Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for grade 5 titanium price
Navigating the complexities of sourcing grade 5 titanium can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With its superior strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility, grade 5 titanium, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, is a critical material in high-demand industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive. However, fluctuating prices and varying quality standards can complicate the purchasing process, especially for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Brazil.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of grade 5 titanium pricing, providing insights into its various types, applications, and the importance of supplier vetting. Buyers will explore critical factors influencing cost, such as market demand, geopolitical factors, and material purity. Additionally, we will highlight best practices for navigating the global supply chain, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your specific operational needs.
By equipping you with actionable knowledge and strategic insights, this guide empowers you to effectively manage procurement processes, minimize risks, and optimize your sourcing strategies for grade 5 titanium. Whether you are looking to understand current market trends or seeking reliable suppliers, our resource is designed to facilitate successful purchasing decisions in a competitive landscape.
Understanding grade 5 titanium price Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercially Pure Titanium (Grade 1 & 2) | Lower strength, corrosion-resistant, no alloying elements | Chemical processing, heat exchangers, architecture | Pros: Cost-effective, good corrosion resistance. Cons: Limited strength for structural applications. |
| Titanium 6-4 Alloy (Grade 5) | High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatible | Aerospace components, medical implants, military applications | Pros: Superior mechanical properties, versatile applications. Cons: Higher cost compared to commercially pure titanium. |
| Titanium Scrap | Reclaimed material from manufacturing processes, lower purity | Non-structural applications, recycling projects | Pros: Lower cost, sustainable option. Cons: Inconsistent quality, limited applications. |
| Titanium 6-2-4-2 Alloy | Enhanced strength and toughness, good weldability | Aerospace, automotive, marine applications | Pros: Better performance in demanding environments. Cons: More expensive than Grade 5. |
| Titanium 5-2-3-2 Alloy | Excellent fatigue resistance, medium strength | High-performance aerospace and automotive parts | Pros: Suitable for dynamic loading applications. Cons: Limited availability and higher price. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Commercially Pure Titanium?
Commercially pure titanium, encompassing Grades 1 and 2, is characterized by its lower strength and absence of alloying elements. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where high strength is not critical, such as chemical processing and architectural uses. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of these grades, especially for projects that prioritize corrosion resistance over structural integrity. However, the limited strength may not meet the requirements for more demanding applications.
Why is Titanium 6-4 Alloy (Grade 5) a Preferred Choice for B2B Buyers?
Titanium 6-4, or Grade 5, is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, making it a preferred material in aerospace, medical, and military sectors. This alloy offers versatility in applications where performance is paramount. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of its superior mechanical properties against its higher cost. While it may represent a significant investment, the long-term performance and reliability can justify the expenditure, particularly in critical applications.
What Should Buyers Consider When Looking at Titanium Scrap?
Titanium scrap consists of reclaimed material, often available at a lower cost compared to virgin titanium. It is suitable for non-structural applications and recycling projects, providing a sustainable option for budget-conscious buyers. However, the quality of scrap can vary, which may limit its use in high-performance applications. B2B buyers must assess their specific needs and the potential trade-offs between cost savings and material integrity.
How Does Titanium 6-2-4-2 Alloy Enhance Performance in Demanding Environments?
Titanium 6-2-4-2 alloy is known for its enhanced strength and toughness, making it suitable for challenging environments such as aerospace and automotive applications. This alloy also boasts good weldability, which can be beneficial in complex manufacturing processes. B2B purchasers should consider the balance of performance and cost when selecting this alloy, as it is typically more expensive than Grade 5 but offers significant advantages in demanding applications.
What Advantages Does Titanium 5-2-3-2 Alloy Offer for High-Performance Applications?
Titanium 5-2-3-2 alloy is recognized for its excellent fatigue resistance and medium strength, making it suitable for high-performance aerospace and automotive parts. This alloy can withstand dynamic loading, providing reliability in critical applications. However, buyers should be aware of its limited availability and higher price point. When considering this alloy, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific performance requirements of their projects against the potential costs involved.
Key Industrial Applications of grade 5 titanium price
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of grade 5 titanium price | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Airframe Components | High strength-to-weight ratio enhances fuel efficiency and performance. | Certification of materials to ensure compliance with aviation standards. |
| Medical Devices | Biomedical Implants | Biocompatibility and corrosion resistance improve patient outcomes. | Need for certified suppliers who meet stringent medical regulations. |
| Automotive | High-Performance Engine Components | Reduces weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and performance. | Availability of custom shapes and sizes for specific engine designs. |
| Oil and Gas | Pressure Vessels and Heat Exchangers | Excellent corrosion resistance in harsh environments ensures longevity. | Sourcing from suppliers with experience in high-pressure applications. |
| Marine | Components for Marine Equipment | Resistance to seawater corrosion extends equipment lifespan. | Requirement for reliable supply chains to avoid delays in critical projects. |
How is Grade 5 Titanium Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, grade 5 titanium is pivotal for manufacturing airframe components due to its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio. This characteristic not only enhances the structural integrity of aircraft but also contributes to improved fuel efficiency, which is crucial for airlines looking to reduce operational costs. International buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, must ensure that their suppliers can provide materials that comply with stringent aviation standards and certifications.
What Role Does Grade 5 Titanium Play in Medical Device Manufacturing?
Grade 5 titanium is extensively utilized in the production of biomedical implants, such as dental and orthopedic devices, owing to its biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion. These properties are essential for ensuring that implants do not trigger adverse reactions in patients, thereby improving long-term health outcomes. For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing from suppliers who can guarantee compliance with medical regulations is critical to ensure safety and effectiveness.
How is Grade 5 Titanium Beneficial for Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, grade 5 titanium is increasingly used for high-performance engine components. Its lightweight nature allows for significant reductions in overall vehicle weight, leading to enhanced fuel efficiency and improved performance metrics. B2B buyers in regions like Brazil and Germany should focus on sourcing custom titanium parts that meet specific design requirements, ensuring they partner with suppliers capable of delivering precision-engineered products.
Why is Grade 5 Titanium Important for Oil and Gas Industries?
The oil and gas industry leverages grade 5 titanium for pressure vessels and heat exchangers due to its exceptional corrosion resistance in harsh environments. This durability translates to longer equipment lifespans and reduced maintenance costs, which are vital for maximizing operational efficiency. Buyers must prioritize suppliers who have a proven track record in providing materials for high-pressure applications, ensuring reliability and safety in critical projects.
How Does Grade 5 Titanium Enhance Marine Equipment Performance?
In marine applications, grade 5 titanium is favored for components exposed to seawater due to its outstanding resistance to corrosion. This property significantly extends the lifespan of marine equipment, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions with extensive maritime activities, establishing reliable supply chains is essential to avoid delays and ensure timely project execution.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘grade 5 titanium price’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Fluctuating Market Prices for Grade 5 Titanium
The Problem: In today’s volatile market, B2B buyers often find themselves challenged by the fluctuating prices of grade 5 titanium (Ti-6Al-4V). Factors such as geopolitical tensions, global demand, and raw material scarcity contribute to unpredictable price swings. For companies in industries like aerospace and medical devices, where titanium is a critical component, these fluctuations can lead to budget overruns and strained supplier relationships. Buyers may feel anxious about committing to purchases when prices may drop or rise dramatically shortly thereafter.
The Solution: To mitigate the impact of price volatility, buyers should establish long-term relationships with trusted suppliers who can provide consistent pricing and reliable supply chains. Engaging in forward contracts can also lock in prices for future deliveries, providing financial predictability. Additionally, buyers should stay informed about market trends through industry reports and price indices, which can help them identify the best times to purchase. By adopting a proactive approach and leveraging strategic partnerships, companies can better navigate the complexities of titanium pricing.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Understanding Pricing Structures for Grade 5 Titanium
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to comprehend the various pricing structures associated with grade 5 titanium. The costs can vary significantly based on factors such as material grade, quantity purchased, and specific application requirements. This lack of clarity can lead to confusion during procurement processes, ultimately impacting project timelines and budgets. Buyers may find themselves unsure of whether they are receiving a fair price or if there are hidden costs associated with their orders.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should invest time in understanding the factors that influence grade 5 titanium pricing. A detailed breakdown of costs should be requested from suppliers, including elements like shipping, handling, and any potential tariffs. Creating a checklist of specifications for their needs can also help buyers communicate effectively with suppliers, ensuring they receive quotes that accurately reflect their requirements. Furthermore, participating in industry forums and engaging with peers can provide insights into standard pricing practices, helping buyers make more informed purchasing decisions.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Sourcing Quality Grade 5 Titanium at Competitive Prices
The Problem: Sourcing high-quality grade 5 titanium at competitive prices can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly in regions with limited supplier options. Buyers may encounter issues such as inconsistent quality, delayed shipments, and inflated prices due to a lack of competition. This situation is especially problematic for industries that require stringent material specifications, as subpar titanium can compromise product integrity and safety.
The Solution: To effectively source quality grade 5 titanium, buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify reputable suppliers with proven track records. Utilizing online resources, such as supplier directories and industry-specific platforms, can aid in locating trustworthy vendors. Additionally, buyers should request certifications and quality assurance documents to verify the material’s specifications before making a purchase. Establishing a diverse supplier network can also mitigate risks associated with reliance on a single source, ensuring that buyers can obtain quality titanium at competitive prices without compromising on performance or delivery times.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for grade 5 titanium price
What Are the Key Properties of Grade 5 Titanium?
Grade 5 titanium, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred choice in high-performance applications across various industries. This alloy exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments, and can withstand temperatures up to 600°F (316°C). Its biocompatibility makes it suitable for medical implants, while its mechanical properties lend themselves well to aerospace and automotive applications.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Grade 5 Titanium?
Pros:
– Durability: Grade 5 titanium is highly resistant to fatigue and stress, ensuring longevity in demanding applications.
– Corrosion Resistance: It withstands oxidation and corrosion in various environments, including saltwater and acidic conditions.
– Lightweight: Compared to other metals with similar strength, titanium is significantly lighter, which is crucial in aerospace and automotive sectors.
Cons:
– Cost: The price of grade 5 titanium is relatively high, ranging from $10 to $15 per pound, which can be a barrier for budget-sensitive projects.
– Manufacturing Complexity: Machining titanium requires specialized tools and processes, increasing production times and costs.
– Weldability Issues: While it can be welded, specific techniques and precautions are necessary to avoid contamination and ensure structural integrity.
How Does Grade 5 Titanium Impact Specific Applications?
Grade 5 titanium is particularly advantageous in applications requiring high strength and low weight, such as aerospace components, medical devices, and military hardware. Its compatibility with various media, including body fluids and corrosive chemicals, makes it ideal for biomedical implants and chemical processing equipment. However, buyers must consider the specific environmental conditions the material will face, as these can influence performance and longevity.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Sourcing Grade 5 Titanium?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local and international standards is critical. Familiarity with ASTM, DIN, and JIS standards ensures that the titanium sourced meets the necessary quality and safety requirements. Additionally, logistical considerations such as shipping costs, import tariffs, and supplier reliability can significantly impact the overall cost-effectiveness of purchasing grade 5 titanium. Buyers should also evaluate the supplier’s ability to provide certifications and traceability, which are essential for industries like aerospace and medical.
Summary Table of Grade 5 Titanium Material Analysis
| Material | Typical Use Case for grade 5 titanium price | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 5 Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) | Aerospace components, medical implants, military hardware | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance | High cost, complex manufacturing processes | High |
| Commercially Pure Titanium (Grade 1 & 2) | Chemical processing, heat exchangers | Lower cost, easier to machine | Limited strength, not suitable for high-stress applications | Medium |
| Titanium Scrap | Non-structural applications, recycling | Cost-effective, sustainable source | Lower quality, variable properties | Low |
| Titanium Alloys (Other Grades) | Specialized applications (e.g., marine, automotive) | Tailored properties for specific needs | May require extensive testing and certification | Medium to High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the strategic selection of grade 5 titanium, highlighting its properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international sourcing. Understanding these factors can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements and budget constraints.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for grade 5 titanium price
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Grade 5 Titanium?
The manufacturing process for Grade 5 titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) involves several critical stages, each crucial for ensuring the material meets the high standards required for its diverse applications in aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation:
The first step involves sourcing high-quality titanium sponge or ingot, which is the primary raw material. The material undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets specified chemical and mechanical properties. This step may include cleaning and cutting the titanium into manageable sizes for further processing.
Forming Techniques:
Titanium forming can be accomplished through various methods such as forging, casting, and machining. In forging, the titanium is heated and shaped under high pressure to enhance its mechanical properties. For casting, molten titanium is poured into molds, allowing for complex shapes. Machining involves subtractive processes like turning and milling to create precise dimensions, often used for components requiring tight tolerances.
Assembly Procedures:
In instances where components are made from multiple parts, assembly becomes necessary. Techniques such as welding, bolting, or adhesive bonding are employed to create a unified structure. Each assembly method has its own set of requirements concerning heat treatment and surface preparation to ensure optimal bonding and strength.
Finishing Processes:
Finishing is essential for enhancing the surface characteristics of Grade 5 titanium. This stage may include processes such as anodizing, which improves corrosion resistance, or polishing to achieve a specific aesthetic. Additionally, surface treatments may be applied to prepare the titanium for specific environments, particularly in medical or aerospace applications.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing Process for Grade 5 Titanium?
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process for Grade 5 titanium, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer specifications. Several key methodologies and checkpoints are integral to this process.
International Standards for Quality Assurance:
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems. This certification helps ensure that the manufacturing processes are efficient and produce consistent, high-quality products. Industry-specific standards, such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area and API specifications for oil and gas applications, further reinforce quality assurance practices.
Quality Checkpoints:
The quality assurance process typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications. This includes checking chemical composition and mechanical properties through standardized testing methods.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor production quality. This may involve dimensional checks and non-destructive testing (NDT) to detect any defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, final inspections are performed to ensure that the products meet all required specifications. This may include destructive testing, such as tensile strength tests, to validate the material’s performance.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Control for Grade 5 Titanium?
Quality control for Grade 5 titanium incorporates a variety of testing methods to ensure that the material meets the stringent requirements of its applications. Common testing methods include:
-
Chemical Analysis: To verify the alloy composition, manufacturers use techniques such as Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) or X-ray Fluorescence (XRF). This ensures that the titanium meets the specified alloying element percentages.
-
Mechanical Testing: Tensile tests, fatigue tests, and hardness tests are conducted to assess the material’s mechanical properties. These tests determine how the titanium will perform under different stress conditions.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, and radiographic testing are employed to detect internal and surface flaws without damaging the material.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing Grade 5 titanium from international suppliers, must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential partners. Here are several strategies to ensure supplier reliability:
Supplier Audits:
Conducting on-site audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards and their commitment to quality.
Requesting Quality Reports:
Buyers should ask for detailed quality control reports, including results from mechanical and chemical testing. This documentation helps validate the supplier’s claims about their products.
Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging independent third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. These services can perform audits and testing, providing an additional layer of assurance.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential. Buyers should be aware of:
Regional Standards and Certifications:
Different regions may have specific quality standards that manufacturers must meet. Familiarity with these standards can help buyers make informed decisions and ensure compliance.
Import Regulations:
Buyers should also understand import regulations concerning certification and quality standards in their respective countries. Non-compliance can lead to delays and increased costs.
Cultural Differences in Quality Assurance:
Cultural approaches to quality control may vary by region. Buyers should consider these differences and ensure that their suppliers align with their quality expectations.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for Grade 5 titanium are complex yet critical. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification strategies, international B2B buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality materials that meet their specific needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘grade 5 titanium price’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring Grade 5 titanium, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, which is renowned for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Understanding the pricing and sourcing process for this critical material is essential for industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive. The following checklist outlines the key steps to ensure a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific requirements for the Grade 5 titanium you need. This includes dimensions, tolerances, and any relevant certifications (e.g., ASTM standards). By having precise specifications, you can streamline the selection process and ensure compatibility with your project needs.
Step 2: Research Current Market Prices
Stay informed about the prevailing market prices for Grade 5 titanium. Prices can fluctuate based on demand and geopolitical factors, so understanding the price range (approximately $10–$15 per pound) will help you make informed purchasing decisions. Regularly check industry reports, supplier catalogs, and online metal marketplaces for up-to-date pricing.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from existing clients within your industry. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering Grade 5 titanium and ensure they have the necessary certifications to meet your quality requirements.
- Ask for Samples: Request material samples to assess quality and verify that the titanium meets your specifications.
- Check Delivery Capabilities: Ensure the supplier can meet your timeline and logistics needs, especially if you require large quantities.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers possess the necessary certifications relevant to your industry, such as ISO 9001 or AS9100 for aerospace applications. Certification not only reflects quality but also adherence to international standards that can minimize risks in your supply chain.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions with your selected suppliers to negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery conditions. Be transparent about your budget constraints while seeking the best value. Consider bulk purchase discounts or long-term contracts for better pricing stability.
Step 6: Assess Supply Chain Stability
Investigate the supplier’s supply chain to ensure reliability and resilience. Factors such as sourcing of raw materials, production capabilities, and geographic location can impact lead times and pricing stability. Suppliers with diversified sourcing strategies are often better equipped to handle market fluctuations.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Place Orders
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize all contractual agreements. Ensure that terms regarding quality assurance, delivery schedules, and payment conditions are clearly outlined. Placing a well-documented order will help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing Grade 5 titanium, ensuring they secure high-quality materials at competitive prices while minimizing risks in their supply chains.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for grade 5 titanium price Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of Grade 5 titanium is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis delves into the key components that influence the pricing of Grade 5 titanium, helping buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components of Grade 5 Titanium?
Materials: The primary cost driver for Grade 5 titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) is the raw material itself. The extraction and processing of titanium from ores like ilmenite and rutile are energy-intensive, impacting the final price. The market price for Grade 5 titanium typically ranges from $10 to $15 per pound, influenced by the purity and alloying elements involved.
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs associated with machining and fabricating titanium parts are significant due to the specialized skills required. Manufacturing overhead, including facility maintenance and operational costs, also contributes to the overall pricing structure. High-quality machining processes are essential to meet the stringent specifications required in aerospace and medical applications.
Tooling and Quality Control: The production of Grade 5 titanium components often requires specialized tooling, which adds to the initial setup costs. Furthermore, rigorous quality control (QC) measures are necessary to ensure compliance with industry standards, particularly in high-stakes sectors like aerospace and healthcare. These QC processes can drive up costs but are essential for maintaining product integrity.
Logistics and Margins: Transportation and logistics costs are particularly relevant for international buyers. Shipping Grade 5 titanium can be costly, especially when considering import tariffs and fees. Suppliers typically include a margin that reflects their operational costs and market positioning, which can vary significantly based on geographic location and supplier reputation.
What Influences the Price of Grade 5 Titanium?
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Pricing is often influenced by the volume of the order. Larger quantities can lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs with suppliers to optimize pricing.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can significantly affect pricing. Tailored solutions, such as specific dimensions or additional treatments, may incur extra charges. Buyers should provide detailed requirements to obtain accurate quotes.
Material Quality and Certifications: The quality of titanium and relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100 for aerospace) can impact costs. Suppliers with established reputations for quality often command higher prices, reflecting the assurance they provide.
Supplier Factors and Incoterms: Supplier reliability and the terms of delivery (Incoterms) are critical in determining the total cost. Buyers should assess the supplier’s capability to deliver on time and the associated risks in the pricing model.
How Can Buyers Optimize Their Purchasing Strategy for Grade 5 Titanium?
Negotiation Tactics: Effective negotiation is key to securing favorable terms. Buyers should leverage their purchasing power, especially when placing bulk orders, to negotiate better pricing and payment terms.
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, logistics, and potential scrap costs. A comprehensive TCO analysis can reveal hidden costs that may impact long-term profitability.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions. Engaging with local suppliers may also yield cost advantages due to reduced shipping and tariffs.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices for Grade 5 titanium are indicative and subject to change based on market dynamics, supplier conditions, and geopolitical factors. Buyers are encouraged to obtain current quotes and consider all relevant factors when making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing grade 5 titanium price With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Grade 5 Titanium Pricing
In the world of industrial materials, grade 5 titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) is revered for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice in aerospace and medical applications. However, as international B2B buyers seek cost-effective solutions, it becomes essential to evaluate viable alternatives that can deliver similar performance without the premium price tag. Below, we compare grade 5 titanium against two notable alternatives: aluminum alloys and stainless steel.
| Comparison Aspect | Grade 5 Titanium Price | Aluminum Alloys | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Good strength-to-weight ratio, less corrosion resistance than titanium | Strong, durable, good corrosion resistance |
| Cost | $10-$15 per pound | $2-$5 per pound | $3-$8 per pound |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex machining and fabrication | Easier to work with, readily available | Moderate, can require specific welding techniques |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, highly durable | Moderate, can corrode without proper care | Low, but prone to rust if not maintained |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, medical implants, military applications | Automotive, structural components | General construction, kitchenware, industrial applications |
Evaluating Aluminum Alloys as an Alternative
Aluminum alloys are a popular alternative to grade 5 titanium due to their lightweight properties and lower cost. With prices ranging from $2 to $5 per pound, they present a budget-friendly option for applications requiring good strength without the weight penalty of steel. Aluminum alloys are easier to work with, making them favorable for mass production and fabrication processes. However, they do not match the corrosion resistance or strength of titanium, particularly in high-stress environments, which can limit their use in critical applications like aerospace and medical implants.
Considering Stainless Steel for Cost-Effectiveness
Stainless steel, priced between $3 and $8 per pound, offers a robust alternative that excels in durability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from construction to kitchenware. While it is generally heavier than titanium, stainless steel’s strength and resistance to rust provide reliable performance in various conditions. The machining and welding of stainless steel can be more straightforward compared to titanium, but it may still require specific techniques to achieve the best results. Its versatility makes it a solid choice, although it may not provide the same level of performance in specialized aerospace or medical applications where titanium shines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When deciding between grade 5 titanium and its alternatives, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including application requirements, budget constraints, and performance needs. Grade 5 titanium remains unmatched for high-performance applications due to its superior properties, but alternatives like aluminum alloys and stainless steel can offer significant cost savings and sufficient performance for less demanding applications. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their projects and weigh the long-term benefits against initial costs to select the most suitable material for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for grade 5 titanium price
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Grade 5 Titanium?
1. Material Grade
Grade 5 titanium, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, is the most widely used titanium alloy due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. This alloy comprises 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, and 4% vanadium, making it suitable for high-performance applications in aerospace, medical devices, and automotive sectors. Understanding the material grade is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly impacts the suitability of the titanium for specific applications and its overall cost.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For grade 5 titanium, tight tolerances are often critical in industries like aerospace and medical devices, where precision is paramount. In B2B transactions, specifying the required tolerances ensures that the delivered products meet operational standards, thereby reducing the risk of costly errors or product failures.
3. Yield Strength
Yield strength is the amount of stress a material can withstand before deforming. Grade 5 titanium exhibits a yield strength of approximately 880 MPa (128,000 psi), making it ideal for applications that require high strength without additional weight. For buyers, understanding yield strength is vital for determining whether the material can withstand the stresses encountered in its intended application, influencing both safety and performance.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Grade 5 titanium is renowned for its high resistance to corrosion, particularly in harsh environments, including seawater and acidic conditions. This property is essential for industries such as marine engineering and chemical processing. Buyers should consider this aspect when evaluating the lifespan and maintenance costs associated with titanium components, as reduced corrosion can lead to lower long-term operational costs.
5. Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility refers to the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response when introduced into the body. Grade 5 titanium is frequently used in medical implants due to its compatibility with human tissue. For B2B buyers in the healthcare sector, understanding biocompatibility is crucial for compliance with regulatory standards and ensuring patient safety.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Grade 5 Titanium Pricing?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of grade 5 titanium, OEMs often source titanium components for integration into larger systems, such as aircraft or medical devices. Understanding this term helps buyers identify potential partnerships and sourcing strategies in their supply chain.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For grade 5 titanium, MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product configuration. Buyers need to be aware of MOQs to manage their inventory effectively and ensure they meet production requirements without incurring excess costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the titanium market, an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they get the best possible price and terms for grade 5 titanium. Properly drafting an RFQ can facilitate better negotiations and faster procurement processes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. For grade 5 titanium, knowing the relevant Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost implications, enabling smoother international trade.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time that elapses from the initiation of a process until its completion. In the context of grade 5 titanium, lead times can affect project timelines and inventory management. Buyers must factor in lead times when planning their procurement strategies to avoid delays in production or project delivery.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions regarding grade 5 titanium, optimizing their supply chain and ensuring product performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the grade 5 titanium price Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Grade 5 Titanium Price Market?
The global market for grade 5 titanium, particularly the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, is driven by several interrelated factors. First, the aerospace and medical sectors remain the largest consumers, as these industries require materials that offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. The increasing focus on lightweight materials in aerospace to enhance fuel efficiency and performance is pushing demand for grade 5 titanium. Moreover, the automotive industry’s shift towards lightweight components to improve fuel economy is also contributing to this demand.
Emerging sourcing trends include the rise of digital procurement platforms that facilitate easier access to suppliers and more competitive pricing. International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging these technologies to streamline their purchasing processes and enhance supply chain efficiency. Additionally, the ongoing geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions can lead to volatility in titanium pricing. Buyers must stay informed about these dynamics, as they can affect supply availability and cost.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Grade 5 Titanium Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the titanium market. The extraction and production of titanium, particularly through traditional mining methods, can have significant environmental impacts. Thus, companies are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and ethical sourcing. This includes utilizing recycled titanium, which not only reduces environmental impact but also helps stabilize pricing by decreasing reliance on virgin materials.
Furthermore, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) can provide assurance that suppliers are committed to sustainable practices. Buyers are encouraged to look for ‘green’ certifications when sourcing grade 5 titanium, as these can indicate a supplier’s commitment to minimizing their ecological footprint. Emphasizing ethical sourcing not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but can also enhance brand reputation in a market that increasingly values sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of Grade 5 Titanium and Its Pricing Trends?
Grade 5 titanium has its roots in the aerospace industry, where its unique properties were first recognized in the mid-20th century. Over the decades, its applications have expanded significantly, with the material becoming a staple in sectors ranging from medical devices to automotive manufacturing. The pricing trends of grade 5 titanium have historically been influenced by factors such as mining costs, technological advancements in production, and shifts in global demand.
In recent years, the rise of additive manufacturing and 3D printing has introduced new avenues for titanium sourcing and application. These technologies not only reduce waste but also allow for more efficient use of materials, potentially lowering costs over time. As the market evolves, understanding the historical context of grade 5 titanium will equip B2B buyers with insights into pricing dynamics and future trends, enabling more informed purchasing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of grade 5 titanium price
-
How do I determine the current market price for grade 5 titanium?
To ascertain the current market price for grade 5 titanium (Ti-6Al-4V), it’s essential to monitor industry reports and pricing platforms that aggregate data from suppliers. Factors influencing the price include global demand, market trends, and geopolitical events. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can also provide insights into pricing fluctuations. Regularly consulting industry publications and participating in trade shows can keep you informed about market conditions affecting titanium prices. -
What are the most common applications for grade 5 titanium?
Grade 5 titanium is widely utilized in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Typical applications include aircraft components, biomedical implants, and high-performance automotive parts. Its biocompatibility also makes it a preferred choice for surgical tools and implants. Understanding these applications can help you assess whether grade 5 titanium meets your specific project needs. -
How can I ensure the quality of the grade 5 titanium I purchase?
To guarantee the quality of grade 5 titanium, always request certifications from suppliers, such as ISO certifications or material test reports. Engage suppliers who conduct rigorous quality assurance (QA) processes, including non-destructive testing and chemical composition analysis. It’s also advisable to visit manufacturing facilities or request third-party inspections to validate the quality of the titanium before placing a significant order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for grade 5 titanium?
Minimum order quantities for grade 5 titanium can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from 10 to 100 kg depending on the product form (sheets, bars, or custom cuts). High-volume suppliers may offer lower MOQs, while specialized manufacturers might require larger orders to justify production costs. When negotiating with suppliers, discuss your specific needs and see if they can accommodate smaller orders, especially if you are testing a new application. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing grade 5 titanium?
Payment terms for grade 5 titanium can vary based on supplier policies and the size of your order. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or payment upon delivery. For larger orders, suppliers might require a deposit upfront. Always clarify payment methods accepted (wire transfer, credit card, etc.) and inquire about any potential discounts for early payment or bulk orders to optimize your purchasing budget. -
How do international trade regulations affect sourcing grade 5 titanium?
International trade regulations can significantly impact the sourcing of grade 5 titanium, especially regarding tariffs, export controls, and import duties. Buyers should familiarize themselves with regulations in both the exporting and importing countries to avoid delays and additional costs. Engaging a logistics partner with expertise in international trade can help navigate these complexities, ensuring compliance and smooth transactions. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing grade 5 titanium?
When importing grade 5 titanium, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance procedures. Air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight, which may be more economical for larger shipments. Ensure all shipping documents are in order, including commercial invoices and packing lists, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in handling metal imports can streamline the process and reduce potential delays. -
How can I vet suppliers for grade 5 titanium effectively?
Vetting suppliers for grade 5 titanium involves assessing their reputation, certifications, and production capabilities. Start by reviewing online reviews, testimonials, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients and verify their experience with similar products. Additionally, assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures to ensure they align with your standards. Attending trade shows or industry events can also provide opportunities to interact with potential suppliers and gauge their reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Grade 5 Titanium Price Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Online Metals – Ti6Al4V Grade 5 Titanium
Domain: onlinemetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Ti6Al4V – Grade 5 Titanium; Popular for medical and aerospace applications; Biocompatible; High corrosion resistance; Strength comparable to 6061-T6 aluminum; High strength-to-weight ratio; Applications include airframe components, cryogenic vessels, heat exchangers, condenser tubing, pickling baskets, blades, discs, rings, fasteners, pressure vessels, biomedical implants; Available in rectangle b…
2. Palm Beach – Titanium Sheet Grade 5
Domain: palmbeachbots.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Titanium Sheet – 1.0mm Thick – Grade 5 (Gr5, 6AL-4V)”, “Price”: “$29.99”, “Stock Status”: “Sold out”, “Specifications”: {“Grade”: “Gr5 (6AL-4V)”, “ASTM Standard”: “B265”, “Sheet Size”: “20.32×25.4cm (8x10in)”, “Density”: “4.43g/cm3 (2.56oz/in3)”, “Thickness and Weight”: {“0.5mm (0.02in)”: “137g (4.83 oz)”, “0.8mm (0.03in)”: “183g (6.45 oz)”, “1.0mm (0.04in)”: “229g (8.07 oz)”}, “…
3. VMT CNC – Titanium Pricing Overview
Domain: vmtcnc.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: The cost of titanium per pound varies significantly based on its grade and market conditions. Key details include: 1. Commercially Pure Titanium (Grade 1 and 2): Price Range: $6–$9 per pound, used in applications requiring lower strength. 2. Titanium 6-4 Alloy (Grade 5): Price Range: $10–$15 per pound, known for high strength and corrosion resistance, commonly used in aerospace and medical applica…
4. Pakshal Steel – Titanium Metal Pricing
Domain: pakshalsteel.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Titanium Metal Price Per Kg – Latest 2025 Price List:
– Titanium Price in India: Rs 5500/- ($80, €68)
– Titanium Price in Japan: Rs 6200/- ($91, €78)
– Titanium Price in UK/Europe: Rs 6900/- ($101, €87)
– Titanium Price in USA: Rs 7500/- ($110, €94)
Titanium Tubing Prices:
– .250″ o.d. x .020″ w x 12″: $25.00
– .250″ o.d. x .020″ w x 36″: $40.00
– .313″ od x .034″ w x 36″: $65.00 …
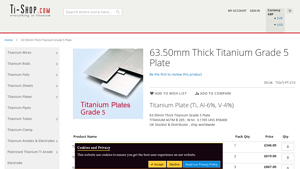
5. Titanium – Grade 5 Plate 63.50mm Thick
Domain: ti-shop.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Titanium Grade 5 Plate 63.50mm Thick”, “SKU”: “TiGr5-PT-210”, “Material”: “Titanium (Ti, Al-6%, V-4%)”, “Thickness”: “63.50mm”, “Standards”: [“ASTM B 265”, “W.Nr. 3.1765”, “UNS R56400”], “Pack Quantities and Prices”: [{“Pack Qty”: 1, “Dimensions”: “100mm x 100mm”, “Price”: “£346.00”}, {“Pack Qty”: 2, “Dimensions”: “100mm x 100mm”, “Price”: “£619.00”}, {“Pack Qty”: 3, “Dimensions”…
6. Tiger Titanium – Ti-6Al-4V Plates, Sheets & Blocks
Domain: tigertitanium.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Titanium plate, sheet and blocks Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) available in various thicknesses, widths, and lengths. Thickness options include 0.012in. and 0.014in. Widths range from 9.500in. to 61in. Lengths vary from 28.000in. to 96.125in. Prices range from $268.80 to $576.00 depending on dimensions. On-hand quantities vary for each item.
7. Titan Services – Titanium Sheet Grade 5
Domain: titane-services.eu
Introduction: Titanium Sheet Grade5 (TA6V) – Thickness: 3 mm – Product no.: tole-titane-G5-3xLxl – Price: From 36.60 € (incl. VAT, not including shipping costs) – Available dimensions for cuts: 100×100 mm, 200×100 mm, 200×200 mm, 500×100 mm, 500×200 mm, 1000×100 mm, 1000×200 mm, 1000×500 mm, 1000×1000 mm, 2000×1000 mm – Material characteristics: Grey titanium is rustproof, non-magnetic, 40% lighter than steel, …
8. MultiEtch – Titanium Grade 5 Coupon Kit
Domain: multietch.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Titanium Grade 5 Coupon Kit – 3 Pack: Quantity = 3, Thickness = .020″, Length = 2″, Width = 4″, Material = Titanium Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), Price = $24.99, Features = Strongest titanium alloy, good corrosion resistance, weldability, strength to weight ratio, easy anodizing, reusable coupons for testing and practice.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for grade 5 titanium price
In navigating the complexities of grade 5 titanium pricing, international B2B buyers must remain attuned to the multifaceted factors influencing market dynamics. The unique properties of titanium, particularly the 6Al-4V alloy, offer exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it a prime choice for industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive. As the demand for high-performance materials continues to rise, so does the importance of strategic sourcing to secure favorable pricing and consistent supply.
Understanding the impact of geopolitical factors, extraction costs, and technological advancements is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, businesses can mitigate risks associated with price fluctuations and ensure access to quality materials. Engaging with reliable suppliers and exploring options for recycled titanium can further enhance cost-effectiveness.
Looking ahead, the titanium market presents opportunities for growth and innovation. As industries evolve, so too will the applications for grade 5 titanium. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should seize the moment to refine their sourcing strategies, ensuring they remain competitive in this vital sector. Embrace the future of titanium procurement by fostering strong supplier relationships and exploring new market trends.