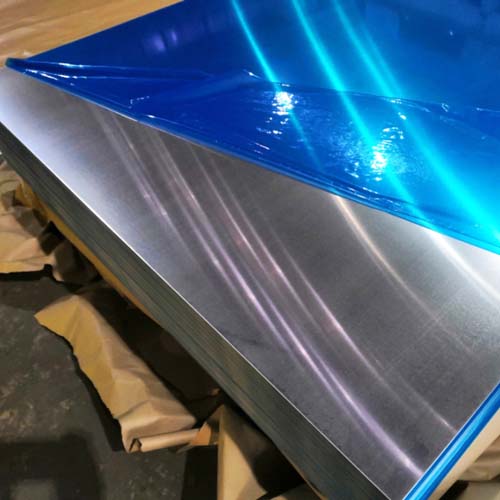
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ga aluminum
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing ga aluminum presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. From understanding the nuances of aluminum gauge systems to navigating supplier reliability, businesses must be well-informed to make strategic procurement decisions. This guide aims to streamline the purchasing process by providing a comprehensive overview of ga aluminum, including its various types, applications across industries, and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
Buyers will gain insights into the specific thickness measurements and properties of ga aluminum, ensuring they select the right materials for their projects. The guide also addresses cost factors, allowing businesses to budget effectively while ensuring quality and compliance with industry standards. By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed choices, this resource empowers them to optimize their procurement strategies.
Ultimately, whether you’re in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or any other global market, understanding the dynamics of ga aluminum procurement will facilitate smoother transactions and foster long-term supplier relationships. This guide is your key to navigating the complexities of the global aluminum market with confidence and precision.
Understanding ga aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 Aluminum | High corrosion resistance, excellent workability | Food processing, chemical handling | Pros: Non-heat treatable, good for welding. Cons: Lower strength compared to other alloys. |
| 2024 Aluminum | High strength, good fatigue resistance | Aerospace, military applications | Pros: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: Prone to corrosion without proper treatment. |
| 3003 Aluminum | Good formability, moderate strength | Cooking utensils, storage tanks | Pros: Easy to fabricate and weld. Cons: Not as strong as other alloys. |
| 6061 Aluminum | Versatile, good mechanical properties | Structural applications, automotive parts | Pros: Good corrosion resistance, weldable. Cons: More expensive than some other alloys. |
| 7075 Aluminum | Very high strength, lower workability | Aerospace, high-stress applications | Pros: Exceptional mechanical properties. Cons: Difficult to weld and form. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of 1100 Aluminum?
1100 aluminum is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications in the food processing and chemical industries. This alloy is non-heat treatable, which means it maintains its properties well during fabrication. Buyers should consider its lower strength compared to other aluminum types, making it less suitable for structural applications where higher strength is required.
How Does 2024 Aluminum Perform in B2B Applications?
2024 aluminum stands out for its high strength and fatigue resistance, making it a preferred choice in aerospace and military applications. It is heat treatable, which enhances its strength characteristics. However, buyers must be cautious of its susceptibility to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings or treatments. This alloy is best for applications where weight and strength are critical.
What Makes 3003 Aluminum a Popular Choice?
3003 aluminum is favored for its good formability and moderate strength, making it suitable for cooking utensils and storage tanks. Its ability to be easily fabricated and welded is a significant advantage for manufacturers. However, buyers should note that while it is versatile, it does not provide the same level of strength as other aluminum alloys, which may limit its use in more demanding applications.
Why is 6061 Aluminum Considered Versatile?
6061 aluminum is one of the most versatile aluminum alloys available, offering good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. This alloy is commonly used in structural applications and automotive parts due to its weldability and strength. While it may be more expensive than other alloys, its overall performance and durability can justify the cost for buyers looking for reliable materials.
What are the Key Considerations for 7075 Aluminum?
7075 aluminum is recognized for its very high strength, making it ideal for high-stress applications like aerospace components. However, it has lower workability compared to other aluminum types, making it challenging to weld and form. Buyers should weigh the benefits of its exceptional mechanical properties against the potential difficulties in fabrication and the need for specialized processing techniques.
Key Industrial Applications of ga aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ga aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Lightweight structural components | Reduces vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency | Compliance with automotive standards and specifications |
| Construction | Roofing and siding materials | Enhanced durability and weather resistance | Local regulations and availability of specific gauges |
| Aerospace | Aircraft skin and structural parts | High strength-to-weight ratio, reducing operational costs | Certification requirements and material traceability |
| Packaging | Aluminum cans and containers | Lightweight, recyclable, and corrosion-resistant | Sustainability certifications and supply chain reliability |
| Electrical and Electronics | Heat sinks and enclosures | Effective thermal management and lightweight design | Precision in gauge specifications and electrical standards |
How is ga aluminum used in the automotive industry?
In the automotive sector, ga aluminum is primarily utilized for manufacturing lightweight structural components such as chassis parts and body panels. This application addresses the industry’s need for reducing vehicle weight, which directly correlates to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing aluminum that meets stringent automotive standards is crucial. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide detailed certifications and specifications that comply with local and international regulations.
What role does ga aluminum play in construction?
In construction, ga aluminum is favored for roofing and siding materials due to its enhanced durability and resistance to weather elements. This application is particularly beneficial in regions with extreme climates, ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance costs. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider local regulations regarding building materials and the availability of specific gauges to meet project requirements. Understanding the regional supply chain dynamics can also facilitate better procurement strategies.
Why is ga aluminum critical in aerospace applications?
Aerospace applications leverage ga aluminum for aircraft skin and structural components, capitalizing on its high strength-to-weight ratio. This characteristic is vital for reducing operational costs and improving fuel efficiency, which is a significant consideration for airlines operating in competitive markets. International B2B buyers must navigate complex certification requirements and ensure material traceability to comply with industry standards. This focus on quality and compliance is essential for maintaining safety and performance in aerospace manufacturing.
How does ga aluminum enhance packaging solutions?
In the packaging industry, ga aluminum is extensively used for producing cans and containers, offering benefits such as lightweight design and excellent corrosion resistance. These properties enhance the product’s shelf life and sustainability, appealing to eco-conscious consumers. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, it is important to source aluminum that aligns with sustainability certifications and local recycling initiatives. Ensuring a reliable supply chain is also critical to maintaining consistent production schedules.
What advantages does ga aluminum provide in electrical applications?
In the electrical and electronics sector, ga aluminum is commonly used for heat sinks and enclosures, where effective thermal management is paramount. Its lightweight nature aids in reducing overall device weight, an essential factor in consumer electronics. Buyers should focus on precision in gauge specifications to meet electrical standards, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where regulations may be stricter. Establishing relationships with suppliers who understand these standards can streamline the procurement process and enhance product quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ga aluminum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Aluminum Gauge Confusion
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter confusion when selecting the appropriate gauge of aluminum for their projects. This confusion stems from the fact that the gauge system is not standardized across different materials. For instance, an 18 gauge steel sheet differs in thickness from an 18 gauge aluminum sheet, leading to potential miscalculations in material requirements. This can result in costly delays, product defects, or wasted resources, particularly for manufacturers and fabricators who rely on precise specifications.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate this confusion, buyers should utilize a comprehensive aluminum gauge thickness chart that outlines the specific thicknesses corresponding to various gauge numbers. Before placing an order, it is crucial to determine the exact gauge needed for the project based on the application requirements, such as strength and weight considerations. Buyers should also verify the specifications with suppliers to ensure that the aluminum matches the required gauge. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of errors and ensures that the right material is sourced from the start, ultimately saving time and costs.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality Control in Aluminum Sourcing
The Problem:
Quality control is a significant concern for B2B buyers when sourcing aluminum, especially from international suppliers. Variations in manufacturing processes, material composition, and adherence to industry standards can lead to inconsistencies in quality. For instance, inferior quality aluminum may not withstand the intended application, leading to product failures and dissatisfied customers. This is particularly critical for industries like construction and automotive, where safety and durability are paramount.
The Solution:
To ensure quality control in aluminum sourcing, buyers should establish a rigorous vetting process for suppliers. This includes requesting certification for material standards, such as ISO certifications or compliance with ASTM specifications, which guarantee the aluminum meets specific quality criteria. Additionally, buyers can consider conducting audits or requesting samples for testing prior to large-scale orders. Establishing long-term relationships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record can also enhance quality assurance. By prioritizing supplier quality, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure the longevity and reliability of their products.
Scenario 3: Cost Management in Aluminum Procurement
The Problem:
Cost management presents a persistent challenge for B2B buyers dealing with aluminum procurement. Fluctuating aluminum prices, driven by market demand, geopolitical factors, and supply chain disruptions, can significantly impact budgeting and profitability. Additionally, the hidden costs associated with poor material choices—such as increased machining time or waste due to incorrect thickness—further complicate financial planning.
The Solution:
To effectively manage costs, buyers should implement a strategic procurement plan that includes regular market analysis to stay informed about aluminum price trends. Establishing long-term contracts with suppliers can help lock in prices and provide more predictable budgeting. Furthermore, utilizing the aluminum gauge thickness chart can optimize material usage, ensuring that the correct gauge is selected for each application, thereby reducing waste and unnecessary expenditures. Buyers can also explore bulk purchasing options or group purchasing organizations to benefit from economies of scale. By taking a proactive and informed approach to procurement, B2B buyers can control costs and enhance their competitive edge.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ga aluminum
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for ga Aluminum?
When selecting materials for ga aluminum applications, understanding the properties of various aluminum alloys is crucial. Here, we analyze four common aluminum materials, focusing on their performance characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
1. 6061 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: The 6061 aluminum alloy is known for its good mechanical properties and weldability. It has a temperature rating of up to 200°C (392°F) and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: This alloy is durable and relatively lightweight, which is beneficial for applications where weight savings are essential. However, it can be more expensive than other alloys, and its manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for precise machining.
Impact on Application: The 6061 alloy is compatible with a wide range of media, including water and chemicals, making it versatile for different industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and JIS. The demand for this alloy is rising in construction and automotive sectors, which may influence pricing and availability.
2. 5052 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: The 5052 aluminum alloy offers excellent corrosion resistance and is particularly effective in marine environments. It has a temperature rating of up to 150°C (302°F) and provides good weldability.
Pros & Cons: This alloy is highly durable and resistant to fatigue, making it suitable for applications requiring long-term performance. However, it is heavier than other aluminum alloys, which may not be ideal for all applications.
Impact on Application: The 5052 alloy is particularly effective in applications exposed to saltwater or other corrosive environments, such as marine and automotive components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in South America and Europe should verify that the alloy meets local environmental regulations. The alloy’s popularity in marine applications means that it may be subject to specific compliance standards.
3. 3003 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: Known for its excellent workability and moderate strength, the 3003 aluminum alloy has a temperature rating of up to 150°C (302°F) and offers good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: This alloy is cost-effective and easy to fabricate, making it suitable for a variety of applications. However, its lower strength compared to other alloys may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: The 3003 alloy is commonly used in applications such as cooking utensils, chemical equipment, and storage tanks, where moderate strength and lightweight properties are advantageous.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Nigeria should consider the availability of this alloy and its compliance with local manufacturing standards. Its affordability makes it a popular choice for budget-sensitive projects.
4. 7075 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: The 7075 aluminum alloy is known for its high strength and toughness, with a temperature rating of up to 120°C (248°F). It has lower corrosion resistance compared to other alloys but is often used in structural applications.
Pros & Cons: This alloy is one of the strongest aluminum alloys available, making it ideal for aerospace and military applications. However, its higher cost and lower workability can complicate manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: The 7075 alloy is suitable for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as aircraft components and high-stress structural parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the stringent quality standards for aerospace materials. Compliance with standards like ASTM and EN is critical for successful procurement.
Summary Table of Material Selection for ga Aluminum
| Material | Typical Use Case for ga aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminum | Structural components in automotive | Good mechanical properties | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| 5052 Aluminum | Marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Heavier than other alloys | Medium |
| 3003 Aluminum | Cooking utensils, chemical equipment | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Lower strength | Low |
| 7075 Aluminum | Aerospace and military applications | High strength and toughness | Higher cost and lower workability | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers considering ga aluminum. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific applications and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ga aluminum
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing ga Aluminum?
The manufacturing process for ga aluminum involves several critical stages, each of which contributes to the overall quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing aluminum products.
1. Material Preparation: How Is Aluminum Prepared for Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality aluminum alloys based on the desired characteristics for the final product. The aluminum is then cut into sheets or coils, depending on the specifications. This stage may also include processes such as annealing, which softens the material, and cleaning, which removes any surface contaminants that could affect later stages of manufacturing.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Aluminum?
Once the aluminum is prepared, the next step is forming. This can involve various techniques such as stamping, bending, and extrusion. For instance, stamping is commonly used for creating precise shapes and designs, while bending is essential for producing components with specific angles and curves. Extrusion allows for the creation of long, continuous shapes, ideal for structural applications. Each technique is chosen based on the product’s design requirements and intended use.
3. Assembly: How Are Aluminum Components Joined Together?
The assembly stage involves joining different aluminum components to create the final product. This can be achieved through methods such as welding, riveting, or using adhesives. The choice of assembly technique depends on factors like the required strength, the environment in which the product will be used, and cost considerations. Proper alignment and fit during assembly are crucial to ensure the structural integrity and performance of the finished product.
4. Finishing: What Processes Enhance the Appearance and Durability of Aluminum?
Finishing processes are applied to improve both the aesthetic and functional properties of aluminum products. Common techniques include anodizing, painting, and powder coating. Anodizing enhances corrosion resistance and allows for color customization, while powder coating provides a durable finish that can withstand harsh environments. The finishing process not only adds visual appeal but also extends the lifespan of the aluminum components, making them suitable for various applications.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance in ga Aluminum Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for ga aluminum. Adhering to international standards ensures that products meet specific quality and safety requirements, which is particularly important for B2B buyers operating in diverse markets.
ISO 9001: What Does This Standard Entail?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems (QMS). It provides a framework for organizations to ensure they consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Companies involved in aluminum manufacturing often seek ISO 9001 certification to demonstrate their commitment to quality. This certification involves regular audits and continuous improvement processes.
CE Marking: Why Is It Important for European Markets?
For products sold in Europe, CE marking is essential. It indicates that the product complies with European safety, health, and environmental protection legislation. Manufacturers must conduct rigorous testing and documentation to obtain this mark, which reassures B2B buyers about the safety and reliability of their products.
API Standards: How Do They Apply to Specific Industries?
The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards specifically for products used in the oil and gas industry. Manufacturers of aluminum components for this sector must comply with API standards to ensure that their products can withstand the demanding conditions typical of oil and gas applications. Compliance with these standards is crucial for buyers in industries where safety and performance are paramount.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in ga Aluminum Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is vital throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the final products meet the required specifications. Various checkpoints are established to monitor quality at different stages.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): How Is Raw Material Quality Assessed?
IQC involves inspecting incoming materials to verify their quality before they enter the manufacturing process. This includes checking the chemical composition and physical properties of the aluminum sheets or coils. Effective IQC helps prevent defects from being introduced into the production line.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): How Is Quality Monitored During Production?
During the manufacturing process, IPQC techniques are employed to monitor quality at various stages. This can involve regular inspections and measurements of critical dimensions and tolerances. Any deviations from specifications can be addressed immediately, reducing the likelihood of defects in the final product.
Final Quality Control (FQC): What Is Done Before Products Are Shipped?
FQC is the last checkpoint before products are shipped to customers. This stage involves comprehensive inspections and testing to ensure that the products meet all specifications. Common testing methods include dimensional checks, surface quality assessments, and functional testing. Only products that pass these evaluations are approved for shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain stringent quality control practices. This can be achieved through several methods:
Supplier Audits: What Should Buyers Look For?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s QC processes. Buyers should look for evidence of compliance with international standards, documentation of QC procedures, and records of previous audits. These audits can provide insights into the manufacturer’s capabilities and commitment to quality.
Quality Reports: How Can They Aid in Supplier Evaluation?
Requesting quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC performance. These reports should detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC, along with any corrective actions taken for defects. Consistent positive results in these reports can indicate a reliable supplier.
Third-Party Inspections: What Are the Benefits?
Engaging third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can verify compliance with industry standards and assess product quality before shipment. This step is particularly valuable for buyers in regions with less stringent regulatory oversight.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of QC and certification is crucial. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that can affect product quality. Buyers should be aware of:
- Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in your target market, as these can impact product compliance.
- Certification Validity: Ensure that certifications are recognized in your region and are relevant to the specific products being sourced.
- Cultural Differences: Understand that quality expectations may vary by region, influencing how suppliers approach quality management.
By carefully considering these factors, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing ga aluminum products, ensuring they receive high-quality materials that meet their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ga aluminum’
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in the procurement of ‘ga aluminum’ by providing a clear checklist that outlines critical steps in the sourcing process. By following this guide, international buyers can ensure they select the right materials and suppliers to meet their project specifications efficiently.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your aluminum needs, including gauge thickness, alloy type, and intended application. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for your sourcing decisions. For example, understanding the specific gauge required (e.g., 18 gauge aluminum is 0.0403 inches thick) helps in accurately matching your project’s needs with supplier offerings.
Step 2: Research the Market
Conduct thorough market research to identify potential suppliers of ‘ga aluminum’. Analyze their product offerings, market reputation, and industry experience. Pay attention to geographic factors, as suppliers in specific regions may have advantages in terms of logistics and material costs, especially if you’re sourcing from Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your industry. Evaluate their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and customer service reputation to ensure they can meet your specific requirements consistently.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that suppliers hold relevant certifications that ensure compliance with international standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems or specific aluminum manufacturing standards. These certifications provide assurance that the supplier adheres to industry best practices and can deliver high-quality products.
Step 5: Request Samples and Test Quality
Always request samples of the aluminum before finalizing a purchase. This allows you to evaluate the material’s quality and suitability for your application. Conduct tests to ensure that the gauge and alloy specifications match your requirements. This step is vital to avoid costly mistakes later in your project.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations with your selected suppliers to establish favorable terms and pricing. Consider factors such as minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of all costs involved, including shipping and handling fees, to avoid unexpected expenses.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Set up a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier. Regular updates on order status, potential delays, and quality checks are essential for maintaining a smooth procurement process. This proactive approach helps build a strong relationship with the supplier and can lead to better service and support in future transactions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for ‘ga aluminum’, ensuring that they secure the right materials from reliable suppliers while minimizing risks and maximizing value.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ga aluminum Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing GA Aluminum?
When sourcing GA aluminum, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The base cost of aluminum fluctuates based on global market conditions. Prices can vary significantly depending on the quality of aluminum, alloy composition, and market demand.
-
Labor: This includes the cost of skilled labor required for manufacturing processes, which can vary by region. In countries with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, this component can significantly impact the overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, maintenance, and other indirect costs associated with production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial costs for molds and dies used in production can be substantial. Custom tooling may be necessary for specific applications, further increasing upfront costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet industry standards incurs costs related to inspections, testing, and certification. For international buyers, certifications like ISO can add to costs but may enhance product credibility.
-
Logistics: Transporting aluminum from suppliers to buyers can be a significant expense. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and customs duties must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition and market conditions.
How Do Price Influencers Affect GA Aluminum Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of GA aluminum, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized aluminum products often come with higher prices due to the complexity of manufacturing processes. Buyers should weigh the necessity of custom specifications against their budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality aluminum and those with recognized certifications may command premium prices. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better consistency and support.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade (Incoterms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. These can significantly influence overall costs, especially in international transactions.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating GA Aluminum Prices?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to optimize costs when sourcing GA aluminum:
-
Negotiate: Always engage suppliers in discussions about pricing. Highlighting potential for long-term partnerships or bulk orders can incentivize suppliers to offer better rates.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase prices, consider logistics, maintenance, and disposal costs when assessing the value of aluminum products.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, sourcing from suppliers in regions with lower labor costs can yield savings.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about global aluminum prices and market trends. Knowledge of these factors can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Consider Supplier Location: Proximity to suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times. Evaluate the total logistics costs when selecting a supplier.
What Should International Buyers Be Aware of When Sourcing GA Aluminum?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the complexities of sourcing GA aluminum is vital. Be mindful of:
-
Import Duties and Tariffs: These can add significant costs to imported goods. Familiarize yourself with trade agreements between your country and the supplier’s country.
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can impact the overall cost of sourcing. Locking in prices or using hedging strategies may mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations.
-
Cultural Differences in Business Practices: Understanding and respecting cultural nuances can enhance negotiations and foster stronger supplier relationships.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that sourced products comply with local regulations and standards to avoid potential legal issues.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, price influencers, and negotiation strategies will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing GA aluminum. Always remember that indicative prices can vary based on multiple factors, making it essential to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluation.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ga aluminum With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Ga Aluminum: A Comparative Analysis
In the competitive landscape of materials used for various industrial applications, ga aluminum stands out due to its unique properties and versatility. However, understanding alternative solutions is vital for B2B buyers aiming to make informed decisions that meet their operational needs. This analysis compares ga aluminum against two viable alternatives: galvanized steel and stainless steel.
| Comparison Aspect | Ga Aluminum | Galvanized Steel | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal conductivity | Good strength, corrosion-resistant due to zinc coating | High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, high durability |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost, but lower lifecycle costs due to durability | Lower initial cost, but potential for higher maintenance costs | Higher initial investment, justified by longevity and performance |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to fabricate and shape, requires minimal tooling | Relatively easy to work with, but may require additional coatings for extended life | More complex fabrication processes due to hardness |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to rust and corrosion | Moderate maintenance needed due to wear of zinc coating | Low maintenance, highly durable and resistant to staining |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for lightweight structures, automotive, and aerospace applications | Suitable for construction, fencing, and outdoor applications | Perfect for high-end applications in food processing, chemical industries, and medical equipment |
Galvanized Steel: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Galvanized steel is a popular choice for many industries due to its lower initial cost and decent strength. The zinc coating provides a layer of corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, the longevity of galvanized steel can be compromised if the coating is scratched or wears off, leading to rust formation. While it is a cost-effective solution, it may require more frequent maintenance compared to ga aluminum, especially in harsh environments.
Stainless Steel: Premium Performance with High Durability
Stainless steel is often seen as a premium alternative due to its outstanding strength and resistance to corrosion and staining. It is particularly beneficial in applications requiring hygiene and durability, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. However, the trade-off is a significantly higher initial investment. Stainless steel’s fabrication process can also be more complex and may require specialized tools. Despite these factors, its longevity and performance make it a worthy consideration for high-end applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Material for Your Needs
When selecting between ga aluminum, galvanized steel, and stainless steel, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and long-term operational goals. Ga aluminum offers excellent lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making it ideal for industries like aerospace. In contrast, galvanized steel is a budget-friendly option for general construction, while stainless steel stands out in demanding environments where durability and hygiene are paramount. By aligning the material choice with operational needs and expected lifecycle costs, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and value.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ga aluminum
What Are the Key Technical Properties of ga Aluminum?
When evaluating ga aluminum for procurement or manufacturing, several critical specifications play a vital role in ensuring that the material meets the requirements of your specific application. Understanding these properties can aid in making informed decisions that affect product quality, cost, and performance.
1. Material Grade
Material grades indicate the composition and mechanical properties of aluminum alloys. Common grades for ga aluminum include 6061, 5052, and 3003, each suited for different applications. For instance, 6061 offers good corrosion resistance and weldability, making it ideal for structural components, while 5052 is known for its excellent workability and is often used in marine environments. Selecting the right grade is crucial for achieving optimal performance in your application.
2. Thickness and Gauge
The thickness of ga aluminum is typically measured in gauges, which can differ from other metals. For example, an 18 gauge aluminum sheet is approximately 0.0403 inches thick. Understanding gauge specifications is essential for ensuring compatibility with design requirements, as different gauges can affect the strength, weight, and manufacturing processes of the final product.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and properties of the aluminum sheets. It is critical for ensuring that the aluminum parts fit correctly within assemblies or meet specific design criteria. High tolerance levels are especially important in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount. Poor tolerance could lead to assembly issues, increased costs, and product failures.
4. Surface Finish
The surface finish of ga aluminum can significantly impact its aesthetic and functional properties. Common finishes include mill finish, anodized, and painted. Anodizing enhances corrosion resistance and allows for color customization, while mill finish is more cost-effective for applications where aesthetics are less critical. The choice of surface finish should align with both functional requirements and branding considerations.
5. Mechanical Properties
These include tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation, which indicate how the material will perform under stress. For instance, the tensile strength of 6061 aluminum can reach up to 310 MPa, making it suitable for structural applications. Buyers should consider these properties to ensure that the material can withstand the operational demands of their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to ga Aluminum?
Navigating the procurement process involves understanding certain trade terminologies that are frequently used in the aluminum industry. Familiarity with these terms can streamline communication and negotiation with suppliers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring that the aluminum components you procure meet the quality and performance standards required by your end product.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers as it impacts inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning purchases and managing budgets effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. It is an essential tool for buyers to gauge pricing, lead times, and terms of sale. A well-crafted RFQ can lead to better negotiations and cost savings.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is vital for managing logistics and minimizing risks in cross-border trade.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and ensuring timely project completion. Delays in lead time can affect project timelines and costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology related to ga aluminum is fundamental for B2B buyers. By familiarizing yourself with these specifications and terms, you can make informed decisions that enhance product quality and streamline procurement processes, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ga aluminum Sector
What Are the Current Trends in the Global ga Aluminum Market?
The global market for ga aluminum is experiencing significant growth driven by various factors. Demand for lightweight, durable materials is increasing in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. As companies seek to enhance efficiency and reduce fuel consumption, aluminum’s properties make it an attractive alternative to heavier metals. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy technologies is propelling the demand for aluminum components, further solidifying its position in the market.
Emerging technologies in sourcing and procurement are also shaping the landscape. Digital platforms and e-commerce solutions are becoming more prevalent, enabling international B2B buyers to streamline their purchasing processes. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics are being leveraged to optimize supply chain management, allowing businesses to anticipate market fluctuations and adjust their sourcing strategies accordingly. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can provide not only competitive pricing but also transparency and reliability in their supply chains.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the ga Aluminum Sector?
The environmental impact of aluminum production has led to a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing practices within the ga aluminum sector. As concerns about climate change intensify, businesses are under pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes sourcing aluminum from suppliers who utilize eco-friendly methods, such as recycling and low-emission production processes.
Ethical supply chains are becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers. Companies are now seeking suppliers that adhere to recognized sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001 and the Aluminum Stewardship Initiative (ASI) certification. These certifications ensure that the materials sourced are produced responsibly and with minimal environmental impact. By prioritizing ethical sourcing, businesses not only enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) but also appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers and stakeholders.
What Is the Historical Context of the ga Aluminum Market?
The history of aluminum as a material dates back to the 19th century, with its commercial production beginning in the 1880s. Initially considered a precious metal, aluminum has evolved into a widely-used industrial material due to its unique properties, including lightweight, corrosion resistance, and malleability. The development of new extraction and processing technologies has further facilitated its rise, making aluminum more accessible and affordable for various applications.
Over the decades, the aluminum industry has experienced substantial transformations, particularly with the introduction of recycling technologies that significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with primary aluminum production. Today, the ga aluminum sector is positioned at the forefront of innovation, with ongoing advancements in manufacturing processes aimed at improving efficiency and sustainability. This historical evolution not only provides insight into the material’s growing importance but also highlights the need for international B2B buyers to stay informed about sourcing trends and market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ga aluminum
-
How do I determine the right gauge of ga aluminum for my project?
To select the appropriate gauge of ga aluminum, first assess the specific requirements of your application, such as strength, weight, and environmental conditions. Utilize a gauge thickness chart to identify the corresponding thickness in inches or millimeters. Consider factors like durability and flexibility; for example, lighter gauges may be suitable for applications requiring less structural support, while thicker gauges offer enhanced strength. If unsure, consult with your supplier for recommendations based on your project specifications. -
What is the best aluminum gauge for construction applications?
For construction applications, a gauge thickness of 14 to 16 is typically recommended, as it balances strength and weight effectively. Thicker gauges provide better resistance to environmental stressors, while lighter gauges can be easier to work with. However, specific requirements may vary depending on structural loads and local building codes. Always consult with engineers or construction specialists to ensure compliance with safety standards and material performance. -
How can I verify the quality of ga aluminum from suppliers?
Verifying the quality of ga aluminum involves several steps. First, request certifications such as ISO 9001 or other industry-specific quality standards. Secondly, ask for material test reports (MTRs) that include mechanical properties, chemical composition, and thickness measurements. Additionally, consider conducting a physical inspection or utilizing third-party quality assurance services to assess the aluminum before finalizing any purchase. Building a relationship with reliable suppliers who prioritize quality is essential for long-term success. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQ) for ga aluminum?
Minimum order quantities for ga aluminum can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific product. Typically, MOQs can range from 100 kg to several tons. It’s essential to clarify MOQs when sourcing, as smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs. Some suppliers might offer flexibility for trial orders, especially for new customers. Communicating your needs upfront can help negotiate favorable terms that align with your project requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing ga aluminum internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of ga aluminum often include options like advance payment, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). The choice of terms can depend on your relationship with the supplier, order size, and country-specific regulations. It’s advisable to conduct due diligence on suppliers and consider escrow services for large transactions. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly defined in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for ga aluminum imports?
When importing ga aluminum, ensure you have a comprehensive logistics plan in place. This includes selecting reliable shipping partners, understanding incoterms (like FOB or CIF), and preparing all necessary documentation for customs clearance. Factor in shipping costs, potential duties, and delivery timelines when budgeting. Consider using freight forwarders who specialize in metal imports, as they can help navigate regulations and ensure timely delivery to your location. -
Can I customize the thickness of ga aluminum sheets?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for ga aluminum sheets, allowing you to specify the thickness based on your project requirements. Custom thicknesses may be subject to minimum order quantities and additional lead times. Communicate your needs clearly with suppliers to explore available options and pricing. Custom orders can enhance product performance, but ensure that any specifications align with industry standards for your application. -
What should I do if I encounter issues with the quality of received ga aluminum?
If you experience quality issues with received ga aluminum, immediately document the discrepancies with photographs and detailed descriptions. Contact your supplier to discuss the problem and refer to your purchase agreement for quality assurance clauses. Most reputable suppliers will work with you to resolve issues, which may include refunds, replacements, or credit. Maintaining open communication and a good relationship with your supplier can facilitate smoother resolutions in the future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Ga Aluminum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Metal Supermarkets – Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Gauge Chart – Metal Supermarkets offers a variety of metals including mild steel, aluminum, stainless steel, alloy steel, brass, bronze, and copper. The gauge system is used to specify the thickness of sheet metal, with different gauge designations for specific metal types. The chart includes gauge numbers and their corresponding thickness in inches and millimeters for mild steel, alum…
2. Alfiniti – Aluminum Gauge Thickness Chart
Domain: alfiniti.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Gauge Thickness Chart provides detailed information on the thickness of aluminum sheets. It includes gauge numbers (3 to 36), standard steel thickness in inches, galvanized steel thickness in inches, and aluminum thickness in inches. The chart is a valuable resource for manufacturers, engineers, and professionals working with aluminum, ensuring precision and consistency in material select…
3. Unipunch – Metal Gauge Chart
Domain: unipunch.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Metal Gauge Chart for Steel, Aluminum, and Stainless Steel. The chart provides standard gauge numbers converted to decimals of an inch for sheet steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Gauge numbers range from 1 to 29, with corresponding thicknesses in inches and millimeters for each material. For example, Gauge 1 for sheet steel is .2893 inches (7.3 mm), while Gauge 1 for aluminum is .2812 inches (…
4. Engineering Toolbox – Weight vs. Gauges Chart
Domain: engineeringtoolbox.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Weight vs. Gauges Chart for sheet steel, galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and strip & tubing. The chart includes US Standard Gauge, Decimal (inches), and Weight (lb/ft²) for various gauges ranging from 44 to 0/0 (00000).
5. Scotsmun Steel – 8 GA Aluminum Sheet Metal
Domain: scotsmunsteel.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: 8 GA Aluminum Sheet Metal available in three sizes: 4 x 8 x 8 GA (.125), 4 x 10 x 8 GA (.125), and 5 x 10 x 8 GA (.125). Customers can enter the square feet needed for full or partial sheets when ordering.
6. All Points Fasteners – Sheet Metal Gauge Thickness Chart
Domain: allpointsfasteners.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Gauge Thickness Chart: Standard steel, galvanized steel, and aluminum are used to make sheet metal. Gauge indicates thickness; lower numbers mean thicker metal. Standard range is 30 (thin) to 7 (thick). Actual thickness varies by metal type. For example, 30-gauge standard steel is 0.012 inches, galvanized steel is 0.0157 inches, and aluminum is 0.01 inches. Types of sheet metal screws …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ga aluminum
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of GA aluminum is essential for international B2B buyers seeking quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their supply chains. Understanding the nuances of aluminum gauge specifications, such as thickness variations and their implications for different applications, enables businesses to make informed procurement decisions. Additionally, leveraging reliable suppliers ensures consistent quality and compliance with industry standards, which is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in diverse markets.
As global demand for aluminum continues to rise, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should prioritize building relationships with reputable manufacturers who can meet their specific needs. Emphasizing long-term partnerships will facilitate better pricing, timely deliveries, and access to innovations in aluminum applications.
Looking ahead, the landscape of aluminum sourcing is set to evolve with advances in technology and sustainability. International buyers are encouraged to stay abreast of industry trends and adapt their sourcing strategies accordingly. By doing so, they can not only secure their supply chains but also position themselves as leaders in their respective markets. Engage with suppliers now to explore the potential of GA aluminum in your next project.