Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Glass Filled Nylon Properties
Material Performance Meets Precision Manufacturing Expertise
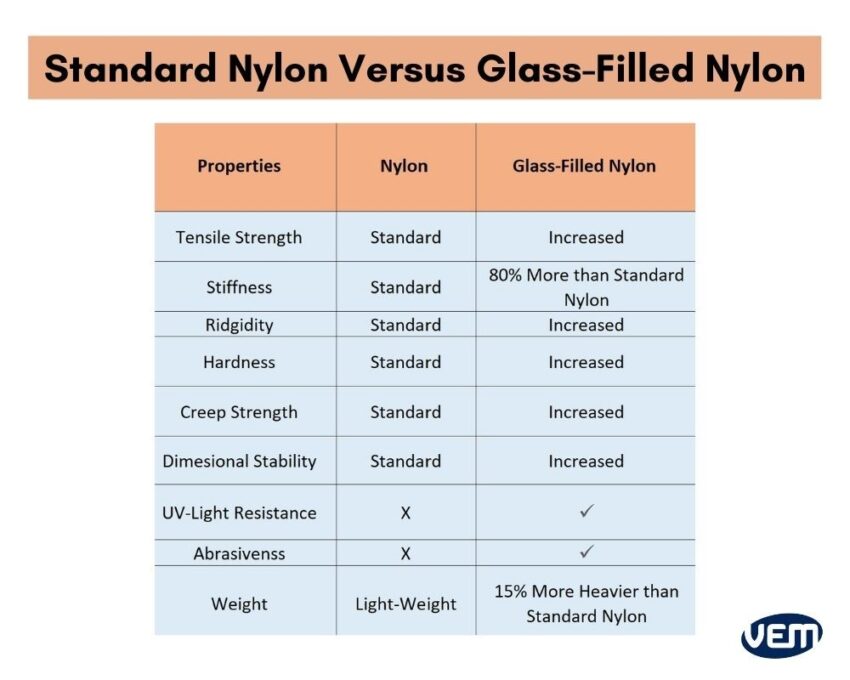
Selecting the optimal engineering polymer for functional prototypes demands careful evaluation of mechanical, thermal, and dimensional stability requirements. Glass-filled nylon—typically reinforced with 15–50% glass fiber—delivers exceptional stiffness, creep resistance, and thermal performance compared to unfilled variants, making it indispensable for high-stress applications like automotive under-hood components, industrial housings, and power tool assemblies. Its elevated tensile strength, reduced coefficient of thermal expansion, and improved wear characteristics address critical design challenges where standard nylons fall short. However, achieving tight tolerances in this abrasive material requires specialized CNC machining capabilities to mitigate fiber pull-out, tool wear, and surface finish inconsistencies.
Honyo Prototype’s CNC Machining Excellence for Demanding Polymers
At Honyo, we leverage purpose-built CNC protocols engineered specifically for glass-filled nylons such as PA6-GF30 and PA66-GF35. Our process integrates optimized cutting parameters, diamond-coated tooling, and controlled chip evacuation to maintain dimensional accuracy within ±0.05 mm while preserving material integrity. This expertise ensures components exhibit consistent mechanical behavior under load, critical for validation testing prior to injection molding. Below are key properties of a typical 30% glass-filled nylon grade and how our machining approach addresses associated challenges:
| Property | Value (PA6-GF30) | Honyo Machining Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 160–180 MPa | Precision toolpath sequencing to prevent fiber delamination |
| Heat Deflection Temp (1.8 MPa) | 210–230°C | Coolant management minimizing thermal distortion |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.35 (vs. steel) | Surface finish optimization to 0.8–1.6 μm Ra |
| Abrasiveness | High (accelerates tool wear) | Proprietary tooling alloys and real-time wear monitoring |
Accelerate Your Development Cycle with Seamless Quoting
When prototyping with glass-filled nylon, lead time predictability directly impacts your project timeline. Honyo’s Online Instant Quote platform provides validated manufacturability feedback and precise pricing within 60 seconds—factoring in material-specific machining complexity, geometric tolerances, and secondary operations. This eliminates traditional quotation bottlenecks, allowing engineering teams to iterate faster while ensuring the final prototype accurately reflects end-product performance. Trust Honyo’s material science expertise and precision CNC capabilities to transform your glass-filled nylon designs into functionally validated prototypes, ready for rigorous testing and production handoff.
Technical Capabilities

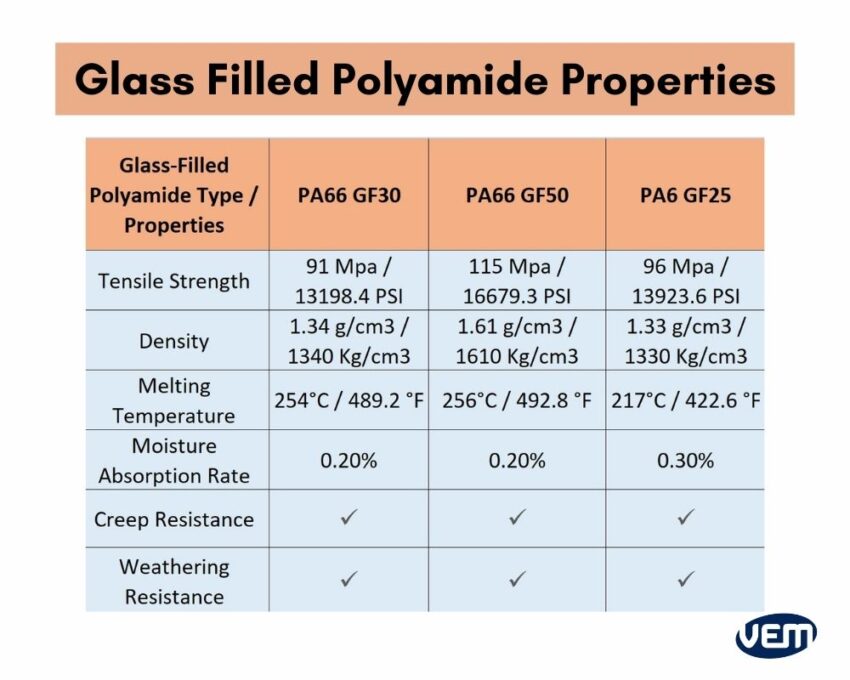
Glass filled nylon, typically referred to as glass-reinforced nylon (e.g., PA6-GF or PA66-GF), is an engineering thermoplastic incorporating 20–50% glass fibers by weight. This reinforcement significantly enhances mechanical strength, dimensional stability, creep resistance, and thermal performance compared to unfilled nylon. These characteristics make it suitable for precision machining operations such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling, as well as CNC turning, especially in applications requiring tight tolerances (±0.001″ to ±0.005″).
The material behaves differently than metals (e.g., aluminum, steel) or other plastics (e.g., ABS), requiring optimized toolpaths, cutting speeds, and fixturing to achieve high accuracy and surface finish. Glass fibers increase abrasive wear on cutting tools, necessitating the use of carbide or polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tooling. Additionally, low thermal conductivity requires effective chip evacuation to prevent heat buildup.
Below is a comparison of glass filled nylon with other commonly machined materials in the context of multi-axis milling and turning for tight tolerance components:
| Property / Material | Glass Filled Nylon (PA6/PA66 + 30% GF) | Aluminum (6061-T6) | Steel (1018) | ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | Nylon (Unfilled PA6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 130–150 | 310 | 440 | 40–45 | 70–85 |
| Flexural Modulus (GPa) | 6.0–7.5 | 69 | 200 | 2.0–2.4 | 2.5–3.0 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.36–1.40 | 2.70 | 7.85 | 1.04–1.06 | 1.13–1.15 |
| Thermal Expansion (µm/m·°C) | 20–30 | 23 | 12 | 80–100 | 80–100 |
| Max Continuous Use Temp (°C) | 150–180 | 120–150 | 400+ | 80–90 | 80–100 |
| Machinability Rating | Moderate (abrasive due to glass) | Excellent | Good | Good | Good |
| Tool Wear (Relative) | High (due to glass fibers) | Low | Medium | Low | Low |
| Typical Tolerance (± in) | 0.001–0.005 | 0.0005–0.002 | 0.0005–0.002 | 0.005–0.010 | 0.002–0.005 |
| Surface Finish (Ra, µm) | 1.6–3.2 (machined) | 0.8–1.6 | 0.8–1.6 | 3.2–6.3 | 1.6–3.2 |
| Recommended Tooling | Carbide, PCD | Carbide, HSS | Carbide | Carbide | Carbide |
| Fixturing Requirements | Moderate (low clamping force) | Moderate to High | High | Low | Low to Moderate |
| Moisture Absorption | 1.5–2.5% (saturated) | Negligible | Negligible | 0.2–0.4% | 6–9% |
Key Considerations for Machining Glass Filled Nylon:
Tool Selection: Use sharp, polished carbide end mills and turning tools with positive rake angles to reduce cutting forces. PCD tools are recommended for long production runs due to high abrasion resistance.
Cutting Parameters: Moderate speeds (600–1000 SFM) and feeds; avoid excessive heat buildup. Peck drilling and proper chip clearance are essential.
Tolerance Control: Dimensional stability is better than unfilled nylon but still affected by humidity. Post-machining conditioning (stabilization at controlled RH) may be required for critical parts.
Comparison to Alternatives:
Aluminum and steel offer higher precision and rigidity but are heavier and more costly to machine.
ABS is easier to machine but lacks strength and thermal performance.
Unfilled nylon is more prone to deformation and moisture absorption, making it less suitable for tight tolerance applications.
Glass filled nylon is ideal for structural, non-metallic components in aerospace, automotive, and industrial automation where weight savings, corrosion resistance, and mechanical performance are critical—provided machining parameters are carefully controlled.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype’s Process for Glass Filled Nylon Parts: CAD to Delivery
Our end-to-end workflow for glass filled nylon (typically 30% glass fiber reinforced PA6 or PA66) integrates material-specific engineering controls at every phase to ensure mechanical performance, dimensional stability, and functional reliability. Unlike standard nylons, glass filled variants exhibit higher stiffness, reduced creep, and improved thermal resistance but require precise handling due to anisotropic shrinkage, abrasive wear on tooling, and moisture sensitivity. Below is our rigorously validated process:
CAD Upload and Material Specification
Upon receiving your CAD model, our system immediately identifies glass filled nylon as the selected material. We require explicit confirmation of the grade (e.g., PA6-GF30, ULTEM™ GF9000) and critical properties (e.g., tensile strength ≥150 MPa, HDT ≥210°C). Missing specifications trigger an automated query to prevent downstream errors. Moisture content requirements (<0.2% pre-processing) are validated here, as hygroscopic behavior directly impacts print quality and final part integrity.
AI-Powered Quoting with Material Intelligence
Our AI engine cross-references your CAD geometry against a proprietary database of glass filled nylon behavior. It calculates:
Estimated warpage from fiber orientation effects
Minimum wall thickness feasibility (typically ≥1.5 mm to avoid sink marks)
Tooling wear factors for injection molding (if applicable)
Drying time/cost implications (4+ hours at 80°C)
Quotes include material-specific surcharges for specialized drying equipment and hardened tooling, with lead time adjustments for extended conditioning cycles. Real-time cost/performance trade-offs (e.g., 30% vs. 50% glass content) are presented for engineering review.
Material-Optimized DFM Analysis
Our DFM team conducts a dual-layer review focused on glass filled nylon’s unique constraints:
| DFM Checkpoint | Glass Filled Nylon Requirement | Risk if Ignored |
|---|---|---|
| Wall Thickness Variation | Max 15% differential across part | Severe warpage/cracking |
| Gate Location | Avoid thin sections; prioritize thick zones | Fiber jamming, weak weld lines |
| Draft Angles | ≥2° per side (vs. 1° for unfilled nylon) | Ejection scratches |
| Rib Design | Height ≤3x wall thickness; radiused bases | Stress concentration failure |
| Moisture Sensitivity | Mandate drying protocol in manufacturing notes | Bubbles, reduced strength |
The DFM report explicitly calls out adjustments needed to achieve target properties (e.g., “Increase rib radius to 0.8 mm to prevent 20% tensile strength loss at stress points”).
Production with Material-Specific Controls
All production parameters are locked to glass filled nylon standards:
Drying: Parts undergo 6 hours at 80°C in dehumidifying hoppers (monitored via dew point sensors)
Processing:
SLS/3D Printing: Layer adhesion optimized at 175–185°C bed temp; recoater speed reduced 20% to minimize fiber displacement
Injection Molding: Melt temp 275–290°C; mold temp 90–110°C to control crystallization; back pressure increased 15% to prevent fiber settling
In-Process Validation: Every 10th part undergoes CT scanning to verify fiber distribution homogeneity. Shrinkage is measured against anisotropic tolerance bands (±0.3% vs. ±0.15% for unfilled nylon).
Delivery with Certified Property Validation
Final parts ship with:
ASTM D638 tensile test report (showing achieved strength/modulus vs. datasheet)
Warpage analysis comparing as-built geometry to CAD (using GD&T-compliant CMM data)
Moisture content certification (<0.1% via Karl Fischer titration)
Vacuum-sealed packaging with desiccant and humidity indicator cards
All documentation includes traceability to your original CAD revision and a summary of how material-specific DFM adjustments preserved functional properties.
This closed-loop process ensures glass filled nylon parts meet structural requirements out-of-box, eliminating iterative redesign cycles. For mission-critical applications, we recommend our optional Accelerated Stress Validation service, which subjects prototypes to thermal cycling and load testing per your operational profile.
Start Your Project

Discover the exceptional mechanical strength and thermal stability of glass filled nylon for your next engineering project. Ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and dimensional accuracy.
Contact Susan Leo at [email protected] to discuss material specifications, prototyping, or production support. Our manufacturing facility is located in Shenzhen, ensuring rapid turnaround and strict quality control for both prototypes and volume manufacturing.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.