Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for haas mill g and m codes
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, understanding Haas mill G and M codes is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their machining capabilities. The challenge of sourcing accurate and efficient CNC programming solutions can significantly impact production timelines and operational efficiency. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into the intricacies of G and M codes specific to Haas milling machines, detailing their applications across various industries.
From the foundational principles of these codes to advanced programming techniques, this guide covers everything you need to know, including types of codes, practical applications, supplier vetting strategies, and cost considerations. By equipping buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Nigeria and Germany—with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, we empower them to optimize their operations effectively.
Navigating the global market for Haas mill G and M codes does not have to be daunting. With this guide, you will gain insights into selecting the right suppliers, understanding the cost implications, and maximizing the potential of your CNC machinery. Whether you are looking to enhance your current operations or embark on new projects, this resource is designed to support your journey towards operational excellence.
Understanding haas mill g and m codes Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| G-Codes | Control movement, speed, and tool path. | CNC machining, milling, drilling | Pros: Precise control, flexible programming. Cons: Steep learning curve for beginners. |
| M-Codes | Control machine functions like coolant and spindle. | Tool changes, setup operations | Pros: Streamlines operations, essential for automation. Cons: Limited to machine-specific functions. |
| Variable Codes | Adjust settings like feed rate and speed dynamically. | Custom machining tasks | Pros: Enhances adaptability, optimizes production. Cons: Requires understanding of machine capabilities. |
| Subprogram Codes | Allows nesting of programs for complex operations. | Multi-stage machining processes | Pros: Reduces programming time, enhances efficiency. Cons: Can complicate troubleshooting. |
| Tool Path Codes | Defines paths for tools to follow during machining. | Complex shapes and contours | Pros: High precision in part production. Cons: May require advanced programming knowledge. |
What Are G-Codes and Their Importance in Haas Mills?
G-Codes are fundamental in CNC programming, dictating the movement of the machine. They control everything from the position of the tool to the speed at which it operates. For B2B buyers, understanding G-Codes is crucial as they enable precise machining operations, essential for high-quality production. However, the complexity of G-Codes can pose a challenge for those new to CNC technology, necessitating training or skilled personnel to maximize their potential.
How Do M-Codes Enhance Machine Functionality?
M-Codes serve as the control commands for machine functions that are not directly related to movement, such as activating the coolant or changing tools. These codes are integral for streamlining operations in CNC machines, making them vital for businesses looking to optimize their manufacturing processes. While M-Codes significantly enhance automation and efficiency, they can be limited to specific machine functions, which may restrict flexibility in multi-machine setups.
Why Consider Variable Codes for Custom Machining?
Variable Codes allow for dynamic adjustments in machining parameters like feed rate and spindle speed during operation. This capability is particularly beneficial for businesses that require custom machining solutions tailored to specific materials or designs. The flexibility offered by Variable Codes can lead to optimized production cycles; however, they demand a thorough understanding of the machine’s capabilities, making proper training essential for effective use.
What Are the Advantages of Using Subprogram Codes?
Subprogram Codes facilitate the nesting of programs, allowing for complex machining operations to be executed in a streamlined manner. This is particularly advantageous for multi-stage processes where different operations are required sequentially. For B2B buyers, the use of Subprogram Codes can significantly reduce programming time and enhance overall efficiency. However, this complexity may lead to challenges in troubleshooting, requiring skilled operators to manage and maintain the programs effectively.
How Do Tool Path Codes Contribute to Precision Machining?
Tool Path Codes define the exact paths that tools will follow during machining, which is critical for producing intricate shapes and contours. These codes are essential for businesses focused on high-precision manufacturing, as they ensure accuracy in the final product. While Tool Path Codes enhance the quality of output, they also necessitate advanced programming knowledge, which can be a barrier for companies without experienced personnel.
Key Industrial Applications of haas mill g and m codes
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of haas mill g and m codes | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision machining of components like turbine blades and airframe parts | Enhanced accuracy and reduced waste in production | Need for high-quality materials and compliance with industry standards |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of engine blocks and transmission housings | Increased production efficiency and lower costs | Availability of skilled labor and technological support |
| Medical Devices | Production of surgical instruments and implants | High precision and reliability in critical applications | Regulatory compliance and quality assurance processes |
| Energy (Oil & Gas) | Machining of valve bodies and fittings for pipelines | Improved safety and durability in harsh environments | Access to specialized tooling and machine maintenance services |
| Electronics | Fabrication of circuit boards and housings for electronic devices | Faster prototyping and reduced time-to-market | Supplier reliability and capabilities in rapid prototyping |
How Are Haas Mill G and M Codes Utilized in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace sector, Haas mill G and M codes are employed to achieve the high precision required for components such as turbine blades and airframe parts. These codes enable the programming of complex machining operations that ensure tight tolerances and surface finishes critical for aircraft performance and safety. Buyers in this industry must consider sourcing materials that meet stringent aerospace standards and ensure their machining processes comply with regulatory requirements.
What Role Do Haas Mill G and M Codes Play in Automotive Production?
The automotive industry leverages Haas mill G and M codes for the efficient production of engine blocks and transmission housings. By automating machining processes, manufacturers can achieve higher production rates while minimizing material waste. International buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer advanced CNC capabilities and support to maintain productivity and quality, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where automotive markets are expanding rapidly.
Why Are Haas Mill G and M Codes Important for Medical Device Manufacturing?
In medical device manufacturing, Haas mill G and M codes are essential for producing high-precision surgical instruments and implants. The ability to program intricate designs with exact specifications ensures that devices are reliable and safe for patient use. Buyers must focus on suppliers who can guarantee compliance with health regulations and provide quality assurance to meet the rigorous standards of the medical industry.
How Do Haas Mill G and M Codes Enhance Production in the Energy Sector?
The energy sector, particularly oil and gas, utilizes Haas mill G and M codes for machining valve bodies and fittings used in pipelines. These codes facilitate the creation of durable components that can withstand extreme conditions, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. Buyers should consider sourcing from manufacturers that offer specialized tooling and maintenance services to ensure the longevity and reliability of their equipment.
What Advantages Do Haas Mill G and M Codes Provide in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, Haas mill G and M codes are used for fabricating circuit boards and housings for electronic devices. The precision and speed afforded by these codes allow for rapid prototyping and shorter lead times, which are crucial in a fast-paced market. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to deliver reliable prototypes and scalable production solutions to keep pace with technological advancements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘haas mill g and m codes’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Understanding G and M Code Syntax
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those new to CNC programming, struggle with the intricate syntax and structure of G and M codes used in Haas mills. This confusion can lead to misprogramming, machine errors, and ultimately, production delays. For companies operating on tight schedules, even minor mistakes can result in significant costs. Additionally, the lack of comprehensive training resources in certain regions can exacerbate this issue, leaving operators feeling lost and frustrated.
The Solution: To address this challenge, companies should invest in structured training programs that focus specifically on G and M code syntax and their applications in Haas mills. Online courses and workshops that cater to different experience levels can be beneficial. Moreover, utilizing the Haas operator’s manual and online resources can provide valuable insights into the specific codes used for various operations. Creating a reference guide that summarizes the most commonly used codes and their functions can serve as a quick reference for operators during programming. Engaging with Haas-certified training centers can also provide hands-on experience, allowing operators to practice coding in a controlled environment before applying it on the shop floor.
Scenario 2: Inefficiencies Due to Code Errors in Production Runs
The Problem: A common pain point for businesses is the occurrence of code errors during production runs, often resulting from minor typos or incorrect command usage. These errors can lead to wasted materials, machine downtime, and the need for rework, which can be particularly detrimental for companies with limited resources. Furthermore, frequent disruptions can lower team morale and productivity, creating a cycle of inefficiency that impacts overall profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate code errors, companies should implement a robust quality control process that includes code verification before running production. Utilizing simulation software can help in visualizing the machining process and identifying potential issues before they arise on the shop floor. Encouraging a culture of peer review, where operators double-check each other’s codes, can also help catch mistakes early. Additionally, investing in software tools that provide syntax highlighting and error checking for G and M codes can significantly reduce the likelihood of errors. Regular training sessions to reinforce best practices in coding can further enhance the skills of the workforce, ensuring that everyone is up-to-date on the latest techniques and standards.
Scenario 3: Limited Resources for Custom Code Development
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face limitations in developing custom G and M codes tailored to their specific machining needs. This can be particularly challenging for companies that require unique processes or intricate parts. Without the technical expertise or resources to create these codes, they may have to settle for standard solutions that do not fully meet their operational requirements, leading to inefficiencies and suboptimal performance.
The Solution: To overcome this barrier, businesses should consider partnering with CNC programming specialists or consultants who have extensive experience with Haas mills. These experts can assist in developing custom G and M codes that cater specifically to the needs of the business. Additionally, companies can foster in-house expertise by encouraging experienced operators to take on mentorship roles, guiding less experienced staff in custom code development. Utilizing forums and community groups focused on Haas machines can also provide insights and shared experiences that can facilitate the creation of tailored solutions. Lastly, investing in advanced programming software that supports custom code development can empower operators to innovate and refine their machining processes, ultimately enhancing productivity and product quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for haas mill g and m codes
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Haas Mill G and M Codes?
Aluminum is a widely used material in CNC machining due to its favorable properties. It has excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight characteristics, and good thermal conductivity. These properties make aluminum particularly suitable for applications requiring precision and efficiency. Its ability to withstand moderate temperatures and pressures also ensures that it performs well in various machining environments.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum
The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which allows for faster machining speeds and reduced wear on tools. Additionally, aluminum is relatively inexpensive compared to other metals, making it an attractive option for cost-sensitive projects. However, its lower strength compared to materials like steel can limit its use in high-stress applications. Furthermore, aluminum can be more challenging to machine due to its tendency to chip, which may affect the surface finish.
Impact on Application
Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water-based coolants and lubricants, making it a versatile choice for different machining processes. Its corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of aluminum grades suitable for their specific applications, as preferences may vary by region.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for Haas Mill G and M Codes?
Steel is another prevalent material in CNC machining, known for its strength and durability. It offers high-temperature resistance and excellent wear properties, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros and Cons of Using Steel
The key advantage of steel is its superior strength, which allows it to withstand high loads and stresses without deforming. This makes it ideal for components that require high durability. However, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can lead to increased machining times and tool wear. Additionally, the cost of high-quality steel can be significantly higher than aluminum, impacting overall project budgets.
Impact on Application
Steel’s compatibility with various cutting fluids and its ability to maintain structural integrity under high temperatures make it suitable for heavy-duty machining applications. However, its susceptibility to corrosion necessitates protective coatings or treatments, especially in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers
International buyers should be aware of the different steel grades and their corresponding standards, such as JIS or ASTM. Understanding local regulations regarding steel sourcing and environmental impact can also influence purchasing decisions.
What Role Does Titanium Play in Haas Mill G and M Codes?
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it a premium choice for specialized applications in aerospace and medical industries.
Pros and Cons of Using Titanium
The primary advantage of titanium is its lightweight yet robust nature, allowing for high-performance applications without adding significant weight. However, titanium is more expensive than aluminum and steel, which can be a barrier for budget-conscious projects. Additionally, machining titanium requires specialized tools and techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application
Titanium is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments. Its corrosion resistance ensures longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Considerations for International Buyers
For B2B buyers, especially in regions with stringent quality standards, understanding titanium grades and their specific applications is essential. Compliance with international standards can also influence sourcing decisions, particularly in industries like aerospace.
How Does Plastic Material Fit into Haas Mill G and M Codes?
Plastic materials, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in CNC machining for lightweight and cost-effective solutions.
Pros and Cons of Using Plastic
The main advantage of plastics is their lightweight nature and ease of machining, allowing for rapid production and lower costs. However, plastics generally have lower strength and temperature resistance compared to metals, which may limit their use in high-stress applications. Additionally, certain plastics can be more susceptible to chemical degradation.
Impact on Application
Plastics are compatible with various media and are often used in non-structural applications, such as enclosures and fixtures. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of industries, from consumer goods to automotive.
Considerations for International Buyers
International buyers should consider the specific plastic grades and their compliance with local regulations. Understanding the environmental impact of plastic use and disposal is also increasingly important in many regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Haas Mill G and M Codes
| Material | Typical Use Case for Haas Mill G and M Codes | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy machinery, structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier and more expensive than aluminum | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical applications | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex machining | High |
| Plastic | Enclosures, fixtures, non-structural parts | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower strength and temperature resistance | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for haas mill g and m codes
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Haas Mill G and M Codes?
The manufacturing processes for Haas Mill G and M codes encompass several key stages, each critical for ensuring the final product meets quality and performance standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: The first stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials suitable for CNC machining. This often includes metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, which are chosen based on the specific application requirements. The material is inspected for defects, and appropriate cutting tools are selected to ensure efficiency and accuracy during machining.
Forming: Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This process involves using Haas CNC machines to apply G and M codes that dictate the machine’s operations. G codes control the movement of the machine, while M codes manage auxiliary functions such as tool changes and coolant flow. Precision in this stage is critical, as any errors can lead to significant deviations from specifications.
Assembly: After the individual components are machined, they are assembled. This stage may include integrating various parts, such as motors, drives, and control systems, to create a fully functional CNC machine. The assembly process must adhere to strict guidelines to ensure compatibility and performance.
Finishing: The final stage is finishing, which may involve surface treatments, coatings, or additional machining processes to enhance the product’s durability and appearance. Quality checks are performed at this stage to verify that the product meets the required standards before it is packaged and shipped.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Haas Mill Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of Haas Mill G and M codes is a systematic process aimed at ensuring that all products meet international and industry-specific standards.
Relevant International Standards: The most widely recognized standard is ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, specific certifications like CE mark for safety and API standards for oil and gas applications may also apply depending on the industry.
Quality Control Checkpoints: Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting incoming materials for conformity to specifications. Any non-compliant materials are rejected or reworked.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the forming and assembly stages, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the process. This helps identify defects early, minimizing waste and rework.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a thorough inspection is performed to verify that the final product meets all specifications. This may include dimensional checks, functional tests, and safety assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Haas Mill Production?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and reliability of Haas Mill G and M codes. Common techniques include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing calipers and gauges to measure critical dimensions against specifications.
-
Functional Testing: Running the machine to verify that all functions operate as intended, including movement accuracy and tool changes.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection are used to identify internal defects without damaging the product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers, ensuring that the products they receive meet their standards.
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the supplier’s facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This includes reviewing documentation related to quality management systems.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide quality reports that detail inspection results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring third-party inspection services can offer an impartial assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes, providing additional assurance of product quality.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of quality control and certification nuances, particularly when sourcing from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific standards and regulations applicable in their target markets. For instance, CE certification may be required for products sold in Europe, while local regulations may govern imports in African or South American countries.
-
Cross-Border Compliance: Ensuring that suppliers comply with both international and local standards can be challenging. Buyers should assess suppliers’ capabilities to meet these requirements and consider the implications for logistics and delivery.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is critical when dealing with suppliers from different regions. Buyers should establish clear expectations regarding quality standards and timelines to mitigate misunderstandings.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance for Haas Mill G and M codes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that uphold high standards of quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘haas mill g and m codes’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure Haas Mill G and M codes. Understanding these codes is essential for optimizing CNC operations, enhancing productivity, and ensuring compatibility with Haas machinery. By following this checklist, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s crucial to outline your specific technical requirements. This includes identifying the types of operations you need the G and M codes to perform, such as milling, drilling, or tapping.
– Consider your machine model: Different Haas mills may support different sets of codes.
– Assess your production needs: Are you focusing on high-speed production or intricate part designs?
Step 2: Research Available G and M Codes
Familiarize yourself with the complete list of G and M codes applicable to Haas mills. Understanding these codes will help you identify which are necessary for your operations.
– Refer to official manuals: Use resources from Haas Automation to ensure you have the most current and comprehensive information.
– Identify standard vs. custom codes: Determine if standard codes meet your needs or if custom codes are required for specialized tasks.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. This step ensures that you partner with a reputable source that can provide the necessary codes and support.
– Request company profiles: Ask for documentation that highlights their experience with Haas products.
– Seek references: Speak to other businesses in your industry that have previously worked with the supplier.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certification
Ensure that the supplier complies with international standards and possesses the necessary certifications. This is critical for maintaining quality and reliability in your operations.
– Check for ISO certification: Suppliers with ISO certifications demonstrate adherence to quality management systems.
– Inquire about product support: Confirm that the supplier offers ongoing support and updates for the G and M codes.
Step 5: Request a Demonstration or Trial
Before finalizing your order, ask for a demonstration or a trial period to assess the G and M codes in action. This will help you determine their effectiveness in real-world applications.
– Evaluate performance: Observe how the codes integrate with your existing systems and machinery.
– Gather feedback from operators: Input from your CNC operators can provide valuable insights into usability and functionality.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, discuss pricing, delivery timelines, and support services. Clear agreements can help avoid misunderstandings later on.
– Consider total cost of ownership: Look beyond initial costs to include long-term maintenance and support.
– Clarify warranty and service agreements: Ensure that you understand the terms related to warranty claims and service provisions.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase and Plan Implementation
After agreeing on terms, finalize the purchase and prepare for implementation. This includes training your staff on the new codes and integrating them into your operational processes.
– Develop a training plan: Ensure that your team is well-equipped to use the new codes effectively.
– Monitor performance post-implementation: Regularly review the impact of the G and M codes on your productivity and make adjustments as necessary.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement of Haas Mill G and M codes with confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that will enhance their CNC operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for haas mill g and m codes Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Haas Mill G and M Codes?
When sourcing Haas mill G and M codes, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials required for the production of G and M codes are relatively low, as they primarily involve software and programming data. However, if specialized tooling or hardware is needed, these costs can escalate.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for programming, testing, and verifying the G and M codes. Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the region. In countries with a high cost of living, such as Germany, labor will be a larger portion of the overall cost compared to regions like Nigeria or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and other indirect expenses associated with the production process. Overhead costs can differ based on geographical location and factory efficiency.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling required to implement the G and M codes, including fixtures and cutting tools, can add to the total cost. Buyers should consider the longevity and quality of tooling to maximize value.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the codes function correctly and meet industry standards is crucial. Investing in robust QC processes can reduce the risk of costly errors in production.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are a significant factor, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can influence the final price.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary widely. Understanding the standard markup in your region can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Haas Mill G and M Codes Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of Haas mill G and M codes, which can impact the overall cost:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchasing if feasible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom G and M codes tailored to specific applications can incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the added expense.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and whether they come with quality certifications can affect pricing. Higher-quality materials often lead to better performance and longevity, which can justify the initial investment.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (Incoterms) can significantly affect total costs. Terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) or FOB (Free on Board) can lead to different pricing structures depending on who bears the risk and cost during transit.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Haas Mill G and M Codes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always be prepared to negotiate. Understanding the cost structure allows buyers to engage suppliers effectively and seek discounts based on order size or long-term partnership commitments.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, tooling, and potential downtime costs. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Leverage Local Suppliers: Whenever possible, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. This is particularly beneficial in regions with less robust shipping infrastructure.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and market conditions. Economic factors, currency fluctuations, and supply chain disruptions can all impact prices.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and preferential treatment in future transactions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for Haas mill G and M codes can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing aligned with their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing haas mill g and m codes With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in CNC Machining: A Comparative Analysis
In the world of CNC machining, G and M codes are essential for programming and operating milling machines. While Haas Mill G and M codes are widely recognized and utilized, there are alternative solutions that can also achieve similar operational goals. Evaluating these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and specific use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Haas Mill G And M Codes | Fanuc G and M Codes | Siemens Sinumerik 840D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and reliability | High performance with extensive features | Advanced functionalities with real-time processing |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Varies based on machine; often higher | Generally high due to advanced technology |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly with extensive documentation | Requires specialized training for complex features | Steeper learning curve; comprehensive manuals available |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; widely supported | Moderate; support varies by region | Higher maintenance due to complexity; specialized support needed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small to medium-sized manufacturing | Best for high-volume production and automation | Suitable for complex, high-precision applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Fanuc G and M Codes
Fanuc G and M codes are another industry-standard set of instructions used primarily in Fanuc CNC machines. They are known for their high performance and extensive feature set, making them suitable for complex machining tasks. The primary advantage of using Fanuc codes is their adaptability to various manufacturing environments, especially in high-volume production. However, the need for specialized training can make implementation challenging for companies unfamiliar with the system. Additionally, while the initial costs can vary widely depending on the machine, ongoing support and maintenance can be a consideration in overall budgeting.
2. Siemens Sinumerik 840D
The Siemens Sinumerik 840D control system is recognized for its advanced functionalities and real-time processing capabilities, making it a robust solution for intricate machining tasks. This system excels in environments that require high precision and flexibility. One of its significant advantages is its ability to handle complex processes, which can enhance productivity. However, the complexity of the system can lead to a steeper learning curve, necessitating more intensive training for operators. Moreover, the overall costs, including installation and maintenance, tend to be higher, which may be a barrier for smaller operations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right CNC programming solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific operational requirements, including the scale of production, budget constraints, and the level of training their workforce can undergo. Haas Mill G and M codes are ideal for those seeking a balance of reliability and user-friendliness, particularly in small to medium-sized operations. In contrast, Fanuc and Siemens offer advanced capabilities suited for high-volume or complex applications but may require more investment in training and support. Ultimately, the choice should align with the company’s strategic goals and operational needs, ensuring that the selected solution enhances productivity and efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for haas mill g and m codes
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Haas Mill G and M Codes?
When evaluating Haas mill G and M codes, understanding specific technical properties is essential for effective decision-making in a B2B environment. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Precision Tolerance
– Definition: This refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. For CNC machining, typical tolerances can range from ±0.001 inches (0.025 mm) to ±0.0001 inches (0.0025 mm).
– B2B Importance: High precision is crucial for industries like aerospace and medical devices, where even minor deviations can lead to product failure. Buyers must ensure that the machining capabilities align with their project requirements. -
Material Compatibility
– Definition: The types of materials that the Haas mill can effectively machine, including metals (aluminum, steel), plastics, and composites.
– B2B Importance: Understanding material compatibility helps businesses select the right milling processes and tools, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of equipment. This is particularly relevant for companies in industries with stringent material specifications. -
Cycle Time
– Definition: The total time taken to complete a machining operation, including setup, cutting, and finishing.
– B2B Importance: Shorter cycle times can significantly enhance productivity and reduce labor costs. Businesses must assess cycle time against their production schedules and delivery commitments to maintain competitiveness. -
Spindle Speed Range
– Definition: The range of rotational speeds at which the spindle can operate, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
– B2B Importance: Different materials and cutting tools require specific spindle speeds for optimal results. A broader speed range allows for more versatility in operations, enabling businesses to adapt to varying production needs. -
Tool Change Time
– Definition: The time it takes for the machine to switch from one tool to another during a machining operation.
– B2B Importance: Faster tool change times lead to less downtime and increased efficiency in production runs. This is especially important for manufacturers who need to switch frequently between different tasks. -
Power Consumption
– Definition: The amount of electrical power required for the machine to operate, typically measured in kilowatts (kW).
– B2B Importance: Understanding power consumption is critical for cost management. High energy efficiency can lead to reduced operational costs, making it an essential factor for businesses focused on sustainability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Haas Mill Operations?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers seeking quality parts and reliable service. It also affects warranty and support considerations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases efficiently and manage inventory, particularly for specialized components like G and M code tooling. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to invite them to bid on providing specific goods or services.
– Importance: An RFQ is crucial for price comparison and supplier selection, enabling businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms helps businesses navigate shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, ensuring smoother international trade operations. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time from the initiation of an order until its completion.
– Importance: Knowing lead times is essential for planning production schedules and meeting customer delivery expectations, which can be a competitive advantage in the market. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
– Definition: A method used to automate control of machine tools through computer programming.
– Importance: CNC technology is central to modern machining processes, enhancing precision, repeatability, and efficiency in production.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding Haas mill G and M codes, ultimately leading to improved operational outcomes and profitability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the haas mill g and m codes Sector
Global drivers in the Haas mill G and M codes sector are shaped by the increasing demand for precision machining and automation in manufacturing. The rise of Industry 4.0 has led to a significant shift towards smart manufacturing, where integrating advanced technologies like IoT and AI into CNC machining processes is becoming commonplace. This evolution allows for enhanced productivity, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial as they navigate sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends include the adoption of cloud-based technologies that enable remote monitoring and management of Haas CNC machines, facilitating a more agile manufacturing environment. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on modularity and flexibility in machine design, allowing for rapid reconfiguration to meet varying production needs. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that offer not only robust technical support but also comprehensive training programs to optimize the use of G and M codes, ensuring that their workforce is skilled in these essential programming languages.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing in the Haas Mill G and M Codes Sector?
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers. Companies are recognizing the importance of sustainability and ethical sourcing in their supply chains. For the Haas mill G and M codes sector, this means sourcing materials and components that are not only high quality but also environmentally friendly. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that can demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste.
Green certifications are becoming a standard expectation in many industries. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems indicate a supplier’s commitment to reducing their ecological footprint. Furthermore, companies are exploring innovative tooling and machining techniques that reduce energy consumption and improve overall efficiency. By investing in sustainable technologies, B2B buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What is the Historical Context of Haas Mill G and M Codes in B2B Manufacturing?
The evolution of Haas mill G and M codes has been instrumental in shaping modern CNC machining practices. Initially developed to control machine tools, these codes have undergone significant advancements since their inception. As CNC technology evolved, so did the complexity and capabilities of G and M codes, allowing for more intricate machining tasks and greater automation.
This historical context is essential for B2B buyers as it highlights the importance of understanding the programming language that drives their machinery. Knowledge of G and M codes empowers manufacturers to optimize their machining processes, reduce errors, and enhance overall productivity. As the industry continues to evolve, staying informed about these developments will be crucial for international buyers looking to maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of haas mill g and m codes
-
How do I troubleshoot common issues with Haas mill G and M codes?
To troubleshoot common issues with Haas mill G and M codes, start by reviewing the machine’s error messages and operational logs. Ensure that the G and M codes are entered correctly according to the specific program requirements. Familiarize yourself with the machine’s manual, which outlines troubleshooting steps for various codes. Additionally, consider conducting a dry run to identify any unexpected movements or errors without material. If issues persist, consulting with a Haas technician or your local distributor can provide specialized support. -
What is the best resource for learning Haas mill G and M codes?
The best resource for learning Haas mill G and M codes is the official Haas Automation website, where you can access comprehensive manuals and guides. Online forums and communities dedicated to CNC machining can also offer practical insights and shared experiences from other users. Additionally, consider enrolling in training sessions offered by Haas or certified distributors, which provide hands-on learning opportunities. Investing in educational resources will significantly enhance your understanding and application of these codes. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for Haas mill G and M code programs?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for Haas mill G and M code programs typically depends on the supplier and the specific requirements of your project. Many suppliers do not impose a strict MOQ for digital code files, as they can be shared electronically. However, when sourcing hardware or customized programming services, it’s wise to discuss potential MOQs with your supplier. Establishing a clear understanding of your needs and the supplier’s capabilities can help negotiate favorable terms. -
How can I ensure the quality of Haas mill G and M codes from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of Haas mill G and M codes from suppliers, request samples of their previous work and verify their compliance with industry standards. It’s essential to evaluate the supplier’s experience and reputation in CNC programming. Additionally, consider implementing a quality assurance process that includes reviewing code functionality through simulations and test runs. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can facilitate better communication and troubleshooting, ensuring high-quality outcomes. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Haas mill G and M codes internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of Haas mill G and M codes can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Common terms include upfront payments, net 30, or net 60 days upon receipt of goods or services. It’s advisable to clarify these terms before finalizing any agreements. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, to protect your investment and ensure compliance with contractual obligations. -
What customs regulations should I be aware of when importing Haas mill G and M codes?
When importing Haas mill G and M codes, it’s crucial to understand the customs regulations of your country. This includes knowing the necessary documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Different countries may have specific import tariffs or restrictions on software or digital goods. Consulting with a customs broker can help navigate these regulations and ensure compliance, minimizing delays and additional costs during the import process. -
How do I vet suppliers for Haas mill G and M codes?
Vetting suppliers for Haas mill G and M codes involves several steps. Start by researching their background, focusing on their experience with CNC programming and the specific codes you require. Request references from previous clients and assess their feedback. Additionally, review their certifications and compliance with industry standards. A visit to their facility, if feasible, can provide insight into their operations and quality control processes, further ensuring you choose a reliable partner. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for sourcing Haas mill G and M codes?
When sourcing Haas mill G and M codes, logistics considerations include shipping times, costs, and the method of delivery. If you’re sourcing physical products alongside the code, factor in customs clearance and potential delays. Ensure that the supplier can meet your delivery timelines, especially if you have production deadlines. It’s also important to establish a clear communication channel for tracking shipments and addressing any issues that may arise during transit.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
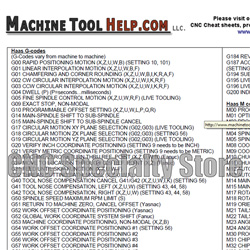
Top 5 Haas Mill G And M Codes Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HAAS – Toolroom Mill Programming
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: HAAS Toolroom mill, G code programming, conversational programming function, operator’s manual, programming manual.
2. CNC Cookbook – Haas CNC Programming Essentials
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Haas CNC machines utilize unique G-Codes and M-Codes for programming. Key G-Codes include: G12 & G13 for Circular Pockets (clockwise and counter-clockwise cutting), G51 for Scaling (with optional center and scaling factor), G53 for Non-Modal Machine Coordinate System (cancels work coordinate system for one block), G68 for Rotation (specifies angle and center of rotation), G101 for Mirror Image (pr…
3. Practical Machinist – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining; HAAS mill; multiple tools; 2 setups; G150 cycle; end mills with 3 mm and 6 mm diameter; manual Z-offset reset; features milled in multiple depth steps; use of subprograms; vise setup and clamping considerations; cutting parameters based on axial depth.
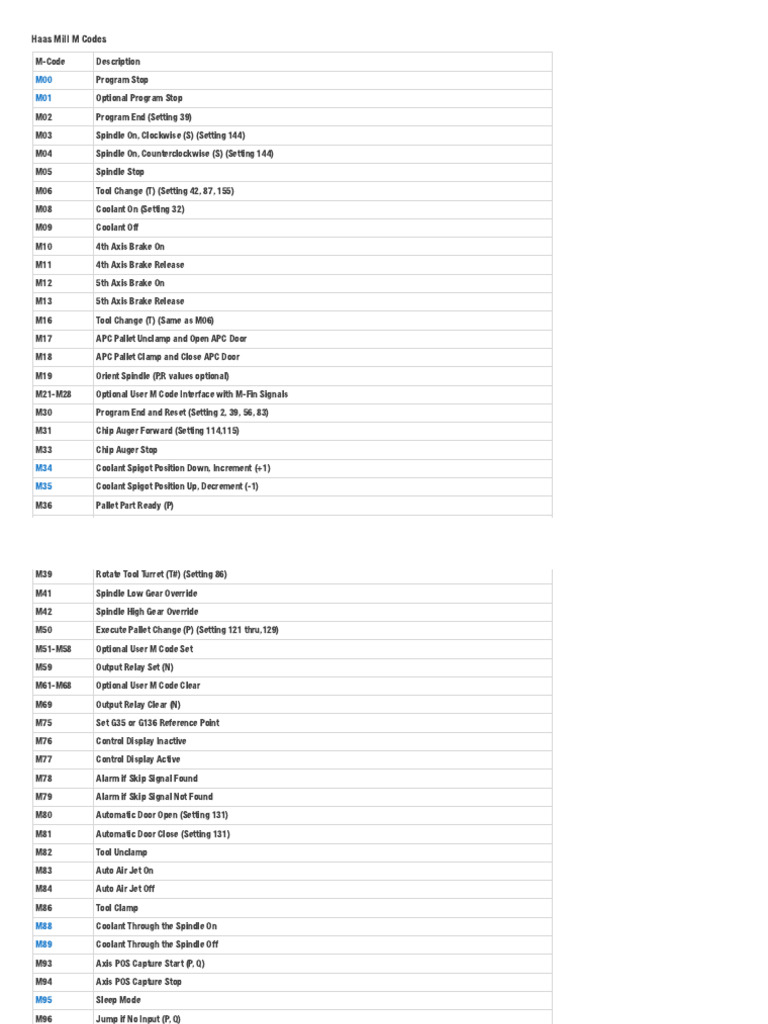
4. Control.com – Essential M-Codes for CNC Operations
Domain: control.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: M-Codes are non axes-moving commands for CNC machines, formatted as ‘M’ followed by two numbers (e.g., M03). Key M-Codes include: M00 (Stop Program), M01 (Optional Program Stop), M02 (Program End), M03/M04/M05 (Spindle Commands), M06 (Tool Change), M08 (Coolant On), M09 (Coolant Off), M10 (Engage 4th Axis Brake), M12 (Engage 5th Axis Brake), M19 (Orient Spindle), and M30 (Program End and Reset). E…
5. Independently Published – Most Common G and M Codes for Haas CNC Mill
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {‘title’: ‘Most Common G and M Codes for Haas CNC Mill: NOT ALL G AND M CODES ARE USED!’, ‘price’: ‘$14.76’, ‘condition’: ‘New’, ‘quantity_available’: 1, ‘item_number’: ‘226662423123’, ‘publisher’: ‘Independently published’, ‘publication_date’: ‘September 16, 2021’, ‘language’: ‘English’, ‘format’: ‘Paperback’, ‘pages’: 47, ‘ISBN_13’: ‘979-8467737676’, ‘item_weight’: ‘2.89 ounces’, ‘dimensions’: ‘…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for haas mill g and m codes
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Operations with Haas Mill G and M Codes?
In the realm of CNC machining, understanding Haas mill G and M codes is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and precision. By strategically sourcing quality equipment and components, international buyers can enhance their manufacturing capabilities, reduce operational costs, and improve lead times. The integration of advanced G and M codes not only streamlines programming but also maximizes machine performance, enabling businesses to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Investing in training and resources related to Haas mill codes can significantly impact your operational effectiveness. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with trusted suppliers and distributors who can provide both equipment and technical support. This approach ensures that your team is equipped with the necessary skills to leverage these codes effectively.
As we look to the future, the importance of strategic sourcing will only grow. Embrace the potential of Haas mill G and M codes to enhance your production capabilities. Connect with industry leaders and invest in the right technologies to position your business for success in the global market. The time to act is now—optimize your sourcing strategy and elevate your manufacturing processes.