Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for glass reinforced nylon
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, sourcing high-performance materials like glass reinforced nylon can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. This advanced synthetic polyamide thermoplastic, enhanced with glass fibers, offers remarkable strength, rigidity, and thermal stability—qualities essential for applications ranging from automotive components to industrial machinery. However, navigating the complexities of sourcing, evaluating suppliers, and understanding cost implications requires a comprehensive approach.
This guide serves as an essential resource for B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, who seek to make informed purchasing decisions. We will delve into various types of glass reinforced nylon, explore its diverse applications, and provide insights into the supplier vetting process. Additionally, we’ll discuss the cost factors associated with different grades of glass filled nylon, enabling you to assess value against performance needs effectively.
Empowering you with actionable insights, this guide aims to streamline your procurement process, enhance your understanding of material properties, and ultimately support your strategic sourcing initiatives. By leveraging this information, you can confidently select the right glass reinforced nylon solutions that align with your operational requirements and market demands, paving the way for improved product performance and competitive advantage.
Understanding glass reinforced nylon Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6/6 (30% Glass-Filled) | High strength, good rigidity, moderate thermal resistance | Automotive components, industrial machinery | Pros: Excellent mechanical properties. Cons: More brittle than standard nylon. |
| Nylon 12 (40% Glass-Filled) | Superior heat deflection, lower moisture absorption | Aerospace parts, electrical housings | Pros: High thermal stability. Cons: Higher cost due to glass content. |
| Nylon 66 (33% Glass-Filled) | Enhanced stiffness and wear resistance | Structural components, gears | Pros: Good dimensional stability. Cons: May warp in humid environments. |
| Nylon 6 (15% Glass-Filled) | Balanced toughness and stiffness, lower weight | Consumer goods, sporting equipment | Pros: Lightweight with decent strength. Cons: Limited high-temperature applications. |
| Nylon 66 (13% Glass-Filled) | Improved chemical resistance and tensile strength | Medical devices, automotive interiors | Pros: Good for applications with chemical exposure. Cons: Less impact resistance compared to higher glass content. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Nylon 6/6 (30% Glass-Filled)?
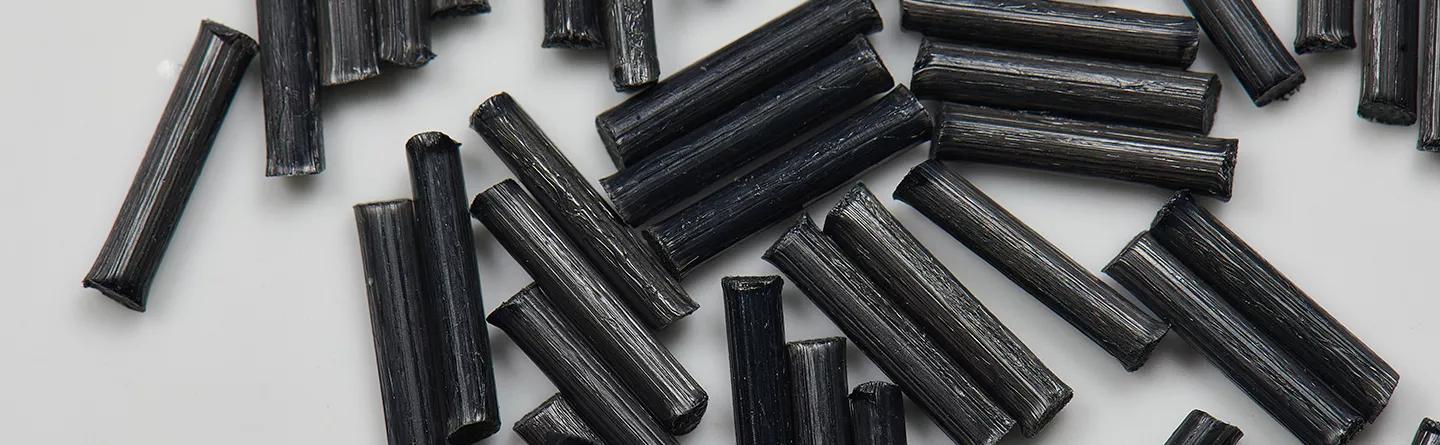
Nylon 6/6 reinforced with 30% glass fibers is renowned for its remarkable mechanical strength and rigidity, making it suitable for demanding applications in automotive and industrial machinery. This variation offers excellent resistance to wear, fatigue, and high static loads, which are crucial for components subjected to harsh operating conditions. However, its increased brittleness compared to standard nylon should be a consideration for buyers, particularly in applications where flexibility is necessary.
How does Nylon 12 (40% Glass-Filled) stand out for B2B applications?
Nylon 12 with 40% glass filling is particularly advantageous in industries such as aerospace and electronics due to its superior thermal stability and lower moisture absorption. This material excels in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for applications that require consistent performance under stress. While it offers significant benefits, buyers should be mindful of the higher costs associated with its advanced properties, balancing performance needs against budget constraints.
Why choose Nylon 66 (33% Glass-Filled) for structural components?
Nylon 66 reinforced with 33% glass fibers is recognized for its enhanced stiffness and wear resistance, making it a preferred choice for structural components and gears. Its good dimensional stability allows it to maintain shape under varying temperatures, which is vital for precision parts. However, buyers should consider its potential for warping in humid conditions, necessitating careful environmental assessments before selection.
What are the benefits of using Nylon 6 (15% Glass-Filled) in consumer goods?
Nylon 6 with 15% glass filling strikes a balance between toughness and lightweight characteristics, making it suitable for consumer goods and sporting equipment. This material provides decent strength while being less heavy than other variants, appealing for applications where weight is a critical factor. However, its limitations in high-temperature applications should be noted, as it may not withstand extreme conditions as effectively as higher glass-filled alternatives.
In what scenarios is Nylon 66 (13% Glass-Filled) most effective?
Nylon 66 with 13% glass filling is particularly effective in applications requiring good chemical resistance and tensile strength, such as medical devices and automotive interiors. Its ability to withstand exposure to various chemicals makes it a reliable choice for manufacturers in sensitive environments. However, its lower impact resistance compared to other glass-filled nylons may limit its use in high-stress applications, prompting buyers to evaluate the specific demands of their projects carefully.
Key Industrial Applications of glass reinforced nylon
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of glass reinforced nylon | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Structural components (e.g., brackets, housings) | Enhanced strength and reduced weight improve fuel efficiency. | Sourcing from reliable manufacturers to ensure quality and consistency. |
| Aerospace | Interior cabin parts (e.g., seat frames) | High strength-to-weight ratio increases safety and performance. | Compliance with aviation standards and testing requirements. |
| Electrical & Electronics | Insulating components (e.g., connectors) | Excellent electrical insulation properties reduce failure rates. | Evaluate thermal stability and moisture absorption characteristics. |
| Consumer Goods | Durable housings for appliances | Improved wear resistance extends product lifespan, enhancing customer satisfaction. | Consider aesthetics and surface finish for market appeal. |
| Industrial Equipment | Gear components and machinery parts | Increased durability under stress minimizes downtime and maintenance costs. | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and operational environments. |
How is Glass Reinforced Nylon Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, glass reinforced nylon is widely utilized for manufacturing structural components such as brackets and housings. These parts benefit from the material’s enhanced strength and reduced weight, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. For international buyers, especially from regions with varying environmental conditions, it is crucial to source materials that meet specific automotive standards and regulations to ensure safety and reliability.
What are the Applications of Glass Reinforced Nylon in Aerospace?
In aerospace, glass reinforced nylon is employed in the production of interior cabin parts, including seat frames and support structures. The material’s high strength-to-weight ratio is essential for enhancing safety while reducing overall aircraft weight, which is critical for fuel efficiency. Buyers in this sector must consider compliance with stringent aviation standards and ensure that materials undergo rigorous testing to meet safety requirements.
How Does Glass Reinforced Nylon Benefit Electrical and Electronics Industries?
Glass reinforced nylon serves as an ideal material for insulating components like connectors and housings in the electrical and electronics industries. Its excellent electrical insulation properties help reduce failure rates, ensuring the reliability of electronic devices. International B2B buyers should focus on sourcing materials that maintain thermal stability and resist moisture absorption, as these factors are vital for performance in diverse climates.
In What Ways is Glass Reinforced Nylon Used in Consumer Goods?
In the consumer goods sector, glass reinforced nylon is commonly used for creating durable housings for appliances, providing both aesthetic appeal and functional strength. The material’s improved wear resistance extends the lifespan of products, leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced return rates. When sourcing, businesses should consider the surface finish and color options to meet market demands.
What are the Industrial Applications of Glass Reinforced Nylon?
Glass reinforced nylon is essential in the industrial equipment sector, where it is used to manufacture gear components and various machinery parts. The material’s increased durability under high stress reduces downtime and maintenance costs, making it a cost-effective choice for manufacturers. Buyers should ensure compatibility with existing systems and assess the operational environments to select the most suitable grades of glass reinforced nylon for their applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘glass reinforced nylon’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Cost Management in High-Performance Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges related to the high costs associated with glass reinforced nylon (GRN). As industries demand materials that can withstand extreme conditions—such as high temperatures and mechanical stress—buyers may find that while GRN offers superior performance, the upfront investment can significantly impact budgets. This is particularly concerning for manufacturers in sectors like automotive or aerospace, where material choices can dramatically affect overall production costs.
The Solution: To manage costs effectively, buyers should focus on a strategic approach to sourcing and specification. First, consider bulk purchasing or long-term contracts with suppliers to secure lower prices. Additionally, conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis can help justify the initial investment by highlighting GRN’s longevity and reduced maintenance costs in high-performance applications. It’s also beneficial to collaborate with material engineers to determine the optimal percentage of glass filler required for specific applications. This tailored approach can lead to cost savings while ensuring the material meets performance expectations.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Machining and Fabrication
The Problem: Machining glass reinforced nylon can pose considerable challenges due to its abrasive nature. B2B buyers often report accelerated wear on tools and increased operational downtime, leading to potential delays in production schedules. This is especially problematic for companies relying on precise CNC machining to create intricate parts where dimensional accuracy is critical.
The Solution: To address these machining challenges, buyers should invest in high-quality, durable cutting tools specifically designed for abrasive materials. Utilizing carbide or ceramic tools can significantly extend tool life and reduce wear. Furthermore, implementing a careful machining strategy that includes slower feed rates and optimized cutting speeds can improve the efficiency of the machining process. Regular monitoring of tool condition and adjusting machining parameters as necessary will also contribute to better outcomes. Engaging with experienced machinists who understand the nuances of working with GRN can provide additional insights and best practices tailored to the specific production environment.
Scenario 3: Managing Moisture Absorption and Environmental Factors
The Problem: One common concern among B2B buyers is the hygroscopic nature of nylon materials, including glass reinforced nylon. As GRN absorbs moisture from the environment, it can lead to dimensional instability and compromised mechanical properties, particularly in humid regions such as parts of South America and Africa. This can result in product failures or inconsistencies in quality, which are unacceptable in high-stakes industries like medical devices or industrial equipment.
The Solution: To mitigate moisture-related issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing GRN that has been specifically treated to resist moisture absorption, such as using nylon variants with reduced hygroscopic properties. Additionally, implementing proper storage protocols—such as keeping materials in climate-controlled environments—can help maintain material integrity. Buyers can also explore coatings or treatments that enhance moisture resistance for finished components, ensuring long-term performance. Lastly, conducting regular environmental assessments can help predict and adapt to changes that may impact material behavior, allowing companies to proactively manage quality control in their production lines.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for glass reinforced nylon
What Are the Key Properties of Common Glass Reinforced Nylon Materials?
Glass reinforced nylon (GRN) is a versatile material that combines the favorable properties of nylon with the added strength and stiffness provided by glass fibers. When selecting GRN for specific applications, it is essential to consider the various formulations available, each with unique properties and performance characteristics.
1. Nylon 6/6 with 30% Glass Fiber
Key Properties: Nylon 6/6 with 30% glass fiber offers excellent tensile strength, rigidity, and thermal stability. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and has low thermal expansion, making it suitable for precision applications.
Pros & Cons: This formulation provides high mechanical strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for parts subjected to static loads and friction. However, it is more expensive than standard nylon and can be prone to brittleness under certain conditions, which may limit its use in dynamic applications.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly effective in automotive and industrial applications where high strength and temperature resistance are required. Its compatibility with various media, including oils and fuels, enhances its usability in diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and ISO. The higher cost may also necessitate a thorough cost-benefit analysis, especially for large-scale applications.
2. Nylon 6 with 40% Glass Fiber
Key Properties: Nylon 6 reinforced with 40% glass fiber exhibits superior stiffness and heat deflection temperatures, making it suitable for applications requiring enhanced dimensional stability.
Pros & Cons: The increased glass content significantly improves wear resistance and fatigue strength. However, the material is heavier and can lead to increased tool wear during machining processes, which may complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application: This variant is well-suited for structural components in machinery and automotive parts, where dimensional stability under load is critical. Its weight may be a consideration in applications where minimizing mass is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the material’s heavier weight and potential impact on shipping costs. Understanding local machining capabilities is crucial, as the abrasive nature of the glass fibers can affect tooling choices.
3. Nylon 6/12 with 33% Glass Fiber
Key Properties: Nylon 6/12 with 33% glass fiber offers a balance between strength and flexibility, with good chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption compared to other nylon variants.
Pros & Cons: This formulation provides excellent dimensional stability and is less prone to warping, making it suitable for applications in humid environments. However, it may not achieve the same level of tensile strength as Nylon 6/6 variants.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications in the agricultural and food processing industries, where moisture resistance is crucial. Its chemical resistance also makes it suitable for exposure to various cleaning agents.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety regulations is essential for buyers in the food processing sector. Additionally, understanding the local climate conditions can inform the choice of material based on moisture exposure.
4. Nylon 66 with 20% Glass Fiber
Key Properties: This formulation provides moderate strength and stiffness, with improved wear resistance compared to unfilled nylon. It can operate effectively in moderate temperature ranges.
Pros & Cons: The lower glass content results in a more cost-effective solution, making it attractive for applications with budget constraints. However, it may not perform as well under high-stress conditions compared to higher glass content variants.
Impact on Application: Suitable for general-purpose applications, including consumer goods and electrical housings, where high strength is not the primary requirement.
Considerations for International Buyers: This material’s lower cost can be appealing for manufacturers in developing regions. However, buyers should be aware of the potential trade-offs in performance, especially in high-stress environments.
Summary Table of Glass Reinforced Nylon Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for glass reinforced nylon | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6/6 with 30% Glass Fiber | Automotive and industrial components | High strength and thermal stability | Higher cost and brittleness | High |
| Nylon 6 with 40% Glass Fiber | Structural components in machinery | Superior stiffness and wear resistance | Increased tool wear during machining | High |
| Nylon 6/12 with 33% Glass Fiber | Agricultural and food processing parts | Good moisture resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Nylon 66 with 20% Glass Fiber | General-purpose consumer goods | Cost-effective solution | Moderate performance under stress | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for glass reinforced nylon
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Glass Reinforced Nylon?
The manufacturing of glass reinforced nylon involves several critical stages that ensure the material achieves its desired mechanical properties. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Glass Reinforced Nylon?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality nylon resin and glass fibers, which are essential for achieving optimal performance. The glass fibers can be introduced into the nylon matrix in two primary ways: either by adding powdered glass to the nylon resin or by extruding the nylon with glass fibers. The proportion of glass fibers typically ranges from 13% to 40%, depending on the intended application and required mechanical properties.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo a mixing process to ensure uniform distribution of the glass fibers within the nylon. This is critical as it affects the final strength, stiffness, and thermal properties of the composite material.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Glass Reinforced Nylon Production?
After material preparation, the next phase is forming, which can be achieved through various techniques, including injection molding, extrusion, and 3D printing.
-
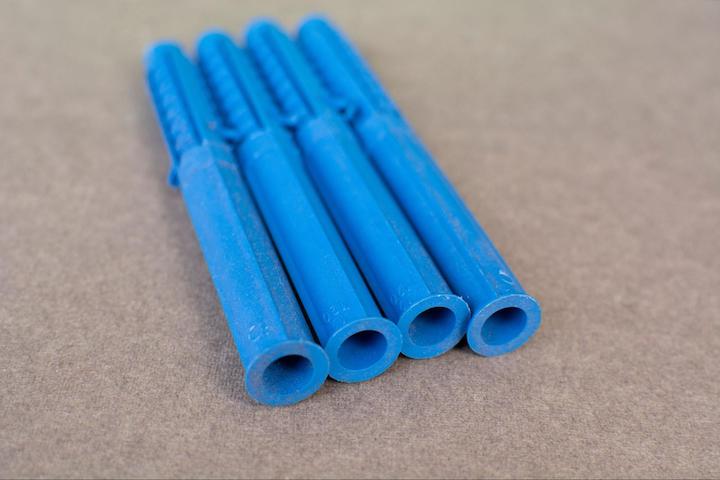
Injection Molding: This is one of the most common methods used for producing glass reinforced nylon parts. The prepared material is heated until it becomes molten and then injected into a mold. This process allows for high-volume production and complex geometries, making it suitable for a wide array of applications from automotive components to consumer goods.
-
Extrusion: In this process, the mixed nylon and glass fibers are forced through a die to create continuous shapes, such as rods and sheets. Extruded products are often used in structural applications where length and consistency are critical.
-
3D Printing: With advancements in additive manufacturing, glass reinforced nylon can also be produced using techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Multi Jet Fusion (MJF). This method is particularly advantageous for prototyping and low-volume production, offering flexibility in design and customization.
What Are the Finishing Steps in Glass Reinforced Nylon Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of glass reinforced nylon products. Typical finishing steps include machining, surface treatment, and quality checks. Machining may involve CNC operations to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. Surface treatments can improve aesthetics and increase resistance to environmental factors, such as UV light and moisture.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Glass Reinforced Nylon?
Quality assurance is paramount in ensuring that glass reinforced nylon products meet international standards and customer expectations. Several key measures and standards guide the quality assurance process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International quality standards, such as ISO 9001, are essential for manufacturers to demonstrate their commitment to quality management systems. For specialized applications, additional industry-specific certifications may be relevant, including CE marking for compliance with EU regulations and API standards for oil and gas applications.
Adherence to these standards not only assures product quality but also facilitates market entry in various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is typically structured into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. For glass reinforced nylon, this may include assessing the quality of nylon resin and glass fibers.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing checks are performed to monitor the production process. This can include monitoring temperature and pressure during injection molding or extrusion to ensure consistency and prevent defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify that they meet all specifications. This may involve mechanical testing, dimensional checks, and surface inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in diverse regions like Africa, South America, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their quality management practices and adherence to international standards. This can include reviewing their quality control documentation, processes, and facilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC. This transparency allows buyers to assess the reliability and consistency of the products.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an independent verification of product quality. This is particularly valuable when sourcing from new or unfamiliar suppliers, as it provides an added layer of assurance.
What Testing Methods Are Common for Glass Reinforced Nylon?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the mechanical properties and durability of glass reinforced nylon. Common tests include:
-
Tensile Testing: This assesses the material’s strength and elasticity by measuring how much it stretches under tension.
-
Impact Testing: This evaluates the toughness of the material, determining how well it can withstand sudden forces.
-
Thermal Analysis: Techniques like Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) measure the material’s thermal properties, crucial for applications involving temperature fluctuations.
-
Dimensional Stability Tests: These tests evaluate how well the material maintains its shape and size under varying environmental conditions, which is particularly important for applications in humid or extreme climates.
Conclusion: Why Is Quality Assurance Integral for International B2B Buyers?
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, particularly for materials like glass reinforced nylon, rigorous quality assurance processes are indispensable. For B2B buyers, understanding these manufacturing and quality control intricacies not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also ensures the procurement of high-performance materials that meet international standards. By prioritizing quality, businesses can enhance their product offerings and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘glass reinforced nylon’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing glass reinforced nylon, this guide provides a step-by-step checklist. By following these actionable steps, you will ensure that you select the right material and supplier for your needs, optimizing your procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating any procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements for glass reinforced nylon. This includes factors such as tensile strength, thermal resistance, and specific application needs. Understanding these parameters will help you identify suitable material grades and ensure compatibility with your intended use.
- Considerations:
- Determine the percentage of glass fill required (e.g., 30% vs. 40%).
- Assess the environment in which the material will be used (e.g., exposure to chemicals, temperature variations).
Step 2: Research Material Properties
Familiarize yourself with the different properties of glass reinforced nylon compared to standard nylon. Glass reinforcement enhances strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability, but it also introduces challenges such as brittleness and increased weight.
- Key Properties to Review:
- Creep resistance and dimensional stability.
- Abrasiveness and its effect on machining processes.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers to ensure they can meet your technical specifications and provide reliable products. Request detailed company profiles, product datasheets, and customer references to gauge their credibility.
- What to Look For:
- Experience in supplying glass reinforced nylon for similar applications.
- Certifications that validate their quality control processes (e.g., ISO 9001).
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the glass reinforced nylon from shortlisted suppliers. Testing samples in your specific application will provide insights into performance and compatibility.
- Testing Considerations:
- Conduct tests for mechanical properties, thermal resistance, and wear characteristics.
- Evaluate how the material performs under operational stresses similar to those it will face.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have evaluated the suppliers and tested samples, compare pricing structures, minimum order quantities, and payment terms. This analysis should also consider the long-term value of the material based on its properties and expected lifespan.
- Pricing Factors:
- Be wary of significantly lower prices, as they may indicate inferior quality.
- Consider logistics costs, especially for international shipping.
Step 6: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the selected supplier complies with relevant industry standards and regulations. This is particularly important when sourcing materials for specific applications such as automotive or medical devices.
- Compliance Checks:
- Request documentation proving compliance with safety and environmental standards.
- Confirm that materials meet any regional regulations applicable to your market.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Channel
Establishing effective communication with your chosen supplier is vital for a smooth procurement process. Make sure that there are designated points of contact for technical support, order updates, and issue resolution.
- Communication Best Practices:
- Set regular check-ins throughout the procurement process.
- Utilize project management tools to track progress and address any concerns promptly.
By following this comprehensive sourcing checklist, you will be well-equipped to make informed decisions when procuring glass reinforced nylon, ensuring that you select a material and supplier that align with your business needs and operational demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for glass reinforced nylon Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Glass Reinforced Nylon?
When sourcing glass reinforced nylon, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary components influencing the total cost include:
-
Materials: The base nylon resin and glass fibers are significant contributors to the overall cost. The percentage of glass fiber used directly affects the strength and rigidity of the final product, and higher glass content typically leads to increased material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Machining glass-filled nylon requires skilled labor due to its abrasiveness, which can increase labor costs compared to standard nylon.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, maintenance, and other indirect costs associated with production. Given the specialized equipment needed for processing glass-filled nylon, overhead can be a considerable factor.
-
Tooling: The abrasiveness of glass-filled nylon can lead to faster wear on cutting tools, necessitating more frequent replacements. Therefore, tooling costs should be factored into the overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the produced parts meet the required specifications incurs costs related to testing and inspection. This is particularly crucial for applications requiring high precision and reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the weight and volume of the products, as well as the distance to the buyer’s location. International shipping, especially to regions like Africa and South America, may involve higher logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin based on their operational costs, market demand, and competition. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers gauge fair pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Glass Reinforced Nylon?
Several factors can influence the pricing of glass reinforced nylon:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders typically reduce the per-unit cost due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom orders tailored to specific applications can increase costs. Buyers should be clear about their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The quality and type of raw materials used can impact pricing. For instance, nylon with a higher percentage of glass fibers will cost more but provide superior performance.
-
Quality and Certifications: Certifications that guarantee material properties (e.g., ISO standards) can increase costs but are essential for applications in regulated industries.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can affect the final cost. Buyers should understand Incoterms to anticipate additional charges that may arise during shipping.
What Tips Can Help International B2B Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies to optimize their procurement:
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Leverage larger order quantities to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers are often willing to reduce prices for bulk purchases.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, replacement, and logistics costs over the product’s life cycle. This approach can highlight more cost-effective options.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional market conditions and currency fluctuations. Prices may vary significantly based on local demand and supply dynamics.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Comparing quotes from multiple suppliers can provide insights into competitive pricing and help in negotiations.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms, loyalty discounts, and priority in production scheduling.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices for glass reinforced nylon materials and components can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain updated quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing glass reinforced nylon With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Glass Reinforced Nylon
When considering materials for engineering applications, glass reinforced nylon (GRN) often stands out due to its strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate alternatives that may better suit specific project requirements in terms of performance, cost, and application. This analysis will compare GRN with two viable alternatives: carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) and aluminum alloys.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Glass Reinforced Nylon | Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) | Aluminum Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength, good fatigue resistance, but brittle under stress. | Superior strength-to-weight ratio, excellent fatigue resistance, and stiffness. | Good strength and ductility, can corrode under certain conditions. |
| Cost | Moderate to high cost due to manufacturing complexity. | Higher cost due to raw materials and production processes. | Generally lower cost, widely available. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized machining due to abrasiveness. | Complex fabrication and design processes; requires expertise. | Relatively easy to work with using standard machining methods. |
| Maintenance | Resistant to wear but can be affected by moisture. | Requires careful handling; excellent durability but can be costly to repair. | Low maintenance; however, susceptible to corrosion without proper treatment. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-load applications in automotive and electrical industries. | Best suited for aerospace, automotive, and high-performance sports equipment. | Commonly used in structural applications across various industries. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP)?
CFRP is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred choice in high-performance applications like aerospace and automotive sectors. Its stiffness and fatigue resistance outperform that of glass reinforced nylon. However, the production costs of CFRP are significantly higher due to the complexity of manufacturing and material sourcing. Additionally, the fabrication process can be intricate and requires specialized knowledge, making it less accessible for some manufacturers.
How Do Aluminum Alloys Compare to Glass Reinforced Nylon?
Aluminum alloys are widely used due to their lower cost and availability. They provide good strength and ductility, making them suitable for various structural applications. Unlike GRN, aluminum can corrode if not adequately treated, which can be a disadvantage in certain environments. However, aluminum is easier to machine and fabricate using standard methods, reducing overall implementation time and costs. While GRN excels in high-load scenarios, aluminum is often the go-to for applications requiring lightweight and cost-effective solutions.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the appropriate material for a project hinges on specific requirements, including performance expectations, budget constraints, and application context. For applications demanding high strength and thermal stability, glass reinforced nylon remains a strong contender. However, if weight reduction is paramount, carbon fiber reinforced polymer might be the best choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, aluminum alloys serve as a practical alternative for those prioritizing cost-effectiveness and ease of machining. By carefully assessing these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and project goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for glass reinforced nylon
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Glass Reinforced Nylon?
Glass reinforced nylon (GRN) is a specialized material that combines nylon with glass fibers, enhancing its mechanical properties and making it suitable for demanding applications. Understanding its critical specifications is vital for B2B buyers looking to optimize their products and manufacturing processes.
-
Material Grade
Material grades of glass reinforced nylon, such as Nylon 6/6 or Nylon 12, denote the specific type of nylon used and the percentage of glass reinforcement (commonly 30% or 40%). These grades affect the overall performance, including tensile strength and thermal stability. For buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the final product meets specific mechanical and thermal performance requirements. -
Tensile Strength
This property measures the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. Glass reinforced nylon typically exhibits significantly higher tensile strength compared to standard nylon, making it ideal for applications subjected to high static loads. For B2B buyers, understanding tensile strength is crucial when designing components that require durability and reliability under stress. -
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
The heat deflection temperature indicates the temperature at which a material deforms under a specified load. GRN’s HDT is notably higher than that of standard nylon, allowing it to maintain structural integrity in elevated temperature environments. Buyers must consider HDT for applications in automotive, electrical, and industrial settings where heat resistance is a critical factor. -
Creep Resistance
Creep resistance refers to a material’s ability to resist deformation under a constant load over time. Glass reinforced nylon has improved creep resistance compared to unfilled nylon, which is essential for components that will be under continuous load. For manufacturers, this property is vital to ensure long-term performance and minimize maintenance costs. -
Dimensional Stability
This property describes how well a material maintains its dimensions when subjected to temperature changes and moisture absorption. GRN’s lower thermal expansion rate and improved stability make it suitable for precision applications. Buyers should prioritize dimensional stability to avoid costly reworks and ensure product consistency. -
Wear Resistance
Glass reinforced nylon offers superior wear resistance due to the abrasive nature of the glass fibers. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications involving friction and wear, such as gears and bearings. Understanding wear resistance helps buyers select materials that prolong the lifespan of components and reduce downtime.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Glass Reinforced Nylon?
Navigating the world of materials procurement requires familiarity with specific industry jargon. Here are some essential terms related to glass reinforced nylon:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of GRN, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality components tailored to specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and production planning. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their production needs and budget constraints. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For buyers of glass reinforced nylon, issuing RFQs can help compare costs and lead times from different suppliers, ultimately aiding in making informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they determine shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost allocations, ensuring clarity in contracts. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead times for glass reinforced nylon products is essential for effective supply chain management and project planning. Buyers should factor in lead times to ensure timely delivery and avoid production delays. -
Tolerances
Tolerances define the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension. In glass reinforced nylon applications, understanding tolerances is critical for ensuring that components fit correctly and function as intended. Buyers must communicate specific tolerance requirements to manufacturers to achieve optimal results.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing glass reinforced nylon, ultimately enhancing their product offerings and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the glass reinforced nylon Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Glass Reinforced Nylon Sector?
The global market for glass reinforced nylon is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Notably, the surge in lightweight materials for fuel efficiency and performance enhancement is pushing manufacturers towards glass-filled nylon, which offers superior strength and thermal stability. Key trends include the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing and CNC machining, enabling customized solutions that meet specific industry requirements. Moreover, the rise of automation and smart manufacturing is streamlining sourcing processes, allowing international B2B buyers to optimize their supply chains effectively.
In regions like Africa and South America, where industrial growth is accelerating, there is a notable push towards adopting innovative materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Meanwhile, European markets are focusing on sustainability and compliance with stringent regulations, emphasizing the need for high-quality, durable materials. As global supply chains adapt to meet these diverse demands, strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers become crucial for businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainable and Ethical Sourcing of Glass Reinforced Nylon?
As environmental concerns gain prominence, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability in their sourcing strategies. The production of glass reinforced nylon can have significant environmental impacts, including energy consumption and waste generation. Therefore, companies are urged to evaluate their suppliers based on sustainability practices and certifications, such as ISO 14001, which indicates a commitment to effective environmental management.
Furthermore, the concept of ethical sourcing is becoming integral to corporate responsibility. Buyers should seek suppliers who implement fair labor practices and ensure transparency in their supply chains. Incorporating ‘green’ materials, such as recycled glass fibers or bio-based nylons, can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of products. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals, international buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Evolution of Glass Reinforced Nylon and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
The development of glass reinforced nylon dates back to the mid-20th century, evolving from traditional nylon to enhance its mechanical properties. Initially used in niche applications, the material gained traction as industries recognized its benefits, such as increased strength, reduced weight, and improved thermal resistance. Over the decades, advancements in manufacturing techniques and material science have further expanded its applications.
For B2B buyers, understanding the historical context of glass reinforced nylon is essential, as it underscores the material’s reliability and versatility. This knowledge enables informed decision-making when selecting materials for diverse applications, ultimately ensuring that businesses can meet the evolving demands of their markets while leveraging the advantages that glass reinforced nylon offers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of glass reinforced nylon
-
How do I choose the right type of glass reinforced nylon for my application?
Selecting the appropriate glass reinforced nylon depends on several factors, including the required mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and intended application. Assess the tensile strength, stiffness, and temperature resistance needed for your project. For high-load applications, consider options with higher glass content. Additionally, evaluate how the material will perform in specific environments, such as exposure to moisture or chemicals. Collaborating with suppliers who can provide samples and technical data sheets can also help you make an informed decision. -
What are the key advantages of using glass reinforced nylon compared to other materials?
Glass reinforced nylon offers superior strength, stiffness, and thermal stability compared to standard nylon and many metals. It exhibits lower thermal expansion, high wear resistance, and excellent fatigue strength, making it suitable for demanding applications like automotive and industrial components. However, it is essential to consider its increased brittleness and weight, which might not be ideal for all projects. Evaluating these characteristics against your specific requirements will help determine if glass reinforced nylon is the right choice. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for glass reinforced nylon?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, reputation, and certifications. Look for companies that provide transparency in their manufacturing processes and offer detailed product specifications. Request samples to evaluate the material quality and performance before placing bulk orders. Additionally, consider the supplier’s ability to meet your customization needs, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and their logistics capabilities for international shipping. Establishing clear communication regarding lead times and potential delays is also crucial. -
What customization options are available for glass reinforced nylon products?
Many suppliers offer customization for glass reinforced nylon, including variations in glass content, color, and specific formulations tailored to unique applications. You can request modifications in dimensions, shapes, and mechanical properties to better fit your project requirements. It is advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and inquire about their capabilities in producing bespoke solutions. This can ensure that the final product aligns with your operational demands. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for glass reinforced nylon?
Minimum order quantities for glass reinforced nylon can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors like material type and customization. Generally, MOQs can range from a few kilograms for standard products to larger quantities for custom formulations. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time orders or smaller projects, while others may have strict requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing glass reinforced nylon internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include advance payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Discussing payment options upfront is crucial to ensure mutual agreement. Be aware of additional costs such as shipping, customs duties, and taxes that may affect the total expenditure. Establishing clear payment terms can help avoid misunderstandings and facilitate smoother transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing glass reinforced nylon?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Consider conducting third-party quality inspections or audits to verify compliance with industry standards. Additionally, ask for documentation on the material’s mechanical properties, environmental resistance, and any testing results. Establishing a clear QA process with your supplier can help maintain consistent product quality throughout your supply chain. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing glass reinforced nylon?
When importing glass reinforced nylon, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. It’s crucial to work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide reliable logistics support. Understanding the import duties and taxes applicable to your order can prevent unexpected costs. Proper documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is essential to facilitate smooth customs clearance and timely delivery.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Glass Reinforced Nylon Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Curbell Plastics – Glass-Filled Nylon Products
Domain: curbellplastics.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Glass-Filled Nylon products available in various sizes and lengths. Key specifications include:
– Diameter options: 0.25 in, 0.375 in, 0.5 in, 0.625 in, 0.75 in, 0.875 in, 1 in
– Length options: 5 ft, 10 ft
– Material: Natural, 30% Glass-Filled, Extruded
– Pricing: Ranges from $20.87 to $134.69 depending on size.
2. Europlas – Glass Filled Nylon
Domain: europlas.com.vn
Introduction: Glass Filled Nylon is a technical plastic made from Nylon compounds combined with glass fibers, enhancing strength, stiffness, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. It is also known as glass reinforced Nylon or glass fiber reinforced Nylon. Key properties include high tensile strength, high rigidity, high creep resistance, high thermal stability, low thermal expansion, good wear resistance, …
3. Ensinger – Glass Filled Polyamides (GF)
Domain: ensingerplastics.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Glass filled polyamides (GF) are high-performance engineering thermoplastics known for their very high rigidity, mechanical strength, hardness, toughness, and creep strength. They exhibit high dimensional stability, good fatigue strength, and high mechanical damping properties, making them suitable for parts exposed to high static loads in high-temperature conditions. However, due to the abrasive …
4. 3DXTech – FIBREX™ Nylon PA6+GF30
Domain: 3dxtech.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: FIBREX™ Nylon PA6+GF30
SKU: NYL05GF100750BK01
Regular price: $56.00
Benefits:
– Printable on practically any 3D printer with a heated bed
– Ideal for structural engineering-grade applications
– Exceptionally stiff and strong, without being brittle
– Excellent chemical resistance suitable for automotive and industrial applications
– Resists fuels, lubricants, heat, and mechanical loading
– High the…
5. MatterHackers – NylonG Glass Fiber Reinforced Filament
Domain: matterhackers.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: NylonG – Glass Fiber Reinforced Filament
– Available Colors: Black, Blue, Silver, Olive Green, White, Red, Safety Orange, Desert Tan
– Diameter Options: 1.75mm, 2.85mm
– Weight Options: 0.5kg, 3kg
– Price Range: $70.00 (0.5kg) to $329.00 (3kg)
– Features: Excellent impact resistance, high tensile strength, low warp, high dimensional accuracy, minimal post-processing required.
– Extruder Temperatur…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for glass reinforced nylon
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers Considering Glass Reinforced Nylon?
Incorporating glass reinforced nylon into your sourcing strategy offers significant advantages, including enhanced strength, thermal stability, and wear resistance. These properties make it an ideal choice for high-performance applications across diverse industries, from automotive to consumer goods. However, potential challenges such as higher costs, brittleness, and abrasive characteristics must be carefully evaluated to optimize your supply chain decisions.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain?
Strategic sourcing is vital for navigating the complexities associated with glass reinforced nylon. By partnering with reliable suppliers and understanding the material’s specific performance metrics, international buyers can mitigate risks and secure cost-effective solutions that meet their operational needs. Leveraging local and global resources can also foster innovation and improve supply chain resilience.
What Does the Future Hold for Glass Reinforced Nylon in Global Markets?
As demand for high-performance materials continues to rise, glass reinforced nylon is poised for growth in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize sustainability and technological advancements. By staying informed and strategically sourcing, you can position your business to capitalize on the evolving landscape of material technology. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your product offerings and drive competitive advantage in your market.