Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high carbon spring steel
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing and engineering, sourcing high carbon spring steel presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers across the globe. This versatile material, known for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and fatigue resistance, is critical in the production of various industrial components such as technical springs, automotive parts, and heavy machinery. However, navigating the complexities of global suppliers, varying quality standards, and competitive pricing can be daunting, especially for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower B2B buyers by providing insights into the diverse types of high carbon spring steel available, their specific applications, and essential considerations for supplier vetting. Buyers will gain a thorough understanding of the chemical compositions that define different grades, such as C55S and C100S, and the implications these have on performance and cost. Additionally, the guide will outline best practices for evaluating suppliers to ensure quality and reliability in sourcing.
By leveraging the information within this guide, buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Ultimately, our goal is to simplify the procurement process, enabling businesses to secure the right materials for their applications while fostering long-term partnerships with trustworthy suppliers.
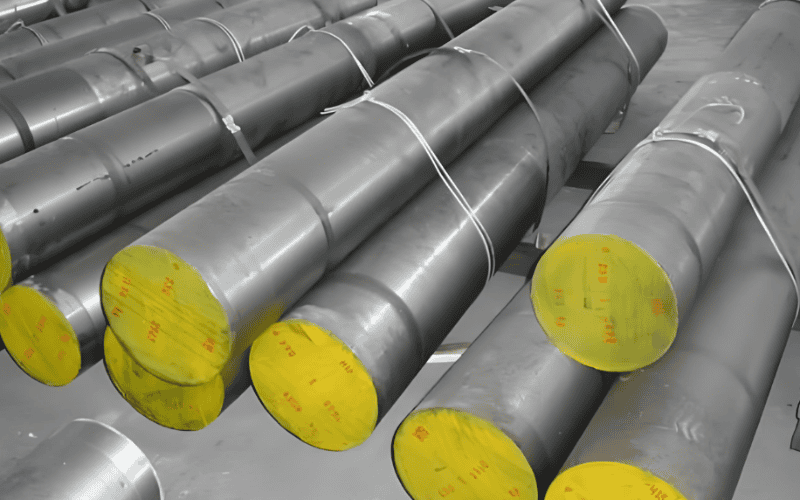
Understanding high carbon spring steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| C55S | Carbon content: 0.52 – 0.60%; good toughness | Technical springs; industrial use | Pros: Excellent balance of flexibility and strength. Cons: Moderate corrosion resistance. |
| C75S | Carbon content: 0.70 – 0.80%; high hardenability | Automotive components; machinery | Pros: Strong retention of elasticity. Cons: Requires careful heat treatment to avoid brittleness. |
| 51CrV4 | Added chromium and vanadium for enhanced durability | Heavy-duty springs; suspension systems | Pros: Excellent wear resistance; suitable for dynamic applications. Cons: Higher cost due to alloying elements. |
| 5160 | Contains chromium; known for toughness | Manufacturing tools; spring blades | Pros: Outstanding toughness and fatigue resistance. Cons: Regular maintenance required for longevity. |
| C100S | Carbon content: 0.95 – 1.05%; excellent for hardening | Specialty springs; precision applications | Pros: Exceptional strength and elasticity. Cons: More challenging to work with due to high carbon content. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of C55S High Carbon Spring Steel?
C55S is characterized by its balanced carbon content of 0.52-0.60%, providing good toughness and elasticity, essential for a variety of spring applications. It finds its primary utilization in technical springs used in industrial environments. For buyers, the appealing aspect of C55S lies in its strong performance in bending and retaining shape, but it does present some concerns regarding corrosion resistance, necessitating proper coatings or treatments depending on the application environment.
Why is C75S Effective for Automotive Components?
C75S, with its higher carbon content (0.70-0.80%), offers remarkable hardenability and elasticity, making it ideal for automotive components and machinery applications where resilience is paramount. Its ability to retain elasticity under strain is a significant advantage for manufacturers seeking durability. However, buyers should note that C75S requires meticulous heat treatment processes to prevent brittleness after hardening, thus influencing its overall cost-effectiveness.
How Does 51CrV4 Stand Out in Dynamic Applications?
The 51CrV4 variant boosts durability and performance through the addition of chromium and vanadium. It is predominantly used in heavy-duty springs and suspension systems, where enhanced wear resistance is critical. Buyers can benefit from its performance in dynamic applications; however, it incurs a higher cost due to its alloying constituents. This increase in investment often yields long-term savings through reduced failure and maintenance needs.
What Makes 5160 Steel Ideal for Manufacturing Tools?
5160 high carbon spring steel is highly regarded for its toughness, making it suitable for manufacturing tools and spring blades. Its chromium content significantly enhances wear resistance and fatigue life. While it excels in providing a durable edge, ensuring proper maintenance is vital for longevity, as this type requires regular attention to prevent rust and degradation. B2B buyers must consider service conditions that may impose additional care requirements.
Why is C100S Recognized for Specialty Springs?
C100S features a carbon range of 0.95-1.05%, presenting exceptional strength and elasticity, suitable for specialty springs and precision applications. Its hardening capability offers superior performance in critical environments, ensuring that it holds its shape under considerable stress. However, due to its high carbon content, working with C100S can be more challenging, often requiring specialized knowledge in heat treatment, which can pose additional considerations for B2B buyers assessing manufacturing capabilities.
Key Industrial Applications of high carbon spring steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of high carbon spring steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Suspension springs | Enhanced vehicle stability and performance | Compliance with automotive standards and specifications |
| Manufacturing | Industrial machinery springs | Improved machinery reliability and operational efficiency | Availability of various grades and customization options |
| Aerospace | Aircraft landing gear springs | Increased safety and performance under extreme conditions | Certification and traceability of materials used |
| Construction | Heavy-duty springs for cranes and lifts | Enhanced lifting capacity and durability | Sourcing from reputable suppliers with quality assurance |
| Consumer Products | High-performance springs in sporting equipment | Improved product performance and user satisfaction | Consideration of weight, size, and material properties |
How is High Carbon Spring Steel Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, high carbon spring steel is primarily utilized in the manufacture of suspension springs. These components are critical for vehicle stability, absorbing shocks and maintaining alignment. By using high carbon spring steel, manufacturers can achieve a balance of flexibility and strength, ensuring that the springs can endure repeated loads without permanent deformation. International buyers must consider automotive standards and specifications, ensuring that the steel grades meet the necessary safety and performance benchmarks.
What Role Does High Carbon Spring Steel Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, high carbon spring steel is essential for producing industrial machinery springs, which are vital for equipment reliability. These springs often endure significant stress and require materials that can withstand fatigue while maintaining elasticity. The use of high carbon spring steel enhances the operational efficiency of machinery, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Buyers should focus on sourcing from suppliers that offer a range of grades and customization options to meet specific machinery requirements.
Why is High Carbon Spring Steel Important in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, high carbon spring steel is used in components such as aircraft landing gear springs, which must perform under extreme conditions. These springs are designed to absorb the impact of landings and provide structural integrity during flight. The use of high carbon spring steel ensures durability and performance, which are critical for safety in aviation. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing materials that come with proper certification and traceability to meet stringent aerospace regulations.
How is High Carbon Spring Steel Applied in Construction?
High carbon spring steel is also utilized in the construction industry, particularly in heavy-duty springs for cranes and lifting equipment. These springs enhance the lifting capacity and durability of machinery, ensuring that they can handle heavy loads without failure. The reliability of these springs is crucial for safety on construction sites. Buyers should consider sourcing from reputable suppliers that provide quality assurance to ensure the springs can withstand the rigors of construction environments.
What Benefits Does High Carbon Spring Steel Offer in Consumer Products?
In the consumer products sector, high carbon spring steel is frequently found in sporting equipment, where high-performance springs contribute to better product performance and user satisfaction. These springs are designed to provide the right amount of tension and flexibility, enhancing the functionality of items such as bicycles and fitness machines. Buyers should consider the weight, size, and material properties when sourcing these springs to ensure they meet the specific needs of their products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high carbon spring steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Grade of High Carbon Spring Steel
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges in selecting the appropriate grade of high carbon spring steel for their specific applications. The vast variety of grades, such as C55S, C75S, or 51CrV4, can be overwhelming, especially when each grade has distinct mechanical properties, chemical compositions, and heat treatment requirements. This confusion can lead to suboptimal performance in end products, increased costs, or even project delays due to improper material specifications.
The Solution: To effectively select the right grade of high carbon spring steel, buyers should first conduct a thorough analysis of their application requirements. This includes understanding the environmental factors, load conditions, and performance expectations. Consulting with suppliers who offer detailed technical support can also be invaluable. Buyers should request material datasheets that outline tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and elongation properties. Furthermore, leveraging industry standards (like DIN EN 10132-4) can guide the selection process. Finally, consider prototyping with smaller quantities of different grades to evaluate performance under actual conditions before committing to larger orders.
Scenario 2: Challenges in the Heat Treatment Process
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues during the heat treatment of high carbon spring steel, which is critical for achieving desired mechanical properties. Improper heat treatment can lead to problems such as brittleness, inadequate hardness, or a failure to meet specific performance standards. This not only results in wasted materials but also affects the durability and reliability of the final products, potentially leading to costly recalls or replacements.
The Solution: To mitigate heat treatment challenges, it is essential to collaborate closely with experienced metallurgists or suppliers who specialize in spring steels. Understanding the specific heat treatment processes—such as hardening, tempering, and isothermal transformation—is crucial. Buyers should invest in training for their technical teams on these processes, ensuring they are well-versed in temperature control, cooling rates, and time requirements for each treatment. Implementing quality control measures, such as regular monitoring of heat treatment processes and conducting post-treatment inspections, will help ensure that the steel meets the required specifications.
Scenario 3: Sourcing High Carbon Spring Steel in Diverse Markets
The Problem: Buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe often struggle with sourcing high carbon spring steel due to limited availability and inconsistent quality. Variability in supply chains, along with fluctuating market prices, can hinder timely procurement and impact project timelines. Additionally, navigating import regulations and tariffs can complicate sourcing decisions.
The Solution: To streamline sourcing efforts, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions to diversify their supply chain. This approach not only mitigates risks associated with single-source dependency but also provides leverage in negotiating prices. Utilizing online platforms and industry-specific trade shows can facilitate connections with reputable suppliers. Additionally, buyers should conduct regular market research to stay informed about price trends and availability. Implementing a strategic inventory management system that anticipates demand fluctuations can further ensure a steady supply of high carbon spring steel, reducing the likelihood of production delays.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high carbon spring steel
What Are the Key Properties of High Carbon Spring Steel Materials?
High carbon spring steels are primarily characterized by their carbon content, which typically ranges from 0.55% to 1.05%. This high carbon content contributes to their superior hardness and tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring resilience and elasticity. Common grades include C55S, C60S, C67S, C75S, and C100S, each offering distinct properties suited for various industrial applications.
These materials exhibit excellent fatigue resistance, allowing them to endure repeated stress without failure. Additionally, they can be treated through processes such as hardening, tempering, and isothermal transformation to enhance their performance characteristics further. The incorporation of alloying elements like silicon, manganese, chromium, and vanadium also contributes to their mechanical properties, making them suitable for demanding environments.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using High Carbon Spring Steel?
C55S: This grade is known for its good balance between strength and ductility. It is often used in automotive applications for suspension components. The primary advantage of C55S is its cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for mass production. However, it may not perform well in highly corrosive environments unless treated.
C75S: With a higher carbon content, C75S offers improved hardness and wear resistance. It is ideal for applications requiring high strength, such as industrial springs. The downside is that its increased hardness can lead to brittleness, making it less suitable for applications where flexibility is crucial.
C100S: This grade provides exceptional hardness and is often used in high-performance applications. Its key advantage is its ability to withstand high stress and temperature conditions. However, the cost is relatively high, and it may require specialized processing techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
How Does Material Selection Impact Application Performance?
Material selection significantly affects the performance of high carbon spring steel in various applications. For instance, C60S is often preferred for automotive springs due to its excellent fatigue resistance and ability to return to its original shape after deformation. Conversely, C100S is favored in high-stress applications, such as in aerospace, where performance under extreme conditions is critical.
International B2B buyers must also consider compliance with regional standards. For example, European buyers may require adherence to DIN standards, while those in the Middle East and Africa might look for compliance with ASTM standards. Understanding these requirements is crucial for ensuring product quality and market acceptance.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing High Carbon Spring Steel?
International buyers should be aware of several factors when sourcing high carbon spring steel. Compliance with local regulations and standards is paramount. Buyers from Africa and South America may face challenges related to supply chain logistics and material availability. In contrast, European buyers often prioritize sustainability and environmental impact, necessitating a focus on manufacturers who adhere to eco-friendly practices.
Additionally, understanding the specific applications and end-use requirements can guide buyers in selecting the appropriate grade of spring steel. For instance, industries such as automotive and aerospace may have more stringent requirements regarding material properties and certifications.
| Material | Typical Use Case for high carbon spring steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C55S | Automotive suspension components | Cost-effective with good ductility | Poor performance in corrosive environments | Low |
| C75S | Industrial springs | High strength and wear resistance | Increased brittleness | Medium |
| C100S | High-performance applications | Exceptional hardness and stress resistance | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| C60S | Automotive springs | Excellent fatigue resistance | Limited flexibility compared to lower grades | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of high carbon spring steel materials, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high carbon spring steel
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing High Carbon Spring Steel?
The manufacturing process of high carbon spring steel involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing materials.
Material Preparation: What Is Involved?
The initial phase begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. High carbon spring steel typically contains carbon content ranging from 0.55% to 1.00%, along with alloying elements such as manganese, silicon, and chromium. The steel is often produced from high-quality scrap or direct reduced iron (DRI) to ensure purity and consistency.
Once the raw materials are selected, they undergo melting in an electric arc furnace (EAF) or induction furnace. This step is crucial for achieving the desired chemical composition. After melting, the molten steel is poured into molds and allowed to solidify into billets or slabs, which serve as the starting point for further processing.
How Is High Carbon Spring Steel Formed?
The forming stage encompasses several methods, including hot rolling, cold rolling, and heat treatment. Hot rolling involves reheating the billets to a temperature above their recrystallization point, allowing them to be shaped into desired profiles while maintaining the steel’s mechanical properties.
Cold rolling, on the other hand, is performed at room temperature, which enhances the strength and surface finish of the steel. This technique is particularly beneficial for applications requiring precision and tighter tolerances.
Heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering, are employed to enhance the hardness and elasticity of the spring steel. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the steel to lock in hardness, while tempering reduces brittleness and improves toughness.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Finishing processes for high carbon spring steel typically include surface treatment, coating, and stress relieving. Surface treatments such as shot peening enhance fatigue resistance by inducing compressive stresses on the surface.
Coating may involve galvanizing or applying other protective layers to prevent corrosion, especially for products used in harsh environments. Stress relieving is crucial for minimizing residual stresses that may have developed during forming or heat treatment, ensuring the steel maintains its shape and performance under load.
What Quality Control Measures Are in Place for High Carbon Spring Steel?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of high carbon spring steel, particularly for international B2B transactions where compliance with various standards is critical.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets or API for oil and gas applications are essential indicators of compliance with safety and quality regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production helps identify any deviations from established standards, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all required specifications before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Common testing methods for high carbon spring steel include tensile testing, hardness testing (Rockwell or Brinell), and impact testing. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection, are also employed to detect any internal flaws without compromising the integrity of the material.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial to ensuring product reliability and compliance with local regulations. Here are several strategies:
What Steps Should Be Taken for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s quality management system and compliance with international standards. Buyers should request documentation of past audits and quality certifications, as well as information on the manufacturer’s processes and quality assurance protocols.
How Important Are Quality Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Quality reports generated during the manufacturing process provide insights into compliance with specifications. Buyers should request these reports, along with certificates of compliance that verify the materials meet required standards. Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance trust, as independent inspectors can validate quality claims and ensure adherence to international standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of local regulations and standards that may affect quality certification. For instance, certain countries may require specific certifications for imported steel products, which can vary based on the intended application (e.g., automotive, construction).
Buyers should familiarize themselves with these nuances to ensure that their suppliers can meet all necessary compliance requirements, thus avoiding potential delays or complications in the supply chain.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for high carbon spring steel is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable and high-quality materials. By being informed about the various stages of production, relevant international standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make well-informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high carbon spring steel’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure high carbon spring steel. By following these actionable steps, you will ensure that you select the right material and supplier to meet your operational needs, thereby enhancing the quality and durability of your products.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for your application is critical. High carbon spring steel comes in various grades, each with unique properties such as tensile strength, hardness, and elongation.
– Consider the application: Identify whether you need steel for suspension springs, return springs, or other types of technical springs.
– Specify dimensions: Clearly outline the thickness and width required, as these can impact performance.
Step 2: Research Steel Grades and Properties
Familiarize yourself with the different grades of high carbon spring steel, such as C55S, C60S, C67S, and C100S. Each grade offers distinct characteristics that may suit specific applications better.
– Understand chemical compositions: Look for grades with the right balance of carbon, manganese, chromium, and other alloying elements for optimal performance.
– Evaluate heat treatment options: Consider whether the steel needs to be hardened or tempered based on your usage conditions.
Step 3: Identify Reputable Suppliers
Finding reliable suppliers is essential for ensuring product quality and consistency. Conduct a thorough search for manufacturers and distributors that specialize in high carbon spring steel.
– Check supplier certifications: Verify compliance with international standards such as ISO or ASTM to ensure quality.
– Look for industry experience: Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in your specific sector, as they will better understand your needs.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, always request samples of the high carbon spring steel you are considering. Testing these samples will help validate their suitability for your application.
– Conduct performance tests: Assess properties such as tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and elasticity under load conditions similar to your operational environment.
– Review documentation: Ensure that the supplier provides material test reports for transparency.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified potential suppliers, engage in negotiations to secure the best deal. This includes not only price but also delivery timelines, payment terms, and warranties.
– Consider total cost of ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but also factors like shipping costs and potential tariffs, especially for international transactions.
– Request bulk purchase discounts: If you plan to order large quantities, inquire about volume discounts or long-term agreements for better pricing.
Step 6: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
After agreeing on terms, ensure that all details are clearly documented in a purchase agreement. This protects both parties and minimizes the risk of disputes.
– Include quality assurance clauses: Specify that the steel must meet agreed-upon specifications and standards.
– Outline delivery schedules: Clearly define timelines for delivery to avoid delays in your production process.
Step 7: Implement Quality Control Measures
Once the steel is received, establish a quality control process to verify that it meets your specifications before use.
– Conduct inspections: Use tools to measure dimensions and verify material properties.
– Document findings: Keep records of inspections and tests for future reference and compliance.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source high carbon spring steel that meets their technical requirements and supports their business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high carbon spring steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in High Carbon Spring Steel Sourcing?
When sourcing high carbon spring steel, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary components influencing cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, specifically the alloys used in high carbon spring steel, significantly impacts pricing. For instance, the carbon content, typically ranging from 0.55% to 1.05%, along with the presence of alloying elements like chromium and vanadium, plays a vital role in determining the steel’s properties and, consequently, its cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the manufacturing process. High carbon spring steel often requires skilled labor for processes such as heat treatment and finishing, which can increase production costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to equipment maintenance, utilities, and factory management. Given the specialized nature of spring steel production, overhead can be a considerable portion of total costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for producing high carbon spring steel can be substantial. Custom dies and molds tailored to specific applications may be necessary, impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring the steel meets industry standards involves rigorous testing and inspection, adding to the cost. Certifications like ISO or material-specific validations may also be required, further influencing pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary depending on the origin of the steel and the destination. For international buyers, tariffs and freight charges can substantially affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin that reflects their operational costs and desired profit. This margin can vary significantly based on supplier reputation, market demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect High Carbon Spring Steel Pricing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of high carbon spring steel:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often qualify for volume discounts, reducing the per-unit cost. Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can also dictate pricing strategies, with suppliers incentivizing bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized steel formulations or specific dimensions can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized production methods. Standard grades typically carry lower prices than bespoke options.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality standards or certifications can increase costs, but they may provide long-term savings through enhanced performance and reduced failure rates.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and reliability can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping can significantly impact total costs. For instance, CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) pricing includes shipping costs, while EXW (Ex Works) pricing requires the buyer to handle logistics, often resulting in lower upfront costs but potentially higher total costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing High Carbon Spring Steel?
When engaging in high carbon spring steel procurement, consider the following tips to optimize your sourcing strategy:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms, especially on volume orders. Building relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as lifespan, maintenance, and performance to ensure long-term savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Be aware of additional costs such as tariffs, customs duties, and exchange rates when importing steel. This is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where these factors can vary significantly.
-
Request Samples: Before making significant purchases, request samples to assess quality and suitability for your applications. This reduces the risk of costly mistakes and ensures you receive the desired product.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keep abreast of global steel market trends, including fluctuations in raw material prices and geopolitical factors that can affect supply chains. This knowledge can inform your purchasing decisions and timing.
By understanding these cost components and influencers, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their sourcing strategies for high carbon spring steel, ultimately leading to better quality products at competitive prices.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high carbon spring steel With Other Solutions
In the realm of industrial applications, selecting the right material for springs and other components is crucial for performance, cost efficiency, and longevity. High carbon spring steel is a popular choice due to its unique combination of strength and elasticity. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific needs depending on application requirements, budget constraints, and operational environments. Below, we compare high carbon spring steel with two viable alternatives: stainless steel and composite materials.
| Comparison Aspect | High Carbon Spring Steel | Stainless Steel | Composite Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent tensile and fatigue strength, high elasticity. | Good corrosion resistance, moderate strength. | Varies widely, can be tailored for specific applications. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, especially in large quantities. | Higher initial investment due to alloying elements. | Can be expensive due to manufacturing processes. |
| Ease of Implementation | Widely available and easy to work with, requires proper heat treatment. | Requires specialized techniques for fabrication. | Complex manufacturing may involve additional processing. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspections for fatigue failure. | Low maintenance due to corrosion resistance. | Dependent on the type; some may require periodic checks. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for automotive and industrial springs under high stress. | Suitable for applications requiring corrosion resistance, like marine environments. | Best for lightweight applications or where custom properties are needed. |
What are the advantages and disadvantages of stainless steel as an alternative to high carbon spring steel?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice in environments where moisture or chemicals are prevalent. While it does not match the tensile strength of high carbon spring steel, it offers sufficient performance in many applications, particularly those in the automotive and marine industries. The downside is that stainless steel is generally more expensive and requires specialized fabrication techniques, which can increase overall project costs and lead times.
How do composite materials compare with high carbon spring steel in terms of performance?
Composite materials, particularly fiber-reinforced polymers, offer significant advantages in weight reduction and can be engineered for specific mechanical properties. They excel in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace or automotive industries. However, the performance of composites can vary greatly depending on the formulation, and they may not provide the same level of fatigue resistance as high carbon spring steel. Additionally, the manufacturing processes for composites can be complex and costly, which may deter some B2B buyers.
How can B2B buyers select the best solution for their specific needs?
When deciding between high carbon spring steel and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors: the operational environment, required mechanical properties, budget constraints, and the intended application. High carbon spring steel remains a robust choice for applications demanding high strength and elasticity, especially when cost is a significant factor. However, if corrosion resistance or weight is more critical, stainless steel or composite materials may offer better long-term value. Ultimately, understanding the specific requirements of their projects will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high carbon spring steel
High carbon spring steel is a crucial material in various industrial applications, particularly in the manufacturing of springs due to its unique mechanical properties. Understanding its technical specifications and industry terminology can greatly enhance decision-making for B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of High Carbon Spring Steel?
-
Material Grades
Material grades like C55S, C60S, C67S, C75S, and C100S denote different carbon content and alloy compositions. For example, C100S contains 0.95-1.05% carbon, offering superior hardness and strength. Selecting the correct grade is vital for ensuring the right performance in applications like automotive suspension or machinery components. -
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the material’s ability to withstand tension without breaking. High carbon spring steels typically exhibit tensile strengths ranging from 800 to over 2000 MPa, making them suitable for demanding applications where resilience is essential. Understanding tensile strength can help buyers assess the suitability of the steel for their specific use cases. -
Hardness
Hardness is a critical property that affects wear resistance and the ability to maintain shape under stress. High carbon spring steels can be heat-treated to achieve hardness levels of up to 58 HRC (Rockwell hardness scale). This property is essential for industries that require materials that can endure repeated loading and unloading cycles. -
Elongation at Break
This property indicates how much a material can stretch before it fractures. High carbon spring steels typically have elongation values ranging from 5% to 15%. High elongation is crucial for applications that involve bending and flexing, as it ensures that the material can return to its original shape without permanent deformation. -
Fatigue Strength
Fatigue strength refers to the maximum stress that a material can withstand for a specified number of cycles without failure. High carbon spring steels are designed to have excellent fatigue resistance, making them ideal for applications that involve repeated loading, such as automotive springs and industrial machinery.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to High Carbon Spring Steel?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM requirements is critical for B2B buyers looking to source high carbon spring steel for specific applications, ensuring compatibility and quality standards are met. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their procurement strategy effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods. For high carbon spring steel, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare different suppliers and negotiate better prices based on their requirements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B transactions involving high carbon spring steel, as they dictate aspects such as shipping, insurance, and risk management. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management, ensuring that production schedules are met without delays.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding high carbon spring steel procurement, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high carbon spring steel Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the High Carbon Spring Steel Sector?
The global high carbon spring steel market is driven by several factors, including the rising demand for durable and high-performance materials across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery. With carbon content ranging from 0.55% to 1.00%, these steels offer exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and fatigue resistance, making them ideal for applications like suspension springs and technical springs. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are witnessing increased infrastructure development and industrialization, leading to heightened demand for high carbon spring steel.
Furthermore, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, such as heat treatment and alloying techniques, are enhancing the performance characteristics of spring steels. B2B buyers should pay attention to the growing trend of digital procurement platforms that facilitate easier sourcing and supply chain management, particularly in regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, where traditional sourcing methods may still dominate. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI, is also shaping how manufacturers and suppliers engage, allowing for more precise forecasting and inventory management.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in the High Carbon Spring Steel Industry?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the sourcing of high carbon spring steel. Buyers are urged to consider the environmental impact of their procurement choices. The production of high carbon steels can be resource-intensive, contributing to carbon emissions and waste. Therefore, opting for suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices can mitigate these effects.
Ethical sourcing involves ensuring that materials are obtained from suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and fair labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and responsible sourcing initiatives can guide B2B buyers in selecting suppliers committed to sustainability. Additionally, the use of recycled materials in the production of high carbon spring steel is gaining traction, offering a ‘green’ alternative that aligns with global sustainability goals.
What is the Historical Context of High Carbon Spring Steel for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of high carbon spring steel can be traced back to the early industrial era when the need for stronger and more resilient materials became apparent. Initially, these steels were primarily used in the manufacturing of springs for machinery and vehicles. Over time, advancements in metallurgical science and heat treatment processes have significantly improved the performance characteristics of high carbon spring steels.
In recent decades, the globalization of supply chains has enabled international B2B buyers to access a wider range of products from various manufacturers. This evolution has led to enhanced competition, pushing suppliers to innovate and meet the diverse needs of global markets, particularly in developing regions. As a result, high carbon spring steel has become a staple in industries requiring reliable performance under strenuous conditions, underscoring its importance in modern manufacturing and engineering applications.
In summary, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical context can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions in sourcing high carbon spring steel, ultimately leading to more strategic partnerships and successful procurement strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high carbon spring steel
-
How do I choose the right grade of high carbon spring steel for my application?
Selecting the appropriate grade of high carbon spring steel depends on specific application requirements, such as load-bearing capacity, fatigue resistance, and environmental conditions. Common grades like C55S, C67S, and C100S offer varying carbon content and mechanical properties. Assess factors such as tensile strength, hardness, and ductility to ensure optimal performance in your application. Consulting with suppliers about your unique requirements can provide valuable insights into the most suitable grade for your needs. -
What is the best high carbon spring steel for automotive applications?
For automotive applications, grades like C75S and 51CrV4 are often recommended due to their exceptional toughness and fatigue resistance. These materials can withstand high-stress conditions and offer good hardenability, making them ideal for components like suspension springs and other critical parts. Always consider the specific performance criteria needed for your automotive application and discuss these with your supplier to confirm the best fit. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for high carbon spring steel?
Minimum order quantities for high carbon spring steel can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific grade of steel. Typically, MOQs range from a few tons to several hundred tons. It’s essential to communicate your project needs with potential suppliers to negotiate suitable order sizes that align with your production schedules and inventory management practices. -
How can I ensure the quality of high carbon spring steel before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request detailed material certifications and test reports from your supplier, including mechanical properties and chemical composition analyses. Consider suppliers who adhere to international standards like ASTM or DIN. Additionally, visiting the manufacturing facility or using third-party inspection services can provide further assurance of the steel’s quality and compliance with your specifications. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing high carbon spring steel internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of high carbon spring steel typically vary by supplier and region. Common terms include Letter of Credit (LC), advance payment, or open account arrangements. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow and financial management practices. Additionally, consider discussing options for partial payments based on order milestones to mitigate risks. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing high carbon spring steel?
When importing high carbon spring steel, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Collaborate with a logistics partner who has experience in handling heavy industrial materials to ensure efficient transport. Also, factor in lead times for manufacturing and shipping, as they can impact your overall production schedule. Understanding the logistics framework in your region is crucial for a smooth import process. -
Can high carbon spring steel be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for high carbon spring steel, including specific dimensions, heat treatments, and surface finishes. Customization can enhance the steel’s performance in specialized applications. When seeking customized solutions, provide detailed specifications and engage in discussions with suppliers to understand their capabilities and lead times for producing tailored materials. -
How can I vet suppliers of high carbon spring steel to ensure reliability?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their industry reputation, customer reviews, and previous project references. Consider their certifications, quality control processes, and experience in your specific market. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can also help gauge their responsiveness and willingness to meet your needs. Participating in trade shows or industry events can provide opportunities to connect with reputable suppliers and assess their offerings firsthand.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
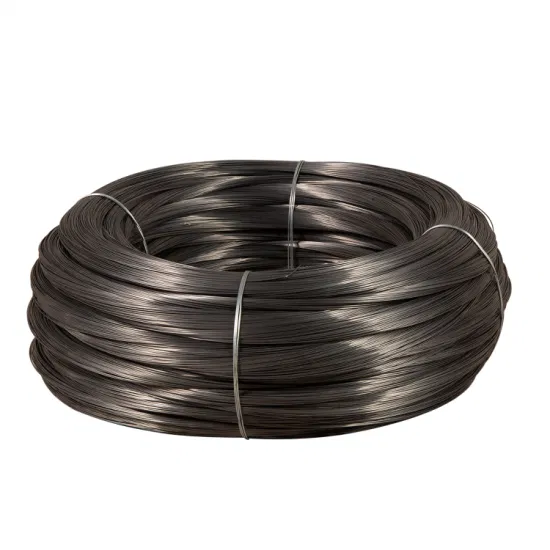
Top 7 High Carbon Spring Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Knifemaking – 5160 Hi-Carbon Steel
Domain: knifemaking.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 5160 Hi-Carbon Steel, Price: $15.40 – $107.61, Type: High Carbon alloy spring steel with chromium added for hardenability, Features: Good wear resistance, outstanding toughness, Hardening capability: 57-58 HRC, Typical Rockwell: 32-35, Typical chemistry: C .63, Mn .86, Si .23, CR .83, Available sizes: 1/4″ x 1 1/2″ x 36″, 1/4″ x 1 1/2″ x 48″, 1/4″ x 2″ x 36″, 1/4″ x 2″ x 48″, 1/4″ x 4″ x 36″, 1/4″…
2. Optimum Spring – Custom Spring Manufacturing
Domain: optimumspring.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Optimum Spring manufactures extension, torsion, and compression springs using high-carbon spring steels. These materials are cost-effective, readily available, and easy to work with, but are not suitable for high or low temperatures or for shock or impact loading. Key specifications include: 1. Music Wire (ASTM A 228): Chemistry – C 0.70 – 1.00%, Mn 0.20 – 0.60%; Minimum Tensile Strength – 230-399…
3. Reddit – Steel Sourcing for Sword Making
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: High carbon steel or spring steel for sword making; local steel supplier offers Hardox corten S355 5mm plate; characteristics: 450 brinel hardness, 0.2% carbon; consideration of using suspension springs and leaf springs for spring steel; advice on sourcing barstock like 1084 or 80Crv2 for ease of heat treatment; alternative supplier suggestions include GFS (Groundflatstock) and Andy at Furnival st…
4. Thyssenkrupp – Spring Steels for Industrial Applications
Domain: thyssenkrupp-steel.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Spring steels for industrial springs; includes hardenable manganese-boron steel and hardenable boron steel; suitable for demanding applications in various industries such as automotive, appliance, packaging, and energy sectors.
5. Valiant Armoury – Craftsman Series Blade
Domain: valiant-armoury.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Craftsman Series – 6150 High Carbon Spring Steel
– Handmade by Zach and Sonny Suttles
– Blade material: 5160 high carbon spring steel
– Hand ground to exacting specifications
– Heat treated in-house for improved resilience and durability
– High-quality leather work
– Estimated current work queue: 8 to 12 months
– Contact for customization inquiries: [email protected] or call 817-501-9706
6. Steel Pro Group – 5160 High Carbon Spring Steel
Domain: steelprogroup.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: 5160 High Carbon Spring Steel is a high-carbon chromium alloy known for its excellent strength, flexibility, and resistance to fatigue. It is primarily used in automotive heavy-duty spring applications, especially leaf springs, and in the production of knives and swords. Advantages include high toughness, good wear resistance, cost-effectiveness, and formability after heat treatment. Disadvantages…
7. Three D Metals – High Carbon Spring Steel Coil
Domain: threedmetals.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: High Carbon Steel – High Carbon Spring Steel Coil
– Distributor: Largest in North America
– Industries Served: Automotive, Appliance, Building and Construction
– Stock: Low Carbon and Stainless Steel Coil
– Special Features: Oscillate winding to reduce changeover time, less material handling, reduced scrap, consistent quality, improved productivity.
Product Specifications:
1. High Carbon Spring S…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high carbon spring steel
In the evolving landscape of high carbon spring steel procurement, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for businesses looking to enhance their operational efficiency and product quality. The unique properties of high carbon spring steel—such as its excellent tensile and fatigue strength—make it indispensable in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. By leveraging the diverse grades available, such as C55S, C75S, and 5160, buyers can tailor their material choices to specific application needs, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
As global supply chains continue to adapt, international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize partnerships with reliable suppliers who can deliver consistent quality and technical support. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks associated with sourcing but also positions companies to capitalize on emerging market opportunities.
Looking ahead, the demand for high carbon spring steel is expected to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increased industrialization. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies, engage with reputable suppliers, and align your procurement practices with market trends to ensure your business remains competitive. Embrace this opportunity to secure a sustainable supply chain that supports your growth objectives.