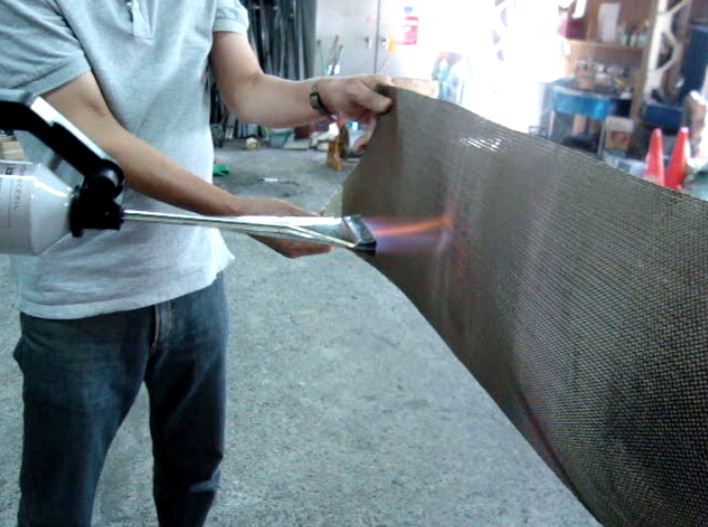
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heat resistant sheeting
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing high-quality heat resistant sheeting presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse sectors such as manufacturing, construction, and food processing. As industries increasingly demand materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, understanding the specifications, applications, and sourcing options for heat resistant sheeting becomes crucial. This guide aims to equip international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam—with the insights needed to navigate this complex landscape.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will explore various types of heat resistant sheeting, including silicone rubber, thermoplastics, and composite materials, each with unique properties and applications. Additionally, we will address critical factors such as supplier vetting, material certification, and cost considerations, enabling you to make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the nuances of heat resistant sheeting, buyers can enhance their operational efficiency, ensure compliance with industry standards, and ultimately drive their business success.
Arming yourself with the knowledge contained within this guide will empower you to confidently select the right materials for your specific needs, ensuring that your projects not only meet but exceed performance expectations.
Understanding heat resistant sheeting Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone Rubber Sheets | High-temperature resistance, flexible, durable | Gaskets, seals, insulation | Pros: Excellent heat resistance; Cons: Can be more expensive than alternatives. |
| Polycarbonate Sheets | Impact-resistant, lightweight, high clarity | Machine guards, safety shields | Pros: High durability; Cons: Limited thermal resistance compared to others. |
| PTFE (Teflon) Sheets | Non-stick, chemical resistance, high thermal tolerance | Food processing, chemical industries | Pros: Excellent non-stick properties; Cons: Lower mechanical strength. |
| Fiberglass Reinforced Panels | Strong, lightweight, and moisture resistant | Construction, automotive, and aerospace | Pros: High strength-to-weight ratio; Cons: Can be more costly than standard panels. |
| Acrylic Sheets | Lightweight, good optical clarity, UV resistant | Signage, displays, protective barriers | Pros: Versatile and easy to fabricate; Cons: Lower heat resistance than other materials. |
What Are the Characteristics of Silicone Rubber Sheets?
Silicone rubber sheets are known for their exceptional resistance to high temperatures, capable of withstanding heat up to 500°F (260°C). Their flexibility and durability make them ideal for applications requiring gaskets, seals, and insulation. B2B buyers should consider the specific temperature requirements of their applications and the potential for wear and tear over time. While silicone sheets can be more expensive, their longevity and performance often justify the investment.
How Do Polycarbonate Sheets Stand Out?
Polycarbonate sheets are recognized for their impact resistance and lightweight nature, making them suitable for machine guards and safety shields. They offer high optical clarity, which is essential for applications where visibility is crucial. However, while they are durable, their thermal resistance is not as high as other materials, which is a key consideration for buyers in high-heat environments.
What Are the Advantages of PTFE (Teflon) Sheets?
PTFE sheets, commonly known as Teflon, are celebrated for their non-stick properties and outstanding chemical resistance. They perform exceptionally well in food processing and chemical industries where exposure to high temperatures and corrosive substances is common. Buyers should note that while PTFE provides excellent thermal tolerance, it may lack the mechanical strength found in other materials, which could limit its use in certain applications.
Why Choose Fiberglass Reinforced Panels?
Fiberglass reinforced panels are characterized by their strength, lightweight design, and resistance to moisture. These panels are widely used in construction, automotive, and aerospace applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio. B2B buyers should evaluate the cost against the performance benefits, as fiberglass panels can be pricier than standard options but offer superior durability and longevity.
What Makes Acrylic Sheets a Good Option?
Acrylic sheets are lightweight and provide good optical clarity, making them ideal for signage, displays, and protective barriers. They are also UV resistant, which helps prevent yellowing over time. However, buyers should be aware that acrylic sheets have lower heat resistance compared to silicone or PTFE options, which may limit their application in high-temperature environments. Overall, their versatility and ease of fabrication make them a popular choice in various industries.
Key Industrial Applications of heat resistant sheeting
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Heat Resistant Sheeting | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Insulation for Engine Components | Enhances safety by preventing overheating and fires | Ensure compliance with aviation standards and certifications. |
| Food Processing | Protective Linings for Ovens and Grills | Improves hygiene and reduces maintenance costs | Verify FDA compliance and heat tolerance ratings. |
| Manufacturing | Gaskets and Seals in High-Temperature Equipment | Reduces downtime and increases operational efficiency | Look for durability and resistance to chemical exposure. |
| Automotive | Under-hood Components and Insulation | Increases reliability and lifespan of vehicle parts | Source materials that withstand extreme temperatures and vibrations. |
| Construction | Thermal Barriers in Building Materials | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces heating costs | Consider local climate conditions and fire safety regulations. |
How is Heat Resistant Sheeting Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, heat resistant sheeting is critical for insulation in engine components and other high-temperature areas. This material helps to prevent overheating, which can lead to catastrophic failures. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing products that comply with stringent aviation standards is essential. Suppliers should provide documentation of certifications and detailed performance specifications to ensure safety and reliability.
What Role Does Heat Resistant Sheeting Play in Food Processing?
In food processing, heat resistant sheeting is utilized as protective linings for ovens and grills. This application not only helps maintain hygiene standards but also minimizes maintenance costs by protecting equipment from thermal damage. Buyers in South America and Europe should prioritize materials that meet food safety regulations, such as FDA compliance, and ensure that the sheeting can withstand the high temperatures typical in food preparation environments.
How is Heat Resistant Sheeting Beneficial in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often employ heat resistant sheeting for gaskets and seals in high-temperature equipment. This application is vital for reducing downtime due to equipment failure, thus enhancing operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, particularly in developing markets, sourcing durable materials that can resist chemical exposure and maintain integrity under pressure is crucial. Suppliers should provide detailed specifications on temperature ratings and chemical compatibility.
What are the Automotive Applications of Heat Resistant Sheeting?
In the automotive industry, heat resistant sheeting is used for under-hood components and insulation. These materials increase the reliability and lifespan of vehicle parts by protecting them from extreme temperatures and vibrations. International buyers, especially from regions like Vietnam and Nigeria, should consider the sheeting’s resistance to wear and tear, ensuring that the products sourced can endure the rigors of automotive applications.
How Does Heat Resistant Sheeting Enhance Construction Projects?
Heat resistant sheeting serves as a thermal barrier in construction materials, promoting energy efficiency and reducing heating costs in buildings. This is particularly important in regions with extreme climates. When sourcing these materials, buyers in Europe and the Middle East must consider local building codes and fire safety regulations. Ensuring that the sheeting meets these requirements is essential for compliance and safety in construction projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘heat resistant sheeting’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Durability in High-Temperature Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find heat resistant sheeting that can withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without compromising performance. Industries such as manufacturing, food processing, and automotive face the challenge of selecting materials that not only resist heat but also maintain structural integrity under pressure. Buyers frequently encounter products that fail prematurely, leading to costly downtime and safety hazards.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should consider sourcing heat resistant sheeting made from high-performance materials such as silicone, PTFE, or specialized polymers. When specifying these materials, look for detailed thermal resistance ratings, as well as certifications that align with industry standards. Additionally, ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive data sheets that outline temperature limits, tensile strength, and other critical performance metrics. Engaging with manufacturers who offer customization options can also help tailor solutions to specific operational needs, ensuring that the sheeting will perform reliably in high-temperature environments.
Scenario 2: Managing Supply Chain and Sourcing Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often face delays in the procurement of heat resistant sheeting due to global supply chain disruptions or vendor inconsistencies. This can result in production halts and missed deadlines, which can severely impact client relationships and profitability. Buyers may also be overwhelmed by the variety of options available, making it difficult to determine the most reliable sources.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain issues, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers to create a more resilient procurement strategy. Regularly evaluating supplier performance based on delivery times, quality assurance, and responsiveness can help identify the most reliable partners. Additionally, buyers should consider sourcing from local manufacturers or distributors to reduce lead times and shipping costs. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can also aid in better managing stock levels, ensuring that heat resistant sheeting is available when needed without incurring excess inventory costs.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Proper Installation and Maintenance
The Problem: Even after successfully sourcing heat resistant sheeting, B2B buyers often encounter difficulties during installation and maintenance. Improper installation can lead to performance issues, while inadequate maintenance can shorten the lifespan of the material. Industries such as aerospace and chemical processing require meticulous adherence to installation protocols to ensure safety and compliance, yet many buyers lack the necessary training or resources.
The Solution: To overcome installation challenges, buyers should invest in training programs for their teams, focusing on best practices for working with heat resistant materials. Collaborating with suppliers who offer technical support and guidance during the installation phase can also be beneficial. It’s essential to create comprehensive installation guidelines that include step-by-step procedures, recommended tools, and safety measures. For maintenance, establishing a routine inspection schedule can help identify wear and tear early, allowing for timely interventions that extend the lifespan of the sheeting. Providing users with access to maintenance manuals and support resources can empower teams to manage the sheeting effectively and ensure ongoing performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heat resistant sheeting
What Are the Key Materials for Heat Resistant Sheeting?
When selecting heat resistant sheeting, various materials offer unique properties and advantages. Understanding these materials is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is an analysis of four common materials used for heat resistant sheeting: silicone rubber, PTFE (Teflon), fiberglass, and polyimide.
How Does Silicone Rubber Perform in Heat Resistant Applications?
Silicone rubber is renowned for its excellent thermal stability, withstanding temperatures ranging from -60°C to 260°C (-76°F to 500°F). It exhibits good flexibility and resilience, making it suitable for various applications, including gaskets and seals in high-temperature environments.
Pros: Silicone rubber is highly durable and resistant to UV light, ozone, and extreme temperatures. Its flexibility allows it to maintain a tight seal, which is critical in many industrial applications.
Cons: The primary limitation is its cost, which can be higher than other materials. Additionally, silicone rubber may not be suitable for applications involving certain chemicals, which can degrade its properties.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, it is essential to ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, when sourcing silicone products.
What Advantages Does PTFE Offer for Heat Resistant Sheeting?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, is another popular choice for heat resistant sheeting. It can withstand temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) and is known for its exceptional chemical resistance.
Pros: PTFE’s non-stick properties make it ideal for applications in food processing and chemical industries. Its low friction coefficient also enhances its performance in mechanical applications.
Cons: PTFE can be more expensive than other materials and is often more challenging to fabricate. Its mechanical strength is lower than that of silicone rubber, which may limit its use in certain structural applications.
International buyers should be aware of the specific certifications required for PTFE in food-related applications, particularly in regions with stringent food safety regulations.
Why Is Fiberglass a Reliable Option for Heat Resistant Sheeting?
Fiberglass sheeting is widely used in high-temperature applications due to its ability to withstand temperatures up to 540°C (1000°F). It is often reinforced with resins to enhance its mechanical properties.
Pros: Fiberglass is highly durable and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments. It is also lightweight, which can reduce shipping costs.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher production costs. Additionally, fiberglass may not be as flexible as silicone or PTFE, limiting its applications in certain scenarios.
For B2B buyers in regions like South America and Europe, understanding the local regulations regarding fiberglass use in construction and manufacturing is vital to ensure compliance.
How Does Polyimide Compare in High-Temperature Applications?
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer that can withstand temperatures exceeding 300°C (572°F). It is often used in aerospace and electronics due to its excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation properties.
Pros: Polyimide offers superior thermal resistance and is lightweight, making it ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor. It also has excellent mechanical properties.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, as polyimide is generally more expensive than other materials. Additionally, it may require specialized processing techniques, which can complicate manufacturing.
For international buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, ensuring that polyimide materials meet industry standards and certifications for aerospace or electronics applications is crucial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heat Resistant Sheeting
| Material | Typical Use Case for heat resistant sheeting | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone Rubber | Gaskets and seals in high-temperature environments | Excellent thermal stability | Higher cost, chemical sensitivity | Medium |
| PTFE | Food processing, chemical industries | Exceptional chemical resistance | Higher cost, fabrication challenges | High |
| Fiberglass | Industrial applications, construction | Corrosion resistance, lightweight | Complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Polyimide | Aerospace, electronics | Superior thermal resistance | High cost, specialized processing | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the key materials used in heat resistant sheeting, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heat resistant sheeting
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Heat Resistant Sheeting?
The manufacturing of heat resistant sheeting involves several critical stages, each tailored to ensure the final product meets the demanding specifications required by various industries. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality materials.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Heat resistant sheeting is typically made from silicone rubber, thermoplastics, or specialized polymers that can withstand elevated temperatures. Suppliers often conduct rigorous assessments to choose materials based on their thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo processing to eliminate impurities and ensure consistency. This may involve grinding, mixing with additives, or preheating to achieve the desired viscosity. The importance of this step cannot be overstated, as the quality of the raw materials directly impacts the performance of the final product.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Heat Resistant Sheeting?
After preparation, the next stage is forming, where the processed materials are shaped into sheets. Various techniques are employed, including:
-
Calendering: This involves passing the material through rollers to create uniform sheets of specified thickness. Calendering is particularly effective for rubber and silicone materials.
-
Extrusion: In this method, the material is forced through a die to create continuous sheets. This technique is widely used for thermoplastics and allows for precise control over dimensions.
-
Molding: For more complex shapes or thicker materials, molding techniques such as compression or injection molding may be used. This method is beneficial for creating intricate designs that may not be feasible through other processes.
Each of these techniques has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the specific requirements of the application and the material properties.
Assembly: How Are Multiple Layers or Components Integrated?
For applications requiring enhanced performance, multiple layers of heat resistant sheeting may be assembled together. This could involve adhesive bonding or thermal bonding processes to create composite materials that offer superior thermal and mechanical resistance.
The assembly stage may also include the incorporation of additional features, such as reinforcement with fabrics or other materials to enhance durability. Understanding the assembly techniques used by suppliers can provide B2B buyers with insights into the potential performance and longevity of the sheeting.
Finishing: What Are the Final Steps in Preparing Heat Resistant Sheeting for Market?
The finishing stage involves several processes aimed at enhancing the product’s functionality and aesthetics. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Cutting and Trimming: Sheets are cut to specific sizes and shapes based on customer requirements. Precision cutting is essential to ensure the dimensions meet exact specifications.
-
Surface Treatment: This may involve treatments like texturing, coating, or applying anti-adhesive finishes to improve performance under specific conditions.
-
Quality Inspection: Before the sheets are packaged and shipped, they undergo final quality inspections to ensure they meet the established standards.
This stage is crucial for ensuring that the products are ready for use in demanding environments, such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Essential for Heat Resistant Sheeting?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for heat resistant sheeting. B2B buyers must be aware of the relevant international and industry-specific standards that govern product quality.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Suppliers adhering to this standard demonstrate their commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, compliance with specific industry standards such as CE marking for European markets or API specifications for oil and gas applications can further assure buyers of the product’s reliability.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Structured in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that any defects are identified and rectified early. Typical QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves the inspection of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. It ensures that only high-quality materials proceed to production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This ongoing inspection occurs during the manufacturing process. It helps monitor production parameters and material properties, allowing for immediate corrective actions if deviations occur.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection stage assesses the finished product against established specifications. It often includes physical testing for thermal resistance, tensile strength, and other performance metrics.
Understanding these checkpoints helps B2B buyers gauge the thoroughness of a supplier’s quality assurance processes.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Heat Resistant Sheeting?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the performance of heat resistant sheeting. These may include:
-
Thermal Conductivity Tests: Assessing how well the material insulates against heat, which is critical for applications in high-temperature environments.
-
Mechanical Testing: Evaluating properties such as tensile strength, elongation, and tear resistance to ensure the material can withstand operational stresses.
-
Chemical Resistance Tests: Testing how the material interacts with various chemicals, particularly for applications in industries like oil and gas or food processing.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods used by suppliers and request test reports to validate compliance with required standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is paramount. Here are several actionable steps to ensure quality assurance:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation, including ISO certifications, test reports, and quality control checklists, to demonstrate compliance with relevant standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing independent third-party inspectors can add an additional layer of assurance, particularly for bulk orders or high-value contracts.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate specific nuances in quality assurance and certification. Variations in regulatory requirements, language barriers, and differences in industrial practices can complicate sourcing efforts.
Buyers should ensure that suppliers are familiar with regional certifications and standards. Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations and compliance requirements can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from different markets.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for heat resistant sheeting enables B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions, ensuring they procure materials that meet their operational needs and quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘heat resistant sheeting’
In today’s competitive market, sourcing heat resistant sheeting requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers, focusing on critical steps to ensure quality, compliance, and suitability for your specific applications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, it’s essential to outline your requirements. Consider factors such as temperature resistance, thickness, and material type (e.g., silicone, rubber, or plastic). This clarity will help you communicate your needs effectively and ensure that the products you evaluate meet your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Market Options
Conduct thorough research to identify available products in the market. Utilize online resources, industry publications, and supplier websites to gather information. Pay particular attention to performance metrics and application suitability, as this will inform your decision-making process and help you identify potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers with a proven track record of quality and reliability, as this can significantly impact your supply chain efficiency.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure suppliers hold relevant industry certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) that validate their product quality and manufacturing processes.
- Review Customer Feedback: Analyze reviews and testimonials to gauge customer satisfaction and service levels.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the heat resistant sheeting. Testing these samples in your specific environment will provide insights into their performance under actual conditions.
- Assess Durability and Resistance: Evaluate how the material responds to heat exposure and mechanical stress, ensuring it meets your operational needs.
- Check Compatibility: Confirm that the sheeting is compatible with other materials used in your processes.
Step 5: Understand Pricing Structures
Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing to understand their cost structures. Look for transparency in pricing and be wary of hidden costs that could affect your budget.
- Consider Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, as this can significantly reduce overall costs.
- Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in shipping, handling, and potential maintenance costs to get a true picture of the financial implications.
Step 6: Verify Delivery Capabilities
Assess suppliers’ logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery of your orders. Delays can disrupt operations, so it’s vital to confirm that they can meet your lead times.
- Inquire About Inventory Levels: Suppliers with robust inventory systems can often fulfill orders more quickly.
- Discuss Shipping Options: Explore various shipping methods and their associated costs to find the best fit for your timeline and budget.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Partnership
Once you’ve selected a supplier, aim to build a strong relationship for future transactions. Open lines of communication can lead to better pricing, improved service, and collaborative problem-solving.
- Regularly Review Performance: Schedule periodic evaluations of supplier performance to ensure ongoing satisfaction and quality.
- Stay Informed on Product Innovations: Engage with suppliers to stay updated on new products or advancements that may benefit your operations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for heat resistant sheeting with confidence, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heat resistant sheeting Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Heat Resistant Sheeting?
Understanding the cost structure of heat resistant sheeting is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials for heat resistant sheeting include silicone rubber, thermoplastics, and specialized coatings. High-performance materials tend to command higher prices due to their enhanced durability and heat resistance properties.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for specialized production methods, which can increase the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and indirect labor costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these overheads.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for manufacturing heat resistant sheets can involve significant tooling costs, particularly for custom designs. These costs are amortized over the production volume, impacting unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet specific quality standards is essential. QC processes add to the cost structure but are vital for maintaining product reliability, especially in industries where safety is paramount.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, must be considered. These can vary widely depending on the origin of the materials and the destination markets.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This can vary based on market competition and the uniqueness of the product offered.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Heat Resistant Sheeting Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of heat resistant sheeting:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Negotiating favorable terms for bulk purchases can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions that meet specific technical requirements can increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of materials and the presence of certifications (such as ISO or ASTM standards) can affect pricing. Products with higher quality assurance often come at a premium.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence costs. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to enter the market.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They define who is responsible for various shipping costs and liabilities, which can significantly impact the total cost.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers?
To effectively manage costs when sourcing heat resistant sheeting, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Conduct Thorough Market Research: Understand the pricing landscape by comparing multiple suppliers and product offerings. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate orders to meet MOQ thresholds for better pricing. Consider long-term contracts for consistent supply, which can also lead to cost reductions.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess not just the purchase price but also factors like durability, maintenance, and potential replacements. A higher upfront cost may be justified if it leads to lower long-term expenses.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment options can improve cash flow. Discussing extended payment terms or discounts for early payment can yield financial benefits.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing structures influenced by local regulations, tariffs, and supply chain dynamics. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these nuances can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for heat resistant sheeting can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors. This analysis serves as a guideline; actual costs should be confirmed with suppliers for accurate quotes tailored to specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing heat resistant sheeting With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Heat Resistant Sheeting: What Are Your Options?
When selecting materials for high-temperature applications, businesses often consider various solutions that can withstand extreme conditions. While heat resistant sheeting is a popular choice, several alternatives might also meet specific needs effectively. This analysis compares heat resistant sheeting with silicone rubber sheeting and high-temperature plastic sheeting, providing insights into their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Heat Resistant Sheeting | Silicone Rubber Sheeting | High-Temperature Plastic Sheeting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent thermal resistance; suitable for a wide range of temperatures | Superior elasticity and durability; withstands extreme temperatures | Good thermal resistance; less flexible than rubber |
| Cost | Moderate to high; varies by thickness and brand | Generally higher; premium for elasticity and durability | Typically lower; cost-effective for bulk applications |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward; can be cut and shaped easily | Requires specialized tools for cutting and shaping | Easy to install; can be thermoformed for specific shapes |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to moisture and chemicals | Low maintenance; resistant to wear and tear | Moderate maintenance; may require replacement over time |
| Best Use Case | Industrial applications, automotive, aerospace | Sealing applications, gaskets, and high-wear environments | Electrical insulation, protective covers, and food processing |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Silicone Rubber Sheeting?
Silicone rubber sheeting stands out for its exceptional elasticity and ability to withstand extreme temperatures ranging from -100°F to 500°F. Its durability makes it ideal for applications requiring high wear resistance, such as gaskets or seals in machinery. However, silicone rubber can be more expensive than other materials, which may deter cost-sensitive buyers. Additionally, specialized tools may be needed for cutting and shaping, making it less accessible for some users.
How Does High-Temperature Plastic Sheeting Compare?
High-temperature plastic sheeting offers a cost-effective alternative, particularly for applications in electrical insulation or protective covers. It generally withstands temperatures up to 200°F and is relatively easy to install, often requiring no special tools. However, while it provides decent thermal resistance, it lacks the flexibility and durability of silicone rubber sheeting. This can limit its use in high-wear applications or where flexibility is crucial.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the appropriate heat-resistant material depends on specific application needs, budget constraints, and performance requirements. Heat resistant sheeting is ideal for industrial environments requiring superior thermal resistance. In contrast, silicone rubber sheeting offers unmatched durability and flexibility, making it suitable for high-stress applications. Alternatively, high-temperature plastic sheeting may be the best choice for buyers seeking a budget-friendly option with moderate performance. By carefully assessing these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance overall efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heat resistant sheeting
When considering heat resistant sheeting for various industrial applications, understanding its technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide will provide essential insights into these aspects, helping B2B buyers navigate the complexities of heat resistant materials.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Heat Resistant Sheeting?
-
Material Grade
– Heat resistant sheeting is typically made from materials like silicone, rubber, or specialized plastics, each rated for different temperature thresholds. For instance, silicone sheeting can withstand temperatures up to 500°F (260°C). Selecting the right material grade is critical for ensuring the sheeting meets specific application requirements, such as those found in manufacturing or food processing environments. -
Thickness and Tolerance
– The thickness of heat resistant sheets can vary, commonly ranging from 1/16 inch to several inches. Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions. Accurate thickness and tolerance are vital for applications that require precise fits, such as gaskets or seals, where improper dimensions could lead to inefficiencies or failures in performance. -
Thermal Conductivity
– This property measures how well heat can pass through a material. Low thermal conductivity is desirable for applications needing insulation, while higher conductivity may be required for heat transfer applications. Understanding thermal conductivity helps buyers determine the most suitable sheeting for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance in thermal management. -
Flame Retardancy
– Many heat resistant sheets are treated to resist ignition and slow the spread of flames. This property is particularly important in industries such as construction and manufacturing, where fire safety regulations are stringent. Buyers should look for certifications indicating compliance with relevant fire safety standards to mitigate risks. -
Chemical Resistance
– Heat resistant sheeting may be exposed to various chemicals, including oils, solvents, and acids. Evaluating the chemical resistance of the material is essential to ensure longevity and performance, especially in environments where spills or exposure to harsh substances are likely. -
Flexibility and Durability
– The flexibility of the sheeting allows it to conform to various shapes and surfaces, making it versatile for different applications. Durability refers to the material’s ability to withstand wear, tear, and environmental factors. These characteristics are crucial for applications involving constant movement or exposure to harsh conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Heat Resistant Sheeting Industry?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of heat resistant sheeting, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who meet industry standards and specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy, especially for bulk orders, ensuring they meet supplier requirements while managing inventory effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products. For heat resistant sheeting, issuing an RFQ can facilitate competitive pricing and help buyers compare options from different suppliers, enhancing their procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, which can significantly impact the total cost of purchasing heat resistant sheeting. -
Lead Time
– This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is critical for buyers who need heat resistant sheeting for projects with tight schedules, allowing for better planning and resource allocation. -
Certification Standards
– Various certification standards, such as ISO or ASTM, indicate that a product meets specific quality and safety requirements. Buyers should look for certified heat resistant sheeting to ensure they are procuring materials that adhere to industry regulations and best practices.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing heat resistant sheeting, ultimately leading to better performance and compliance in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the heat resistant sheeting Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Heat Resistant Sheeting Sector?
The global market for heat resistant sheeting is experiencing significant growth, driven by increased demand across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and construction. The rise in industrial activities, particularly in emerging economies in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, is propelling this demand. For international B2B buyers, understanding the dynamics of this sector is crucial. Key trends include the integration of advanced materials such as silicone and specialized polymers that offer superior heat resistance and durability. Moreover, digital transformation is reshaping sourcing strategies, with more companies leveraging e-commerce platforms and digital supply chain management tools to enhance procurement efficiency.
Emerging technologies, such as 3D printing and advanced manufacturing techniques, are also influencing sourcing trends by allowing for customized solutions tailored to specific applications. As industries increasingly prioritize performance, suppliers are focusing on developing high-quality products that meet stringent regulatory standards. Furthermore, the rise of sustainability initiatives is prompting companies to seek suppliers that align with eco-friendly practices, which can affect supplier selection and pricing strategies.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Heat Resistant Sheeting Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal factor in the sourcing of heat resistant sheeting. As global awareness of environmental issues rises, B2B buyers are increasingly considering the ecological impact of their procurement choices. This includes assessing the lifecycle of materials, energy consumption during production, and end-of-life recyclability. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains is also gaining traction. Buyers are seeking out suppliers who uphold fair labor practices and transparency in their operations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish credibility in the marketplace. These certifications not only enhance a supplier’s reputation but also provide buyers with assurance regarding compliance with international environmental standards.
Moreover, the adoption of “green” materials, such as bio-based polymers and eco-friendly coatings for heat resistant sheeting, is on the rise. This trend not only meets consumer demand for sustainable products but can also offer competitive advantages in terms of market positioning and customer loyalty.
What Is the Evolution of Heat Resistant Sheeting in the B2B Market?
The heat resistant sheeting market has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from traditional materials like rubber and fiberglass to advanced composites and high-performance polymers. Initially, heat resistant sheets were primarily utilized in industrial applications, but their use has expanded into consumer products and specialized sectors like electronics and food processing.
In recent years, innovations in material science have led to the development of more efficient and durable products, such as silicone rubber sheets and advanced thermoplastics. These innovations not only enhance performance but also cater to the growing demand for lighter and more versatile materials. As industries continue to innovate, the heat resistant sheeting market is expected to witness further advancements, providing B2B buyers with more options to meet their specific needs.
In conclusion, navigating the heat resistant sheeting sector requires an understanding of market dynamics, a commitment to sustainable sourcing, and awareness of the historical context that shapes current offerings. By focusing on these areas, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with both operational needs and corporate social responsibility goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heat resistant sheeting
-
How do I choose the right heat resistant sheeting for my application?
Selecting the appropriate heat resistant sheeting involves evaluating the specific temperature and environmental conditions it will face. Consider the material type—silicone, rubber, or plastic—as each has distinct properties regarding heat tolerance and durability. Assess other factors like chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and whether the sheet will be exposed to direct flames or radiant heat. It’s advisable to consult with suppliers to understand the performance characteristics of their products and to request samples for testing in your specific conditions. -
What are the benefits of using silicone rubber sheeting over other materials?
Silicone rubber sheeting offers exceptional flexibility and can withstand extreme temperatures, ranging from -60°F to 500°F (-51°C to 260°C). Its resistance to UV light, ozone, and moisture makes it ideal for outdoor applications. Additionally, silicone sheeting maintains its properties over time without hardening or cracking, which is beneficial for long-term applications. This material is also food-safe, making it suitable for industries requiring high hygiene standards, such as food processing and medical applications. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing heat resistant sheeting?
MOQs for heat resistant sheeting can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from 50 to 100 square meters. Factors influencing MOQ include the type of material, the complexity of customization, and the supplier’s production capabilities. When negotiating with suppliers, it’s crucial to discuss your specific needs, as some may be willing to accommodate smaller orders for new customers or trial projects. Building a strong relationship with your supplier may also lead to more favorable terms in the future. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing heat resistant sheeting internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, begin by vetting potential suppliers through verified certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Request samples before placing large orders to assess the material’s performance and durability. Establish clear specifications and tolerances in your purchase agreement, and consider conducting third-party inspections during production and before shipment. Additionally, maintaining open lines of communication with your supplier can help address any concerns and ensure adherence to quality standards. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted for international orders of heat resistant sheeting?
Payment terms for international orders may vary by supplier but commonly include options such as letters of credit, advance payments, or net 30/60/90 days payment terms. Letters of credit are often preferred for larger transactions as they provide security for both parties. It’s essential to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they are documented in the contract. Additionally, consider currency fluctuations and transaction fees when planning your budget, especially when dealing with suppliers in different countries. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing heat resistant sheeting?
When importing heat resistant sheeting, it is vital to consider shipping methods, delivery timelines, and customs regulations. Determine whether air freight or sea freight is more cost-effective based on your order size and urgency. Familiarize yourself with import duties, taxes, and documentation requirements specific to your country to avoid delays. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider experienced in international trade can help streamline the process and ensure that your products arrive safely and on time. -
How can I customize heat resistant sheeting for my specific needs?
Customization options for heat resistant sheeting may include variations in thickness, size, color, and material composition. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements. To initiate the customization process, provide detailed specifications and, if possible, samples of the existing products you wish to modify. Collaborate closely with the supplier’s engineering or design team to ensure that the final product meets your expectations while adhering to performance standards. -
What are the common applications for heat resistant sheeting across different industries?
Heat resistant sheeting is utilized in various industries, including automotive, food processing, manufacturing, and construction. Common applications include gaskets, seals, insulation, and protective covers that are exposed to high temperatures. In the food industry, silicone sheeting is often used for baking mats and food storage solutions due to its non-toxic properties. Understanding your industry’s specific needs can help you select the most appropriate material and application for your heat resistant sheeting requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Heat Resistant Sheeting Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Interstate Plastics – Heat Resistant Plastic Sheets
Domain: interstateplastics.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Heat Resistant Plastic Sheet: Various types of plastic sheets including UHMW, HDPE, Acetal, ABS, Polycarbonate, Acrylic, Nylon, PEEK, PETG, Phenolic, Polypropylene, PTFE, PVC. Specific products include Worbla Hand-Formable Thermoplastic Sheets (Black and Beige), Delrin® Plastic Sheet (Black), Acetal Plastic Sheet (Natural Color), Craft Plastic Mirror Sheets (various colors), Craft Plastic Sheets (…
2. McMaster – High Temperature Plastic Sheets
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – High Temperature Plastic Sheets, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. A&C Plastics – Fire Rated Polycarbonate Sheets
Domain: acplasticsinc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: A&C Plastics offers fire rated polycarbonate sheets that are flame-inhibiting, UV-stable, and virtually unbreakable. These sheets are stronger than glass and plexiglass and can be easily die cut, punched, and sheared. The fire resistant plastic sheeting is ideal for various industries including electrical devices, aircraft components, and construction. Tuffak’s flame retardant polycarbonate meets …
4. Tarps Now – Flame Resistant Poly Sheeting
Domain: tarpsnow.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Flame Resistant Poly Sheeting features reinforced polyethylene material suitable for light to medium duty applications. Available thicknesses: 5 Mil, 6 Mil, and 10 Mil. The sheeting is 100% waterproof and cost-effective. Ideal for temporary building enclosures, construction sites, building wraps, and temporary walls. Meets national fire safety requirements. Available in 20-foot and 40-foot widths …
5. Prime Pick – Heat-Resistant Teflon Sheet
Domain: primepickusa.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: {“name”:”Heat-Resistant Sheet”,”type”:”Teflon Sheet for HTV”,”brand”:”Prime Pick”,”price”:”$3.99″,”description”:”Heat-resistant sheets from Prime Pick are essential when you’re working with materials that are more susceptible to higher temperatures. By placing the Teflon sheet for HTV between the press and the material, it can withstand temperatures of up to 600 degrees Fahrenheit. Protect your vi…
6. Pensacola Vinyl Shop – Heat Resistant Sheet
7. Professional Plastics – High-Temperature Plastic Materials
Domain: professionalplastics.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Plastic materials for high temperature applications (>425° F) including sheets, rods, and tubing. Key materials listed include PEEK, UHMW, Nylon, PTFE, Polycarbonate, and more. The company has been a leader in plastic sheets, rods, tubing, profiles, and parts since 1984. Contact information and product categories are provided, along with solutions by industry and application.
8. AB Thermal – Flexible Graphite Sheets & Rolls
Domain: abthermal.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Flexible Graphite Sheet & Roll – High Temperature & Heat Resistant; Continuous Exposure: 950°F / 510°C; Higher Intermittent: up to 5400°F / 2982°C; Material: GraphTek™ Flexible graphite, available in sheets, laminate, and rolls; Applications: Extreme heat protection, thermal dissipation, lubrication.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heat resistant sheeting
In the evolving landscape of heat resistant sheeting, strategic sourcing remains pivotal for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains. By prioritizing quality materials such as silicone and thermoplastics, companies can enhance their operational efficiency and product durability. Understanding the unique requirements of various industries—from manufacturing to construction—enables buyers to select the most suitable solutions that meet specific thermal resistance needs.
Leveraging data-driven insights and fostering strong supplier relationships can significantly mitigate risks associated with procurement. It is essential for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to remain proactive in evaluating market trends and technological advancements in heat resistant materials. This approach not only ensures access to superior products but also positions businesses competitively in their respective markets.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative heat resistant sheeting solutions is set to grow. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who can offer customized solutions and sustainability practices. By doing so, they can ensure their operations are resilient and aligned with future market demands. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your sourcing strategy today—your business’s success depends on it.