Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hardness of titanium vs stainless steel
In today’s competitive landscape, B2B buyers face the critical challenge of selecting the right materials for their projects, especially when it comes to understanding the hardness of titanium versus stainless steel. This guide delves deep into the intricate properties of these metals, aiding decision-makers in sourcing materials that align with their specific operational needs. Whether you are operating in aerospace, automotive, or medical sectors, knowing the differences in hardness, corrosion resistance, and weight can significantly influence your project’s success and sustainability.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of titanium and stainless steel, including their physical and mechanical properties, typical applications, and considerations for supplier vetting. We will also address cost implications, ensuring that you can evaluate options that not only meet technical requirements but also fit within your budget constraints.
This guide is tailored for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia. By equipping you with actionable insights and a thorough understanding of these materials, we empower you to make informed purchasing decisions that will enhance your business operations and contribute to your competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding hardness of titanium vs stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercially Pure Titanium | High corrosion resistance, lightweight | Aerospace, medical implants | Pros: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: Higher cost, limited hardness. |
| Titanium Alloys | Enhanced strength and hardness through alloying | Automotive, marine applications | Pros: Improved mechanical properties. Cons: More complex processing. |
| Standard Stainless Steel | Affordable, versatile, varying hardness levels | Construction, kitchenware | Pros: Cost-effective, good machinability. Cons: Heavier, lower corrosion resistance. |
| Hardened Stainless Steel | Very high hardness, good wear resistance | Industrial machinery, tooling | Pros: Excellent durability. Cons: More brittle, less ductile. |
| Titanium vs. Stainless Steel | Comparative analysis of hardness and performance | General engineering, manufacturing | Pros: Informed material selection. Cons: Requires detailed understanding of applications. |
What are the Characteristics of Commercially Pure Titanium?
Commercially pure titanium is characterized by its high corrosion resistance and lightweight nature. This metal is often utilized in critical applications such as aerospace and medical implants due to its biocompatibility and strength-to-weight ratio. B2B buyers should consider the higher costs associated with pure titanium, as well as its limited hardness compared to alloys. When selecting this material, the project’s specific requirements for weight and corrosion resistance should guide the decision.
How Do Titanium Alloys Enhance Strength and Hardness?
Titanium alloys incorporate elements like aluminum and vanadium, which significantly enhance their strength and hardness. These alloys are commonly used in automotive and marine applications where durability is crucial. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific alloy type for their projects, as different compositions can offer varying mechanical properties. While these alloys are more expensive and complex to process, their superior performance often justifies the investment in high-demand industries.
What Makes Standard Stainless Steel a Popular Choice?
Standard stainless steel is known for its affordability and versatility, making it a staple in construction and kitchenware. Its varying hardness levels allow for a wide range of applications, though it typically offers lower corrosion resistance compared to titanium. For B2B buyers, the cost-effectiveness and ease of machining are significant advantages. However, it’s essential to consider the weight factor, as stainless steel is generally heavier, which may affect overall project specifications.
Why Choose Hardened Stainless Steel for Tough Applications?
Hardened stainless steel boasts very high hardness and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for industrial machinery and tooling applications. While it provides outstanding durability, it can also be more brittle and less ductile than other materials, which may lead to challenges in certain applications. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of durability against the potential for brittleness, especially in high-stress environments where flexibility might be necessary.
How Does the Comparison of Titanium and Stainless Steel Inform Material Selection?
The comparative analysis of titanium and stainless steel hardness provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in various industries. Understanding the specific mechanical properties and applications of each material enables informed decision-making. While titanium offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance, stainless steel is often more cost-effective and versatile. Buyers should consider the specific demands of their projects, including environmental factors, mechanical stress, and budget constraints, to make the best material choice for their needs.
Key Industrial Applications of hardness of titanium vs stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hardness of titanium vs stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components (e.g., landing gear, frames) | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance | Certification of materials, compliance with aviation standards |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Biocompatibility, wear resistance | Regulatory approvals, traceability of materials |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline fittings and valves | Resistance to harsh environments, durability | Material certifications, performance under extreme conditions |
| Automotive | Engine components and chassis | Lightweight design, improved fuel efficiency | Cost-effectiveness, availability of specific grades |
| Marine | Ship hulls and marine hardware | Corrosion resistance in saltwater environments | Sourcing from certified suppliers, ensuring quality standards |
How Does Hardness Affect Aerospace Applications for Titanium and Stainless Steel?
In the aerospace sector, the hardness of titanium and stainless steel plays a critical role in the performance of aircraft components. Titanium is often preferred for parts like landing gear due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to fatigue, which is essential for safety and efficiency in flight. Conversely, stainless steel is used in applications where cost-effectiveness is paramount, such as in secondary structures. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, must ensure that materials meet stringent aviation standards and certifications to guarantee safety and reliability.
What Are the Key Medical Applications for Titanium and Stainless Steel Hardness?
In the medical field, the hardness of titanium and stainless steel directly influences the durability and effectiveness of surgical instruments and implants. Titanium’s hardness allows for the creation of long-lasting implants that withstand wear while being biocompatible, making it ideal for orthopedic applications. Stainless steel, while generally softer, is often utilized for surgical tools due to its affordability and ease of sterilization. Buyers in South America and Europe should prioritize suppliers that provide materials with necessary regulatory approvals and traceability to ensure patient safety.
How Is Hardness Relevant in Oil & Gas Industry Applications?
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on the hardness of materials like titanium and stainless steel for components such as pipeline fittings and valves. Titanium’s high hardness provides exceptional resistance to corrosive environments, while stainless steel is favored for its toughness and cost-effectiveness. Buyers in this sector, especially in regions like Nigeria and the Middle East, should consider sourcing materials that have been certified for performance under extreme pressure and temperature conditions to ensure operational integrity and safety.
What Are the Automotive Sector Needs Regarding Material Hardness?
In automotive applications, the hardness of titanium and stainless steel significantly impacts engine performance and vehicle efficiency. Titanium’s lightweight and high hardness contribute to improved fuel efficiency and performance in high-stress components, while stainless steel offers a balance of strength and affordability for chassis and body parts. B2B buyers in South America must focus on the availability of specific grades that meet industry standards and offer competitive pricing to optimize production costs.
Why Is Hardness Important in Marine Applications?
For marine applications, the hardness of titanium and stainless steel is crucial for components such as ship hulls and marine hardware. Titanium’s hardness ensures exceptional corrosion resistance in saltwater environments, making it suitable for long-term use in harsh conditions. Stainless steel is also used for its durability and cost-effectiveness. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing from certified suppliers that adhere to quality standards to ensure the longevity and performance of marine products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘hardness of titanium vs stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Cost vs. Performance for Aerospace Applications
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the aerospace industry is faced with a critical decision between titanium and stainless steel for a new aircraft component. While titanium offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, it comes with a significantly higher price tag and processing challenges. The buyer is under pressure to keep costs low while ensuring the component meets stringent safety and performance standards, leading to confusion and potential delays in the project timeline.
The Solution: To address this issue, the buyer should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis that factors in both short-term and long-term implications of using titanium versus stainless steel. First, they can explore titanium alloys specifically designed for aerospace applications, such as Ti-6-4, which balances performance and cost effectively. Collaborating with suppliers who specialize in aerospace materials can provide insights into the latest innovations that may offer competitive pricing. Additionally, the buyer should assess the total lifecycle costs of the components, including maintenance and replacement costs, to make a more informed decision that aligns with project budgets and performance expectations. Engaging with material engineers during the design phase can also enhance understanding of how to effectively utilize titanium’s properties while minimizing machining costs.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Durability in Marine Environments
The Problem: A B2B buyer for a marine equipment manufacturing company needs to select materials for components that will be exposed to harsh marine conditions. The buyer understands that both titanium and stainless steel offer corrosion resistance, but is unsure which material will perform better under constant exposure to saltwater and varying temperatures. This uncertainty could lead to premature failure of components and increased warranty claims, affecting customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
The Solution: The buyer should prioritize materials based on their specific environmental conditions and performance requirements. For marine applications, titanium’s exceptional resistance to corrosion in saltwater makes it a strong candidate, particularly for critical components like fasteners and hulls. However, if budget constraints are significant, high-grade stainless steels, such as 316 or duplex stainless steel, can also perform well. The buyer can consult with metallurgists to determine the best grade of stainless steel that offers enhanced corrosion resistance while remaining cost-effective. Additionally, incorporating protective coatings or treatments for stainless steel components can further improve their lifespan in marine environments. Conducting field tests or pilot projects using both materials can provide valuable data to guide future material selection.
Scenario 3: Managing Production Challenges in Heavy Machinery
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the heavy machinery sector is tasked with selecting materials for a new line of construction equipment. The challenge lies in balancing the hardness and machinability of the materials chosen. While hardened stainless steel may offer the durability needed for demanding applications, it can be more difficult and costly to machine compared to titanium, which is less hard but easier to work with. This dilemma puts the production schedule at risk, as any delays could lead to significant financial losses.
The Solution: The buyer should first evaluate the specific application requirements of the machinery components to determine the critical properties needed—hardness, wear resistance, and machinability. For components requiring high hardness, opting for hardened stainless steel grades like 440C may be beneficial despite the machining challenges. In contrast, for parts where weight savings are essential and machining time is limited, titanium could be the preferred choice. The buyer can also explore hybrid approaches, using titanium for non-load-bearing components and stainless steel for critical load-bearing areas. Partnering with experienced machinists and material specialists can help identify optimal machining techniques that reduce costs and improve efficiency. Additionally, investing in advanced machining technologies that are capable of handling harder materials can also lead to better production outcomes and timelines.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hardness of titanium vs stainless steel
How Does Hardness Affect the Selection of Titanium and Stainless Steel?
When assessing the hardness of titanium versus stainless steel, it is essential to consider the specific properties of each material and how they align with the requirements of various applications. This analysis will explore the key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Titanium Alloys: A Strong Yet Lightweight Option
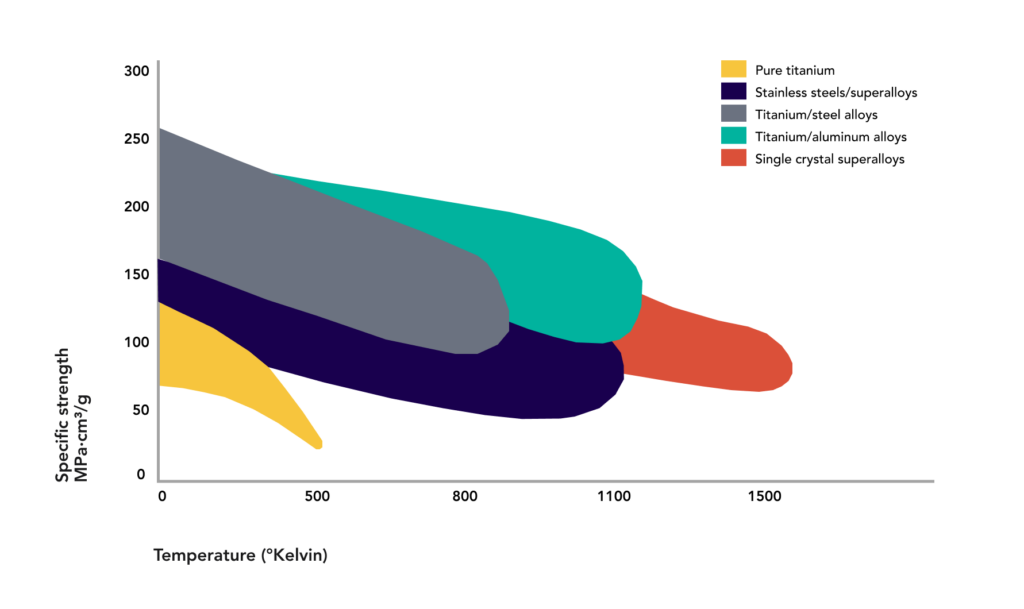
Key Properties: Titanium alloys, particularly Ti-6Al-4V, are known for their hardness, which typically ranges from 300 to 400 HV. They exhibit excellent tensile strength (900 to 1,200 MPa) and yield strength (800 to 1,100 MPa), making them suitable for high-stress applications. Their corrosion resistance is exceptional, particularly in aggressive environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium alloys is their high strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for aerospace and medical applications. However, they are more expensive and challenging to machine compared to stainless steel, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium’s hardness and fatigue resistance make it suitable for applications in harsh environments, such as offshore oil rigs or aerospace components. Its compatibility with various media, including seawater and chemicals, enhances its usability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. The high cost may be a barrier in price-sensitive markets, necessitating a thorough cost-benefit analysis.
Stainless Steel: Versatile and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Stainless steel hardness varies widely, with standard grades ranging from 150 to 300 HV. However, hardened stainless steels can exceed 700 HV. Its tensile strength typically ranges from 480 to 1,100 MPa, depending on the grade.
Pros & Cons: Stainless steel is highly versatile, affordable, and easy to machine, making it a popular choice across various industries. However, its lower hardness compared to titanium can be a limitation in high-wear applications.
Impact on Application: Due to its corrosion resistance and durability, stainless steel is commonly used in construction, automotive, and kitchenware applications. However, for applications requiring high hardness, such as cutting tools, specialized stainless steel grades are necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN and JIS is critical for buyers in Europe and Asia. The lower cost of stainless steel can be attractive in emerging markets, but buyers should consider the long-term performance implications.
Comparing Titanium and Stainless Steel Hardness in Specific Applications
Key Properties: In terms of hardness, titanium alloys generally outperform standard stainless steels, but certain hardened stainless steels can match or exceed titanium’s hardness. The choice depends on the specific application requirements, including temperature and pressure ratings.
Pros & Cons: Titanium offers superior fatigue resistance and strength, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Conversely, stainless steel is more cost-effective and easier to work with, which can be advantageous for large-scale production.
Impact on Application: The choice between titanium and stainless steel often hinges on the operational environment. For instance, titanium excels in aerospace applications, while stainless steel is preferred in construction and consumer goods.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the local availability of materials and suppliers, as well as any import regulations that may affect costs and lead times. Understanding regional preferences for material standards can also influence purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Hardness Comparison
| Material | Typical Use Case for hardness of titanium vs stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Alloys | Aerospace components, medical implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and machining complexity | High |
| Stainless Steel | Construction, automotive parts, kitchenware | Versatile and cost-effective | Lower hardness compared to titanium | Low |
| Hardened Stainless Steel | Cutting tools, high-wear applications | High hardness and durability | More expensive than standard stainless | Medium |
| Titanium Alloys (specific grades) | Marine applications, oil and gas equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Limited availability and higher cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the hardness characteristics of titanium versus stainless steel, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hardness of titanium vs stainless steel
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for Titanium and Stainless Steel?
The manufacturing processes for titanium and stainless steel are distinct due to their unique material properties, which significantly influence the stages of production. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where precision and quality are paramount.
How Is Material Prepared for Manufacturing Titanium and Stainless Steel?
Material preparation is the first stage in the manufacturing process for both titanium and stainless steel. For titanium, this stage often involves sourcing titanium ingots or scrap, followed by processes like melting in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent contamination. This is especially vital because titanium is reactive at high temperatures.
In contrast, stainless steel production typically begins with the melting of iron and alloying elements in an electric arc furnace. The resulting molten metal is then cast into slabs or blooms, which can be further processed into sheets, bars, or other forms. Due to its lower melting point, stainless steel is generally easier to process compared to titanium.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Titanium and Stainless Steel Manufacturing?
Forming techniques vary significantly between titanium and stainless steel, reflecting their respective physical properties.
For titanium, common forming methods include:
- CNC Machining: Utilized for precision parts, CNC machining is often preferred due to titanium’s strength and toughness. This method allows for intricate designs and high tolerances.
- Hot Working: Techniques like forging and rolling are employed, especially for titanium alloys, which benefit from heat treatment to enhance ductility and reduce brittleness.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, is often processed using:
- Stamping and Pressing: These techniques are favored for high-volume production, allowing for efficient shaping of components.
- Welding: Stainless steel is highly weldable, making it suitable for assembly in large structures. Various welding methods, including TIG and MIG, are commonly used.
What Are the Finishing Processes for Titanium and Stainless Steel Components?
Finishing processes play a critical role in achieving the desired surface quality and properties. For titanium, finishing can include:
- Anodizing: This electrochemical process enhances corrosion resistance and can also provide aesthetic colors.
- Grinding and Polishing: These methods improve surface finish, which is crucial in applications such as medical implants where biocompatibility is essential.
Stainless steel typically undergoes:
- Pickling and Passivation: These chemical treatments remove oxides and enhance corrosion resistance, making the surface smooth and clean.
- Electropolishing: This technique is particularly useful in the food and pharmaceutical industries, as it provides a smooth surface that minimizes bacterial adhesion.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented for Titanium and Stainless Steel?
Quality control (QC) is vital in ensuring the performance and safety of titanium and stainless steel products. Various international standards and industry-specific regulations guide these processes.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Titanium and Stainless Steel Manufacturing?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are fundamental for both titanium and stainless steel manufacturing, ensuring that organizations meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for medical devices and API certification for oil and gas applications provide further assurance of quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control in manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected to ensure they meet specifications before processing begins. This is crucial for both titanium and stainless steel, as material quality directly impacts the final product’s properties.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify any deviations from quality standards. This may involve measuring dimensions and conducting non-destructive testing (NDT) to detect flaws early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished products undergo rigorous testing, including hardness tests (Rockwell, Brinell) and mechanical property evaluations. For titanium, additional tests for corrosion resistance may be performed, while stainless steel might be tested for weld integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This includes checking for certifications and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their QC processes, including test results and compliance certificates. Reviewing these reports can help buyers assess the reliability of the supplier.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and the quality of the finished products. This is particularly important when sourcing from international suppliers, where local regulations and standards may vary.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances related to quality control and certification, particularly when sourcing titanium and stainless steel components. These include:
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Buyers should be aware of regional differences in quality standards, particularly when sourcing from emerging markets. Familiarity with local regulations can help mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
-
Evaluating Supply Chain Transparency: Ensuring transparency in the supply chain can help buyers confirm that materials are sourced ethically and sustainably, which is increasingly becoming a priority for many industries.
-
Navigating Trade Barriers: Buyers should be prepared to address potential trade barriers or tariffs that could affect the cost and availability of materials. Understanding the implications of international trade agreements can be beneficial.
In conclusion, comprehending the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for titanium and stainless steel is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, finishing processes, and robust quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select the right materials for their projects while also mitigating risks associated with international sourcing.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘hardness of titanium vs stainless steel’
Introduction
When it comes to selecting materials for your project, understanding the hardness of titanium versus stainless steel is crucial. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers, helping you navigate the complexities of material selection based on hardness and other mechanical properties. By following these steps, you can ensure that you choose the right material for your specific application, whether it’s for aerospace, automotive, or construction projects.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before diving into the procurement process, clearly outline your technical specifications for hardness, strength, and application requirements. This step is vital as it sets the foundation for your material selection and ensures you’re aligned with your project’s goals. Consider the following:
– Hardness Levels: Determine the required hardness rating (measured in HV or HRC) for your application.
– Environmental Conditions: Identify any environmental factors that may affect material performance, such as exposure to corrosive substances or extreme temperatures.
Step 2: Research Material Properties
Conduct thorough research on the properties of titanium and stainless steel, focusing on their hardness and mechanical characteristics. Understanding the differences will aid in making an informed decision. Pay attention to:
– Hardness Comparisons: Titanium typically ranges from 300 to 400 HV, while hardened stainless steel can exceed 700 HV.
– Suitability for Applications: Assess how each material’s hardness affects its performance in your specific application.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. A reliable supplier will have a proven track record in delivering quality materials that meet your specifications. Look for:
– Certifications: Ensure suppliers have relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) that validate their material quality.
– Case Studies: Request case studies or references from similar industries or projects to gauge their reliability.
Step 4: Request Material Samples
Always request samples of the materials you’re considering. This allows you to evaluate the physical properties firsthand and test them against your project requirements. Consider:
– Hardness Testing: Perform hardness tests on samples to confirm they meet your specified levels.
– Machinability: Assess how easy the material is to work with, as this can impact your overall project timeline.
Step 5: Understand Cost Implications
Analyze the cost differences between titanium and stainless steel, factoring in both material price and processing expenses. Titanium is generally more expensive due to its processing challenges, while stainless steel offers a more cost-effective solution for many applications. Consider:
– Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond initial costs and consider long-term benefits such as durability and maintenance.
– Budget Constraints: Ensure your choice aligns with your budget while still meeting performance standards.
Step 6: Make an Informed Decision
Compile all the gathered information and insights to make a well-informed decision. Weigh the pros and cons of each material based on your technical specifications, supplier reliability, and cost analysis. This step is essential to ensure that your final choice aligns with your project requirements and expectations.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Plan
Once you have selected your material and supplier, implement a quality assurance plan to monitor the incoming materials. This step is critical to ensure that the delivered products consistently meet the agreed specifications. Consider:
– Regular Inspections: Schedule inspections during the production and delivery phases.
– Documentation: Keep detailed records of material certifications and quality tests to ensure compliance throughout the project lifecycle.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing materials based on hardness, ensuring that their final selection meets both technical and budgetary requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hardness of titanium vs stainless steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Titanium vs Stainless Steel?
When assessing the hardness of titanium versus stainless steel, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: Titanium is generally more expensive than stainless steel due to its rarity and extraction costs. The price of titanium alloys can fluctuate significantly based on global demand, while stainless steel, being more abundant, tends to have a more stable pricing structure. When sourcing, it is essential to consider the specific alloy grades, as the composition will impact cost.
-
Labor: The complexity of working with titanium often requires skilled labor, especially in industries like aerospace and medical where precision is paramount. Conversely, stainless steel is easier to machine, which can reduce labor costs. However, the level of expertise required can vary based on the specific application.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: The overhead costs associated with titanium processing are typically higher due to the need for specialized equipment and techniques. For instance, titanium’s high melting point necessitates advanced furnaces and tooling, which can inflate manufacturing costs. Stainless steel, with its more established processing methods, usually incurs lower overhead.
-
Tooling: The tooling costs for titanium are substantially higher. The hardness of titanium can lead to increased wear on tools, necessitating frequent replacements or upgrades. Stainless steel, while also requiring quality tooling, generally presents lower wear rates, allowing for longer tool life.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC measures are essential in both materials, but titanium’s use in critical applications demands stricter compliance and testing, which can add to overall costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs may vary based on the material’s weight and bulk. Titanium, being lighter, can sometimes offer savings in shipping, but its higher value can lead to increased insurance and handling costs. Stainless steel, while heavier, is often produced in larger volumes, potentially allowing for more favorable shipping rates.
-
Margin: Suppliers often apply higher margins on titanium due to its cost and the complexity of sourcing. Buyers should be aware of this when negotiating prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Titanium and Stainless Steel Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of titanium and stainless steel, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to optimize costs.
-
Specs/Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs for both materials. Buyers should evaluate whether standard options can meet their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of specific alloys will influence pricing. Titanium alloys often command a premium due to their superior properties, while stainless steel grades may vary widely in cost.
-
Quality/Certifications: Materials with certifications, especially in regulated industries, can incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of these certifications against project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery is vital. Incoterms dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, influencing the total cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Titanium vs Stainless Steel Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers early to discuss pricing and terms. Building relationships can lead to better deals and more favorable payment terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the full lifecycle costs of materials, including maintenance, durability, and potential resale value. This approach can offer a clearer picture of long-term value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, should factor in currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions when evaluating pricing.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and commodity prices. This knowledge can empower negotiations and purchasing decisions.
-
Supplier Diversity: Engage multiple suppliers to compare quotes and capabilities. This can foster competition and may yield better pricing and terms.
Understanding these factors will equip B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions regarding the sourcing of titanium and stainless steel based on hardness and other critical properties. Always remember that indicative prices may vary, and it is advisable to obtain formal quotes for accurate budgeting.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing hardness of titanium vs stainless steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives: Evaluating Hardness of Titanium vs Stainless Steel Against Other Solutions
When considering the hardness of titanium versus stainless steel, it’s essential to evaluate alternative materials and technologies that can meet similar performance needs. This analysis will help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific project requirements, budget constraints, and operational environments.
| Comparison Aspect | Hardness Of Titanium Vs Stainless Steel | Alternative 1: Carbon Steel | Alternative 2: Aluminum Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Titanium: 300-400 HV; Stainless Steel: 150-700 HV (hardened) | Hardness: 200-300 HV; suitable for high-load applications | Hardness: 70-150 HV; lighter but less durable |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing; titanium alloys expensive | Generally lower cost; widely available | Moderate cost; varies by alloy |
| Ease of Implementation | Difficult to machine; requires specialized tools | Easy to machine; good workability | Easy to machine; versatile |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to corrosion resistance | Moderate; susceptible to rust without treatment | Low; corrosion-resistant but can deform under stress |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, medical implants, high-performance engineering | Construction, automotive, heavy machinery | Aerospace, consumer goods, structural components |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a widely used alternative known for its strength and durability. It has a hardness range of approximately 200-300 HV, making it suitable for high-load applications. While its cost is generally lower than titanium and stainless steel, carbon steel can be prone to rust and corrosion if not properly treated, necessitating regular maintenance. Its excellent machinability allows for easy fabrication, making it a go-to choice for construction and automotive industries. However, the trade-off for its lower cost is often a reduction in corrosion resistance compared to titanium and stainless steel.
2. Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys offer a lightweight solution with a hardness range of 70-150 HV. While they do not match the hardness of titanium or stainless steel, their low density and excellent corrosion resistance make them attractive for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace and consumer products. The machinability of aluminum alloys is high, allowing for quick and cost-effective manufacturing. However, their susceptibility to deformation under heavy loads limits their use in high-stress environments compared to titanium and stainless steel.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
In summary, selecting the right material involves weighing various factors, including hardness, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and specific application use cases. Titanium and stainless steel excel in durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for demanding applications. However, alternatives like carbon steel and aluminum alloys may offer viable solutions depending on budget and performance needs. B2B buyers should evaluate their project requirements holistically, considering the operational environment and long-term maintenance implications to make the most informed choice.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hardness of titanium vs stainless steel
What are the Key Technical Properties of Hardness in Titanium and Stainless Steel?
When evaluating materials for industrial applications, understanding the hardness of titanium and stainless steel is crucial. Hardness is a measure of a material’s resistance to deformation, which directly influences its performance in various settings. Here are some essential technical properties related to hardness:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of titanium or stainless steel based on its composition and mechanical properties. For titanium, common grades include Grade 2 (commercially pure) and Ti-6Al-4V (an alloy). Stainless steel grades like 304 and 316 are widely used due to their corrosion resistance and strength. Selecting the correct grade is vital for ensuring the material can withstand the operational conditions it will face, impacting durability and performance.
2. Hardness Measurement (HV, HB, HRC)
Hardness is often quantified using different scales, such as Vickers (HV), Brinell (HB), and Rockwell (HRC). Titanium typically exhibits hardness values ranging from 300 to 400 HV, while stainless steel can vary widely, from 150 HV for softer grades up to over 700 HV for hardened varieties. Understanding these metrics allows buyers to choose materials that meet specific wear resistance and load-bearing requirements, particularly in high-stress applications.
3. Yield Strength
Yield strength indicates the maximum stress that a material can withstand before it begins to deform permanently. For titanium, yield strength ranges from 800 to 1,100 MPa, while stainless steel generally falls between 240 to 800 MPa. This property is critical for applications where the material will be subjected to high loads, ensuring that it maintains its structural integrity under stress.
4. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures a material’s ability to withstand pulling forces. Titanium’s tensile strength can reach up to 1,200 MPa, while stainless steel often ranges from 480 to 1,100 MPa. Understanding tensile strength is essential for B2B buyers, as it influences the selection of materials for applications like aerospace components or structural supports where strength-to-weight ratios are crucial.
5. Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue resistance reflects a material’s ability to withstand cyclic loading over time without failing. Titanium excels in this area, making it ideal for applications that involve repeated stress, such as in aerospace and automotive sectors. Stainless steel also offers good fatigue resistance but may not perform as well in extreme environments. Buyers should consider this property when evaluating materials for long-term applications.
What are Common Trade Terms Related to Hardness in Titanium and Stainless Steel?
Navigating the procurement process involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon. Here are several key terms that are often used:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of titanium and stainless steel, OEMs often specify material grades and hardness requirements for components used in their products, making it crucial for suppliers to understand these specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant when sourcing titanium or stainless steel, as higher-quality materials may have higher MOQs, impacting project budgets and planning.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers. It typically includes specifications such as material grade and hardness. A well-prepared RFQ ensures that suppliers provide accurate quotes, facilitating better decision-making for procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for managing shipping costs and risks, especially when sourcing titanium and stainless steel from global suppliers.
5. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment refers to a controlled process of heating and cooling metals to alter their physical and sometimes chemical properties. This process can significantly enhance hardness and strength in both titanium and stainless steel, making it a vital consideration during material selection.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting between titanium and stainless steel based on hardness and other critical performance factors.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the hardness of titanium vs stainless steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Hardness of Titanium vs Stainless Steel?
The global market for titanium and stainless steel is influenced by several key drivers, including the demand for lightweight materials in aerospace and automotive applications, as well as the growing need for corrosion-resistant materials in various industries. Notably, the aerospace sector continues to propel the demand for titanium, owing to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to extreme environments. Conversely, stainless steel remains a staple in construction, automotive, and consumer goods due to its affordability and versatility.
Emerging trends in sourcing highlight the integration of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) for optimized supply chain management. These technologies enable B2B buyers to track material properties, assess supplier capabilities, and forecast demand more accurately. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is reshaping procurement processes, allowing international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, to access a broader range of suppliers and products.
Market dynamics are also shifting as manufacturers increasingly focus on producing specialized alloys that enhance the hardness and performance of titanium and stainless steel. For example, the development of titanium alloys that incorporate aluminum and vanadium is gaining traction, particularly in high-performance applications. This trend reflects a broader movement towards customization, where tailored solutions are preferred to generic materials.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Hardness of Titanium vs Stainless Steel Market?
The environmental impact of sourcing titanium and stainless steel is becoming a focal point for B2B buyers who prioritize sustainability. Titanium extraction and processing can be resource-intensive, leading to increased scrutiny regarding its environmental footprint. In contrast, stainless steel recycling is more established, contributing to its appeal among environmentally conscious buyers.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly important as international buyers, particularly in Europe and South America, seek suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and responsible sourcing certifications can guide buyers in making informed decisions.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials is gaining traction, with manufacturers exploring ways to produce titanium and stainless steel using less energy and fewer harmful chemicals. This shift not only reduces the environmental impact but also enhances the marketability of products that meet these criteria. B2B buyers are therefore encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, which can also positively influence brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What is the Historical Context of Hardness in Titanium vs Stainless Steel?
The use of titanium and stainless steel dates back to the 20th century, with titanium emerging in the aerospace industry during the 1950s due to its unique properties. Initially, titanium was expensive and challenging to work with, limiting its applications. However, advances in alloying techniques and processing methods have significantly improved its machinability and affordability, expanding its use across various sectors.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, has a longer history, originating in the early 1900s as a corrosion-resistant alternative to traditional steels. Its development marked a significant milestone in engineering and manufacturing, leading to widespread adoption in diverse applications, from kitchenware to heavy machinery. The evolution of both materials reflects ongoing advancements in metallurgy, highlighting the importance of hardness and durability in meeting the demands of modern industries.
Understanding these historical developments not only provides context for current market dynamics but also helps B2B buyers appreciate the technological advancements that continue to shape sourcing decisions in the titanium and stainless steel sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hardness of titanium vs stainless steel
-
1. How do I determine the hardness of titanium and stainless steel for my project?
To determine the hardness of titanium and stainless steel, you can refer to the Vickers Hardness (HV) scale or the Brinell Hardness (HB) scale. Titanium typically exhibits hardness levels ranging from 300 to 400 HV, while standard stainless steel falls between 150 to 300 HV. However, hardened stainless steel grades, such as 440C, can exceed 700 HV. Consider the specific requirements of your application, including wear resistance and mechanical stress, to choose the right material based on its hardness characteristics. -
2. What is the best metal choice for high-wear applications: titanium or stainless steel?
For high-wear applications, titanium is often the preferred choice due to its superior hardness and fatigue resistance. Titanium alloys provide excellent wear resistance and maintain strength under repeated stress, making them suitable for demanding environments. However, if cost is a significant factor, certain hardened stainless steels can also perform well. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis based on your specific application and environment will help in making the best decision. -
3. How does the hardness of titanium compare with that of stainless steel in terms of applications?
The hardness of titanium allows it to excel in applications requiring high wear resistance, such as aerospace and biomedical devices. In contrast, while stainless steel generally has lower hardness, it can be engineered to meet specific performance criteria through alloying. Applications in construction and automotive sectors often prefer stainless steel for its lower cost and ease of machining, even though it may not match titanium’s hardness in all cases. -
4. What factors should I consider when sourcing titanium or stainless steel for international projects?
When sourcing titanium or stainless steel internationally, consider the material’s hardness, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties suitable for your specific application. Additionally, evaluate supplier certifications, quality assurance processes, and the ability to provide customized solutions. Logistics, including shipping costs, lead times, and import regulations in your region, should also be factored into your sourcing strategy to ensure timely delivery and compliance. -
5. How can I vet suppliers for titanium and stainless steel materials?
To vet suppliers for titanium and stainless steel materials, start by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific certifications. Review their track record for quality control, customer reviews, and case studies of previous projects. It’s also beneficial to request samples and conduct on-site visits if possible. Establish clear communication regarding specifications, lead times, and after-sales support to ensure a reliable partnership. -
6. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for titanium and stainless steel?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for titanium and stainless steel can vary widely based on the supplier and material type. Generally, titanium products may have higher MOQs due to their cost and processing requirements, often starting at 100 kg or more. Stainless steel typically offers more flexibility, with MOQs ranging from 50 kg to 200 kg. Discuss your project requirements with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate accordingly. -
7. What payment terms should I expect when ordering titanium or stainless steel internationally?
Payment terms for international orders of titanium or stainless steel can vary by supplier and region. Common terms include upfront deposits (often 30% to 50%), with the balance due upon shipment or after receipt of goods. Some suppliers may offer credit terms based on your business relationship and order volume. Always clarify payment methods, currency, and any potential transaction fees to avoid misunderstandings. -
8. How can I ensure quality assurance for titanium and stainless steel products?
To ensure quality assurance for titanium and stainless steel products, request detailed material certifications and test reports from your supplier. Look for compliance with international standards, such as ASTM or EN specifications. Establish a quality control process that includes inspections at various production stages and final product testing. Engaging third-party inspection services can also provide an additional layer of assurance, especially for critical applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Hardness Of Titanium Vs Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SteelPRO Group – Stainless Steel Products
Domain: steelprogroup.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Titanium vs Stainless Steel: Which is Suitable for Your Project? – SteelPRO Group offers a wide range of stainless steel products including various types of steel bars (high strength, hot rolled, cold rolled, plain carbon, alloy, structural, tool), sheets, coils, pipes, and specialized steel types for different applications. The text also mentions services such as steel cutting, bending, welding, …
2. Metal Supermarkets – Titanium Solutions
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Titanium is an elemental earth metal, known for its high corrosion resistance, impact absorption, and exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. Commonly alloyed with metals like iron and aluminum, it is used in high-performance industries such as aerospace, automotive, and marine equipment. Steel, an iron-carbon alloy, is favored for its strength, temperature resistance, and excellent machinability, m…
3. Garmin – Epix (Gen 2) Series
Domain: forums.garmin.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: The Garmin Epix (Gen 2) series features a bezel made from Grade 2 titanium, which is softer than Grade 5 titanium and comparable to 316 stainless steel. The protective oxidation layer on titanium can make scratches more apparent, but superficial scratches can heal themselves or be easily removed. The black steel version of the watch has 16GB less memory and lacks multiGNSS capabilities compared to…
4. Make It From – Mechanical Properties Insights
Domain: makeitfrom.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Make It From – Mechanical Properties Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hardness of titanium vs stainless steel
In evaluating the hardness of titanium versus stainless steel, it is clear that each material presents unique advantages tailored to specific applications. Titanium, while generally softer, excels in wear resistance and fatigue strength, making it ideal for high-performance sectors such as aerospace and medical devices. On the other hand, certain hardened stainless steels demonstrate superior hardness, making them a strong contender for applications requiring robust wear resistance, such as automotive and construction.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing decisions must prioritize the specific mechanical properties that align with project demands. Understanding the nuances of material performance, including hardness, can lead to more informed purchasing strategies that enhance product longevity and overall value.
As industries evolve and demand for high-performance materials increases, now is the time to reassess your sourcing strategies. Engage with suppliers who offer tailored solutions and insights into material selection. By investing in the right materials today, you position your business for greater resilience and competitiveness in the global market. Explore partnerships that can elevate your procurement processes and drive innovation in your projects.