Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gd&t bonus tolerance
In today’s competitive global landscape, navigating the complexities of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) bonus tolerance can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Understanding how to effectively implement bonus tolerance strategies is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and ensuring product quality. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of GD&T bonus tolerance, encompassing its various types, real-world applications, and the essential considerations for selecting reliable suppliers.
We delve into the intricacies of Maximum Material Condition (MMC) and Least Material Condition (LMC), illustrating how these concepts can enhance production efficiency and reduce costs. Additionally, we provide insights on how to assess supplier capabilities, ensuring that your sourcing decisions align with your organization’s quality standards and operational goals.
By empowering B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Brazil and Germany—this guide serves as a valuable resource for making informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to improve your quality control processes or seeking to enhance your product specifications, our expert analysis and actionable recommendations will equip you with the knowledge necessary to thrive in the global market. Prepare to transform your approach to GD&T bonus tolerance and drive your business forward.
Understanding gd&t bonus tolerance Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Bonus Tolerance | Tolerance increases as feature size moves away from MMC. | Automotive, Aerospace, Machinery | Pros: Enhances manufacturing flexibility. Cons: Complexity in measurement may increase. |
| Feature-Specific Bonus | Tailored to specific features (pins, holes) with unique MMC. | Precision Engineering, Medical Devices | Pros: Optimizes fit for unique applications. Cons: May require specialized tools for verification. |
| Composite Bonus | Combines multiple tolerances into a single bonus structure. | Heavy Equipment, Construction | Pros: Streamlines tolerance management. Cons: Requires careful planning and design considerations. |
| Virtual Condition Bonus | Considers both MMC and additional geometric tolerances. | Aerospace, Defense | Pros: Provides comprehensive control over part functionality. Cons: Can complicate design specifications. |
| Dynamic Bonus Tolerance | Adjusts based on real-time manufacturing variations. | High-Volume Production, Electronics | Pros: Increases adaptability in production. Cons: May introduce variability that complicates quality control. |
What Are the Characteristics of Basic Bonus Tolerance in GD&T?
Basic Bonus Tolerance is a foundational concept in GD&T that allows for an increase in positional tolerance as the size of a feature moves away from its Maximum Material Condition (MMC). This type is particularly applicable in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precise fit and function are critical. Buyers should consider that while this approach enhances manufacturing flexibility, it may also complicate measurement processes, necessitating more sophisticated tools and training.
How Does Feature-Specific Bonus Tolerance Enhance Precision?
Feature-Specific Bonus Tolerance is designed to cater to individual features such as pins or holes, each having its own MMC. This specificity is vital in precision engineering and medical device manufacturing, where the fit of components can significantly impact performance and safety. While this type offers tailored optimization for unique applications, buyers must be aware that it may require specialized verification tools, potentially increasing costs.
What Are the Benefits of Composite Bonus Tolerance?
Composite Bonus Tolerance integrates multiple tolerances into a single structure, simplifying the management of complex parts. This is especially beneficial in heavy equipment and construction industries, where components often require various tolerances for different features. The primary advantage is streamlined tolerance management, but it requires careful planning and design to ensure all aspects are addressed effectively, which can be a challenge for some buyers.
How Does Virtual Condition Bonus Provide Comprehensive Control?
Virtual Condition Bonus incorporates both MMC and additional geometric tolerances, offering a more holistic approach to part functionality. This type is crucial in aerospace and defense sectors, where the reliability of components is non-negotiable. While it allows for greater control, buyers should be mindful that it can complicate design specifications, requiring thorough understanding and communication among design, manufacturing, and quality assurance teams.
What Is the Role of Dynamic Bonus Tolerance in High-Volume Production?
Dynamic Bonus Tolerance adjusts based on real-time variations during manufacturing, making it particularly suitable for high-volume production environments such as electronics. This adaptability can significantly enhance production efficiency and responsiveness to changing conditions. However, buyers should consider that while it increases flexibility, it may introduce variability that complicates quality control processes, necessitating robust monitoring systems to maintain standards.
Key Industrial Applications of gd&t bonus tolerance
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gd&t bonus tolerance | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Ensuring precise assembly of aircraft components | Enhanced safety and reliability in flight | Certifications for aerospace standards, material quality assurance |
| Automotive | Optimizing fit and function of engine parts | Improved performance and reduced manufacturing costs | Supplier capability to meet stringent tolerances, lead times |
| Heavy Machinery | Manufacturing hydraulic systems with precise alignment | Increased durability and operational efficiency | Robust quality control processes, availability of advanced measurement tools |
| Electronics | Assembling circuit boards with varying component sizes | Higher yield rates and reduced rework costs | Supplier experience with GD&T in electronics, flexibility in production |
| Medical Devices | Fabricating implants and surgical tools with tight tolerances | Enhanced patient safety and product efficacy | Compliance with medical regulations, traceability of materials |
How is GD&T Bonus Tolerance Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, GD&T bonus tolerance is crucial for ensuring the precise assembly of components like fuselage sections and wing structures. By allowing additional positional tolerances based on the size of features, manufacturers can accommodate variances in part dimensions while maintaining the integrity of assembly. This flexibility results in improved safety and reliability, which are paramount in aviation. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with certifications that meet aerospace standards and demonstrate robust material quality assurance.
What Role Does GD&T Bonus Tolerance Play in the Automotive Sector?
In automotive manufacturing, GD&T bonus tolerance is applied to optimize the fit and function of engine parts and other critical components. As parts are often produced in high volumes, the ability to adjust tolerances based on the maximum material condition can lead to significant cost savings and improved performance. This adjustment helps manufacturers reduce rework and scrap rates. Buyers in this sector should consider suppliers’ capabilities to meet stringent tolerances and their ability to deliver on time, which is crucial for maintaining production schedules.
Why is GD&T Bonus Tolerance Important for Heavy Machinery?
Heavy machinery manufacturers utilize GD&T bonus tolerance to ensure the precise alignment of hydraulic systems and other critical assemblies. This practice enhances the durability and operational efficiency of the machinery, which is essential for performance in demanding environments. For international B2B buyers, sourcing from suppliers with robust quality control processes and advanced measurement tools can significantly mitigate risks associated with dimensional inaccuracies and improve product reliability.
How Does GD&T Bonus Tolerance Benefit the Electronics Industry?
In the electronics industry, GD&T bonus tolerance is vital for assembling circuit boards where components vary in size. The added tolerance allows for greater flexibility in production, leading to higher yield rates and reduced rework costs. For buyers, selecting suppliers experienced in applying GD&T principles in electronics manufacturing is crucial, as this expertise can lead to better product performance and reliability in the final assembly.
What Advantages Does GD&T Bonus Tolerance Offer in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device sector, GD&T bonus tolerance is used to fabricate implants and surgical tools with tight tolerances, directly impacting patient safety and product efficacy. By allowing for variations in size while maintaining the necessary fit and function, manufacturers can enhance the overall quality of their products. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with medical regulations and have a reliable traceability system for materials used in their devices, ensuring the highest standards of safety and efficacy are met.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gd&t bonus tolerance’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding Bonus Tolerance Implications
The Problem: A manufacturer in Brazil faces significant issues due to misunderstandings about the application of bonus tolerances in their production processes. When engineering teams specify tolerances without a clear understanding of how bonus tolerances work, it leads to parts being manufactured at Maximum Material Condition (MMC) without considering the resulting positional deviations. This results in misalignments during assembly, increased scrap rates, and delays in production, ultimately affecting the company’s bottom line.
The Solution: To address this issue, it is essential for engineering teams to undergo training on GD&T principles, specifically focusing on bonus tolerances. Companies should invest in workshops or online courses that illustrate real-world applications and the implications of these tolerances in production. Additionally, implementing a standardized procedure for specifying GD&T on engineering drawings can ensure that all team members understand how to calculate and apply bonus tolerances effectively. Using 3D modeling software that visualizes these tolerances can also enhance understanding and prevent future errors.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Interpretation Across Teams
The Problem: A European aerospace company struggles with inconsistencies in interpreting GD&T bonus tolerances among different departments, leading to confusion and errors in production. Design engineers and quality control inspectors often have varying levels of expertise in GD&T, resulting in discrepancies in how tolerances are applied and measured. This misalignment not only affects the quality of the products but also complicates communication between teams, ultimately impacting project timelines.
The Solution: Establishing a cross-functional GD&T task force can help unify the interpretation of bonus tolerances across departments. This team should include representatives from design, production, and quality assurance, allowing for collaborative discussions on GD&T standards and practices. Additionally, creating a comprehensive GD&T guide that outlines definitions, examples, and best practices tailored to the company’s specific needs can serve as a reference tool for all employees. Regular training sessions should be scheduled to keep teams updated on GD&T standards and to encourage a culture of continuous learning.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Accurate Measurements
The Problem: A South American automotive parts supplier is experiencing challenges in sourcing accurate measurements for components that utilize bonus tolerances. The reliance on outdated measurement techniques leads to inaccurate data, resulting in parts that do not meet the required specifications. This not only increases the risk of product failures but also damages the supplier’s reputation with clients who demand high-quality components.
The Solution: To combat this issue, the supplier should invest in modern measurement technologies, such as 3D scanning and computer-aided inspection tools that can accurately capture the dimensions of parts in relation to bonus tolerances. Training staff on how to effectively use these tools is crucial for ensuring that measurements are taken correctly. Additionally, establishing partnerships with certified metrology service providers can offer external validation of measurements, providing an extra layer of assurance for quality control. Implementing a robust quality management system that tracks measurements and tolerances in real-time will further enhance the supplier’s ability to deliver reliable and precise components.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gd&t bonus tolerance
How Do Common Materials Affect GD&T Bonus Tolerance in B2B Applications?
When selecting materials for applications involving GD&T bonus tolerance, it is crucial to consider the properties and characteristics that influence product performance and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in various industries, discussing their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in GD&T Bonus Tolerance Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C, making it suitable for various applications. Its relatively low density and high strength-to-weight ratio make it an attractive option for industries like automotive and aerospace.
Pros: Aluminum offers good machinability, leading to lower manufacturing complexity. Its lightweight nature can reduce shipping costs and improve energy efficiency in applications.
Cons: While durable, aluminum may not withstand extreme temperatures or high-pressure environments as well as some other metals. Additionally, it can be more expensive than some alternatives, which may affect overall project budgets.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals, such as marine environments. However, it may require additional coatings for enhanced protection in harsher conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B221 and DIN 1725. In regions like Europe and South America, aluminum alloys are commonly used, so understanding local preferences and specifications is essential.
How Does Steel Compare for GD&T Bonus Tolerance Applications?
Steel is renowned for its strength and durability, with a wide range of grades available to suit various applications. It can handle high temperatures (up to 600°C) and pressures, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications in industries such as construction and manufacturing.
Pros: Steel’s high tensile strength allows for thinner designs without compromising structural integrity. It is also widely available and generally more cost-effective than aluminum.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings or treatments, which can complicate manufacturing processes. Additionally, its weight can increase shipping costs.
Impact on Application: Steel’s robustness makes it suitable for load-bearing applications, but its susceptibility to rust in humid environments must be addressed, especially in regions with high moisture levels.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A36 and DIN 17100 is vital. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should also consider local environmental conditions that may affect steel performance.
What Advantages Does Plastic Offer for GD&T Bonus Tolerance?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics like polycarbonate and nylon, are lightweight and offer good chemical resistance. They can typically withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C, making them versatile for various applications.
Pros: Plastics are often less expensive than metals and can be molded into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing complexity. They are also resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making them suitable for diverse environments.
Cons: Plastics may not provide the same level of strength as metals, limiting their use in load-bearing applications. They can also be susceptible to UV degradation unless treated.
Impact on Application: The chemical resistance of plastics makes them ideal for applications in the automotive and consumer goods sectors, where exposure to various substances is common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM D638 and ISO 527. In regions like Brazil, where plastic components are prevalent, understanding local regulations regarding material properties is essential.
How Does Titanium Stand Out for GD&T Bonus Tolerance?
Titanium is a high-performance metal known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C, making it suitable for aerospace and high-performance applications.
Pros: Titanium’s durability and lightweight characteristics make it ideal for applications where strength and weight are critical. Its biocompatibility also makes it suitable for medical applications.
Cons: The primary drawback of titanium is its high cost and manufacturing complexity, which can limit its use in cost-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Titanium is often used in aerospace and medical devices, where performance and reliability are paramount. Its corrosion resistance allows it to perform well in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM F136 and ISO 5832 is crucial for titanium applications. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the specific regulations governing the use of titanium in their industries.
Summary Table of Material Selection for GD&T Bonus Tolerance
| Material | Typical Use Case for gd&t bonus tolerance | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Steel | Structural beams | High strength and cost-effective | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic | Consumer goods and automotive parts | Low cost and complex shapes | Lower strength compared to metals | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for GD&T bonus tolerance applications, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gd&t bonus tolerance
What are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for GD&T Bonus Tolerance?
Understanding the manufacturing processes associated with GD&T bonus tolerance is essential for B2B buyers. The production of components that utilize GD&T principles involves several key stages, each contributing to the overall quality and precision of the final product.
How Does Material Preparation Impact GD&T?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves selecting the appropriate raw materials that meet the specifications required for the final product. This stage may include processes such as cutting, machining, and heat treatment to ensure that the material properties align with design requirements. For GD&T applications, particularly those involving bonus tolerances, it’s crucial that the material is consistently sized and shaped according to the Maximum Material Condition (MMC). This adherence ensures that subsequent manufacturing processes can maintain the tolerances necessary for proper assembly and function.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming. This can include processes such as casting, forging, or machining, depending on the component design. For example, CNC machining is often used for precision parts, allowing manufacturers to achieve tight tolerances that are critical in GD&T applications. During this phase, it’s vital to monitor the dimensions closely, as any deviation can affect the bonus tolerance calculations. Techniques such as laser cutting or waterjet cutting can also be employed to enhance precision and reduce material wastage.
How Important is the Assembly Process in GD&T?
The assembly stage is where various components come together, and the importance of GD&T becomes apparent. Proper assembly ensures that parts fit together as intended, which is particularly important when working with bonus tolerances. The assembly process should incorporate checks to verify that components are within the specified tolerances. This might involve the use of alignment tools and fixtures to maintain the correct positioning of parts during assembly. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers have robust assembly procedures that account for GD&T specifications, including the consideration of MMC and Least Material Condition (LMC) throughout the assembly process.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance Quality Assurance?
Finishing processes, such as grinding, polishing, and coating, are crucial for achieving the desired surface quality and dimensional accuracy. These processes can also impact the final tolerances, making it essential to incorporate GD&T principles into finishing operations. Techniques like surface treatment can enhance durability and performance, especially in applications where components are subject to wear and tear. B2B buyers should inquire about the finishing processes their suppliers employ to ensure they align with the quality standards necessary for GD&T applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Necessary for GD&T?
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring that manufactured parts meet the stringent requirements of GD&T, particularly when it comes to bonus tolerance. Implementing a comprehensive quality control system is essential for maintaining product integrity and consistency.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems that can help manufacturers ensure consistent quality. Compliance with these standards indicates that a supplier has established processes for continual improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific standards, such as those from the American Petroleum Institute (API) or the CE marking in Europe, may be relevant depending on the application of the components being manufactured. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers adhere to these standards to mitigate risks associated with quality issues.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process are essential for identifying defects and ensuring compliance with GD&T specifications. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring processes during manufacturing to catch deviations early, allowing for corrective actions before final assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product to verify that all GD&T requirements, including bonus tolerances, are met before shipment.
These checkpoints help maintain the integrity of the manufacturing process and the quality of the final product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should actively verify the quality control measures of their suppliers. This can be achieved through:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers to assess their adherence to quality standards and GD&T practices.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline inspection results, non-conformance issues, and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Utilizing third-party inspection services to provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product quality.
By implementing these verification methods, buyers can ensure that they are sourcing from suppliers who prioritize quality assurance in line with GD&T principles.
What Are the Specific QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements, which can affect the certification process.
- Regional Standards: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards that may impact manufacturing and quality control. For instance, the European Union has stringent regulations regarding CE marking, which certifies that products meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- Cultural and Logistical Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in quality expectations and communication styles can enhance collaboration with suppliers across different regions. Additionally, logistical considerations such as shipping and customs can impact timelines and the quality of components upon arrival.
By being aware of these nuances, B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of international sourcing and ensure that they receive products that meet their GD&T requirements.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures surrounding GD&T bonus tolerance are multifaceted and require careful consideration. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside robust quality control practices, B2B buyers can ensure they source high-quality components that meet the stringent demands of their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gd&t bonus tolerance’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in effectively procuring components that utilize Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) bonus tolerance. Understanding bonus tolerance is essential for ensuring compatibility and functionality in assemblies, particularly when sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This checklist will streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you engage with suppliers who can meet your GD&T requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly articulating your technical requirements related to GD&T bonus tolerance. This includes the specific features of size, Maximum Material Condition (MMC), and Least Material Condition (LMC) relevant to your components.
- Why It Matters: A well-defined specification helps suppliers understand your exact needs, reducing the risk of miscommunication and ensuring that the parts will fit as intended.
- What to Look For: Specify tolerances, materials, and any applicable standards such as ASME Y14.5-2009 to guide suppliers.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in GD&T components. Use online platforms, industry directories, and trade associations to compile a list of potential vendors.
- Why It Matters: Not all suppliers are equipped to handle specialized GD&T requirements. A focused search will help you find those with relevant expertise.
- What to Look For: Look for suppliers with experience in your industry and positive reviews regarding their understanding of GD&T principles.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers possess relevant certifications and quality management systems, such as ISO 9001 or specific GD&T training credentials.
- Why It Matters: Certifications provide assurance that suppliers adhere to industry standards, which is crucial for maintaining quality and consistency in GD&T applications.
- What to Look For: Request documentation of certifications and inquire about any GD&T-specific training programs they offer to their staff.
Step 4: Request Sample Components
Before placing a large order, request samples of components that incorporate GD&T bonus tolerance. This will allow you to assess the quality and compliance of their manufacturing processes.
- Why It Matters: Evaluating samples helps ensure that the supplier can meet your specifications and tolerances in practice, not just in theory.
- What to Look For: Examine the samples for dimensional accuracy, finish quality, and adherence to the specified tolerances.
Step 5: Engage in Technical Discussions
Initiate discussions with suppliers about their understanding and application of GD&T principles, particularly bonus tolerance. This dialogue can clarify their capabilities and willingness to accommodate your needs.
- Why It Matters: A supplier’s depth of knowledge in GD&T can significantly impact the final product’s quality and functionality.
- What to Look For: Look for suppliers who can clearly explain their processes and how they incorporate GD&T into their manufacturing.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Production Capabilities
Inquire about the lead times and production capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers. Understanding their capacity to meet deadlines is critical for planning your projects.
- Why It Matters: Delays in receiving parts can disrupt your production schedules. Knowing a supplier’s capabilities helps you manage expectations and project timelines.
- What to Look For: Request detailed timelines for sample delivery and full production runs, and consider their flexibility in accommodating urgent requests.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Finally, ensure that there are clear communication channels between your team and the supplier. This includes defining points of contact and preferred methods of communication.
- Why It Matters: Open lines of communication facilitate quick resolution of issues and foster a collaborative relationship, which is crucial in complex projects involving GD&T.
- What to Look For: Identify key personnel on both sides who will be responsible for ongoing communication throughout the sourcing process.
By following this checklist, you can enhance your procurement process for GD&T bonus tolerance components, ensuring a successful partnership with your suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gd&t bonus tolerance Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in GD&T Bonus Tolerance Sourcing?
When sourcing products that utilize GD&T bonus tolerance, several key cost components come into play. Understanding these can help international B2B buyers manage their budgets effectively. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly impacts the overall cost. For instance, specialized alloys or plastics may increase costs due to their higher price and sourcing complexities. Buyers should consider sourcing materials locally to mitigate transport costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the precise manufacturing of components that adhere to GD&T standards. Labor costs can vary greatly depending on the region. For instance, skilled labor in Germany may command higher wages compared to labor in Brazil or South Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Buyers should inquire about how these costs are calculated, as they can vary widely between suppliers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required to achieve specific tolerances. The initial investment in tooling can be significant, but it often pays off in terms of efficiency and precision during production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet GD&T specifications necessitates rigorous quality control processes. This adds to the overall cost but is crucial for minimizing defects and ensuring compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Effective logistics planning can help reduce these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a margin in their pricing to ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s business model, market demand, and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect GD&T Bonus Tolerance Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of GD&T bonus tolerance components, which B2B buyers should carefully consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to reduced unit prices. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether they need highly customized components or if standard options suffice.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the need for certifications (like ISO) can drive up costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their services but often offer better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Buyers should select terms that align with their logistical capabilities and budget.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for GD&T Bonus Tolerance Sourcing?
To enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing GD&T bonus tolerance components, buyers can adopt several strategies:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if committing to larger order quantities. Leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, consider the long-term costs associated with the product, including maintenance, quality issues, and potential rework.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware that factors like tariffs, currency fluctuations, and regional economic conditions can influence pricing. It’s crucial to assess these elements when sourcing internationally, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
-
Build Strong Relationships with Suppliers: Cultivating relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and preferential treatment in terms of production timelines and quality assurance.
-
Seek Local Suppliers: Whenever possible, consider sourcing from local suppliers to reduce logistics costs and lead times. This can also enhance communication and collaboration.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for GD&T bonus tolerance components can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are getting a competitive price that meets their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gd&t bonus tolerance With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to GD&T Bonus Tolerance
In the realm of manufacturing and engineering, precision and accuracy are crucial for product quality and performance. While GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) bonus tolerance is a widely used method to enhance dimensional control and facilitate assembly, several alternative solutions can achieve similar outcomes. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Gd&T Bonus Tolerance | Alternative 1: Traditional Tolerancing | Alternative 2: Statistical Tolerance Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for complex assemblies, flexible with size variations | Lower precision; may not accommodate all assembly scenarios | Can predict variation but less effective for individual part control |
| Cost | Moderate initial costs; potential for savings through improved quality | Generally lower costs but may incur higher rework costs | Higher upfront costs for statistical software and training |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training for effective use; can be complex for beginners | Easier to implement; familiar to many engineers | Requires statistical knowledge and understanding of data analysis |
| Maintenance | Ongoing training needed to keep staff updated | Minimal maintenance; established practices | Requires continuous data collection and analysis for accuracy |
| Best Use Case | Best for complex assemblies where parts interact in multiple ways | Suitable for simpler designs with fewer interactions | Ideal for processes where variations can be statistically monitored |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Traditional Tolerancing?
Traditional tolerancing methods rely on straightforward dimensional limits without the nuanced control offered by GD&T. The simplicity of traditional tolerancing can be advantageous for straightforward parts where interactions are minimal. However, this method often leads to tighter tolerances that can increase manufacturing costs and reduce flexibility in part dimensions. In more complex assemblies, traditional tolerancing may not adequately account for the relationships between parts, potentially leading to assembly issues.
How Does Statistical Tolerance Analysis Compare?
Statistical tolerance analysis leverages statistical methods to predict how variations in part dimensions affect the overall assembly. This approach can provide valuable insights into the manufacturing process and is particularly effective in high-volume production scenarios. However, it requires significant investment in training and software tools, making it less accessible for smaller manufacturers. Additionally, while statistical methods can predict overall performance, they may not be as effective in addressing specific part-to-part variations, which can lead to unexpected assembly challenges.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Manufacturing Needs
When selecting between GD&T bonus tolerance and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including the complexity of their assemblies, budget constraints, and the skill level of their workforce. GD&T bonus tolerance is particularly beneficial for intricate assemblies where dimensional variation is common, providing flexibility and precision. In contrast, traditional tolerancing may be more suitable for simpler parts where cost and ease of implementation are paramount. Statistical tolerance analysis can offer insights for high-volume production but requires investment in resources. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on balancing precision needs with operational capabilities and costs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gd&t bonus tolerance
What Are the Key Technical Properties of GD&T Bonus Tolerance?
Understanding the technical properties of GD&T bonus tolerance is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to enhance their manufacturing processes. Here are some essential specifications that play a pivotal role:
-
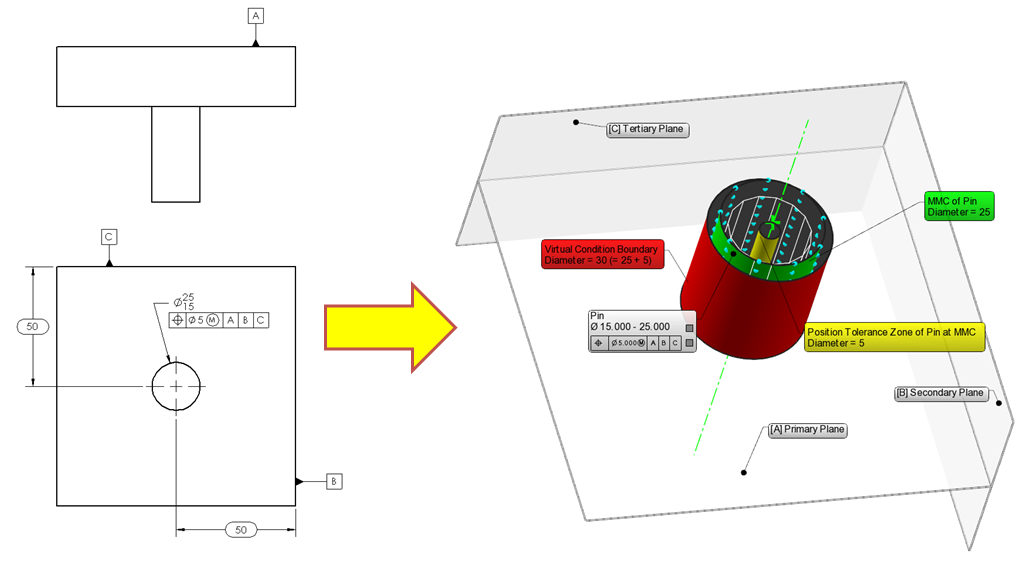
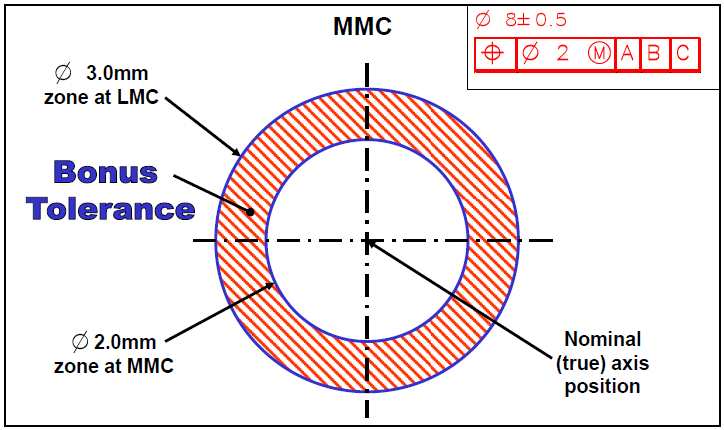
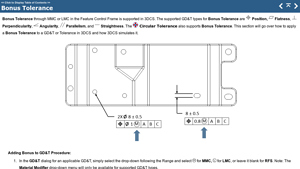
Maximum Material Condition (MMC)
MMC refers to the condition of a feature containing the maximum amount of material. For example, the smallest hole or largest pin within the specified limits. This property is vital as it defines the worst-case scenario for assembly, ensuring parts fit correctly even when produced at their largest allowable sizes. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who understand MMC, as it directly affects product quality and assembly efficiency. -
Least Material Condition (LMC)
LMC is the opposite of MMC and describes the condition where the feature has the least amount of material. In practical terms, it represents the largest hole or smallest pin. Understanding LMC helps businesses assess the flexibility of parts during assembly and the potential for increased tolerances when features are produced closer to LMC. This knowledge can lead to cost savings and improved production timelines. -
Bonus Tolerance
Bonus tolerance is the additional tolerance allowed when a feature is produced smaller than its MMC. It is calculated as the difference between the MMC and the actual size. This specification is crucial for manufacturers, as it allows for greater positional tolerance, enhancing flexibility in production. Buyers should seek suppliers who can effectively leverage bonus tolerance to optimize manufacturing processes. -
Feature Control Frame
This is a rectangular box that contains geometric tolerances and specifies the requirements for a part. It includes details such as the type of tolerance, the size of the feature, and the material condition (e.g., MMC or LMC). Understanding this frame is essential for ensuring that parts meet design specifications and quality standards, which is critical for maintaining competitiveness in global markets. -
Position Tolerance
This specification defines how much a feature’s actual position can deviate from its true position. It is directly influenced by MMC and bonus tolerance. Position tolerance is vital for ensuring that parts fit together correctly, thereby reducing assembly errors and improving overall product quality.
What Are Common Trade Terms in GD&T Bonus Tolerance?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to GD&T bonus tolerance:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of GD&T, understanding the role of OEMs helps buyers identify reliable suppliers who adhere to stringent quality standards, ensuring that the components meet necessary tolerances. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory and production costs effectively. It can influence purchasing decisions, especially for companies looking to scale their operations or introduce new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. This process is essential for buyers to compare costs and ensure they are getting competitive pricing for parts that meet GD&T specifications. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to navigate shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities effectively, ensuring smooth transactions across borders. -
True Position
This term refers to the exact location where a feature should be according to design specifications. True position is a critical concept in GD&T, as it directly impacts the assembly and functionality of parts. Buyers must ensure that suppliers have the capability to measure and maintain true position to guarantee product quality.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product quality, streamline manufacturing processes, and ultimately improve their bottom line.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gd&t bonus tolerance Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing GD&T Bonus Tolerance Sourcing?
The GD&T bonus tolerance sector is experiencing significant growth fueled by globalization, technological advancements, and increasing demand for precision engineering across various industries. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance manufacturing efficiency, the understanding and application of GD&T principles, particularly bonus tolerance, become crucial. Key drivers include the need for improved quality control, reduced manufacturing costs, and the ability to accommodate tighter tolerances in complex assemblies.
Emerging technologies like 3D scanning and advanced CAD systems are reshaping the landscape by enabling better visualization and measurement of GD&T parameters. Moreover, automation in quality assurance processes is streamlining operations and ensuring compliance with international standards. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate a robust understanding of GD&T practices, as this leads to higher product quality and reduced rework rates. As companies adopt lean manufacturing principles, they are more inclined to source components that utilize GD&T bonus tolerances, ensuring a competitive edge in the market.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the GD&T Bonus Tolerance Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a pivotal concern for B2B buyers, affecting sourcing decisions in the GD&T bonus tolerance sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, and companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices. Buyers are now favoring suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and sustainably. This trend is particularly strong in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks and consumer expectations push for transparency and eco-friendly practices.
In the context of GD&T, the use of ‘green’ materials can enhance product performance while reducing the environmental footprint. For instance, sourcing components that meet specific environmental certifications, such as ISO 14001, demonstrates a commitment to sustainability. Additionally, employing materials that have a lower carbon footprint can be advantageous in competitive bidding situations. As buyers look for suppliers who align with their sustainability goals, integrating ethical considerations into sourcing strategies becomes imperative for maintaining market relevance and fostering long-term partnerships.
What Is the Historical Context of GD&T Bonus Tolerance in B2B Markets?
The concept of GD&T has evolved significantly since its introduction in the mid-20th century, reflecting advancements in manufacturing technology and the increasing complexity of engineered systems. Initially developed to standardize the dimensioning and tolerancing of engineering drawings, GD&T has become essential for ensuring interoperability among components in global supply chains. Bonus tolerance, as a specific aspect of GD&T, allows manufacturers greater flexibility in their processes, enabling them to optimize production without compromising quality.
The adoption of GD&T practices has been particularly transformative for sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery, where precision is paramount. As globalization accelerated in the late 20th century, the need for a common language in engineering design became evident, prompting widespread adoption of GD&T standards like ASME Y14.5. This evolution has laid the groundwork for current practices, where understanding bonus tolerance is critical for navigating complex assembly requirements and meeting the demands of international markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gd&t bonus tolerance
-
How do I solve issues related to GD&T bonus tolerance in my manufacturing process?
To address issues with GD&T bonus tolerance, start by ensuring that your design specifications clearly define the Maximum Material Condition (MMC) and Least Material Condition (LMC) for each feature. Utilize advanced measurement tools, such as 3D scanners and coordinate measuring machines, to accurately assess the actual sizes of your components. Regular training for your engineering and quality control teams on GD&T principles can also enhance understanding and application, allowing for better troubleshooting and adjustments in your manufacturing processes. -
What is the best approach for selecting suppliers that understand GD&T bonus tolerance?
When selecting suppliers, prioritize those with proven expertise in GD&T, particularly in bonus tolerance applications. Request samples of their past work to evaluate their adherence to GD&T standards. Additionally, inquire about their quality control processes and whether they utilize advanced measurement technologies. Consider suppliers who offer training or support in GD&T for your team, ensuring a collaborative approach to maintaining quality and precision in your projects. -
How can I customize GD&T specifications for my unique manufacturing needs?
Customizing GD&T specifications involves collaborating closely with your design and engineering teams to understand the specific requirements of your components. You can adjust tolerances based on functional needs, ensuring that the MMC and LMC reflect realistic production capabilities. Engage with your suppliers early in the design phase to incorporate their insights into manufacturability and cost-effectiveness while maintaining compliance with GD&T standards. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for components requiring GD&T bonus tolerance?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for components that require GD&T bonus tolerance can vary widely based on the supplier, complexity of the parts, and production methods. Generally, MOQs may range from as low as 50 to several hundred units. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify your needs and explore options for smaller initial orders or pilot runs, especially if you are testing new designs or materials. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing GD&T-compliant components internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing can vary, but common arrangements include net 30, net 60, or letters of credit. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on these terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Consider the impact of currency fluctuations and ensure that payment methods are secure, such as wire transfers or trusted escrow services. Establishing a clear contract outlining payment schedules can also protect both parties. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for GD&T bonus tolerance during production?
To ensure quality assurance for GD&T bonus tolerance, implement a robust inspection process that includes both in-process and final inspections. Utilize calibrated measurement tools to verify that parts meet specified tolerances throughout production. Consider third-party inspections or certifications to provide additional assurance, and maintain open lines of communication with your suppliers regarding quality expectations and any potential issues. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing GD&T components internationally?
When sourcing GD&T components internationally, consider factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Work with logistics providers experienced in handling technical components to ensure compliance with international standards. Additionally, plan for contingencies related to delays or damage during transit, and maintain clear communication with your suppliers regarding delivery schedules and tracking. -
How does GD&T bonus tolerance impact the cost of manufacturing?
GD&T bonus tolerance can significantly influence manufacturing costs, as tighter tolerances may require more advanced machining processes and increased inspection efforts. However, utilizing bonus tolerance effectively can reduce costs by allowing for greater flexibility in production. By optimizing designs and leveraging bonus tolerance, you can minimize waste and improve assembly efficiency, ultimately leading to cost savings while maintaining quality standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Gd&T Bonus Tolerance Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. GD&T Basics – Maximum Material Condition Explained
Domain: gdandtbasics.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Maximum Material Condition (MMC) is a GD&T symbol that indicates the condition of a feature where the maximum amount of material exists within its dimensional tolerance. It applies to features of size, specifically holes (internal features) and pins (external features). The MMC for a hole is its smallest size, while for a pin, it is the largest size. MMC is used to ensure that parts do not interfe…
2. eMachineShop – Bonus Tolerance Solutions
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Bonus tolerance is a modification of GD&T tolerance that increases tolerance under certain conditions, specifically when the maximum material condition (MMC) symbol is used. It allows for more straightness tolerance if the feature-of-size is smaller than the MMC, potentially leading to lower manufacturing costs as it avoids the need for tightly controlled geometry.
3. 3DCS – Material Modifiers
Domain: 3dcs.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Material Modifiers: MMC (Maximum Material Condition), LMC (Least Material Condition), RFS (Regardless of Feature Size). MMC is the condition with the maximum amount of material (smallest hole/largest pin), allowing for bonus tolerance as size departs from MMC. LMC is the condition with the least amount of material (largest hole/smallest pin), with tolerance dependent on actual mating size. RFS is …
4. 3DCS – Bonus Tolerance Support
Domain: community.3dcs.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Bonus Tolerance is supported in 3DCS for GD&T types including Position, Flatness, Perpendicularity, Angularity, Parallelism, Straightness, and Circular Tolerance. Users can apply Bonus Tolerance through Material Modifiers (MMC, LMC, RFS) in the GD&T and Circular Tolerance dialogs. The procedure for adding Bonus Tolerance involves selecting the appropriate option from drop-down menus and ensuring s…
5. GD&T – MMC, LMC, and RFS Explained
Domain: s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The text discusses the concepts of Maximum Material Condition (MMC), Least Material Condition (LMC), and Regardless of Feature Size (RFS) in Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T). Key details include:
– Features of Size (FOS) are surfaces associated with size dimensions, such as hole diameters and plate thicknesses.
– MMC represents the feature of size with the greatest material, indicat…
6. Quasylearn – Bonus Tolerances in GD&T
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Quasylearn Article 1.23 focuses on Bonus Tolerances within Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T). Key details include: 1. Bonus tolerance provides additional tolerance when a feature is manufactured below Maximum Material Condition (MMC). 2. It applies to features with size dimensions, such as holes or shafts. 3. Example 1: A hole with a diameter of 10.0 mm and a geometric position toleran…
7. Elsmar – GD&T Bonus Tolerance Discussion
Domain: elsmar.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: GD&T Bonus Tolerance OOS discussion regarding handling dimensions that fall outside specifications, specifically focusing on a circular hole with a GD&T callout for true position based on MMC. The conversation highlights that if the hole diameter is too small, the part fails, making MMC irrelevant, and suggests analyzing the hole location without considering MMC. It also mentions calculating the p…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gd&t bonus tolerance
What Are the Key Benefits of Implementing GD&T Bonus Tolerance in Your Sourcing Strategy?
Incorporating GD&T bonus tolerance into your sourcing strategy can significantly enhance product quality and assembly efficiency. By understanding the dynamics of Maximum Material Condition (MMC) and Least Material Condition (LMC), international B2B buyers can leverage bonus tolerances to allow for greater manufacturing flexibility. This can lead to cost savings through reduced scrap rates and improved production timelines, particularly in complex supply chains prevalent in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Drive Competitive Advantage with GD&T?
Strategic sourcing that effectively integrates GD&T principles allows companies to better align their specifications with supplier capabilities. This alignment fosters stronger partnerships and encourages suppliers to optimize their processes, ultimately enhancing product quality. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a clear understanding of GD&T, as this will ensure that tolerances are met consistently, reducing the risk of costly rework.
What Should B2B Buyers Do Next to Optimize Their GD&T Knowledge?
As the global market continues to evolve, staying informed about GD&T practices is crucial. B2B buyers are encouraged to invest in training and resources to deepen their understanding of these concepts. By doing so, they will be better equipped to make informed sourcing decisions that drive efficiency and quality. Embracing GD&T is not just a technical improvement; it is a strategic move toward achieving long-term competitive advantage in an increasingly complex marketplace.