than that of aluminum, often resulting in higher manufacturing costs. Additionally, the hardness of stainless steel can lead to increased tool wear, necessitating specialized cutting tools.
Impact on Application: Its strength and corrosion resistance make stainless steel ideal for medical devices, food processing equipment, and automotive components, where hygiene and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or JIS G4303 is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific grades, as this can vary significantly across regions.
Titanium: The Premium Material for High-Performance Applications
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures (up to 1,600°C). Its low thermal conductivity can complicate machining processes.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its unmatched strength and durability, making it suitable for aerospace and medical applications. However, it is significantly more expensive than aluminum or stainless steel and requires specialized machining techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Titanium’s biocompatibility makes it ideal for medical implants, while its strength and lightweight properties are advantageous in aerospace applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM F136 for medical applications. The high cost and specialized machining requirements may limit its use for certain projects, particularly in cost-sensitive regions.
Polymer Composites: The Lightweight Alternative
Key Properties: Polymer composites offer excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand moderate temperatures (up to 200°C). They are lightweight and can be engineered for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polymer composites is their lightweight nature and flexibility in design. However, they are generally less durable than metals and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: These materials are commonly used in industries such as aerospace and automotive for non-structural components, where weight reduction is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 is essential. The availability of specific composite materials may vary by region, influencing project timelines.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for high precision cnc machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower hardness leads to wear | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing equipment | Exceptional durability and corrosion resistance | Higher machining complexity | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace applications, medical implants | Unmatched strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and specialized machining | High |
| Polymer Composites | Aerospace non-structural components | Lightweight and design flexibility | Less durable than metals | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed decisions when sourcing materials for high precision CNC machining applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high precision cnc machine
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing High Precision CNC Machines?
Manufacturing high precision CNC machines involves a multi-stage process designed to ensure that every component meets stringent quality standards. Here are the primary stages:
-
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing CNC machines is material selection. Typically, high-quality metals such as steel, aluminum, and sometimes composites are chosen for their durability and machinability. These materials are then cut to size and prepared for further processing. Rigorous inspections are conducted to verify material properties, ensuring that they comply with industry standards such as ASTM or ISO. -
Forming
In this stage, various techniques such as machining, casting, and forging are employed to shape the components. CNC machining centers are often used for their precision and efficiency. Techniques like milling, turning, and grinding are utilized to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finishes. Advanced technologies, including 5-axis milling, are employed to produce complex geometries with high accuracy. -
Assembly
After forming, the components undergo assembly, which may involve both manual and automated processes. Each assembly stage is crucial for maintaining the machine’s overall precision and functionality. During this phase, components such as spindles, tool changers, and control systems are integrated. Assemblers follow detailed schematics and perform checks to ensure all parts fit correctly and function as intended. -
Finishing
The finishing stage includes processes that enhance the machine’s performance and aesthetics. This may involve surface treatments like anodizing, painting, or powder coating, which improve corrosion resistance and surface hardness. Precision measurements are taken to ensure that tolerances remain within specified limits.
How Is Quality Control Implemented in High Precision CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of manufacturing high precision CNC machines, ensuring that each unit meets the required specifications and international standards. Key components of a robust QC process include:
-
International Standards Compliance
High precision CNC machine manufacturers often adhere to recognized international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for quality management systems. Compliance with CE marking standards is also crucial for machines sold in Europe, ensuring safety and environmental responsibility. -
Industry-Specific Certifications
Some industries require additional certifications. For example, aerospace components may need to comply with AS9100, while oil and gas industries might require API certifications. Understanding these specific standards is essential for B2B buyers, as they can impact machine performance and reliability. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically divided into several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, processes are continuously monitored to catch defects early. Techniques like statistical process control (SPC) are often used.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each machine undergoes a final inspection where it is tested for functionality, precision, and compliance with specifications. -
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of CNC machines. These include dimensional checks using coordinate measuring machines (CMM), functional tests for operational efficiency, and stress tests to evaluate the machine’s durability. Additionally, thermal imaging may be used to identify potential overheating issues during operation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control standards. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits
Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers allows buyers to directly observe the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and adherence to international standards. -
Reviewing Quality Assurance Reports
Requesting and reviewing quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports and compliance certificates, can help buyers assess a supplier’s track record. Look for documentation that details the QC processes and results, including any deviations from standards and corrective actions taken. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control practices. These services often include detailed reports on compliance with industry standards, material certifications, and testing outcomes.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers operating in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences
Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality standards and practices. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and industry practices to ensure compliance and avoid potential pitfalls. -
Language and Communication Barriers
Miscommunication can lead to misunderstandings regarding specifications and quality expectations. It’s essential to establish clear lines of communication and possibly engage translators or local representatives to facilitate discussions. -
Logistical Considerations
International shipping can introduce risks that affect quality, such as handling damage or environmental exposure. Buyers should discuss packaging and shipping methods with suppliers to minimize these risks, ensuring that machines arrive in optimal condition. -
Post-Sale Support and Warranty
Quality assurance doesn’t end at the sale. Buyers should inquire about post-sale support, warranty terms, and service agreements. Understanding the supplier’s commitment to after-sales service can be a decisive factor in ensuring long-term satisfaction with the purchase.
By paying close attention to these manufacturing processes and quality control measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and overall productivity in the high precision CNC machine sector.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high precision cnc machine’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring high precision CNC machines. As businesses seek to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, understanding the complexities of selecting the right CNC machine is crucial. This checklist provides actionable steps to ensure you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and quality standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your CNC machine. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will be machining, the required precision levels, and the dimensions of the parts you intend to produce.
– Precision Tolerance: Specify the precision range (e.g., ±0.0003 inches) that your applications demand.
– Material Compatibility: Identify materials (metals, plastics, composites) that the machine must handle effectively.
Step 2: Assess Machine Capabilities
Evaluate the capabilities of potential CNC machines against your specifications. Look for machines that offer high spindle speeds and robust construction, which are essential for achieving high precision.
– Spindle Speed: Higher RPMs can lead to faster machining and better surface finishes.
– Machine Stability: Consider machines with solid bases, such as granite tables, to enhance stability and accuracy.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
– Supplier Reputation: Research online reviews and industry forums to gauge customer satisfaction.
– Experience in Your Industry: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific sector, such as aerospace or medical manufacturing.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the machines and suppliers comply with international standards and certifications relevant to your industry. This verification is critical for maintaining quality and safety.
– ISO Certifications: Confirm that the supplier adheres to ISO standards, which reflect quality management practices.
– Local Regulations: Be aware of any specific regulations in your region, such as CE marking in Europe or ANSI standards in the U.S.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Samples
Before finalizing your purchase, ask for machine demonstrations or trial runs to assess performance. This hands-on evaluation can provide valuable insights into the machine’s operational efficiency.
– Live Demonstrations: Arrange visits to the supplier’s facility to see the machine in action.
– Sample Parts: Request the production of sample parts to evaluate quality and precision firsthand.
Step 6: Consider After-Sales Support and Training
Inquire about the level of after-sales support and training provided by the supplier. Effective support is essential for maximizing the machine’s performance and ensuring a smooth operation.
– Technical Support: Ensure that the supplier offers responsive technical assistance and maintenance services.
– Operator Training: Look for suppliers that provide comprehensive training programs for your staff to optimize machine usage.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Purchase
Once you have evaluated your options, negotiate the terms of the purchase, including price, warranty, and delivery timelines. A well-negotiated contract can protect your investment and clarify responsibilities.
– Warranty Terms: Ensure that the warranty covers critical components and includes on-site support if necessary.
– Payment Terms: Discuss flexible payment options that align with your budget and cash flow requirements.
By following this checklist, you can ensure that your sourcing process for high precision CNC machines is thorough and aligned with your business goals, ultimately enhancing your manufacturing capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high precision cnc machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in High Precision CNC Machine Sourcing?
When sourcing high precision CNC machines, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The cost components generally include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials used significantly impacts the overall cost. High-grade metals and composites tend to be more expensive but offer better durability and precision.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for both manufacturing and programming CNC machines. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location, with regions like Europe typically having higher labor costs compared to Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility costs. Manufacturers with advanced technology and automated processes may have lower overheads over time.
-
Tooling Costs: Precision machining often requires specialized tools that can add to initial costs. The choice of tooling can affect production efficiency and the quality of the finished product.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures adds to costs but is essential for ensuring that the machines meet the required specifications and certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs vary depending on the machine’s size and weight, as well as the shipping distance. Import duties and tariffs can further influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect High Precision CNC Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of high precision CNC machines:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specialized tooling or software, can significantly increase costs. Clearly defining specifications can help in obtaining accurate quotes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Machines built with high-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) generally come at a premium but ensure reliability and compliance with international standards.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, manufacturing capabilities, and geographic location of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international commercial terms can help buyers manage shipping costs and responsibilities. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in CNC Machine Sourcing?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Suppliers often have flexibility in their pricing structures, particularly for bulk orders.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime when evaluating the TCO of a CNC machine.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing. Look for suppliers that offer comprehensive support and training, as these can add value beyond the machine itself.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic conditions, import duties, and transportation costs. Understanding these nuances can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Request Indicative Prices: Always ask for indicative prices to gauge market rates. However, remember that these prices can fluctuate based on market demand and other external factors.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for high precision CNC machines can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors and are subject to change. It is crucial for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high precision cnc machine With Other Solutions
When exploring manufacturing solutions, particularly for high-precision tasks, businesses often evaluate alternatives to high precision CNC machines. These alternatives can offer varying levels of performance, cost-effectiveness, and operational efficiency. Understanding these options can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific manufacturing needs.
| Comparison Aspect | High Precision CNC Machine | Alternative 1 Name: Laser Cutting Machine | Alternative 2 Name: Traditional Machining (Manual) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Exceptional accuracy (4-5 microns) and speed (up to 30 m/min) | High precision for cutting thin materials, less effective for thick materials | Variable precision depending on operator skill; slower than CNC |
| Cost | High initial investment; long-term savings through efficiency | Moderate initial cost; lower operational costs due to minimal material waste | Low initial cost; higher labor costs and longer production times |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and training for optimal use | Easier to operate with minimal training; software-controlled | High skill requirement; training necessary for effective operation |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; reliance on software updates | Low maintenance; occasional lens replacements | High maintenance due to wear and tear on manual tools |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for complex, high-volume production across various industries | Best for precision cutting of metals and plastics in industries like automotive | Suitable for small-scale operations or prototyping where flexibility is needed |
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a Laser Cutting Machine?
Laser cutting machines utilize focused beams of light to cut materials, offering high precision, particularly for thin sheets of metal and plastics. One of the primary advantages is their speed and efficiency, leading to minimal material waste. However, they tend to be less effective for thicker materials and can incur higher operational costs if used extensively on heavy-duty projects. Additionally, they may require specific safety measures due to the laser technology involved.
How does Traditional Machining compare as an alternative?
Traditional machining, particularly manual processes, can be advantageous for smaller-scale operations or custom projects where flexibility is essential. It often requires a lower initial investment in equipment compared to CNC machines. However, this method is heavily reliant on the operator’s skill and experience, which can lead to variability in precision and longer production times. Maintenance can also be more demanding due to the wear and tear of manual tools, making it less suitable for high-volume production environments.
How can B2B buyers select the right manufacturing solution for their needs?
Choosing the right manufacturing solution involves assessing your specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and production goals. For high-volume, precision-focused projects, high precision CNC machines offer unmatched accuracy and speed, making them a worthwhile investment despite the higher initial costs. Alternatively, if your operations focus on cutting thin materials with a need for speed and efficiency, a laser cutting machine might be more suitable. For smaller projects or custom work, traditional machining may be sufficient. Ultimately, aligning the chosen technology with your production needs and budget will lead to optimal operational outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high precision cnc machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of High Precision CNC Machines?
When evaluating high precision CNC machines, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in machining processes. High precision CNC machines typically operate within very tight tolerances, often in the range of microns. For B2B buyers, tighter tolerances mean improved part accuracy and a reduction in the need for rework, ultimately leading to cost savings and enhanced product quality. -
Spindle Speed
The spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicates how fast the cutting tool rotates. High-speed spindles, such as those reaching 40,000 RPM or more, allow for quicker machining operations and the ability to work with harder materials. This is particularly important for industries like aerospace and medical manufacturing, where speed and precision are paramount. -
Feed Rate
Feed rate is the speed at which the cutting tool advances through the material, usually measured in meters per minute. An optimal feed rate can enhance productivity and surface finish quality. B2B buyers should assess how the feed rate aligns with their production needs, as it directly impacts machining efficiency and overall throughput. -
Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of CNC machines, such as cast iron, steel, and granite, significantly affect their performance. Machines with a solid granite base, for instance, offer enhanced thermal stability and rigidity, which are crucial for maintaining precision over extended periods. Selecting machines with appropriate material grades ensures durability and long-term reliability. -
Control System
The CNC machine’s control system dictates its functionality and ease of use. Advanced control systems offer features such as automated tool changers and intuitive programming interfaces, which can significantly reduce setup time and operator error. For B2B buyers, investing in machines with sophisticated control systems can lead to smoother operations and a faster return on investment. -
Axis Configuration
The number of axes on a CNC machine (e.g., 3-axis, 5-axis) determines its capability to perform complex machining tasks. Multi-axis machines allow for more intricate designs and greater flexibility in production. For manufacturers looking to produce intricate components, investing in multi-axis machines can enhance versatility and competitiveness in the market.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the CNC Machine Industry?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When purchasing CNC machines, buyers often deal with OEMs to ensure they receive high-quality components that meet specific operational standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant in B2B transactions where buyers need to meet certain order thresholds to receive favorable pricing or terms. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by potential buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare pricing and terms from various vendors. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms helps buyers manage risks and costs associated with international shipping of CNC machines. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is fulfilled. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and inventory management. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools via a computer. This technology allows for high precision and repeatability in manufacturing processes, making it a cornerstone of modern machining operations.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting high precision CNC machines that best fit their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high precision cnc machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the High Precision CNC Machine Sector?
The global high precision CNC machine market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation and precision engineering across various industries. As businesses in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing expand, the need for high-quality, reliable, and efficient machining solutions has surged. This demand is particularly evident in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where advanced manufacturing technologies are pivotal to maintaining competitive advantages.
Emerging trends include the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, which emphasize connectivity and data analytics in manufacturing processes. Buyers are increasingly looking for CNC machines equipped with IoT capabilities, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This shift not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances decision-making through data-driven insights. Additionally, the rise of additive manufacturing is influencing CNC machine designs, prompting manufacturers to integrate hybrid solutions that can handle both subtractive and additive processes.
International B2B buyers from Africa and South America are also becoming more discerning, prioritizing suppliers who offer comprehensive support, including training and after-sales services. This trend reflects a broader shift towards partnerships rather than transactional relationships, as companies seek long-term value and collaboration in their sourcing strategies.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the CNC Machine Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of business strategy in the high precision CNC machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has led to increased scrutiny from stakeholders, prompting companies to seek CNC machines that minimize waste and energy consumption. This includes selecting machines with energy-efficient motors and systems designed for optimal resource utilization.
Moreover, the importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the provenance of materials and the conditions under which they are produced. Companies that demonstrate commitment to ethical supply chains—through transparency and adherence to environmental regulations—are more likely to build trust and loyalty among international buyers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of recycled materials can enhance a manufacturer’s appeal in global markets.
As the demand for ‘green’ manufacturing solutions grows, buyers are advised to prioritize suppliers who not only comply with sustainability standards but also actively innovate in this area. This proactive approach not only supports corporate social responsibility initiatives but can also lead to cost savings and improved brand reputation.
What Is the Evolution of High Precision CNC Machines and Its Relevance to Current B2B Trends?
The evolution of high precision CNC machines can be traced back to the early days of numerical control technology in the 1950s. Initially developed for the aerospace industry, these machines have undergone significant advancements, incorporating computer technologies that allow for unprecedented levels of accuracy and complexity in machining.
In recent decades, the introduction of multi-axis CNC systems has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, enabling the production of intricate parts with reduced lead times. As industries continue to demand higher precision and faster production cycles, CNC machines have adapted by integrating advanced materials and automation technologies.
This historical context is critical for B2B buyers as it highlights the trajectory of innovation in the sector. Understanding these developments can inform purchasing decisions, guiding companies toward machines that not only meet current needs but also have the capacity for future upgrades and adaptations. Investing in high precision CNC technology is no longer just about meeting present specifications; it’s about positioning for future growth in a rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high precision cnc machine
-
How do I select the right high precision CNC machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right high precision CNC machine involves assessing your specific manufacturing requirements, including part dimensions, materials, and tolerances. Consider factors such as the machine’s spindle speed, rigidity, and accuracy. Evaluate the available workspace and the machine’s footprint to ensure it fits your production area. Additionally, review the machine’s capabilities for automation and integration with your existing systems. Engaging with suppliers for demonstrations and consulting their technical specifications can provide valuable insights. -
What are the key features to look for in a high precision CNC machine?
Key features include a high RPM spindle for fast machining, linear scales for precision, and a robust construction to minimize vibration. Look for machines with integrated probing systems for accurate setup and material compensation. A solid granite table enhances stability and accuracy, while brushless servo motors improve response times and precision. Additionally, consider the machine’s software capabilities for user-friendly operation and programming flexibility, which can significantly enhance productivity. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering a high precision CNC machine?
Lead times can vary based on the manufacturer, machine specifications, and order volume. Generally, expect a lead time of 8 to 16 weeks for standard machines. Custom-built machines may require longer, typically 16 to 24 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss timelines with suppliers during the initial inquiry phase. Planning ahead and placing orders in advance can help mitigate delays, especially when incorporating specific customizations or advanced features. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for high precision CNC machines?
Most manufacturers do not have strict MOQs for CNC machines, as each machine is often made to order. However, some suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders or multiple machines. Discuss your needs with the supplier to understand their pricing structure and any potential savings for larger orders. Be sure to clarify whether your order includes additional tooling or accessories, as this may affect the overall cost and delivery terms. -
How do I vet suppliers when sourcing high precision CNC machines internationally?
When vetting suppliers, research their reputation through online reviews, industry forums, and referrals. Request references from previous customers to gauge their experience. Evaluate the supplier’s certifications, such as ISO, which indicate adherence to quality standards. Additionally, consider visiting the manufacturing facility if possible or using virtual tours. Ensure they have reliable after-sales support and warranty terms, which are crucial for ongoing maintenance and service. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for high precision CNC machines?
Payment terms can vary widely between suppliers, but they typically include options such as upfront deposits (usually 30-50%) followed by the balance before shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing or leasing options, which can be beneficial for businesses looking to manage cash flow. Always clarify the terms in writing and understand any implications regarding delivery timelines and warranty coverage based on the payment structure. -
How is quality assurance handled for high precision CNC machines?
Quality assurance processes often include rigorous testing at various production stages, including pre-shipment inspections. Many manufacturers utilize advanced measuring tools to ensure precision specifications are met, along with documented quality control procedures. Request detailed QA protocols from suppliers, including any certifications and test results. Understanding these processes can provide confidence in the machine’s performance and longevity. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC machines?
When importing CNC machines, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure the supplier provides adequate packaging to protect the machinery during transit. Work with logistics providers experienced in handling heavy machinery to navigate import regulations specific to your country. Additionally, confirm that the supplier offers support for installation and training, which can facilitate smoother integration into your operations upon arrival.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
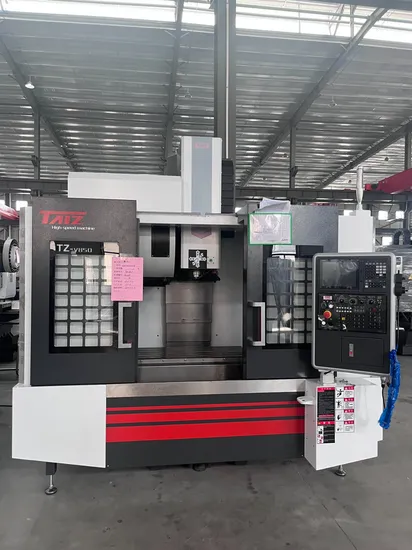
Top 5 High Precision Cnc Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. DATRON – M10 Pro Ultra-Precision CNC Machine
Domain: datron.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: DATRON M10 Pro – Ultra-Precision CNC Machine with Largest Workspace in Smallest Footprint. Designed for high-precision machining of large parts with minimal errors. Features include:
– Travel: 1,020 x 830 x 240 mm (40” x 33” x 9.5”) (X, Y, Z)
– Spindle: Up to 40,000 RPM, 3 kW HSK spindle
– Feed Rate: Up to 30 m/min (1,181 in/min)
– Tool Changer: Up to 24 stations automatic tool changer
– Control S…
2. DMG MORI – CNC Machines for Metal Processing
Domain: en.dmgmori.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: DMG MORI offers a comprehensive range of CNC machines for various applications in metal processing, including non-ferrous metals, steel, stainless steel, strong alloys, plastics, composite materials, glass, and diamond. Key industries served include tool and mould construction, aerospace, medical technology, and the semiconductor industry. The product range is modular, featuring modern CNC control…
3. Reading Plastic – Precision CNC Milling
Domain: readingplastic.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: High Precision CNC Milling Provider at Reading Plastic & Metal offers precision plastic machining with tolerances of +/- .001 and surface finishes as smooth as 15Ra. The services include advanced plastic parts production, secondary post-milling operations (adding threads, finishing through-bores, mounting surfaces, branding), and machining of associated metal parts. CNC milling machines provide ve…
4. Avant Engineering – High Precision Machining
Domain: avantiengineering.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: High precision machining is a critical manufacturing process that ensures parts are made with exceptional accuracy and consistency. It utilizes subtractive methods to remove material and create intricate designs, meeting strict tolerances. Key industries served include aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics. Avanti Engineering offers various machining services such as CNC Multi-Spindle Ma…
5. Fadal – CNC Machines & Vertical Machining Centers
Domain: fadal.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Fadal is a CNC machine builder offering a range of Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs) including models VMC 2015HS, VMC 2520, VMC 3320, VMC 4020, VMC 4022, VMC 6032, VMC 8032, VMC 6032/50T, and VMC 8032/50T. They also provide 5-Axis Machines (VM5ax320) and various workholding accessories such as MULTIRISERS, RISERS, ADJUSTABLE RISERS, FAST MILL ZERO, SPECIAL, STANDARD, and MODULAR PLATES, and MINI R…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high precision cnc machine
In the competitive landscape of precision manufacturing, strategic sourcing of high precision CNC machines is paramount for businesses aiming to enhance productivity and quality. As highlighted throughout this guide, investing in advanced CNC technology—such as those offered by DATRON, NS CNC, and DMG MORI—enables companies to achieve exceptional accuracy, reduce scrap rates, and streamline operations. By selecting machines with robust features like integrated measuring systems, high-speed spindles, and thermal stability, organizations can meet the stringent demands of various industries including aerospace, medical, and automotive.
International B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize sourcing partners that not only provide top-tier machinery but also offer comprehensive support, training, and automation solutions. This holistic approach will empower your business to adapt to evolving market needs and enhance competitive advantage.
Looking ahead, embracing innovative CNC technologies is essential for sustaining growth and operational excellence. Engage with trusted suppliers today to explore tailored solutions that can transform your manufacturing capabilities and position your organization for future success.