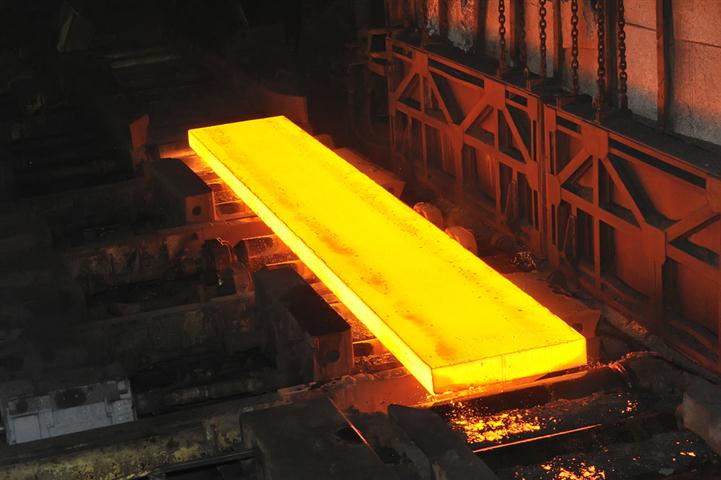
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heat treating stainless steel
Navigating the complexities of sourcing heat treating stainless steel can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the diverse array of heat treatment methods available, understanding which approach will best enhance the properties of stainless steel for specific applications is critical. This comprehensive guide delves into various heat treatment techniques, including aging, hardening, and annealing, while also exploring their respective applications across industries such as aerospace, petrochemicals, and manufacturing.
Additionally, we cover essential aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and regional nuances that influence purchasing decisions in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By equipping buyers with in-depth knowledge and actionable insights, this guide empowers them to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and quality standards.
Understanding the intricacies of heat treating stainless steel not only enhances product performance but also helps mitigate risks associated with improper processing. Whether you’re a procurement manager in Nigeria, a manufacturing director in Vietnam, or a supply chain specialist in Europe, this guide serves as a crucial resource to help you navigate the global market effectively and secure the best materials for your projects.
Understanding heat treating stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aging | Enhances malleability and stress corrosion resistance | Aerospace, medical devices | Pros: Improved ductility; Cons: Limited hardening |
| Hardening | Increases hardness through heat treatment and quenching | Cutting tools, automotive components | Pros: High strength; Cons: Increased brittleness |
| Tempering | Reduces brittleness while enhancing toughness | Structural components, machinery parts | Pros: Balanced strength; Cons: Potential cost increase |
| Annealing | Softens metal, relieves internal stresses, improves ductility | Food processing, architectural fixtures | Pros: Enhanced workability; Cons: May reduce hardness |
| Work Hardening | Strengthens through cold deformation, enhancing hardness | Manufacturing, construction tools | Pros: Significant strength increase; Cons: Reduced ductility |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Aging in Stainless Steel Heat Treatment?
Aging, also known as precipitation hardening, is a heat treatment process that increases the malleability of stainless steel by dispersing particles within the metal’s grain structure. This method is particularly suitable for applications requiring enhanced ductility, such as in aerospace and medical devices. Buyers should consider that while aging improves certain properties, it does not significantly harden the material, which may limit its applications in high-stress environments.
How Does Hardening Affect the Properties of Stainless Steel?
Hardening involves heating stainless steel to transform its structure and then rapidly cooling it through quenching. This method is highly effective for increasing the hardness of materials used in cutting tools and automotive components. However, it can lead to increased brittleness, making it essential for buyers to consider the trade-off between strength and ductility when selecting this treatment for their applications.
Why is Tempering Important After Hardening?
Tempering is a crucial process that follows hardening, as it reduces brittleness while enhancing toughness. This method is commonly used in structural components and machinery parts, where a balance of strength and flexibility is vital. Buyers should be aware that while tempering improves the overall durability of stainless steel, it may also lead to a slight increase in costs due to additional processing requirements.
What Benefits Does Annealing Offer for Stainless Steel?
Annealing is a widely used heat treatment that softens stainless steel, relieves internal stresses, and improves ductility. It is particularly beneficial in industries such as food processing and construction, where formability and workability are critical. However, buyers should consider that while annealing enhances these properties, it can also reduce the overall hardness of the material, which may not be suitable for all applications.
How Does Work Hardening Enhance Stainless Steel Strength?
Work hardening is a process that strengthens stainless steel through cold deformation, significantly increasing its hardness. This method is often applied in manufacturing and construction tools. While work hardening provides substantial strength improvements, it can compromise ductility, making it essential for buyers to assess the specific performance requirements of their applications before choosing this treatment.
Key Industrial Applications of heat treating stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of heat treating stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Components for aircraft structures and engines | Enhanced strength and corrosion resistance for safety | Certification of materials, compliance with aviation standards |
| Petrochemical | Piping and valves in chemical processing | Improved durability under extreme conditions | Material grade specifications, resistance to corrosion |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Increased sterilization effectiveness and biocompatibility | Regulatory compliance, precision machining requirements |
| Food Processing | Equipment such as mixers and conveyors | Resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning | Compliance with food safety regulations, material certifications |
| Automotive | Engine components and exhaust systems | Enhanced performance and longevity | Material traceability, adherence to automotive standards |
How is Heat Treating Stainless Steel Utilized in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, heat treating stainless steel is critical for manufacturing components such as aircraft structures and engine parts. The heat treatment processes enhance the material’s strength and corrosion resistance, ensuring safety and reliability in high-stress environments. Buyers in this industry must prioritize sourcing materials that meet stringent aviation standards and certifications, as any failure can lead to catastrophic outcomes. Additionally, suppliers should provide detailed documentation to demonstrate compliance with aerospace quality assurance protocols.
What Role Does Heat Treating Stainless Steel Play in the Petrochemical Industry?
The petrochemical industry relies heavily on heat-treated stainless steel for piping and valves used in chemical processing. The heat treatment enhances the durability of these components, allowing them to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. For international B2B buyers, it’s crucial to consider the specific material grades that offer optimal resistance to stress corrosion cracking and pitting. Furthermore, suppliers should ensure that their products meet industry standards to mitigate risks associated with equipment failure.
How is Heat Treating Stainless Steel Applied in Medical Devices?
In the medical devices industry, heat treating stainless steel is essential for creating surgical instruments and implants that require high levels of biocompatibility and sterilization effectiveness. The heat treatment processes refine the material’s properties, making it suitable for rigorous sterilization procedures. Buyers in this sector must ensure that their suppliers comply with regulatory standards such as ISO 13485, which governs quality management systems for medical devices. Additionally, precision machining capabilities are a key requirement for achieving the necessary tolerances and finishes.
Why is Heat Treating Stainless Steel Important in Food Processing?
Heat treating stainless steel is vital in the food processing industry for equipment such as mixers and conveyors, where resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning are paramount. The treatment processes enhance the material’s durability, ensuring it can withstand the harsh conditions often found in food production environments. Buyers must source materials that comply with food safety regulations, such as FDA standards, and should verify that suppliers provide appropriate certifications to ensure safety and hygiene.
How Does Heat Treating Stainless Steel Benefit the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, heat treating stainless steel is used for engine components and exhaust systems, where enhanced performance and longevity are critical. The heat treatment improves the mechanical properties of the steel, making it more resilient to wear and environmental factors. International B2B buyers need to focus on sourcing from suppliers that offer traceability of materials and adherence to automotive industry standards, such as IATF 16949, to ensure quality and reliability in their applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘heat treating stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Inconsistent Heat Treatment Results
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with inconsistent heat treatment results when dealing with stainless steel. Variability in temperatures, cooling rates, and even the composition of the stainless steel can lead to products that do not meet required specifications. This inconsistency can result in higher rejection rates and increased costs due to rework or replacement, ultimately affecting project timelines and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, it is crucial to implement a robust quality control system that includes precise temperature monitoring and control during the heat treatment process. Invest in high-quality thermocouples and data loggers to continuously monitor temperature fluctuations. Moreover, standardizing the heat treatment process with documented procedures for each stainless steel grade will help ensure uniformity. Collaborating with suppliers who have expertise in heat treatment can also provide valuable insights into the best practices for specific stainless steel types. Regular training for staff on the nuances of heat treatment can further improve consistency and reduce variability.
Scenario 2: Facing Challenges with Stainless Steel Sensitization
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the risk of sensitization in austenitic stainless steels, such as 304 or 316 grades, during the heat treatment process. Sensitization occurs when the material is held at intermediate temperatures, leading to the formation of chromium carbides at the grain boundaries. This phenomenon can significantly compromise corrosion resistance, particularly in environments where the stainless steel is exposed to aggressive chemicals or moisture.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of sensitization, it is essential to carefully control the temperature and duration of the heat treatment process. Opt for lower temperature ranges (below 425°C or 797°F) whenever possible, and limit exposure times to these temperatures. Additionally, consider using stabilized stainless steels, such as 321 or 347 grades, which are specifically designed to reduce the risk of sensitization. When sourcing stainless steel, ensure that your supplier provides comprehensive documentation on the alloy’s heat treatment and its susceptibility to sensitization. Implementing a post-heat treatment passivation process can also help enhance corrosion resistance by removing any surface contaminants.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Heat Treatment Method
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter confusion when selecting the appropriate heat treatment method for their stainless steel applications. With various methods available, such as hardening, tempering, and annealing, determining the right approach can be overwhelming. This lack of clarity can lead to improper treatment, resulting in materials that do not meet performance requirements or are unsuitable for their intended application.
The Solution: To make informed decisions about heat treatment methods, it is crucial to conduct a thorough analysis of the specific requirements for your application. Understand the mechanical properties you need, such as hardness, ductility, and corrosion resistance, and how each treatment method affects these properties. Engaging with metallurgical experts or heat treatment specialists can provide valuable guidance tailored to your unique needs. Additionally, consider running small-scale trials to evaluate different treatment methods before full-scale production. Documenting the outcomes of these trials will help create a reference guide for future heat treatment processes, ensuring more efficient and effective selections.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heat treating stainless steel
What Are the Key Materials for Heat Treating Stainless Steel?
When selecting materials for heat treating stainless steel, it’s essential to consider the specific properties, advantages, and limitations of various stainless steel grades. Here, we analyze four common materials, focusing on their performance characteristics, application impacts, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Grade 304 Stainless Steel: The Versatile Choice
Key Properties: Grade 304 stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. It has a temperature rating of up to 870°C (1600°F) and is non-magnetic in the annealed condition.
Pros & Cons: Its versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from kitchen equipment to chemical containers. However, it cannot be hardened through traditional heat treatment methods, limiting its use in applications requiring high strength. While it is relatively affordable, the need for cold working to enhance hardness adds to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Grade 304 is compatible with various media, including food and chemicals, making it an ideal choice for the food processing and pharmaceutical industries. However, sensitization can occur if held at intermediate temperatures for too long, which can compromise corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM A240 standards and consider local regulations regarding food safety and chemical handling. In regions like Africa and South America, the availability of 304 stainless steel may vary, impacting lead times.
2. Grade 316 Stainless Steel: Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Key Properties: Grade 316 stainless steel contains molybdenum, which enhances its corrosion resistance, especially in chloride environments. It has a similar temperature rating to 304 but offers better performance in marine and chemical applications.
Pros & Cons: Its superior corrosion resistance makes it ideal for harsh environments, such as marine applications. However, it is more expensive than 304, which could affect budget-sensitive projects. The manufacturing process is also more complex due to its alloying elements.
Impact on Application: Grade 316 is particularly suitable for applications involving saltwater or corrosive chemicals, such as in the petrochemical industry. Its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion is a significant advantage in these applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM A240 and EN 10088 standards is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should also consider local sourcing options to mitigate costs associated with importing high-grade stainless steel.
3. Grade 410 Stainless Steel: The Hardening Option
Key Properties: Grade 410 stainless steel is a martensitic stainless steel that can be hardened through heat treatment. It has a temperature rating of up to 650°C (1200°F) and offers moderate corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: Its ability to be heat-treated allows for enhanced hardness and strength, making it suitable for applications like cutlery and surgical instruments. However, its corrosion resistance is lower than that of austenitic grades, which may limit its use in highly corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Grade 410 is ideal for applications requiring a balance of hardness and corrosion resistance, such as in tooling and machinery. However, careful consideration must be given to the environmental conditions it will face.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM A276 and similar standards. In regions like Nigeria, understanding the local demand for hardenable stainless steels can guide purchasing decisions.
4. Grade 17-4 PH Stainless Steel: The Precipitation Hardening Solution
Key Properties: Grade 17-4 PH is a precipitation-hardening stainless steel that offers high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C (1112°F) and is known for its good mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons: Its ability to achieve high strength through heat treatment makes it suitable for aerospace and high-stress applications. However, the heat treatment process can be complex and requires precise control, which may increase manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: This grade is often used in aerospace components, valves, and pumps where strength and corrosion resistance are critical. Its performance in high-stress environments makes it a preferred choice in demanding applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM A693 and similar standards is essential. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider the availability of this grade and potential lead times for sourcing.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for heat treating stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 304 | Kitchen equipment, chemical containers | Excellent corrosion resistance | Limited hardness from heat treatment | Medium |
| Grade 316 | Marine applications, petrochemical industry | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost than 304 | High |
| Grade 410 | Cutlery, surgical instruments | Can be hardened for strength | Moderate corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Grade 17-4 PH | Aerospace components, valves | High strength and corrosion resistance | Complex heat treatment process | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties and applications of various stainless steel grades, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heat treating stainless steel
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Stainless Steel Heat Treating?
The manufacturing process for heat treating stainless steel involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary specifications and performance criteria. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Heat Treatment?
Material preparation is the first step in the heat treating process. It involves selecting the appropriate grade of stainless steel, such as 304 or 316, based on the desired mechanical properties and application requirements. The selected material undergoes a thorough inspection to assess its quality, including checking for any defects or inconsistencies.
Once the material is approved, it is cut to the required dimensions and subjected to pre-heat treatment cleaning processes, such as degreasing and descaling. This step is crucial as contaminants can adversely affect the heat treatment results.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Stainless Steel?
Forming is the next stage, where the stainless steel is shaped into its desired configuration. Techniques such as forging, rolling, or bending may be employed, depending on the application. Each technique requires precise control to avoid introducing stresses that could compromise the integrity of the material.
During this stage, it is essential to monitor the temperature and environment to prevent oxidation or other forms of contamination. Proper forming techniques not only enhance the material’s mechanical properties but also set the foundation for effective heat treatment.
How Does Assembly Fit into the Heat Treating Process?
In the assembly stage, the formed components are brought together to create the final product. This may involve welding, bolting, or other joining methods. It is crucial that the assembly process maintains the integrity of the stainless steel, ensuring that no additional stresses are introduced.
Quality checks are conducted at this stage to confirm that the assembly adheres to design specifications. Any deviations can affect the performance of the final product, making this stage a critical checkpoint in the manufacturing process.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied After Heat Treatment?
Finishing processes follow heat treatment and are designed to enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of the stainless steel. Techniques such as polishing, passivation, and coating may be applied to improve corrosion resistance and surface finish.
Finishing not only impacts the visual appeal of the product but also its longevity and performance in various environments. For instance, passivation helps remove free iron and enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel, making it suitable for applications in harsh conditions.
What Are the Key Quality Control Standards for Heat Treating Stainless Steel?
Quality assurance is paramount in the heat treating process, particularly for B2B buyers who demand high standards. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality throughout the production process.
Which Industry-Specific Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA) and API certification for oil and gas equipment are critical. These certifications indicate compliance with specific regulatory requirements and industry standards, which can vary significantly across regions.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these certifications can be vital in assessing supplier reliability and product quality.
What Are the Common QC Checkpoints During the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the stainless steel meets the required specifications. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival. It ensures that they meet predetermined specifications before they enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is conducted to identify any deviations from the expected standards. This includes monitoring temperatures during heat treatment and checking for dimensional accuracy during forming and assembly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the final product is completed, it undergoes rigorous testing and inspection. This may include mechanical testing (such as tensile and hardness tests), non-destructive testing (like ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection), and visual inspections to ensure surface quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure the quality of stainless steel heat-treated products, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. This can include:
-
Conducting Supplier Audits: On-site audits provide an opportunity to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes, QC measures, and adherence to international standards. Buyers should look for documentation of past audits and corrective actions taken.
-
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports outlining their quality control measures, test results, and compliance with relevant standards. These documents offer insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These services can conduct tests and inspections throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers operating in diverse markets must navigate various QC and certification nuances that can impact their procurement processes. For instance, regional regulations may dictate specific testing and certification requirements, which can differ significantly from one country to another.
Buyers should familiarize themselves with the local standards in their target markets, such as those established by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Understanding these nuances not only aids in supplier selection but also ensures compliance with local regulations, reducing the risk of costly delays or rejections.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for heat treating stainless steel is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these elements, companies can make informed decisions that enhance product quality, improve performance, and ensure compliance with international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘heat treating stainless steel’
Introduction
This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing heat-treated stainless steel. Given the diversity of heat treatment methods and the specifications required for different applications, understanding the procurement process is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of stainless steel products.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes specifying the type of stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316, martensitic), desired heat treatment method (e.g., annealing, hardening), and any mechanical properties essential for your application.
– Considerations: Identify the end-use environment, whether it involves exposure to corrosive elements or high temperatures, as these factors will influence your specifications.
Step 2: Research Heat Treatment Methods
Familiarize yourself with various heat treatment methods applicable to stainless steel. Understanding processes such as aging, hardening, and annealing will help you make informed decisions about which treatments best suit your needs.
– Key Points: Each method alters the properties of stainless steel differently, impacting factors like hardness, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Knowing these distinctions is essential for selecting the right supplier.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications. Request detailed company profiles, production capabilities, and case studies demonstrating their experience with heat-treated stainless steel.
– Important Actions: Look for suppliers who can provide references from similar industries or geographical regions, which can offer insights into their reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that your selected suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 or specific quality certifications for heat treatment processes. This is crucial for ensuring consistent quality and compliance with international standards.
– Why It Matters: Certifications indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality management and their ability to consistently meet specifications, which is vital for your project’s success.
Step 5: Request Material Test Reports
Ask for material test reports that include mechanical properties, heat treatment conditions, and compliance with specifications. These reports should provide a clear overview of the material’s performance characteristics.
– What to Check: Ensure that the reports detail the heat treatment processes used, as this information is essential for validating the quality and suitability of the stainless steel for your application.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Delivery Capabilities
Evaluate the lead times and logistics capabilities of your potential suppliers. Understanding their ability to meet your timelines is crucial, especially if your project has tight deadlines.
– Considerations: Inquire about their inventory levels and whether they can accommodate rush orders, as this may impact your overall project schedule.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Clear communication of expectations is essential to avoid misunderstandings later in the process.
– Key Points: Ensure that all agreements are documented, including warranties or guarantees related to the heat-treated stainless steel, to protect your investment.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement process for heat-treated stainless steel, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their specific applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heat treating stainless steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Heat Treating Stainless Steel?
The cost structure for heat treating stainless steel encompasses several critical components, each contributing to the overall pricing. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The type of stainless steel and any additional alloys significantly impact costs. For instance, higher grades such as 316 or 304 stainless steel may command a premium due to their enhanced corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for effective heat treatment processes. The complexity of the treatment—whether it involves hardening, tempering, or annealing—dictates the level of expertise required, affecting labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with equipment maintenance, facility utilities, and administrative expenses. The sophistication of the machinery used for heat treating can also influence overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The tools and fixtures needed for heat treatment can be a significant upfront investment. For custom or specialized treatments, the cost of tooling may rise, especially for unique shapes or sizes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the integrity of heat-treated products is paramount. QC processes, including inspections and certifications, add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly, particularly for international shipments. Factors like distance, mode of transport, and packaging requirements all influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their operational costs and profit margins. This varies by supplier and market conditions.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Heat Treating Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of heat treating services:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often benefit from economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom treatments tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Clear communication of requirements is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of base materials directly affects pricing. Stainless steel grades with higher alloy content are generally more expensive.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products requiring specific certifications or higher quality standards can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications based on application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and historical performance can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants may offer lower rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery is vital. Incoterms dictate who bears responsibility for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transportation, which can significantly affect total costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Heat Treating?
When sourcing heat treating services, particularly in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers can leverage several strategies to optimize costs:
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the initial cost but also the long-term implications, including maintenance, durability, and lifecycle costs of the treated products. This broader perspective can justify higher upfront expenses if it leads to lower long-term costs.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market rates and what similar companies are paying. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing. Long-term partnerships often yield favorable pricing structures.
-
Flexibility on Specifications: If possible, offer flexibility in specifications or order sizes to encourage suppliers to provide better pricing.
-
Be Aware of Regional Nuances: Different regions may have unique cost structures and supplier capabilities. Buyers should adjust their expectations and strategies based on local market conditions.
What Should International Buyers Know About Pricing Nuances?
International buyers must navigate various challenges that can affect pricing. Currency fluctuations, import duties, and tariffs can alter costs unexpectedly. Additionally, the logistics of international shipping introduce complexities that can affect lead times and overall costs. Therefore, it is advisable for buyers to include these potential expenses in their financial planning.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost components and pricing influencers for heat treating stainless steel is vital for effective B2B sourcing. By leveraging negotiation strategies and being mindful of regional pricing nuances, buyers can enhance their purchasing decisions and achieve more favorable outcomes. This comprehensive approach will enable businesses to optimize their supply chain and ensure the highest quality of heat-treated stainless steel products.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing heat treating stainless steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Heat Treating Stainless Steel
In the realm of material processing, especially in industries where stainless steel is prevalent, heat treating is a common method used to enhance the material’s properties. However, there are alternative solutions that can also achieve similar objectives, such as improving strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. This analysis will compare heat treating stainless steel with two viable alternatives: Cold Working and Surface Hardening.
| Comparison Aspect | Heat Treating Stainless Steel | Cold Working | Surface Hardening |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Enhances hardness and ductility; effective for various grades | Increases strength and hardness; may reduce ductility | Improves surface hardness while maintaining core toughness |
| Cost | Moderate to high; depends on method and scale | Generally low; requires minimal equipment | Moderate; cost varies with process complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise | Relatively simple; can be done in-house | Requires specific machinery; moderate skill needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of heat treatment equipment needed | Minimal maintenance; mostly manual labor | Maintenance required for specialized hardening equipment |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, medical devices, high-stress applications | Manufacturing of tools, automotive parts | Components needing wear resistance, like gears and shafts |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Cold Working
Cold working involves deforming stainless steel at room temperature to increase its strength through strain hardening. This method is particularly effective for materials like 304 stainless steel, which cannot be hardened through traditional heat treatment. The advantages of cold working include lower costs and the ability to improve yield strength without the need for high-temperature processing. However, the downside is that it can lead to reduced ductility, which may not be suitable for applications requiring flexibility.
Surface Hardening
Surface hardening techniques, such as carburizing or nitriding, focus on enhancing the surface properties of stainless steel while maintaining the toughness of the core material. These methods are particularly beneficial in applications where wear resistance is critical, such as in gears and shafts. Surface hardening is moderately priced and requires specific machinery and expertise, which may present a barrier for some companies. The key advantage lies in achieving a hard surface layer without compromising the underlying material properties, making it ideal for high-performance components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When selecting between heat treating stainless steel and its alternatives, B2B buyers must carefully evaluate their specific needs. Factors such as performance requirements, cost constraints, and the nature of the application will guide this decision. For instance, if enhanced surface hardness is paramount, surface hardening may be preferable. Conversely, if ductility and formability are essential, cold working might provide the desired results without the need for extensive heat treatment processes. By understanding the unique benefits and limitations of each method, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and manufacturing capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heat treating stainless steel
What are the Critical Technical Properties of Heat Treating Stainless Steel?
Understanding the essential technical properties of heat-treated stainless steel is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chain and product performance. Here are key specifications that should be considered:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of stainless steel, which dictates its composition and properties. Common grades include 304 and 316, each offering varying levels of corrosion resistance, strength, and ductility. For buyers, selecting the appropriate grade is vital for ensuring that the final product meets application-specific requirements, especially in industries such as aerospace and petrochemicals.
2. Hardness
Hardness is a measure of a material’s resistance to deformation or indentation. It is crucial in applications requiring wear resistance, such as cutting tools or machinery components. Hardness is typically quantified using scales like Rockwell or Brinell. In B2B transactions, understanding hardness can help buyers assess the suitability of stainless steel for their specific operational environments.
3. Ductility
Ductility refers to a material’s ability to deform under tensile stress, which is essential for applications requiring bending or shaping. Stainless steels with higher ductility are easier to work with and can withstand more significant deformation without fracturing. For buyers, knowing the ductility of a stainless steel grade aids in predicting how it will behave during processing and end-use.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from specified dimensions during manufacturing. In heat-treated stainless steel, tight tolerances are often necessary to ensure compatibility with other components and systems. B2B buyers must pay attention to tolerances to prevent costly rework and ensure product reliability.
5. Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how well a material can conduct heat. It is particularly important in applications involving heat exchangers or high-temperature processes. A thorough understanding of thermal conductivity helps buyers select the right stainless steel grades for thermal management applications.
What are Common Trade Terms Used in Heat Treating Stainless Steel?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms associated with heat treating stainless steel:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of heat-treated stainless steel, OEMs may require specific grades and properties to meet their design criteria. Understanding OEM requirements ensures that buyers can procure materials that align with product specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For heat-treated stainless steel, MOQs can vary based on the complexity of the treatment process and the grade of steel. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their production needs while managing inventory costs effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. When requesting quotes for heat-treated stainless steel, including detailed specifications (such as grade, treatment methods, and tolerances) helps suppliers provide accurate and competitive pricing, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of globally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms related to heat-treated stainless steel shipments can help B2B buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and delivery timelines, ensuring smoother logistics and compliance.
5. Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process that softens stainless steel, relieving internal stresses and improving ductility. This term is essential for buyers seeking to enhance the workability of stainless steel for manufacturing processes. Knowing about annealing can guide procurement strategies to ensure the right treatments are applied.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing heat-treated stainless steel, optimizing both product performance and supply chain efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the heat treating stainless steel Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Heat Treating Stainless Steel Sector?
The heat treating stainless steel market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and energy. Global trends indicate a rising preference for high-performance stainless steel grades, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These markets are witnessing a surge in infrastructure development, which fuels the need for durable and corrosion-resistant materials.
Emerging technologies in heat treatment processes, such as advanced furnace designs and automation, are enhancing efficiency and precision in the treatment of stainless steel. For B2B buyers, these advancements present opportunities to source materials that offer improved mechanical properties and reduced lead times. Furthermore, the integration of Industry 4.0 principles, including IoT and data analytics, is revolutionizing supply chain management, allowing for better tracking of materials and processes.
Sourcing trends are also shifting towards localized suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing partnerships with suppliers who can provide customized solutions, tailored to specific applications. In regions like Vietnam and Nigeria, the focus on developing local manufacturing capabilities is reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling businesses to respond more agilely to market demands.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Heat Treating Stainless Steel Market?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the heat treating stainless steel sector, as businesses seek to minimize their environmental impact. The process of heat treating can be energy-intensive, prompting many companies to adopt energy-efficient practices and technologies. B2B buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers that implement sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and optimizing heat treatment processes to reduce waste.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with companies looking for suppliers who adhere to responsible sourcing practices. This includes ensuring that raw materials are sourced from ethical suppliers who prioritize fair labor practices and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential benchmarks for suppliers to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, there is a growing demand for ‘green’ materials, which are produced with lower environmental impact. Buyers are encouraged to inquire about the lifecycle assessments of materials and the sustainability credentials of their suppliers, ensuring that their sourcing decisions align with global sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Heat Treating Stainless Steel?
The history of heat treating stainless steel dates back to the early 20th century, coinciding with the development of stainless steel itself. Initially, the focus was on enhancing corrosion resistance, which was achieved through the addition of chromium. As the industrial applications for stainless steel grew, so did the need for various heat treatment methods to improve its mechanical properties.
Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and materials science led to the refinement of heat treatment processes, including annealing, hardening, and tempering. By the 1970s, the importance of heat treating in achieving desired performance characteristics became widely recognized, particularly in high-stress applications like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. Today, as industries continue to evolve, the heat treating of stainless steel remains a vital process, ensuring that materials meet the rigorous demands of modern applications while adhering to sustainability and ethical sourcing standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heat treating stainless steel
-
How do I solve issues related to heat treatment quality in stainless steel?
To address quality issues in heat-treated stainless steel, first, ensure that your supplier follows established industry standards such as ASTM or ISO certifications. Conduct regular audits of their heat treatment processes and equipment to verify compliance. Request detailed documentation of heat treatment parameters, including temperature, duration, and cooling methods. Engage in regular communication with the supplier to discuss quality expectations and improvements, and consider third-party testing for assurance. Establishing a clear quality assurance protocol can significantly mitigate risks related to product performance. -
What is the best heat treatment method for enhancing the properties of 304 stainless steel?
The most effective heat treatment method for 304 stainless steel is annealing, which involves heating the material to a temperature range of 1010-1120°C (1850-2050°F) and then rapidly cooling it. This process improves ductility and relieves internal stresses, enhancing the material’s formability and resistance to stress corrosion. Since 304 stainless steel cannot be hardened through traditional heat treatment, using cold working techniques alongside annealing can achieve a balance between strength and ductility. Always consult with your supplier to tailor the heat treatment process to your specific application needs. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for heat-treated stainless steel?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience and specialization in heat treating stainless steel. Review their certifications and quality management systems to ensure compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients and assess their capacity for customization based on your specifications. Evaluate their production capabilities, lead times, and flexibility in meeting minimum order quantities (MOQ). A supplier’s ability to provide detailed documentation and traceability of heat treatment processes can also indicate their reliability and commitment to quality. -
What are the common customization options available for heat-treated stainless steel?
Customization options for heat-treated stainless steel typically include variations in heat treatment processes, such as annealing, hardening, and tempering, tailored to specific applications. Suppliers may also offer different alloy compositions to enhance desired properties like corrosion resistance or strength. Additionally, manufacturers can modify dimensions, shapes, and surface finishes based on client specifications. Communicate your unique requirements clearly to ensure that the supplier can meet your expectations and provide samples or prototypes if necessary. -
What are typical payment terms for international purchases of heat-treated stainless steel?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include upfront payments, deposits (typically 30-50%), and balance payments upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or trade financing options, especially for larger orders. It’s essential to discuss payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider the currency exchange rates and any potential tariffs or taxes that may affect the overall cost. Establishing clear payment terms can facilitate smoother transactions and foster long-term relationships. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the procurement of heat-treated stainless steel?
Logistics and shipping play a crucial role in the procurement process of heat-treated stainless steel. Factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations can significantly affect delivery schedules. Choose suppliers with robust logistics capabilities that can ensure timely shipping and handling of your materials. Collaborate with freight forwarders who are experienced in international shipping to navigate customs documentation and tariffs efficiently. Understanding the entire supply chain, including potential bottlenecks, can help you manage costs and ensure the timely arrival of your products. -
What quality assurance practices should I implement when sourcing heat-treated stainless steel?
Implementing robust quality assurance practices involves setting clear specifications for the heat-treated stainless steel you require. Establish acceptance criteria for mechanical properties, surface finish, and dimensional tolerances. Request batch testing and certifications from your supplier to verify compliance with your specifications. Conduct regular inspections and audits of your supplier’s processes to ensure they meet industry standards. Utilizing third-party testing labs for independent verification can also enhance confidence in the product quality and performance. -
What are the risks of using improperly heat-treated stainless steel?
Using improperly heat-treated stainless steel can lead to several risks, including compromised mechanical properties, increased brittleness, and susceptibility to corrosion. These issues can result in product failures, safety hazards, and financial losses. In critical applications, such as aerospace or medical equipment, inadequate heat treatment can have severe consequences. It’s crucial to work with reputable suppliers who adhere to established heat treatment processes and conduct thorough quality checks to mitigate these risks and ensure the reliability of your stainless steel components.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Heat Treating Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Amazon – Cheap Chinese Knife
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Knife purchased on Amazon, described as a cheap Chinese knife. The user attempted to regrind the blade but faced issues with hardening and achieving a sharp edge. The user used canola oil for quenching and a small MAP gas blow torch for heating. Recommendations from commenters included sending the knife out for professional heat treatment, using a propane forge, stainless foil, and specific temper…
2. Hot Shot Ovens – Heat Treat and Knife Makers Kilns
Domain: hotshotovens.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Hot Shot Ovens offers a variety of heat treating ovens suitable for stainless steel heat treating, including: 1200ci Heat Treat Oven, 360ci Heat Treat Oven, and 360ci Tempering Oven. They also provide specialized kilns for knife making, such as the 18″D Knife Makers Kiln, 24″D Knife Makers Kiln, and 1200ci Knife Heat Treat Oven. The ovens are designed to improve properties such as hardness, ductil…
3. iForge Iron – Stainless Steels for At-Home Heat Treating
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Stainless steels suitable for at-home heat treating include AEB-L and XHP. These steels can be heat treated in open atmosphere, but require high heat quickly and evenly. Proper heat treatment is crucial for achieving desired hardness and toughness. AEB-L has been tested to achieve hardness around 60.5 after double tempering at 340F. The process may require a furnace for consistent results, especia…
4. Bodycote – Heat Treatment Services
Domain: bodycote.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Bodycote – Heat Treatment Services, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Nordic Edge – Heat Treating 12C27 Stainless Steel
Domain: nordicedge.com.au
Introduction: Instructions for Heat Treating 12C27 Stainless Steel at home. 12C27 is a stainless steel made by Sandvik in Sweden, known for its ease of heat treatment at home. Suggested heat treating process: Heat to 1080 C (1976 F) for 5 minutes, quench in heated canola oil (40 C or 104 F), optional freezer step to -20 C, temper at 170 C (338 F) for 2 hours. 12C27 composition: 0.6% Carbon, 13.5% Chromium, with…
6. KnifeDogs – AEB-L Stainless Steel Blades
Domain: knifedogs.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Thin stainless steel (~1/16″) AEB-L, heat treated in a propane forge, not requiring ultra-hard heat treatment or cryogenic treatment. Desired outcome is a soft and springy temper. Anti-scale coating is used. Recommendations include wrapping in heat treat foil, using a muffler tube in the forge, monitoring temperature with a thermocouple, and cooling between aluminum plates. Suggested tempering at …
7. Bladeforums – AEB-L Stainless Steel
Domain: bladeforums.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Easiest stainless steel to heat treat: AEB-L. Characteristics: forgiving, easy to grind, reasonably priced. Heat treat process: High Temperature stainless steel foil is needed to protect the blade during high austenizing temperatures. AEB-L does not require cryogenic treatment but benefits from it for optimal hardness. Can be plate quenched and tempered in an oven without cryo. Recommended for sma…
8. Knife Steel Nerds – AEB-L Stainless Steel
Domain: knifesteelnerds.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: AEB-L stainless steel is recommended for forging bladesmiths due to its fine carbide structure and properties similar to low alloy and simple carbon steels. It is often referred to as “stainless 52100” for its excellent toughness and fine carbide size. AEB-L is also relatively low cost, making it an attractive option for knifemakers.
9. Practical Machinist – Stainless Steel Hardening Solutions
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 316 stainless steel can only be hardened by work hardening and can be annealed by heat. The 400 series includes martensitic grades (hardenable) and ferritic grades (non-hardenable). 17-4 stainless steel hardens at 900 deg F with less distortion. Heat treatment for 316 involves a solution anneal to prevent stress corrosion cracking and improve ductility.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heat treating stainless steel
As the global demand for high-performance materials continues to rise, understanding the nuances of heat treating stainless steel becomes increasingly vital for B2B buyers. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting appropriate heat treatment methods tailored to specific applications, such as aging, hardening, and annealing, each offering distinct advantages for enhancing material properties. Additionally, recognizing the limitations of certain stainless steel grades, like 304, in heat treatment processes underscores the necessity of strategic sourcing and collaboration with suppliers who possess the expertise to guide you through these complexities.
Strategic sourcing not only ensures access to high-quality materials but also fosters long-term partnerships that can enhance your supply chain resilience. As international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, continue to evolve, staying informed about advancements in heat treatment technologies will position your business for success.
We encourage B2B buyers to engage with reputable suppliers and invest in research to optimize their sourcing strategies. By doing so, you will not only improve product quality but also contribute to sustainable practices in your industry. Embrace the future of stainless steel applications and ensure your business remains competitive in a dynamic global landscape.